ediutrics AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS, INC. PROCEEDINGS AND REPORTS Round Table Discussion PEDIATRIC X-RAY DIAGNOSIS Tucson, Iowa, Secretaries
|
|
|
- Abraham Benson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ediutrics VOLUME 11 JUNE 1953 NUMBER 6 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS, INC. PROCEEDINGS AND REPORTS Round Table Discussion PEDIATRIC X-RAY DIAGNOSIS EDWARD B. D. NEUHAUSER, M.D., Boston, Chairman PIERCE D. KNOTT, M.D., Sioux City, Iowa, and BRICK P. STORTS, M.D., JR., Tucson, Iowa, Secretaries Chairman Neuhauser: I have been very much impressed with the pediatricians who know much more about diseases and abnormalities of the heart and lungs than they give themselves credit for, but the roentgen manifestations of abnormalities of the gastrointestinal tract do not appear to be as well understood. Many of the lesions that occur in the gastrointestinal tract, even the common ones, are overlooked. An understanding of the simple lesions and many of the more complicated ones is essential if the proper roentgen examination is to be carried out. Most of the congenital malformations that occur have a rather simple embryologic explanation. There is defective recanahization of the fetal gut. When the fetal gut is first formed it is an open tube, but during the first few weeks of fetal life there is proliferation of the cpitheliah lining cells with obliteration of the lumen. Recanahization promptly ensues. Many of the abnormalities occur during this process of recanahization. Stenosis, atresia, diverticuhar, duplication and many of the fistuhas have their origin during this period of recanahization. The very simple lesions of stenosis and atresia are best demonstrated by lantern slides. Trachco-esophageal fistula without atresia or stenosis of the esophagus is not at all uncommon. Many are overlooked because the condition is not suspected ; others may be overlooked because the roentgen examination is not properly carried out. Certainly a fistula between the esophagus and trachea running obliquely upward from the anterior aspect of the upper third of the esophagus to the trachea cannot be visualized if the patient is examined only in the supine or prone position. The patient must be examined in the lateral projection so that the trachea and esophagus are seen without superimposition and so that the opaque medium has an opportunity of passing through the fistula into the trachea. Occasionally the fistula itself cannot be identified, but flooding of the trachea by the opaque medium may be seen. Dr. Maxwell P. Borovsky, Chicago. We had an experience here at Cook County Hospital with a baby about 2 months of age. It had episodes of apnea and dysphagia on feeding, but only when Presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, Chicago, Oct. 20 and 21,
2 640 ROUND TABLE DISCUSSION: PEDIATRIC X-RAY DIAGNOSIS it was being fed did it have this difficulty. We tried some ordinary physiologic studies and got nowhere. We very fortunately have a good congenital cardiac set up with Dr. Gasul. We suspected that there might be a congenital malformation of the heart. We took a number of spot films and there was one film that showed a communication between the trachea and esophagus. The interesting thing about this was that the fistula was against gravity, running upward from the esophagus to the trachea with the consequence that there wasn t much of an aspiration because of the upward route of the food. That baby was operated on very successfully. Chairman Neuhauser: It is of the utmost importance for the pediatrician to have the courage of his convictions if a fistula is suspected. A single negative examination cannot be relied upon to exclude this abnormality. I well recall one patient where the fistula was not demonstrated until the third examination. When examining the esophagus radiographicahhy the correct choice of opaque medium is irnportant. For the ordinary routine examination of the esophagus where no particular lesion is suspected, we ordinarily use a thin barium sulphate paste flavored with chocolate and sweetened with sugar. However, in small infants this cannot be satisfactorily used and a thin barium fed by spoon or through the feeding bottle is more satisfactory. We now only employ iodized oil in the presence of a known or suspected atresia of the esophagus and we no longer use it in a search for an isolated tracheo-esophageah fistula as the difficulty of the examination is increased when iodized oil is used as most infants are unable to properly swallow the oil and a considerabhe amount passes through the larynx into the trachea. I feel that no examination of the esophagus in an infant or small child should be carried out unless a suction machine is at hand in the fluoroscopic room. We have had to use the suction machine on many occasions and I am convinced that we would have lost several if the suction machine had not been immediately available. Congenital stenosis of the esophagus occurs primarily in the upper third. Only rarely is a stenosis of the lower third congenital in origin. It is more apt to be acquired from esophagitis. Stenosis of the upper esophagus may produce in addition to dysphagia respiratory signs and symptoms as the dilated upper esophageal segment may produce considerable encroachment upon the lumen and displacement of the trachea. Atresia of the esophagus is certainly well known to you. The results of surgical treatment are getting better all the time and I think that we can look forward to a survival rate of at least 75%. The rather typical signs and symptoms suggest the diagnosis. Constant drooling of saliva and immediate regurgitation of feeding should suggest the diagnosis and the proper roentgen examination should be carried out. This examination is not only important in establishing the diagnosis, but it is also of an aid in determining the length of the atretic segment, the exact site of the atresia and the presence or absence of a fistula. Under fluoroscopic guidance a catheter should be passed into the upper esophagus and a few cc. of warm iodized oil instilled. The patient should be turned into the lateral decubitus in an attempt to visualize a fistulous communication between the upper esophagus and the trachea. A fistulous communication between the trachea and lower esophagus can naturally be diagnosed by the presence of gas in the gastrointestinal tract. If there is no lower fistula the atretic segment is apt to be unduly long and surgical correction very much more difficult. Duplications of the esophagus are not uncommon. The signs and symptoms produced may be variable or signs may be absent unless there is pressure or encroachment upon adjacent structures. They usually appear as small or large cystic masses which will vary somewhat in shape during change in position and are found in chose juxtaposition to the esophagus, but may not deform or displace the esophagus very much. I personally have not as yet seen one where there was a cornmunication between the esophagus and the duplication. Question. When you see a case hike this how do you make the diagnosis? Chairman Neuhauser. The diagnosis cannot be made with certainty as the appearance can be simulated by other lesions, particularly a cystic hygroma of the mediastinum. It is possible to have combinations of duplication, stenosis or atresia and fistula and one must be prepared for bizarre abnormalities and combinations. All the lesions that we have discussed so far can also occur in the intestinal tract. The use of an opaque medium is rarely necessary in most patients with severe stenosis or atresia of the bowel. Although it is not always possible to make an exact diagnosis as to the type of atresia, it is usually
3 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS 641 possible to estimate the degree of obstruction and to localize the obstruction within reasonable limits, so that definitive surgical treatment can promptly be carried out. Duplications associated with the small bowel are very difficult to recognize as they may produce no or only minimal displacement of the adjacent bowel. However, those in association with the distal ileum may produce intussusception with its typical clinical and roentgen findings. Occasionally a duplication may calcify. Duplications and even triplications of the colon have been reported. During the past few years it has become evident that lesions of the esophagus in young infants are common and important. However, it is equally clear that at the moment the nature and origin of all these lesions is not well understood. There is a group of abnormalities that have as a common denominator relaxation of the lower esophagus with free regurgitation of gastric content into the esophagus. One may find simple relaxation of the hiatus portion of the esophagus, gastric hiatus hernia, para-esophageal hiatus hernia and apparent extension of gastric mucosa into the lower esophagus. Although on occasion the exact nature of the primary abnormality cannot be determined with certainty, the regurgitation and relaxation of the hiatus can be identified. Because of this resultant esophagitis and peptic ulceration of the lower esophagus leading to spasm, shortening and stenosis may occur. In our hospital, ulceration of the lower esophagus is very much more frequent than ulceration anywhere else in the intestinal tract. The roentgen signs of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis are too well known to require much elaboration here, but unfortunately during the past few years there has been an unfortunate tendency to attempt shortcuts to avoid the necessarily rather laborious procedure which must be carriecl,out to establish an exact diagnosis. One cannot rely on film examination alone and we believe that dependence on opening time of the pylorus or emptying time of the stomach is likewise unreliable. The diagnosis can be made with certainty only by demonstration of the narrow elongated pyloric canal on spot films. The examination should be carried out in a normal physiologic manner with barium mixture administered by mouth as if the stomach is filled by catheter many of the important lesions of the esophagus will be overlooked. The roentgen diagnosis of meconium ileus is frequently difficult and occasionally impossible. However, approximately three-quarters of the patients with this abnormality present a rather characteristic roentgen picture. There are multiple dilated loops of small bowel and in the distal hoops of ileum the meconium may be outlined by numerous bubbles of gas that have been forced into this tenacious mucilaginous material that blocks the bowel proximal to the iheo-cecal valve. l hc colon is usually free of gas and fecal matter. The appearance may be mimicked by fecah impaction in the proximal colon or by inspissated meconium in the distal ileum, and if the abnormal meconium cannot be identified on the film the picture may be similar to or identical with that produced by an atresia or severe stenosis of the distal iheum. It may be necessary to carry out a barium enema to localize the obstruction, By this means an infantile Hirschsprung s disease can be clearly differentiated as in the presence of meconium ileus a micro-colon will be present. A microcolon is naturally a colon that has not as yet functioned. It appears short and extraordinarily narrow as to lumen. However, unless the colon is aganglionic normal function will properly ensue after the obstruction has been corrected. In association with obstruction of the bowel one may find intrauterine perforation with extrusion of epithelial cells and calcific deposit about these epithehial cells outlining a portion of the peritoneal cavity. This must be distinguished from the calcific deposit that may occur in meconium or in the wall of an atretic bowel segment. Question. What is this calcification due to? Chairman Neuhasiser. I don t know what it is due to, but we do know where it is. It is calcific deposit about the extruded epithelial cells. It can occur very promptly and according to reports within 24 to 48 hours. If the patient survives the calcific deposit tends to disappear, although in one instance I know that a portion has still been present at the end of 4 years. In addition to the calcific deposit, numerous adhesions are present. Question. What do you do for meconium ileus patients after you have made the diagnosis? Chairman Neuhauser. There are many things that can be done, but survival is still unusual. It is usually necessary to do an ileostomy, milk out as much of the abnormal meconium as is possible and to lavage the bowel with pancreatic solution or saline. New Speaker. When our patient was operated on, the surgeon used saline in and around the meconium and he was able to free the bowel. The child has advanced pancreatic fibrosis and we
4 642 ROUND TABLE DISCUSSION: PEDIATRIC X-RAY DIAGNOSIS come back to the question of whether we should do anything for the patient with rneconium ileus. As far as I know they go on and develop the full blown disease and only live 2, 4 or 6 years. Chairman Neuhause,: That is, of course, true. I think that even with our present knowledge we should make every effort to pull these patients through their initial obstruction as our knowledge of this disease is increasing and the results of more modern treatment of the pulmonary changes has led to considerable success. First Speaker. It is difficult whatever you do and the prognosis is not good. Question. I frequently have parents call mc on the phone and say that their child has swallowed a foreign body of some sort. Shall I rush him right over to the hospital for x-ray film? Do you feel that these foreign bodies should be x-raycd to discover just where the object is, or are we justified in waiting 48 hours to see if the child passes the object? Chairman Neuhauser. I personally feel that you had better get a film. Certainly a foreign body should not be allowed to remain in the esophagus and it is wise to identify the location and the type of foreign body swallowed. Many are quite innocuous, but others, such as open safety pins or bobby pins, are likely to produce trouble. I would hazard a statement that more of our patients are operated upon for removal of a bobby pin than any other foreign body as these pass the duodenojejunal junction only with difficulty. Question: What about the plastic toys the children play with and sometimes swallow-arc they opaque? Chairman Neuhauser. Nearly all of them are nonopaque. Question: One of the problems that we encounter in children from 4 to 8 years, and we see a few every day, is pain in the abdomen. On examination it appears to us that it is associated with anxiety, but we invariably get a report back from the radiologist that it is a pyloric spasm. Have you seen the same thing and is there a definite picture of it? Chairman Neuhauser. I doubt very much if there is such a thing as pyhoric spasm as an isolated lesion. However, I am sure that you can get pyloric spasm with gastric ulceration or with ulceration of the duodenum and true hypertrophic pyloric stenosis may occur in association with ulcers close or near to the pyloric canal. Certainly the child with abdominal pain is a difficult problem and in many instances we arc never successful in elucidating the nature of the complaint. In addition to lesions of the gastrointestinal tract which should be excluded, it is truly important to exclude a hidden lesion of kidney, and I believe it wise to carry out an intravenous urogram if all other studies have not been helpful.
5 Round Table Discussion: PEDIATRIC X-RAY DIAGNOSIS EDWARD B. D. NEUHAUSER, PIERCE D. KNOTT and BRICK P. STORTS, JR. Pediatrics 1953;11;639 Updated Information & Services Permissions & Licensing Reprints including high resolution figures, can be found at: Information about reproducing this article in parts (figures, tables) or in its entirety can be found online at: Information about ordering reprints can be found online:
6 Round Table Discussion: PEDIATRIC X-RAY DIAGNOSIS EDWARD B. D. NEUHAUSER, PIERCE D. KNOTT and BRICK P. STORTS, JR. Pediatrics 1953;11;639 The online version of this article, along with updated information and services, is located on the World Wide Web at: Pediatrics is the official journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics. A monthly publication, it has been published continuously since Pediatrics is owned, published, and trademarked by the American Academy of Pediatrics, 141 Northwest Point Boulevard, Elk Grove Village, Illinois, Copyright 1953 by the American Academy of Pediatrics. All rights reserved. Print ISSN:
PAEDIATRIC GASTROINTESTINAL RADIOLOGY
 Objective Guide to Radiology of the Paediatric Intestinal Tract Responsibility / Registrar Frequency As required Associated Documents : RADFLPAEPR003 Contrast mixes RADFLPAEPR001 Paediatric Barium swallow
Objective Guide to Radiology of the Paediatric Intestinal Tract Responsibility / Registrar Frequency As required Associated Documents : RADFLPAEPR003 Contrast mixes RADFLPAEPR001 Paediatric Barium swallow
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
GIT RADIOLOGY. Water-soluble contrast media (e.g. gastrograffin) are the other available agents.which doesn t cause inflammatory peritonitis..
 GIT RADIOLOGY Imaging techniques-general principles: Contrast examinations: Barium sulphate is the best contrast for GIT (with good mucosal coating & excellent opacification & being inert); but is contraindicated
GIT RADIOLOGY Imaging techniques-general principles: Contrast examinations: Barium sulphate is the best contrast for GIT (with good mucosal coating & excellent opacification & being inert); but is contraindicated
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina
 Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients).
 Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings. M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid
 Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success
 Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Hirschprung s. Meconium plug R/S >1 R/S <1
 NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
The Role of Adrenal Steroids in the Treatment of Tuberculosis
 CLINICAL CONFERENCE The Role of Adrenal Steroids in the Treatment of Tuberculosis By Margaret H. D. Smith, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, New York University-Bellevue Medical Center DRu MARGARET H. D.
CLINICAL CONFERENCE The Role of Adrenal Steroids in the Treatment of Tuberculosis By Margaret H. D. Smith, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, New York University-Bellevue Medical Center DRu MARGARET H. D.
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS 993 THE NATURAL HISTORY OF CERTAIN CONGENITAL CARDIOVASCULAR MALFORMATIONS. Alexander S. Nadas, M.D.
 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS 993 tnicular overload is the major problem and left ventricular failure occurs. Since for many years the importance of hepatomegaly in the diagnosis of cardiac failure has
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS 993 tnicular overload is the major problem and left ventricular failure occurs. Since for many years the importance of hepatomegaly in the diagnosis of cardiac failure has
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine
 Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Long-gap Oesophageal Atresia
 Long-gap Atresia A guide for parents Nate (6 weeks old) Atresia Research Association Are there different types of OA? There are four main types of oesophageal atresia with or without TOF. These include
Long-gap Atresia A guide for parents Nate (6 weeks old) Atresia Research Association Are there different types of OA? There are four main types of oesophageal atresia with or without TOF. These include
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion
 Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Gastrointestinal tract
 Chapter 7 Gastrointestinal tract NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY Sonographically, the fetal stomach is visible from 9 weeks of gestation as a sonolucent cystic structure in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen.
Chapter 7 Gastrointestinal tract NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY Sonographically, the fetal stomach is visible from 9 weeks of gestation as a sonolucent cystic structure in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen.
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis?
 Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Congenital anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract: A radiological review
 Congenital anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract: A radiological review Poster No.: C-1669 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: S. P. Ramachandra, M. Bydder, N. Gurjar,
Congenital anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract: A radiological review Poster No.: C-1669 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: S. P. Ramachandra, M. Bydder, N. Gurjar,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis?
 Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. MNARI, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. MAATOUK, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. MNARI, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. MAATOUK, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Small bowel atresia. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families
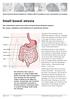 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Small bowel atresia This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains the causes, symptoms and treatment
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Small bowel atresia This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains the causes, symptoms and treatment
THE mainstay of the radiographic study of the upper gastrointestinal tract has
 BARIUM-SPRAY EXAMINATION OF THE STOMACH- PRELIMINARY REPORT OF A NEW ROENTGENOGRAPHIC TECHNIC EDWARD BUONOCORE, M.D., and THOMAS F. MEANEY, M.D. Department of Hospital Radiology THE mainstay of the radiographic
BARIUM-SPRAY EXAMINATION OF THE STOMACH- PRELIMINARY REPORT OF A NEW ROENTGENOGRAPHIC TECHNIC EDWARD BUONOCORE, M.D., and THOMAS F. MEANEY, M.D. Department of Hospital Radiology THE mainstay of the radiographic
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學
 Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help. Print this Page Add to my Bookmarks Page 3 of 10
 Welcome Kristin Ingstrup [ Logout ] SEARCH Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help Overview Editorial Board My Learning Plan January February March May June July August
Welcome Kristin Ingstrup [ Logout ] SEARCH Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help Overview Editorial Board My Learning Plan January February March May June July August
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
Objectives: Resources:
 Objectives: Realize the impact of Age : - Where/who are the history sources Recognize and interpret the : - Important symptoms - Important signs Resources: Davidson s. Slides Surgical recall. Raslan s
Objectives: Realize the impact of Age : - Where/who are the history sources Recognize and interpret the : - Important symptoms - Important signs Resources: Davidson s. Slides Surgical recall. Raslan s
The Alimentary System
 The Alimentary System Contrast Medium: 1. Barium Examinations of different parts of the GI tract require different densities of Barium suspension. The escape of Barium into the peritoneal cavity is extremely
The Alimentary System Contrast Medium: 1. Barium Examinations of different parts of the GI tract require different densities of Barium suspension. The escape of Barium into the peritoneal cavity is extremely
- Tamara Wahbeh. - Fareed Khdair. 0 P a g e
 -1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
-1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia
 Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
Topics for discussion. Pediatric General Surgery. Physiology. Surgical Newborns. Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction
 Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases. Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT)
 Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Cyanosis and Pulmonary Disease in Infancy
 CLINICAL CONFERENCE Cyanosis and Pulmonary Disease in Infancy By Robert A. Miller, M.D. Division of Cardiology, Children s Memorial Hospital, and the Department of Pediatrics, Northwestern University Medical
CLINICAL CONFERENCE Cyanosis and Pulmonary Disease in Infancy By Robert A. Miller, M.D. Division of Cardiology, Children s Memorial Hospital, and the Department of Pediatrics, Northwestern University Medical
Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions
 Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions Miah MAY Introduction In our day to day practice we have to face many of the acute abdominal conditions. As we know acute abdomen
Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions Miah MAY Introduction In our day to day practice we have to face many of the acute abdominal conditions. As we know acute abdomen
Anal Atresia FACTS: There is no known cause for anal atresia. Children with anal atresia can lead very happy lives post surgery!
 Anal Atresia FACTS: Anal atresia affects 1 in 5,000 births and is slightly more common in boys. There is no known cause for this condition. With anal atresia, any of the following can occur: The anal passage
Anal Atresia FACTS: Anal atresia affects 1 in 5,000 births and is slightly more common in boys. There is no known cause for this condition. With anal atresia, any of the following can occur: The anal passage
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1-
 Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE)
 Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
Hiatus Hernia. Endoscopy Department. Patient information leaflet
 Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
Introduction and Definitions
 Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract Lower gastrointestinal tract radiography or lower GI uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy and a barium-based contrast material to
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract Lower gastrointestinal tract radiography or lower GI uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy and a barium-based contrast material to
Pediatric Bowel Obstruction
 Pediatric Bowel Obstruction Matt Zerden, Harvard Medical School III Patient 1 16 year old presents with severe, episodic abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Questionable abdominal mass in RLQ Previous
Pediatric Bowel Obstruction Matt Zerden, Harvard Medical School III Patient 1 16 year old presents with severe, episodic abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Questionable abdominal mass in RLQ Previous
Congenital Digestive Malformation and Associated Anomalies
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. VI, Issue 5/ August 2018 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Congenital Digestive Malformation and Associated Anomalies AUREL
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. VI, Issue 5/ August 2018 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Congenital Digestive Malformation and Associated Anomalies AUREL
The Physician as Medical Illustrator
 The Physician as Medical Illustrator Francois Luks Arlet Kurkchubasche Division of Pediatric Surgery Wednesday, December 9, 2015 Week 5 A good picture is worth a 1,000 bad ones How to illustrate an operation
The Physician as Medical Illustrator Francois Luks Arlet Kurkchubasche Division of Pediatric Surgery Wednesday, December 9, 2015 Week 5 A good picture is worth a 1,000 bad ones How to illustrate an operation
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography)
 Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography) What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography) What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look
USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System
 USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A surgeon is planning to remove a patient s gallbladder endoscopically. During the procedure, the endoscope will traverse
USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A surgeon is planning to remove a patient s gallbladder endoscopically. During the procedure, the endoscope will traverse
Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts. David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology
 Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Basic Imaging Concepts Contrast Resolution vs Spacial Resolution Spacial Resolution......refers to the ability
Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Basic Imaging Concepts Contrast Resolution vs Spacial Resolution Spacial Resolution......refers to the ability
Certain genes passed on from parent to child increase the risk of developing Crohn's disease, if the right trigger occurs.
 Topic Page: Crohn's disease Definition: Crohn's disease from Benders' Dictionary of Nutrition and Food Technology Chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel, commonly the terminal ileum, of unknown aetiology,
Topic Page: Crohn's disease Definition: Crohn's disease from Benders' Dictionary of Nutrition and Food Technology Chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel, commonly the terminal ileum, of unknown aetiology,
Chapter 14: Training in Radiology. DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12
 DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
Gastrointestinal Disorders. Disorders of the Esophagus 3/7/2013. Congenital Abnormalities. Achalasia. Not an easy repair. Types
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Radiology of GI system diseases
 GI Cycle - Lecture 12 436 Teams Radiology of GI system diseases Objectives 1. 2. 3. To know common GIT Pathologies presentation. To understand step wise approach in requesting GIT Radiology Investigations.
GI Cycle - Lecture 12 436 Teams Radiology of GI system diseases Objectives 1. 2. 3. To know common GIT Pathologies presentation. To understand step wise approach in requesting GIT Radiology Investigations.
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Transfer guidelines for surgical infants
 Transfer guidelines for surgical infants Document Title and Reference : Transfer guidelines for surgical infants Main Author (s) Transport Team Clinical Guidelines group Ratified by: GMNICP Date Ratified:
Transfer guidelines for surgical infants Document Title and Reference : Transfer guidelines for surgical infants Main Author (s) Transport Team Clinical Guidelines group Ratified by: GMNICP Date Ratified:
INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION ESCAPED SURGERY: MECONIUM PLUG
 7 INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION ESCAPED SURGERY: MECONIUM PLUG Oluwayemi IO 1 *, Ade-Ojo IP 2, Olofinbiyi BA 2 1. Department of Paediatrics, Ekiti State University Teaching Hospital, Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria
7 INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION ESCAPED SURGERY: MECONIUM PLUG Oluwayemi IO 1 *, Ade-Ojo IP 2, Olofinbiyi BA 2 1. Department of Paediatrics, Ekiti State University Teaching Hospital, Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria
Fluoroscopy Protocols. Upper GI with Barium Swallow-Combination UGIBS
 Fluoroscopy Protocols Upper GI with Barium Swallow-Combination UGIBS Fluoro Time Target Limit: 4.0 minutes Scheduling and Prep: Supplies: *The patient should be NPO from midnight before their exam Until
Fluoroscopy Protocols Upper GI with Barium Swallow-Combination UGIBS Fluoro Time Target Limit: 4.0 minutes Scheduling and Prep: Supplies: *The patient should be NPO from midnight before their exam Until
The Children s Hospital Intussusception and its treatment Information for parents
 The Children s Hospital Intussusception and its treatment Information for parents What is intussusception? Intussusception occurs when one part of the bowel slides into another part of bowel, like a telescope,
The Children s Hospital Intussusception and its treatment Information for parents What is intussusception? Intussusception occurs when one part of the bowel slides into another part of bowel, like a telescope,
pthaigastro.org Caustic injury The 5 th Pediatric GI Days Pediatric GI & Liver Emergency : Current Practical Management
 The 5 th Pediatric GI Days Pediatric GI & Liver Emergency : Current Practical Management Caustic injury Phisek Yimyaem Pediatric Department, Khon Kaen Regional Hospital 18 July 2013 Outlines Introduction
The 5 th Pediatric GI Days Pediatric GI & Liver Emergency : Current Practical Management Caustic injury Phisek Yimyaem Pediatric Department, Khon Kaen Regional Hospital 18 July 2013 Outlines Introduction
Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes
 Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes V Chidambaram-Nathan Consultant Transplant and General Surgeon Sheffield Kidney Institute Northern General Hospital Intestinal Obstruction One of the
Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes V Chidambaram-Nathan Consultant Transplant and General Surgeon Sheffield Kidney Institute Northern General Hospital Intestinal Obstruction One of the
Foker technique for long-gap oesophageal atresia
 Issue date: January 2006 Foker technique for long-gap oesophageal atresia Understanding NICE guidance information for parents and carers considering the procedure, and for the public Information about
Issue date: January 2006 Foker technique for long-gap oesophageal atresia Understanding NICE guidance information for parents and carers considering the procedure, and for the public Information about
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
RECONSTRUCTION OF THE CARDIA AND FUNDUS OF THE STOMACH
 Thorax (1956), 11, 275. RECONSTRUCTION OF THE CARDIA AND FUNDUS OF THE STOMACH BY From tile United Leeds Hospitals (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION SEPTEMBER 15, 1956) This is a preliminary report describing
Thorax (1956), 11, 275. RECONSTRUCTION OF THE CARDIA AND FUNDUS OF THE STOMACH BY From tile United Leeds Hospitals (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION SEPTEMBER 15, 1956) This is a preliminary report describing
The Foregut. At first the esophagus is short. but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly
 GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
Spleen indications of splenectomy complications OPSI
 Intestinal obstruction Differences between adynamic ileus and mechanical obstruction Aetiology Pathophysiology (Cluster contractions- bowel proximal to the obstruction dilate- wall of obstructed gut is
Intestinal obstruction Differences between adynamic ileus and mechanical obstruction Aetiology Pathophysiology (Cluster contractions- bowel proximal to the obstruction dilate- wall of obstructed gut is
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus
 A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
What is Your Diagnosis?
 What is Your Diagnosis? Izabela Ragan, Class of 2014 Signalment Species: Canine Breed: English Bulldog Sex: Male castrated Date of birth: 04/14/11 Presenting Complaint Dog was presented for vomiting and
What is Your Diagnosis? Izabela Ragan, Class of 2014 Signalment Species: Canine Breed: English Bulldog Sex: Male castrated Date of birth: 04/14/11 Presenting Complaint Dog was presented for vomiting and
INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC
 INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 16 S. Amjad Hussain, Chinda Suriyapa, Karl Grubaugh ( Depts. of Surger and
INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 16 S. Amjad Hussain, Chinda Suriyapa, Karl Grubaugh ( Depts. of Surger and
SURGICAL PROBLEMS IN CHILDHOOD
 Symposium SURGICAL PROBLEMS IN CHILDHOOD HERBERT E. GOE, M.D., Seattle, Chairman; ALEXANDER H. BILL, JR., M.D., Seattle; ORVAR SWENSON, M.D., Boston ; C. EVERETT Koop, M.D., Sc.D., Philadelphia; HENRY
Symposium SURGICAL PROBLEMS IN CHILDHOOD HERBERT E. GOE, M.D., Seattle, Chairman; ALEXANDER H. BILL, JR., M.D., Seattle; ORVAR SWENSON, M.D., Boston ; C. EVERETT Koop, M.D., Sc.D., Philadelphia; HENRY
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)?
 EOSINOPHILIC ESOPHAGITIS What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)? Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an illness found in the esophagus (the tube that links your mouth and stomach). EoE is the result of an
EOSINOPHILIC ESOPHAGITIS What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)? Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an illness found in the esophagus (the tube that links your mouth and stomach). EoE is the result of an
Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception
 Scan for mobile link. Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception Therapeutic enema is used to help identify and diagnose intussusception, a serious disorder in which one part of the intestine slides into another
Scan for mobile link. Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception Therapeutic enema is used to help identify and diagnose intussusception, a serious disorder in which one part of the intestine slides into another
SOUTHERN WEST MIDLANDS NEWBORN NETWORK
 SOUTHERN WEST MIDLANDS NEWBORN NETWORK Hereford, Worcester, Birmingham, Sandwell & Solihull Title : Person Responsible for Review : Management of Gastro-Intestinal Stomata In Neonates R. Wragg & G.Jawaheer
SOUTHERN WEST MIDLANDS NEWBORN NETWORK Hereford, Worcester, Birmingham, Sandwell & Solihull Title : Person Responsible for Review : Management of Gastro-Intestinal Stomata In Neonates R. Wragg & G.Jawaheer
Ulcerative Colitis. ulcerative colitis usually only affects the colon.
 Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
What can you expect after your ERCP?
 ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
Pediatric Surgery MUHC MCH Siste. Objectives of Training
 Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
HREE Questions. Setting 3: Inpatient Facilities. Block
 Block HREE Questions Setting 3: Inpatient Facilities You have general admitting privileges to the hospital. You may see patients in the critical care unit, the pediatrics unit, the maternity unit, or recovery
Block HREE Questions Setting 3: Inpatient Facilities You have general admitting privileges to the hospital. You may see patients in the critical care unit, the pediatrics unit, the maternity unit, or recovery
Chapter Outline. Structural defects. Obstructive disorders. Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 3 of 98. Cleft lip and cleft palate
 Structural defects Chapter Outline Cleft lip and cleft palate Page 3 of 98 Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Hernias Obstructive disorders Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Intussusception Anorectal
Structural defects Chapter Outline Cleft lip and cleft palate Page 3 of 98 Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Hernias Obstructive disorders Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Intussusception Anorectal
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong.
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #10 Acute GI Bleeds
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #10 Acute GI Bleeds Gastrointestinal bleeding is a very common problem in emergency medicine. Between
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #10 Acute GI Bleeds Gastrointestinal bleeding is a very common problem in emergency medicine. Between
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work?
 Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Surgery while taking Protonix? 1,368 conversations on the web about experiences with taking Protonix before or after having a Surgery.
 Surgery while taking Protonix? 1,368 conversations on the web about experiences with taking Protonix before or after having a Surgery. Everything you ever wanted to know about gastric sleeve surgery. What
Surgery while taking Protonix? 1,368 conversations on the web about experiences with taking Protonix before or after having a Surgery. Everything you ever wanted to know about gastric sleeve surgery. What
Diarrhea may be: Acute (short-term, usually lasting several days), which is usually related to bacterial or viral infections.
 Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
There are many different symptoms of GER. Your child may only have a few of these symptoms. The most common symptoms include:
 This document is a short Overview of Pediatric Acid Reflux and GERD from www.reflux.org web site. Dozens of other documents about Pediatric GERD can be found in the Reading Room section of this web site.
This document is a short Overview of Pediatric Acid Reflux and GERD from www.reflux.org web site. Dozens of other documents about Pediatric GERD can be found in the Reading Room section of this web site.
Case Report The Combination of Gastroschisis, Jejunal Atresia, and Colonic Atresia in a Newborn
 Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2015, Article ID 129098, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/129098 Case Report The Combination of Gastroschisis, Jejunal Atresia, and Colonic Atresia in a Newborn
Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2015, Article ID 129098, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/129098 Case Report The Combination of Gastroschisis, Jejunal Atresia, and Colonic Atresia in a Newborn
Small Intestine Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Small Intestine Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that
Small Intestine Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently
 Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Gastrointestinal Obstruction
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Gastrointestinal Obstruction (Blockage of the Gastrointestinal Tract) Basics OVERVIEW
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Gastrointestinal Obstruction (Blockage of the Gastrointestinal Tract) Basics OVERVIEW
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Gastro Intestinal pg 1 of 6
 Gastro Intestinal pg 1 of 6 Diabetic Ketoacidosis -Treatment differences True Na: adjust upward 1.6 mleq/l for every 100 mg/dl increase in blood glucose Potential serious CNS effects; 2-5% mortality rate
Gastro Intestinal pg 1 of 6 Diabetic Ketoacidosis -Treatment differences True Na: adjust upward 1.6 mleq/l for every 100 mg/dl increase in blood glucose Potential serious CNS effects; 2-5% mortality rate
Dissection: The Fetal Pig
 Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Uroradiology For Medical Students
 Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
An Overview on Pediatric Esophageal Disorders. Annamaria Staiano Department of Translational Medical Sciences University of Naples Federico II
 An Overview on Pediatric Esophageal Disorders Annamaria Staiano Department of Translational Medical Sciences University of Naples Federico II Case report F.C. 3 year old boy Preterm born from emergency
An Overview on Pediatric Esophageal Disorders Annamaria Staiano Department of Translational Medical Sciences University of Naples Federico II Case report F.C. 3 year old boy Preterm born from emergency
Gastro- Intestinal Bleeding in Children
 Gastro- Intestinal Bleeding in Children Upper G1 Bleeding. Lower G1 Bleeding. Upper G1 Bleeding :- Presentation : Hematemesis Causes :- Neonate reflux esophagitis (dark, small amount) PyLoric stenosis
Gastro- Intestinal Bleeding in Children Upper G1 Bleeding. Lower G1 Bleeding. Upper G1 Bleeding :- Presentation : Hematemesis Causes :- Neonate reflux esophagitis (dark, small amount) PyLoric stenosis
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC
 Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC Gastrointestinal Emergencies is 7% of the CEN A. Acute abdomen B. Bleeding C. Cholecystitis D. Cirrhosis E. Diverticulitis
Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC Gastrointestinal Emergencies is 7% of the CEN A. Acute abdomen B. Bleeding C. Cholecystitis D. Cirrhosis E. Diverticulitis
Development of Respiratory System. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra
 Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Gastrointestinal Tract Imaging. Objectives. Reference. VMB 960 April 6, Stomach Small Intestine Colon. Radiography & Ultrasound
 Gastrointestinal Tract Imaging VMB 960 April 6, 2009 Stomach Small Intestine Colon Objectives Radiography & Ultrasound Contrast Examination of the Small Intestine Reference Chapters 45 47 Pages 750 805
Gastrointestinal Tract Imaging VMB 960 April 6, 2009 Stomach Small Intestine Colon Objectives Radiography & Ultrasound Contrast Examination of the Small Intestine Reference Chapters 45 47 Pages 750 805
Intraperitoneal cysts in infancy and childhood An overview and sonographic differentiation
 Intraperitoneal cysts in infancy and childhood An overview and sonographic differentiation M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Intraperitoneal cysts
Intraperitoneal cysts in infancy and childhood An overview and sonographic differentiation M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Intraperitoneal cysts
