Deformity correction during growth after partial physeal arrest
|
|
|
- Lilian Manning
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, ORIGINAL STUDY Deformity correction during growth after partial physeal arrest Joachim HORN, Leif Pål KRISTIANSEN, Harald STEEN From the Department of Orthopaedics, University Hospital Rikshospitalet Oslo, Norway The purpose of this study was to evaluate our treatment protocol for certain physeal injuries requiring complete epiphysiodesis of an injured physis, angular correction and lengthening with the Ilizarov method and overcorrection of length according to calculated loss of remaining growth. Five patients (age : 12 to 14 years) were operated with angular correction and lengthening in combination with complete epiphysiodesis. Angular deformities measured 12 to 24 and limb length discrepancies (LLD s) 15 to 60 mm. Mean overcorrection of length according to remaining growth of the affected physis was 12 mm (range : 7 to 15). All deformity parameters were fully corrected in all patients. Mechanical axis deviation (MAD) was within ± 5 mm compared to the healthy side in 4 patients, 20 mm in one patient. Median LLD at maturity was 8 mm (range : 3 to 13). In cases of partial physeal arrest with severe symptomatic deformities, complete epiphysiodesis of the injured physis, angular correction and lengthening with the Ilizarov method with overcorrection of length according to estimated loss of remaining growth of the affected physis is a suitable method. Keywords : epiphysiodesis ; physeal arrest ; Ilizarov method ; deformity correction ; leg length discrepancy. INTRODUCTION Fractures of the long bones in the lower extremity with involvement of the physis are common injuries in children and adolescents (25). According to Salter (27) approximately 15% of all long bone injuries during childhood involve the physeal plate. Fortunately, most of the physeal injuries are not associated with any disturbance of growth. If the entire physeal plate ceases to grow, the result is progressive shortening without angulation (27). However, peripheral partial growth arrest may result in significant angular deformity and leglength discrepancy, dependent upon the localisation and magnitude of the injury, the age of the patient and the anticipated remaining growth (3,8,19). Treatment is indicated in patients with existing or developing deformities and a significant amount of remaining growth (17). Treatment options are : resection of the physeal bridge, physeal distraction, acute corrective osteotomy or gradual correction using the Ilizarov method with callotasis and complete epiphysiodesis of the affected physis. These Joachim Horn, MD, Orthopaedic Surgeon. Leif Pål Kristiansen, MD, Orthopaedic Surgeon. Harald Steen, MD, PhD, Orthopaedic Surgeon. Department of Orthopaedics, University Hospital Rikshospitalet, Oslo, Norway. Correspondence : Joachim Horn, MD, Department of Orthopaedics, University Hospital Rikshospitalet, Sognsvannsveien 20, N 0027 Oslo, Norway. joachim.horn@rikshospitalet.no 2009, Acta Orthopædica Belgica. No benefits or funds were received in support of this study
2 220 J. HORN, L. P. KRISTIANSEN, H. STEEN procedures can be used in combination with contralateral shortening or epiphysiodesis. In cases where the size of the physeal bridge, the amount of angular deformity, the shortening and the limited remaining growth potential make it unlikely to expect an acceptable degree of spontaneous correction after physeal bridge resection, corrective osteotomy or gradual correction with the Ilizarov method may be required. When the deformity is symptomatic and a risk for secondary structural changes in the adjacent joints exists, a correction before skeletal maturity is indicated. In this regard complete epiphysiodesis of the affected physis will be necessary to prevent recurrent deformity after correction. Either acute or gradual correction with the Ilizarov method is used. The remaining growth potential of the involved physis has to be considered in order to prevent leg length discrepancy at skeletal maturity. The aim of the current study was to present and evaluate our treatment protocol including : complete epiphysiodesis of the injured physis, combined with angular correction and lengthening with the Ilizarov method and overcorrection of length according to the estimated loss of remaining growth of the affected physis. To our knowledge there are no former studies describing this topic. PATIENTS AND METHODS From February 2001 until November 2005 five patients were operated at our institution by angular correction and lengthening in combination with complete epiphysiodesis after partial physeal arrest of a growth plate. Three were boys and two girls with a mean age of 13 years (range : 12 to 14) at the time of surgery. Three patients had a partial physeal arrest in the distal femoral physis, 2 in the proximal tibial physis. All patients were evaluated clinically and radiographically with standard 2-plane standing radiographs using long cassettes, orthoroentgenograms for measurement of leg length inequalities and left hand radiographs for assessing skeletal age (12). If there were clinical signs of rotational deformity, measurement of rotation was performed with a CT scan. The mechanical axis was drawn on the standing full-leg frontal radiograph as a straight line from the center of the hip joint to the center of the ankle joint, and the mechanical axis deviation (MAD) was assessed by comparing the injured side with the normal limb. Based on the malalignment- and malorientation-tests, as described by Paley (23), the deformity parameters were measured on the radiographs and the CORA (center of rotation of angulation) determined. As a result of the physeal injury with partial arrest, the CORA was located in the injured physis in all our patients. The remaining longitudinal growth potential of the affected physis was quantified based on skeletal age (12) and the Green- Anderson remaining growth chart (2). Epiphysiodesis of the intact part of the injured growth plates was performed with a percutaneous technique as described by Bowen and Johnson (6). Preoperatively planned and fitted configurations of the Ilizarov or Taylor Spatial Frame (TSF) were applied. In order to avoid translation of the fragments the osteotomies were performed as close as possible to the CORA. After 7 days of latency gradual correction was initiated with a lengthening rate of 1 mm/day in the femur and 0.75 mm/day in the tibia. All patients were overcorrected in lengthening distance according to the estimated LLD at maturity. RESULTS All deformity parameters were fully corrected in all patients and the frames were removed after bony consolidation. The median time in the frame was 6.5 months (range : 4 to 8), resulting in a lengthening index of 1.6 months/cm (range : 0.9 to 2.0). In some of the patients oral antibiotics were indicated in short periods due to pin-track infection. One patient developed a valgus deformity in the proximal tibial lengthening zone, because of failure in frame stability, probably due to pin track infection. This patient was later corrected by an additional TSF procedure. One patient was operated for a knee extension contracture a few months after frame removal. Another patient underwent a triplearthrodesis due to a posttraumatic foot deformity on the same side where lengthening of the femur was performed. This procedure might have influenced final leg length in some degree. No other complications were observed. The patients were followed until skeletal maturity and full-leg standing radiographs and orthoroentgenograms for measurement of leg lengths and inequalities were obtained. All patients had regained a normal functional level. They had no clinical or radiological signs of angular deformity in the affected limb. At skeletal
3 DEFORMITY CORRECTION DURING GROWTH 221 Table I. Deformity parameters at the time of surgery, estimated LLD at maturity, amount of overcorrection and LLD at maturity for all patients. Age and skeletal age are given in years/month. Numbers for varus, valgus, procurvatum, recurvatum, internal and external rotation are given in degrees ( ). LLD and amount of overcorrection are given in mm. Numbers for LLD at maturity refer to the operated extremity. (+) operated side is longer than contralateral side, ( ) operated side is shorter than contralateral side at maturity Pat. nr. Age (yrs)/ Gender Skel. age Deformity parameters Varus Valgus Pro. Rec. Int. rot Ext. rot LLD Estimated LLD at maturity Overcorrection 1 14/0 m 14/2 femur /9 m 13/4 tibia /4 f 13/0 tibia /1 m 14/0 femur /9 f 12/4 femur LLD at maturity maturity four patients had less than 10 mm (range : 3 to 9) of LLD, whereas one patient had a LLD of 13 mm (table I). All deformity parameters were fully corrected in all patients. MAD was within ± 5 mm compared to the healthy side in 4 patients, whereas one patient had a medial mechanical axis deviation of 20 mm. Figures 1-5 show the patients standing full-leg radiographs before and after correction. DISCUSSION Deformities in the lower limb might cause secondary compartmental osteoarthritis in adjacent joints due to deviation of the mechanical axis, and leg length discrepancy can lead to spinal disorders and gait abnormalities (4,14,16,30). The risk of compartmental osteoarthritis is more present in the knee joint than in the hip or ankle joint. The knee joint is a hinge joint with limited ability to compensate for deformities and deviation of the mechanical axis, whereas the hip joint as a ball in socket joint and the ankle joint with its underlying subtalar joints have greater abilities for compensation. Physeal injuries in the lower extremity are most frequent in the proximal tibia and the distal femur (8,22) ; resulting deformities affect the mechanical axis more than deformities close to the ankle or hip joint. From our point of view, the nature of the deformities in this study with severe angulation and shortening required a combined reconstructive procedure including both angular correction and adjustment of bone length. Acute corrective osteotomy on the affected side combined with epiphysiodesis or acute shortening on the contralateral side to gain leg length equality was not considered to be appropriate. The high degree of valgus both in the femoral and tibial deformities limited the possibility of acute correction due to possible traction injury to the peroneal nerve. Secondly, a shortening procedure would affect standing height at maturity and was therefore considered to be unfavourable by our patients. Resection of the physeal bridges only was not indicated due to the high degree of angular deformity. Spontaneous correction of the deformities after bridge resection was unlikely. In some cases resection of physeal bridges might be bene - ficial, but it remains unpredictable, with poor and fair results ranging from 15% to 38% success rate (13,15,17). Physeal distraction shows controversial results both experimentally and clinically with frequent premature complete physiodesis after distraction of the physis (5,7,18). We considered epiphysiodesis of the remaining part of the injured physis in combination with gradual deformity correction with axial lengthening as the most appropriate treatment option. In the past similar cases were frequently treated using the Ilizarov device (1,11,29). Several recent reports show the use of the distraction method with TSF (9,10,21, 26,28). However, there are no reports describing the use of the Ilizarov method in combination with
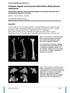
4 222 J. HORN, L. P. KRISTIANSEN, H. STEEN Fig. 2. Patient with partial physeal arrest at the proximal tibial physis after osteomyelitis (left). First operation resulted in an overcorrection into valgus due to failure of the external fixator (middle). A second correction with TSF was performed in order to achieve correct alignment of the extremity (right). Fig. 1. Patient with partial physeal arrest in the distal lateral femoral physis after a car accident. Left : Preoperatively. Right : After correction, at skeletal maturity. epiphysiodesis and corrective lengthening osteotomy in patients with deformities due to partial physeal arrest and a significant amount of remaining growth. All our patients had symptomatic deformities with knee pain and a significantly reduced activity level. Without surgical intervention the remaining growth potential in the injured physis would have resulted in exacerbation of symptoms and deformity until skeletal maturity. We considered therefore that correction was indicated before skeletal maturity, although this required complete epiphysiodesis of the injured physis and an appropriate overcorrection of the length. Four out of five patients showed a LLD below 10 mm at maturity and do not need any form of compensation, whereas one patient had a LLD of 13 mm and might need an adjustment by use of an insole. Fig. 3. Patient with partial physeal arrest anteriorly in the proximal tibial physis after a traumatic knee dislocation. Left : Preoperative frontal view. Middle : Frontal view after the correction. Right : Sideview before and after the correction. Nevertheless, our investigation showed some clear limitations. One patient (fig 1) underwent a triple arthrodesis on the lengthened extremity ; this
5 DEFORMITY CORRECTION DURING GROWTH 223 Fig. 4. Patient with lateral partial physeal arrest after distal femoral fracture. Left : Preoperatively. Right : After the correction, at skeletal maturity. might have influenced final leg length to some degree. Furthermore, our report is based on five patients only. However, patients with partial physeal arrest and such advanced stages of deformities when treatment is initiated are rare. Predictions of remaining growth were made based on Green and Anderson s growth chart. Other, more sophis - ticated, methods for leg length prediction like Moseley s (20) or Paley s method (24) might have given more accurate results. However, our study shows that in cases of partial physeal arrest with severe symptomatic deformities, Fig. 5. Patient with partial physeal arrest at lateral and anterior part of the right distal femoral physis. Left : Preoperative full-leg standing radiograph with severe valgus deformity and shortening. Right : After correction, with slight overcorrection into varus angulation. complete epiphysiodesis of the injured physis, angular correction and lengthening with the Ilizarov method with overcorrection of length according to estimated loss of remaining growth of the affected physis is a suitable method. Worsening of symptoms and deformity during growth can be prevented, and existing deformity can be fully corrected. REFERENCES 1. Aaron AD, Eilert RE. Results of the Wagner and Ilizarov methods of limb-lengthening. J Bone Joint Surg 1996 ; 78-A : Anderson M, Green WT, Messner MB. Growth and predictions of growth in the lower extremities. J Bone Joint Surg 1963 ; 45-A : 1-14.
6 224 J. HORN, L. P. KRISTIANSEN, H. STEEN 3. Beck A, Kinzl L, Ruter A et al. [Fractures involving the distal femoral epiphysis. Long-term outcome after completion of growth in primary surgical management.] (in German). Unfallchirurg 2001 ; 104 : Bhave A, Paley D, Herzenberg JE. Improvement in gait parameters after lengthening for the treatment of limblength discrepancy. J Bone Joint Surg 1999 ; 81-A : Bjerkreim I. Limb lengthening by physeal distraction. Acta Orthop Scand 1989 ; 60 : Bowen JR, Johnson WJ. Percutaneous epiphysiodesis. Clin Orthop 1984 ; 190 : de Pablos J, Villas C, Canadell J. Bone lengthening by physeal distraction. An experimental study. Int Orthop 1986 ; 10 : Eid AM, Hafez MA. Traumatic injuries of the distal femoral physis. Retrospective study on 151 cases. Injury 2002 ; 33 : Fadel M, Hosny G. The Taylor spatial frame for deformity correction in the lower limbs. Int Orthop 2005 ; 29 : Feldman DS, Madan SS, Koval KJ et al. Correction of tibia vara with six-axis deformity analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame. J Pediatr Orthop 2003 ; 23 : Ghoneem HF, Wright JG, Cole WG et al. The Ilizarov method for correction of complex deformities. Psycho - logical and functional outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg 1996 ; 78-A : Greulich WW, Pyle SI. Radiographic Atlas of Skeletal Development of the Hand and Wrist. Stanford University Press, Hasler CC, Foster BK. Secondary tethers after physeal bar resection : a common source of failure? Clin Orthop 2002 ; 405 : Kakushima M, Miyamoto K, Shimizu K. The effect of leg length discrepancy on spinal motion during gait : threedimensional analysis in healthy volunteers. Spine 2003 ; 28 : Kasser JR. Physeal bar resections after growth arrest about the knee. Clin Orthop 1990 ; 255 : Kettelkamp DB, Hillberry BM, Murrish DE et al. Degenerative arthritis of the knee secondary to fracture malunion. Clin Orthop 1988 ; 234 : Khoshhal KI, Kiefer GN. Physeal bridge resection. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2005 ; 13 : Langlois V, Laville JM. [Physeal distraction for limb length discrepancy and angular deformity.] (in French). Rev Chir Orthop 2005 ; 91 : Makela EA, Vainionpaa S, Vihtonen K et al. The effect of trauma to the lower femoral epiphyseal plate. An experi - mental study in rabbits. J Bone Joint Surg 1988 ; 70-B : Moseley CF. A straight-line graph for leg-length dis cre - pancies. J Bone Joint Surg 1977 ; 59-A : Nakase T, Ohzono K, Shimizu N et al. Correction of severe post-traumatic deformities in the distal femur by distraction osteogenesis using Taylor Spatial Frame : a case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2006 ; 126 : Ogden JA. Skeletal growth mechanism injury patterns. J Pediatr Orthop 1982 ; 2 : Paley D. Principles of Deformity Correction. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, Paley D, Bhave A, Herzenberg JE et al. Multiplier method for predicting limb-length discrepancy. J Bone Joint Surg 2000 ; 82-A : Peterson HA, Madhok R, Benson JT et al. Physeal fractures : Part 1. Epidemiology in Olmsted County, Minnesota, J Pediatr Orthop 1994 ; 14 : Rozbruch SR, Helfet DL, Blyakher A. Distraction of hypertrophic nonunion of tibia with deformity using Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame. Report of two cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2002 ; 122 : Salter RB. Injuries of the epiphyseal plate. Instr Course Lect 1992 ; 41 : Sluga M, Pfeiffer M, Kotz R et al. Lower limb defor mities in children : two-stage correction using the Taylor spatial frame. J Pediatr Orthop B 2003 ; 12 : Stanitski DF, Bullard M, Armstrong P et al. Results of femoral lengthening using the Ilizarov technique. J Pediatr Orthop 1995 ; 15 : Tetsworth K, Paley D. Malalignment and degenerative arthropathy. Orthop Clin North Am 1994 ; 25 :
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Small-wire circular fixators and hybrid external fixation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
Accuracy of complex lower-limb deformity correction with external fixation: a comparison of the Taylor Spatial Frame with the Ilizarov Ringfixator
 J Child Orthop (2007) 1:55 61 DOI 10.1007/s11832-006-0005-1 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Accuracy of complex lower-limb deformity correction with external fixation: a comparison of the Taylor Spatial Frame
J Child Orthop (2007) 1:55 61 DOI 10.1007/s11832-006-0005-1 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Accuracy of complex lower-limb deformity correction with external fixation: a comparison of the Taylor Spatial Frame
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest
 Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
LIMB LENGTH DISCREPANCIES
 LIMB LENGTH DISCREPANCIES Jill C Flanagan, MD OBJECTIVES Evaluate the patient with a possible limb length difference (LLD) Understand general treatment principles when managing limb length differences
LIMB LENGTH DISCREPANCIES Jill C Flanagan, MD OBJECTIVES Evaluate the patient with a possible limb length difference (LLD) Understand general treatment principles when managing limb length differences
Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame
 Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 23:387 391 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman,
Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 23:387 391 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman,
Limb lengthening for radiation-induced growth arrest of the pelvis and femur
 CASE REPORT Limb lengthening for radiation-induced growth arrest of the pelvis and femur Paul E. Matuszewski and S. Robert Rozbruch INTRODUCTION Aggressive treatment, including surgery and highdose irradiation,
CASE REPORT Limb lengthening for radiation-induced growth arrest of the pelvis and femur Paul E. Matuszewski and S. Robert Rozbruch INTRODUCTION Aggressive treatment, including surgery and highdose irradiation,
Guided growth with tension band plate or definitive epiphysiodesis for treatment of limb length discrepancy?
 Borbas et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2019) 14:99 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1139-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Guided growth with tension band plate or definitive epiphysiodesis for
Borbas et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2019) 14:99 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1139-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Guided growth with tension band plate or definitive epiphysiodesis for
Multiple Exostoses / Multiple Osteochondroma of the Lower Limb Guide By Dror Paley M.D.,
 Multiple Exostoses / Multiple Osteochondroma of the Lower Limb Guide By Dror Paley M.D., Director of the Paley Advanced Limb Lengthening Institute at St. Mary s Hospital in West Palm Beach, Florida. Located
Multiple Exostoses / Multiple Osteochondroma of the Lower Limb Guide By Dror Paley M.D., Director of the Paley Advanced Limb Lengthening Institute at St. Mary s Hospital in West Palm Beach, Florida. Located
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Lower Extremity Fracture Management. Fractures of the Hip. Lower Extremity Fractures. Vascular Anatomy. Lower Extremity Fractures in Children
 Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum
 Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery
 S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy
 Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities
 Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities BRUNO GLADBACH, DMED*; ETIENNE HEIJENS, DMED*; JOACHIM PFEIL, PROFDMED*; DROR PALEY, MD abstract External
Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities BRUNO GLADBACH, DMED*; ETIENNE HEIJENS, DMED*; JOACHIM PFEIL, PROFDMED*; DROR PALEY, MD abstract External
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016
 SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
The role of Taylor Spatial Frame for the treatment of acquired and congenital tibial deformities in children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 419-425 ORIGINAL STUDY The role of Taylor Spatial Frame for the treatment of acquired and congenital tibial deformities in children Haridimos Tsibidakis, Anastasios D. Kanellopoulos,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 419-425 ORIGINAL STUDY The role of Taylor Spatial Frame for the treatment of acquired and congenital tibial deformities in children Haridimos Tsibidakis, Anastasios D. Kanellopoulos,
Correction of Angular Deformities by Physeal Distraction
 Correction of Angular Deformities by Physeal Distraction Jose Cañadell, M.D., and Julio De Pablos, M.D. From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Navarra,
Correction of Angular Deformities by Physeal Distraction Jose Cañadell, M.D., and Julio De Pablos, M.D. From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Navarra,
Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children
 PATIENT INFORMATION Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children The Guided Growth System eight-plate quad-plate INTRODUCTION Children need gentle guidance and correction in many
PATIENT INFORMATION Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children The Guided Growth System eight-plate quad-plate INTRODUCTION Children need gentle guidance and correction in many
Does langenskiold staging have a good prognostic value in late onset tibia vara?
 Khanfour Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2012, 7:23 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does langenskiold staging have a good prognostic value in late onset tibia vara? Ashraf Ahmad Khanfour * Abstract
Khanfour Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2012, 7:23 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does langenskiold staging have a good prognostic value in late onset tibia vara? Ashraf Ahmad Khanfour * Abstract
The Efficacy of Percutaneous Lateral Hemiepiphysiodesis on Angular Correction in Idiopathic Adolescent Genu Varum
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:92-98 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.92 The Efficacy of Percutaneous Lateral Hemiepiphysiodesis on Angular Correction in Idiopathic Adolescent
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:92-98 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.92 The Efficacy of Percutaneous Lateral Hemiepiphysiodesis on Angular Correction in Idiopathic Adolescent
Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Supramalleolar Osteotomy Using Circular External Fixation with Six-Axis Deformity Correction of the Distal Tibia
 FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2011.0986 Supramalleolar Osteotomy Using Circular External Fixation with Six-Axis Deformity Correction of the Distal Tibia Daniel M. Horn, MD 1 ; Austin T. Fragomen,
FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2011.0986 Supramalleolar Osteotomy Using Circular External Fixation with Six-Axis Deformity Correction of the Distal Tibia Daniel M. Horn, MD 1 ; Austin T. Fragomen,
Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening
 Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (3): 271 275 271 Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening 60 patients followed for mean 5 years Seung-Ju Kim, Mandar Vikas Agashe, Sang-Heon Song, and
Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (3): 271 275 271 Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening 60 patients followed for mean 5 years Seung-Ju Kim, Mandar Vikas Agashe, Sang-Heon Song, and
Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE. Limb Reconstruction System. Part B: Correction of Deformities. By Dr. S. Nayagam
 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE 11 Limb Reconstruction System Part B: Correction of Deformities By Dr. S. Nayagam CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE... Page
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE 11 Limb Reconstruction System Part B: Correction of Deformities By Dr. S. Nayagam CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE... Page
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Temporary Intentional Leg Shortening and Deformation to Facilitate Wound Closure Using the Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame
 TECHNICAL TRICK Temporary Intentional Leg Shortening and Deformation to Facilitate Wound Closure Using the Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame Shane J. Nho, MD, David L. Helfet, MD, and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
TECHNICAL TRICK Temporary Intentional Leg Shortening and Deformation to Facilitate Wound Closure Using the Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame Shane J. Nho, MD, David L. Helfet, MD, and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
Operative Technique. by PROF. NAYAGAM. LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities
 Operative Technique by PROF. NAYAGAM LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities 11 Quick Reference Guide CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part A: General Principles Page N o I Introduction
Operative Technique by PROF. NAYAGAM LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities 11 Quick Reference Guide CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part A: General Principles Page N o I Introduction
Leg-length discrepancy and Its management 성균관의대 삼성서울병원 심종섭
 and Its management 성균관의대 삼성서울병원 심종섭 Etiology of Undergrowth Congenital limb deficiency : congenital femoral deficiency, congenital fibular deficiency, tibial hemimelia Asymmetrical neurological disorders
and Its management 성균관의대 삼성서울병원 심종섭 Etiology of Undergrowth Congenital limb deficiency : congenital femoral deficiency, congenital fibular deficiency, tibial hemimelia Asymmetrical neurological disorders
Equalization of Limb Length Discrepancy using Growth Arrest vs Intramedullary Lengthening
 Equalization of Limb Length Discrepancy using Growth Arrest vs Intramedullary Lengthening Ahmed Hammouda, MD Vivian Szymczuk, MD Martin G. Gesheff, BS Shawn Standard, MD John E. Herzenberg, MD International
Equalization of Limb Length Discrepancy using Growth Arrest vs Intramedullary Lengthening Ahmed Hammouda, MD Vivian Szymczuk, MD Martin G. Gesheff, BS Shawn Standard, MD John E. Herzenberg, MD International
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
A technique for calculating limb length inequality and epiphyseodesis timing using the multiplier method and a spreadsheet
 J Child Orthop (2007) 1:151 155 DOI 10.1007/s11832-007-0016-6 TECHNICAL NOTE A technique for calculating limb length inequality and epiphyseodesis timing using the multiplier method and a spreadsheet James
J Child Orthop (2007) 1:151 155 DOI 10.1007/s11832-007-0016-6 TECHNICAL NOTE A technique for calculating limb length inequality and epiphyseodesis timing using the multiplier method and a spreadsheet James
Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity
 Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity F. E. Bilen, M. Kocaoglu, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul Medical School, Istanbul
Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity F. E. Bilen, M. Kocaoglu, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul Medical School, Istanbul
Is Distraction Histiogenesis a Reliable Method to Reconstruct Segmental Bone and Acquired Leg Length Discrepancy in Tibia Fractures and Non Unions?
 Is Distraction Histiogenesis a Reliable Method to Reconstruct Segmental Bone and Acquired Leg Length Discrepancy in Tibia Fractures and Non Unions? James J Hutson Jr MD Professor Orthopedic Trauma Ryder
Is Distraction Histiogenesis a Reliable Method to Reconstruct Segmental Bone and Acquired Leg Length Discrepancy in Tibia Fractures and Non Unions? James J Hutson Jr MD Professor Orthopedic Trauma Ryder
Leg-length discrepancy and Its management
 and Its management 성균관의대 삼성서울병원 심종섭 Etiology of Undergrowth Congenital limb deficiency i : Congenital femoral deficiency, congenital fibular deficiency, tibial hemimelia Asymmetrical neurological disorders
and Its management 성균관의대 삼성서울병원 심종섭 Etiology of Undergrowth Congenital limb deficiency i : Congenital femoral deficiency, congenital fibular deficiency, tibial hemimelia Asymmetrical neurological disorders
Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report
 Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report Nina Agrawal, BA, Danielle Cameron, BA, Lawrence Wells, MD Abstract A 12-year-old girl underwent a bilateral distal femoral and proximal
Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report Nina Agrawal, BA, Danielle Cameron, BA, Lawrence Wells, MD Abstract A 12-year-old girl underwent a bilateral distal femoral and proximal
Long term self esteem assessment after height increase by lengthening and then nailing
 40 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2017, 83, k. emara, 40-44 m. a. al kersh, a. k. emara ORIGINAL STUDY Long term self esteem assessment after height increase by lengthening and then nailing Khaled Emara, Mohamed
40 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2017, 83, k. emara, 40-44 m. a. al kersh, a. k. emara ORIGINAL STUDY Long term self esteem assessment after height increase by lengthening and then nailing Khaled Emara, Mohamed
The use of the Taylor spatial frame in adolescent Blount s disease: is fibular osteotomy necessary?
 J Child Orthop (2008) 2:199 204 DOI 10.1007/s11832-008-0099-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE The use of the Taylor spatial frame in adolescent Blount s disease: is fibular osteotomy necessary? Mark Eidelman
J Child Orthop (2008) 2:199 204 DOI 10.1007/s11832-008-0099-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE The use of the Taylor spatial frame in adolescent Blount s disease: is fibular osteotomy necessary? Mark Eidelman
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle
 Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring Fixator
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring S Dhar, M Mir Citation S Dhar, M
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring S Dhar, M Mir Citation S Dhar, M
Malrotation can occur following closed intramedullary
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Effects of Femoral Shaft Malrotation on Lower Extremity Anatomy Joseph J. Gugenheim, MD,* Robert A. Probe, MD, and Mark R. Brinker, MD* Objective: To determine how axial rotation around
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Effects of Femoral Shaft Malrotation on Lower Extremity Anatomy Joseph J. Gugenheim, MD,* Robert A. Probe, MD, and Mark R. Brinker, MD* Objective: To determine how axial rotation around
Bone Lengthening for Management of Type 1a Proximal Femoral Deficiency with or without Varus Deformity
 American Research Journal of Orthopedics and Traumatology (ARJOT) Volume 2016, 8 Pages Research Article Keywords: Bone lengthening, proximal, femoral deficiency, deformity. Introduction Open Access Bone
American Research Journal of Orthopedics and Traumatology (ARJOT) Volume 2016, 8 Pages Research Article Keywords: Bone lengthening, proximal, femoral deficiency, deformity. Introduction Open Access Bone
Lengthening & Deformity correction with. Fixator Assisted Nailing
 Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Distal tibial physeal arrest after meningococcal septicaemia
 CHILDREN S ORTHOPAEDICS Distal tibial physeal arrest after meningococcal septicaemia MANAGEMENT AND OUTCOME IN SEVEN ANKLES F. P. Monsell, J. R. Barnes, R. Kirubanandan, A. M. B. McBride From Bristol Royal
CHILDREN S ORTHOPAEDICS Distal tibial physeal arrest after meningococcal septicaemia MANAGEMENT AND OUTCOME IN SEVEN ANKLES F. P. Monsell, J. R. Barnes, R. Kirubanandan, A. M. B. McBride From Bristol Royal
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
Computer Assisted Deformity Correction Using the Ilizarov Method
 Computer Assisted Deformity Correction Using the Ilizarov Method A.L. Simpson 1,B.Ma 1,D.P.Borschneck 2, and R.E. Ellis 1,2,3 1 School of Computing 2 Department of Surgery 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Computer Assisted Deformity Correction Using the Ilizarov Method A.L. Simpson 1,B.Ma 1,D.P.Borschneck 2, and R.E. Ellis 1,2,3 1 School of Computing 2 Department of Surgery 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
FORCES AND STRAIN IN ARTHRODIATASIS
 FORCES AND STRAIN IN ARTHRODIATASIS REDUCED INTRA-ARTICULAR LOAD BY JOINT DISTRACTION FORCE AND LOAD-SHARE MEASUREMENTS AND RADIOSTEREOMETRIC ANALYSIS (RSA) IN PATIENTS WITH TALOCRURAL ARTHROSIS Harald
FORCES AND STRAIN IN ARTHRODIATASIS REDUCED INTRA-ARTICULAR LOAD BY JOINT DISTRACTION FORCE AND LOAD-SHARE MEASUREMENTS AND RADIOSTEREOMETRIC ANALYSIS (RSA) IN PATIENTS WITH TALOCRURAL ARTHROSIS Harald
Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia with Complex Deformity and Multiple Previous Surgeries Treated by Taylor Spatial Frame at Age of 16 Years
 JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 17 No. 1, pp: 67-78 (2010 A.D. / 1431 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 17-1.7 Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia with Complex Deformity and Multiple Previous Surgeries Treated by Taylor
JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 17 No. 1, pp: 67-78 (2010 A.D. / 1431 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 17-1.7 Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia with Complex Deformity and Multiple Previous Surgeries Treated by Taylor
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation
 Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Knee spanning solutions
 Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Modern Rx of Polio. with Ilizarov & new techniques
 Modern Rx of Polio with Ilizarov & new techniques Poliomyelitis Best Teacher of Orthopaedics Teaches Thorough clinical examination Muscle charting Gait Analysis Analysis of Joint Instability Precision
Modern Rx of Polio with Ilizarov & new techniques Poliomyelitis Best Teacher of Orthopaedics Teaches Thorough clinical examination Muscle charting Gait Analysis Analysis of Joint Instability Precision
The Accuracy of Current Methods in Deciding the Timing of Epiphysiodesis
 The Accuracy of Current Methods in Deciding the Timing of Epiphysiodesis Soon Chul Lee MD 1, Sung Wook Seo MD 2, Kyung Sup Lim MD 2, Jong Sup Shim MD 2 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, 1 Bundang CHA
The Accuracy of Current Methods in Deciding the Timing of Epiphysiodesis Soon Chul Lee MD 1, Sung Wook Seo MD 2, Kyung Sup Lim MD 2, Jong Sup Shim MD 2 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, 1 Bundang CHA
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation
 Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
AMBULATORY OR1HOPAEDICS
 ChildrensHospitalLosAngeles HISTORY: The patient is a 15-year-old Caucasian male status post motor vehicle accident in 1989 with a subsequent growth arrest of his right lateral condyle in a valgus deformity.
ChildrensHospitalLosAngeles HISTORY: The patient is a 15-year-old Caucasian male status post motor vehicle accident in 1989 with a subsequent growth arrest of his right lateral condyle in a valgus deformity.
Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna with Distraction Osteogenesis: Three Cases
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
Computer-assisted distraction osteogenesis by Ilizarov s method
 THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL ROBOTICS AND COMPUTER ASSISTED SURGERY Int J Med Robotics Comput Assist Surg 2008; 4: 310 320. Published online 15 October 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com)..211
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL ROBOTICS AND COMPUTER ASSISTED SURGERY Int J Med Robotics Comput Assist Surg 2008; 4: 310 320. Published online 15 October 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com)..211
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points. Christopher Iobst, MD
 Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
Physeal injuries of the ankle joint constitute 11% of all
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome of Physeal and Epiphyseal Injuries of the Distal Tibia With Intra-Articular Involvement Savvas P. Nenopoulos, MD, Vasilios A. Papavasiliou, MD, and Athanasios V. Papavasiliou,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome of Physeal and Epiphyseal Injuries of the Distal Tibia With Intra-Articular Involvement Savvas P. Nenopoulos, MD, Vasilios A. Papavasiliou, MD, and Athanasios V. Papavasiliou,
Large segmental defects of the tibia caused by highenergy. Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects
 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 3 & 4 2003-2004 101 Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects Gene D. Bobroff, M.D., Stuart Gold, M.D., and Daniel
Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 3 & 4 2003-2004 101 Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects Gene D. Bobroff, M.D., Stuart Gold, M.D., and Daniel
ILIZAROV METHOD IN TREATMENT OF TIBIAL AND FEMORAL INFECTED NON-UNIONS IN PATEITNES WITH HIGH-ENERGY TRAUMA AND BATTLE-FIELD WOUNDS
 ILIZAROV METHOD IN TREATMENT OF TIBIAL AND FEMORAL INFECTED NON-UNIONS IN PATEITNES WITH HIGH-ENERGY TRAUMA AND BATTLE-FIELD WOUNDS M. N. Tahmasebi * and Sh. Jalali Mazlouman Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
ILIZAROV METHOD IN TREATMENT OF TIBIAL AND FEMORAL INFECTED NON-UNIONS IN PATEITNES WITH HIGH-ENERGY TRAUMA AND BATTLE-FIELD WOUNDS M. N. Tahmasebi * and Sh. Jalali Mazlouman Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Two Plane Deformity Correction byilizarov Ring Fixatorlessons
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XII (June 2016), PP 46-51 www.iosrjournals.org Two Plane Deformity Correction byilizarov
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XII (June 2016), PP 46-51 www.iosrjournals.org Two Plane Deformity Correction byilizarov
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART)
 CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
Epiphysiodesis of the greater trochanter in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease : The importance of timing
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 309-313 ORIGINAL STUDY Epiphysiodesis of the greater trochanter in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease : The importance of timing Alexander VAN TONGEL, Guy FABRY From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 309-313 ORIGINAL STUDY Epiphysiodesis of the greater trochanter in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease : The importance of timing Alexander VAN TONGEL, Guy FABRY From the University
Femoral Lengthening by Ilizarov Technique: Results and Complications
 SHORT ARTICLE Femoral Lengthening by Ilizarov Technique: Results and Complications Abstract Altaf A. Kawoosa, Suhail Majid*, Manzoor A. Halwai, Mohd. Ramzan Mir, G.R. Mir Femoral lengthening using Ilizarov
SHORT ARTICLE Femoral Lengthening by Ilizarov Technique: Results and Complications Abstract Altaf A. Kawoosa, Suhail Majid*, Manzoor A. Halwai, Mohd. Ramzan Mir, G.R. Mir Femoral lengthening using Ilizarov
S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2013) 37:1995 2000 DOI 10.1007/s00264-013-1962-x ORIGINAL PAPER S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method Xia Lan & Lihai
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2013) 37:1995 2000 DOI 10.1007/s00264-013-1962-x ORIGINAL PAPER S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method Xia Lan & Lihai
Knee Arthritis in Congenital Short Femur after Wagner Lengthening
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 451, pp. 177 181 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Knee Arthritis in Congenital Short Femur after Wagner Lengthening Changhoon Jeong, MD *, ; Muharrem
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 451, pp. 177 181 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Knee Arthritis in Congenital Short Femur after Wagner Lengthening Changhoon Jeong, MD *, ; Muharrem
Development of genu varum in achondroplasia
 Development of genu varum in achondroplasia RELATION TO FIBULAR OVERGROWTH S. T. Lee, H. R. Song, R. Mahajan, V. Makwana, S. W. Suh, S. H. Lee From Korea University, Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea Genu varum
Development of genu varum in achondroplasia RELATION TO FIBULAR OVERGROWTH S. T. Lee, H. R. Song, R. Mahajan, V. Makwana, S. W. Suh, S. H. Lee From Korea University, Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea Genu varum
Simultaneous joint fusion and limb lengthening for knee deformities in children: a one-stage procedure The Kampala experience
 CLINICAL ARTICLE SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Spring 2009 / Page 47 C LINICAL A RTICLE Simultaneous joint fusion and limb lengthening for knee deformities in children: a one-stage procedure The Kampala experience
CLINICAL ARTICLE SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Spring 2009 / Page 47 C LINICAL A RTICLE Simultaneous joint fusion and limb lengthening for knee deformities in children: a one-stage procedure The Kampala experience
The effect of proximal tibial fractures on the limb axis in children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 345-353 ORIGINAL STUDY The effect of proximal tibial fractures on the limb axis in children Sawas NENOPOULOS, Aristides VRETTAKOS, Nikolaos CHAFTIKIS, Theodoros BESLIKAS,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 345-353 ORIGINAL STUDY The effect of proximal tibial fractures on the limb axis in children Sawas NENOPOULOS, Aristides VRETTAKOS, Nikolaos CHAFTIKIS, Theodoros BESLIKAS,
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD
 Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Instructional Course Lecture 2011
 Instructional Course Lecture 2011 Yoon Hae Kwak Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital Hallym University Medical Center Rotational and Angular variations of the lower extremities
Instructional Course Lecture 2011 Yoon Hae Kwak Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital Hallym University Medical Center Rotational and Angular variations of the lower extremities
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
EPI PLATE. Product summary. VaWiKo Hemi-epiphysiodesis plate 4.0
 EPI PLATE Product summary VaWiKo Hemi-epiphysiodesis plate 4.0 HEMI-EPIPHYSIODESIS The minimally invasive treatment to guide growth Congenital abnormalities, but also infections and injury, can cause the
EPI PLATE Product summary VaWiKo Hemi-epiphysiodesis plate 4.0 HEMI-EPIPHYSIODESIS The minimally invasive treatment to guide growth Congenital abnormalities, but also infections and injury, can cause the
Growth disturbance after osteomyelitis of femoral condyles in infants
 Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Growth disturbance after osteomyelitis of femoral condyles in infants Anders Langenskiöld
Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Growth disturbance after osteomyelitis of femoral condyles in infants Anders Langenskiöld
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease. Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center
 Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Torsional Deformity (Rotational
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Torsional Deformity (Rotational
Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the Literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the R Rose Citation R Rose. Metatarsal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the R Rose Citation R Rose. Metatarsal
Title: Ipsilateral Distal Femoral And Proximal Tibial Epiphyseal Growth Plate Injury: A Case Presentation
 Author's response to reviews Title: Ipsilateral Distal Femoral And Proximal Tibial Epiphyseal Growth Plate Injury: A Case Presentation Authors: Deniz Gulabi (dgulabi@yahoo.com) Mehmet Erdem (drmehmeterdem@gmail.com)
Author's response to reviews Title: Ipsilateral Distal Femoral And Proximal Tibial Epiphyseal Growth Plate Injury: A Case Presentation Authors: Deniz Gulabi (dgulabi@yahoo.com) Mehmet Erdem (drmehmeterdem@gmail.com)
External Fixator Brochure
 External Fixator Brochure Response Ortho is a global orthopaedic trauma solutions manufacturer offering premium products created under its founding principles of innovation, excellence by design and functional
External Fixator Brochure Response Ortho is a global orthopaedic trauma solutions manufacturer offering premium products created under its founding principles of innovation, excellence by design and functional
Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions)
 Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Growth in the lower lim b following chem otherapy for a malignant prim ary bone tumour: a straight-line graph
 Sarcoma (1997) 1, 75± 77 O RIGINAL ARTIC LE Growth in the lower lim b following chem otherapy for a malignant prim ary bone tumour: a straight-line graph PAUL COOL, M ARK D AVIES, ROB J. GRIM ER, SIM ON
Sarcoma (1997) 1, 75± 77 O RIGINAL ARTIC LE Growth in the lower lim b following chem otherapy for a malignant prim ary bone tumour: a straight-line graph PAUL COOL, M ARK D AVIES, ROB J. GRIM ER, SIM ON
Pediatric and Adolescent Applications of the Taylor Spatial Frame
 n Review Article Instructions 1. Review the stated learning objectives at the beginning of the CME article and determine if these objectives match your individual learning needs. 2. Read the article carefully.
n Review Article Instructions 1. Review the stated learning objectives at the beginning of the CME article and determine if these objectives match your individual learning needs. 2. Read the article carefully.
Options in the Young ACL Deficient Knee
 BOSTON SHOULDER AND SPORTS SYMPOSIUM 2013 Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Disclosure Information Disclosure Information: The following relationships exist: Research Support from: 1. Musculoskeletal Transplant
BOSTON SHOULDER AND SPORTS SYMPOSIUM 2013 Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Disclosure Information Disclosure Information: The following relationships exist: Research Support from: 1. Musculoskeletal Transplant
Investigation performed at The Center for Problem Fractures and Limb Restoration, Texas Orthopedic Hospital, Houston, Texas
 1229 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Bone Realignment with Use of Temporary External Fixation for Distal Femoral Valgus and Varus Deformities BY JOSEPH J. GUGENHEIM
1229 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Bone Realignment with Use of Temporary External Fixation for Distal Femoral Valgus and Varus Deformities BY JOSEPH J. GUGENHEIM
Preliminary Outcome Using a New Free Motion Offloading KAFO for Postoperative Management of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Adolescent Tibia Vara
 Preliminary Outcome Using a New Free Motion Offloading KAFO for Postoperative Management of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Adolescent Tibia Vara Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH
Preliminary Outcome Using a New Free Motion Offloading KAFO for Postoperative Management of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Adolescent Tibia Vara Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH
Change in Effective Leg Length after Angular Deformity Correction by Hemiepiphyseal Stapling
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:85-89 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.2.85 Change in Effective Leg Length after Angular Deformity Correction by Hemiepiphyseal Stapling Ho-Joong Jung, MD,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:85-89 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.2.85 Change in Effective Leg Length after Angular Deformity Correction by Hemiepiphyseal Stapling Ho-Joong Jung, MD,
REMODELLING OF ANGULAR DEFORMITY AFTER FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES IN CHILDREN
 REMODELLING OF ANGULAR DEFORMITY AFTER FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES IN CHILDREN MURRAY E. WALLACE, EDUARD B. HOFFMAN From the Red Cross Children s Hospital, Cape Town We reviewed 28 children with unilateral
REMODELLING OF ANGULAR DEFORMITY AFTER FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES IN CHILDREN MURRAY E. WALLACE, EDUARD B. HOFFMAN From the Red Cross Children s Hospital, Cape Town We reviewed 28 children with unilateral
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease. Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center
 Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Rotational Deformity Intoeing Outtoeing
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Rotational Deformity Intoeing Outtoeing
Early experience with medial femoral tension band plating in idiopathic genu valgum
 J Child Orthop (2011) 5:11 17 DOI 10.1007/s11832-010-0310-6 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Early experience with medial femoral tension band plating in idiopathic genu valgum Humberto Guzman Burt Yaszay Vanessa
J Child Orthop (2011) 5:11 17 DOI 10.1007/s11832-010-0310-6 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Early experience with medial femoral tension band plating in idiopathic genu valgum Humberto Guzman Burt Yaszay Vanessa
Kocaoglu, Mehmet MD; Eralp, Levent MD; Sen, Cengiz MD; Cakmak, Mehmet MD; Dincyürek, Hakan MD; Göksan, S. Bora MD
 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Volume 17(8), September 2003, pp 543-548 Management of Stiff Hypertrophic Nonunions by Distraction Osteogenesis: A Report of 16 Cases [Original Articles] Kocaoglu,
2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Volume 17(8), September 2003, pp 543-548 Management of Stiff Hypertrophic Nonunions by Distraction Osteogenesis: A Report of 16 Cases [Original Articles] Kocaoglu,
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
