ON A NEW ACANTHOCEPHALA, ACANTHOSENTIS SIRCARI~ SP. NOV., FROM A CALCUTTA FISH, RASBORA ELANGA (HAM.).
|
|
|
- Melissa Sims
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ON A NEW ACANTHOCEPHALA, ACANTHOSENTIS SIRCARI~ SP. NOV., FROM A CALCUTTA FISH, RASBORA ELANGA (HAM.). By T. N. PODDER, 1Jtl.Sc., M.B., P,rofessor of Zoology, Oarmichael Medical Oollege, Oalctttta. In the course of my investigations on the parasitic infections of various fishes of Bengal and other provinces available in the Ca.lcutta markets, I found a new acanthocephalan parasite in the intestine of Rasbora elanga (Haln.). This fish is known in Bengal as " Elang ba ta ", and is generally available in the local markets from September to lvlarch. I found that nearly 60 per cent of the fishes were infected with these parasites and the highest number of parasites in one specimen was 8-10 ; all the parasites were found in the intestine of the host. This worm is described be]o\v as Acanthosentis sircari 1, sp. nov. Acanthosentis sircari, sp. nov. The body is usually cylindrical \vith a broad anterior end, while the post.erior portion tapers a little to'w'ards the extremity. Sexual dimor- //.--- /' /t' TEXT-FIG. I.-Anterior portion of Acanthosentis sircari, sp. nov. bh., body hooks; l., lemnisci; ng., eentral nerve ganglion; nl., nucleus of tlw lemnisci; p., proboscis; ph., prohoseis hooks. 1 The species has been named after Sir ~ilratan Sh'car, ~f.a., M.D., D.Sc., as il mari( of gratitude for his keen interest in this line (Jf research. [ ] ~)7 ] c
2 138 Records of the Tndian M useu-m. [VOL. XLIII, phism is well marked, the females being much larger than the males. 'The colour of fresh specimens is creamy-white. The proboscis is globular with 3 rows of 6 hooks each. The hooks of the first and second rows are much larger than those of the third row. 'There is no definite neck, but in fully stretched specimens a comparatively small space, devoid of spines, corresponding to the neck can be distinguished. The anterior half of the body is armed with circular rows of curved spines. In the anterior region these spines are closely set, but the rows near the middle are wide apart. In the body-wall there are a few giant sub-cuticular nuclei, five on the dorsal and two in the ventral aspect of -the body, some branched nuclei are also present. The lacunar system is well developed. The transverse canals are very prominent, their course in the body-wall corresponds to the circles of cuticular spines and suggests a pseudosegmentation of the body. The proboscis sheath is a single-layered, thin walled muscular sac, hanging down from the middle region of the proboscis. The central nerve ganglion is situated at the posterior extremity of the proboscis sheath. pg. jjr.- TEXT-FIG. 2.-Posterior portion of male Acanthosentis sircari, sp. nov. b.,. bursa; p., penis; pd. prostatic duct; pg., Prostatic glands; pr., Prostatic reservoir; t., testes; vd., vas deferens; ve., vasa efferentia. ~he two lemnisci are situated normally on either side of the proboscis sheath. One of the lemnisci is much longer than the other, being
3 1941.] T. N. PODDER: A new Acanthocephalafromfish. 139 nearly t,vice its length. This is a constant feature in all the specimens examined. There are three nuclei in the shorter lemniscus, and two in the longer. The male genitalia consist of t,vo ovoid testes situated closely apposed to each other. The vasa efferentia join one another near the prostatic,reservior to form a thick and elongated vas deferens which ends in the penis. The prostatic gland.is a single syncitial mass with 6 to 8 nuclei.embedded in it. It lies closely behind the posterior testis. The prostatic reservoir is a rounded organ which is continued as a narrow prostatic duct opening at the base of the penis. The seminal vesicle is a long baloon-shaped sac which also opens near the opening of the vas deferens into the penis. The penis is a conical muscular organ which ends at the top of the eversible bursa. The bursa is a funnel-shaped structure,:which, in most cases, is retracted within the body. nb.- nl ng. ---if. -abe --lj. TEXT-FIG. 3.-Young female A. sircari, sp. nov. showing developing ovary. l., lemnisci; nb., body nucleus; nf., nerve retinaculi; ng., central nerve ganglion;.0., ovary; ps., proboscis sheath; u., uterus; ub., uterine bell; v., vagina. The female genitalia consist of a thick walled uterine-bell. which at its posterior end is continued as a long, tubular uterus. At the posterior extremity of the uterine-bell just near its opening into the uterus there.are 5 to 6 giant cells, the" guard cells" which control the passage of the mature ova into the uterus. The wall of the uterus is thick, its postetior half is very muscular, and its lumen is much narrower posteriorly than anteriorly. At the junction of the anterior and posterior portions
4 140 Records of the Indian Museum. [ VOL. XLIII,. of the uterus there are two giant cells situated within the uterine wall ;~ these are the flask cells (Verma & Datta). The uterus leads into the thick and muscular vagina, which is situated at the postero-ventral end of the worm. yt.-- -oj). ---yc. --:foe TEXT-FIG. 4.-}~emale genitalia of A.. ~ircar i sp. nov. fc. flash cell; g~., guard cell; gl., genitalligame'nt; O~., oya; 11., ute'ru~ ; 'ub., uterine' bell; v., vagina. Measurements.-Males mnl. X mm.; females mm. X O mm.; proboscis 0 138xO 115mm.; proboscis hooks, row (i) 0 055mm. long, row (ii) 0 048mm. long, row (iii) O 018mm. long; proboscis sheath X 0 150mm.; lemnisci (i) X 0 104mm., (ii) X 0 161mm. ; testis, anterior X mm., posterior 0'379 X 0 322mm.; prostatic gland X O 207mm. ; vas deferens O 667mm. long; prostatic reservoir X 0 104mm. ; prostatic duct 0 598mm. long; bursa O 437mm. long; uterine bell 0 115mm. long; uterus 0 133mm. long; vagina O 161mm. long. Ova not liberated. In the new species the males are generdjly 'much smaller than the females. The lemnisci are much longer tharl the proboscis sheath and one of the lemnisci is nearly double in length of the other. There are _ 3 npclei in the shorter and 2 in the longer lelnnisci. The,vall of theproboscis sheath is single layered. The central nerve ganglion is situ[lted.
5 TABLE I. Showing measurements of closely related species. Name of species. San. Dimensions. I Proboscis. Probe Sheath. J.. emnisci. Terminal Hooks. Sub-cuticular nuclei. A. CJlItspinus Verma & Datta 1 Cl-I 25 0' ,17-0,38 0,04-0,17 3 rows of 6 hooks. few oval & branched. & x x x x mm. 0'04-0'05 mm mm '07 mm. (i) 7~(J. both equal. (H) ' '0 mm..a. holospintls Sen '1 xo'os mm. 0 3 xo'os mm. Slender and little longer.... 4: dorsal & 2 ventral. & x than the proboscis 0'2-0' 1 mm. sheath. 1'6-9' mm. A. dattai Podder.... 1'34-3' x mm x 0 12 mm. (i) 0 68 x mm. (i) 0'05 mm. 4-6 dorsal & 2 ven- & x (U) 0'59 x 0'055 mm. (ii) 0 03 mm. tral '42 mm. Slightly longer than the (iii) 0'026 mm. proboscis sheath. 1 () '9 mm. A. sarcari, 8p. nov '76 0'138 x mm xo 150 mm. Much longer than the (i) mm. S dorsal & 2 ventrl'll. & x proboscis sheath, one (ii) 0'048 mm. 0'48-0'67 mm. nearly double the (iii) mm. length of the other ~9 (i) x mm. 0 3!l-1 01 mm. (ii) x mm. (iii) 48~
6 142 Reco'rds of the Indian Museum. [ VOL. XLIII, near the posterior extremity of the proboscis sheath. The prostatic gland is a single, syncitial mass, with 6-8 nuclei and the lacunar system is well developed. Host.-Rasbora elanga (Ham.) Location.-Intestine. Locality.-Calcutta, India. Type specimens.-(reg. No. W3445jl) Deposited in the collections of the Zoological Survey of India (Ind. Mus.), Calcutta. In conclusion, I have to express my hearty thanks to Dr. Baini Prashad, Director, Zoological Survey of India, Calcutta, for giving me facilities to consult the literature in the library and to Mr. M. N. Datta of the same department for his valuable suggestions. LIST OF REFERENCES. Podder, T. N., A new species of Acanthocephala, Acanthosentis dattai, n. sp., from a fresh-water fish of Bengal, Barbus tic to (Ham. Buch.) and B. stigma (Cuv. & Val.). Parasitology, XXX, pp Sen, P., n a new species of Acanthocephala, Acanthosentis holospinus sp. nov. from the fish Barbus stigma (Cu v. & Val.). Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci. VII, pp Verma, S. C. & Datta, M. N., Acanthocephala from N. India. I. A new genus of Acanthocephala from a Calcutta fish. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. XXII, pp
ACANTHOCEPHALAN PARASITES OF CERTAIN FISHES FROM CALCUrfA.
 ACANTHOCEPHALAN PARASITES OF CERTAIN FISHES FROM CALCUrfA. By'M. N. DATTA, M.Sc., M.R.A.S., Zoological Survey of India, OalcuUa, and T. N. PODDAR, M.B., M.Sc., Carmichael Medical Oollege, Oalcutta. (Plate
ACANTHOCEPHALAN PARASITES OF CERTAIN FISHES FROM CALCUrfA. By'M. N. DATTA, M.Sc., M.R.A.S., Zoological Survey of India, OalcuUa, and T. N. PODDAR, M.B., M.Sc., Carmichael Medical Oollege, Oalcutta. (Plate
On Devendrosentis garnai, Gen. et sp. nov (Neoechinorhynchidae Southwell and Macfie, 1925, Quadrigyridae Van Cleave 1920, Acanthocephala
 Annales de Parasitologie (Paris), t. 4 6, 1971, n 1, pp. 69 à 80 On Devendrosentis garnai, Gen. et sp. nov (Neoechinorhynchidae Southwell and Macfie, 1925, Quadrigyridae Van Cleave 1920, Acanthocephala
Annales de Parasitologie (Paris), t. 4 6, 1971, n 1, pp. 69 à 80 On Devendrosentis garnai, Gen. et sp. nov (Neoechinorhynchidae Southwell and Macfie, 1925, Quadrigyridae Van Cleave 1920, Acanthocephala
The Repr duct ve System. Function: producing offspring
 The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology
 Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology Development of the Pituitary Gland Lec 5: Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development Stomodeum Brain Infundibulum Rathke s Pouch Germ Cell Migration
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology Development of the Pituitary Gland Lec 5: Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development Stomodeum Brain Infundibulum Rathke s Pouch Germ Cell Migration
PHYLUM NEMATODA. Introduction. Ascaris lubricoides. External anatomy - preserved specimen. Internal anatomy - preserved specimen
 PHYLUM NEMATODA Introduction Commonly called round worms the phylum includes both free living and parasitic forms. Distinctive features include: a nearly perfect cylindrical body, radial or biradial arrangement
PHYLUM NEMATODA Introduction Commonly called round worms the phylum includes both free living and parasitic forms. Distinctive features include: a nearly perfect cylindrical body, radial or biradial arrangement
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology"
 Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System. Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems
 Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Zoology Exercise #10: Phylum Nematoda Lab Guide
 Zoology Exercise #10: Phylum Nematoda Lab Guide All animals with bilateral symmetry, except the acoelomates, have a body cavity. They are either true coelomates (where peritoneum covers both the inner
Zoology Exercise #10: Phylum Nematoda Lab Guide All animals with bilateral symmetry, except the acoelomates, have a body cavity. They are either true coelomates (where peritoneum covers both the inner
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
ZOOLOGISCHE MEDEDELINGEN
 MINISTERIE VAN ONDERWIJS, KUNSTEN EN WETENSCHAPPEN ZOOLOGISCHE MEDEDELINGEN UITGEGEVEN DOOR HET RIJKSMUSEUM VAN NATUURLIJKE HISTORIE TE LEIDEN DEEL XXX, No. 13 6 April 1949 NOTES ON SACCULINA CARPILIAE
MINISTERIE VAN ONDERWIJS, KUNSTEN EN WETENSCHAPPEN ZOOLOGISCHE MEDEDELINGEN UITGEGEVEN DOOR HET RIJKSMUSEUM VAN NATUURLIJKE HISTORIE TE LEIDEN DEEL XXX, No. 13 6 April 1949 NOTES ON SACCULINA CARPILIAE
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
The Male and Female Internal Genitalia. Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Male and Female Internal Genitalia Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Overview The reproductive role of the male is to produce sperm, deliver them to the female Primary sex organs are the gonads
The Male and Female Internal Genitalia Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Overview The reproductive role of the male is to produce sperm, deliver them to the female Primary sex organs are the gonads
SOME RHIZOCEPHALAN PARASITES OF XANTHID CRABS
 ZOOLOGY SOME RHIZOCEPHALAN PARASITES OF XANTHID CRABS BY H. BOSCHMA (Communicated at the meeting of May 20, 1950) The present paper deals with variation in two species of the genus LoxothylaCU8, each occurring
ZOOLOGY SOME RHIZOCEPHALAN PARASITES OF XANTHID CRABS BY H. BOSCHMA (Communicated at the meeting of May 20, 1950) The present paper deals with variation in two species of the genus LoxothylaCU8, each occurring
List of Equipment, Tools, Supplies, and Facilities:
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
NORTH AMERICAN TRICLAD TURBELLARIA, XIII:
 . PROCEEDINGS OF THE UNITED STATES NATIONAL MUSEUM issued pj^jn»il SSj^i h th* SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION U. S. NATIONAL MUSEUM Vol. 103 Washington: 1954 No. 3333 NORTH AMERICAN TRICLAD TURBELLARIA, XIII:
. PROCEEDINGS OF THE UNITED STATES NATIONAL MUSEUM issued pj^jn»il SSj^i h th* SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION U. S. NATIONAL MUSEUM Vol. 103 Washington: 1954 No. 3333 NORTH AMERICAN TRICLAD TURBELLARIA, XIII:
 STUDIES ON THE HELMINTH FAUNA OF JA Title55. FOUR NEW GENERA OF ACANTHOCEPHA FISHES Author(s) Yamaguti, Satyu Citation PUBLICATIONS OF THE SETO MARINE BIO LABORATORY (1959), 7(3): 319-326 Issue Date 1959-12-20
STUDIES ON THE HELMINTH FAUNA OF JA Title55. FOUR NEW GENERA OF ACANTHOCEPHA FISHES Author(s) Yamaguti, Satyu Citation PUBLICATIONS OF THE SETO MARINE BIO LABORATORY (1959), 7(3): 319-326 Issue Date 1959-12-20
ACANTHOMULUS. NOTE XIII. On two new species of the genus Acanthodrilus, Perr. from Liberia. Dr. R. Horst. Perr. from New-Caledonia,
 ACANTHOMULUS. 103 NOTE XIII. On two new species of the genus Acanthodrilus, Perr. from Liberia BY Dr. R. Horst Among the Invertebrates collected by Büttikofer and the late Sala during their journey in
ACANTHOMULUS. 103 NOTE XIII. On two new species of the genus Acanthodrilus, Perr. from Liberia BY Dr. R. Horst Among the Invertebrates collected by Büttikofer and the late Sala during their journey in
Internal Morphology. 1.Cut the legs and wings (if present) off your specimen. 5.Use forceps to pull skeleton apart, exposing internal systems.
 Internal Morphology Insect Dissections Often the best approach to understanding internal morphology is by way of a dissection. For this reason, the entire chapter should be treated as a laboratory activity.
Internal Morphology Insect Dissections Often the best approach to understanding internal morphology is by way of a dissection. For this reason, the entire chapter should be treated as a laboratory activity.
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology
 Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
THE SPECIFIC CHARACTERS OF SACCULINA ROTUNDATA MIERS AND SACCULINA YATSUI NOV. SPEC.
 THE SPECIFIC CHARACTERS OF SACCULINA ROTUNDATA MIERS AND SACCULINA YATSUI NOV. SPEC. by H. BOSCHMA In a previous paper (Boschma, 1935) I made some remarks concerning the parasites of Pachygrapsus crassipes
THE SPECIFIC CHARACTERS OF SACCULINA ROTUNDATA MIERS AND SACCULINA YATSUI NOV. SPEC. by H. BOSCHMA In a previous paper (Boschma, 1935) I made some remarks concerning the parasites of Pachygrapsus crassipes
To General Embryology Dr: Azza Zaki
 Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
FIGURE 54 represents the urogenital apparatus
 CHAPTER VI THE UROGENITAL ORGANS FIGURE 54 represents the urogenital apparatus of a thirty-inch female specimen of Alligator mississippiensis. Figure 55 shows the corresponding organs of a male A lucius;
CHAPTER VI THE UROGENITAL ORGANS FIGURE 54 represents the urogenital apparatus of a thirty-inch female specimen of Alligator mississippiensis. Figure 55 shows the corresponding organs of a male A lucius;
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Acta Medica Okayama. Parasitic Worms from Celebes. Part 8. Acantho-cephala. Satyu Yamaguti MARCH Volume 8, Issue Article 7
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 8, ssue 4 1952 Article 7 MARCH 1954 Parasitic Worms from Celebes. Part 8. Acantho-cephala Satyu Yamaguti Okayama University, Copyright c 1999 OKAYAMA UNVERSTY MEDCAL SCHOOL.
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 8, ssue 4 1952 Article 7 MARCH 1954 Parasitic Worms from Celebes. Part 8. Acantho-cephala Satyu Yamaguti Okayama University, Copyright c 1999 OKAYAMA UNVERSTY MEDCAL SCHOOL.
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Research Article ISSN VOL 5/ ISSUE 2/APRIL 2015 PRAGATI RASTOGI*, KAVITA RANI**, DEEPMALA MISHRA AND JYOTI SINGH
 REDESCRIPTION OF DACTYLOGYRUS KALYANENSIS, MUSSELIUS AND GUSSEV (1973) FROM GILLS OF WALLAGO ATTU AT GHAZIABAD. PRAGATI RASTOGI*, KAVITA RANI**, DEEPMALA MISHRA AND JYOTI SINGH *Assistant Professor, Department
REDESCRIPTION OF DACTYLOGYRUS KALYANENSIS, MUSSELIUS AND GUSSEV (1973) FROM GILLS OF WALLAGO ATTU AT GHAZIABAD. PRAGATI RASTOGI*, KAVITA RANI**, DEEPMALA MISHRA AND JYOTI SINGH *Assistant Professor, Department
Genus : Chilomastix mesnili Considered to be a non-pathogen, it ' s resides in cecum and colon. The life cycle of this parasite have two stages :
 Lecturer : Nerran K.F.AL- Rubaey Practical parasites Lab - 4 - Genus : Chilomastix mesnili Considered to be a non-pathogen, it ' s resides in cecum and colon. The life cycle of this parasite have two stages
Lecturer : Nerran K.F.AL- Rubaey Practical parasites Lab - 4 - Genus : Chilomastix mesnili Considered to be a non-pathogen, it ' s resides in cecum and colon. The life cycle of this parasite have two stages
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and
 Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
under its influence, male development occurs; in its absence, female development is established.
 Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Planktothuria diaphana, gen. et sp. n.
 PLANKTOTHCJEIA DIAPHANA. 375 Planktothuria diaphana, gen. et sp. n. By J. I>. F. Gilcluist, M.A., D.Sc, Ph.D., Professor of Zoology in the University of Cape Town. "With 4 Text-figures. THE subject of
PLANKTOTHCJEIA DIAPHANA. 375 Planktothuria diaphana, gen. et sp. n. By J. I>. F. Gilcluist, M.A., D.Sc, Ph.D., Professor of Zoology in the University of Cape Town. "With 4 Text-figures. THE subject of
CHAPTER 1 THE HUMAN BODY
 HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
The Alimentary Canal of the Aphid Prociphilus Tesselata Fitch
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 38, Issue 3 (May, 1938) 1938-05 The Alimentary Canal of the Aphid Prociphilus
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 38, Issue 3 (May, 1938) 1938-05 The Alimentary Canal of the Aphid Prociphilus
THE RESEARCH BULLETIN OF THE MEGURO PARASITOLOGICAL MUSEUM
 THE RESEARCH BULLETIN OF THE MEGURO PARASITOLOGICAL MUSEUM JULY 1971 NUMB!;R 5 RES. BU LL. MEGURO PARASIT. MUS. No.5, p. 1-5 1971 ON SOME PARASITES OF A COELACANTH (LATIMERIA CHALUMNAE): A NEW MONOGENEA,
THE RESEARCH BULLETIN OF THE MEGURO PARASITOLOGICAL MUSEUM JULY 1971 NUMB!;R 5 RES. BU LL. MEGURO PARASIT. MUS. No.5, p. 1-5 1971 ON SOME PARASITES OF A COELACANTH (LATIMERIA CHALUMNAE): A NEW MONOGENEA,
 Name: Date: Period: The Dissection 1. Place your specimen dorsal side down. Make your incisions following the diagram below. Make sure to make shallow cuts with the scissors. DO NOT CUT TOO DEEP! You will
Name: Date: Period: The Dissection 1. Place your specimen dorsal side down. Make your incisions following the diagram below. Make sure to make shallow cuts with the scissors. DO NOT CUT TOO DEEP! You will
Subfzmily Proterodiplostominae Dubois, 1936
 Rev Biol Trop, 14(1): 93 97, 1966 On Capsulodiplostomum crocodilinum n g, n sp (Trematoda, Digenea), from the Indian crocodile Crocodil us pal ustris by M P Dwivedi* Received for publication March 31,
Rev Biol Trop, 14(1): 93 97, 1966 On Capsulodiplostomum crocodilinum n g, n sp (Trematoda, Digenea), from the Indian crocodile Crocodil us pal ustris by M P Dwivedi* Received for publication March 31,
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
Penis and Prostate. Holly White Jennifer Zang September 7, Penis and Prostate. 1) Other Names None
 Penis and Prostate Penis and Prostate Holly White Jennifer Zang September 7, 2006 1) Other Names None 2) Definition/ Location The prostate is a doughnut-like gland that lies inferior to the urinary bladder
Penis and Prostate Penis and Prostate Holly White Jennifer Zang September 7, 2006 1) Other Names None 2) Definition/ Location The prostate is a doughnut-like gland that lies inferior to the urinary bladder
The Female Reproductive System
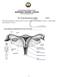 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Human Reproduction. Human Reproductive System. Scrotum. Male Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Digestive System. The group of organs which performs the function of digestion constitute digestive system.
 Digestive System Definition:- The active biological process by which food materials impermeable to the cell membrane is converted into permeable to the cell membrane is called digestion. The group of organs
Digestive System Definition:- The active biological process by which food materials impermeable to the cell membrane is converted into permeable to the cell membrane is called digestion. The group of organs
ENDOCRINE AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS MODULE. Academic Year Study Guide
 ENDOCRINE AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide Objectives of The Endocrine and Reproductive Systems At the end of these systems the students should recognize: 1. The histological
ENDOCRINE AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide Objectives of The Endocrine and Reproductive Systems At the end of these systems the students should recognize: 1. The histological
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Zoology. - Rhizocephalan parasites of crabs of the genus Metopograpsus. By H. BOSCHMA.
 Zoology. - Rhizocephalan parasites of crabs of the genus Metopograpsus. By H. BOSCHMA. (Communicated at the meeting of September 24, 1949.) The present paper contains notes on Rhizocephala of the crabs
Zoology. - Rhizocephalan parasites of crabs of the genus Metopograpsus. By H. BOSCHMA. (Communicated at the meeting of September 24, 1949.) The present paper contains notes on Rhizocephala of the crabs
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
A New Terrestrial Prosobranch Family (Tutuilanidae) I from Samoa, with Descriptions of a New Genus and a New Species*
 OCCASIONAL PAPERS OF BERNICE P. BISHOP MUSEUM HONOLULU, HAWAII Volume XX June 13, 1952 Number 18 A New Terrestrial Prosobranch Family (Tutuilanidae) I from Samoa, with Descriptions of a New Genus and a
OCCASIONAL PAPERS OF BERNICE P. BISHOP MUSEUM HONOLULU, HAWAII Volume XX June 13, 1952 Number 18 A New Terrestrial Prosobranch Family (Tutuilanidae) I from Samoa, with Descriptions of a New Genus and a
Inferior Pelvic Border
 Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Chapter 16 Endocrine and Reproductive Health
 Note Taking Lesson 2 The Male Reproductive System Directions: Use the following outline to help organize your notes as you read through the lesson. Key Concept Consider and Reconsider Before reading the
Note Taking Lesson 2 The Male Reproductive System Directions: Use the following outline to help organize your notes as you read through the lesson. Key Concept Consider and Reconsider Before reading the
31-2. The Earthworm. . Relate the structure of systems. . Demonstrate dissection technique. . Identifythe major advancesof
 Name Class Date INVESTIGATION 31-2 The Earthworm Introduction The earthworm is a segmented worm. It exhibits more complex structures than any of the more primitive animals that you have studied thus far.
Name Class Date INVESTIGATION 31-2 The Earthworm Introduction The earthworm is a segmented worm. It exhibits more complex structures than any of the more primitive animals that you have studied thus far.
Draft. Draft. 2. The system of breeding which breeds a registered male to a registered female animal of the same breed is:
 Student Name: Draft Teacher: Date: District: Wake County Assessment: 9_12 Agriculture AA21 - Animal Science I Test 4 Description: Test 7: Reproduction & Genetics Form: 501 Draft 1. Superior traits of offspring
Student Name: Draft Teacher: Date: District: Wake County Assessment: 9_12 Agriculture AA21 - Animal Science I Test 4 Description: Test 7: Reproduction & Genetics Form: 501 Draft 1. Superior traits of offspring
Four New Lepocreadiid Digeneans (Trematoda) from Marine Fishes of Southern Japan and the Philippines
 Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Ser. A, 38(4), pp. 149 157, November 22, 2012 Four New Lepocreadiid Digeneans (Trematoda) from Marine Fishes of Southern Japan and the Philippines Masaaki Machida Department
Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Ser. A, 38(4), pp. 149 157, November 22, 2012 Four New Lepocreadiid Digeneans (Trematoda) from Marine Fishes of Southern Japan and the Philippines Masaaki Machida Department
Growth and Development 6 th Grade
 Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Rec. zoot. Surv. India, 97 (Part-2) : , 1999
 Rec. zoot. Surv. India, 97 (Part-2) : 167-172, 1999 DESCRIPTIONS OF TWO NEW GALL MIDGES (DIPTERA : CECIDOMYIIDAE).FROM NILGIRI BIOSPHERE RESERVE, KARNATAKA R. M. SHARMA Zoological Survey of India, Western
Rec. zoot. Surv. India, 97 (Part-2) : 167-172, 1999 DESCRIPTIONS OF TWO NEW GALL MIDGES (DIPTERA : CECIDOMYIIDAE).FROM NILGIRI BIOSPHERE RESERVE, KARNATAKA R. M. SHARMA Zoological Survey of India, Western
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Pop Quiz 2. Give the dominant body form for each. List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Scyphozoa anthozoa
 Pop Quiz 2 Give the dominant body form for each Scyphozoa anthozoa List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms - the Simplest Bilateral Animals
Pop Quiz 2 Give the dominant body form for each Scyphozoa anthozoa List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms - the Simplest Bilateral Animals
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Genital Ganglion and Associated Nerves in Male Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus (Acanthocephala)1
 Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 46(1), 1979, pp. 106-114 Genital Ganglion and Associated Nerves in Male Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus (Acanthocephala)1 T. T. DUNAGAN AND DONALD M. MlLLER Department of
Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 46(1), 1979, pp. 106-114 Genital Ganglion and Associated Nerves in Male Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus (Acanthocephala)1 T. T. DUNAGAN AND DONALD M. MlLLER Department of
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Guide to Small Animal Reproductive Imaging using the Vevo 770
 Guide to Small Animal Reproductive Imaging using the Vevo 770 Course Objectives: After completion of this module, the participant will be able to accomplish the following: Recognize reproductive female
Guide to Small Animal Reproductive Imaging using the Vevo 770 Course Objectives: After completion of this module, the participant will be able to accomplish the following: Recognize reproductive female
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
General Body Plan. Diploblastic. Tissue. Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes. epidermis gastrodermis
 General Body Plan Diploblastic Tissue epidermis gastrodermis Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes General Body Plan Dimorphism: 2 different body forms are usually present in the life cycle: oral aboral aboral
General Body Plan Diploblastic Tissue epidermis gastrodermis Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes General Body Plan Dimorphism: 2 different body forms are usually present in the life cycle: oral aboral aboral
Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop
 Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop Animal Nutrition and Physiology Center, North Dakota State University Sponsors: American Sheep and Goat Center, North Dakota State University, University
Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop Animal Nutrition and Physiology Center, North Dakota State University Sponsors: American Sheep and Goat Center, North Dakota State University, University
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
258 DANIEL A. TEXTORIS Vol. 63
 258 DANIEL A. TEXTORIS Vol. 63 STUDIES OF THE GYPONINAE 1. THE GENUS MARGANANA DELONG* (HOMOPTERA: CICADELLIDAE) DWIGHT M. DELONG AND PAUL H. PREYTAG Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State
258 DANIEL A. TEXTORIS Vol. 63 STUDIES OF THE GYPONINAE 1. THE GENUS MARGANANA DELONG* (HOMOPTERA: CICADELLIDAE) DWIGHT M. DELONG AND PAUL H. PREYTAG Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State
Chapter 22 - Nematodes: Form, Function, and Classification
 1 Chapter 22 - Nematodes: Form, Function, and Classification Structure of the Adult Nematodes are elongate, cylindrical, and tapered at both ends The basic body design is a tube within a tube, the outer
1 Chapter 22 - Nematodes: Form, Function, and Classification Structure of the Adult Nematodes are elongate, cylindrical, and tapered at both ends The basic body design is a tube within a tube, the outer
Male Anatomy. testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics
 Male Anatomy Male Anatomy Primary Organ testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics 1) Secondary Organs internal
Male Anatomy Male Anatomy Primary Organ testes, genetically determined in mammals - testis releases hormones that then control the development of secondary sex characteristics 1) Secondary Organs internal
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
