OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA
|
|
|
- Leonard Lang
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 46 SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL V01. I. No. 1 March OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA By A. Lim Siew Meng, M.B., B.S. The following is a report of three cases. CASE I (Figures 1-8) This Chinese boy, L.C.S., aged 3 years was admitted with a history (given by the father) of having sustained frequent fractures in all four limbs during the past two years. In all, he sustained more than 20 fractures, each of which resulted from often trivial injuries. The following are examples: (a) A fall, when the patient tripped while walking. (b) Dressing or undressing against the wishes of the patient. (c) While playing with other brothers and sisters. Im ye. wet et d For the first few fractures the patient was treated by Chinese bone setters, but the father having learnt the art from them, treated the patient himself subsequently. All the fractures occurred in either the femurs or the humerus and they healed rapidly. The child did not appear to have suffered unduly from the fractures as they did not cause pain. Milestones:.A normal delivery, the child weighed 51 lbs. was able to sit up and talk at about the age of 12 months and walk at the age of 18 months. ' Fig. 2. Fig. 1. Case I. Age 3 with deformity of left upper arm. Patient was treated with "gallows- traction for fracture of femoral shaft. Fig. 3. Figs. 2 and 3. Case I. Age 3 with skull showing prominence of parietal and occipital bobes. Family History: The patient was the 5th in the family of 7 children and they were all well except that the 6th child also had occassional fractures from trivial injuries (Case 11).
2 oçi :d Fig. 1. Fig. 5. Figs. 4 and 5. Case I. Age 3 with vertebral bodies showing osteoporosis and biconcavity and ribs showing multiple fractures. Fig. 6. Pigs. 6 and 7. Case I. Age 3 with slender lower I thin conten and multiple factures. Fig. 7. rib long bones showing general nste
3 -18 SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL Differential count: Polymorphs 65%, Lymphocytes 28%, Monocytes 3%, Eosinophils 4%. Blood chemistry: Serum calcium 11.8 mgm% Serum phosphorus 2.4 mgm% Blood alkaline phosphatase 14 units Fig. 8. Case I. Age 3 with upper limb long bone showing general osteoporosis, slender shafts, thin coxtex and multiple fractures of both humerus. On Examination: Child was small for his age (Fig. 1) was pale and irritable. He resisted examination. There was bossing of both parietal regions and there was a bluish tinge of the sclera. He had bad teeth. There was no clinical abnormality of the spine. There were fusiform swellings and deformities of both upper arms, but neither of these were tender: the forearms were normal. There was also a swelling over the jell thigh. which was tender on applying pressure. The lungs and heart were clinically normal except for some rhonchi over the lungs. The Central Nervous System was normal. There was no undue laxity of his joints. There was bossing of the parietal bones bilaterally and biconcavity of many of the ertebral bodies. The long bones were slender with general osteoporosis and thin characteristic cortex. There were fractures of several ribs, and of both humeral and femural shafts. Other Investigations: Blood counts. Total red count 4.17 million per cu. mm. Total white count 11,200 per cu. nun. CASE II This Chinese girl, L.C.H. aged 2 years the younger sister of Case I, sustained a fracture of her left femur while the mother was dressing her against her will. Her mother said that she did not use any undue force. The patient had 3 previous fractures, all of which resulted from trivial injuries. None of the fractures caused severe pain. Milestones: A normal delivery, she weighed 51 lbs, was able to sit up at 12 months and speak at 18 months. Family History: Younger sister of Case I. The 6th child in the family. On Examination: There was no clinical abnormality detected except the evidence of ''callus" in the left upper arm and swelling, deformity and tenderness in the left thigh. The chill was normal in size for her age and there was no bluish tinge in her sclera. The only other significant feature was that she had bad teeth. X-rays: There was thinning of the cortex of the long bones generally, and some biconcave spinal vertebral bodies. There were fractures of both the left femoral and humeral shafts. Other Investigations: Blood count: Total red count 3.82 million per cu. mm. Hb. 78%. Total white count 7,800 per cu. mm. Differential count: Polymorphs 65%, lymphocytes 32%, monocytes 1%, eosinophils Blood chemistry: Serum calcium 12.4 mgm% Serum alkaline phosphatase 20 units. CASE Ill (Figures 9-12) This Malay boy B.B.A., aged 12 years was admitted with a history of having blue sclerotics since birth and deformity of his legs. At the age of 14 months, when he began to stand, it was noticed that his legs began to bend. At the same time he began to.sustain fractures from
4 MARCH t Figs. 9 and 10. Case Ill. Age 12 with marked anteriorly curved deformity of both tibias. The feet were everted due to medial curvature of the tibiae..7'2'17? e - 0 d o Fig. I1. Case Ill. Age 12 with femurs showing marked bowing of the upper one-third of the shaft. chºoar teristit osteoporosis and thin coxtex. e ` Y.. :.í=,-. Fig. 12. Case Iii. Age 12 with tibia and fibula markedly deformed. Huth hones were osteopurntit with thin tastes.
5 50 SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL trivial injuries such as while crying in a fit of temper or when one of his elder brothers carried him to the bathroom (as he had never been able to walk). Often the fractures occurred without any apparent cause. All the fractures healed rapidly. The last fracture occurred about 10 weeks ago. The brothers observed that during the first few days after sustaining a fracture the colour of his sclera deepened. Milestones: A normal delivery, his growth was described as normal. He began to stand and speak at about 14 months. Family History: There was no family history of similar illness. The patient was the 6th in a family of six sons. Other siblings were normal. On Examination: The patient was well developed. The shape of his head was normal and the sclera of his eyes was deep blue in colour. He had good teeth. He had scoliosis of his spine and marked bowing of the shafts of both his femur and tibia: the tibia was bowed anteriorly 90. There was no undue laxity of his joints. His respiratory central nervous and cardiovascular systems were normal. There was no abnormality of his abdomen. X-rays (Figures 11-12): The skull was normal. There was osteoporosis of his bones generally. His spinal vertebral bodies were binconcave. His long bones were not only osteoporotic but the cortex were generally thin, and they were slender. There was evidence of healed fractures of the left radial and ulna shafts and both the femur and tibia shafts. Other Investigations: Blood count: Total red count 4.09 million per cu. mm. Hb. 83%. Total white count 5,700 per cu. mm. Differential count: Polymorphs 62%, Lymphocytes 34%, Monocytes 2%, Eosinophils 2%. Blood chemistry: Serum calcium 12.5 mgm% Blood alkaline phosphatase 16 units. COMMENTS Osteogenesis imperfecta (synonyms: fragilitas ossium, idiopathic osteopsathyrosis, periosteal dysplasia, brittle bones or Lobstein's disease) in a disorder of the skeleton characterised by its marked liability to pathological fractures. Two types are recognised: osteogenesis imperfecta congenita (prenatal) and osteogenesis imperfecta tarda (post -natal); the former is congenital, more severe and often fatal at or soon after birth, the latter is relatively mild. The etiology is unknown, some observers, however, associate the disease with endocrine disturbances particularly to hyperthyroidism. It is hereditary only in a minority of cases. The prenatal type is believed to be transmitted through a Mendelian recessive and the prenatal type a variable dominant. It is a rare disease and both sexes are equally affected. The clinical features are variable. They include blue sclerotics, otosclerosis and deafness, laxity of joints, osteomalacia, fractures, dwarfing, skull with prominent parietal and occipital bones (crane a'retord) defective milk teeth and often poor muscular development due largely to disuse. The blood chemistry usually normal, except for the occasional raised alkaline phosphatase and is of no diagnostic value. There is a tendency to improve and severe cases are known to have survived many years, although grossly disabled. Fairbank considers that the essential pathology is imperfect formation and imperfect calcification of bone trabeculae. The bones are slender with thin cortex. Islets of cartilage, thickened periosteum, pathological fractures and a deficiency in the number of osteoblasts are features described. Radiological áppearances: Fairbank describes three types: Type I-Thick bone type (Fairbank, 1930). These occur in severe prenatal cases whose major long bones are short, thick and osteoporotic with multiple fractures. Type II-Slender fragile type. These are seen in the less severe prenatal and all postnatal cases. The major long bones are slender and osteoporotic with characteristically thin cortex. Type III-Osteogenesis imperfecta cystica. This is extremely rare. It is progressive and is characterised by cystic appearance of the bones. Case I is an example of a case of osteogenesis imperfecta tarda presenting with classical clinical and radiological features. The history that he sustained over 20 fractures, all of which
6 MARCH, occurred in the shafts of the femur and the humerus is not a new observation. Fairbanks described a case with 23 fractures in 3 bones. Case II is the sister of Case I and has the same disease. It is interesting to note that their parent's ascribed their disease to unsuccessful attempts to abort them, as no such attempts were made on the other apparently normal children. Case Ill showed marked anteriorly curved deformity of the tibia, which is not uncommonly associated with the disease and is probably due to repeated fractures and softening of the bones, both of which are features of the disease. Wiles (1955) described that the bones may be soft and bend causing striking deformities and Howott (1952) wrote that the tibia is apt to be curved anteriorly. The surprising finding was the observation by his three brothers (all of whom were intelligent adults) that the sclera became more blue soon after a fracture. Such a feature has not been previously described. It is generally accepted that the blue sclerotic is not due to alteration in the thickness of the sclera but to its translucency, thus the choroidal pigment is more visible through it. Lastly, the serum alkaline phosphatase which has been described as often raised was found to be above normal limits in Cases II and III, being respectively 20 and 16 units (normal 3-13 King -Armstrong Unit). SUMMARY Three cases of Osteogenesis imperfecta are described, two of which are from the same family. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I am indebted to Mr. D. W. C. Gawne, M.A., M.D., F.R.C.S. and Dr. Khoo Oon Teik, M.D., M.R.C.P.E., F.R.F.P.S.G., for their valuable advice in the writing of this article. REFERENCES Fairbank, T. (1928) Some general diseases of the skeleton. Brit. J. Surg., 15, 120. Fairbank, T. (1948) Osteogenesis imperfecta and osteogenesis imperfecta cystica. J. B. Jt. Surg., 30B, 164. Hills, R.G. and McLanahan, S. (1937) Brittle bones and blue sclerotics in five generations. Arch. Int. Med., 59, 41. Howott, M.B. (1952) A textbook of Orthopaedics, Section Ill, p 408. Saunders. Riesenmaun, F.R. and Yater, W.M. (1941) Osteogenesis Imperfecta: its incidence and manifestations in seven families. Arch. Int. Med., Wiles Philip (1955) Essentials of Orthopaedics, p495, Churchill.
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX
 DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
Understanding Osteoporosis
 Understanding Osteoporosis Professor Juliet E. Compston Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
Understanding Osteoporosis Professor Juliet E. Compston Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action!
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Section 1. What is osteoporosis? Your bones. Bones and osteoporosis. Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis
 4 Section 1 What is osteoporosis? Your bones Bones and osteoporosis Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Less common types of osteoporosis Other bone conditions 5 Osteoporosis
4 Section 1 What is osteoporosis? Your bones Bones and osteoporosis Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Less common types of osteoporosis Other bone conditions 5 Osteoporosis
= Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue
 = Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue Common Orthopedic Problems Dwarfism Short Stature Pathologic Short Stature Normal Variant Short Stature Proportionate Short Stature Midget Endocrine/nutritional
= Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue Common Orthopedic Problems Dwarfism Short Stature Pathologic Short Stature Normal Variant Short Stature Proportionate Short Stature Midget Endocrine/nutritional
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Congenita in a nigerian baby
 Osteogenesis Imperfecta Congenita in a nigerian baby O Akiode ( ), OB Ogunfowora, A. Shonubi, AA Bajomo, AA Musa & SA Sotimehin Olabisi Onabanjo University Teaching Hospital, Sagamu, Nigeria. Correspondence:
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Congenita in a nigerian baby O Akiode ( ), OB Ogunfowora, A. Shonubi, AA Bajomo, AA Musa & SA Sotimehin Olabisi Onabanjo University Teaching Hospital, Sagamu, Nigeria. Correspondence:
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation Vol. 7, Issue 4, October - December 2015
 ASSOCIATION OF BILATERAL RADIOULNAR SYNOSTOSIS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA TYPE 1 CASE PRESENTATION Valeriu V. Lupu 1, Mirabela Subotnicu 1, Ancuța Ignat 1, Gabriela Păduraru 1 *, Irina Naumcieff 1, Bogdan
ASSOCIATION OF BILATERAL RADIOULNAR SYNOSTOSIS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA TYPE 1 CASE PRESENTATION Valeriu V. Lupu 1, Mirabela Subotnicu 1, Ancuța Ignat 1, Gabriela Păduraru 1 *, Irina Naumcieff 1, Bogdan
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
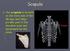 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
Childhood Fractures. Incomplete fractures more common. Ligaments stronger than bone. Tendons stronger than bone. Fractures may be pathologic
 Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Part I : Study of Osteoporotic Fractures (SOF) Fractures and Falls History: History of Fractures Questionnaire
 PhenX Measure: Fracture History (#170900) PhenX Protocol: Fracture History (#170901) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): Part I : Study of Osteoporotic Fractures (SOF) Fractures and Falls History:
PhenX Measure: Fracture History (#170900) PhenX Protocol: Fracture History (#170901) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): Part I : Study of Osteoporotic Fractures (SOF) Fractures and Falls History:
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS. Ms. Doshi
 CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture
 Patient Information Leaflet Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture Produced By: Orthopaedic Department September 2013 Review due September 2016 1 If you require this leaflet in another language, large print or another
Patient Information Leaflet Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture Produced By: Orthopaedic Department September 2013 Review due September 2016 1 If you require this leaflet in another language, large print or another
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
Scoliosis. About idiopathic scoliosis and its treatment. Patient and Family Education. What types of scoliosis are there?
 Patient and Family Education Scoliosis About idiopathic scoliosis and its treatment This handout covers the most common type of scoliosis, adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Other types of scoliosis may
Patient and Family Education Scoliosis About idiopathic scoliosis and its treatment This handout covers the most common type of scoliosis, adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Other types of scoliosis may
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Rickets
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Rickets 1 Rickets IS defined as failure of mineralization of growing bone or osteoid tissue due to vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D appear as rickets in children and as oteomalacia
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Rickets 1 Rickets IS defined as failure of mineralization of growing bone or osteoid tissue due to vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D appear as rickets in children and as oteomalacia
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW
 Unit 5 Skeletal System 5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW Section Objectives Identify the major structures and functions of the skeletal system. Differentiate between the two divisions (axial and appendicular) of
Unit 5 Skeletal System 5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW Section Objectives Identify the major structures and functions of the skeletal system. Differentiate between the two divisions (axial and appendicular) of
Warm-Up Activity. Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram.
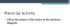 Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
QUICK ASSESSMENT: CONCEPT MAP
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
Scoliosis and Deformity Screening
 Scoliosis and Deformity Screening A program approved by the Botswana Department of Education PowerPoint presentation: Courtesy of the American Red Cross of Northeast Tennessee. Modified by WSC. World Spine
Scoliosis and Deformity Screening A program approved by the Botswana Department of Education PowerPoint presentation: Courtesy of the American Red Cross of Northeast Tennessee. Modified by WSC. World Spine
Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics
 Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics Vitamin D physiology Introduction Etiology Clinical feature Radiology Diagnosis Lab Treatment Source: -Fish, liver and oil, - Human milk (30-40 IU/L) - Exposure to sun light
Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics Vitamin D physiology Introduction Etiology Clinical feature Radiology Diagnosis Lab Treatment Source: -Fish, liver and oil, - Human milk (30-40 IU/L) - Exposure to sun light
Skeletal System Tour Lab. Station Label the bones on your answer sheet.
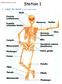 Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
The Skeletal System. Support Systems Unit 2
 The Skeletal System Support Systems Unit 2 The Basic Functions of the Skeletal System Hematopoiesis Structure Support Muscle Attachment and Movement Mineral Storage Axial vs. Appendicular The Axial Skeleton
The Skeletal System Support Systems Unit 2 The Basic Functions of the Skeletal System Hematopoiesis Structure Support Muscle Attachment and Movement Mineral Storage Axial vs. Appendicular The Axial Skeleton
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Facts about Scoliosis
 Facts about Scoliosis Have you or someone in your family recently been diagnosed with scoliosis? Or do you suspect somebody you know has the condition? That is when we usually start googling to learn all
Facts about Scoliosis Have you or someone in your family recently been diagnosed with scoliosis? Or do you suspect somebody you know has the condition? That is when we usually start googling to learn all
Chioma Okechukwu. Course: Biology 205. Instructor: Dr Danil Hammoudi. Topic Scoliosis
 Course: Biology 205 Instructor: Dr Danil Hammoudi Topic Scoliosis 1 Definition Scoliosis is a medical condition with no particular causative agent. It occurs when the spinal cord is curved and it curves
Course: Biology 205 Instructor: Dr Danil Hammoudi Topic Scoliosis 1 Definition Scoliosis is a medical condition with no particular causative agent. It occurs when the spinal cord is curved and it curves
PROTOCOLS. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Principal investigator. Co-investigators. Background
 Osteogenesis imperfecta Principal investigator Leanne M. Ward, MD, FRCPC, paediatric endocrinologist Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Children s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, 401 Smyth Rd., Ottawa
Osteogenesis imperfecta Principal investigator Leanne M. Ward, MD, FRCPC, paediatric endocrinologist Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Children s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, 401 Smyth Rd., Ottawa
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
SOME RADIOGRAPHIC MANIFESTATIONS OF EARLY SCURVY
 SOME RADIOGRAPHIC MANIFESTATIONS OF EARLY SCURVY BY JAMES F. BRAILSFORD From the Royal Orthopaedic Hospital, Birmingham (RECEIVED FOR PULBUCATION OCTOBER 28, 1952) Though scurvy is associated with characteristic
SOME RADIOGRAPHIC MANIFESTATIONS OF EARLY SCURVY BY JAMES F. BRAILSFORD From the Royal Orthopaedic Hospital, Birmingham (RECEIVED FOR PULBUCATION OCTOBER 28, 1952) Though scurvy is associated with characteristic
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System. Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section
 Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION
 Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
Forensic Anthropology. What can it tell us?
 Forensic Anthropology What can it tell us? History 1800s scientists began using skull measurements to differentiate human bodies 1897 Luetgert murder case; man killed his wife and boiled down her remains
Forensic Anthropology What can it tell us? History 1800s scientists began using skull measurements to differentiate human bodies 1897 Luetgert murder case; man killed his wife and boiled down her remains
Juvenile Osteoporosis
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1971, 46, 66. Juvenile Osteoporosis P. LAPATSANIS, A. KAVADIAS, and K. VRETOS From the Paediatric and Orthopaedic Departments, Aghia Sophia Children's Hospital, Athens,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1971, 46, 66. Juvenile Osteoporosis P. LAPATSANIS, A. KAVADIAS, and K. VRETOS From the Paediatric and Orthopaedic Departments, Aghia Sophia Children's Hospital, Athens,
OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA
 OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA BY J. G. A. DAVEL, T. FICHARDT and D. VAN DER SPUY From the Department of Radiology, Pretoria Hospital and University, South Africa (REcIEcv FOR PUBLICATION JuNE 7, 1956) Osteogenesis
OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA BY J. G. A. DAVEL, T. FICHARDT and D. VAN DER SPUY From the Department of Radiology, Pretoria Hospital and University, South Africa (REcIEcv FOR PUBLICATION JuNE 7, 1956) Osteogenesis
LEG LENGTH INEQUALITY: Sports Medicine Perspective
 LEG LENGTH INEQUALITY: Sports Medicine Perspective Debra A. Zillmer, M.D. M&M Orthopaedics, Ltd 18 Year Old Experienced Cross Country Runner: Sept Sr Year Pain in left lower leg with running Pain now prevents
LEG LENGTH INEQUALITY: Sports Medicine Perspective Debra A. Zillmer, M.D. M&M Orthopaedics, Ltd 18 Year Old Experienced Cross Country Runner: Sept Sr Year Pain in left lower leg with running Pain now prevents
Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 2 Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma P George, N Philip, B Pawar Citation P George,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 2 Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma P George, N Philip, B Pawar Citation P George,
Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid Carcinoma: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Hip Pelvis 28(3): 173-177, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.3.173 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid
CASE REPORT Hip Pelvis 28(3): 173-177, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.3.173 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid
SKELETAL SYPHILIS IN THE ADULT*
 Brit. J. vener. Dis. (1956), 32, 165. SKELETAL SYPHILIS IN THE ADULT* BY IAN A. KELLOCK Senior Medical Registrar, Manchester Royal Infirmary Late adult bone syphilis, in which the characteristic lesion
Brit. J. vener. Dis. (1956), 32, 165. SKELETAL SYPHILIS IN THE ADULT* BY IAN A. KELLOCK Senior Medical Registrar, Manchester Royal Infirmary Late adult bone syphilis, in which the characteristic lesion
TERMINOLOGY. portion of a bone ossified from a primary center. portion of a bone ossified from a secondary center.
 Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
28/04/2016. I have nothing to declare and no financial. interest or relationship to disclose
 I have nothing to declare and no financial interest or relationship to disclose Skeletal Anomalies are diverse range of complexities which is NOT Easy to diagnose. It is NOT Difficult to detect-just be
I have nothing to declare and no financial interest or relationship to disclose Skeletal Anomalies are diverse range of complexities which is NOT Easy to diagnose. It is NOT Difficult to detect-just be
FATIGUE FRACTURE OF THE FIBULA IN
 FATIGUE FRACTURE OF THE FIBULA IN BY 0 ALAN L. GRIFFITHS From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children Fatigue, or stress, fractures have been described as occurring in many situations and at widely
FATIGUE FRACTURE OF THE FIBULA IN BY 0 ALAN L. GRIFFITHS From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children Fatigue, or stress, fractures have been described as occurring in many situations and at widely
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. locomotion.
 STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics
 Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe common accidental injuries which can be confused with child abuse Describe
Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe common accidental injuries which can be confused with child abuse Describe
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
Bone Composition. Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are:
 Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Upper limb injuries in children. Key points, # & dislocations 7/23/2009 (MIMIC)
 Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
12/13/16. Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016
 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD, has no financial relationships with any commercial interests. The learner will be able to:! Articulate
Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD, has no financial relationships with any commercial interests. The learner will be able to:! Articulate
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
YOGA ANATOMY. Part Three - Bones. Yoga Teacher Training Robin Bennett 200 RYT
 YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test
 Name: Date: 1/2/18 Section Broughton High School 1 Section 1: - True or False Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test 1. The number of bones in the body increases from the time of birth to adulthood.
Name: Date: 1/2/18 Section Broughton High School 1 Section 1: - True or False Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test 1. The number of bones in the body increases from the time of birth to adulthood.
Women s Imaging ICD-10-CM
 Women s Imaging ICD-10-CM Clinical Documentation Guides Brought to you by www.codingstrategies.com The Resource for Physician and Outpatient Coding, Compliance & ICD-10-CM OTHER CLINICAL DOCUMENTATION
Women s Imaging ICD-10-CM Clinical Documentation Guides Brought to you by www.codingstrategies.com The Resource for Physician and Outpatient Coding, Compliance & ICD-10-CM OTHER CLINICAL DOCUMENTATION
Forensic Anthropology. What can it tell us?
 Forensic Anthropology What can it tell us? History 1800s scientists began using skull measurements to differentiate human bodies 1897 Luetgert murder case; man killed his wife and boiled down her remains
Forensic Anthropology What can it tell us? History 1800s scientists began using skull measurements to differentiate human bodies 1897 Luetgert murder case; man killed his wife and boiled down her remains
FIBROUS CORTICAL DEFECT AND NON-OSSIFYING FIBROMA
 POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 672. FIBROUS CORTICAL DEFECT AND NON-OSSIFYING FIBROMA PETER G. BULLOUGH, M.B., Ch.B. JON WALIFY, F.R.C.S. Nuffield Department of Orthopaedic University of Oxford, Surgery,
POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 672. FIBROUS CORTICAL DEFECT AND NON-OSSIFYING FIBROMA PETER G. BULLOUGH, M.B., Ch.B. JON WALIFY, F.R.C.S. Nuffield Department of Orthopaedic University of Oxford, Surgery,
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Osteoporosis. Dr. C. C. Visser. MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK) Member: Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK)
 Osteoporosis Dr. C. C. Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK) Member: Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Effect of age on trabecular bone. Fatfree dry bone cylinders obtained
Osteoporosis Dr. C. C. Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK) Member: Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Effect of age on trabecular bone. Fatfree dry bone cylinders obtained
FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING OSTEOSARCOMA
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Vol. 52, No. 1 Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Printed in U.S.A. FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Vol. 52, No. 1 Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Printed in U.S.A. FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING
Functions of Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Skeletal System Adult Human has 206 Bones This slideshow will offer fun ways to remember the names of some of the bones, and you can come up with your own tricks! Functions of Skeletal
Skeletal System Skeletal System Adult Human has 206 Bones This slideshow will offer fun ways to remember the names of some of the bones, and you can come up with your own tricks! Functions of Skeletal
Bone (2) Chapter 8. The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer.
 Bone (2) Chapter 8 The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer. The innercellular layer contains osteoprogenitor cells,
Bone (2) Chapter 8 The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer. The innercellular layer contains osteoprogenitor cells,
THE RISK OF ITERATIVE FRACTURES IN PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - CASE REPORT
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 1 SURGERY CASE REPORTS THE RISK OF ITERATIVE FRACTURES IN PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - CASE REPORT D. Popescu 1*, B. Puha 1, B. Veliceasa
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 1 SURGERY CASE REPORTS THE RISK OF ITERATIVE FRACTURES IN PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - CASE REPORT D. Popescu 1*, B. Puha 1, B. Veliceasa
Adult New Patient Intake. Your Health Summary
 Adult New Patient Intake Name Age Birth Date / / Soc. Sec. # - - Home Phone Cell Phone Address: City: State: Zip: Occupation: Email Marital Status: M W D S Spouse s Name: Children # and Ages: Whom may
Adult New Patient Intake Name Age Birth Date / / Soc. Sec. # - - Home Phone Cell Phone Address: City: State: Zip: Occupation: Email Marital Status: M W D S Spouse s Name: Children # and Ages: Whom may
PBL. Pain: we have to understand the physiology of pain, why we feel it and what it means.
 PBL Problem based learning; when you try to find a solution for the patient's problem, involves both clinical skills and knowledge of basic sciences. Slides 3,4 What is the meaning of Orthopaedics? Orthos:
PBL Problem based learning; when you try to find a solution for the patient's problem, involves both clinical skills and knowledge of basic sciences. Slides 3,4 What is the meaning of Orthopaedics? Orthos:
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Diagnostic imaging of. Musculoskeletal diseases
 Diagnostic imaging of Musculoskeletal diseases Investigating methods 1. X ray tha basic technique 2. CT more accurate anatomy, reconstructions 3. MRI bones no, but bone marrow 4. Scintigraphy : osteoblast
Diagnostic imaging of Musculoskeletal diseases Investigating methods 1. X ray tha basic technique 2. CT more accurate anatomy, reconstructions 3. MRI bones no, but bone marrow 4. Scintigraphy : osteoblast
Pediatric Injuries/Fractures. Rena Heathcote
 Pediatric Injuries/Fractures Rena Heathcote INTRODUCTION Incidence Anatomy of the Growing Bone Injury Patterns What can we X-ray PEDIATRIC FRACTURES INCIDENCE What makes children susceptible to fractures?
Pediatric Injuries/Fractures Rena Heathcote INTRODUCTION Incidence Anatomy of the Growing Bone Injury Patterns What can we X-ray PEDIATRIC FRACTURES INCIDENCE What makes children susceptible to fractures?
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 2.417, ISSN: , Volume 3, Issue 11, December 2015
 MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
Fractures Healing & Management. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4
 Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Bell Work. Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies.
 Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSIALIS MULTIPLEX IN THREE SISTERS
 DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
SPARROW FAMILY CHIROPRACTIC
 Whom may we thank for referring you to this office? SPARROW FAMILY CHIROPRACTIC Today s Date: PATIENT DEMOGRAPHICS PM#: Name: Birth Date: - - Age: Male Female Address: City: State: Zip: E-mail Address:
Whom may we thank for referring you to this office? SPARROW FAMILY CHIROPRACTIC Today s Date: PATIENT DEMOGRAPHICS PM#: Name: Birth Date: - - Age: Male Female Address: City: State: Zip: E-mail Address:
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: Objective for Portfolio #1: Part I: Skeletal Stations Station A: Bones of the Body
 SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
Section 11.1 Your Skeletal System
 Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
New Patient Questionnaire Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery
 Page 1 of 5 New Patient Questionnaire Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery First Name: Last Name: Middle: DOB: Height: Weight: Primary Care Physician/Pediatrician Name: Address: Phone Number: Chief Compliant
Page 1 of 5 New Patient Questionnaire Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery First Name: Last Name: Middle: DOB: Height: Weight: Primary Care Physician/Pediatrician Name: Address: Phone Number: Chief Compliant
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS
 Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
14.3 Skeletal System Exploration
 14.3 Skeletal System Exploration Read It! Directions: Each member of the group will read the passage and answer the task questions. It is important to remember that the answers will come directly from
14.3 Skeletal System Exploration Read It! Directions: Each member of the group will read the passage and answer the task questions. It is important to remember that the answers will come directly from
THE CHILD WITH NEUROFIBROMATOSIS TYPE 1 (NF1) A GUIDE FOR
 THE CHILD WITH NEUROFIBROMATOSIS TYPE 1 (NF1) A GUIDE FOR HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS Neurofibromatosis is actually a term that encompasses at least two distinct disorders, Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1)
THE CHILD WITH NEUROFIBROMATOSIS TYPE 1 (NF1) A GUIDE FOR HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS Neurofibromatosis is actually a term that encompasses at least two distinct disorders, Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1)
Beyond BMD: Bone Quality and Bone Strength
 Beyond BMD: Bone Quality and Bone Strength Consultant / advisor: Amgen, Eli Lilly, Merck Disclosures Mary L. Bouxsein, PhD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA mbouxsei@bidmc.harvard.edu
Beyond BMD: Bone Quality and Bone Strength Consultant / advisor: Amgen, Eli Lilly, Merck Disclosures Mary L. Bouxsein, PhD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA mbouxsei@bidmc.harvard.edu
Bone Development. Two Types of OssificaDon 10/18/14. Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages. Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B
 Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
The Skeletal System 5PART F. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5PART F Joints Articulations of bones Functions of joints Hold bones together Allow
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5PART F Joints Articulations of bones Functions of joints Hold bones together Allow
Skeletal System. Std. VIII
 Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System. By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr.
 Skeletal System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Learning Outcomes Describe the parts of a long
Skeletal System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Learning Outcomes Describe the parts of a long
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
