Disruption of the Ventral Visual Stream in a Case of Reduplicative Paramnesia
|
|
|
- Barbara Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Disruption of the Ventral Visual Stream in a Case of Reduplicative Paramnesia ANDREW E. BUDSON, a,b,c,d HEIDI L. ROTH, e DORENE M. RENTZ, b,c,f AND MICHAEL RONTHAL c,f b Division of Cognitive and Behavioral Neurology, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, USA c Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA d Department of Psychology, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA e Department of Neurology, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, USA f Department of Neurology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, USA INTRODUCTION Reduplicative paramnesia (RP), a syndrome named by Pick in 1903 to describe a specific and limited disturbance of memory, is characterized by a subjective certainty that a familiar place or person has been duplicated. 1 Most often seen in posttraumatic brain injuries, this syndrome has been described in a variety of neurologic conditions, including strokes, intracerebral hemorrhages, tumors, dementias, encephalopathies, and various psychiatric conditions. 2 The classic and most commonly described neuroanatomical localization is the combination of bilateral frontal lobe and right hemisphere lesions. 3,4 Although many theories have been advanced to explain how these lesions could produce this syndrome, the specific pathophysiology is unknown. We report a patient who provides anatomical and neuropsychological support for the theory that RP is a syndrome that may develop in a vulnerable brain by a lesion in the ventral visual stream, disrupting communication between the visual cortex and both visual processing areas in the inferior temporal lobe and visual memory in the nondominant parahippocampal region. CASE REPORT The patient, OB, was a 45-year-old left-handed man with a history of alcoholism, diabetes, and hypertension, who had been admitted to the hospital for a minor operation. Two weeks prior to admission, he stopped drinking. Ten days into his hospital stay, the nursing staff reported that OB was confused, not knowing where his room was. The neurology service was consulted. Most of the bedside mental status examination, carried out in his hospital room, was normal, including being oriented to a Address for correspondence: Andrew E. Budson, Division of Cognitive and Behavioral Neurology, Brigham and Women s Hospital, 221 Longwood Avenue, Boston, MA Tel.: (617) ; fax: (617) abudson@yahoo.com 447
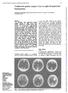
2 448 ANNALS NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Boston, Beth Israel Hospital, 7th floor. However, when OB was asked to put on his glasses for the visual exam, he pointed to his roommate s bed and said that the glasses were in his other room, explaining that we were presently in his room in the hallway. When pressed about why he should have a room in the hallway and why he should have two rooms, he acknowledged that he was unable to resolve these contradictions. Over the next few days, when questioned as to where he was (when in his hospital room), he again sometimes reported that he was in his room in the hallway and at other times that he was in his room at his house. At all times, he believed that he had another room that was located in the correct place in the hospital, although he never reported being in this other room. He was not concerned about his orientation difficulties. He was able to provide a coherent history of his hospitalization. His neurological examination was significant for mild clumsiness and autotopagnosia (incorrect somatotopic localization) of the right hand. Neuropsychological testing was obtained, revealing decreased performance of complex attention and response inhibition tasks, mild right-sided neglect, and moderately impaired visuospatial integration and visual memory (see TABLE 1 for these and other results). An electroencephalogram and lumbar puncture were obtained. Brain MRI revealed a small, linear, nonenhancing lesion in the white matter of the left temporo-parieto-occipital junction, which was hyperintense on T2 and proton density images and isointense on T1, consistent with a subacute stroke (see FIG. 1). The duplication of his hospital room persisted throughout the remainder of his hospitalization. In follow-up visits to the neurology clinic, although his paramnesia and autotopagnosia had resolved, he now complained of memory problems. DISCUSSION Explanations as to the etiology of RP began with Pick, who hypothesized that his patient produced the duplication due to a convulsive attack interrupting conscious memory. 1 Weinstein and Kahn postulated a psychodynamic theory based upon a patient s denial of illness. 5 Benson, Gardner, and Meadows studied three patients with traumatic brain injury, all of whom had both right hemisphere and bifrontal damage. 3 They suggested that the right hemisphere injury rendered patients unable to correctly update their orientation due to impaired visuospatial perception and visual memory, while their frontal lobe dysfunction left them unable to resolve the conflict that inevitably arose when the assumptions of their orientation were challenged. Other authors have also found disruption of visual perception, including facial recognition, in patients with Capgras syndrome (CS), a subset of RP in which close acquaintances are regarded as imposters. 4,6 8 Because CS can be thought of as the mirror image of proposagnosia, Ellis and Young hypothesized that it was likely due to a lesion that disrupts the dorsal visual stream. 6 In their discussion of a case of a patient with CS in the visual (but not the auditory) modality, Hirstein and Ramachandran argued that it was more likely that this syndrome would be caused by disruption of the ventral visual stream, producing in their patient a failure of communication between the temporal lobe and the limbic complex. 9 Imaging studies of this patient, however, did not show the specific lesion that they postulated. Our patient developed a reduplicative paramnesic disturbance specific to the location of his room following a small left hemisphere stroke. Although one might ar-
3 BUDSON et al.: REDUPLICATIVE PARAMNESIA 449 FIGURE 1. T2-weighted axial MRI image demonstrating a small, linear area of hyperintensity consistent with a subacute stroke (arrow) in the white matter adjacent to Brodmann areas 19 and 37, a localization consistent with the occipitotemporal projection system, the fiber pathway of the ventral visual stream. 10 Location of the stroke was confirmed by lesion analysis as described by Damasio and Damasio. 13 gue that his paramnesia may have been part of a more general confusional state, this is unlikely given that he showed no evidence of confusion other than for the location of his room, he had no difficulty in providing a coherent history of recent events, and he performed well on tests of simple attention such as Digit Span (7 forward, 7 backward). The stroke damaged the white matter adjacent to Brodmann areas 19 and 37 and most likely disrupted the occipitotemporal projection system, the fiber pathway of the ventral visual stream. 10 This disruption, interfering with the communication between the visual cortex and both visual processing areas in the inferior temporal lobe and visual memory of the nondominant parahippocampal region, can explain OB s difficulty with tests of visuospatial perception and visual memory. Our lefthanded patient may also have reversed dominance for visual memory, which would
4 450 ANNALS NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TABLE 1. Results and interpretation of tests and examinations Tests and examinations Results Interpretation Bedside mental status testing Months backward Intact Normal Calculations Intact Normal Confrontational naming Intact Normal Comprehension of complex commands Intact Normal Writing a sentence Intact Normal Repetition Intact Normal Right/left confusion Absent Normal Finger agnosia Absent Normal Recent memory: current events Intact Normal Remote memory: personal history Intact Normal Copy 3-dimensional figure Normal Normal Clock drawing Intact Normal Neurological examination Cranial nerves including vision Intact Normal Strength Normal Normal Reflexes Loss of ankle reflexesabnormal Sensation General Mild peripheral Abnormal neuropathy Two-point discrimination Intact Normal Autotopagnosia (somatotopic localization) Mild disruption on Abnormal right hand Stereognosis & graphesthesia Intact Normal Coordination Mild right-sided Abnormal clumsiness Plantar reflexes Flexor Normal Asterixis Absent Normal Neuropsychological tests 12 General Intelligence American National Adult Reading Test Est. IQ = 118 High average Simple and complex attention Digit Span 7F, 7B High average Trails A 58 s, 10th percentile Mild to moderate Trails B 115 s, 15th percentile Mild to moderate Response inhibition Short Stroop 67 s, 2 errors Mild to moderate Verbal fluency Word generation: F words 20 words High average Word generation: animals 18 words High average Language Boston Naming Test 55/60 Average Verbal memory Wechsler: Logical Memory I immediate 32nd percentile Average Wechsler: Logical Memory II delayed 62nd percentile Average Visual memory Wechsler: Visual Memory I immediate 32nd percentile Average continued
5 BUDSON et al.: REDUPLICATIVE PARAMNESIA 451 TABLE 1. Results and interpretation of tests and examinations Tests and examinations Results Interpretation Wechsler: Visual Memory II delayed 12th percentile Mild to moderate Visuospatial ability Hooper Visual Organization Test 15/25 Moderate Ravens Colored Matrices 5th percentile, est. visual IQ = 75 Moderate to severe Visuospatial attention Letter cancellation test Mild right-sided Mild omissions Lumbar puncture Unremarkable Normal Electroencephalogram Transient bi-temporal and independent left mid-temporal theta activity with hyperventilation Abnormal Brain MRI (see FIG. 1) Left posterior stroke Abnormal explain why the disturbance of left parahippocampal pathways could more likely produce the syndrome in his case. (Support for the possibility of reversed dominance comes from the fact that, with a left-sided lesion, our patient s verbal memory was above average and his visual memory a nondominant hemisphere function was impaired.) In addition, OB had evidence of frontal lobe dysfunction, as can be seen in his poor performance on tests of complex attention and response inhibition. Alcoholism has been shown to be a cause of selective bifrontal dysfunction 11 and is most likely the cause of his difficulty with those tests. Our patient thus provides radiologic evidence to support the theory that the critical pathology in RP is the combination of disruption of the ventral visual stream of the nondominant hemisphere, leading to inaccurate orientation, and bifrontal dysfunction that allows this inaccurate and confused orientation to be tolerated. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thank Daniel Z. Press, Jeremey D. Schmahmann, and Kirk R. Daffner for their thoughtful discussions. REFERENCES 1. PICK, A Clinical studies: III. On reduplicative paramnesia. Brain 26: FORSTL, H., O.P. ALMEIDA, A.M. OWEN, A. BURNS & R. HOWARD Psychiatric, neurological, and medical aspects of misidentification syndromes: a review of 260 cases. Psychiatr. Med. 21: BENSON, D.F., H. GARDNER & J.C. MEADOWS Reduplicative paramnesia. Neurology 26: ALEXANDER, M.P., D.T. STUSS & D.F. BENSON Capgras syndrome: a reduplicative phenomenon. Neurology 29:
6 452 ANNALS NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES 5. WEINSTEIN, E.A. & R.L. KAHN Denial of Illness: Symbolic and Physiological Aspects. Thomas. Springfield, IL. 6. ELLIS, H.D. & A.W. YOUNG Accounting for delusional misidentifications. Br. J. Psychiatry 157: ELLIS, H.D The role of the right hemisphere in the Capgras delusion. Psychopathology 27: SILVA, J.A. & G.B. LEONG Visual-perceptual abnormalities in delusional misidentification. Can. J. Psychiatry 40: HIRSTEIN, W. & V.S. RAMACHANDRAN Capgras syndrome: a novel probe for understanding the neural representation of the identity and familiarity of persons. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 264: TUSA, R.T. & L.G. UNGERLEIDER The inferior longitudinal fasciculus: a reexamination in humans and monkeys. Ann. Neurol. 18: HAKIM, H., N.P. VERMA & M.F. GREIFFENSTEIN Pathogenesis of reduplicative paramnesia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 51: LEZAK, M.D Neuropsychological Assessment. Oxford Univ. Press. London/ New York. 13. DAMASIO, H. & A.R. DAMASIO Lesion Localization in Neuropsychology. Oxford Univ. Press. London/New York.
우측전두정엽뇌경색환자에서발생한재생가능성기억착오증 증례보고
 Brain & NeuroRehabilitation Vol. 6, No. 1, March, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.12786/bn.2013.6.1.41 우측전두정엽뇌경색환자에서발생한재생가능성기억착오증 증례보고 고려대학교안암병원재활의학과 최태웅ㆍ편성범 Reduplicative Paramnesia after Right Frontoparietal
Brain & NeuroRehabilitation Vol. 6, No. 1, March, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.12786/bn.2013.6.1.41 우측전두정엽뇌경색환자에서발생한재생가능성기억착오증 증례보고 고려대학교안암병원재활의학과 최태웅ㆍ편성범 Reduplicative Paramnesia after Right Frontoparietal
Pick Paterson 1944
 383 33 1 1 28 4 383 391 2008 Key Words reduplicative paramnesia geographical mislocation double orientation identity right frontal lobe reduplicative paramnesia Pick 1901 1903 2 Ruff 1981 Staton 1982 Patterson
383 33 1 1 28 4 383 391 2008 Key Words reduplicative paramnesia geographical mislocation double orientation identity right frontal lobe reduplicative paramnesia Pick 1901 1903 2 Ruff 1981 Staton 1982 Patterson
Excellent Network Courses. Department of Neurology Affiliated hospital of Jiangsu University
 Excellent Network Courses Department of Neurology Affiliated hospital of Jiangsu University Agnosia Visual Agnosia Lissauer (1890) described 2 types: a) Apperceptive Cannot see objects b) Associative Does
Excellent Network Courses Department of Neurology Affiliated hospital of Jiangsu University Agnosia Visual Agnosia Lissauer (1890) described 2 types: a) Apperceptive Cannot see objects b) Associative Does
Chapter 3: 2 visual systems
 Chapter 3: 2 visual systems Overview Explain the significance of the turn to the brain in cognitive science Explain Mishkin and Ungerleider s hypothesis that there are two distinct visual systems Outline
Chapter 3: 2 visual systems Overview Explain the significance of the turn to the brain in cognitive science Explain Mishkin and Ungerleider s hypothesis that there are two distinct visual systems Outline
Sensorimotor Functioning. Sensory and Motor Systems. Functional Anatomy of Brain- Behavioral Relationships
 Sensorimotor Functioning Sensory and Motor Systems Understanding brain-behavior relationships requires knowledge of sensory and motor systems. Sensory System = Input Neural Processing Motor System = Output
Sensorimotor Functioning Sensory and Motor Systems Understanding brain-behavior relationships requires knowledge of sensory and motor systems. Sensory System = Input Neural Processing Motor System = Output
FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION. Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni
 FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni VISUAL AGNOSIA -damage to the extrastriate visual regions (occipital, parietal and temporal lobes) disrupts recognition of complex visual stimuli
FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni VISUAL AGNOSIA -damage to the extrastriate visual regions (occipital, parietal and temporal lobes) disrupts recognition of complex visual stimuli
Disorders of Object and Spatial perception. Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital.
 Disorders of Object and Spatial perception Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital. Take Home Message 1 Where there are lesions of the posterior cerebrum and posterior temporal
Disorders of Object and Spatial perception Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital. Take Home Message 1 Where there are lesions of the posterior cerebrum and posterior temporal
What theoretical interpretations of Capgras Delusion exist and to what extent are they supported by neurological evidence?
 1 What theoretical interpretations of Capgras Delusion exist and to what extent are they supported by neurological evidence? Abstract Capgras Delusion (CD) is a rare Delusional Misidentification Syndrome
1 What theoretical interpretations of Capgras Delusion exist and to what extent are they supported by neurological evidence? Abstract Capgras Delusion (CD) is a rare Delusional Misidentification Syndrome
Physical Assessment. Class 1
 Physical Assessment Class 1 Objectives Class 1: Objectives: Review Syllabus and Class Goals and Format At the end of the class, the student will be able to: Understand the components and functions of the
Physical Assessment Class 1 Objectives Class 1: Objectives: Review Syllabus and Class Goals and Format At the end of the class, the student will be able to: Understand the components and functions of the
Use a diagnostic neuropsychology HOW TO DO IT PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY
 170 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY HOW TO DO IT Pract Neurol: first published as 10.1046/j.1474-7766.2003.08148.x on 1 June 2003. Downloaded from http://pn.bmj.com/ Use a diagnostic neuropsychology on 16 October
170 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY HOW TO DO IT Pract Neurol: first published as 10.1046/j.1474-7766.2003.08148.x on 1 June 2003. Downloaded from http://pn.bmj.com/ Use a diagnostic neuropsychology on 16 October
shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all of the above.
 Section: Chapter 14: Multiple Choice 1. Alex the parrot: pp.529-530 shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all
Section: Chapter 14: Multiple Choice 1. Alex the parrot: pp.529-530 shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all
Agnosia, Epilepsy, Sleep Walking, and DID. D. Kiper
 Agnosia, Epilepsy, Sleep Walking, and DID D. Kiper 6.12.2018 Agnosia A-gnosis (absence of knowledge); Seelenblindheit; agnosia (Freud) Akinetopsia Achromatopsia Capgras syndrome DF: A Visual Agnostic DF
Agnosia, Epilepsy, Sleep Walking, and DID D. Kiper 6.12.2018 Agnosia A-gnosis (absence of knowledge); Seelenblindheit; agnosia (Freud) Akinetopsia Achromatopsia Capgras syndrome DF: A Visual Agnostic DF
Identify these objects
 Pattern Recognition The Amazing Flexibility of Human PR. What is PR and What Problems does it Solve? Three Heuristic Distinctions for Understanding PR. Top-down vs. Bottom-up Processing. Semantic Priming.
Pattern Recognition The Amazing Flexibility of Human PR. What is PR and What Problems does it Solve? Three Heuristic Distinctions for Understanding PR. Top-down vs. Bottom-up Processing. Semantic Priming.
Chapter 2, Wondrous Strange: The Neuropsychology of Abnormal Beliefs
 PHIL 5983: Irrational Belief Seminar Prof. Funkhouser 1/30/13 Pathologies of Belief, Chapters 2-4 Chapter 2, Wondrous Strange: The Neuropsychology of Abnormal Beliefs 1. * Delusions are bizarre and not
PHIL 5983: Irrational Belief Seminar Prof. Funkhouser 1/30/13 Pathologies of Belief, Chapters 2-4 Chapter 2, Wondrous Strange: The Neuropsychology of Abnormal Beliefs 1. * Delusions are bizarre and not
Models of Face Recognition and Delusional Misidentification: A Critical Review
 Models of Face Recognition and Delusional Misidentification: A Critical Review Nora Breen1,2, Diana Caine2,3, Max Coltheart1 1 Department of Psychology, Macquarie University, NSW, Australia. 2 Neuropsychology
Models of Face Recognition and Delusional Misidentification: A Critical Review Nora Breen1,2, Diana Caine2,3, Max Coltheart1 1 Department of Psychology, Macquarie University, NSW, Australia. 2 Neuropsychology
The Neuropsychology of
 The Neuropsychology of Stroke Tammy Kordes, Ph.D. Northshore Neurosciences Outline What is the Role of Neuropsychology Purpose of Neuropsychological Assessments Common Neuropsychological Disorders Assessment
The Neuropsychology of Stroke Tammy Kordes, Ph.D. Northshore Neurosciences Outline What is the Role of Neuropsychology Purpose of Neuropsychological Assessments Common Neuropsychological Disorders Assessment
Cerebral Cortex Structure, Function, Dysfunction Reading Ch 10 Waxman Dental Neuroanatomy Lecture. Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D.
 Cerebral Cortex Structure, Function, Dysfunction Reading Ch 10 Waxman Dental Neuroanatomy Lecture Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D. March 7, 2012 Anatomy Review Lobes and layers Brodmann s areas Vascular Supply
Cerebral Cortex Structure, Function, Dysfunction Reading Ch 10 Waxman Dental Neuroanatomy Lecture Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D. March 7, 2012 Anatomy Review Lobes and layers Brodmann s areas Vascular Supply
Learning Objectives.
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language
 Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language Based on: Chapter 18 and 19, Breedlove, Watson, Rosenzweig, 6e/7e. Cerebral Cortex Brain s most complex area with billions of neurons and
Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language Based on: Chapter 18 and 19, Breedlove, Watson, Rosenzweig, 6e/7e. Cerebral Cortex Brain s most complex area with billions of neurons and
The significance of sensory motor functions as indicators of brain dysfunction in children
 Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 18 (2003) 11 18 The significance of sensory motor functions as indicators of brain dysfunction in children Abstract Ralph M. Reitan, Deborah Wolfson Reitan Neuropsychology
Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 18 (2003) 11 18 The significance of sensory motor functions as indicators of brain dysfunction in children Abstract Ralph M. Reitan, Deborah Wolfson Reitan Neuropsychology
Higher Cortical Function
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
FRONTAL LOBE. Central Sulcus. Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Sulcus. Cingulate Sulcus. Lateral Sulcus
 FRONTAL LOBE Central Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Cingulate Lateral Lateral View Medial View Motor execution and higher cognitive functions (e.g., language production, impulse inhibition, reasoning
FRONTAL LOBE Central Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Cingulate Lateral Lateral View Medial View Motor execution and higher cognitive functions (e.g., language production, impulse inhibition, reasoning
Unilateral spatial neglect due to right frontal lobe haematoma
 J7ournal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:89-93 Unilateral spatial neglect due to right frontal lobe haematoma Shinichiro Maeshima, Kazuyoshi Funahashi, Mitsuhiro Ogura, Toru Itakura,
J7ournal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:89-93 Unilateral spatial neglect due to right frontal lobe haematoma Shinichiro Maeshima, Kazuyoshi Funahashi, Mitsuhiro Ogura, Toru Itakura,
DISORDERS OF PATTERN RECOGNITION
 DISORDERS OF PATTERN RECOGNITION A. Visual agnosia inability to identify objects by sight Types (1) apperceptive agnosia unable to form stable [presemantic] representations of objects (2) associative agnosia
DISORDERS OF PATTERN RECOGNITION A. Visual agnosia inability to identify objects by sight Types (1) apperceptive agnosia unable to form stable [presemantic] representations of objects (2) associative agnosia
Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex. 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations. 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage
 Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage Sensory to Motor Transformation Sensory information (visual,
Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage Sensory to Motor Transformation Sensory information (visual,
How to Think like a Neurologist Review of Exam Process and Assessment Findings
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
battery assessing general cognitive functioning (Mini-Mental State Examination, MMSE),
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Neuropsychological battery Patients tested at the Rotman Research Institute were administered a neuropsychological battery assessing general cognitive functioning (Mini-Mental State
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Neuropsychological battery Patients tested at the Rotman Research Institute were administered a neuropsychological battery assessing general cognitive functioning (Mini-Mental State
Exam 1 PSYC Fall 1998
 Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology
 Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
M P---- Ph.D. Clinical Psychologist / Neuropsychologist
 M------- P---- Ph.D. Clinical Psychologist / Neuropsychologist NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION Name: Date of Birth: Date of Evaluation: 05-28-2015 Tests Administered: Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Fourth
M------- P---- Ph.D. Clinical Psychologist / Neuropsychologist NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION Name: Date of Birth: Date of Evaluation: 05-28-2015 Tests Administered: Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Fourth
EARLY ONSET FRONTOTERMPORAL DEMENTIA AND ALZHEIMERS DISEASE: DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT AND CARE
 EARLY ONSET FRONTOTERMPORAL DEMENTIA AND ALZHEIMERS DISEASE: DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT AND CARE John Rudge, BA Hons This thesis is presented as partial requirement for the degree of Doctor of Psychology at
EARLY ONSET FRONTOTERMPORAL DEMENTIA AND ALZHEIMERS DISEASE: DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT AND CARE John Rudge, BA Hons This thesis is presented as partial requirement for the degree of Doctor of Psychology at
How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? brain. deprived of sight?
 How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? What happens to visual-devoted brain structure in individuals who are born deprived of sight?
How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? What happens to visual-devoted brain structure in individuals who are born deprived of sight?
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg
 Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Frégoli Syndrome Accompanied with Prosopagnosia in a Woman with a 40-year History of Schizophrenia.
 Case Report Frégoli Syndrome Accompanied with Prosopagnosia in a Woman with a 40-year History of Schizophrenia. Yasushi Moriyama, 1 Taro Muramatsu, 2 Motoichiro Kato, 2 Masaru Mimura, 3 Tomoko Akiyama,
Case Report Frégoli Syndrome Accompanied with Prosopagnosia in a Woman with a 40-year History of Schizophrenia. Yasushi Moriyama, 1 Taro Muramatsu, 2 Motoichiro Kato, 2 Masaru Mimura, 3 Tomoko Akiyama,
The origins of localization
 Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
MOS SF-36 health survey (Ware &
 Biomedical and Physical Functioning General Health Height Weight Waist Circumfernece % Body Fat Tanita scale BMI Self-rated Health - overall clinical protocol Self-rated Health - rel. to age clinical protocol
Biomedical and Physical Functioning General Health Height Weight Waist Circumfernece % Body Fat Tanita scale BMI Self-rated Health - overall clinical protocol Self-rated Health - rel. to age clinical protocol
Russell M. Bauer, Ph.D. February 27, 2006
 1 Neuropsychological Aspects of Frontal Lobe Function Russell M. Bauer, Ph.D. February 27, 2006 2 Important Concepts Phylogenetically newest area of cortex Exquisite connectivity based on feedback loops
1 Neuropsychological Aspects of Frontal Lobe Function Russell M. Bauer, Ph.D. February 27, 2006 2 Important Concepts Phylogenetically newest area of cortex Exquisite connectivity based on feedback loops
Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) Overview for Best Practice in Stroke and Complex Neurological Conditions March 2013
 Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) Overview for Best Practice in Stroke and Complex Neurological Conditions March 2013 1 MoCA 2 Overview of the MoCA Takes approximately 15 minutes to administer Requires
Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) Overview for Best Practice in Stroke and Complex Neurological Conditions March 2013 1 MoCA 2 Overview of the MoCA Takes approximately 15 minutes to administer Requires
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions. Michael E. Goldberg, M.D.
 Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Godefroy, O., Fickl, A., Roussel, M., Auribault, C., Bugnicourt, J. M., Lamy, C., Petitnicolas, G. (2011). Is the Montreal cognitive assessment superior to the mini-mental
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Godefroy, O., Fickl, A., Roussel, M., Auribault, C., Bugnicourt, J. M., Lamy, C., Petitnicolas, G. (2011). Is the Montreal cognitive assessment superior to the mini-mental
Understanding Brain-Behavior Relationships in Children p. 123 Medical and Neurological Disorders of Childhood p. 124 Issues Particular to Pediatric
 Contributors About this handbook p. 3 Clinical Neuropsychology: General Issues The Medical Chart: Efficient Information-Gathering Strategies and Proper Chart Noting p. xix The Chart Review p. 10 The Progress
Contributors About this handbook p. 3 Clinical Neuropsychology: General Issues The Medical Chart: Efficient Information-Gathering Strategies and Proper Chart Noting p. xix The Chart Review p. 10 The Progress
Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues. Outline. Starting Points. Starting Points
 Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Background Maintenance: Modality specificity and buffers Interference resolution: Distraction and
Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Background Maintenance: Modality specificity and buffers Interference resolution: Distraction and
PARIETAL LOBE. Vasilios A. Zerris MD, MPH, MSc, FAANS
 PARIETAL LOBE Vasilios A. Zerris MD, MPH, MSc, FAANS Diplomate of the American Board of Neurological Surgery Fellow of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons Professor of Neurosurgery, European
PARIETAL LOBE Vasilios A. Zerris MD, MPH, MSc, FAANS Diplomate of the American Board of Neurological Surgery Fellow of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons Professor of Neurosurgery, European
Dementia. Assessing Brain Damage. Mental Status Examination
 Dementia Assessing Brain Damage Mental status examination Information about current behavior and thought including orientation to reality, memory, and ability to follow instructions Neuropsychological
Dementia Assessing Brain Damage Mental status examination Information about current behavior and thought including orientation to reality, memory, and ability to follow instructions Neuropsychological
Human Paleoneurology and the Evolution of the Parietal Cortex
 PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Devenney E, Bartley L, Hoon C, et al. Progression in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia: a longitudinal study. JAMA Neurol. Published online October 26, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.2061.
Supplementary Online Content Devenney E, Bartley L, Hoon C, et al. Progression in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia: a longitudinal study. JAMA Neurol. Published online October 26, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.2061.
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal.
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural activity in the brain This leads to several interesting
Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural activity in the brain This leads to several interesting
The Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes 3/2/2011. Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions. Readings: KW Ch.
 The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications.
 Dr. Peter J. Fiester November 14, 2012 Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications. Briefly discuss a few examples
Dr. Peter J. Fiester November 14, 2012 Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications. Briefly discuss a few examples
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2010)
 PERSEVERATIONS IN ALZHEIMER DISEASE: ANALYSIS OF THE DISTURBANCE AND POSSIBLE CORRELATIONS M. D Antonio¹, L. Trojano², M. R. De Riso², D. Grossi ² and A. M. Fasanaro¹, ¹Alzheimer Unit, Neurology Department,
PERSEVERATIONS IN ALZHEIMER DISEASE: ANALYSIS OF THE DISTURBANCE AND POSSIBLE CORRELATIONS M. D Antonio¹, L. Trojano², M. R. De Riso², D. Grossi ² and A. M. Fasanaro¹, ¹Alzheimer Unit, Neurology Department,
Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. Lecture 3: Disorders of Perception
 Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology Lecture 3: Disorders of Perception Sensation vs Perception Senses capture physical energy from environment that are converted into neural signals and elaborated/interpreted
Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology Lecture 3: Disorders of Perception Sensation vs Perception Senses capture physical energy from environment that are converted into neural signals and elaborated/interpreted
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory
 Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Table 7.2B: Summary of Select Screening Tools for Assessment of Vascular Cognitive Impairment in Stroke Patients
 Table 7.2B: Summary of Select Screening Tools for Assessment of Vascular Cognitive Impairment in Stroke Patients Recommended First Line Screening and s Montreal Cognitive (MoCA) The MoCA is available for
Table 7.2B: Summary of Select Screening Tools for Assessment of Vascular Cognitive Impairment in Stroke Patients Recommended First Line Screening and s Montreal Cognitive (MoCA) The MoCA is available for
Surgery for Medically Refractory Focal Epilepsy
 Surgery for Medically Refractory Focal Epilepsy Seth F Oliveria, MD PhD The Oregon Clinic Neurosurgery Director of Functional Neurosurgery: Providence Brain and Spine Institute Portland, OR Providence
Surgery for Medically Refractory Focal Epilepsy Seth F Oliveria, MD PhD The Oregon Clinic Neurosurgery Director of Functional Neurosurgery: Providence Brain and Spine Institute Portland, OR Providence
Memory. Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith
 Memory Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith Note: Due to copyright restrictions, I had to remove the images from the Weschler Memory Scales from the slides I posted online. Wechsler Memory Scales
Memory Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith Note: Due to copyright restrictions, I had to remove the images from the Weschler Memory Scales from the slides I posted online. Wechsler Memory Scales
Process of a neuropsychological assessment
 Test selection Process of a neuropsychological assessment Gather information Review of information provided by referrer and if possible review of medical records Interview with client and his/her relative
Test selection Process of a neuropsychological assessment Gather information Review of information provided by referrer and if possible review of medical records Interview with client and his/her relative
Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis
 97 Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis a) Name the 5 main subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal, and limbic (on the medial side) b) Locate the
97 Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis a) Name the 5 main subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal, and limbic (on the medial side) b) Locate the
Dominant Limb Motor Impersistence Associated with Anterior Callosal Disconnection
 Dominant Limb Motor Impersistence Associated with Anterior Callosal Disconnection S. W. Seo, MD, 1 K. Jung, MS, 2 H. You, PhD 2, E. J. Kim, MD, PhD 1, B. H. Lee, MA, 1 D. L. Na, MD 1 1 Department of Neurology,
Dominant Limb Motor Impersistence Associated with Anterior Callosal Disconnection S. W. Seo, MD, 1 K. Jung, MS, 2 H. You, PhD 2, E. J. Kim, MD, PhD 1, B. H. Lee, MA, 1 D. L. Na, MD 1 1 Department of Neurology,
Chapter 6. Attention. Attention
 Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
SECTION 1: as each other, or as me. THE BRAIN AND DEMENTIA. C. Boden *
 I read all the available books by other [people with] Alzheimer s disease but they never had quite the same problems as each other, or as me. I t s not like other diseases, where there is a standard set
I read all the available books by other [people with] Alzheimer s disease but they never had quite the same problems as each other, or as me. I t s not like other diseases, where there is a standard set
P1: OTA/XYZ P2: ABC c01 BLBK231-Ginsberg December 23, :43 Printer Name: Yet to Come. Part 1. The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 Part 1 The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 2 Chapter 1 Neurological history-taking The diagnosis and management of diseases of the nervous system have been revolutionized in recent years by
Part 1 The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 2 Chapter 1 Neurological history-taking The diagnosis and management of diseases of the nervous system have been revolutionized in recent years by
T he neurological examination is often used to decide
 545 PAPER Detection of focal cerebral hemisphere lesions using the neurological examination N E Anderson, D F Mason, J N Fink, P S Bergin, A J Charleston, G D Gamble... See end of article for authors affiliations...
545 PAPER Detection of focal cerebral hemisphere lesions using the neurological examination N E Anderson, D F Mason, J N Fink, P S Bergin, A J Charleston, G D Gamble... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing. Comprehensive Assessment. Scope of Practice. Chapter 11 Assessment
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 11 Assessment Comprehensive Assessment Enables nurse to: Make sound clinical judgments Plan appropriate interventions Scope of Practice Collect and
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 11 Assessment Comprehensive Assessment Enables nurse to: Make sound clinical judgments Plan appropriate interventions Scope of Practice Collect and
THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. February 16, 2012 Objectives: THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS A. Draw the expected visual fields seen in classic lesions of the nerve, chiasm, thalamus, optic
Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. February 16, 2012 Objectives: THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS A. Draw the expected visual fields seen in classic lesions of the nerve, chiasm, thalamus, optic
Disorders of spelling
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1964, 27, 224 M. KINSBOURNE AND ELIZABETH K. WARRINGTON From the National Hospital, Queen Square, London, and the Department of Neurology, United Oxford Hospitals The writing
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1964, 27, 224 M. KINSBOURNE AND ELIZABETH K. WARRINGTON From the National Hospital, Queen Square, London, and the Department of Neurology, United Oxford Hospitals The writing
Recognition memory in psychotic patients
 Behavioural Neurology (1992), S, 23-26 Recognition memory in psychotic patients H. Ellis1, K. De Pauw2, G.N. Christodoulou3, J.-P. Luaute4, E. Bidault 4 and K. Szulecka 5 1 School of Psychology, University
Behavioural Neurology (1992), S, 23-26 Recognition memory in psychotic patients H. Ellis1, K. De Pauw2, G.N. Christodoulou3, J.-P. Luaute4, E. Bidault 4 and K. Szulecka 5 1 School of Psychology, University
Cortical Organization. Functionally, cortex is classically divided into 3 general types: 1. Primary cortex:. - receptive field:.
 Cortical Organization Functionally, cortex is classically divided into 3 general types: 1. Primary cortex:. - receptive field:. 2. Secondary cortex: located immediately adjacent to primary cortical areas,
Cortical Organization Functionally, cortex is classically divided into 3 general types: 1. Primary cortex:. - receptive field:. 2. Secondary cortex: located immediately adjacent to primary cortical areas,
Nature, prevalence and clinical significance. Barcelona, Spain
 Nature, prevalence and clinical significance Jaime Kulisevsky Barcelona, Spain 1 Non motor (neuropsychiatric) symptoms are an integral part of Parkinson s s disease (PD) Affective disorders And are associated
Nature, prevalence and clinical significance Jaime Kulisevsky Barcelona, Spain 1 Non motor (neuropsychiatric) symptoms are an integral part of Parkinson s s disease (PD) Affective disorders And are associated
RECOGNITION AND MANAGEMENT OF DEMENTIA IN THE ACUTE CARE SETTING
 RECOGNITION AND MANAGEMENT OF DEMENTIA IN THE ACUTE CARE SETTING Alex Hishaw, MD Department of Neurology University of Arizona Objectives: Recognize the impact of history and presentation on the diagnosis
RECOGNITION AND MANAGEMENT OF DEMENTIA IN THE ACUTE CARE SETTING Alex Hishaw, MD Department of Neurology University of Arizona Objectives: Recognize the impact of history and presentation on the diagnosis
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Fundamentals of Cognitive Psychology, 3e by Ronald T. Kellogg Chapter 2. Multiple Choice
 Multiple Choice 1. Which structure is not part of the visual pathway in the brain? a. occipital lobe b. optic chiasm c. lateral geniculate nucleus *d. frontal lobe Answer location: Visual Pathways 2. Which
Multiple Choice 1. Which structure is not part of the visual pathway in the brain? a. occipital lobe b. optic chiasm c. lateral geniculate nucleus *d. frontal lobe Answer location: Visual Pathways 2. Which
Neuropsychological Evaluation of
 Neuropsychological Evaluation of Alzheimer s Disease Joanne M. Hamilton, Ph.D. Shiley-Marcos Alzheimer s Disease Research Center Department of Neurosciences University of California, San Diego Establish
Neuropsychological Evaluation of Alzheimer s Disease Joanne M. Hamilton, Ph.D. Shiley-Marcos Alzheimer s Disease Research Center Department of Neurosciences University of California, San Diego Establish
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics August 2014, Volume 16, Number 8:
 Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics August 2014, Volume 16, Number 8: 626-630. STATE OF THE ART AND SCIENCE Use of Art Making in Treating Older Patients with Dementia Laura T.
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics August 2014, Volume 16, Number 8: 626-630. STATE OF THE ART AND SCIENCE Use of Art Making in Treating Older Patients with Dementia Laura T.
Psy /16 Human Communication. By Joseline
 Psy-302 11/16 Human Communication By Joseline Lateralization Left Hemisphere dominance in speech production in 95% of right handed and 70% of left handed people Left -> Timing, Sequence of events Right
Psy-302 11/16 Human Communication By Joseline Lateralization Left Hemisphere dominance in speech production in 95% of right handed and 70% of left handed people Left -> Timing, Sequence of events Right
The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology?
 ECOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY, 13(2), 117 122 Copyright 2001, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology? Patrick R. Green Department
ECOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY, 13(2), 117 122 Copyright 2001, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology? Patrick R. Green Department
Number perseveration in healthy subjects: Does prolonged stimulus exposure influence performance on a serial addition task?
 Number perseveration in healthy subjects: Does prolonged stimulus exposure influence performance on a serial addition task? Vaitsa Giannouli School of Medicine, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece
Number perseveration in healthy subjects: Does prolonged stimulus exposure influence performance on a serial addition task? Vaitsa Giannouli School of Medicine, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece
Cognitive recovery after severe head injury 2. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale during post-traumatic amnesia
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 1127-1132 Cognitive recovery after severe head injury 2. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale during post-traumatic amnesia IAN A. MANDLEBERG
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 1127-1132 Cognitive recovery after severe head injury 2. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale during post-traumatic amnesia IAN A. MANDLEBERG
Northeast Center for Special Care Grant Avenue Lake Katrine, NY
 300 Grant Avenue Lake Katrine, NY 12449 845-336-3500 Information Bulletin What is Brain Mapping? By Victor Zelek, Ph.D., Director of Neuropsychological Services Diplomate, National Registry of Neurofeedback
300 Grant Avenue Lake Katrine, NY 12449 845-336-3500 Information Bulletin What is Brain Mapping? By Victor Zelek, Ph.D., Director of Neuropsychological Services Diplomate, National Registry of Neurofeedback
Anosognosia for Hemiplegia
 Anosognosia for Hemiplegia Anosognosia Denial of illness (paralysis, also blindness) Limb doesn t move, but no expression of frustration Confabulation: arm belongs to someone else Rationalization: didn
Anosognosia for Hemiplegia Anosognosia Denial of illness (paralysis, also blindness) Limb doesn t move, but no expression of frustration Confabulation: arm belongs to someone else Rationalization: didn
Memory Development. Cognitive Development
 Memory Development Cognitive Development Memory as information storage Memory Why does our memory sometimes fail us? Memory Schachter s Seven Sins of Memory 1. Transience 2. Absent-Mindedness 3. Blocking
Memory Development Cognitive Development Memory as information storage Memory Why does our memory sometimes fail us? Memory Schachter s Seven Sins of Memory 1. Transience 2. Absent-Mindedness 3. Blocking
Copyright 2002 American Academy of Neurology. Volume 58(8) 23 April 2002 pp
 Copyright 2002 American Academy of Neurology Volume 58(8) 23 April 2002 pp 1288-1290 Improved executive functioning following repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation [Brief Communications] Moser,
Copyright 2002 American Academy of Neurology Volume 58(8) 23 April 2002 pp 1288-1290 Improved executive functioning following repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation [Brief Communications] Moser,
Topics in Spatial Cognition from Barbara Hidalgo-Sotelo
 Topics in Spatial Cognition from Barbara Hidalgo-Sotelo Spatial frames of reference Structure of space Arriving at a unified sense of space is complex Three cases: (1)Hemispatial Neglect (2)Visual form
Topics in Spatial Cognition from Barbara Hidalgo-Sotelo Spatial frames of reference Structure of space Arriving at a unified sense of space is complex Three cases: (1)Hemispatial Neglect (2)Visual form
A Healthy Brain. An Injured Brain
 A Healthy Brain Before we can understand what happens when a brain is injured, we must realize what a healthy brain is made of and what it does. The brain is enclosed inside the skull. The skull acts as
A Healthy Brain Before we can understand what happens when a brain is injured, we must realize what a healthy brain is made of and what it does. The brain is enclosed inside the skull. The skull acts as
HAL author manuscript
 HAL author manuscript Cortex; a journal devoted to the study of the nervous system and behavior 2008;44(2):10 The neural correlates of visual mental imagery: an ongoing debate Paolo Bartolomeo Inserm Unit
HAL author manuscript Cortex; a journal devoted to the study of the nervous system and behavior 2008;44(2):10 The neural correlates of visual mental imagery: an ongoing debate Paolo Bartolomeo Inserm Unit
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Hemispheric Specialization (lateralization) Each lobe of the brain has specialized functions (Have to be careful with this one.)
 Cerebral Cortex Principles contralaterality the right half of your brain controls the left half of your body and vice versa. (contralateral control.) Localization of function Specific mental processes
Cerebral Cortex Principles contralaterality the right half of your brain controls the left half of your body and vice versa. (contralateral control.) Localization of function Specific mental processes
Exploration of a weighed cognitive composite score for measuring decline in amnestic MCI
 Exploration of a weighed cognitive composite score for measuring decline in amnestic MCI Sarah Monsell NACC biostatistician smonsell@uw.edu October 6, 2012 Background Neuropsychological batteries used
Exploration of a weighed cognitive composite score for measuring decline in amnestic MCI Sarah Monsell NACC biostatistician smonsell@uw.edu October 6, 2012 Background Neuropsychological batteries used
NO LOWER COGNITIVE FUNCTIONING IN OLDER ADULTS WITH ATTENTION-DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER
 CHAPTER 6 NO LOWER COGNITIVE FUNCTIONING IN OLDER ADULTS WITH ATTENTION-DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER INT PSYCHOGERIATR, 2015, 27(9): 1467 1476 DOI: 10.1017/S1041610215000010 73 NO LOWER COGNITIVE FUNCTIONING
CHAPTER 6 NO LOWER COGNITIVE FUNCTIONING IN OLDER ADULTS WITH ATTENTION-DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER INT PSYCHOGERIATR, 2015, 27(9): 1467 1476 DOI: 10.1017/S1041610215000010 73 NO LOWER COGNITIVE FUNCTIONING
Cesarean section for breech presentation. Jonathan H. Waters, M.D.
 Cesarean section for breech presentation Jonathan H. Waters, M.D. 1 26 y.o. G1P0 presented to triage in labor at 38 weeks. Patient was a known breech with a failed version 5 days before presentation. PMH
Cesarean section for breech presentation Jonathan H. Waters, M.D. 1 26 y.o. G1P0 presented to triage in labor at 38 weeks. Patient was a known breech with a failed version 5 days before presentation. PMH
October 2, Memory II. 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome. 9 Recent/Remote Distinction. 11 Frontal/Executive Contributions to Memory
 1 Memory II October 2, 2008 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay Impaired recollection of events learned prior
1 Memory II October 2, 2008 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay Impaired recollection of events learned prior
C:\Documents and Settings\sstensaas\Desktop\dental visual 2010\VisualPath dental 2010.docVisualPath dental 2010.doc
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas April 8, 2010, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15, Computer Resources: HyperBrain Ch 7 THE VISUAL PATHWAY Objectives: 1. Describe the pathway of visual information from
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas April 8, 2010, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15, Computer Resources: HyperBrain Ch 7 THE VISUAL PATHWAY Objectives: 1. Describe the pathway of visual information from
Cognitive Assessment. Part Two: Assessing Capacity, Beyond The Basics. Using Information To Make Decisions (Appreciating) What s s The Correct Method?
 AUTONOMY, CAPACITY AND UNDUE INFLUENCE: KEMP Page 1 of 9 Part Two: Assessing Capacity, Beyond The Basics Cognitive Assessment Bryan Kemp, Ph. D. Center of Excellence in Elder Abuse and Neglect UC Irvine
AUTONOMY, CAPACITY AND UNDUE INFLUENCE: KEMP Page 1 of 9 Part Two: Assessing Capacity, Beyond The Basics Cognitive Assessment Bryan Kemp, Ph. D. Center of Excellence in Elder Abuse and Neglect UC Irvine
Neuroscience Tutorial
 Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
Functional Neuroanatomy. IBRO ISN African Neuroscience School 4-13 th Dec 2014 Nairobi, Kenya
 Functional Neuroanatomy IBRO ISN African Neuroscience School 4-13 th Dec 2014 Nairobi, Kenya What is/are the function(s) of the nervous system? Sensation Perception Visceral activities (Homeostasis) Behavior
Functional Neuroanatomy IBRO ISN African Neuroscience School 4-13 th Dec 2014 Nairobi, Kenya What is/are the function(s) of the nervous system? Sensation Perception Visceral activities (Homeostasis) Behavior
High Yield Neurological Examination
 High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization
 Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 1 7.1 Overview This chapter aims to provide a framework for modeling cognitive phenomena based
Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 1 7.1 Overview This chapter aims to provide a framework for modeling cognitive phenomena based
ACCESS CENTER:
 ACCESS CENTER: 1-877-367-8855 Emergency Specialty Services: BRAIN ATTACK Criteria: Stroke symptom onset time less than 6 hours Referring Emergency Department Patient Information Data: Time last known normal:
ACCESS CENTER: 1-877-367-8855 Emergency Specialty Services: BRAIN ATTACK Criteria: Stroke symptom onset time less than 6 hours Referring Emergency Department Patient Information Data: Time last known normal:
Assessing the Stroke Patient. Arlene Boudreaux, MSN, RN, CCRN, CNRN
 Assessing the Stroke Patient Arlene Boudreaux, MSN, RN, CCRN, CNRN Cincinnati Pre-Hospital Stroke Scale May be done by EMS o One of many o F facial droop on one side o A arm drift (hold a pizza box, close
Assessing the Stroke Patient Arlene Boudreaux, MSN, RN, CCRN, CNRN Cincinnati Pre-Hospital Stroke Scale May be done by EMS o One of many o F facial droop on one side o A arm drift (hold a pizza box, close
