Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit VIIIa The Axial Skeleton Chapter 8 (Sections )
|
|
|
- Linette Byrd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit VIIIa The Axial Skeleton Chapter 8 (Sections ) I. Divisions of the skeletal system a) An adult human skeleton has 206 named bones b) Most are paired bilaterally (on both left & right) c) There are two principal divisions of the adult skeleton i) The Axial Skeleton: down the center (1) Skull, Spine, Ribs, Sternum ii) ii. The Appendicular Skeleton: the periphery (1) Shoulder, Hip, Upper limb & Lower limb d) ARTICULATE: to form a joint with. II. Bone Surface Markings a) Surface markings are structural features on bones that are adapted for specific functions. b) Can be raised surfaces, holes, depressions, or projections off the bone. c) See Table 8.1 in the text for a list of all the bones of the human body. d) See Table 8.2 in the text for a list of bone surface markings. e) Bones are listed in bold type and their surface markings are listed below each bone in italics III. The Skull a) There are 22 bones in the skull, which rests on the superior end of the vertebral column b) There are two sets of skull bones c) Cranial Bones (8): forms the cranial cavity to protect the brain i) 1 Frontal bone, 2 parietal bones, 2 temporal, 1 occipital, 1 ethmoid, & 1 sphenoid d) Facial Bones (14): forms the face i) 2 Nasal, 2 maxillae, 2 zygomatic, mandible, 2 lacrimal, 2 palantine, 2 inferior nasal conchae, vomer. e) The skull also forms the nasal cavity and orbits. f) The skull is held together by immoveable joints called sutures g) The inner surface of the brain provides attachment sites for three membranes called the meninges, which function to stabilize the position of the brain, blood vessels, and nerves h) The outer surface of the skull has many surface markings for attachment of muscles that move the head and form facial expression. i) The Facial bones form the shape of the face as well as provide protection and support for the entrances of the digestive system and respiratory system and the delicate special sense for hearing, taste, vision, and smell. j) Cranial Bones i) Frontal Bone: forms the forehead at the anterior portion of the cranium, the superior roof of the orbits, and the anterior floor of the cranial cavity (interiorly). (1) Frontal Sinuses: two mucous-membrane lined cavities superior to the orbits (2) Supraorbital foramen: two small holes superior to the orbits for branches of the facial nerve to exit the skull and innervate muscles and skin. ii) Parietal Bones (2): bilateral. Form the greater portion of the sides and roof of the cranial cavity. (1) Sagittal suture: joint between bilateral parietal bones iii) Temporal Bones (2): bilateral. Form the inferior lateral aspects of the cranium and part of the internal cranial floor. (1) Surrounded by the squamous suture (2) contributes to the zygomatic arch via its zygomatic process (3) Provides the Mandibular Fossa for articulation with the mandible to form the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) (4) The temporal bone also contains the mastoid process and styloid process for muscle attachments.
2 (5) External Auditory Meatus: allows for the ear canal to conduct sound waves into the skull. (6) jugular foramen: hole for jugular vein to pass through (7) formamen ovale: hole for mandibular nerve (8) foramen lacerum: hole internal carotid artery iv) Occipital Bone: forms the posterior portion of the cranium. (1) Foramen Magnum: a large hole in the inferior portion of the bone, which allows the brainstem to pass into the spinal canal. (2) Occipital Condyles: Oval processes with convex surfaces for articulation with the atlas, the first vertebra of the neck. (3) External occipital protuberance: a large bump on the occipital bone, just superior to the foramen magnum for attachment of the ligamentum nuchae, which provides stability to the neck and head. (4) Superior & Inferior nuchal lines: two ridges lateral to the external occipital protuberance that provide attachment for muscles of the neck. (5) Foramen Spinosum: hole for the middle meningeal artery v) Sphenoid Bone: lies at the middle part of the base of the skull (1) resembles a butterfly (2) Sella Turcica: a saddle-shaped structure on the superior portion of the sphenoid, which provided protection for the pituitary gland. vi) Ethmoid Bone: a light, sponge-like bone on the midline, in the anterior part of the cranial floor; medial to the orbits; anterior to the sphenoid, posterior to the nasal bones. (1) Cribiform Plate: part of the ethmoid that lies in the inferior floor of the anterior cranial cavity and makes the roof of the nasal cavity. (2) Crista Galli: triangular projection supriorly from the cribiform plate providing attachment for the membrane that covers and supports the brain. (3) Superior & Middle Nasal Conchae: causes turbulence to the air entering the nostrils, resulting in particles being trapped in the mucus as well as moistening and warming the air before it enters the lungs. k) Facial Bones i) Nasal Bones (2): two paired bones meeting at the midline to form part of the bridge of the nose. ii) Maxilla (2): Form the upper jawbone and articulates with every bone of the face except the mandible. (1) Form part of the floor of the orbits, part of the lateral walls of the nasal cavity, and part of the hard palate (roof of the mouth) (2) The maxillae are usually completely fused together by birth (a) Cleft Palate: failure of the maxillary bones to unite before birth. (3) Alveolar Process: arched process for attachment of the upper teeth. (4) Infraorbital foramen: hole for the passage of a branch of the facial nerve iii) Zygomatic Bones (2): forms the prominence of the cheeks. (1) Forms part of the lateral wall of the orbit. iv) Lacrimal Bones (2): thin, fingernail-size bones postero-lateral to the nasal bones (a) Lacrimal Fossa: formed with the maxilla and hold the lacrimal sac for tear production. v) Palatine Bones (2): form the posterior portion of the hard-palate. vi) Inferior Nasal Concha (2): inferior to the middle nasal concha of the ethmoid bone. Separate from the ethmoid bone vii) Vomer: on the floor of the nasal cavity. Part of the nasal septum, which divides the naal cavity into right and left sides. viii) Mandible: the lower jawbone. (1) The largest, strongest facial bone. (2) The only moveable skull bone (other than the auditory ossicles) (3) Consists of a bilateral ramus, body, angle, mandibular condyle, mental foramen, coronoid process, and mandibular notch. (4) Alveolar processes: provide attachment for lower teeth l) Orbits: Seven bones of the skull form each orbit, or eye socket.
3 i) Roof: frontal and sphenoid bones ii) Lateral Wall: zygomatic and sphenoid iii) Floor: maxilla, zygomatic, palatine bones iv) Medial Wall: maxilla, lacrimal, ethmoid, sphenoid bones m) Sutures: immoveable joint in adult skull i) Coronal Suture: unites frontal bone with both parietal bones ii) Sagittal Suture: Unites the two parietal bones in the superior midline iii) Lambdoid Suture: unites the two parietal bones with the occipital bone iv) Squamous Suture (2): unites the parietal bones to the temporal bones n) Fontanelles: areas of the embryonic & newborn skull of fibrous connective tissue that will eventually be replaced by bone after birth. i) Allow for flexibility of the skull to ease childbirth. ii) Anterior fontanel: diamond-shaped junction of the 2 parietal bones and the fontal bone. iii) Posterior fontanel: at the juncture of the 2 parietal bones and the occipital bone. iv) Anterolateral Fontanelles (2): small, irregularly shaped. Located bilaterally between the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones. v) Posterolateral Fontanelles (2): irregularly shaped, located bilaterally at the junction of the parietal, occipital, and temporal bones. o) Hyoid Bone: U-shaped bone that does not articulate with any other bone i) Suspended from the styloid processes of the temporal bones by ligaments and muscles. ii) Located in the anterior neck inferior to the mandible, superior to the larynx (adam s apple) iii) Provides attachments for tongue muscles, neck muscles, and pharyngeal muscles (swallowing) IV. The Vertebral Column a) Also called the spinal column, spine, backbone. b) Consists of a series of bones, each called a vertebra (plural: vertebrae) c) During early development, the total number of vertebrae is 33. i) Then several vertebrae fuse, leaving 26 in the adult. d) The vertebral column is distributed into 5 section: e) The Cervical Spine: the neck i) Contains 7 vertebrae listed as C1-C7 ii) C1 & C2 called the Atlas & Axis f) The Thoracic Spine: the upper and mid back i) Contains 12 vertebrae listed as T1-T12 g) The Lumbar Spine: the lower back i) Contains 5 vertebrae listed as L1-L5 h) The Sacrum: the posterior portion of the pelvis i) Contains 5 fused sacral vertebrae (listed as S1-S5) ii) located median to the posterior hips i) The Coccyx: the tailbone i) Contains four fused coccygeal vertebrae ii) The cervical, thoracic, & lumbar vertebrae are moveable segments of the spine, the sacrum and coccyx are not. j) Movement of the vertebral column: i) Flexion: forward bending ii) Extension: backward bending iii) Right & Left Lateral Flexion: bending to the side iv) Right & Left Rotation: turning to the side k) Normal Curves of the Vertebral Column i) When viewed from the side, the spinal column has a normal S-shaped curved designed for weight-bearing. ii) The curves increase strength, maintain upright balance, absorb shock when walking, and help protect the vertebrae from fracturing. iii) Relative to the anterior, the cervical and lumbar spine have a convex curve called a lordosis. (1) Convex: the bulging part of the curve is toward the anterior.
4 iv) Relative to the anterior, the thoracic and sacral spine have a concave (bulging toward the posterior) curve called a kyphosis. v) Each of these curves can be measured in degrees and they each have specific normal ranges that are best for spinal function. Decreases or increases in the normal curve measurements are called hypo- and hyper- kyphosis or lordosis. (1) i.e.: A decrease in the normal cervical lordosis (aka: a straightened neck), is called a cervical hypolordosis. l) Intervertebral Discs (aka IVD) i) Between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae from C2-S1, there are shock-absorbing discs ii) Composed of a fibrocartilage exterior called the annulus fibrosus and a jelly-like interior called the nucleus pulposus iii) The IVD increase strength, absorb shock, and contribute flexibility for movement m) Structure of a typical vertebra i) The anatomy of vertebrae differ slightly from region to region of the spine. ii) Each Vertebra has a body, sup. & inf. articular facets, vertebral foramen, spinous process, transverse process, sup. and inf. vertebral notches, a vertebral foramen, laminae, & pedicles. (1) The laminae, pedicles, and spinous process form the vertebral arch (2) The foramen formed by the vertebral arch in the center of the vertebra is called the vertebral foramen (3) When all the vertebrae are stacked up to form the spine, the vertebral foramina form the vertebral canal, which is where the spinal cord lives & travels from the brain down through the spine. iii) Superior & Inferior vertebral notches: semi-circular notches in the pedicles that, when lined up with another vertebra, form a full-circle notch called the interverteral foramen (IVF). This allows spinal nerves formed from the spinal cord to exit the vertebral column and travel to all other parts of the body n) The Cervical Region i) The exception to the typical vertebral anatomy is C1, which has lateral masses and an anterior tubercle instead of a body, a posterior turbercle instead of a spinous process, a posterior arch instead of laminae, and an anterior arch instead of pedicles. ii) The cervical region has unique anatomical differences for specific functions (1) C2, or Axis, has a superior process called the odontoid process, or the dens. (a) The dens articulates with the posterior portion of the anterior arch of atlas to form a pivot joint that allows for rotational movement. iii) There are foramen in the bilateral transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae called the transverse foramen for passage of the vertebral artery, which comes from the aorta and travels superiorly to the brainstem area. iv) Bifid Spinous Process: the spinous processes of C2-C6 are split into two v) The vertebral foramen of the cervical vertebrae is wide and triangle-shaped, to allow for a cervical enlargement of the spinal cord in this region. o) The Thoracic Region a. Thoracic vertebrae are larger and stronger than cervical vertebrae b. The spinous processes are longer than those of the cervical region, not bifid, and most are directed inferiorly to allow for the thoracic kyphosis. c. The vertebral foramen is small and circular for a thinning circular spinal cord. d. Thoracic vertebrae articulate with the ribs at the costal facets of the bodies and the transverse facets on the transverse processes. e. The joints formed by ribs & thoracic vertebra are called the vertebrocostal joints p) The Lumbar Region i) The largest and strongest in the vertebral column for maximum weight-bearing ii) The spinous processes are thick & broad, projecting posteriorly. iii) The body of the vertebra lies superior to the spinous process. iv) The vertebral foramen is small and triangular due to the ending of the spinal cord at L1-2.
5 v) The superior articular facets face medially and the inferior articular facets face laterally. q) The Sacrum & Coccyx i) Triangular bone formed by 5 fused sacral vertebra ii) Divided into fused segments called S1-S5. iii) L5 & S1 form a joint called the lumbosacral joint iv) The auricular surfaces articulate with the Ilium of the hip bone, and form the sacroiliac joints. v) The sacrum forms the posterior 1/3 of the pelvis. vi) The sacral ala is formed on either side by the fused transverse processes of the sacral vertebrae. vii) The coccyx is inferior to the sacrum, is triangular, and formed by the fusion of four coccygeal vertebrae V. The Thorax a) The Sternum (breastbone) i) Flat, narrow, located at the center of the anterior chest wall. ii) Articulates bilaterally with the cartilage of the 1 st through 6 th ribs to form sternocostal joints iii) Articulates bilaterally with the left & right clavicles to form the sternoclavicular joints iv) Contains the manubrium, body,sternal angle, suprasternal notch (aka jugular notch), clavicular notches, & xiphoid process. b) The Ribs (12): latin = costa i) The ribs are numbered 1-12 based on the thoracic vertebra they articulate with. ii) Posteriorly, the ribs articulate directly with the vertebrae and anteriorly articulate with the costal cartilage, which eventually articulates with the sternum iii) Ribs 1-7 (true ribs) have their own costal cartilage that articulates directly with the sternum iv) Ribs 8-10 s (false ribs) costal cartilages fuse together with that of the 7 th rib and share its articulation v) The 11 th & 12 th ribs (false ribs) terminate without costal cartilage along the mid-axillary line and do not articulate with the sternum (1) 11 th & 12 th ribs called floating ribs (2) The spaces in between ribs is known as the intercostal spaces and contain intercostal muscles, blood vessels, and nerves (3) The head of the rib is found posteriorly and contains the superior and inferior facets for articulation with the thoracic vertebrae. (4) The tubercle of the rib has an articular portion for articulation with the transverse process of a thoracic vertebra.
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial Skeleton
 A. Major Divisions Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial keleton 1. Axial: Part of skeleton lies along long axis of body 2. Appendicular: Bones & features of the appendages B. AXIAL KELETON
A. Major Divisions Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial keleton 1. Axial: Part of skeleton lies along long axis of body 2. Appendicular: Bones & features of the appendages B. AXIAL KELETON
Chapter 8A. The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton. The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton. Types of Bones. Types of Bones
 Chapter 8A The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton 206 named bones Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear
Chapter 8A The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton 206 named bones Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Exercise 10. The Axial Skeleton
 Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
o Diaphysis o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found o Epiphyseal plate AXIAL SKELETON Skull
 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
The Axial Skeleton. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
 C h a p t e r 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An
C h a p t e r 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System
 Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton
 The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton The Big Idea The Axial Skeleton & Homeostasis The bones of the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis by protecting many of the body s organs such as the brain, spinal
The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton The Big Idea The Axial Skeleton & Homeostasis The bones of the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis by protecting many of the body s organs such as the brain, spinal
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton
 Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
BIO 137 AXIAL SKELETON BONE STUDY THE HUMAN SKELETON
 BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Spring Written By: J. E. Sutton. Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV.
 Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Axial skeleton bones and markings
 Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Vertebral Column. Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions. Cervical
 Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
The Skeletal System. Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments
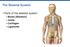 The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7
 TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM
 AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1
 Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Labs 9 and 10. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes 1/05/13. Skeletal system overview. Bone are identified by:
 Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
A. Incorrect! The axial skeleton includes bones of the skull, inner ear, chest and spinal column.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System II No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? A. The axial skeleton includes bones of the skull,
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System II No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? A. The axial skeleton includes bones of the skull,
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Skeletal system overview. Classification of Bones
 Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord
 1 Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord 1. Skull The skull is anterior to the spinal column and is the bony structure that encases the brain. Its purpose is to protect the brain and allow attachments for the facial
1 Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord 1. Skull The skull is anterior to the spinal column and is the bony structure that encases the brain. Its purpose is to protect the brain and allow attachments for the facial
The Thoracic Cage ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process
ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Spine and Neck
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 7.1 Using Figure 7.1, match the following: 1) Articulates with hip bones of the pelvis.
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 7.1 Using Figure 7.1, match the following: 1) Articulates with hip bones of the pelvis.
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN. Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms.
 THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives
 Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE:
 SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE: SKELETON: 1. Performs a mechanical function in forming the skeletal support of the body and in forming a leverage system whereby work and movement are possible. 2. Serves as
SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE: SKELETON: 1. Performs a mechanical function in forming the skeletal support of the body and in forming a leverage system whereby work and movement are possible. 2. Serves as
Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings
 Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Bones of the wrist and ankle Bones that form within tendons (e.g., patella)
 Skeletal System Review Surface Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Function of Bones Support form the framework that supports the body and cradles soft organs Protection provide a protective case for the brain, spinal
Skeletal System Review Surface Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Function of Bones Support form the framework that supports the body and cradles soft organs Protection provide a protective case for the brain, spinal
Nervous & Skeletal Systems. Virtual Science University
 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
NOTES SKELETAL SYSTEM
 NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
The Thoracic Cage. Role of the Thoracic Cage 2/13/2019. Anatomy 2: Thoracic Cage and Vertebral Column
 PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Anatomy 2: Thoracic Cage and Column The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process 12 thoracic
PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Anatomy 2: Thoracic Cage and Column The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process 12 thoracic
The SKELETAL System. The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion.
 The SKELETAL System The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion. Functions of the Skeletal System Support Protection Movement Facilitation
The SKELETAL System The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion. Functions of the Skeletal System Support Protection Movement Facilitation
Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Bone. Mental Foramen Mandible
 Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE
 THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Bio 5/6 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide
 Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Skeletal System. Axial Division
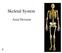 Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5)
 Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Skeletal System. It s all about the bones!!!
 Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Terms: Structures of Bones Articulations: Contacts with other bones Landmarks (Bone
An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Terms: Structures of Bones Articulations: Contacts with other bones Landmarks (Bone
2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
 CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
human anatomy 2015 lecture four Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System)
 Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Chapter 7: Skeletal System
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Bone List Anatomy
 1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System
 107 Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Adult Skull Bony orbit (FLEZMS) Frontal bone supraorbital foramen frontal sinus Lacrimal bone Ethmoid bone perpendicular plate of ethmoid middle nasal conchae cribriform
107 Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Adult Skull Bony orbit (FLEZMS) Frontal bone supraorbital foramen frontal sinus Lacrimal bone Ethmoid bone perpendicular plate of ethmoid middle nasal conchae cribriform
Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh. Razi kittaneh. Maher hadidi
 1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
the Skeletal System provided by Academic Web Services Grand Canyon University
 Anatomy Resource Center Study Guides the Skeletal System HEAD & NECK REGIONAL VIEW SKULL BONES CRANIUM FACE SKULL LANDMARKS ANTERIOR SIDE SUPERIOR/INFERIOR VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL REGIONS CERVICAL C1
Anatomy Resource Center Study Guides the Skeletal System HEAD & NECK REGIONAL VIEW SKULL BONES CRANIUM FACE SKULL LANDMARKS ANTERIOR SIDE SUPERIOR/INFERIOR VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL REGIONS CERVICAL C1
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
The Axial Skeleton Hyoid Bone. Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14 1 Axial Skeleton Hyoid bone Bones of the orbit Paranasal sinuses Infantile skull Vertebral column
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14 1 Axial Skeleton Hyoid bone Bones of the orbit Paranasal sinuses Infantile skull Vertebral column
The vault bones Frontal Parietals Occiput Temporals Sphenoid Ethmoid
 The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
Important Parts of Bones
 Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System
 BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5. Subject: The Skeletal System
 Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Skeletal System - Prelab 1
 Skeletal System - Prelab 1 1. Which bones contain the paranasal sinuses? What function do the sinuses serve? 2. What two areas are separated from each other by the hard palate? Name the two bones that
Skeletal System - Prelab 1 1. Which bones contain the paranasal sinuses? What function do the sinuses serve? 2. What two areas are separated from each other by the hard palate? Name the two bones that
Skeletal System: Skull.
 Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System
 153 Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Unit 6: Skeletal System: Bone tissue, Bones and Joints (p. 105-152) Ex. 6-1: Histology of Osseous Tissue, p. 113 Model: Osteon Tiss Lamella Osteocyte Lacunae Canaliculi
153 Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Unit 6: Skeletal System: Bone tissue, Bones and Joints (p. 105-152) Ex. 6-1: Histology of Osseous Tissue, p. 113 Model: Osteon Tiss Lamella Osteocyte Lacunae Canaliculi
In This Chapter: The Axial Skeleton 56 Head and Neck Region 56 Back Region 58
 In This Chapter: The Axial Skeleton 56 Head and Neck Region 56 Back Region 58 The Appendicular Skeleton 6 Pectoral Girdle 6 Scapulohumeral Region 68 Upper Limb 69 Pelvic Girdle 76 Lower Limb 79 Putting
In This Chapter: The Axial Skeleton 56 Head and Neck Region 56 Back Region 58 The Appendicular Skeleton 6 Pectoral Girdle 6 Scapulohumeral Region 68 Upper Limb 69 Pelvic Girdle 76 Lower Limb 79 Putting
The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD summary of bones/structures in Chapter 15 of the manual need tp be print as soon as possible http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/biology/humananatomy/skeletal/skul l/frontal/frontal.html
The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD summary of bones/structures in Chapter 15 of the manual need tp be print as soon as possible http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/biology/humananatomy/skeletal/skul l/frontal/frontal.html
A&P 1 Skeletal Lab Week 1 Pre-lab Guide Skeletal Background Information
 A&P 1 Skeletal Lab Week 1 Pre-lab Guide Skeletal Background Information Note: These notes are very similar to those found in your lecture notes. This info is for BOTH LECTURE AND LAB! Read through them
A&P 1 Skeletal Lab Week 1 Pre-lab Guide Skeletal Background Information Note: These notes are very similar to those found in your lecture notes. This info is for BOTH LECTURE AND LAB! Read through them
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
