Chicken Wing Dissection Lab
|
|
|
- Cornelius Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Period Assignment # Chicken Wing Dissection Lab Prelab (Questions 1-12) A tissue is composed of a layer or group of cells of similar size, shape, and function. Within the human body, there are four major types of tissues: 1) epithelial, which cover the body s external and internal surfaces; 2) connective, which bind and support parts; 3) muscle, which make movement possible; and 4) nervous, which conduct impulses from one part of the body to another and help to control and coordinate body activities. 1) What are the 4 main tissue types? Tissues Connective tissues contain a variety of cell types and occur in all regions of the body. They bind structures together, provide support and protection, fill spaces, store fat, and produce blood cells. Connective tissues can be divided into four categories: connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood. Connective tissue proper can be divided into two categories: loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue. Loose connective tissue can be divided into three categories: areolar, adipose, and reticular. Dense connective tissue can be divided into three categories: regular, irregular, and elastic. Cartilage can be divided into three categories: fibrocartilage, hyaline, and elastic. Bone can be divided into two categories: dense and spongy. 2) What are the functions of connective tissue? I. II. III. IV. V.
2 3) Fill out the graphic organizer below based on the reading above. Connective Tissues
3 Bones of the Human Arm The proximal portion of the arm is formed by one long bone, the humerus. The top end of the humerus is rounded and fits into a cup-shaped depression in the scapula forming a ball-and socket joint. Ball-and-socket joints allow for circular movement. The two bones of the forearm are the radius and the ulna. The ulna is fixed in position, but the radius can rotate over the ulna. This makes rotation of the forearm possible in motions such as twisting a screwdriver. When an organism wants to move, signals travel from the brain to the skeletal muscle cells. The muscle cells then contract (get shorter). Strands of dense regular connective tissue connect the skeletal muscles to bones. These strands of tissue are called tendons. When a muscle that connects two bones gets shorter, the bones are pulled closer to each other. For example, tendons attach the biceps muscle to your scapula (the coracoid process and the supra glenoid tubercle) and to the radius of your forearm. When the biceps muscle shortens, your forearm bends toward your shoulder. The skeletal muscles often work in pairs to produce smooth, controlled motions by pulling, or contracting. When one muscle in the pair bends part of the body, the other muscle extends or straightens part of the body. 4) What are the 3 types of joints? (Question #23: How does the skeleton move?) I. II. III. 5) Label the joints featured below 6) Describe the movement that each joint featured above allows.
4 7) For the following words: state the function, type of tissue (for example, irregular dense connective tissue proper), and give an example found in a human arm. (Question #18: How do the structures of the integumentary system determine its function?; Question #20: What are the functions of the axial and appendicular skeletal systems; Question #28: How does the structure of muscle tissue relate to its function?). Function Tissue classification Example found in human arm and explanation of its function in the human arm Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer (hypodermis) Flexor muscle Types of tissue found in a muscle Extensor muscle Tendon Ligament Articular cartilage
5 With your left hand, grasp something with weight such as a heavy textbook or bag and hold it at your side. Place your right hand on your left biceps. Now slowly lift the object. Repeat this motion a few times. Place your right hand on your triceps and slowly lift the object. Repeat this motion a few times. 8) What joint did you use to lift the weight? 9) Which muscle was the flexor? 10) Which muscle was the extensor? 11) Which bones in the arm moved? 12) Which bone in the arm did not move? Purpose: To observe the structure and function of the tissue types found in a chicken wing Materials: Gloves Scissors Probes Chicken wing Procedure: 1) Pick up the chicken wing and bend it straight 2) Now push the chicken wing together Record at least 3 questions below (consider the muscles, skin, and bones) Questions
6 3) Using the scissors, cut down the middle of the skin, starting at the top end of the upper wing. Try not to cut through the muscles below the skin. Do this by piercing the skin and then slipping the scissors between the skin layer and the muscle. Cut until you reach the shoulder joint. 4) Cut down the sides of the skin to make a T-shaped cut. Start at the first cut and cut away from it in both directions. Peel the skin and cut to loosen it. (Take your time peeling it back so as not to damage the tissues underlying it) Complete the data table in the results section as you work through the following procedures 5) Observe the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer (hypodermis) 6) Find the two muscle groups in the proximal end of the wing. Hold the wing down by the shoulder and move the wing tip back and forth. Watch how the muscles move. Each muscle pulls on the lower wing bones in one direction (the flexor bends the joint). Since the flexor cannot lengthen by itself to push the bone back to straighten the joint, another muscle pulls the bone in the opposite direction (extensor). 7) Find the distal muscle group of the wing. Hold the wing down at the shoulder and move the wing tip back and forth. Watch how the distal muscles move. 8) Tendons are shiny white tissues at the ends of the muscles that attach muscles to bones. Find as many tendons as you can on the chicken wing 9) Pull on a tendon to see how it helps the chicken move its wing 10) Demonstrate to your teacher Teacher initials 11) Use scissors to remove the muscles from the bone. Cut the tendons as close to the bone as possible. 12) Closely examine the elbow joint between the upper and lower wing and identify the ligaments.
7 13) Locate the ball-in-socket joint and the hinge joint of the wing. Move different parts of the wing to observe these joints in action. 14) Identify the articular cartilage. Explore how the cartilage helps bone move without grinding against one another. 15) Pull the articular cartilage away from the proximal and distal ends of the humerus 16) Throw the chicken remains away and wash all equipment with soapy water Results: Epidermis Description (Color, texture, etc.) Dermis Subcutaneous layer (hypodermis) Flexor muscle Extensor muscle Tendon Ligament Articular cartilage Analysis: 13) Explain how muscles cause movement. Your answer must include the following words underlined: bone, muscle, tendon, extensor, flexor, shorten, and lengthen. 14) What tissue is referred to as the meat of a chicken wing?
8 15) Imagine ordering a dozen chicken wings. You get a combination of different shaped pieces often called legs and wings. Explain why this is an incorrect description of your food. Use anatomical vocabulary to support your answer. Teacher initials Search for osteoarthritis on Wikipedia. 16) Define arthritis 17) Define osteoarthritis 18) What structure and tissue type observed in this lab is degenerated when someone has this condition?
Winging It. A Musculoskeletal System Lab
 Winging It A Musculoskeletal System Lab How are the muscles and skeleton held together? How do the muscles and bones work together to provide motion? Why do we dissect? Most higher animals have body plans
Winging It A Musculoskeletal System Lab How are the muscles and skeleton held together? How do the muscles and bones work together to provide motion? Why do we dissect? Most higher animals have body plans
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION
 SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
SHHS Gen Bio Muscular System Lab
 SHHS Gen Bio Muscular System Lab Background: Skeletal muscle is the most abundant tissue in the body of healthy adults, comprising anywhere from about 30 to 50% of total body mass. The amount of muscle
SHHS Gen Bio Muscular System Lab Background: Skeletal muscle is the most abundant tissue in the body of healthy adults, comprising anywhere from about 30 to 50% of total body mass. The amount of muscle
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
Support, Movement and Locomotion
 Support, Movement and Locomotion Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Support, Movement and Locomotion Question Paper Time llowed:
Support, Movement and Locomotion Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Support, Movement and Locomotion Question Paper Time llowed:
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
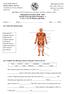 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Skeletal & Muscular Systems Chicken Wing Dissection
 Skeletal & Muscular Systems Chicken Wing Dissection Name: What is Really in a Chicken Wing? Use the picture to the left to answer the following two questions: Doctors often have to do surgery to repair
Skeletal & Muscular Systems Chicken Wing Dissection Name: What is Really in a Chicken Wing? Use the picture to the left to answer the following two questions: Doctors often have to do surgery to repair
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS. Chapter 22 Sections
 THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
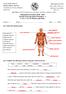 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Types of Body Movements
 Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Anatomy
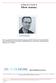 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Anatomy Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can better understand and
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Anatomy Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can better understand and
Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place
 Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
Section Chapter 36. The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems. Go to Section:
 Section 35-1 Chapter 36 The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems Section Outline Section 36-1 36 1 The Skeletal System A. The Skeleton B. Structure of Bones C. Development of Bones D. Types of
Section 35-1 Chapter 36 The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems Section Outline Section 36-1 36 1 The Skeletal System A. The Skeleton B. Structure of Bones C. Development of Bones D. Types of
Boardworks Ltd Types of Synovial Joint
 1 of 37 Types of Synovial Joint Definition: 2 of 37 3 of 37 3. Freely movable or synovial joints 90% of the joints in the body are synovial joints. They are freely movable. Synovial joints contain synovial
1 of 37 Types of Synovial Joint Definition: 2 of 37 3 of 37 3. Freely movable or synovial joints 90% of the joints in the body are synovial joints. They are freely movable. Synovial joints contain synovial
THe Skeletal System 1
 THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below.
 SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
BIO 2 GO! 3213b Movement in Animals-Skeletal Muscular System
 BIO 2 GO! 3213b Movement in Animals-Skeletal Muscular System All multicellular animals that can move to escape harm or to capture food have an advantage over those animals that cannot move. After the successful
BIO 2 GO! 3213b Movement in Animals-Skeletal Muscular System All multicellular animals that can move to escape harm or to capture food have an advantage over those animals that cannot move. After the successful
Joints. Vi Michelle Austin
 Joints Vi Michelle Austin Joints Overview A joint, otherwise known as an articulation, is a point at which points connect. They are constructed to allow movement (except for skull bones) and provide mechanical
Joints Vi Michelle Austin Joints Overview A joint, otherwise known as an articulation, is a point at which points connect. They are constructed to allow movement (except for skull bones) and provide mechanical
Chapter 6 part 2. Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 6 part 2 Skeletal Muscles of the Body Basic Principles 600 + muscles in the human body (you are required to learn 45, lucky kids)! Skeletal Muscles pull on bones Origin of a muscle = point of attachment
Chapter 6 part 2 Skeletal Muscles of the Body Basic Principles 600 + muscles in the human body (you are required to learn 45, lucky kids)! Skeletal Muscles pull on bones Origin of a muscle = point of attachment
To meet the expectations of this unit, students should already be able to describe the skeleton s role in movement, support and protection.
 GRADE 9: Life science 4 Movement UNIT 9L.4 4 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 9. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
GRADE 9: Life science 4 Movement UNIT 9L.4 4 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 9. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems
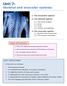 Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
The skeleton consists of: Bones: special connective tissue, hard. Cartilage: special connective tissue, less hard than bones. Joints: joint is the
 The skeleton consists of: Bones: special connective tissue, hard. Cartilage: special connective tissue, less hard than bones. Joints: joint is the location at witch two bones make contact, whereas ligaments
The skeleton consists of: Bones: special connective tissue, hard. Cartilage: special connective tissue, less hard than bones. Joints: joint is the location at witch two bones make contact, whereas ligaments
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology. Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
Names: Block: Date: Building an Articulated Model of the Hand
 Names: Block: Date: Building an Articulated Model of the Hand Background : Musculoskeletal movement Humans are large and complex organisms that require muscular and skeletal systems for support and locomotion.
Names: Block: Date: Building an Articulated Model of the Hand Background : Musculoskeletal movement Humans are large and complex organisms that require muscular and skeletal systems for support and locomotion.
Skeletal System. Std. VIII
 Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU!
 SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
04/10/2013. Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT!
 04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of
04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO
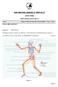 SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO SIXTH FORM Half Yearly Exam 2014 Name: Subject: Physical Education Intermediate Time: 2 Hours Answer ALL questions Question 1: (The Skeleton) The human skeleton is made up of 206
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO SIXTH FORM Half Yearly Exam 2014 Name: Subject: Physical Education Intermediate Time: 2 Hours Answer ALL questions Question 1: (The Skeleton) The human skeleton is made up of 206
The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action!
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Shoulder Instability. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
 Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Every Flex is Quite Complex
 Name Class Date Every Flex is Quite Complex Struture and Funtion in a Chiken Wing Investigative Lab 27 8 Question How do the tissues of a hiken wing work together during movement? Lab Overview In this
Name Class Date Every Flex is Quite Complex Struture and Funtion in a Chiken Wing Investigative Lab 27 8 Question How do the tissues of a hiken wing work together during movement? Lab Overview In this
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
What type of tissue is this
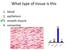 What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups:
 MUSCLES The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups: 1. VOLUNTARY or SKELETAL MUSCLESthese muscles are under the control of our will. All these muscles are attached to the skeleton. These
MUSCLES The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups: 1. VOLUNTARY or SKELETAL MUSCLESthese muscles are under the control of our will. All these muscles are attached to the skeleton. These
The Articular System OBJECTIVES ACTIVITIES. A. Completion
 C H A P T E R 8 The Articular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name and describe the three types of joints. 2. Name the two types of synarthroses joints. 3. Name
C H A P T E R 8 The Articular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name and describe the three types of joints. 2. Name the two types of synarthroses joints. 3. Name
Arm Model. Wrap a rubber band around the three bamboo skewers so that they are in this position. This is the elbow joint.
 Arm Model Category: Biology: Human Body; Physics: Force & Motion Type: Make & Take Rough Parts List: 3 Pipe cleaners 2 Craft sticks 2 ½ Pieces of straw 3 Bamboo skewers 2 Rubber bands Tools List: Scissors
Arm Model Category: Biology: Human Body; Physics: Force & Motion Type: Make & Take Rough Parts List: 3 Pipe cleaners 2 Craft sticks 2 ½ Pieces of straw 3 Bamboo skewers 2 Rubber bands Tools List: Scissors
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE. CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement?
 PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL
 LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
Skin. the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight
 Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide
 DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy?
 CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
Muscles. Grade Level: 4-6
 Muscles Grade Level: 4-6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 6 Activity Page pages 7 Practice Page page 8-9 Homework Page page 10 Answer Key page 11-13 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask
Muscles Grade Level: 4-6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 6 Activity Page pages 7 Practice Page page 8-9 Homework Page page 10 Answer Key page 11-13 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. locomotion.
 STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
WORLDS GREATEST WARM UP. Sets Reps Weight Notes DB ALTERNATING BICEP CURLS WITH TWIST
 Jump Start Week # DAY WORLDS GREATEST WARM UP DUMBBELL STIFF LEG DEAD LIFT ***This Week -we are doing circuits. - sets of reps moving from exercise A-B-C-D-E-F and then back round again to A. So A- reps,
Jump Start Week # DAY WORLDS GREATEST WARM UP DUMBBELL STIFF LEG DEAD LIFT ***This Week -we are doing circuits. - sets of reps moving from exercise A-B-C-D-E-F and then back round again to A. So A- reps,
Unsaved Test, Version: 1 1
 Name: Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. Functions of the skeletal system include A. forcing blood to circulate through the body B. sending electrical signals to the brain C. providing support and
Name: Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. Functions of the skeletal system include A. forcing blood to circulate through the body B. sending electrical signals to the brain C. providing support and
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training
 Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
9.1 Joints. Objectives Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints
 Joints 9.1 Joints Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints Joints have both structural and functional classifications: The criteria for classifying joints structurally are anatomical
Joints 9.1 Joints Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints Joints have both structural and functional classifications: The criteria for classifying joints structurally are anatomical
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education Muscles and Muscle Action These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
KS4 Physical Education Muscles and Muscle Action These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives
 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis
 Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis LEARNING OBJECTIVES: At the end of this laboratory exercise the student will be able to: Identify forces used during activities Identify moments used during activities
Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis LEARNING OBJECTIVES: At the end of this laboratory exercise the student will be able to: Identify forces used during activities Identify moments used during activities
YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme
 YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme Half Term/Term Learning objective Learning activity Differentiation and extension Bones. Knowledge of the bones at the following locations: head/neck cranium, vertebrae
YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme Half Term/Term Learning objective Learning activity Differentiation and extension Bones. Knowledge of the bones at the following locations: head/neck cranium, vertebrae
Elbow Anatomy, Growth and Physical Exam. Donna M. Pacicca, MD Section of Sports Medicine Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Children s Mercy Hospital
 Elbow Anatomy, Growth and Physical Exam Donna M. Pacicca, MD Section of Sports Medicine Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Children s Mercy Hospital Contributing Factors to Elbow Injury The elbow is affected
Elbow Anatomy, Growth and Physical Exam Donna M. Pacicca, MD Section of Sports Medicine Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Children s Mercy Hospital Contributing Factors to Elbow Injury The elbow is affected
GENERAL EXERCISES ELBOW BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017
 GENERAL EXERCISES ELBOW BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only are not to be
GENERAL EXERCISES ELBOW BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only are not to be
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Anatomy. TherAccess - Hand and Upper Extremity Rehab Center
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Anatomy TherAccess, PLLC is founded by experienced therapy professionals. The purpose of this website was to develop a simple yet comprehensive collection of resources for our
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Anatomy TherAccess, PLLC is founded by experienced therapy professionals. The purpose of this website was to develop a simple yet comprehensive collection of resources for our
Movin and Shakin. Science Start: Body Works
 Movin and Shakin Organisms and Environments TEKS for Activities and Presentation Kindergarten: K.10 (B) First Grade: 1.10 (A) Second Grade: 2.10 (A) Third Grade: 3.10 (A) Fourth Grade: 4.10 (A) Fifth Grade:
Movin and Shakin Organisms and Environments TEKS for Activities and Presentation Kindergarten: K.10 (B) First Grade: 1.10 (A) Second Grade: 2.10 (A) Third Grade: 3.10 (A) Fourth Grade: 4.10 (A) Fifth Grade:
11.2 Muscles and Movement
 11.2 Muscles and Movement 11.2.1 - State the roles of bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves in human movement Bones Act as anchors for the muscles, and levers to control the movement of muscles,
11.2 Muscles and Movement 11.2.1 - State the roles of bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves in human movement Bones Act as anchors for the muscles, and levers to control the movement of muscles,
Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) Answers to Activity Questions
 Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) 1. Holds bones together; allows the rigid skeleton some flexibility so that gross body movements can occur 2. c, amount of movement allowed by the joint 3. synovial 4.
Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) 1. Holds bones together; allows the rigid skeleton some flexibility so that gross body movements can occur 2. c, amount of movement allowed by the joint 3. synovial 4.
CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS
 CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt
CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt
Urmston Physio Clinic
 Urmston Physio Clinic Patient Information Shoulder Instability Prepared for Mr B. Roy Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon 102 Church Road, Urmston, Manchester, M41 9DB Tel: 0161 748 4100 Shoulder Instability
Urmston Physio Clinic Patient Information Shoulder Instability Prepared for Mr B. Roy Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon 102 Church Road, Urmston, Manchester, M41 9DB Tel: 0161 748 4100 Shoulder Instability
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system.
 L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
2º ESO - PE Workbook - IES Joan Miró Physical Education Department THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
Labral Tears. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
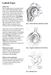 Labral Tears What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone that is
Labral Tears What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone that is
The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity-The Elbow Joint C. Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity-The Elbow Joint C. Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Structure of The Elbow Joint A simple hinge joint, actually categorized as a trochoginglymus joint
The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity-The Elbow Joint C. Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Structure of The Elbow Joint A simple hinge joint, actually categorized as a trochoginglymus joint
SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA
 Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
Main Menu. Elbow and Radioulnar Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints click here Main Menu K.4 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k4entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:29:53 PM] Bones Ulna is much larger proximally than radius Radius is much
1 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints click here Main Menu K.4 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k4entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:29:53 PM] Bones Ulna is much larger proximally than radius Radius is much
Body Organization and Structure
 CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Body Organization and Structure As you read Chapter 19, which begins on page 462 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 462)
CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Body Organization and Structure As you read Chapter 19, which begins on page 462 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 462)
Chapter 09 Articulations Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
Major Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Biology v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems. Skeletomuscular system cards
 Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
I. Introduction. Unit Two. of the Skeletal System. II. Classification of Joints. URLs for this chapter:
 8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
FOR PERSONAL USE. Muscles and Movement BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN ACTIVITY ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES
 activity 22 Muscles and Movement BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 22 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
activity 22 Muscles and Movement BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 22 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
A Patient s Guide to Adult Olecranon (Elbow) Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Olecranon (Elbow) Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Adult Olecranon (Elbow) Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by
 Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by structure and by function: Structural classification focuses
Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by structure and by function: Structural classification focuses
Muscle Tissue. Isometric Contraction. Isotonic Contractions 11/22/2016. Muscles. Anatomy Two Joints And Movements
 Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
The Elbow and the cubital fossa. Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems
 Name Date Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems 1 2 Per. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 12 16 17 18 15 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
Name Date Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems 1 2 Per. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 12 16 17 18 15 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
The skeleton supports the body. The skeleton protects soft body parts The skeleton produces blood cells. The skeleton stores minerals and fat.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton supports the body. The bones of the legs support the entire body when we are standing, and the coxal bones of the pelvic girdle support the abdominal cavity.
SKELETAL SYSTEM SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton supports the body. The bones of the legs support the entire body when we are standing, and the coxal bones of the pelvic girdle support the abdominal cavity.
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems
 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege To move the skeleton, the tension created by the contraction of the fibers in most skeletal muscles
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege To move the skeleton, the tension created by the contraction of the fibers in most skeletal muscles
Chapter 6 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints
 The Elbow & Radioulnar Chapter 6 The Elbow and Radioulnar Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints Usually grouped
The Elbow & Radioulnar Chapter 6 The Elbow and Radioulnar Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints Usually grouped
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
Traumatic Instability Understanding your shoulder injury and its repair
 Patient Education Traumatic Instability Understanding your shoulder injury and its repair Your upper arm bone popped out of the socket of your shoulder blade. When this happened, it tore your ligaments
Patient Education Traumatic Instability Understanding your shoulder injury and its repair Your upper arm bone popped out of the socket of your shoulder blade. When this happened, it tore your ligaments
A. Incorrect! The appendicular skeleton includes bones of the shoulder, arm, hand, pelvis, leg and foot.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
Arthroplasty Of The Shoulder
 Arthroplasty Of The Shoulder 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Arthroplasty Of The Shoulder About Your Shoulder. Ligaments and tendons hold it together. Ligaments connect the bones, while tendons connect muscles to the
Arthroplasty Of The Shoulder 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Arthroplasty Of The Shoulder About Your Shoulder. Ligaments and tendons hold it together. Ligaments connect the bones, while tendons connect muscles to the
CHAPTER 14. Bones Muscles Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
Skeletal Considerations for Movement. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Muscular System. Jannet Musleh Zahra Omairat Namera Khan Aala Omer
 Muscular System Jannet Musleh Zahra Omairat Namera Khan Aala Omer I can: Learn about the Muscular system. Do now: What comes to mind when you hear Muscular system? Major Functions of the Muscular system.
Muscular System Jannet Musleh Zahra Omairat Namera Khan Aala Omer I can: Learn about the Muscular system. Do now: What comes to mind when you hear Muscular system? Major Functions of the Muscular system.
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
REVISION PPT FOR SA II CLASS VI MOVEMENTS IN THE BODY PREPARED BY VIKRANT V. PURANDARE
 REVISION PPT FOR SA II CLASS VI MOVEMENTS IN THE BODY PREPARED BY VIKRANT V. PURANDARE 1] Complete the flow chart including the levels of organization in a human body. cells Tissues Organs Organ system
REVISION PPT FOR SA II CLASS VI MOVEMENTS IN THE BODY PREPARED BY VIKRANT V. PURANDARE 1] Complete the flow chart including the levels of organization in a human body. cells Tissues Organs Organ system
