National Unit specification. General information. Unit title: Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) Unit code: HT8P 45. Unit purpose.
|
|
|
- Oswald Kelly
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 National Unit specification General information Unit code: HT8P 45 Superclass: RH Publication date: September 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 2 Unit purpose This unit is designed to provide learners with an introduction to key biological principles, and to provide a background in biology for those who have no previous knowledge or experience in the subject. The unit is suitable for learners studying at NC level, and will provide the necessary underpinning knowledge and skills to enable progression to further study of biology at Higher level. Outcomes On successful completion of the unit the learner will be able to: 1 Describe the structure and function of living cells. 2 Describe cellular biochemical processes: enzyme activity, respiration and photosynthesis. 3 Describe the structure and function of the digestive and cardiovascular systems. 4 Describe the evolution of life on earth. Credit points and level 1 National Unit credit at SCQF level 5: (6 SCQF credit points at SCQF level 5) Recommended entry to the unit Entry is at the discretion of the centre. HT8P 45, Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) 1
2 National Unit specification: General information (cont) Core Skills Achievement of this unit gives automatic certification of the following Core Skills component: Complete Core Skill None Core Skill component Critical Thinking at SCQF level 4 There are also opportunities to develop aspects of Core Skills which are highlighted in the support notes of this unit specification. Context for delivery If this unit is delivered as part of a group award, it is recommended that it should be taught and assessed within the subject area of the group award to which it contributes. The Assessment Support Pack (ASP) for this unit provides assessment and marking guidelines that exemplify the national standard for achievement. It is a valid, reliable and practicable assessment. Centres wishing to develop their own assessments should refer to the ASP to ensure a comparable standard. A list of existing ASPs is available to download from SQA s website ( Equality and inclusion This unit specification has been designed to ensure that there are no unnecessary barriers to learning or assessment. The individual needs of learners should be taken into account when planning learning experiences, selecting assessment methods or considering alternative evidence. Further advice can be found on our website HT8P 45, Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) 2
3 National Unit specification: Statement of standards Acceptable performance in this unit will be the satisfactory achievement of the standards set out in this part of the unit specification. All sections of the statement of standards are mandatory and cannot be altered without reference to SQA. Outcome 1 Describe the structure and function of living cells. Performance criteria (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Describes the structure and function of animal cells. Describes the structure and function of plant cells. Describes the structure and function of microbial cells Describes diffusion and osmosis in relation to their effects on plant and animal cells. Describes the structure and function of proteins and nucleic acids. Outcome 2 Describe cellular biochemical processes: enzyme activity, respiration and photosynthesis. Performance criteria (a) (b) (c) Explains enzyme action in terms of enzyme properties and factors affecting activity. Compares aerobic respiration and the fermentation pathway in terms of energy release and products. Describes photosynthesis in terms of energy fixation and factors affecting rate. Outcome 3 Describe the structure and function of the digestive and cardiovascular systems. Performance criteria (a) (b) Describes mammalian nutrition in terms of food breakdown and the structure and function of the alimentary canal and associated organs. Describes cardiovascular system in terms of structure and function of heart, blood vessels and lungs. Outcome 4 Describe the evolution of life on earth. Performance criteria (a) (b) Explains biodiversity and adaption to environmental niches. Describes the process of natural selection and evolution of species. HT8P 45, Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) 3
4 National Unit specification: Statement of standards (cont) Evidence requirements for this unit Evidence is required to demonstrate that learners have achieved all outcomes and performance criteria. Written and/or oral recorded evidence for Outcomes 1 to 4 should be assessed using a holistic closed-book assessment under supervised conditions. It is recommended that the assessment be completed within 45 minutes. Unit support notes are offered as guidance and are not mandatory. While the exact time allocated to this unit is at the discretion of the centre, the notional design length is 40 hours. Guidance on the content and context for this unit This unit is intended as part of the framework for the NC Applied Sciences Group Awards but may be suitable for inclusion in other science awards. It is designed to provide learners with an introduction to cell structure, cellular biochemistry, organ systems and evolution. It is envisioned that this unit will provide knowledge and understanding in biological principles to learners undertaking the physical applied sciences route. Outcome 1 Describe the structure and function of living cells In this outcome learners will be introduced to similarities and differences between animal, plant and microbial cell structures, in addition to the function of cellular structures and how this structure relates to function. The process of diffusion as the movement of substances from a high concentration to a low concentration will also be introduced. The semi-permeable nature of the cell membrane should be covered, progressing to the process of osmosis and its effects on both plant and animal cells. The structure and function of DNA and RNA should be discussed in terms of protein synthesis. The nature of DNA as the hereditary information, double helix structure, complementary base pairing and the concept of genes should be discussed, leading on to nature as RNA as a messenger molecule used in protein synthesis. The structure of proteins as fibrous or globular molecules could be introduced to follow on to enzymes in Outcome 2. Transcription and translation could also be introduced but does not need to be covered in terms of the detail of these processes in the cell. Outcome 2 Describe cellular biochemical processes: enzyme activity, respiration and photosynthesis In this outcome learners will be introduced to enzymes as biological catalysts, enzyme specificity and common enzyme catalysed reactions. This should cover both synthesis and degradation reactions, linking into Outcome 3 and the digestive system. Covering the principles of enzyme action, the enzyme catalysed reactions of respiration and photosynthesis should be discussed. The concept of respiration as a two part energy generating reaction; substrate (glycolysis) and oxidative (Krebs cycle and cytochrome system) phosphorylation. Both aerobic respiration and the fermentation pathway should be compared in terms of energy release, yield of ATP and final products of the reactions. The concept of photosynthesis as a two-part energy fixation reaction; photolysis followed by carbon fixation should be covered. Additional factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis, limiting factors and the relationship to horticulture should also be introduced. HT8P 45, Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) 4
5 National Unit Support Notes (cont) Outcome 3 Describe the structure and function of the digestive and cardiovascular systems In this outcome the organ systems in animal physiology should be discussed to provide learners with an overview of the main systems; cardiovascular, respiratory, renal and digestive. Two mammalian organ systems should be described in detail the digestive and cardiovascular systems in terms of structure and function. Learners should be introduced to the requirement for and energy content of food. The breakdown reactions of the three main components of food should be detailed along with the need for digestion. The anatomy and role of the alimentary canal, oesophagus, stomach, small and large intestine and rectum in the breakdown and absorption of food should be covered, alongside the role of the associated organs, salivary glands, pancreas, liver and gall bladder. The structure and function of the heart, lungs and capillary network in gas exchange should also be covered. Learners should be introduced to the anatomy of the heart, blood vessels and lungs and the features that are important for their function in the circulatory system. The capillary network and its role in gas exchange in tissues should also be covered. Outcome 4 Describe the evolution of life on earth In this outcome learners will be introduced to the concepts of biodiversity and diversity of environmental habitats and niches. This should cover adaptation of organisms to habitats and niches and the process of natural selection. Selective breeding and genetic engineering should also be covered, along with speciation and mechanisms that drive speciation. Guidance on approaches to delivery of this unit It is recommended that the outcomes are delivered in numerical order. While there are no assessed practical activities in this unit, it is envisaged that laboratory practicals will play a large part in delivery. Outcome 1 could commence with an overview of cells as the basic unit of life. The similarities and differences in animal, plant and microbial cells could be illustrated with the use of both light and electron microscopy images and cartoons, supported by examination of prepared microscope slides by light microscopy. Learners could also prepare microscope slides of plant, animal and microbial material for examination by light microscopy. Diffusion could be explained through examples of substances which enter and leave the cell by diffusion, eg glucose and amino acids (dissolved food), oxygen, carbon dioxide and waste products, eg urea. Osmosis can be defined as the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane as a result of a water concentration gradient and could be illustrated by the use of real world examples, eg turgor in plant cells. The biomolecules of the cell, DNA, RNA and proteins should be discussed in terms of the central dogma of molecular biology. The terms transcription and translation could be introduced but need not be covered in terms of the detail of these process in the cell. The structure of these molecules could be illustrated with molecular models to enable learners to visualise these molecules. The use of laboratory practical experiments would support the learning of this concept. Demonstration of osmosis could be achieved using model cells or pieces of potato placed in solutions of varying osmolarity. HT8P 45, Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) 5
6 National Unit Support Notes (cont) Outcome 2 could commence with an introduction to enzymes as biological catalysts made by all living cells and essential for the functioning of all living cells. The properties and functions of catalysts (lower the energy input required for chemical reactions; speed up chemical reactions; take part in reactions but remain unchanged) should be described. Enzymes being proteins with unique conformations determining specificity could be illustrated by the use of 3D X-ray crystal structures of proteins and ligands. Respiration and photosynthesis could then be introduced as a series of enzyme controlled reactions. Respiration is the means by which chemical energy stored in glucose is released. Some of this energy is lost as heat from cells but most is used to generate ATP, the energy currency of the cell used for cellular activities such as muscle contraction. The pathways and products of aerobic respiration and fermentation could then be covered and the yield of ATP from the two pathways compared. The idea of oxygen debt could be discussed to illustrate to learners the differences in fermentation pathways of animals, plants and microbes. Photosynthesis could then be introduced as the process of converting light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of ATP, which is used for synthesis of glucose in plants and some microbes. Photosynthesis could be presented as a two part process; photolysis, the splitting of water molecules by light absorbed by chlorophyll and producing oxygen as a by-product and carbon fixation occurring in the stroma of chloroplast in which glucose is synthesised from carbon dioxide and the hydrogen generated during photolysis. The movement of carbon dioxide and oxygen into and out of the leaf could be used to link to diffusion, which was covered in Outcome 1. Factors that limit the rate of photosynthesis could then be covered by the use of real world horticulture examples, eg heat and light and carbon dioxide supplementation to increase yield or produce early crops. Outcome 3 could commence with an overview of how cells combine to produce the tissues which make up organs and the organ system of an organism. The major mammalian organ systems should be outlined and the use of models would be valuable in providing learners with a realistic view of the mammalian anatomy. The main food groups (carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals) and their roles in the body should be introduced. Following on from this, the elemental composition and breakdown products of carbohydrates, fats and proteins could be covered along with examples of enzymes which catalyse these reactions, linking back to Outcome 2. The importance of food and the energy content of the main components of food could then be discussed. Digestion should be described as the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into smaller, soluble food molecules to allow absorption into the blood stream through the lining of the small intestine. The mechanical breakdown of food begins in the mouth. Saliva contains amylase which digests starch into maltose. Mucus in saliva from salivary glands helps to lubricate the mouth and food to aid swallowing. Oesophagus and the mechanism of peristalsis could then be covered. It should be noted that peristalsis occurs throughout the length of the alimentary canal and not just in the oesophagus. Details of the teeth are not required. The role of the stomach in the mechanical and chemical breakdown of proteins could then be covered progressing on to the breakdown of fats in the small intestine by lipase produced by the pancreas, which follows emulsification of fats by bile produced by the liver and stored in the gall bladder. The features of the small intestine which make it suitable for the absorption of materials (villi, microvilli, capillary network) could then be covered and the destinations of the absorbed molecules highlighted: glucose and amino acids carried to the liver via the blood, fats absorbed into the lacteal. The role of the large intestine in water absorption and the rectum and anus in expulsion of waste complete the transit of food through the digestion system. HT8P 45, Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) 6
7 National Unit Support Notes (cont) There are many videos available of both the digestive system via colonoscopy footage and dissections of animal digestive systems. These provide real life views of the digestive system and allow learners to familiarise themselves with the pathway of food transit though the body. Respiration from Outcome 2 and digestion from Outcome 3 could be used to introduce the need for the cardiovascular system. The need for oxygen as a requirement for aerobic respiration and the need to expel carbon dioxide as well as transport nutrients around the body. These points provide the context for the study of the cardiovascular system. The concept of diffusion from Outcome 1 could be integrated in the principle of gas exchange in the lung. The structures of the cardiovascular system (heart, blood vessels, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, overall anatomy of the lungs) could be covered before focusing on the features of the heart as a muscular pump, the function of the arteries, veins and capillaries and gas exchange at the alveoli and the adaptations present that ensure efficient gas exchange. Opportunities for dissection of animal heart and lung tissue would be a useful learning opportunity where available. Outcome 4 could commence with the introduction of the concept of biodiversity, defined as the range of species in an ecosystem. A species is defined as a group of organisms which can interbreed to produce fertile offspring. Within an ecosystem there are a range of habitats and niches which provide the range of materials required by a species for survival; food, shelter, light, water, etc. Learners could then be introduced to the concept of variation within species and the principle that the final appearance of an organism (phenotype) is the result of its genotype and the effects of the environment. If organisms of identical genotype are subject to different environmental conditions they show considerable variation. Learners could then cover natural selection; the process by which organisms better adapted to their environment to survive and breed, while those less well adapted fail to do so. The better adapted organisms are more likely to pass their characteristics to succeeding generations. Natural selection can be illustrated by suitable examples, eg the peppered moth. This leads on to the concept of speciation, the process whereby isolated populations become increasingly dissimilar over time as they are acted on by natural selection in their different habitats. When they are no longer able to interbreed and produce fertile offspring, they have become separate species. Outcome 4 provides excellent material for learners to undertake literature projects investigating the impact of human activity on biodiversity and natural selection. There is also the opportunity to engage learners with discussion and debate as to whether human beings as a species have advanced sufficiently to evade evolutionary forces. Guidance on approaches to assessment of this unit Evidence can be generated using different types of assessment. The following are suggestions only. There may be other methods that would be more suitable to learners. Outcomes 1 4 could be assessed by a single holistic closed-book assessment with an appropriate cut-off score that covers the requirements as detailed in the performance criteria. Assessment should be carried out in supervised conditions, and it is recommended that the assessment be completed within 45 minutes. An exemplar instrument of assessment with marking guidelines has been produced to indicate the national standard of achievement at SCQF level 5. HT8P 45, Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) 7
8 National Unit Support Notes (cont) Centres are reminded that prior verification of centre-devised assessments would help to ensure that the national standard is being met. Where learners experience a range of assessment methods, this helps them to develop different skills that should be transferable to work or further and higher education. Opportunities for e-assessment E-assessment may be appropriate for some assessments in this unit. By e-assessment we mean assessment which is supported by Information and Communication Technology (ICT), such as e-testing or the use of e-portfolios or social software. Centres which wish to use e-assessment must ensure that the national standard is applied to all learner evidence and that conditions of assessment as specified in the evidence requirements are met, regardless of the mode of gathering evidence. The most up-to-date guidance on the use of e-assessment to support SQA s qualifications is available at Opportunities for developing Core and other essential skills This unit has the Critical Thinking component of Problem Solving embedded in it. This means that when learners achieve the unit, their Core Skills profile will also be updated to show they have achieved Critical Thinking at SCQF level 4 The delivery and assessment of this unit will also provide learners with the opportunity to develop the Core Skills of Numeracy, Working with Others and Information and Communication Technology (ICT) at SCQF level 4. Numeracy Using Graphical Information at SCQF level 4 Learners may be required to use graphical methods to present or interpret data on composition of common foodstuff or numbers of species in a range of habitats. Working with Others Working Co-operatively with Others at SCQF level 4 Learners may undertake team work in laboratory activities where tasks must be planned and work carried out cooperatively to achieve end outcomes. Learners may also have the opportunity to carry out group based research projects, presenting results as a presentation or poster. Information and Communication Technology Accessing Information and Providing/Creating Information at SCQF level 4 Learners may be required to use online resources to research factors affecting biodiversity and choose a suitable medium to present the findings. HT8P 45, Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) 8
9 History of changes to unit Version Description of change Date 2 Core Skills Component Critical Thinking at SCQF level 4 embedded. 12/09/2011 Scottish Qualifications Authority 2017 This publication may be reproduced in whole or in part for educational purposes provided that no profit is derived from reproduction and that, if reproduced in part, the source is acknowledged. Additional copies of this unit specification can be purchased from the Scottish Qualifications Authority. Please contact the Business Development and Customer Support team, telephone HT8P 45, Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) 9
10 General information for learners This section will help you decide whether this is the unit for you by explaining what the unit is about, what you should know or be able to do before you start, what you will need to do during the unit and opportunities for further learning and employment. This is a 1 credit unit at SCQF level 5, which you are likely to be studying as part of a NC Applied Sciences programme. This unit is designed to provide you with an introduction to cell structure, cellular biochemistry, organ systems and evolution. On completion of the unit you should be able to: 1 Describe the structure and function of living cells. 2 Describe cellular biochemical processes: enzyme activity, respiration and photosynthesis. 3 Describe the structure and function of the digestive and cardiovascular systems. 4 Describe the evolution of life on earth. Outcome 1 In this outcome you will learn about the structure and function of animal, plant and microbial cells. You will also learn about the processes of diffusion and osmosis and the impacts these processes have on living cells. Furthermore, you will also learn about the structure and function of proteins and nucleic acids. Outcome 2 In this outcome you will learn about the processes by which different cells obtain energy for their activities. You will be introduced to the concept of respiration as the process by which cells obtain energy from food sources and photosynthesis as the process plants use to obtain energy from sunlight. You will also learn about the chemical reactions that require energy in the cell and discover the features of enzymes that enable them to catalyse these reactions. Outcome 3 In this outcome you will learn about the role of the digestive and cardiovascular systems in animal physiology. You will develop your knowledge of enzymes from Outcome 2 by investigating the role of enzymes in the digestive process. You will also learn about the structure of the digestive system and the key organs in the digestive process. You will be introduced to the structure of the heart, lungs and circulatory systems and how these relate to their function. Furthermore you will learn about the role of the circulatory system in the distribution of materials to all of the cells of the body. Outcome 4 In this outcome you will learn about the concept of biodiversity within ecosystems. You will investigate the range of species that live within habitats and how that relates to the resources provided by different habitats. You will also learn about the concept of natural selection and evolution of species. HT8P 45, Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) 10
11 General information for learners (cont) Assessment For Outcomes 1 to 4 you will take a closed-book, end of unit assessment. Core Skills This unit has the Critical Thinking component of Problem Solving embedded in it. This means that when you achieve the unit, your Core Skills profile will also be updated to show you have achieved Critical Thinking at SCQF level 4. You will also have opportunities to develop the Core Skills of Numeracy, Working with Others and Information and Communication Technology (ICT) at SCQF level 4. HT8P 45, Introductory Biology (SCQF level 5) 11
Unit title: Oral Health Improvement: An Introduction (SCQF level 5)
 National Unit Specification General information Unit code: J1DX 45 Superclass: PF Publication date: August 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is designed
National Unit Specification General information Unit code: J1DX 45 Superclass: PF Publication date: August 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is designed
Nutrition for Fitness, Health and Exercise
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H4TF 34 Superclass: RH Publication date: August 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H4TF 34 Superclass: RH Publication date: August 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Nutrition for Sports Therapists. Unit code: DP67 34
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Nutrition for Sports Therapists Unit code: DP67 34 Unit purpose: The Unit is designed to provide the candidate with a good
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Nutrition for Sports Therapists Unit code: DP67 34 Unit purpose: The Unit is designed to provide the candidate with a good
Food Manufacture: Fundamentals of Food Science (SCQF level 6)
 National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H1NE 12 Superclass: WM Publication date: July 2012 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Summary The purpose of this Unit is
National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H1NE 12 Superclass: WM Publication date: July 2012 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Summary The purpose of this Unit is
Sports Therapy: Exercise Principles and Testing
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H4Y4 34 Superclass: PJ Publication date: August 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 03 Unit purpose The Unit is intended
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H4Y4 34 Superclass: PJ Publication date: August 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 03 Unit purpose The Unit is intended
British Sign Language: Using Language in Context (SCQF level 4)
 National Unit Specification General information Unit code: J1FR 44 Superclass: HG Publication date: October 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose The aim of this unit
National Unit Specification General information Unit code: J1FR 44 Superclass: HG Publication date: October 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose The aim of this unit
Intermediate 2. Biology. Learning Outcomes
 Intermediate 2 Biology Learning Outcomes Intermediate 2 Biology Unit 2 Cell structure and function State the similarities and differences between animal, plant and microbial cells. (cheek epithelial cell,
Intermediate 2 Biology Learning Outcomes Intermediate 2 Biology Unit 2 Cell structure and function State the similarities and differences between animal, plant and microbial cells. (cheek epithelial cell,
Unit title: Understanding Mental Health Issues (SCQF level 4)
 National Unit Specification General information Unit code: J1D1 44 Superclass: PH Publication date: August 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is a mandatory
National Unit Specification General information Unit code: J1D1 44 Superclass: PH Publication date: August 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is a mandatory
Higher National Unit specification. General information. Exercise Principles and Programming. Unit code: H4TC 34. Unit purpose.
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H4TC 34 Superclass: MA Publication date: August 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose The Unit is intended
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H4TC 34 Superclass: MA Publication date: August 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose The Unit is intended
Basic Subjective and Objective Assessment
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H4XW 34 Superclass: PJ Publication date: September 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Unit purpose This Unit is
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H4XW 34 Superclass: PJ Publication date: September 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Unit purpose This Unit is
Unit title: Influences on Mental Health and Wellbeing (SCQF level 5)
 National Unit Specification General information Unit code: J1D0 45 Superclass: PH Publication date: August 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is a mandatory
National Unit Specification General information Unit code: J1D0 45 Superclass: PH Publication date: August 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is a mandatory
Unit title: Understanding Mental Health Issues (SCQF level 5)
 National Unit Specification General information Unit code: J1D2 45 Superclass: PH Publication date: August 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is a mandatory
National Unit Specification General information Unit code: J1D2 45 Superclass: PH Publication date: August 2018 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is a mandatory
Animal Care: Anatomy and Physiology of Mammals (SCQF level 5)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F6SL 11 SUMMARY This Unit is designed to provide an introduction to the structure and function of the mammalian animal s body. In this Unit candidates
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F6SL 11 SUMMARY This Unit is designed to provide an introduction to the structure and function of the mammalian animal s body. In this Unit candidates
Higher National Unit specification. General information. Unit title: Electrotherapy (SCQF level 8) Unit code: H71N 35. Unit purpose.
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H71N 35 Superclass: PB Publication date: May 2014 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H71N 35 Superclass: PB Publication date: May 2014 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Contemporary Fitness and Exercise Training Methods: An Introduction (SCQF level 5)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F40B 11 SUMMARY This Unit is a Mandatory Unit of the NC Sport and Fitness (SCQF level 5) award, and has been designed to be undertaken as part of that
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F40B 11 SUMMARY This Unit is a Mandatory Unit of the NC Sport and Fitness (SCQF level 5) award, and has been designed to be undertaken as part of that
UNIT Exercise and Fitness: Exercise to Music (SCQF level 6)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F7JF 12 SUMMARY This Unit is an optional Unit of the National Progression Award in Exercise and Fitness Leadership, but can also be taken as a free-standing
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F7JF 12 SUMMARY This Unit is an optional Unit of the National Progression Award in Exercise and Fitness Leadership, but can also be taken as a free-standing
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Visceral and Dynamic Imaging. Unit code: DW93 34
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Visceral and Dynamic Imaging Unit code: DW93 34 Unit purpose: This Unit enables the candidate to continue to acquire knowledge
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Visceral and Dynamic Imaging Unit code: DW93 34 Unit purpose: This Unit enables the candidate to continue to acquire knowledge
Unit title: Aromatherapy Chemistry (SCQF level 8)
 Higher National unit specification General information Unit code: HL91 35 Superclass: HK Publication date: May 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is designed
Higher National unit specification General information Unit code: HL91 35 Superclass: HK Publication date: May 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is designed
Counselling: Contemporary Psychodynamic Counselling Theory (SCQF level 8)
 Higher National Unit Specification General information Unit code: HT70 35 Superclass: PS Publication date: July 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is designed
Higher National Unit Specification General information Unit code: HT70 35 Superclass: PS Publication date: July 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is designed
Working with Children and Young People with Autism (SCQF level 6)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F7J1 12 SUMMARY This Unit enables candidates to explore the nature of autism and the different ways that particular forms of autism affect children
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F7J1 12 SUMMARY This Unit enables candidates to explore the nature of autism and the different ways that particular forms of autism affect children
Higher National Unit specification: general information. Strength and Conditioning for Sports Performance
 Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FX9T 35 Superclass: MD Publication date: October 2011 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose The purpose of
Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FX9T 35 Superclass: MD Publication date: October 2011 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose The purpose of
1 Higher National Unit credit at SCQF level 8: (8 SCQF credit points at SCQF level 8)
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H928 35 Superclass: PB Publication date: May 2015 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H928 35 Superclass: PB Publication date: May 2015 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
 Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
Higher National Unit specification. General information. Unit title: HIV: An Introduction (SCQF level 7) Unit code: HG3N 34. Unit purpose.
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: HG3N 34 Superclass: PA Publication date: August 2016 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: HG3N 34 Superclass: PA Publication date: August 2016 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
On successful completion of the Unit the learner will be able to:
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H9R8 34 Superclass: PF Publication date: September 2015 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 03 Unit purpose This Unit is
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: H9R8 34 Superclass: PF Publication date: September 2015 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 03 Unit purpose This Unit is
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
UNIT Sports Mechanics: An Introduction (SCQF level 5)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F40K 11 SUMMARY This Unit is an optional Unit of the NC Sport and Fitness (SCQF level 5) award, and has been designed to be undertaken as part of that
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F40K 11 SUMMARY This Unit is an optional Unit of the NC Sport and Fitness (SCQF level 5) award, and has been designed to be undertaken as part of that
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Unit code: F1LF 34
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Dance: Body Conditioning Unit code: F1LF 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to develop the candidate s knowledge and skills
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Dance: Body Conditioning Unit code: F1LF 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to develop the candidate s knowledge and skills
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
Make-up Artistry: Maintenance and Styling of Postiche
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Make-up Artistry: Maintenance and Styling of Postiche Unit code: F0JD 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Make-up Artistry: Maintenance and Styling of Postiche Unit code: F0JD 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates
Counselling: Contemporary Cognitive and Behavioural Theory (SCQF level 8)
 Higher National Unit Specification General information Unit code: HT6X 35 Superclass: PS Publication date: July 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is designed
Higher National Unit Specification General information Unit code: HT6X 35 Superclass: PS Publication date: July 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This unit is designed
S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY
 S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY SCN 3-12a: I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to sustain life SCN
S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY SCN 3-12a: I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to sustain life SCN
What is the function of ribosomes? Draw and label a Bacteria cell.
 Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Station One: Nutrition
 Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
UNIT Forensic Science: Practical Techniques (SCQF level 6)
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F824 12 SUMMARY This Unit develops practical skills and an awareness of the role of science in society by allowing the opportunity for candidates to
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F824 12 SUMMARY This Unit develops practical skills and an awareness of the role of science in society by allowing the opportunity for candidates to
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Dental Fixed Prosthodontics: Veneers and Inlays
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Fixed Prosthodontics: Veneers and Inlays Unit code: F43N 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Fixed Prosthodontics: Veneers and Inlays Unit code: F43N 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable candidates
Prevention and Management of Sports Injury
 Higher National Unit Specification General information Unit code: H4Y1 34 Superclass: PJ Publication date: September 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit provides
Higher National Unit Specification General information Unit code: H4Y1 34 Superclass: PJ Publication date: September 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit provides
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Digestive System. Science 7 HMS 2015
 Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2015 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2015 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Dental Removable Prosthodontics: Complex Complete Dentures
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Removable Prosthodontics: Complex Complete Dentures Unit code: F3G8 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to extend
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Removable Prosthodontics: Complex Complete Dentures Unit code: F3G8 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to extend
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
Dental Removable Prosthodontics: Partial Dentures
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Removable Prosthodontics: Partial Dentures Unit code: F1MD 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is about the theory and skills
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Removable Prosthodontics: Partial Dentures Unit code: F1MD 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is about the theory and skills
7.4 Digestion. Highlight the definition of mechanical digestion.
 7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
Higher National Unit specification: general information. The Community and Culture of Deaf People
 Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FW69 35 Superclass: FB Publication date: October 2011 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is
Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FW69 35 Superclass: FB Publication date: October 2011 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit is
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
***Non-living things may show one or more of these Characteristics, but NEVER ALL of them
 -Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
-Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p.
 NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p. Food (energy) Delivery System into our Bodies Excretory System digestive breaks down food into molecules that cells can use nutrient molecules pass into the bloodstream
NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p. Food (energy) Delivery System into our Bodies Excretory System digestive breaks down food into molecules that cells can use nutrient molecules pass into the bloodstream
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
Counselling Theory for Practice: an Introduction (SCQF level 6)
 National Unit specification General information Unit code: HE1A 46 Superclass: PM Publication date: May 2016 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit has been designed
National Unit specification General information Unit code: HE1A 46 Superclass: PM Publication date: May 2016 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose This Unit has been designed
 CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Unit code: F1BE 35
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Seated Massage Therapy Unit code: F1BE 35 Unit purpose: This Unit has been designed to prepare candidates for industry by
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Seated Massage Therapy Unit code: F1BE 35 Unit purpose: This Unit has been designed to prepare candidates for industry by
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Exercise Principles and Programming. Unit code: DP8E 34
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Exercise Principles and Programming Unit code: DP8E 34 Unit purpose: The Unit is intended to encompass the major functions
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Exercise Principles and Programming Unit code: DP8E 34 Unit purpose: The Unit is intended to encompass the major functions
Biology or Human Biology at SCQF level 6 or Imperial Society of Teachers of Dance (ISTD) s Anatomy and Physiology for Dancers
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dance: Movement Science for Dancers Unit code: F1NM 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide candidates with a comprehensive
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dance: Movement Science for Dancers Unit code: F1NM 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide candidates with a comprehensive
Unit title: Criminology: Crime Scenes (SCQF level 5)
 National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H1WK 11 Superclass: EE Publication date: September 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Summary The purpose of this Unit
National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H1WK 11 Superclass: EE Publication date: September 2017 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Summary The purpose of this Unit
Dental Orthodontics: Fixed Appliance Therapy
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Orthodontics: Fixed Appliance Therapy Unit code: F43R 35 Unit purpose: The Unit allows the candidate to develop the
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Orthodontics: Fixed Appliance Therapy Unit code: F43R 35 Unit purpose: The Unit allows the candidate to develop the
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
1. Analyse interpersonal communication in terms of satisfaction of needs. 2. Analyse the perception of advertising in relation to motivational factors
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit code: D7ME 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is about the analysis of the social and psychological factors which affect communication, and
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit code: D7ME 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is about the analysis of the social and psychological factors which affect communication, and
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract
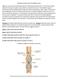 Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
I- Transformation of Food into nutrients: Digestion - Our Food. - Kinds of food. - Food tests. - Chemical transformation of food
 CURRICULUM Grade-9- Biology Cycle:Intermediate Textbook: Life and Earth Science (National Textbook) UNITS Learning Outcomes I- Transformation of Food into nutrients: Digestion - Our Food - Kinds of food
CURRICULUM Grade-9- Biology Cycle:Intermediate Textbook: Life and Earth Science (National Textbook) UNITS Learning Outcomes I- Transformation of Food into nutrients: Digestion - Our Food - Kinds of food
TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 1 st SEMESTER FINAL EXAM:
 TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 1 st SEMESTER FINAL EXAM: FINAL EXAM DETAILS: 80 questions Multiple choice Will assess your mastery of the biological concepts covered in Units 1 and 2 Will assess your
TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 1 st SEMESTER FINAL EXAM: FINAL EXAM DETAILS: 80 questions Multiple choice Will assess your mastery of the biological concepts covered in Units 1 and 2 Will assess your
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
Higher National Unit specification. General information for centres. Unit code: F1M6 34
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Biomaterials Unit code: F1M6 34 Unit purpose: This Unit covers the science of dental biomaterials used in procedures
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Biomaterials Unit code: F1M6 34 Unit purpose: This Unit covers the science of dental biomaterials used in procedures
The Digestive System CP Biology
 The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Unit code: F1B4 34
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Scottish Criminal Law Unit code: F1B4 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide candidates with knowledge and understanding
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Scottish Criminal Law Unit code: F1B4 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide candidates with knowledge and understanding
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
1 Analyse structural and neuromuscular activity. 2 Analyse muscular imbalance and understand how it affects dance movements.
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dance: Movement Science for Dancers Unit code: F4S3 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide candidates with a comprehensive
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dance: Movement Science for Dancers Unit code: F4S3 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to provide candidates with a comprehensive
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
Mark Scheme (Results) March GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01
 Mark Scheme (Results) March 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range of
Mark Scheme (Results) March 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range of
Digestive System. Science 7 HMS 2016
 Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2016 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2016 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion
 Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
This Unit is an optional Unit in the National Certificate in Applied Sciences at SCQF level 5 but it can also be taken as a free-standing Unit.
 National Unit Specification: general information CODE F823 11 SUMMARY This Unit introduces candidates to fundamental techniques of forensic science allowing them to develop skills in biology, chemistry
National Unit Specification: general information CODE F823 11 SUMMARY This Unit introduces candidates to fundamental techniques of forensic science allowing them to develop skills in biology, chemistry
 CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
CP Biology Midterm Review. Scientific Method
 CP Biology Midterm Review Scientific Method 1. Define the following terms: Independent variable Dependent variable Control Constant variables Quantitative Observation Qualitative Observation Variable being
CP Biology Midterm Review Scientific Method 1. Define the following terms: Independent variable Dependent variable Control Constant variables Quantitative Observation Qualitative Observation Variable being
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Childhood Practice and Social Services: Applied Psychology
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Childhood Practice and Social Services: Applied Psychology Unit code: F56T 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Childhood Practice and Social Services: Applied Psychology Unit code: F56T 35 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
chloroplasts cell membrane nucleus nucleus cell wall vacuole cytoplasm Animal cell Plant cell Investigating Cells Summary Booklet page 1
 1. General: state that cells are the basic units of living things. Sections of living tissue, when examined under a microscope are seen to be made up of similar units. These units consist of cytoplasm,
1. General: state that cells are the basic units of living things. Sections of living tissue, when examined under a microscope are seen to be made up of similar units. These units consist of cytoplasm,
1 Higher National Unit credit at SCQF level 7: (8 SCQF credit points at SCQF level 7)
 Flower cards Higher National Unit Specification General information Unit code: H4Y0 34 Superclass: PJ Publication date: September 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose
Flower cards Higher National Unit Specification General information Unit code: H4Y0 34 Superclass: PJ Publication date: September 2013 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose
Human Digestion. Junior Science
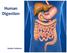 Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Mid Term Review. 1. step 1, only 3. both step 1 and step 2 2. step 2, only 4. neither step 1 nor step 2
 Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
