3. Timpul total estimat (ore/semestru de activitate didactică)
|
|
|
- Magdalen McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Universitatea de Medicină şi Farmacie Comisia pentru asigurarea calităţii FIŞA DISCIPLINEI- MODUL ENGLEZA 1. Date despre program 1.1. UNIVERSITATEA DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE CAROL DAVILA 1.2. FACULTATEA - MEDICINĂ/ DEPARTAMENTUL - Second Department- MORPHOLOGICAL SCIENCES 1.3. DISCIPLINA - ANATOMY - ENGLISH TEACHING MODULE 1.4. DOMENIUL DE STUDII - HEALTH 1.5. CICLUL DE STUDII: GRADUATE STUDIES 1.6. PROGRAMUL DE STUDII: MEDICINE 2. Date despre disciplină 2.1. Denumirea disciplinei : ANATOMY 2.2. Titularul activităților de curs - ` Titularul activităților de seminar: 2.4. Anul de studiu 2.5. Semestrul 2.6. Tipul de evaluare 2.7. Regimul disciplinei I I,II Practical and Fundamental multiple choice Science examination II III,IV Fundamental Science First year Anatomy 3. Timpul total estimat (ore/semestru de activitate didactică) 3.1. Nr ore pe săptămână 3.4. Total ore din planul de învățământ 8-sem I From which : sem II course 196 From which : 3.5. course practical session/ lab practical session/ lab 6-sem I 4-sem II 140 Distributia fondului 28 weeks ore de timp Studiul după manual, suport de curs, bibliografie și notițe Documentare suplimentară în bibliotecă, pe platformele electronice de specialitate și pe teren Pregătire seminarii / laboratoare, teme, referate, portofoloo și eseuri Tutoriat Examinări Alte activități
2 3.7. Total ore de studiu individual 3.9. Total ore pe semestru Numărul de credite First Year - 13 credits 4. Precondiții (acolo unde este cazul) 4.1. de curriculum Not applicable 4.2. de competențe Not applicable 5. Condiții (acolo unde este cazul) 5.1. de desfășurare a cursului Not applicable 5.2. de desfășurare a seminarului / laboratorului Not applicable 6. Competențe specifice acumulate Competențe profesionale (exprimate prin cunoștințe și abilități) Structural and developmental description and recognition of representative human anatomical elements - bones, muscles, vessels, nerves-as guideline for clinical diagnosis Application of techniques methods and acquired anatomical knowledge, in order to establish the diagnosis, to elaborate the scheme of treatment, to identify the most effective prevention measures for diseases Elaboration of a research project for a given study subject, with the investigation and description of anatomical structures Competențe transversale (de rol, de dezvoltare profesională, personale) Identification of objectives wanted to be achieved, of available resources, of their terms of completion, of working steps and time, of their deadline and of the associated risks in various pathologies. Identification of roles and responsibilities in a multidisciplinary team, applying of techniques for effective work and relationships in the team and in relation to the patient. Effective use of information sources, of communication resources but also of the professional aided training resources (internet portals, specialized software applications, databases, on-line courses ) both in Romanian and international languages. 7. Obiectivele disciplinei (reieşind din grila competenţelor specifice acumulate) 7.1. Obiectivul general - Familiarization with the university studying by means of anatomy, as one of the first medical subjects that is studied. Progressive knowledge of the anatomical composition, by gradual learning of the human body systems. Observance of professional values and ethics Obiective specifice Apart from knowledge gaining about each anatomical element, the anatomy aims are to develop the spirit of observation, the capacity of analysis and synthesis, but also to initiate into clinical application of the aquired information. The anatomy is the first medical subject that the students come in contact with and it has an important role in training of a physician/doctor, irrespective of his future medical specialty.
3 8. Conținuturi 8.1. Lectures 1 st year, 1 st Semester Metode de predare Observații 1. - Introduction. Anatomy study objects. 2.- Ovogenesis and ovulation. 3.- Fecundation. Implantation. Cleavage. 4.- Evolution in the second and in the third week. Courses are taught in lecture halls (amphitheaters) and rooms that are technically equipped for this main purpose -laptop, 5.- Derivatives of the germ layers. projector. All lectures are 6. Fetal period. Embryonic annexes. updated, according to the 7. Embryonic annexes - Placenta. reference books, journals, to books published by members of 8. Development of the limbs. Development abnormalities. our discipline, but also to the 9. Notions of biomechanics. Classification of the joints-means new data online publishedof hinging, means of gliding. PowerPoint presentations, 10. Superior limb joints (shoulder) schemes, drawings. Our 11.Superior limb joints (elbow, radio-ulnar joints, radiocarpial discipline has its own library to joint) obtain medical information for 12.Lower limb joints (Hip joint) 13. Lower limb joints (knee joint, talocrural joint) useful university studying by means of anatomy. 14. Radioanatomy and cross sections course 8.2. Lectures 1 st year, 2 nd Semester Metode de predare Observații 1. Development of the neurocranium and vicerocranium. 2. Development of the face-development abnormalities Courses are taught in lecture halls (amphitheaters) and rooms 3. Branchial region, the pharyngeal pouches-evolution, that are technically equipped derivatives. for this main purpose -laptop, 4. Temporomandibular joint- articular surfaces, means of projector. All lectures are updated, according to the joining, means of gliding. reference books, journals, to 5. Oral cavity- walls, content, blood supply, lymph vessels, books published by members of nerve supply. Teeth- structure, deciduous teeth, permanent our discipline, but also to the teeth, group features. new data online published Pharynx PowerPoint presentations, 7. - Larynx 8.- Development of the respiratory system 9, 10 - Development of the heart and of the great vessels 11.- Heart inervation and functional conductory pathways. 12. Coronary circulation. schemes, drawings. Our discipline has its own library to obtain medical information for useful university studying by means of anatomy Topography of thoracic organs Radioanatomy and cross sections course. Bibliografie Gray s Anatomy for students, by Richard Drake, PhD and all, Elsevier Health Gray s Anatomy pentru studenți, Coordonator F.Filipoiu, Editura Elsevier Prior, București Atlas de anatomie nomenclatura latină Gilroy, Coordonator F.Filipoiu, Editura Prior, Bucuresti Aparatul digestiv subdiafragmatic și splina sub redacția Florin Filipoiu, Editura Universitară Anatomia omului - Aparatul urinar, spatiul retroperitoneal, F. Filipoiu, C. Cristescu, D. Mihalea, Editura Universitara Carol Davila, București Anatomie Pereții trunchiului Lucrări practice sub redacția G. Lupu, Editura Universitară Anatomia omului Cap și Gât Lucrări practice sub redacția G. Lupu, Editura Universitară
4 Anatomia omului Aparatul digestiv Lucrări practice sub redacția G.Lupu, Editura Universitară Anatomie Membrele sub redacția G. Lupu, Editura Universitară Carol Davila București Editura Universitară sub redacţia Al.T. Ispas Anatomia omului Aparatul Genital Anatomia omului Sistemul Nervos Central Lucrări practice, sub redacţia Al.T.Ispas, Editura Universitară Sistemul nervos și organele de simț - Atlas color Werner Kahle Coordonator Prof. Al.T. Ispas, Editura Callisto București Anatomia funcțională a toracelui - Cezar Th. Niculescu, Bogdan Voiculescu, Romică Cergan, Mihaela Banu, Editura Universitară Carol Davila București Embriologie Ghid de lucrări practice de microscopie An I sub redacția Al. T. Ispas, Editura Universitară Embriologie Ghid de lucrări practice de microscopie An II sub redacția Al. T. Ispas, Editura Universitară 8.3. Seminar / laborator Metode de predare Observații Lectures 1 st year, 1 st Semester Metode de predare Observații 1. Axes and orientation planes of the body. The main purposes of teaching methods 2. Vertebrae: general vertebral features; are cervical, thoracic, lumbar vertebrae. -recognition, but also structural and Particular developmental description of the a. vertebrae; transition vertebrae. studied anatomical structures - understanding and development of Sacrum and coccyx. skills in clinical using of acquired Vertebral column curvatures. Surface anatomical knowledge anatomy: the palpation and counting of the - development of logical, causal vertebrae; anatomic coordination points for thinking in medical studying the lumbar puncture. Radiological The teaching methods for anatomical anatomy. study: -dissections of human bodies, Sternum. Ribs. Osseous thorax. Surface presentations on anatomical dissected anatomy of the thoracic wall: orientation parts, anatomical preparations, bones, lines, osseous and muscular reliefs; counting sections; -microscopic examinations of of the ribs. Radiological anatomy. histological sections-human embryos and fetuses- at practical sessions of 3. Clavicle, scapula, humerus. embryology; radiological anatomy with Radius, ulna, skeleton of the hand. Surface examination of radiographies; - anatomy and radiological anatomy of the documentation in our discipline upper limb. museum, study on cross-sections of 4. Hip bone, skeletal pelvis. Surface anatomy: human body, study on normal x-rays, internal and external pelvimetry CT and MRI Femur, patella Tibia, fibula, skeleton of the foot. Surface anatomy and radiological anatomy of the lower limb. 5. EXAMINATION 6. Elementary notions of dissection. Dissection of the muscles connecting the upper limb with the vertebral column and of the muscles connecting the ribs to vertebrae:- latissimus dorsi, trapezius, levator scapulae, rhomboids, serrati posterior. Surface anatomy; weak points of the posterior
5 abdominal wall-the lumbar triangle of Petit, the lumbar tetragonal of Grynfelt; the pentagon of Krause Dissection of the nuchal region. Suboccipital muscles, vessels and nerves. Surface anatomy: anatomic coordination points for the anaesthesia of the Arnold nerve. 7. Dissection of the anterolateral wall of the thorax-pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior, subclavius, intercostals. Topography of the intercostal space. Anatomic coordination points for the intercostal puncture. Mammary region: structure of the mammary gland; blood supply, nerve supply, lymphatic drainage of the mammary gland. 8. Dissection of the axilla. Walls of the axilla; main vascular-nervous bundle, secondary vascular-nervous bundles. Axillary artery. Dissection of the axilla. Formation of the brachial plexus. Dissection of the branches of the brachial plexus, axillary lymph nodes. 9. Dissection of the anterior region of the armmuscles, vessels, nerves. Surface anatomy. 10. Dissection of the antero-lateral region of the forearm-muscles, vessels, nerves. Carpal tunnel: delimitation and content. Superficial veins of the upper limb. Surface anatomy. 11. Dissection of the palm. Topographic regions of the palm. Thenar muscles, hypothenar muscles, muscles of midpalmar region. Synovial sheaths of the carpal tendons. Vessels, nerves. Surface anatomy. 12. Dissection of the scapular region- muscles, vessels, nerves. Surface anatomy. 13. Dissection of the posterior region of the armmuscles, vessels, nerves. Triangular and quadrangular spaces bounded by the humerus, long heads of the triceps brachii, teres major and teres minor (triangular space, triangular interval, quadrangular space): delimitation, content. Surface anatomy. 14. Dissection of the posterior region of the forearm- muscles, vessels, nerves. Surface anatomy. 15. Topographic sections at the level of the upper limb.
6 16. EXAMINATION-upper limb 17. Dissection of the anterolateral wall of the abdomen-obliquus externus abdominis, obliquus internus abdominis, transversus abdominis, rectus abdominis; rectus sheath; vessels and nerves. Surface anatomy of the abdominal wall: muscular relief, grooves, projection of the inferior epigastric vessels. 18. Dissection of the inguinal canal- walls and rings of the inguinal canal; content of the inguinal canal in male and female; projection of the weak points of the abdominal wall. Lacuna musculorum, lacuna vasorumlimits and content. Formation and the branches of the lumbar plexus. 19. Dissection of the anteromedial region of the thigh. Femoral triangle- limits, content. Great saphenous vein, femoral vein, femoral artery. Superficial and deep inguinal lymph nodes. Femoral sheath. Adductor canal- limits, content. 20. Dissection of the anterolateral region of the leg- muscles, vessels, nerves. Surface anatomy. 21. Dissection of the gluteal region- muscles, vessels, nerves. Surface anatomy. 22. Suprapiriform and infrapiriform spacesdelimitation, content. Formation of the sacral plexus. 23. Dissection of the posterior region of the thigh- muscles, vessels, sciatic nerve. 24. Dissection of the popliteal region topography and content. Surface anatomy. 25. Dissection of the posterior region of the legmuscles, vessels, nerves. Small a. saphenous vein. Calcaneal canal: delimitation, content. 26. Dissection of the plantar region- muscles, vessels, nerves. 27. Topographic sections at the level of the lower limb. 28. EXAMINATION-review Lectures 1 st year, 2 nd Semester Metode de predare Observații 1. Neuro- and viscerocranium. 2. Walls of the orbit, osseous walls of the nasal The main purposes of teaching methods are cavity, infratemporal fossa, -recognition, but also structural and pterigopalatine fossa. Mandible. developmental description of the 3. Craniofacial muscles and facial nerve. studied anatomical structures - understanding and development of Masticatory muscles and facial artery. skills in clinical using of acquired 4. Trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic and maxillary anatomical knowledge
7 nerves), ciliary ganglion, pterigopalatine ganglion (afferents and branches) 5. Mandibular nerve, otic ganglion (afferents and branches), submandibular ganglion (afferents and branches). 6. Posterior auricular artery, occipital artery, inferior thyroid artery and ascending pharyngeal artery (course and branches) 7. Sternocleidomastoid, scalenes, accessory nerve. 8. Glossopharingeal nerve-course and branches. Vagus nerves at the level of the neck. Superior and inferior laryngeal nerves. 9. Hypoglossal nerve-course and branches 10. Cervical sympathetic trunk-structure, branches 11. Subclavian artery-course, branches. Arterial anastomoses around the scapula. 12. Cervical plexus-formation, superficial and deep branches. Ansa cervicalis (formation, distribution). 13. Infrahyoid and suprahyoid muscles. Cervical fasciae. 14. Veins of the head- internal, external and anterior jugular veins (formation, tributaries). 15. Thyroid gland, parathyroid glands (structure, relations, blood supply). 16. Lymph vessels and nodes of the head and of the neck. 17. Oral cavity and salivary glands. 18. EXAMINATION-the head and the neck 19. Walls of the thoracic cavity. Trachea and bronchi 20. Lungs (description, structure, segmentation). Blood vessels of the lungs (pulmonary and bronchial vessels) 21. Pleura- pleural recesses. Projection of the lung fissures. 22. Heart- external aspect (surfaces, margins, base, apex) 23. Internal aspect of the heart (atria, ventricles, interatrial and interventricular septa, orifices, valvular apparatus). 24. Blood supply of the heart (coronary arteries, coronary sinus). Nerve supply of the heart (cardiac plexus) 25. Serous and fibrous pericardium. Sinuses of the serous pericardium. Blood supply and nerve supply of the pericardium. 26. Mediastinum and its subdivision. Contens of the superior mediastinum: - development of logical, causal thinking in medical studying The teaching methods for anatomical study: -dissections of human bodies, presentations on anatomical dissected parts, anatomical preparations, bones, sections; -microscopic examinations of histological sections-human embryos and fetuses- at practical sessions of embryology; radiological anatomy with examination of radiographies; - documentation in our discipline museum, study on cross-sections of human body, study on normal x-rays, CT and MRI
8 brachiocephalic veins, superior vena cava, aortic arch and its branches, thymus and the nervous structure in the mediastinum. Anterior and middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum (thoracic esophagusstructure, blood supply, nerve supply). 27. Thoracic aorta and its branches. Thoracic duct. Mediastinal lymph nodes. Thoracic sympathetic trunk. 28. Review-thorax and its content Bibliografie Gray s Anatomy pentru studenți, Coordonator F.Filipoiu, Editura Elsevier Prior, București Atlas de anatomie nomenclatura latină Gilroy, Coordonator F.Filipoiu, Editura Prior,Bucuresti Aparatul digestiv subdiafragmatic și splina sub redacția Florin Filipoiu, Editura Universitară Anatomia omului - Aparatul urinar, spatiul retroperitoneal, F. Filipoiu, C. Cristescu, D. Mihalea, Editura Universitara Carol Davila, București Anatomie Pereții trunchiului Lucrări practice sub redacția G. Lupu, Editura Universitară Anatomia omului Cap și Gât Lucrări practice sub redacția G. Lupu, Editura Universitară Anatomia omului Aparatul digestiv Lucrări practice sub redacția G.Lupu, Editura Universitară Anatomie Membrele sub redacția G. Lupu, Editura Universitară Carol Davila București Editura Universitară sub redacţia Al.T. Ispas Anatomia omului Aparatul Genital Anatomia omului Sistemul Nervos Central Lucrări practice, sub redacţia Al.T.Ispas, Editura Universitară Sistemul nervos și organele de simț - Atlas color Werner Kahle Coordonator Prof. Al.T. Ispas, Editura Callisto București Anatomia funcțională a toracelui - Cezar Th. Niculescu, Bogdan Voiculescu, Romică Cergan, Mihaela Banu, Editura Universitară Carol Davila București Embriologie Ghid de lucrări practice de microscopie An I sub redacția Al. T. Ispas, Editura Universitară Embriologie Ghid de lucrări practice de microscopie An II sub redacția Al. T. Ispas, Editura Universitară 9. Coroborarea conţinuturilor disciplinei cu aşteptările reprezentanţilor comunităţii epistemice, asociaţiilor profesionale şi angajatori reprezentativi din domeniul aferent programului Anatomy professional training of the first- and second-year students aims: -recognition and identification of anatomical structures related to the need of effective communication with the patient and academic environment -preparing the future physician/doctor for a proper and good professional communication with the future employer 10. Evaluarea Tip de activitate Criterii de evaluare Metode de evaluare Pondere din nota finală
9 Attendance at practical sessions/labs, at courses/lectures, at dissections on human bodies, presentations on anatomical dissected parts, on preparations, bones, sections and health issues, control tests. Sem I The student receives a 30 MCQ test divided in 3 groups: I-lecture, II-upper limb, III-lower limb and abdominal wall. Each group must be passed with a minimum of 5 points each. Sem II The student receives a 30 MCQ test divided in 3 groups:i-lecture,ii-anatomy of the head and neck,iiianatomy of the thoracic organs.each group must be passed with a minimum of 5 points each Curs MCQ Examination Seminar / laborator PRACTICAL EXAMINATION ORAL EXAMINATION Standard minim de performanță Pass mark is 5. Failure of the practical,the student being marked with grade 4 Data completării: Professor FLORIN FILIPOIU PhD Data avizării în Consiliul Departamentului: Semnătura directorului de departament
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
FIŞA DISCIPLINEI. 1. Date despre program 1.1 Instituţia de învăţământ Universitatea Babeş-Bolyai
 FIŞA DISCIPLINEI 1. Date despre program 1.1 Instituţia de învăţământ Universitatea Babeş-Bolyai superior 1.2 Facultatea Psihologie şi Ştiinţe ale Educaţiei 1.3 Departamentul Psihologie Clinică şi Psihoterapie
FIŞA DISCIPLINEI 1. Date despre program 1.1 Instituţia de învăţământ Universitatea Babeş-Bolyai superior 1.2 Facultatea Psihologie şi Ştiinţe ale Educaţiei 1.3 Departamentul Psihologie Clinică şi Psihoterapie
Topic list for the Anatomy end-semester exam of the First semester Academic year 2018/2019, Autumn term
 University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
ANATOMY. Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks)
 ANATOMY Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks) SEMESTER LECTURES LAB CLASSES SEMINARS TOTAL FIRST 4 hours (2+2) 4 hours (2+2) 1 hour 135 hours SECOND 3 hours 4 hours (2+2) 2 hours 135
ANATOMY Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks) SEMESTER LECTURES LAB CLASSES SEMINARS TOTAL FIRST 4 hours (2+2) 4 hours (2+2) 1 hour 135 hours SECOND 3 hours 4 hours (2+2) 2 hours 135
Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5
 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction 1 5 Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5 Chapter 2: Skeletal System 6 74 Skeleton 6 Skeletal system 8 Bones of superior extremity 12 Articulated skeleton of hand 17 Clinical
Contents Chapter 1: Introduction 1 5 Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5 Chapter 2: Skeletal System 6 74 Skeleton 6 Skeletal system 8 Bones of superior extremity 12 Articulated skeleton of hand 17 Clinical
Acknowledgments Figure Credits List of Clinical Blue Boxes Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p.
 Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
SUBJECTS 1st year, 1st semester
 SUBJECTS 1st year, 1st semester I. Embryology 1. Spermatogenesis and blood testes barrier 2. Spermiogenesis. Sperm characteristics 3. Oogenesis and arrested prophase 4. Follicular cycle 5. Ovulation. Corpus
SUBJECTS 1st year, 1st semester I. Embryology 1. Spermatogenesis and blood testes barrier 2. Spermiogenesis. Sperm characteristics 3. Oogenesis and arrested prophase 4. Follicular cycle 5. Ovulation. Corpus
Anatomy I ANAT 301. Course Description
 Anatomy I ANAT 301 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the osteomyoarticular system and peripheral nervous system, with
Anatomy I ANAT 301 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the osteomyoarticular system and peripheral nervous system, with
Department of Anatomy ESI-PGIMSR, Joka, Kolkata
 Teaching Schedule - 2016-2017, 1st MBBS Date and Day Time Topic Name/ Group 8-9 Orientation, Introduction to theoretical aspects of Practical SC 3.10.2016 Anatomy, Tools of Trade - Anatomical Nomenclature-
Teaching Schedule - 2016-2017, 1st MBBS Date and Day Time Topic Name/ Group 8-9 Orientation, Introduction to theoretical aspects of Practical SC 3.10.2016 Anatomy, Tools of Trade - Anatomical Nomenclature-
Course Specifications
 Cairo University Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy Course Specifications Course title: Human Anatomy and Embryology (1 st year) (Code): ANA-101 Department offering the course: Anatomy Department
Cairo University Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy Course Specifications Course title: Human Anatomy and Embryology (1 st year) (Code): ANA-101 Department offering the course: Anatomy Department
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University
 First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
List of questions for the examination in Human Anatomy Faculty of Stomatology, the 1st semester. (control of theoretical knowledge)
 Pag. 1 / 5 List of questions for the examination in Human Anatomy Faculty of Stomatology, the 1st semester (control of theoretical knowledge) LOCOMOTOR APPARATUS 1. Human Anatomy and its role in medical
Pag. 1 / 5 List of questions for the examination in Human Anatomy Faculty of Stomatology, the 1st semester (control of theoretical knowledge) LOCOMOTOR APPARATUS 1. Human Anatomy and its role in medical
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Teaching Objectives
 Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Presentations o Large group teaching o Small group teaching Prosection-based teaching Osteology teaching Surface anatomy Innovative teaching Conceptual teaching
Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Presentations o Large group teaching o Small group teaching Prosection-based teaching Osteology teaching Surface anatomy Innovative teaching Conceptual teaching
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Gateway to the upper limb. An area of transition between the neck and the arm.
 Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
KARPAGAM FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES & RESEARCH DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMY TEACHING SCHEDULE GENERAL ANATOMY I - MBBS
 TEACHING SCHEDULE GENERAL ANATOMY I - MBBS S.NO DATE & TIME 1. 3.10.16 Monday 2. 4.10.16 Tuesday 8 10 3. 5. 10.16 Wednesday 4. 11 1pm 5. 6.10.16 Thursday 8 10 6. 6.10.16 Thursday 12 1pm 7. 7.10.16 Friday
TEACHING SCHEDULE GENERAL ANATOMY I - MBBS S.NO DATE & TIME 1. 3.10.16 Monday 2. 4.10.16 Tuesday 8 10 3. 5. 10.16 Wednesday 4. 11 1pm 5. 6.10.16 Thursday 8 10 6. 6.10.16 Thursday 12 1pm 7. 7.10.16 Friday
SYLLABUS BDS I PROFESSIONAL GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
UNIVERSITY DEVELOPMENT CENTER. Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department 29/12/2015
 Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department Course Specification: Programme (s) on which the course is given : M.B.B.Ch
Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department Course Specification: Programme (s) on which the course is given : M.B.B.Ch
topographical anatomy
 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Neck. BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat
 The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
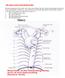
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Peripheral Circulation
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Peripheral Circulation Structures of the Splanchnopleure: receive unpaired vessels of the abdominal aorta. Structures of the
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Peripheral Circulation Structures of the Splanchnopleure: receive unpaired vessels of the abdominal aorta. Structures of the
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh
 3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
Table of Contents: 1 The body. What is anatomy? 4. How can gross anatomy be studied? 4. Important anatomical terms 4. Imaging 7
 Table of Contents: 1 The body What is anatomy? 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? 4 Important anatomical terms 4 Imaging 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques 7 Nuclear medicine imaging 10 Image interpretation
Table of Contents: 1 The body What is anatomy? 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? 4 Important anatomical terms 4 Imaging 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques 7 Nuclear medicine imaging 10 Image interpretation
Anatomy II ANAT 302. Course Description
 Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line
 L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
The body What is anatomy? p. 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? p. 4 Important anatomical terms p. 4 Imaging p. 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques p.
 The body What is anatomy? p. 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? p. 4 Important anatomical terms p. 4 Imaging p. 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques p. 7 Nuclear medicine imaging p. 10 Image interpretation
The body What is anatomy? p. 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? p. 4 Important anatomical terms p. 4 Imaging p. 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques p. 7 Nuclear medicine imaging p. 10 Image interpretation
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI
 IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI MD 2004, Chişinău, Republica Moldova, bd. Ştefan cel Mare, 192, tel.: +373.22.205349
IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI MD 2004, Chişinău, Republica Moldova, bd. Ştefan cel Mare, 192, tel.: +373.22.205349
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
NBME Anatomy Review. Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015
 NBME Anatomy Review Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015 UPPER & LOWER LIMBS 1. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case? A. Rotator cuff tendinitis: pain w/o weakness B. Adhesive capsulitis: absolute
NBME Anatomy Review Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015 UPPER & LOWER LIMBS 1. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case? A. Rotator cuff tendinitis: pain w/o weakness B. Adhesive capsulitis: absolute
Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes
 Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes Introduction about nervous system nervous system central nervous system periphral nervous system brain spinal cord 31 pairs of spinal nerves 12 paris of cranial
Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes Introduction about nervous system nervous system central nervous system periphral nervous system brain spinal cord 31 pairs of spinal nerves 12 paris of cranial
LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2. Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System. A list of the first 3 digits - 72 terms
 1 Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System A list of the first - 72 terms Index + Regional terms 2 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 20 Musculoskeletal system: general terms 201 Skeletal system 202 Muscular system: types
1 Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System A list of the first - 72 terms Index + Regional terms 2 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 20 Musculoskeletal system: general terms 201 Skeletal system 202 Muscular system: types
Academic Year 2017/2018. FALL SEMESTER DDS Program Monday: 5:45pm 7:15pm Thursday: 5:30pm- 7:00pm
 CURRICULUM FOR HUMAN ANATOMY COURSE LAB SESSIONS Academic Year 2017/2018 FALL SEMESTER DDS Program Monday: 5:45pm 7:15pm Thursday: 5:30pm- 7:00pm Category 1: Bones name, type, structure Joints: type, articular
CURRICULUM FOR HUMAN ANATOMY COURSE LAB SESSIONS Academic Year 2017/2018 FALL SEMESTER DDS Program Monday: 5:45pm 7:15pm Thursday: 5:30pm- 7:00pm Category 1: Bones name, type, structure Joints: type, articular
FUNDEMENTALS OF ANATOMY. TBD TBD
 Course Details FUNDEMENTALS OF ANATOMY Course Title Fundamentals of Anatomy Course Number BIOL 160 Department Anatomy Credit Hours 4 Grading Type Letter Course Director Sushama Rich M.D. Director s Email
Course Details FUNDEMENTALS OF ANATOMY Course Title Fundamentals of Anatomy Course Number BIOL 160 Department Anatomy Credit Hours 4 Grading Type Letter Course Director Sushama Rich M.D. Director s Email
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum. Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes
 Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla
 Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 1 Pectoral region Intercostal nerve Anterior branch of lateral cutaneous branch Lateral cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous
Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 1 Pectoral region Intercostal nerve Anterior branch of lateral cutaneous branch Lateral cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Chapter 11: The Muscular System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector. Section I
 Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Applied anatomy. Types of ossification & Epiphysis Kinesiology 2
 .General Anatomy :Cell Cell division types with significance Tissues Functional correlation Syllabus for the Post of Assistant Professor / Associate Profess Terms used in Embryology Functions of bone,
.General Anatomy :Cell Cell division types with significance Tissues Functional correlation Syllabus for the Post of Assistant Professor / Associate Profess Terms used in Embryology Functions of bone,
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES
 1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
Table of Contents: Part I: Introduction and Thorax
 Table of Contents: Part I: Introduction and Thorax Cartoon: The Four "Birds" of the Thorax 1 Planes of the body 2 Anatomic position 3 Some common movements 4 Skeletal landmarks (upper anterior) 5 Bones
Table of Contents: Part I: Introduction and Thorax Cartoon: The Four "Birds" of the Thorax 1 Planes of the body 2 Anatomic position 3 Some common movements 4 Skeletal landmarks (upper anterior) 5 Bones
Group A: Locomotion system (bones, joints, muscles) and Topography blue
 Group A: Locomotion system (bones, joints, muscles) and Topography blue Bones 1. General structure and growth of a bone Main points: types of bones, parts of bones, histological structure, types of bone
Group A: Locomotion system (bones, joints, muscles) and Topography blue Bones 1. General structure and growth of a bone Main points: types of bones, parts of bones, histological structure, types of bone
Anatomy of thoracic wall
 Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
Clinical Anatomy, Embryology and Imaging BMS 6115C. Summer Semester 2009 Lynn J. Romrell, Ph.D. Course Director. Course Schedule
 Anatomy, Embryology and Imaging BMS 6115C Summer Semester 2009 Lynn J. Romrell, Ph.D. Course Director Course Schedule Color codes for course activities: Anatomy Sessions Anatomic Radiology Sessions Embryology
Anatomy, Embryology and Imaging BMS 6115C Summer Semester 2009 Lynn J. Romrell, Ph.D. Course Director Course Schedule Color codes for course activities: Anatomy Sessions Anatomic Radiology Sessions Embryology
thoracic cage inlet and outlet landmarks of the anterior chest wall muscles of the thoracic wall sternum joints ribs intercostal spaces diaphragm
 Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including inlet and outlet. Describe the anatomical landmarks of the anterior chest wall. List various structures making
Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including inlet and outlet. Describe the anatomical landmarks of the anterior chest wall. List various structures making
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck.
 Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
Lab 6: Blood. BIO104 Laboratory Handouts 147. Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics. 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition -
 147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns
 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns CLAVICLE Examine an isolated clavicle and compare it with a clavicle on an articulated skeleton. Viewed from above,
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns CLAVICLE Examine an isolated clavicle and compare it with a clavicle on an articulated skeleton. Viewed from above,
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
A&P 1. Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist
 A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
DAY/TIME
 PROGRAMME COORDINATOR: DR. FAZINA KASIM (fazlinakb@usm.my ; 6952) WEEK: 1 06/09/17 ACADEMIC BRIEFING (Bilik Model Jabatan Anatomi) 10/09/17 AGONG S BIRTHDAY 11/09/17 12/09/17 Tissue Processing for Histology,
PROGRAMME COORDINATOR: DR. FAZINA KASIM (fazlinakb@usm.my ; 6952) WEEK: 1 06/09/17 ACADEMIC BRIEFING (Bilik Model Jabatan Anatomi) 10/09/17 AGONG S BIRTHDAY 11/09/17 12/09/17 Tissue Processing for Histology,
_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]
![_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come] _CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]](/thumbs/81/84146690.jpg) 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Anatomical Language. Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors Ms. Chase
 Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
FIŞA DISCIPLINEI COD DISCIPLINĂ: Universitatea Babeş-Bolyai
 1. Date despre program 1.1 Instituţia de învăţământ superior FIŞA DISCIPLINEI COD DISCIPLINĂ: 1622 Universitatea Babeş-Bolyai 1.2 Facultatea Psihologie şi Ştiinţe ale Educaţiei 1.3 Departamentul Psihologie;
1. Date despre program 1.1 Instituţia de învăţământ superior FIŞA DISCIPLINEI COD DISCIPLINĂ: 1622 Universitatea Babeş-Bolyai 1.2 Facultatea Psihologie şi Ştiinţe ale Educaţiei 1.3 Departamentul Psihologie;
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy
 Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
Module 2 "Splanchnology. Central nervous system and sensory organs. HEART. Vessels and nerves of the head, neck, trunk, limbs" 1.
 Module 2 "Splanchnology. Central nervous system and sensory organs. HEART. Vessels and nerves of the head, neck, trunk, limbs" 1. Classification of internal organs. General plan of tubular organs. 2. The
Module 2 "Splanchnology. Central nervous system and sensory organs. HEART. Vessels and nerves of the head, neck, trunk, limbs" 1. Classification of internal organs. General plan of tubular organs. 2. The
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
PA-1240: CLINICAL ANATOMY
 PA-1240: Clinical Anatomy 1 PA-1240: CLINICAL ANATOMY Cuyahoga Community College Viewing:PA-1240 : Clinical Anatomy Board of Trustees: 2014-06-19 Academic Term: 2014-08-23 Subject Code PA - Physician Assistant
PA-1240: Clinical Anatomy 1 PA-1240: CLINICAL ANATOMY Cuyahoga Community College Viewing:PA-1240 : Clinical Anatomy Board of Trustees: 2014-06-19 Academic Term: 2014-08-23 Subject Code PA - Physician Assistant
Note : I put the sheet's info within the slides to easily understand this lecture Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 Note : I put the sheet's info within the slides to easily understand this lecture Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including
Note : I put the sheet's info within the slides to easily understand this lecture Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments
 Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION
 THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1
 1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System
 Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm
 Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
