Ankle Ligaments on MRI: Appearance of Normal and Injured Ligaments
|
|
|
- Adele Ross
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Perrich et al. MRI of nkle Ligaments Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from by on 03/31/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved FOUS ON: Kiley D. Perrich 1 Douglas W. Goodwin 1 Paul J. Hecht 2 Yvonne heung 1 Perrich KD, Goodwin DW, Hecht PJ, heung Y Keywords: ankle, ligaments, MRI DOI: /JR Received December 21, 2008; accepted after revision February 12, Department of Radiology, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical enter, One Medical enter Dr., Lebanon, NH ddress correspondence to Y. heung (yvonne.cheung@ hitchcock.org). 2 Department of Orthopaedics, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical enter, Lebanon, NH. ME This article is available for ME credit. See for more information. JR 2009; 193: X/09/ merican Roentgen Ray Society nkle Ligaments on MRI: ppearance of Normal and Injured Ligaments OJETIVE. The objective of our study was to provide a pictorial survey of MR images of ankle ligaments in various conditions from intact to disrupted. ONLUSION. MR images of ankle ligaments from a sample of patients with ankle pain or injury are presented and reviewed. E very day in the United States, roughly 10,000 people will suffer an ankle injury, with most of these being sprains [1]. MRI can depict ligament injuries and has been used to differentiate ligament tears from other causes of ankle pain, such as fracture, osteochondral injury, or tendon injury. ppropriate treatment planning for ankle injury requires differentiation between the various types of ligament injury. This article provides an overview of the MRI features of normal and abnormal ligaments of the ankle (ppendix 1). Injured ligaments on MRI may appear disrupted, thickened, heterogeneous, or attenuated in signal intensity, and may be abnormal in contour. Fluid-sensitive sequences are often helpful in detecting injury. Imaging was performed at our institution using our standard protocol (Table 1) on a 1.5-T scanner (Signa Horizon LX, GE Healthcare) with an extremity coil. Images used here were collected from patients referred for ankle MRI for ankle pain or for evaluation of injury from December 29, 2003 through ugust 10, Lateral omplex The lateral collateral ligament complex (Figs. 1 4) is the most commonly injured group of ankle ligaments and is often associated with ligament injury elsewhere in the ankle. The lateral complex, comprising the anterior talofibular, calcaneofibular, and posterior talofibular ligaments, is adequately imaged with routine axial and coronal images [2 6]. Hyalinization of tissue in the an terolateral recess, a meniscoid lesion, may result from injury of the anterior talofibular ligament and can contribute to anterolateral impingement [7]. Medial omplex and Deltoid Ligaments Isolated medial collateral or deltoid ligament injuries (Figs. 1 and 5 9) are infrequent and are commonly associated with injury to other ligaments or malleolar fractures. The medial collateral ligament complex is further divided into superficial and deep layers. The deep ligaments have talar attachments and cross one joint, whereas the superficial ligaments have variable attachments and cross two joints. The three components that are most often visualized on MRI include the tibiospring and tibionavicular ligaments in the superficial layer and the posterior tibiotalar ligament of the deep layer [8]. Syndesmosis The syndesmotic ligaments include the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament, the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament, the inferior transverse tibiofibular ligament, and the inferior interosseous ligament or membrane [9] (Figs. 1 and 10 12). syndesmotic ligament injury or high ankle sprain can be isolated or may occur in conjunction with injury of other ligament groups. It may also be associated with Weber or ankle fractures [9 12]. We have not included an image of the inferior transverse tibiofibular ligament because no such ligament injuries were encountered during the period of this study. JR:193, September
2 Perrich et al. TLE 1: Routine MRI Protocol to Evaluate for Ligament Injury Sequence Plane Frequency- Selective Fat Saturation TR TE Inversion Time (ms) Section Thickness / Interval (mm) Echo Train Length Matrix Spin-echo T1-weighted Sagittal No / Downloaded from by on 03/31/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved STIR Sagittal No 4, / Fast spin-echo proton density weighted Oblique axial a Varies 2,000 3, / Fast spin-echo proton density and T2-weighted xial Yes 3,500 6, / Fast spin-echo proton density weighted oronal Yes 2,000 3, / a 45 degrees between coronal and sagittal planes. Spring alcaneonavicular Ligament omplex The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament is also known as the spring ligament complex (Figs. 1 and 13 15). The complex extends from the calcaneus to the tarsal navicular. fibrocartilaginous portion of the ligament lies superficial to the talar head. The spring ligament consists of three components: the superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament, the medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament, and the inferoplantar longitudinal calcaneonavicular ligament [13, 14]. Of these, the superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament is most often involved in acute traumatic injury. Published studies of isolated spring ligament injuries are rare [15, 16]. ecause of the proximity of the spring ligament to the posterior tibial tendon and its integral function in stabilizing the plantar arch, spring ligament injuries are often associated with posterior tibial tendon dysfunction [17]. Summary MRI provides a means of depicting ligament injuries and can be used to differentiate ligament tears from other causes of ankle pain and injury. In this article we have provided guidelines for the MRI differentiation of the various types of ligament injury. cknowledgment We thank Daniel Deneen for his assistance in preparing and editing this manuscript. References 1. Holmer P, Sondergaard L, Konradsen L, Nielsen PT, Jorgensen LN. Epidemiology of sprains in the lateral ankle and foot. Foot nkle Int 1994; 15: Erickson SJ, Smith JW, Ruiz ME, et al. MR imaging of the lateral collateral ligament of the ankle. JR 1991; 156: Farooki S, Sokoloff RM, Theodorou DJ, et al. Visualization of ankle tendons and ligaments with MR imaging: influence of passive positioning. Foot nkle Int 2002; 23: Kreitner KF, Ferber, Grebe P, Runkel M, erger S, Thelen M. Injuries of the lateral collateral ligaments of the ankle: assessment with MR imaging. Eur Radiol 1999; 9: Labovitz JM, Schweitzer ME, Larka U, Solomon MG. Magnetic resonance imaging of ankle ligament injuries correlated with time. J m Podiatr Med ssoc 1998; 88: Lee SH, Jacobson J, Trudell D, Resnick D. Ligaments of the ankle: normal anatomy with MR arthrography. J omput ssist Tomogr 1998; 22: Robinson P, White LM, Salonen D, Daniels TR, Ogilvie-Harris D. nterolateral ankle impingement: MR arthrographic assessment of the anterolateral recess. Radiology 2001; 221: Mengiardi, Pfirrmann W, Vienne P, Hodler J, Zanetti M. Medial collateral ligament complex of the ankle: MR appearance in asymptomatic subjects. Radiology 2007; 242: artonicek J. natomy of the tibiofibular syndesmosis and its clinical relevance. Surg Radiol nat 2003; 25: rown KW, Morrison W, Schweitzer ME, Parellada J, Nothnagel H. MRI findings associated with distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury. JR 2004; 182: Ebraheim N, Lu J, Yang H, Mekhail O, Yeasting R. Radiographic and T evaluation of tibiofibular syndesmotic diastasis: a cadaver study. Foot nkle Int 1997; 18: Morris JR, Lee J, Thordarson D, Terk MR, rustein M. Magnetic resonance imaging of acute Maisonneuve fractures. Foot nkle Int 1996; 17: Mengiardi, Zanetti M, Schottle P, et al. Spring ligament complex: MR imaging anatomic correlation and findings in asymptomatic subjects. Radiology 2005; 237: Taniguchi, Tanaka Y, Takakura Y, Kadono K, Maeda M, Yamamoto H. natomy of the spring ligament. J one Joint Surg m 2003; 85-: hen JP, llen M. MR diagnosis of traumatic tear of the spring ligament in a pole vaulter. Skeletal Radiol 1997; 26: Pathria MN, Rosenstein, jorkengren G, Gershuni D, Resnick D. Isolated dislocation of the tarsal navicular: a case report. Foot nkle 1988; 9: nderson MW, Kaplan P, Dussault RG, Hurwitz S. ssociation of posterior tibial tendon abnormalities with abnormal signal intensity in the sinus tarsi on MR imaging. Skeletal Radiol 2000; 29: JR:193, September 2009
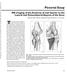
3 MRI of nkle Ligaments Downloaded from by on 03/31/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 1 nkle ligaments. (See ppendix 1 for full ligament names.), Ligaments visible laterally: anterior talofibular (L1), calcaneofibular (L2), anterior inferior tibiofibular (S) ligaments., Ligaments visible posteriorly: interosseous ligament or membrane (S1), posterior inferior tibiofibular (S2), inferior transverse tibiofibular (S3), posterior talofibular (L3), tibiocalcaneal (M4), and posterior tibiotalar (M5) ligaments., Ligaments visible medially: anterior tibiotalar (M1), tibionavicular (M2), tibiospring (M3), tibiocalcaneal (M4), posterior tibiotalar (M5), and superomedial calcaneonavicular (Sp1) ligaments. D, Ligaments composing calcaneonavicular and spring ligament complex: superomedial calcaneonavicular (Sp1), medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular (Sp2), and inferoplantar longitudinal calcaneonavicular (Sp3) ligaments. Tibiospring ligament (M3) belongs to superficial layer of medial complex and is included here to show its insertion to superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament. PPENDIX 1: nkle Ligaments Lateral complex nterior talofibular ligament Posterior talofibular ligament alcaneofibular ligament Medial complex (deltoid) Tibionavicular ligament Tibiospring ligament Tibiocalcaneal ligament nterior tibiotalar ligament Posterior tibiotalar ligament nkle syndesmosis nterior inferior tibiofibular ligament Posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament Inferior transverse ligament Distal interosseous ligament or membrane Spring ligament complex (calcaneonavicular ligament) Superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament Medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament Inferoplantar longitudinal calcaneonavicular ligament D JR:193, September
4 Perrich et al. Downloaded from by on 03/31/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved D Fig. 2 Lateral complex: anterior talofibular ligament. nterior talofibular ligament is weakest of lateral ligaments. It extends from anterolateral malleolar tip to talar neck, stabilizing talus., 44-year-old woman with chronic ankle pain. nterior talofibular ligament is well visualized on fluid-sensitive sequences such as this axial T2-weighted image. Uninjured ligament is of uniform thickness and low T1 and T2 signal intensity (arrow)., 17-year-old boy with pain and swelling and history of remote ankle injury. Partial tear of anterior talofibular ligament on axial T2-weighted image shows thickened ligament with increased internal signal (arrowhead)., 17-year-old boy with ankle pain after injury. omplete tear of anterior talofibular ligament on axial T2- weighted image shows discontinuous ligament surrounded by extensive fluid signal (arrow). D, 19-year-old woman with continued ankle pain after sprain. xial T2-weighted image shows nodular soft tissue occupying anterolateral gutter (arrow). Torn anterior talofibular ligament, seen in more distal image, is not included. Fig. 3 Lateral complex: calcaneofibular ligament. alcaneofibular ligament lies deep in relation to peroneal tendons and extends from lateral malleolar tip to trochlear eminence, stabilizing subtalar joint. alcaneofibular is often partially imaged in coronal or axial planes; multiple images are often needed to visualize its entire course., 31-year-old woman with suspected anterior tibial tendon tear. Oblique axial proton density weighted image of intact calcaneofibular ligament (arrow) shows regular contour and homogeneously low signal. (Fig. 3 continues on next page) 690 JR:193, September 2009
5 MRI of nkle Ligaments Downloaded from by on 03/31/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 3 (continued) Lateral complex: calcaneofibular ligament. alcaneofibular ligament lies deep in relation to peroneal tendons and extends from lateral malleolar tip to trochlear eminence, stabilizing subtalar joint. alcaneofibular is often partially imaged in coronal or axial planes; multiple images are often needed to visualize its entire course., 24-year-old man with Weber type fracture of fibula. Oblique axial T2-weighted image of partial tear of calcaneofibular ligament shows fluid signal in ligament and mildly irregular contour (arrowhead)., 41-year-old woman with ankle trauma. Oblique axial T2-weighted image of complete tear of calcaneofibular ligament shows discontinuous ligament with adjacent fluid signal (arrow). Ligament at its calcaneal insertion (asterisk) is not disrupted. Fig. 4 Lateral complex: posterior talofibular ligament. Posterior talofibular is least frequently injured of three lateral complex ligaments, extending from posterior talus (lateral tubercle) to fibular malleolar fossa. Posterior talofibular often appears striated on MRI because of its fibrofatty composition [7]., 37-year-old man with medial ankle pain. Normal posterior talofibular ligament (arrow) has linear striations on this axial proton density weighted image., 17-year-old boy with ankle pain after injury. omplete tear of posterior talofibular ligament is seen as ligament defect on axial T2-weighted image. Torn ends of discontinuous ligament are surrounded by fluid signal (arrow). Fig. 5 Medial complex and deltoid: tibionavicular ligament. Tibionavicular ligament inserts onto navicular and is visible on only 55% of MR images of asymptomatic subjects. ecause of its variable visualization, it is unreliable in assessing ligament injury. oronal T2-weighted image in 73-year-old woman with tarsal tunnel syndrome and foot pain shows intact tibionavicular ligament (arrow). JR:193, September
6 Perrich et al. Downloaded from by on 03/31/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 7 Medial complex and deltoid: tibiocalcaneal ligament. Tibiocalcaneal connects medial malleolus to sustentaculum tali (asterisk). This ligament is visualized in 88% of asymptomatic subjects on MR images [13]. oronal T2-weighted image in 29-yearold man with ankle pain shows complete tear and distal disruption of tibiocalcaneal ligament (arrow). Fig. 6 Medial complex and deltoid: tibiospring ligament. Tibiospring ligament connects medial malleolar colliculus to superomedial spring ligament., 44-year-old woman with ankle pain. oronal proton density weighted image of intact tibiospring ligament shows its attachment to spring ligament (arrow)., 20-year-old woman with Weber type fracture. omplete tear of tibiospring ligament on coronal T2-weighted image shows discontinuous, irregular fibers (arrow). Fig. 8 Medial complex and deltoid: anterior tibiotalar ligament. nterior tibiotalar ligament is thin and of uniformly low signal intensity on proton density weighted images. It is inconsistently visualized on routine MRI studies. Its absence is not reliable indicator of injury. oronal proton density weighted image in 56-year-old woman with ankle and foot pain shows intact anterior tibiotalar ligament (arrow). 692 JR:193, September 2009
7 MRI of nkle Ligaments Downloaded from by on 03/31/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 9 Medial complex and deltoid: posterior tibiotalar ligament. Posterior tibiotalar is thickest of medial ligaments with intervening fat separating its fascicles, often resulting in striated appearance in normal ligament. Fascicular disruption, irregularity, and loss of striation are indicators of injury., 49-year-old man with chilles tendinopathy. oronal T2-weighted image of intact posterior tibiotalar ligament shows continuous fibers and intervening fat between fascicles (arrow)., 29-year-old man with ankle pain. oronal T2-weighted image of partial tear of posterior tibiotalar ligament shows irregular contour and disrupted fibers with fluid signal near its talar attachment (arrow)., 20-year-old man with persistent ankle pain after eversion injury. oronal T2-weighted image shows complete disruption of posterior tibiotalar ligament and irregular contour of visible fibers, none of which appears attached at its talar insertion (arrowhead). Fig. 10 Syndesmosis: anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament. nterior inferior tibiofibular ligament extends from anterior tibial tubercle to fibular tubercle and is best visualized on axial images. Normal anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament may show fascicular appearance, which should not be confused with injury or tear., 43-year-old woman with ruptured plantar fascia. Intact anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament is low in signal intensity on axial proton density weighted image (arrow)., 19-year-old man with right-ankle pain after injury. xial T2-weighted image of partial tear of anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament shows fluid signal in thickened, irregular ligament (arrowhead)., 44-year-old man with high fibular fracture. xial proton density weighted image of complete tear of anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament shows discontinuous ligament (arrow). JR:193, September
8 Perrich et al. Downloaded from by on 03/31/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 11 Syndesmosis: posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament. Posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament extends from posterior tibial tubercle to posterior fibula. Most inferior fascicles (not shown) comprise inferior transverse ligament., 17-year-old boy with avascular necrosis and steroid therapy. Intact posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (arrow) is seen on axial proton density weighted image., 44-year-old man with high fibular fracture. omplete tear of posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament on axial T2-weighted image is seen as discontinuous ligament (arrow). Fig. 12 Syndesmosis: distal interosseous ligament or membrane. Interosseous ligament is inferiormost portion of interosseous membrane. It connects medial fibula to lateral tibia. Its inferior margin lies adjacent to tibiofibular recess and is lined with synovium [11]. Recess extends superiorly 5 mm from joint line on MR images of healthy subjects [12]. When fluid signal extends more than 12 mm into tibiofibular recess, syndesmotic injury should be considered [12]., 14-year-old girl with ankle pain. Intact interosseous ligament or membrane is seen on coronal T2-weighted image. Note absence of fluid in tibiofibular recess (arrows)., 44-year-old woman with ankle pain. Torn interosseous ligament or membrane is seen on coronal T2-weighted image. Fluid signal extends into tibiotalar recess 13 mm superior to joint line (arrow), indicating high likelihood of interosseous ligament or membrane tear. Fig. 13 Spring ligament complex: superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament. Superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament originates from sustentaculum tali of calcaneus and inserts onto superomedial tarsal navicular. It lies deep in relation to posterior tibial tendon (PTT). Superficial surface of superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament is composed of fibrocartilaginous gliding zone. Of three components of spring ligament complex, superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament is most likely to be injured. PTT dysfunction is often associated with spring ligament injury., 69-year-old man with high fibular fracture and pain. oronal T2-weighted image shows intact superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament (straight arrow) and adjacent PTT (curved arrow). Normal tibiospring ligament is also visible (arrowhead). sterisk indicates fibrocartilaginous gliding zone. (Fig. 13 continues on next page) 694 JR:193, September 2009
9 MRI of nkle Ligaments Downloaded from by on 03/31/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 13 (continued) Spring ligament complex: superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament. Superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament originates from sustentaculum tali of calcaneus and inserts onto superomedial tarsal navicular. It lies deep in relation to posterior tibial tendon (PTT). Superficial surface of superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament is composed of fibrocartilaginous gliding zone. Of three components of spring ligament complex, superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament is most likely to be injured. PTT dysfunction is often associated with spring ligament injury., 69-year-old man with ankle pain and talar osteochondral injury. xial T2-weighted image shows normal contour and homogeneously low signal in superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament (arrowhead)., 50-year-old man with foot and ankle pain. Oblique axial T2-weighted image shows partial tear of superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament (arrow). bnormally thickened, irregular superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament contains bright fluid signal. Fig. 14 Spring ligament complex: medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament. Medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament extends from medial portion of navicular bone to calcaneal coronoid fossa and is best visualized in axial plane., 21-year-old man with chronic foot pain. Normal striated appearance of uninjured medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament is shown on axial T2-weighted image (arrow)., 50-year-old man with foot and ankle pain. omplete tear of medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament is shown on axial T2-weighted image. Note irregular, wavy contour of ligament and interruption at its calcaneal attachment (arrow). Fig. 15 Spring ligament complex: inferoplantar longitudinal calcaneonavicular ligament. Inferoplantar calcaneonavicular ligament lies anterior to medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament, extending from inferior navicular bone to calcaneal coronoid fossa. It is usually thickest of three components of spring ligaments and is seen in 91% of asymptomatic subjects [13]. Sagittal T1-weighted image shows intact inferoplantar longitudinal calcaneonavicular ligament (arrow) in 20-year-old man with ankle pain and suspected osteochondral injury. FOR YOUR INFORMTION This article is available for ME credit. See for more information. JR:193, September
11/2/17. Lateral Collateral Complex Medial Collateral Complex Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Spring Ligament
 Andrew J Grainger Leeds, UK Lateral Collateral Complex ial Collateral Complex Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Spring Ligament Brief anatomy review Scan tips and tricks Pathological appearances andrewgrainger@nhs.net
Andrew J Grainger Leeds, UK Lateral Collateral Complex ial Collateral Complex Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Spring Ligament Brief anatomy review Scan tips and tricks Pathological appearances andrewgrainger@nhs.net
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
The Spring Ligament, PTT Tear, and Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity On MRI
 The Spring Ligament, PTT Tear, and Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity On MRI (Part 2) By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in: The posterior tibial tendon is the primary stabilizer
The Spring Ligament, PTT Tear, and Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity On MRI (Part 2) By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in: The posterior tibial tendon is the primary stabilizer
BIOMECHANICS OF ANKLE FRACTURES
 BIOMECHANICS OF ANKLE FRACTURES William R Reinus, MD MBA FACR Significance of Ankle Fractures Most common weight-bearing Fx 70% of all Fxs Incidence is increasing Bimodal distribution Men 15-24 Women over
BIOMECHANICS OF ANKLE FRACTURES William R Reinus, MD MBA FACR Significance of Ankle Fractures Most common weight-bearing Fx 70% of all Fxs Incidence is increasing Bimodal distribution Men 15-24 Women over
SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY
 Página 1 de 9 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "47 - ANKLE FRACTURES"
Página 1 de 9 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "47 - ANKLE FRACTURES"
None to report. Transverse tendon rupture Partial or complete Acute Focally increased signal Edema Hemorrhage
 None to report Kate O Mara, DO AOCR Annual Conference April 21, 2015 Review pertinent anatomy Discuss typical appearance of injured ligaments & tendons Consider commonly associated injuries Recognize injury
None to report Kate O Mara, DO AOCR Annual Conference April 21, 2015 Review pertinent anatomy Discuss typical appearance of injured ligaments & tendons Consider commonly associated injuries Recognize injury
Downloaded from by on 12/22/17 from IP address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.205.8 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.205.8. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay MR Imaging of the natomy of and Injuries
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.205.8 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.205.8. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay MR Imaging of the natomy of and Injuries
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Deltoid Ligament Study in Terms of its Shape and Size
 Deltoid Ligament Study in Terms of its Shape and Size Dr. Apoorva D 1, Dr. Lalitha C 2, Dr. Girish Patil 3 Abstract: There are two major ligamentous complexes of ankle joint which are appreciated both
Deltoid Ligament Study in Terms of its Shape and Size Dr. Apoorva D 1, Dr. Lalitha C 2, Dr. Girish Patil 3 Abstract: There are two major ligamentous complexes of ankle joint which are appreciated both
Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month a
 Case presentations Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month after Progressive limited elbow flexion
Case presentations Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month after Progressive limited elbow flexion
X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Ankle.
 X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Complex hinge joint Articulations among: Fibula Tibia Talus Tibial plafond Distal tibial articular surface
X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Complex hinge joint Articulations among: Fibula Tibia Talus Tibial plafond Distal tibial articular surface
MRI findings associated with distal. Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Injury
 Kevin W. Brown 1 William B. Morrison 1 Mark E. Schweitzer 1,2 J. ntoni Parellada 1 Henry Nothnagel 1 Received January 6, 2003; accepted after revision July 30, 2003. 1 Department of Radiology, Thomas Jefferson
Kevin W. Brown 1 William B. Morrison 1 Mark E. Schweitzer 1,2 J. ntoni Parellada 1 Henry Nothnagel 1 Received January 6, 2003; accepted after revision July 30, 2003. 1 Department of Radiology, Thomas Jefferson
Original Report. Sonography of Ankle Tendon Impingement with Surgical Correlation
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 162.158.89.91 on 08/23/18 from IP address 162.158.89.91. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Monisha Shetty 1 David P. Fessell 1 John E. Femino
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 162.158.89.91 on 08/23/18 from IP address 162.158.89.91. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Monisha Shetty 1 David P. Fessell 1 John E. Femino
Ankle Tendons in Athletes. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Ankle Tendons in Athletes Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Outline Protocols Normal Anatomy Tendinopathy, partial and complete tears Posterior tibial, Flexor Hallucis Longus, Achilles, Peroneal and Anterior Tibial
Ankle Tendons in Athletes Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Outline Protocols Normal Anatomy Tendinopathy, partial and complete tears Posterior tibial, Flexor Hallucis Longus, Achilles, Peroneal and Anterior Tibial
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
"The Role of Dynamic Ultrasound and MRI in the poorly resolving ankle sprain."
 "The Role of Dynamic Ultrasound and MRI in the poorly resolving ankle sprain." Poster No.: P-0007 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. M. Zietkiewicz, P. Mercouris, M. C. Marshall;
"The Role of Dynamic Ultrasound and MRI in the poorly resolving ankle sprain." Poster No.: P-0007 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. M. Zietkiewicz, P. Mercouris, M. C. Marshall;
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle
 Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888
 The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
17/10/2017. Foot and Ankle
 17/10/2017 Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Foot and Ankle Plantar Fasciitis Hallux Valgus Deformity Achilles Tendinosis Posterior Tibialis Tendon tendinopathy Stress Fracture Ligamentous tearing Turf
17/10/2017 Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Foot and Ankle Plantar Fasciitis Hallux Valgus Deformity Achilles Tendinosis Posterior Tibialis Tendon tendinopathy Stress Fracture Ligamentous tearing Turf
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Deltoid ligament in acute ankle injury: MR imaging analysis
 Skeletal Radiol (2014) 43:655 663 DOI 10.1007/s00256-014-1842-5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Deltoid ligament in acute ankle injury: MR imaging analysis Min Sun Jeong & Yun Sun Choi & Yun Jung Kim & Jin Su Kim &
Skeletal Radiol (2014) 43:655 663 DOI 10.1007/s00256-014-1842-5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Deltoid ligament in acute ankle injury: MR imaging analysis Min Sun Jeong & Yun Sun Choi & Yun Jung Kim & Jin Su Kim &
Anterior Impingement
 Anterior Impingement Ziali Sivardeen BMedSci, (MRCS), AFRCS, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgeon (Shoulder, Knee and Sports Injuries) Aims Causes of Anterior Ankle Pain Ankle Impingement
Anterior Impingement Ziali Sivardeen BMedSci, (MRCS), AFRCS, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgeon (Shoulder, Knee and Sports Injuries) Aims Causes of Anterior Ankle Pain Ankle Impingement
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. VI. Ankle
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines VI. Ankle Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines VI. Ankle Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D.
 Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Ankle (talocrural) joint type: hinge Talocrural joint - medial collateral ligament Medial collateral = deltoid ligament
Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Ankle (talocrural) joint type: hinge Talocrural joint - medial collateral ligament Medial collateral = deltoid ligament
MR Imaging of Ankle Anatomy and Review of Common Ankle Pathologies
 MR Imaging of Ankle Anatomy and Review of Common Ankle Pathologies Poster No.: C-0284 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Flaherty, D. Stedman, M. Chen, G. Bean, R. Loredo; San Antonio,
MR Imaging of Ankle Anatomy and Review of Common Ankle Pathologies Poster No.: C-0284 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Flaherty, D. Stedman, M. Chen, G. Bean, R. Loredo; San Antonio,
Arthroscopy Of the Ankle.
 Arthroscopy Of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Arthroscopy Anatomy Patient setup Portal placement Procedures Complications Anatomy Portals Anterior Anteromedial Anterolateral Anterocentral Posterior
Arthroscopy Of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Arthroscopy Anatomy Patient setup Portal placement Procedures Complications Anatomy Portals Anterior Anteromedial Anterolateral Anterocentral Posterior
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Use of 3D SPCE Sequences for ssessment of nkle Syndesmosis Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Minchul Kim 1 Yun Sun Choi 1 Min Sun Jeong 1 Mira Park
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Use of 3D SPCE Sequences for ssessment of nkle Syndesmosis Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Minchul Kim 1 Yun Sun Choi 1 Min Sun Jeong 1 Mira Park
Introduction. The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking.
 The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
OVERUSE AND SPORTS-RELATED INJURIES. Overuse and sports-related injuries of the ankle and hindfoot: MR imaging findings
 OVERUSE ND SPORTS-RELTED INJURIES CHPTER 10 Overuse and sports-related injuries of the ankle and hindfoot: MR imaging findings Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, d P.G. van Gils 1, Eduard E. de Lange 2 From the
OVERUSE ND SPORTS-RELTED INJURIES CHPTER 10 Overuse and sports-related injuries of the ankle and hindfoot: MR imaging findings Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, d P.G. van Gils 1, Eduard E. de Lange 2 From the
Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D.
 Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Lower limb Pelvic girdle Free lower extremity Hip bone Definitive fusion of the Y- shaped growth plate occurs 16th -18th
Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Lower limb Pelvic girdle Free lower extremity Hip bone Definitive fusion of the Y- shaped growth plate occurs 16th -18th
MRI of ligaments. Ligament biomechanics Spine Shoulder Elbow Hand/wrist Pelvis/hip Knee Foot/ankle
 MRI of ligaments Chang Ho Kang M.D. Korea University Anam Hospital Spine Shoulder Elbow Hand/wrist Pelvis/hip Knee Foot/ankle Introduction Ligament Fibrous connective tissue Attaches bone to bone Holds
MRI of ligaments Chang Ho Kang M.D. Korea University Anam Hospital Spine Shoulder Elbow Hand/wrist Pelvis/hip Knee Foot/ankle Introduction Ligament Fibrous connective tissue Attaches bone to bone Holds
Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology
 Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology Levon N. Nazarian, M.D. Professor of Radiology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Educational Objective Following
Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology Levon N. Nazarian, M.D. Professor of Radiology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Educational Objective Following
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) Index
 Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) 335 344 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Accessory soleus muscle, magnetic resonance imaging of, 300 Achilles tendon injury of, magnetic
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) 335 344 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Accessory soleus muscle, magnetic resonance imaging of, 300 Achilles tendon injury of, magnetic
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE and LOWER LEG
 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE and LOWER LEG Patient Position: ANKLE AP Projection Part Position: True Slight to place foot s long axis Center to Central Ray: to IR Midway Note: Ankle joint is to tips of malleoli
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE and LOWER LEG Patient Position: ANKLE AP Projection Part Position: True Slight to place foot s long axis Center to Central Ray: to IR Midway Note: Ankle joint is to tips of malleoli
Impingement Syndromes of the Ankle. Noaman W Siddiqi MD 5/4/2006
 Impingement Syndromes of the Ankle Noaman W Siddiqi MD 5/4/2006 Ankle Impingement Overview Clinical DX Increasingly recognized cause of chronic ankle pain Etiology can be soft tissue or osseous Professional
Impingement Syndromes of the Ankle Noaman W Siddiqi MD 5/4/2006 Ankle Impingement Overview Clinical DX Increasingly recognized cause of chronic ankle pain Etiology can be soft tissue or osseous Professional
Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology. Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018 Overview: Pathology of the Posteromedial Ankle Flexor Tendon Pathology Accessory Navicular Bone Pathology Tarsal
Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018 Overview: Pathology of the Posteromedial Ankle Flexor Tendon Pathology Accessory Navicular Bone Pathology Tarsal
Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation. Disclosures. Outline. Joint Effusion. Suprapatellar recess
 Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan
Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan
THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE Vol. 56 No. 3 March 2015 Rauscher et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Bone Marrow Edema Patterns in the Ankle and Hindfoot: Distinguishing MRI Features
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Rios et al. MRI of the Ankle and Hindfoot Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Adriana Martins Rios 1 Zehava Sadka Rosenberg 2 Jenny Teresa Bencardino 2 Silvia
Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Rios et al. MRI of the Ankle and Hindfoot Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Adriana Martins Rios 1 Zehava Sadka Rosenberg 2 Jenny Teresa Bencardino 2 Silvia
Ankle Injuries. Resident Guidebook. Achilles tendon sprain/tear. Peroneal tendinopathy Peroneal subluxation. Extensor Hallucis Longus Tenosynovitis
 Ankle Injuries Achilles tendon sprain/tear Peroneal tendinopathy Peroneal subluxation Extensor Hallucis Longus Tenosynovitis Weber Fracture Stress fracture Calcaneal bursitis Calcaneal fracture Base of
Ankle Injuries Achilles tendon sprain/tear Peroneal tendinopathy Peroneal subluxation Extensor Hallucis Longus Tenosynovitis Weber Fracture Stress fracture Calcaneal bursitis Calcaneal fracture Base of
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69 (3), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69 (3), Page 2016-2024 Role of MRI in Evaluation of Traumatic Ankle Injuries Mervat Mohamed Ibrahim Ali Elgohary*, Susan Adel Ali Abdul Rahim*,
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69 (3), Page 2016-2024 Role of MRI in Evaluation of Traumatic Ankle Injuries Mervat Mohamed Ibrahim Ali Elgohary*, Susan Adel Ali Abdul Rahim*,
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation *
 Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
ANKLE SPRAIN: DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY STARTS WITH KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY
 ANKLE SPRAIN: DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY STARTS WITH KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY Written by Pau Golanó, Spain and Jordi Vega, Switzerland A thorough knowledge of anatomy is imperative for adequate assessment of joint
ANKLE SPRAIN: DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY STARTS WITH KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY Written by Pau Golanó, Spain and Jordi Vega, Switzerland A thorough knowledge of anatomy is imperative for adequate assessment of joint
Ankle and Foot Orthopaedic Tests Orthopedics and Neurology DX 612
 Ankle and Foot Orthopaedic Tests Orthopedics and Neurology DX 612 James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Ankle & Foot Anatomy Stability of the ankle is dependent
Ankle and Foot Orthopaedic Tests Orthopedics and Neurology DX 612 James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Ankle & Foot Anatomy Stability of the ankle is dependent
Lateral ankle pain: what is the problem?
 Lateral ankle pain: what is the problem? Poster No.: C-1121 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. LEE, S. J. Lee, H. J. Choo, H. W. Jeong, Y.-M. Park, S. J. Choi; Busan/KR Keywords:
Lateral ankle pain: what is the problem? Poster No.: C-1121 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. LEE, S. J. Lee, H. J. Choo, H. W. Jeong, Y.-M. Park, S. J. Choi; Busan/KR Keywords:
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh:
 5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
Knee: Cruciate Ligaments
 72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
Spring ligament in acquired adult flat foot deformity: static and dynamic sonographic evaluation
 Spring ligament in acquired adult flat foot deformity: static and dynamic sonographic evaluation Poster No.: P-0030 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. GALLARDO AGROMAYOR, H. Vidal
Spring ligament in acquired adult flat foot deformity: static and dynamic sonographic evaluation Poster No.: P-0030 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. GALLARDO AGROMAYOR, H. Vidal
Proximal Tibiofibular Joint: An Often-Forgotten Cause of Lateral Knee Pain
 Forster et al. Tibiofibular Joint Disorders Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.192.55 on 01/17/18 from IP address 37.44.192.55. opyright RRS. For personal
Forster et al. Tibiofibular Joint Disorders Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.192.55 on 01/17/18 from IP address 37.44.192.55. opyright RRS. For personal
Joints of the Lower Limb II
 Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
MR Imaging of normal ankle anatomy: What the radiologists need to know
 MR Imaging of normal ankle anatomy: What the radiologists need to know Poster No.: P-0110 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. M. Simonet Redondo, I. Santos Gomez, A. Marin Canete,
MR Imaging of normal ankle anatomy: What the radiologists need to know Poster No.: P-0110 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. M. Simonet Redondo, I. Santos Gomez, A. Marin Canete,
Anterior Ankle Impingement Syndromes
 Anterior Ankle Impingement Syndromes Hilary R. Umans, M.D. 1,2 and Luiz Cerezal, M.D. 3 ABSTRACT Ankle impingement syndromes are painful conditions that may complicate ankle trauma and are characterized
Anterior Ankle Impingement Syndromes Hilary R. Umans, M.D. 1,2 and Luiz Cerezal, M.D. 3 ABSTRACT Ankle impingement syndromes are painful conditions that may complicate ankle trauma and are characterized
Main Menu. Ankle and Foot Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Ankle and Foot Joints click here Main Menu Copyright HandsOn Therapy Schools 2009 K.8 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k8/k8entry.htm[3/27/18, 1:40:03 PM] Ankle and Foot Joint 26 bones
1 The Ankle and Foot Joints click here Main Menu Copyright HandsOn Therapy Schools 2009 K.8 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k8/k8entry.htm[3/27/18, 1:40:03 PM] Ankle and Foot Joint 26 bones
Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
The Meniscal Roots: Gross Anatomic Correlation with 3-T MRI Findings
 rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity
 OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity Somatic Dysfunction Tenderness Asymmetry Range of Motion Tissue Texture Changes Any one of which must be present to diagnosis somatic dysfunction.
OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity Somatic Dysfunction Tenderness Asymmetry Range of Motion Tissue Texture Changes Any one of which must be present to diagnosis somatic dysfunction.
Foot. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Exercise Science Section 4: Joint Mechanics and Joint Injuries
 Exercise Science Section 4: Joint Mechanics and Joint Injuries An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Types of Joints Fibrous joint Cartilaginous
Exercise Science Section 4: Joint Mechanics and Joint Injuries An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Types of Joints Fibrous joint Cartilaginous
Management of Chronic Lateral Ligament Instability
 Management of Chronic Lateral Ligament Instability Bony Anatomy Curved trochlear surface of talus produces a cone-shaped articulation whose apex is directed medially; thus the fan-shaped deltoid is all
Management of Chronic Lateral Ligament Instability Bony Anatomy Curved trochlear surface of talus produces a cone-shaped articulation whose apex is directed medially; thus the fan-shaped deltoid is all
Ultrasound of the Knee
 Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Physical Examination of the Foot & Ankle
 Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
Deltoid and Syndesmosis Ligament Injury of the Ankle Without Fracture
 Deltoid and Syndesmosis Ligament Injury of the Ankle Without Fracture Chris D. Miller, MD, Walter R. Shelton,* MD, Gene R. Barrett, MD, F. H. Savoie, MD, and Andrea D. Dukes, MS From the Mississippi Sports
Deltoid and Syndesmosis Ligament Injury of the Ankle Without Fracture Chris D. Miller, MD, Walter R. Shelton,* MD, Gene R. Barrett, MD, F. H. Savoie, MD, and Andrea D. Dukes, MS From the Mississippi Sports
PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES
 C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
Peggers Super Summaries: Foot Injuries
 Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY 3. TALRSALS = (FOOT BONES) Fibula. Frances Daly MSc 1 CALCANEUS 2. TALUS 3. NAVICULAR 4. CUBOID 5.
 ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
The fibular incisura of the tibia with recurrent sprained ankle on magnetic resonance imaging
 The fibular incisura of the tibia with recurrent sprained ankle on magnetic resonance imaging Ayfer Mavi, PhD, Hanifi Yildirim, MD, Hasan Gunes, MD, Turan Pestamalci, MD, Erdem Gumusburun, PhD. ABSTRACT
The fibular incisura of the tibia with recurrent sprained ankle on magnetic resonance imaging Ayfer Mavi, PhD, Hanifi Yildirim, MD, Hasan Gunes, MD, Turan Pestamalci, MD, Erdem Gumusburun, PhD. ABSTRACT
Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle. Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle
 Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Outline. Ankle/Foot Anatomy Ankle Sprains Ottawa Ankle Rules DDx: The Sprain That Wasn t
 Ankle Injuries Outline Ankle/Foot Anatomy Ankle Sprains Ottawa Ankle Rules DDx: The Sprain That Wasn t Anatomy: Ankle Mortise Bony Anatomy Lateral Ligament Complex Medial Ligament Complex Ankle Sprains
Ankle Injuries Outline Ankle/Foot Anatomy Ankle Sprains Ottawa Ankle Rules DDx: The Sprain That Wasn t Anatomy: Ankle Mortise Bony Anatomy Lateral Ligament Complex Medial Ligament Complex Ankle Sprains
Hip joint Type: Articulating bones:
 Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and
 Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Longitudinal Split of the Peroneus Longus and Peroneus Brevis Tendons with Disruption of the Superior Peroneal Retinaculum
 Longitudinal Split of the Peroneus Longus and Peroneus Brevis Tendons with Disruption of the Superior Peroneal Retinaculum Gregory C. Diaz, MD, Marnix van Holsbeeck, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD Longitudinal
Longitudinal Split of the Peroneus Longus and Peroneus Brevis Tendons with Disruption of the Superior Peroneal Retinaculum Gregory C. Diaz, MD, Marnix van Holsbeeck, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD Longitudinal
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Pelvic Girdle
 ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
Donald Stewart, MD. Lateral ligament injuries Chronic lateral ligament instability Syndesmosis Injuries
 Donald Stewart, MD Arlington Orthopedic Associates Lateral ligament injuries Chronic lateral ligament instability Syndesmosis Injuries Anatomy Mechanism of Injury Classification Diagnostic Tests Management
Donald Stewart, MD Arlington Orthopedic Associates Lateral ligament injuries Chronic lateral ligament instability Syndesmosis Injuries Anatomy Mechanism of Injury Classification Diagnostic Tests Management
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle]
![EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle] EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle]](/thumbs/78/77875930.jpg) ANATOMY OF ANKLE AND FOOT Lateral aspect: [Dorsal medial to lateral= dorsal under extensor retinaculum] Tibialis Anterior EHL Artery [Dorsal pedal A] and Anterior tibial N EDL Peroneus Tertius Behind the
ANATOMY OF ANKLE AND FOOT Lateral aspect: [Dorsal medial to lateral= dorsal under extensor retinaculum] Tibialis Anterior EHL Artery [Dorsal pedal A] and Anterior tibial N EDL Peroneus Tertius Behind the
The Leg. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
MRI Features of Chronic Injuries of the Superior Peroneal Retinaculum
 Zehava Sadka Rosenberg 1 Jenny Bencardino 2 Donna Astion 3 Mark E. Schweitzer 1 Andrew Rokito 3 Steven Sheskier 3 Received July 31, 2002; accepted after revision June 26, 2003. Presented at the annual
Zehava Sadka Rosenberg 1 Jenny Bencardino 2 Donna Astion 3 Mark E. Schweitzer 1 Andrew Rokito 3 Steven Sheskier 3 Received July 31, 2002; accepted after revision June 26, 2003. Presented at the annual
radiologymasterclass.co.uk
 http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
Tibialis Anterior Tendon and Extensor Retinaculum: Imaging in Cadavers and Patients with
 Tibialis nterior Tendon and Extensor Retinaculum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C D E M N E U T R Y L I M C I G O F I N G Min Hee Lee 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 Jae Hyun Cho 1,3 urea V. Mohana-orges
Tibialis nterior Tendon and Extensor Retinaculum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C D E M N E U T R Y L I M C I G O F I N G Min Hee Lee 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 Jae Hyun Cho 1,3 urea V. Mohana-orges
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
FIBULAR & SYNDESMOSIS MALUNIONS
 FIBULAR & SYNDESMOSIS MALUNIONS MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA MORTISE INHERENTLY UNSTABLE LATERAL MALLEOLUS ACTS AS BUTTRESS / POST RESIST LATERAL TRANSLATION OF TALUS
FIBULAR & SYNDESMOSIS MALUNIONS MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA MORTISE INHERENTLY UNSTABLE LATERAL MALLEOLUS ACTS AS BUTTRESS / POST RESIST LATERAL TRANSLATION OF TALUS
Elbow Effusions in Trauma in Adults and Children: Is There an Occult Fracture?
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain
 Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
CHAPTER 80 BASIC CONSIDERATIONS
 Página 1 de 32 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Loeser, John D. Bonica's Management of Pain, 3rd Edition CHAPTER 80 BASIC CONSIDERATIONS Part of "CHAPTER 80 - Pain in the Leg, Ankle, and Foot"
Página 1 de 32 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Loeser, John D. Bonica's Management of Pain, 3rd Edition CHAPTER 80 BASIC CONSIDERATIONS Part of "CHAPTER 80 - Pain in the Leg, Ankle, and Foot"
Leg. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
MRI assessment of the plantar fascia in diabetic versus nondiabetic patients: How thick should it be?
 MRI assessment of the plantar fascia in diabetic versus nondiabetic patients: How thick should it be? Poster No.: C-2324 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Pierre-Jerome
MRI assessment of the plantar fascia in diabetic versus nondiabetic patients: How thick should it be? Poster No.: C-2324 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Pierre-Jerome
IMAGING TECHNIQUES CHAPTER 4. Imaging techniques
 IMAGING TECHNIQUES Imaging techniques 23 4.1. Conventional radiographic findings Conventional radiography, tomography, arthrography and stress views have traditionally been used for imaging the ankle and
IMAGING TECHNIQUES Imaging techniques 23 4.1. Conventional radiographic findings Conventional radiography, tomography, arthrography and stress views have traditionally been used for imaging the ankle and
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Persistent ankle pain after inversion lesions: what the radiologist must look for
 Persistent ankle pain after inversion lesions: what the radiologist must look for Poster No.: P-0118 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Poster R. Leao, L. C. Zattar-Ramos, E.
Persistent ankle pain after inversion lesions: what the radiologist must look for Poster No.: P-0118 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Poster R. Leao, L. C. Zattar-Ramos, E.
