Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann
|
|
|
- Janice Simon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. Meninges 2. Cerebral cortex-cytoarchitecture 3. Diencephalon (thalamus/hypothalamus) (this replaces the part of reading 1 on the Diencephalon) 4. Basal ganglia 1. Meninges The organs of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are covered by 3 connective tissue layers collectively called the meninges. They support blood vessels and contain cerebrospinal fluid. the pia mater (closest to the CNS structures); it is a delicate thin, transparent membrane that follows the curvature of the cerebral surface arachnoid mater; it is just below the dura mater and has small spider web like filaments that attach to the pia mater creating a little space (subarachnoid space, between arachnoid and pia mater) filled with CerebroSpinalFluid dura mater (farthest from the CNS); it s a thick, durable protective membrane attached to the skull. It consists of two layers and the two layers split to create the large venous channels in which CSF is deposed.
2 2. Cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex that is the grey matter that surrounds the cerebral hemispheres. The Cerebral Cortex is composed of Nerve Cells (: which create the local computational networks) and Glial Cells (: which have supportive functions). There are many different types of nerve cells that have different functions in the CNS. Cytoarchitecture: Studies the local cell arrangement of the cortex in order to classify and distinguish different regions that are suspected to serve different functions. Myeloarchitecture: Studies the local arrangement of myelinated fibers to classify cortical regions. Different Stains being used to make Cytoarchitectonic Maps: -Weigert Stain: Stains the myelin of the Cell Axons. -Nissl Stain: Stains the Cell Bodies. -Golgi Stain: Stains the whole Cell but not all cells in a slice. Subdivisions of Cerebral Cortex: - Archicortex: 3 layered Cortex (Hippocampus) - Paleocortex: 3-5 layered Cortex transition cortex (Parahippocampal Cortex) Together the archicortex and paleocortex constitute the allocortex or heterogenetic cortex
3 - Neocortex: 6 layered cortex. e.g.: most of the Cerebral Cortex of Cerebral Hemispheres. The neocortex can also be referred to as the homogenetic cortex. Korbidius Brodmann (1908/1909) Very renowned scientist in the field of cytoarchitecture (fellow of Oscar and Cecelia Vogt). He created the most widely used cytoarchitectonic map with approximately 50 different areas named with different numbers (noted as Brodmann area [BA] #). The function of the various areas is studied using: - Stimulation of exposed cortex during neurosurgery in awake patients - Recording of electrical potentials during the presentation of different sensory stimuli - In vivo neuroimaging of brain functions with PET, fmri and other imaging techniques.
4 Important remarks A few specific areas you already know: Primary Motor Cortex (cortex lining the caudal precentral Gyrus in particular the rostral bank of the central sulcus / BA 4 / M1) Premotor Cortex (cortex lining the rostral part of the precentral gyrus / BA 6) Primary Somatosensory Cortex (cortex lining the post- central gyrus / BA 3, 1 & 2 / S1) Primary Auditory Cortex (Caudal temporal operculum / cortex lining Heschl s Gyrus/i / Transverse Gyrus/i / BA 41(42), A1) Primary Visual Cortex (Cortex lining the banks of the Calcarine Sulcus / BA 17/ Striate cortex / V1) The primary motor and the premotor areas (BA 4 and 6) do not show a layer IV and are thus called agranular. The two differ because the primary motor cortex has large pyramidal neurons in layer V called Betz cells. Rostral to the premotor cortex the cortex of the pars opercularis (BA 44) shows an ill-defined/inconsistent layer IV and is thus called dysgranular. All primary sensory neocortical areas (S1,A1,V1) have a greatly expanded layer IV (input layer). The large population of granule cells give it a dust-like appearance and cortex with that characteristic is thus called: koniocortex (dust-cortex) The Diencephalon is the part of the cerebral hemispheres that lies in the depth forming the roof of the Brainstem. It is a collection of subcortical nuclei that are arranged around the third ventricle. It has important connections to sensory,
5 motor as well as limbic pathways and acts as a relay station for all senses apart from olfaction and also has important control functions for homeostasis. The lateral walls of the diencephalon are formed by the internal capsule. The ventral surface of the diencephalon is formed by the pituitary gland and mammillary bodies and the optic chiasm. The Diencephalon is composed of the thalamus, the hypothalamus that lies rostroventral to the thalamus, and other structures like the epithalamus (dorsal) and the subthalamus. Thalamus The Thalamus is a bilateral subcortical structure composed of numerous nuclei that have specific connections with the cortex and serve different functions. In most people, a fiber system crosses the midline joining the right and left thalami through the third ventricle. This fiber system can be clearly seen on the medial view of the brain and it is called the Massa Intermedia or Interthalamic Adhesion. Three nuclei you will need to know: - The lateral geniculate body (or nucleus) of the thalamus is in the lateral aspect of the caudal thalamus and it is a relay nucleus for vision projecting to V1. - The medial geniculate body (or nucleus) of the thalamus is in the medial aspect of the caudal thalamus and it is a relay nucleus for audition projecting to A1 (Heschl s gyri). - The anterior nucleus of the thalamus is in the most rostral aspect of the thalamus and it is involved in memory. It receives input from the hippocampus via the fornix and projects via the mammillothalamic tract to the mammillary bodies and also to the cingulate gyrus. It is part of the circuit of Papez.
6 Hypothalamus - Hypothalamus The Hypothalamus is a group of nuclei that form the anterior portion of the walls and floor of the third ventricle. These structures are involved in visceral, endocrine and, metabolic activity as well as emotional behaviour, sleep, thirst, hunger and temperature regulation. The Ventral hypothalamus: Optic Chiasm Decussation of the optic nerves. Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland + Infundibulum) Rostroventral to the Hypothalamus it secretes hormones regulating homeostasis Mammillary Bodies Termination of the Hippocampal Fornix. These structures are connected with the anterior thalamic nucleus via the Mammillothathalamic tract. The other structures (Epi- Subthalamus) Subthalamus Bilateral subcortical nucleus that is found ventral to the thalamus and lateral to the hypothalamus. Epithalamus The Epithalamus that is mainly composed of the Pineal Gland is a structure that is implicated in endocrine functions (circadian rhythm). The Pineal Gland can be seen in the posterior view of the brain just superior to the colliculi of the midbrain.
7 4. Basal Ganglia From an anatomist s point of view (our definition): Basal ganglia are all subcortical structures within the cerebral hemispheres not including the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus ). = Caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, claustrum, amygdala From a clinician s point of view: Basal ganglia are a collection of large subcortical nuclei that are part of the extrapyramidal (motor) system. The term Extrapyramidal System refers to a
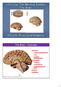
8 system involved in motor function not served by the motor cortex via the corticospinal tract also called pyramidal tract. Damage to this system causes Extrapyramidal syndromes such as muscular rigidity, tremor, motor slowing and, involuntary movements. = Caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus, together with other subcortical structures such as the subthalamus, substantia nigra, etc. The amygdala and claustrum are subcortical nuclei but they do not participate in motor functions The location of the caudate/putamen/globus pallidus/ amygdala Caudate/putamen/globus pallidus/ amygdala in lateral and medial view
9 Naming issues Corpus striatum (largest component of the basal ganglia) this term is used to describe the: Caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus. The terms Neostriatum, dorsal striatum or simply striatum refer to the caudate nucleus and putamen that are the phylogenetically newer parts of the corpus
10 striatum. Bridges of gray matter connect the two nuclei. These bridges that indicate the common origin of the two structures are especially pronounced in the anterior limb of the internal capsule between the head of the caudate nucleus and the anterioraspect of the putamen. The terms Pallidum and Paleostriatum refer to the globus pallidus that is different from the caudate nucleus as well as the putamen in both its histology as well as in its anatomical connections. Lentiform nucleus is an anatomical term that describes the p utamen and the globus pallidus together. These two structures although very different histologically they are next to each other in coronal and horizontal sections and they appear as one triangular structure. More details one the different components of the Basal Ganglia: Caudate nucleus (a term derived from a Latin word that means "having a tail"): Head-Body-Tail. This structure is part of the neostriatum. It is a C- shaped structure with an expanded rostral extremity, its head, which tapers down in size to form its body and tail. The head forms a convexity in the lateral floor of the anterior horn of the lateral ventricles. The body forms the lateral wall of the body of the lateral ventricles. The tail occupies a position in the roof of the inferior (temporal) horn of the lateral ventricles. In essence, it follows the curvature of the lateral ventricles from the floor of the anterior horn and the body to the roof of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricles. Putamen: this subcortical structure that is also part of the neostriatum is separated from the caudate nucleus by the anterior limb of the internal
11 capsule. In the frontal lobes, the caudate nucleus and putamen are continuous around the anterior tip of the internal capsule. Globus Pallidus: wedge-shaped structure between the putamen and the internal capsule. The globus pallidus is composed of two segments, a medial and lateral one, that can be easily distinguished in coronal and horizontal sections. *Amygdala: The amygdala is a bilateral structure located in the medial part of the temporal lobe just in the depth of the uncus (the most medial bulging of the parahippocampal gyrus). This structure consists of several sub-nuclei. It is the phylogenetically oldest part of the basal ganglia. The amygdala is found rostral and dorsal to the hippocampus. The tail of the caudate nucleus courses along the roof of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricles and terminates near the amygdala. The stria terminalis, a projection fiber system originating in the amygdala, travels next to the caudate nucleus to terminate in the hypothalamus. The amygdala is a component of the limbic system having primarily olfactory, visceral, endocrine, and behavioural functions. It is a key structure in emotional processes and formation of emotional memories. Since it has no role in motor control it has traditionally been excluded from the clinical definition of the basal ganglia. *Claustrum: this is a small subcortical nucleus that looks like a thin sheet of grey matter medial to the insula and the extreme capsule. The claustrum is lateral to the lentiform nucleus and the external capsule. Its functions are not well understood, although it seems to be related in function to the insula.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy
 Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX
 CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere)
 Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
DIENCEPHALON. ..Central core of the forebrain..consists of three paired structures
 DIENCEPHALON..Central core of the forebrain..consists of three paired structures ---------- --thalamus, --------hypothalamus, -------epithalamus..encloses the third ventricle Diencephalon between cerebral
DIENCEPHALON..Central core of the forebrain..consists of three paired structures ---------- --thalamus, --------hypothalamus, -------epithalamus..encloses the third ventricle Diencephalon between cerebral
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
LIMBIC SYSTEM. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System
 3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Outline of the next three lectures
 Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Gross Morphology of the Brain
 Gross Morphology of the Brain Done by : Marah Marahleh & Razan Krishan *slides in bold Principal Parts of the Brain Cerebrum : largest part of the brain Diencephalon Thalamus & hypothalamus Cerebellum
Gross Morphology of the Brain Done by : Marah Marahleh & Razan Krishan *slides in bold Principal Parts of the Brain Cerebrum : largest part of the brain Diencephalon Thalamus & hypothalamus Cerebellum
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Stanley Pruisinger 1980's
 Neuroanatomy Prion disease cerebellum chapter b/c cerebellar ataxia here as a warning for obvious reasons. Creutzfeldt - Jakob Disease (CJD) "Spongiform" (brain turns to sponge) Jews in Lybia who ate
Neuroanatomy Prion disease cerebellum chapter b/c cerebellar ataxia here as a warning for obvious reasons. Creutzfeldt - Jakob Disease (CJD) "Spongiform" (brain turns to sponge) Jews in Lybia who ate
Human Brain and Senses October 13, 2008 Page 1. Examination of the Human Brain
 Human Brain and Senses October 13, 2008 Page 1 Examination of the Human Brain With only a few hours today we can only begin to scratch the surface of a complex subject like neuroanatomy. The purpose of
Human Brain and Senses October 13, 2008 Page 1 Examination of the Human Brain With only a few hours today we can only begin to scratch the surface of a complex subject like neuroanatomy. The purpose of
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17. By: Joseline
 PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Human Anatomy. Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Human Anatomy Brain and Cranial Nerves 1 Brain and Cranial Nerves An adult brain weighs between 1.35 and 1.4 kilograms (kg) (around 3 pounds) and has a volume of about 1200 cubic centimeters (cc). Brain
Human Anatomy Brain and Cranial Nerves 1 Brain and Cranial Nerves An adult brain weighs between 1.35 and 1.4 kilograms (kg) (around 3 pounds) and has a volume of about 1200 cubic centimeters (cc). Brain
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
Course Booklet. We have felt the pain that Neuroscience is giving you.
 Exams Stressing You Out? Take Action! Course Booklet NEUR 1202 Carleton University* *TranscendFinals is not affiliated with the university We have felt the pain that Neuroscience is giving you. Our mission
Exams Stressing You Out? Take Action! Course Booklet NEUR 1202 Carleton University* *TranscendFinals is not affiliated with the university We have felt the pain that Neuroscience is giving you. Our mission
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal
 I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
Effects of Cerebellar Damage
 Effects of Cerebellar Damage Impaired rapid alternation movements Directed movements overshoot their mark (past-pointing on finger-tonose). Diencephalon COMPOSED OF THREE THALAMIC STRUCTURES: Thalamus
Effects of Cerebellar Damage Impaired rapid alternation movements Directed movements overshoot their mark (past-pointing on finger-tonose). Diencephalon COMPOSED OF THREE THALAMIC STRUCTURES: Thalamus
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord Cephalization Evolutionary development of rostral (anterior) portion of CNS Increased number of neurons in head
 CNS consists of brain and spinal cord Cephalization Evolutionary development of rostral (anterior) portion of CNS Increased number of neurons in head Highest level reached in human brain 1 Mostly to orient
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord Cephalization Evolutionary development of rostral (anterior) portion of CNS Increased number of neurons in head Highest level reached in human brain 1 Mostly to orient
Embryonic Brain Development
 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience
 CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
The Brain. Brain. Spinal Cord. Cauda Equina
 The Brain Brain Spinal Cord Cauda Equina The Brain Ventricles- cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid connected to the subarachnoid space- fluid filled space surrounding the brain Brain
The Brain Brain Spinal Cord Cauda Equina The Brain Ventricles- cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid connected to the subarachnoid space- fluid filled space surrounding the brain Brain
Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES. nuclei. The lateral ventricles. White substance of cerebral hemispheres. course 1
 Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline Human Anatomy Module 2 Content module 11 Study subject The olfactory brain. Basal nuclei. The lateral ventricles. White substance of cerebral
Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline Human Anatomy Module 2 Content module 11 Study subject The olfactory brain. Basal nuclei. The lateral ventricles. White substance of cerebral
Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Collections of cell body and dendrites (grey matter) are called nuclei/nucleus Nucleus can also
 Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Blood supply to the brain Blood brain barrier isolates neural tissue from general circulation
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa3.0/
The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of:
 The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of: - The Brain: within the skull, composed of cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem.
The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of: - The Brain: within the skull, composed of cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem.
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline *
 Anatomy and Physiology, Seventh Edition Rod R. Seeley Idaho State University Trent D. Stephens Idaho State University Philip Tate Phoenix College Chapter 13 Lecture Outline * *See PowerPoint Image Slides
Anatomy and Physiology, Seventh Edition Rod R. Seeley Idaho State University Trent D. Stephens Idaho State University Philip Tate Phoenix College Chapter 13 Lecture Outline * *See PowerPoint Image Slides
Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 12.1 Overview of the Central Nervous System (Figures 12.1, 12.2, 12.3) A. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the and, and is involved
Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 12.1 Overview of the Central Nervous System (Figures 12.1, 12.2, 12.3) A. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the and, and is involved
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Divisions of the Nervous System
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Lecture 19 1 Divisions of the Nervous System You are here CNS PNS 3 Brain Embryology & Overview Table & Figure From:
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Lecture 19 1 Divisions of the Nervous System You are here CNS PNS 3 Brain Embryology & Overview Table & Figure From:
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP:
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES
 NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Neuroanatomy lecture (1)
 Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Student Lab #: Date. Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System)
 Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges References... 3
 Section I Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges... 1 1 Orientation... 3 References... 3 2 Development... 7 Early Morphogenesis... 7 FormationoftheBrainRegions... 9 Histogenesis...
Section I Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges... 1 1 Orientation... 3 References... 3 2 Development... 7 Early Morphogenesis... 7 FormationoftheBrainRegions... 9 Histogenesis...
Cerebral Cortex 1. Sarah Heilbronner
 Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
Developmental sequence of brain
 Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Model 3-50B or 3-88 III VIII. Olfactory Nerve. Optic Nerve. Oculomotor Nerve. Trochlear Nerve. Trigeminal Nerve. Abducens Nerve.
 Model 3-50B or 3-88 I Olfactory Nerve II Optic Nerve Oculomotor Nerve III IV Trochlear Nerve Trigeminal Nerve V VI Abducens Nerve Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX VII Facial Nerve VIII Vestibocochlear Nerve or
Model 3-50B or 3-88 I Olfactory Nerve II Optic Nerve Oculomotor Nerve III IV Trochlear Nerve Trigeminal Nerve V VI Abducens Nerve Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX VII Facial Nerve VIII Vestibocochlear Nerve or
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 13
 I. embryonic development of the CNS A. neurulation is the formation of the CNS in the embryo invagination of dorsal ectoderm (outer layer of embryo cells) this process is induced (caused) by the notochord
I. embryonic development of the CNS A. neurulation is the formation of the CNS in the embryo invagination of dorsal ectoderm (outer layer of embryo cells) this process is induced (caused) by the notochord
CEREBRUM. Dr. Jamila EL Medany
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Nervous system Telencephalon. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Telencephalon Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Telencephalon Gray matter Cortex Basilar nuclei White matter-medulla Lateral ventricles General introduction
Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Telencephalon Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Telencephalon Gray matter Cortex Basilar nuclei White matter-medulla Lateral ventricles General introduction
The human brain. of cognition need to make sense gives the structure of the brain (duh). ! What is the basic physiology of this organ?
 The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain. MDL231 Principle of Anatomy
 Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide - Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide - Lab Exercises Please make sure you read the entire set of instructions on Dissection the Sheep Brain before beginning to cut. Also, please do not forget to go over
A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide - Lab Exercises Please make sure you read the entire set of instructions on Dissection the Sheep Brain before beginning to cut. Also, please do not forget to go over
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
 Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Neuroanatomy. Dr. Maha ELBeltagy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Prof Yousry 10/15/17 Types of brain fibers THE WHITE MATTER OF THE BRAIN The white matter
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Prof Yousry 10/15/17 Types of brain fibers THE WHITE MATTER OF THE BRAIN The white matter
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
Histology of the CNS
 Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
The Central Nervous System
 The Central Nervous System 1 The Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Components 2 Protection of the Brain The brain is protected from injury by The skull enough said! You already know this. What else
The Central Nervous System 1 The Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Components 2 Protection of the Brain The brain is protected from injury by The skull enough said! You already know this. What else
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally
 KEY BRAIN Brain Gross Anatomy Terms 1) Explain each of the following in terms of structure of the brain a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally b) Lateral fissure- deep groove
KEY BRAIN Brain Gross Anatomy Terms 1) Explain each of the following in terms of structure of the brain a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally b) Lateral fissure- deep groove
Hypothalamus. To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine secretions NTA Ch 14, pgs Key Figs: 14-3; 14-4,
 Hypothalamus Objectives To learn the general organization of the hypothalamus and the functions of the major nuclei NTA Ch 14, pgs. 419-422 Key Figs: 14-2, 14-3 To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine
Hypothalamus Objectives To learn the general organization of the hypothalamus and the functions of the major nuclei NTA Ch 14, pgs. 419-422 Key Figs: 14-2, 14-3 To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
PSY 215 Lecture #5 (01/26/2011) (Anatomy of the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96
 Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 12.3 Using Figure 12.3, match the following: 1) Site of efferent soma. 2) Site of axons
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 12.3 Using Figure 12.3, match the following: 1) Site of efferent soma. 2) Site of axons
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
