Femoral deformity in tibia vara
|
|
|
- Marsha Warren
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Open Access Publications Femoral deformity in tibia vara J. Eric Gordon St. Louis Shriners Hospital for Children David J. King Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Scott J. Luhmann St. Louis Shriners Hospital for Children Matthew B. Dobbs St. Louis Shriners Hospital for Children Perry L. Schoenecker St. Louis Shriners Hospital for Children Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Medicine and Health Sciences Commons Recommended Citation Gordon, J. Eric; King, David J.; Luhmann, Scott J.; Dobbs, Matthew B.; and Schoenecker, Perry L.,,"Femoral deformity in tibia vara." The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery.88, (2006). This Open Access Publication is brought to you for free and open access by Digital It has been accepted for inclusion in Open Access Publications by an authorized administrator of Digital For more information, please contact
2 380 COPYRIGHT 2006 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Femoral Deformity in Tibia Vara BY J. ERIC GORDON, MD, DAVID J. KING, MD, SCOTT J. LUHMANN, MD, MATTHEW B. DOBBS, MD, AND PERRY L. SCHOENECKER, MD Investigation performed at Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis Shriners Hospital for Children, and St. Louis Children s Hospital, St. Louis, Missouri Background: Previous studies have suggested that compensatory valgus deformity of the femur is common in patients with tibia vara, or Blount disease. The availability and routine use of standing long-cassette radiographs of the lower extremities to assess angular deformities has allowed quantitative evaluation of this hypothesis. Methods: The cases of all patients with tibia vara, two years of age or older, seen at our institution prior to treatment, over a thirteen-year period, were reviewed. Seventy-three patients with a total of 109 involved lower limbs were identified and were classified as having either infantile tibia vara (thirty-seven patients with fifty-six involved limbs) or late-onset tibia vara (thirty-six patients with fifty-three involved limbs). Standardized standing radiographs of the lower extremity were examined to assess the deformity at the distal part of the femur and the proximal part of the tibia by measuring the lateral distal femoral angle and the medial proximal tibial angle. Results: The distal part of the femur in the children with infantile tibia vara either was normal or had mild varus deformity, with a mean lateral distal femoral angle of 97 (range, 82 to 129 ). The mean medial proximal tibial angle in these children was 72 (range, 32 to 84 ). Older children with infantile tibia vara were noted to have little distal femoral deformity, with no more than 4 of valgus compared with either normal values or the contralateral, normal limb. Children with late-onset tibia vara had a mean lateral distal femoral angle of 93 (range, 82 to 110 ) and a mean medial proximal tibial angle of 73 (range, 52 to 84 ). On the average, the varus deformity of the distal part of the femur constituted 30% (6 of 20 ) of the genu varum deformity in these patients. Conclusions: Patients with infantile tibia vara most commonly had normal alignment of the distal parts of the femora; substantial valgus deformity was not observed. Distal femoral varus constituted a substantial portion of the genu varum in children with late-onset disease. When correction of late-onset tibia vara is planned, the surgeon should be aware of the possibility that distal femoral varus is a substantial component of the deformity. Tibia vara, or Blount disease, is a complex deformity that can be difficult to correct Treatment recommendations have focused on the tibial deformity. Less severe deformities in older children and in adolescents with open physes have been treated successfully with hemiepiphysiodesis or hemiepiphyseal stapling 7, The most severe deformities in children with neglected infantile tibia vara require osteotomy with or without elevation of the medial tibial plateau 2,12-14,22,23. More severe deformities or deformities in patients with little or no remaining growth require osteotomy combined with internal or external fixation 1,3,5,6,8-11,15,17,22, Femoral deformity has long been noted in patients with tibia vara, and this has complicated the treatment 13,23, Infantile tibia vara has been associated with overgrowth of the medial condyle of the femur, resulting in a valgus deformity of the distal part of the femur 13,23,29,30, Late-onset tibia vara has been associated with both varus and valgus deformity of the distal part of the femur 13,29,33,35,36. Recently, the use of standardized long-cassette radiographs and analysis of the mechanical axis have become the standard for assessing lower-extremity deformities 37,38. The establishment of standard positioning and radiographic techniques has allowed much more exact assessment of complex deformities, particularly tibia vara, than was possible previously At our institution, we have routinely utilized this method of evaluating children with angular deformities of the lower extremity, including tibia vara, since We have found that careful measurement of each of the constituent deformities is essential to correct these deformities accurately. The purpose of this study was to evaluate, with use of standardized long-cassette radiographs, the distal femoral alignment in patients with different forms of tibia vara and to characterize these deformities. Materials and Methods he charts and radiographs of all patients treated for tibia T vara at our institution between January 1, 1990, and December 31, 2002, were retrospectively reviewed. The charts
3 381 were reviewed for demographic data, and patients were classified as having early-onset, or infantile, tibia vara if the age at onset was three years or younger and as having late-onset tibia vara if the age at onset was four years or older. Late-onset disease was further classified as either juvenile (age at onset, four to ten years) or adolescent (age at onset, eleven years or older) 1,41. Patients treated previously with femoral surgical intervention or bracing and those in whom the tibial deformity had resolved prior to presentation at our institution were excluded from the study. The immediate pretreatment standing anteroposterior radiographs were examined, and the lateral distal femoral angle (normal average, 88 ; normal range, 86 to 90 ) and the medial proximal tibial angle (normal average, 87 ; normal range, 85 to 89 ) were measured (Fig. 1) 37,38. These measurements were selected because they characterize the osseous deformity about the knee in the distal part of the femur and the proximal part of the tibia. The radiograph was made with the patient standing and positioned with the distal part of the femur presenting in an anteroposterior view (the contour of the femoral notch was normal, and the patella was facing directly anterior 39 ). When the contralateral side was noted to be normal and was included on the radiographs, the lateral distal femoral angle and the medial proximal tibial angle were measured as controls. Seventy-three patients, with a total of 109 involved limbs, who had tibia vara and standing anteroposterior radiographs of the lower extremity made prior to treatment were identified. Thirty-seven patients with a total of fifty-six involved limbs had infantile tibia vara: nineteen of them (thirty-eight extremities) had bilateral involvement, and eighteen had unilateral involvement. The thirty-seven patients with infantile tibia vara had a mean age of 4.9 years (range, 2.0 to 12.5 years) at presentation, and the nineteen patients with unilateral early-onset disease had a mean age of 4.4 years (range, 2.0 to 9.2 years). Thirty-six patients with a total of fifty-three involved limbs had late-onset tibia vara. Thirteen of them (seventeen involved limbs) had juvenile tibia vara, and twenty-three (thirty-six involved limbs) had adolescent tibia vara. Seventeen of the thirty-six patients with late-onset disease had bilateral tibia vara, and nineteen had unilateral tibia vara. The mean age at presentation was 13.8 years (range, 8.2 to 18.2 years) for the thirty-six patients with late-onset tibia vara and 13.0 years (range, 10.2 to 18.2 years) for the nineteen patients with unilateral late-onset disease. Results Infantile Tibia Vara he fifty-six involved limbs in the thirty-seven patients T with infantile tibia vara had a mean lateral distal femoral angle of 97 (range, 82 to 129 ). Only two patients with infantile tibia vara, who were 5.7 and 7.5 years old at the time of presentation, had a lateral distal femoral angle of <85, and neither angle was <82. Thirty (54%) of the fifty-six limbs with infantile tibia vara had a lateral distal femoral angle of 93 ( 5 of varus deformity), and twenty-two had a lateral distal femoral angle of 98 ( 10 of varus deformity). The lateral distal femoral angle decreased with increasing age at the time of the evaluation, changing from a more varus alignment toward a normal to slightly valgus alignment in the older patients (Fig. 2). The mean medial proximal tibial angle was 72 (range, 32 to 84 ). There was no substantial change in the medial proximal tibial angle with increasing age at the time of evaluation (Fig. 3). Fig. 1 Coronal plane illustration of the lower extremity, demonstrating measurement of the lateral distal femoral angle (LDFA) and the medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA).
4 382 Fig. 2 Lateral distal femoral angle compared with age at the time of the evaluation in patients with infantile tibia vara. The eighteen patients with unilateral infantile tibia vara had a mean lateral distal femoral angle of 99 (range, 83 to 116 ). The mean lateral distal femoral angle on the contralateral, normal side in these patients was 96 (range, 86 to 115 ). The mean difference in the lateral distal femoral angle between the control and involved sides was 3 (range, 4 to +18 ), representing slightly more varus of the femur of the involved extremity. The lateral distal femoral angle of the involved extremity was in more valgus than that of the contralateral extremity in six patients, but this difference was as much as 4 in only two patients. No patient had >4 of valgus angulation of the distal part of the femur compared with the contralateral, normal side. The eighteen patients with unilateral infantile tibia vara had a mean medial proximal tibial angle of 74 (range, 43 to 84 ), with a mean of 89 (range, 79 to 95 ) on the contralateral, normal side and a mean difference between the normal and involved sides of 14 (range, 3 to 38 ), representing more varus in the involved extremity. Fig. 3 Medial proximal tibial angle compared with age at the time of the evaluation in patients with infantile tibia vara.
5 383 Fig. 4 Lateral distal femoral angle compared with age at the time of the evaluation in patients with late-onset tibia vara. Late-Onset Tibia Vara The fifty-three involved limbs in the thirty-six patients with late-onset tibia vara had a mean lateral distal femoral angle of 93 (range, 82 to 110 ). Twenty-nine (55%) of the fifty-three involved limbs had a lateral distal femoral angle of 93 ( 5 of varus deformity), and ten (19%) had a lateral distal femoral angle of 98 ( 10 of varus deformity). Although there was no substantial change in the lateral distal femoral angle with increasing age, distal femoral varus was seen in all age groups (Fig. 4). The nineteen patients with unilateral late-onset tibia vara had a mean lateral distal femoral angle of 95 (range, 82 to 106 ), with a mean of 87 (range, 83 to 92 ) on the contralateral, uninvolved side and a mean difference between the involved and uninvolved sides of 8 (range, 2 to +21 ), representing more varus in the distal part of the femur of the extremity with tibia vara. On the average, the varus deformity of Fig. 5 Medial proximal tibial angle compared with age at the time of the evaluation in patients with late-onset tibia vara.
6 384 unilateral late-onset disease had a mean medial proximal tibial angle of 74 (range, 52 to 81 ), with a mean of 88 (range, 84 to 93 ) on the contralateral side and a mean difference of 14 (range, 7 to 38 ) between the normal and control sides, representing more varus in the tibia of the involved extremity. Fig. 6 Standing anteroposterior radiograph of the left lower extremity of a fourteen-year-old boy with late-onset tibia vara and apparent distal femoral valgus. The lateral distal femoral angle measures 91, representing slight distal femoral varus. the distal part of the femur constituted 30% (6 of 20 ) of the genu varum deformity in these patients. The mean medial proximal tibial angle in the patients with late-onset tibia vara was 73 (range, 52 to 84 ). There was no substantial change in the medial proximal tibial angle with increasing age (Fig. 5). The nineteen patients with Fig. 7 Standing anteroposterior radiograph of the left lower extremity of a thirteen-year-old boy with late-onset tibia vara and an apparently normal distal part of the femur. The lateral distal femoral angle measures 100, representing substantial distal femoral varus.
7 385 Discussion n an assessment of lower-extremity deformity, care must be I taken to measure, on a reproducible radiograph, each of the contributing deformities. In the past, radiographs of the knee or longer non-standardized radiographs were used to assess deformity in patients with tibia vara 13,30,32, Nonstandardized radiographs of the knee or a portion of the lower extremity do not allow the full assessment of deformities that is possible with a review of a long-cassette radiograph made with proper positioning. A long-cassette radiograph can reveal the true contribution of femoral deformity to the overall deformity. It had been assumed that proximal tibial varus was the only substantial deformity in tibia vara. In reality, tibia vara is often a complex deformity that includes distal femoral deformity, proximal tibial varus and procurvatum, internal tibial torsion, and distal tibial deformity 23,29,32,36, These other deformities cannot be ignored when a global strategy is being planned for correction of severe tibia vara. Kline et al. measured the distal femoral component on standardized radiographs of patients with late-onset tibia vara and reported that the distal femoral varus deformity was often as great as the proximal tibial varus deformity 29. All of the six patients in that study had 5 of distal femoral varus compared with the normal value. Persistent distal femoral deformity did not develop in the children with infantile tibia vara in our series. Children with infantile tibia vara who were seven years of age or younger were often observed to have varus in the distal part of the femur, but this deformity seemed to disappear gradually with increasing age (Fig. 2). In older children with residual infantile tibia vara, the distal part of the femur tended to have a normal to slightly valgus mechanical alignment. Valgus deformity was noted in two older children with early-onset tibia vara, but it was mild (never >4 ). Our data further suggest that the distal femoral mechanical axis in children with late-onset tibia vara is always in neutral to varus alignment. Often, the distal femoral varus deformity contributes substantially to the overall genu varum 29. We did not observe substantial valgus deformity in any patient with late-onset tibia vara. However, ten (19%) of the fiftythree extremities with late-onset disease had 10 of varus deformity, a factor that should be taken into account when surgical correction is being planned. Failure to account for the femoral deformity, when it is substantial, could lead either to undercorrection of the entire deformity or to excessive compensatory correction of the tibia with resulting obliquity of the knee joint. One possible reason for the widespread belief that patients with severe tibia vara have distal femoral valgus deformity is the appearance of valgus on radiographs of the knee. Most orthopaedic surgeons interpret distal femoral deformity on the basis of how parallel the knee joint is to the floor. If the knee joint appears to be parallel to the floor, then the distal part of the femur appears normal. If, however, the medial femoral condyle appears to be more distal than the lateral femoral condyle, with a resulting downward medial joint slope, the distal part of the femur is interpreted as having a valgus deformity. In tibia vara, the proximal tibial varus deformity prevents the patient from bringing the knees together in stance. This produces relative hip abduction during stance that leads to an anatomically normal distal part of the femur with an appearance of substantial valgus on anteroposterior radiographs (Fig. 6). In the same way, patients with a substantial genu varum deformity with distal femoral varus can appear to have normal distal femoral alignment because the relative abduction of the hip seems to correct the alignment of the distal part of the femur, placing the knee joint parallel to the floor (Fig. 7). Therefore, varus and valgus changes of the distal part of the femur cannot be accurately assessed by simple visual inspection of either a knee radiograph or even a long-cassette radiograph. It is imperative that long-cassette radiographs be made with the limb in proper alignment when definitive correction is being planned for patients with tibia vara and that angular measurements be performed to assess the true amount of distal femoral deformity 37,38. Our data suggest that distal femoral valgus is seldom present in tibia vara, except in severe, neglected cases of earlyonset disease. Valgus deformity is often more apparent than real in patients with tibia vara, and we believe that varus distal femoral osteotomies are rarely justified, except for older children with severe neglected disease. In conclusion, we found valgus changes in the distal part of the femur in patients with infantile tibia vara to be small and that patients with the appearance of valgus on radiographs often do not have a true deformity. Patients with lateonset tibia vara were found to have varus changes in the distal part of the femur, and the femoral component often represented a substantial portion of the genu varum deformity. J. Eric Gordon, MD Scott J. Luhmann, MD Matthew B. Dobbs, MD Perry L. Schoenecker, MD St. Louis Shriners Hospital for Children, 2001 South Lindbergh Boulevard, St. Louis, MO address for J.E. Gordon: gordone@msnotes.wustl.edu David J. King, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Washington University School of Medicine, 660 South Euclid Avenue, St. Louis, MO The authors did not receive grants or outside funding in support of their research for or preparation of this manuscript. They did not receive payments or other benefits or a commitment or agreement to provide such benefits from a commercial entity. No commercial entity paid or directed, or agreed to pay or direct, any benefits to any research fund, foundation, educational institution, or other charitable or nonprofit organization with which the authors are affiliated or associated. doi: /jbjs.c.01518
8 386 References 1. Thompson GH, Carter JR. Late-onset tibia vara (Blount s disease). Current concepts. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;255: Accadbled F, Laville JM, Harper L. One-step treatment for evolved Blount s disease: four cases and review of the literature. J Pediatr Orthop. 2003;23: Black BE. Tibial opening greenstick osteotomy for Blount s disease. J South Orthop Assoc. 1997;6: Buckley SL, Carlson JR, Robertson WW Jr. Osteotomy of the proximal tibia in the treatment of adolescent tibia vara. Orthop Rev. 1993;22: Ganel A, de Pablos J, Alfaro J, Barios C. Treatment of adolescent Blount disease by asymmetric physeal distraction. J Pediatr Orthop. 1997;17: Hayek S, Segev E, Ezra E, Lokiec F, Wientroub S. Serrated W/M osteotomy. Results using a new technique for the correction of infantile tibia vara. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82: Henderson RC, Kemp GJ Jr, Greene WB. Adolescent tibia vara: alternatives for operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74: Laurencin CT, Ferriter PJ, Millis MB. Oblique proximal tibial osteotomy for the correction of tibia vara in the young. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; 327: Miller S, Radomisli T, Ulin R. Inverted arcuate osteotomy and external fixation for adolescent tibia vara. J Pediatr Orthop. 2000;20: Price CT, Scott DS, Greenberg DA. Dynamic axial external fixation in the surgical treatment of tibia vara. J Pediatr Orthop. 1995;15: Rab GT. Oblique tibial osteotomy for Blount s disease (tibia vara). J Pediatr Orthop. 1988;8: Schoenecker PL, Meade WC, Pierron RL, Sheridan JJ, Capelli AM. Blount s disease: a retrospective review and recommendations for treatment. J Pediatr Orthop. 1985;2: Schoenecker PL, Johnston R, Rich MM, Capelli AM. Elevation of the medial plateau of the tibia in the treatment of Blount disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74: Siffert RS. Intraepiphyseal osteotomy for progressive tibia vara: case report and rationale of management. J Pediatr Orthop. 1982;2: Smith CF. Tibia vara (Blount s disease). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64: Steel HH, Sandrow RE, Sullivan PD. Complications of tibial osteotomy in children for genu varum or valgum. Evidence that neurological changes are due to ischemia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971;53: Wenger DR, Mickelson M, Maynard JA. The evolution and histopathology of adolescent tibia vara. J Pediatr Orthop. 1984;4: Mielke CH, Stevens PM. Hemiepiphyseal stapling for knee deformities in children younger than 10 years: a preliminary report. J Pediatr Orthop. 1996; 16: Blount WP, Clarke GR. Control of bone growth by epiphyseal stapling. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1949;31: Blount WP. A mature look at epiphyseal stapling. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1971;77: Zuege RC, Kempken TG, Blount WP. Epiphyseal stapling for angular deformity at the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61: Laville JM, Chau E, Willemen L, Kohler R, Garin C. Blount s disease: classification and treatment. J Pediatr Orthop B. 1999;8: Schoenecker PL, Rich MM. The lower extremity. In: Morrissy RT, Weinstein SL, editors. Lovell and Winter s pediatric orthopaedics. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; p Hofmann A, Jones RE, Herring JA. Blount s disease after skeletal maturity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64: Ingvarsson T, Hagglund G, Ramgren B, Jonsson K, Zayer M. Long-term results after adolescent Blount s disease. J Pediatr Orthop B. 1997;6: Ippolito E, Cauti D. Tibia vara or Blount s disease: pathogenesis, clinical features and treatment. Ital J Orthop Traumatol. 1983;9: Rajacich N, Bell DF, Armstrong PF. Pediatric applications of the Ilizarov method. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;280: Beskin JL, Burke SW, Johnston CE 2nd, Roberts JM. Clinical basis for a mechanical etiology in adolescent Blount s disease. Orthopedics. 1986;9: Kline SC, Bostrum M, Griffin PP. Femoral varus: an important component in late-onset Blount s disease. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992;12: Langenskiold A, Riska EB. Tibia vara (osteochondrosis deformans tibiae): a survey of seventy-one cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964;46: Langenskiold A. Tibia vara. A critical review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; 246: Langenskiold A. Tibia vara: osteochondrosis deformans tibiae. Blount s disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1981;158: Brooks WC, Gross RH. Genu varum in children: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1995;3: Greene WB. Infantile tibia vara. Instr Course Lect. 1993;42: Alekberov C, Shevtsov VI, Karatosun V, Günal I, Alici E. Treatment of tibia vara by the Ilizarov method. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;409: Gordon JE, Heidenreich FP, Carpenter CJ, Kelly-Hahn J, Schoenecker PL. Comprehensive treatment of late-onset tibia vara. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87: Paley D, Tetsworth K. Mechanical axis deviation of the lower limbs. Preoperative planning of uniapical angular deformities of the tibia or femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;280: Paley D, Tetsworth K. Mechanical axis deviation of the lower limbs. Preoperative planning of multiapical frontal plane angular and bowing deformities of the femur and tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;280: Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ. Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69: Henderson RC, Kemp GJ. Assessment of the mechanical axis in adolescent tibia vara. Orthopedics. 1991;14: Thompson GH, Carter JR, Smith CW. Late-onset tibia vara: a comparative analysis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1984;4: Foreman KA, Robertson WW Jr. Radiographic measurement of infantile tibia vara. J Pediatr Orthop. 1985;5: Blount WP. Tibia vara. Osteochondrosis deformans tibiae. J Bone Joint Surg. 1937;19: Salenius P, Vankka E. The development of the tibiofemoral angle in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57: Levine AM, Drennan JC. Physiological bowing and tibia vara. The metaphyseal-diaphyseal angle in the measurement of bowleg deformities. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64: Siffert RS, Katz JF. The intra-articular deformity in osteochondrosis deformans tibiae. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970;52: Park SS, Gordon JE, Luhmann SJ, Dobbs MB, Schoenecker PL. Outcome of hemiepiphyseal stapling for late-onset tibia vara. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:
Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame
 Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 23:387 391 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman,
Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 23:387 391 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman,
Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report
 Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report Nina Agrawal, BA, Danielle Cameron, BA, Lawrence Wells, MD Abstract A 12-year-old girl underwent a bilateral distal femoral and proximal
Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report Nina Agrawal, BA, Danielle Cameron, BA, Lawrence Wells, MD Abstract A 12-year-old girl underwent a bilateral distal femoral and proximal
Comprehensive treatment of late-onset tibia vara
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 7-1-2005 Comprehensive treatment of late-onset tibia vara J. Eric Gordon St. Louis Shriner's Hospital for Children
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 7-1-2005 Comprehensive treatment of late-onset tibia vara J. Eric Gordon St. Louis Shriner's Hospital for Children
Does langenskiold staging have a good prognostic value in late onset tibia vara?
 Khanfour Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2012, 7:23 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does langenskiold staging have a good prognostic value in late onset tibia vara? Ashraf Ahmad Khanfour * Abstract
Khanfour Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2012, 7:23 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does langenskiold staging have a good prognostic value in late onset tibia vara? Ashraf Ahmad Khanfour * Abstract
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum
 Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Risk Factors for Failure of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Blount Disease: Systema;c Review LLRS Annual Mee,ng Bensen Fan MD, Sanjeev Sabharwal MD, MPH
 Risk Factors for Failure of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Blount Disease: Systema;c Review LLRS Annual Mee,ng 2016 Bensen Fan MD, Sanjeev Sabharwal MD, MPH History of Treatment in Blount Bracing Osteotomy Permanent
Risk Factors for Failure of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Blount Disease: Systema;c Review LLRS Annual Mee,ng 2016 Bensen Fan MD, Sanjeev Sabharwal MD, MPH History of Treatment in Blount Bracing Osteotomy Permanent
Modified dome shaped proximal tibial osteotomy for treatment of infantile tibia vara
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Geith MAA. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):394-399 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164175
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Geith MAA. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):394-399 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164175
Change in Effective Leg Length after Angular Deformity Correction by Hemiepiphyseal Stapling
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:85-89 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.2.85 Change in Effective Leg Length after Angular Deformity Correction by Hemiepiphyseal Stapling Ho-Joong Jung, MD,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:85-89 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.2.85 Change in Effective Leg Length after Angular Deformity Correction by Hemiepiphyseal Stapling Ho-Joong Jung, MD,
Bow legs in young children can be a
 ONLINE EXCLUSIVE ORIGINAL RESEARCH Management of bow legs in children: A primary care protocol This protocol, which is designed to coincide with wellchild visits, distinguishes between normal physiologic
ONLINE EXCLUSIVE ORIGINAL RESEARCH Management of bow legs in children: A primary care protocol This protocol, which is designed to coincide with wellchild visits, distinguishes between normal physiologic
Early experience with medial femoral tension band plating in idiopathic genu valgum
 J Child Orthop (2011) 5:11 17 DOI 10.1007/s11832-010-0310-6 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Early experience with medial femoral tension band plating in idiopathic genu valgum Humberto Guzman Burt Yaszay Vanessa
J Child Orthop (2011) 5:11 17 DOI 10.1007/s11832-010-0310-6 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Early experience with medial femoral tension band plating in idiopathic genu valgum Humberto Guzman Burt Yaszay Vanessa
Valgus rotational -dome shaped -tibial osteotomy in treatment of tibia vara
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine Vol., September I.S.S.N: Valgus rotational -dome shaped -tibial osteotomy in treatment of tibia vara Hossam Kandil MD., Department of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine Vol., September I.S.S.N: Valgus rotational -dome shaped -tibial osteotomy in treatment of tibia vara Hossam Kandil MD., Department of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery
Orthotic Correction of Blount's Disease
 Orthotic Correction of Blount's Disease by Terry J. Supan, C.P.O. John M. Mazur, M.D. INTRODUCTION Infantile tibia vara is the result of abnormal growth in the proximal tibial epiphyseal late of the tibial
Orthotic Correction of Blount's Disease by Terry J. Supan, C.P.O. John M. Mazur, M.D. INTRODUCTION Infantile tibia vara is the result of abnormal growth in the proximal tibial epiphyseal late of the tibial
The use of the Taylor spatial frame in adolescent Blount s disease: is fibular osteotomy necessary?
 J Child Orthop (2008) 2:199 204 DOI 10.1007/s11832-008-0099-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE The use of the Taylor spatial frame in adolescent Blount s disease: is fibular osteotomy necessary? Mark Eidelman
J Child Orthop (2008) 2:199 204 DOI 10.1007/s11832-008-0099-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE The use of the Taylor spatial frame in adolescent Blount s disease: is fibular osteotomy necessary? Mark Eidelman
Instructional Course Lecture 2011
 Instructional Course Lecture 2011 Yoon Hae Kwak Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital Hallym University Medical Center Rotational and Angular variations of the lower extremities
Instructional Course Lecture 2011 Yoon Hae Kwak Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital Hallym University Medical Center Rotational and Angular variations of the lower extremities
There are various causes of coronal angular deformity
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE for Genu Valgum Deformities in Patients With Multiple Hereditary Exostoses: A Comparative Study of Patients With Deformities of Idiopathic Cause Seungcheol Kang, MD, Jae Young Kim, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE for Genu Valgum Deformities in Patients With Multiple Hereditary Exostoses: A Comparative Study of Patients With Deformities of Idiopathic Cause Seungcheol Kang, MD, Jae Young Kim, MD,
Preliminary Outcome Using a New Free Motion Offloading KAFO for Postoperative Management of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Adolescent Tibia Vara
 Preliminary Outcome Using a New Free Motion Offloading KAFO for Postoperative Management of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Adolescent Tibia Vara Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH
Preliminary Outcome Using a New Free Motion Offloading KAFO for Postoperative Management of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Adolescent Tibia Vara Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
COMMON MUSCULOSKELETAL PROBLEMS GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT PATHOLOGIC VS. NORMAL
 COMMON MUSCULOSKELETAL PROBLEMS GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT PATHOLOGIC VS. NORMAL Clifford L. Craig, M.D. M2 Musculoskeletal Fall 2008 I. ANGULAR AND TORSIONAL DEFORMITIES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Examination Relaxed,
COMMON MUSCULOSKELETAL PROBLEMS GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT PATHOLOGIC VS. NORMAL Clifford L. Craig, M.D. M2 Musculoskeletal Fall 2008 I. ANGULAR AND TORSIONAL DEFORMITIES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Examination Relaxed,
Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p.
 Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Brothers with genu recurvatum
 Short Communication Brothers with genu recurvatum Naoto Saito a, *, Keiji Tensyo b, Hiroshi Horiuchi b, Kaoru Aoki b, Seneki Kobayashi b, Hiroyuki Kato b, and Tomoki Kosho c adepartment of Applied Physical
Short Communication Brothers with genu recurvatum Naoto Saito a, *, Keiji Tensyo b, Hiroshi Horiuchi b, Kaoru Aoki b, Seneki Kobayashi b, Hiroyuki Kato b, and Tomoki Kosho c adepartment of Applied Physical
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease. Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center
 Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Rotational Deformity Intoeing Outtoeing
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Rotational Deformity Intoeing Outtoeing
Guided growth with tension band plate or definitive epiphysiodesis for treatment of limb length discrepancy?
 Borbas et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2019) 14:99 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1139-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Guided growth with tension band plate or definitive epiphysiodesis for
Borbas et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2019) 14:99 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1139-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Guided growth with tension band plate or definitive epiphysiodesis for
Reduction of a dislocation of the hip due to developmental dysplasia: Implications for the need for future surgery
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2-1-2003 Reduction of a dislocation of the hip due to developmental dysplasia: Implications for the need for future
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2-1-2003 Reduction of a dislocation of the hip due to developmental dysplasia: Implications for the need for future
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease. Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center
 Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Torsional Deformity (Rotational
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Torsional Deformity (Rotational
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Late Onset Tibia Vara. Acute Correction Strategy : Proper Case Selection and a Simple External Fixation Technique
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 241-250 ORIGINAL STUDY Late Onset Tibia Vara. Acute Correction Strategy : Proper Case Selection and a Simple External Fixation Technique Ashraf A. KhAnFOuR, Mahmoud El-ROSASy
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 241-250 ORIGINAL STUDY Late Onset Tibia Vara. Acute Correction Strategy : Proper Case Selection and a Simple External Fixation Technique Ashraf A. KhAnFOuR, Mahmoud El-ROSASy
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest
 Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Development of genu varum in achondroplasia
 Development of genu varum in achondroplasia RELATION TO FIBULAR OVERGROWTH S. T. Lee, H. R. Song, R. Mahajan, V. Makwana, S. W. Suh, S. H. Lee From Korea University, Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea Genu varum
Development of genu varum in achondroplasia RELATION TO FIBULAR OVERGROWTH S. T. Lee, H. R. Song, R. Mahajan, V. Makwana, S. W. Suh, S. H. Lee From Korea University, Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea Genu varum
Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018
 Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018 What is it? Intoeing: When to worry? Why isn t it always cause for worry? What are the benign causes of intoeing? What are the pathologic causes of
Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018 What is it? Intoeing: When to worry? Why isn t it always cause for worry? What are the benign causes of intoeing? What are the pathologic causes of
Coronal angular deformity of the knee is a not uncommon
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hemiepiphysiodesis for Idiopathic Genu Valgum: Percutaneous Transphyseal Screw Versus Tension-band Plate Hoon Park, MD,* Minjung Park, MD,w Sung Min Kim, MD,* Hyun Woo Kim, MD,z and Dong
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hemiepiphysiodesis for Idiopathic Genu Valgum: Percutaneous Transphyseal Screw Versus Tension-band Plate Hoon Park, MD,* Minjung Park, MD,w Sung Min Kim, MD,* Hyun Woo Kim, MD,z and Dong
Early untreated infantile tibia vara (ITV) as seen in the
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE New Single-stage Double Osteotomy for Late-presenting Infantile Tibia Vara: A Comprehensive Approach Edward Abraham, MD,*w David Toby, MD,w Michelle Welborn, MD,z Cory W. Helder, BS,*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE New Single-stage Double Osteotomy for Late-presenting Infantile Tibia Vara: A Comprehensive Approach Edward Abraham, MD,*w David Toby, MD,w Michelle Welborn, MD,z Cory W. Helder, BS,*
Investigation performed at The Center for Problem Fractures and Limb Restoration, Texas Orthopedic Hospital, Houston, Texas
 1229 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Bone Realignment with Use of Temporary External Fixation for Distal Femoral Valgus and Varus Deformities BY JOSEPH J. GUGENHEIM
1229 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Bone Realignment with Use of Temporary External Fixation for Distal Femoral Valgus and Varus Deformities BY JOSEPH J. GUGENHEIM
Normal Values of Tibio-Femoral Angle in Nigerian Adolescents
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Normal Values of Tibio-Femoral Angle in Nigerian Adolescents T BA, A AO, O AB Citation T BA, A AO, O AB.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Normal Values of Tibio-Femoral Angle in Nigerian Adolescents T BA, A AO, O AB Citation T BA, A AO, O AB.. The Internet Journal of
Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions)
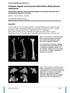 Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Our Experience with Correction of Angular Deformities of Knee by Flexible Figure of 8-plate Hemiepiphysiodesis. Abstract
 68 Original Article Our Experience with Correction of Angular Deformities of Knee by Flexible Figure of 8-plate Hemiepiphysiodesis Sakti Prasad Das 1, S Pradhan 2, PK Sahoo 3, RN Mohanty 4, SK Das 5 Abstract
68 Original Article Our Experience with Correction of Angular Deformities of Knee by Flexible Figure of 8-plate Hemiepiphysiodesis Sakti Prasad Das 1, S Pradhan 2, PK Sahoo 3, RN Mohanty 4, SK Das 5 Abstract
Effectiveness of eight plate in correcting angular deformity around knee: A study at tertiary care hospital
 2018; 4(2): 1024-1028 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 1024-1028 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-02-2018 Accepted: 27-03-2018 Dr. Pradeep A Sangnod Orthopaedic Resident, HBT Dr. Harish U Resident,
2018; 4(2): 1024-1028 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 1024-1028 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-02-2018 Accepted: 27-03-2018 Dr. Pradeep A Sangnod Orthopaedic Resident, HBT Dr. Harish U Resident,
The Efficacy of Percutaneous Lateral Hemiepiphysiodesis on Angular Correction in Idiopathic Adolescent Genu Varum
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:92-98 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.92 The Efficacy of Percutaneous Lateral Hemiepiphysiodesis on Angular Correction in Idiopathic Adolescent
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:92-98 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.92 The Efficacy of Percutaneous Lateral Hemiepiphysiodesis on Angular Correction in Idiopathic Adolescent
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy
 Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Physiological Genu Varum
 Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Physiological Genu Varum Lars Ingvar Hansson & Mohammed Zayer To cite this article:
Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Physiological Genu Varum Lars Ingvar Hansson & Mohammed Zayer To cite this article:
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART)
 CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
The effect of proximal tibial fractures on the limb axis in children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 345-353 ORIGINAL STUDY The effect of proximal tibial fractures on the limb axis in children Sawas NENOPOULOS, Aristides VRETTAKOS, Nikolaos CHAFTIKIS, Theodoros BESLIKAS,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 345-353 ORIGINAL STUDY The effect of proximal tibial fractures on the limb axis in children Sawas NENOPOULOS, Aristides VRETTAKOS, Nikolaos CHAFTIKIS, Theodoros BESLIKAS,
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation
 Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
The coronal hypomochlion
 KNEE The coronal hypomochlion A TIPPING POINT OF CLINICAL RELEVANCE WHEN PLANNING VALGUS PRODUCING HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMIES E. Heijens, P. Kornherr, C. Meister From Gelenkzentrum Rhein-Main, Wiesbaden,
KNEE The coronal hypomochlion A TIPPING POINT OF CLINICAL RELEVANCE WHEN PLANNING VALGUS PRODUCING HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMIES E. Heijens, P. Kornherr, C. Meister From Gelenkzentrum Rhein-Main, Wiesbaden,
REMODELLING OF ANGULAR DEFORMITY AFTER FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES IN CHILDREN
 REMODELLING OF ANGULAR DEFORMITY AFTER FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES IN CHILDREN MURRAY E. WALLACE, EDUARD B. HOFFMAN From the Red Cross Children s Hospital, Cape Town We reviewed 28 children with unilateral
REMODELLING OF ANGULAR DEFORMITY AFTER FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES IN CHILDREN MURRAY E. WALLACE, EDUARD B. HOFFMAN From the Red Cross Children s Hospital, Cape Town We reviewed 28 children with unilateral
BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM)
 BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM) By Dr John Ebnezar INTRODUCTION Have you noticed how your knees look like? If you observe carefully you will see that both your knees are not parallel but deviated slightly outwards
BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM) By Dr John Ebnezar INTRODUCTION Have you noticed how your knees look like? If you observe carefully you will see that both your knees are not parallel but deviated slightly outwards
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
Kordelle J, M.D. 1), Millis M, M.D. 2), Jolesz FA, M.D. 1), Kikinis R, M.D. 1), Richolt JA, M.D. 3)
 Three-dimensional analysis of the proximal femur in patients with slipped capital femoral epiphysis based on computed tomography. Kordelle J, M.D. 1), Millis M, M.D. 2), Jolesz FA, M.D. 1), Kikinis R,
Three-dimensional analysis of the proximal femur in patients with slipped capital femoral epiphysis based on computed tomography. Kordelle J, M.D. 1), Millis M, M.D. 2), Jolesz FA, M.D. 1), Kikinis R,
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation
 Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016
 SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference?
 Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
ANTERIOR MEDIAL AND POSTERIOR MEDIAL DEFORMITY OF THE TIBIA
 ANTERIOR MEDIAL AND POSTERIOR MEDIAL DEFORMITY OF THE TIBIA 5 TH ANNUAL SLAOTI MEETING SAO PAOLO, BRAZIL OCTOBER 12-14, 2017 Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research
ANTERIOR MEDIAL AND POSTERIOR MEDIAL DEFORMITY OF THE TIBIA 5 TH ANNUAL SLAOTI MEETING SAO PAOLO, BRAZIL OCTOBER 12-14, 2017 Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research
Delayed fixation of an unstable Slipped capital femoral epiphysis: A case report and review of literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Delayed fixation of an unstable Slipped capital femoral epiphysis: A case report and review of literature S Lowndes, A Khanna, D
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Delayed fixation of an unstable Slipped capital femoral epiphysis: A case report and review of literature S Lowndes, A Khanna, D
Malrotation can occur following closed intramedullary
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Effects of Femoral Shaft Malrotation on Lower Extremity Anatomy Joseph J. Gugenheim, MD,* Robert A. Probe, MD, and Mark R. Brinker, MD* Objective: To determine how axial rotation around
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Effects of Femoral Shaft Malrotation on Lower Extremity Anatomy Joseph J. Gugenheim, MD,* Robert A. Probe, MD, and Mark R. Brinker, MD* Objective: To determine how axial rotation around
The Factor Causing Poor Results in Late Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
 The Factor Causing Poor Results in Late Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamwong Saisamorn MD*, Tanatip Sisuchinthara MS* Thunchanok Jittivilai PN*, Kamolporn Keawpornsawan
The Factor Causing Poor Results in Late Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamwong Saisamorn MD*, Tanatip Sisuchinthara MS* Thunchanok Jittivilai PN*, Kamolporn Keawpornsawan
Temporary epiphysiodesis with Blount stapling for treatment of idiopathic genua valga in children
 Temporary epiphysiodesis with Blount stapling for treatment of idiopathic genua valga in children Ilse DEGREEF, Pierre MOENS, Guy FABRY Not all idiopathic genua valga in children show an innocuous evolution.
Temporary epiphysiodesis with Blount stapling for treatment of idiopathic genua valga in children Ilse DEGREEF, Pierre MOENS, Guy FABRY Not all idiopathic genua valga in children show an innocuous evolution.
A technique for calculating limb length inequality and epiphyseodesis timing using the multiplier method and a spreadsheet
 J Child Orthop (2007) 1:151 155 DOI 10.1007/s11832-007-0016-6 TECHNICAL NOTE A technique for calculating limb length inequality and epiphyseodesis timing using the multiplier method and a spreadsheet James
J Child Orthop (2007) 1:151 155 DOI 10.1007/s11832-007-0016-6 TECHNICAL NOTE A technique for calculating limb length inequality and epiphyseodesis timing using the multiplier method and a spreadsheet James
Small-wire circular fixators and hybrid external fixation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
Financial Disclosures. The Unpredictable. Early Onset Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Financial Disclosures Vertebral body stapling in children with idiopathic scoliosis < 10 years of age with curve magnitude 30-39 degrees Alexander A. Theologis, MD; Patrick Cahill, MD; Mike Auriemma, BS;
Financial Disclosures Vertebral body stapling in children with idiopathic scoliosis < 10 years of age with curve magnitude 30-39 degrees Alexander A. Theologis, MD; Patrick Cahill, MD; Mike Auriemma, BS;
Deformity correction during growth after partial physeal arrest
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 219-224 ORIGINAL STUDY Deformity correction during growth after partial physeal arrest Joachim HORN, Leif Pål KRISTIANSEN, Harald STEEN From the Department of Orthopaedics,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 219-224 ORIGINAL STUDY Deformity correction during growth after partial physeal arrest Joachim HORN, Leif Pål KRISTIANSEN, Harald STEEN From the Department of Orthopaedics,
Copyright Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 Original article 222 Legg Calvé Perthes disease in patients under 5 years of age does not always result in a good outcome. Personal experience and meta-analysis of the literature Kristof Fabry, Guy Fabry
Original article 222 Legg Calvé Perthes disease in patients under 5 years of age does not always result in a good outcome. Personal experience and meta-analysis of the literature Kristof Fabry, Guy Fabry
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY
 BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Knee Arthritis in Congenital Short Femur after Wagner Lengthening
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 451, pp. 177 181 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Knee Arthritis in Congenital Short Femur after Wagner Lengthening Changhoon Jeong, MD *, ; Muharrem
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 451, pp. 177 181 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Knee Arthritis in Congenital Short Femur after Wagner Lengthening Changhoon Jeong, MD *, ; Muharrem
Correction of Angular Deformities by Physeal Distraction
 Correction of Angular Deformities by Physeal Distraction Jose Cañadell, M.D., and Julio De Pablos, M.D. From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Navarra,
Correction of Angular Deformities by Physeal Distraction Jose Cañadell, M.D., and Julio De Pablos, M.D. From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Navarra,
)116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
 )116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Analysis of the Geometry of the Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia in the Osteoarthritic Knee: A 3D Reconstruction CT Scan Based
)116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Analysis of the Geometry of the Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia in the Osteoarthritic Knee: A 3D Reconstruction CT Scan Based
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
Physeal injuries of the ankle joint constitute 11% of all
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome of Physeal and Epiphyseal Injuries of the Distal Tibia With Intra-Articular Involvement Savvas P. Nenopoulos, MD, Vasilios A. Papavasiliou, MD, and Athanasios V. Papavasiliou,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome of Physeal and Epiphyseal Injuries of the Distal Tibia With Intra-Articular Involvement Savvas P. Nenopoulos, MD, Vasilios A. Papavasiliou, MD, and Athanasios V. Papavasiliou,
Growth modulation with a medial malleolar screw for ankle valgus deformity
 Acta Orthopaedica 015; 86 (5): 611 615 611 Growth modulation with a medial malleolar screw for ankle valgus deformity 79 children with 15 affected ankles followed until correction or physeal closure Martin
Acta Orthopaedica 015; 86 (5): 611 615 611 Growth modulation with a medial malleolar screw for ankle valgus deformity 79 children with 15 affected ankles followed until correction or physeal closure Martin
Lower Extremity Malalignment: When to Refer and When to Reassure?
 Lower Extremity Malalignment: When to Refer and When to Reassure? Mary Aschenbrener, PA-C Minnesota Academy of Physician Assistants 03/18/16 Cary H. Mielke, MD Chief of Staff Orthopaedic Burn Spinal cord
Lower Extremity Malalignment: When to Refer and When to Reassure? Mary Aschenbrener, PA-C Minnesota Academy of Physician Assistants 03/18/16 Cary H. Mielke, MD Chief of Staff Orthopaedic Burn Spinal cord
Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities
 Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities BRUNO GLADBACH, DMED*; ETIENNE HEIJENS, DMED*; JOACHIM PFEIL, PROFDMED*; DROR PALEY, MD abstract External
Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities BRUNO GLADBACH, DMED*; ETIENNE HEIJENS, DMED*; JOACHIM PFEIL, PROFDMED*; DROR PALEY, MD abstract External
The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis
 DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W.
 University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Overview. Acceptance criteria for all protocols
 X-Ray protocol Overview The Smith & Nephew VISIONAIRE X-Ray protocol is essentially an AP leg length image. The images are preferred to be done erect, but can be done supine if necessary due to the type
X-Ray protocol Overview The Smith & Nephew VISIONAIRE X-Ray protocol is essentially an AP leg length image. The images are preferred to be done erect, but can be done supine if necessary due to the type
Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease
 Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease M. Kocaoglu, F. E. Bilen, C. Sen, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical
Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease M. Kocaoglu, F. E. Bilen, C. Sen, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical
Bow legs and knock knees: is it physiological or pathological?
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Ganavi R. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2016 May;3(2):687691 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 23493283 eissn 23493291 Clinical Perspective DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/23493291.ijcp20161068
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Ganavi R. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2016 May;3(2):687691 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 23493283 eissn 23493291 Clinical Perspective DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/23493291.ijcp20161068
Lower Extremity Fracture Management. Fractures of the Hip. Lower Extremity Fractures. Vascular Anatomy. Lower Extremity Fractures in Children
 Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
, MD. physiologic. tibia varum. in utero (in. Disease in. variation. positioning. back and legs. instead of. Blount's. Infant with bowing in both legs
 North Jersey Orthopaedic Institute Rutgers, The Statee University of New Jersey 140 Bergen Street, D1610 Newark, NJ 07101 973-972-2150 South Orange Ambulatory Center Hackensack Medical Plaza Overlook Medical
North Jersey Orthopaedic Institute Rutgers, The Statee University of New Jersey 140 Bergen Street, D1610 Newark, NJ 07101 973-972-2150 South Orange Ambulatory Center Hackensack Medical Plaza Overlook Medical
Intermediate ray deficiency a new type of lower limb hypoplasia
 Skeletal Radiol (2013) 42:377 383 DOI 10.1007/s00256-012-1469-3 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Intermediate ray deficiency a new type of lower limb hypoplasia Paweł Koczewski Milud Shadi Tomasz Kotwicki Marek Tomaszewski
Skeletal Radiol (2013) 42:377 383 DOI 10.1007/s00256-012-1469-3 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Intermediate ray deficiency a new type of lower limb hypoplasia Paweł Koczewski Milud Shadi Tomasz Kotwicki Marek Tomaszewski
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails
 Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery
 S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY 2017
 BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY 2017 B. RESSEQUE, D.P.M., D.A.B.P.O. Professor, N.Y. College of Podiatric Medicine ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY 2017 B. RESSEQUE, D.P.M., D.A.B.P.O. Professor, N.Y. College of Podiatric Medicine ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing
Immature ACL Injuries and Reconstruction
 2017 Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium Immature ACL Injuries and Reconstruction Jason Kennedy, M.D. Disclosures I have no financial/ industry disclosures. Objectives Explain the importance of skeletal immaturity
2017 Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium Immature ACL Injuries and Reconstruction Jason Kennedy, M.D. Disclosures I have no financial/ industry disclosures. Objectives Explain the importance of skeletal immaturity
Limb lengthening for radiation-induced growth arrest of the pelvis and femur
 CASE REPORT Limb lengthening for radiation-induced growth arrest of the pelvis and femur Paul E. Matuszewski and S. Robert Rozbruch INTRODUCTION Aggressive treatment, including surgery and highdose irradiation,
CASE REPORT Limb lengthening for radiation-induced growth arrest of the pelvis and femur Paul E. Matuszewski and S. Robert Rozbruch INTRODUCTION Aggressive treatment, including surgery and highdose irradiation,
Correction of rotational deformity of the tibia in cerebral palsy by percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy
 Correction of rotational deformity of the tibia in cerebral palsy by percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy M. Inan, F. Ferri-de Baros, G. Chan, K. Dabney, F. Miller From The Alfred I. DuPont Hospital for
Correction of rotational deformity of the tibia in cerebral palsy by percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy M. Inan, F. Ferri-de Baros, G. Chan, K. Dabney, F. Miller From The Alfred I. DuPont Hospital for
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
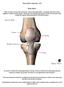 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening
 Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (3): 271 275 271 Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening 60 patients followed for mean 5 years Seung-Ju Kim, Mandar Vikas Agashe, Sang-Heon Song, and
Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (3): 271 275 271 Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening 60 patients followed for mean 5 years Seung-Ju Kim, Mandar Vikas Agashe, Sang-Heon Song, and
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and Varus Knee Deformity Based on Two-Dimensional Assessment of Side-to-Side Differences
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):58-63 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.007 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):58-63 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.007 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and
ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on
 ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on the Knee Presented by: Ivo Waerlop, DC Shawn Allen, DC 1 Focus on The Knee 2 Pertinent Anatomy Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Prepatellar bursa Infrapatellar
ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on the Knee Presented by: Ivo Waerlop, DC Shawn Allen, DC 1 Focus on The Knee 2 Pertinent Anatomy Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Prepatellar bursa Infrapatellar
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity
 Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity F. E. Bilen, M. Kocaoglu, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul Medical School, Istanbul
Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity F. E. Bilen, M. Kocaoglu, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul Medical School, Istanbul
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
Investigation performed at the Department of Orthopedics, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota
 1090 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Total Knee Arthroplasty in Young Patients with Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis BY JAVAD PARVIZI, MD, FRCS, CLAUDETTE M. LAJAM, MD,
1090 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Total Knee Arthroplasty in Young Patients with Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis BY JAVAD PARVIZI, MD, FRCS, CLAUDETTE M. LAJAM, MD,
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE. Limb Reconstruction System. Part B: Correction of Deformities. By Dr. S. Nayagam
 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE 11 Limb Reconstruction System Part B: Correction of Deformities By Dr. S. Nayagam CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE... Page
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE 11 Limb Reconstruction System Part B: Correction of Deformities By Dr. S. Nayagam CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE... Page
