Chapter two Neuroscience and Biological Founda-ons
|
|
|
- Jack Quentin Shields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter two Neuroscience and Biological Founda-ons Our Gene-c Inheritance Neural Bases of Behavior Nervous System Organiza-on A Tour Through the Brain realworldpsychology Things You ll Learn in Chapter 2 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Can our genes influence whom we vote for in presidenaal elecaons? Why can spending the first few months of life in an orphanage lead to long- term problems in cogniave funcaoning? How can a chemical in the brain lead rats to binge- eat M&Ms? How can stem cell injecaons lead to restored vision and improved recovery from strokes? Why are former NFL athletes at increased risk of depression, demenaa, and suicide? OUR GENETIC INHERITANCE 1
2 Behavior Genetics The study of how heredity and environment affect us EvoluAonary psychology = the applica-on of principles of evolu-on to explain behavior and mental processes Genes control the transmission of traits Modern research shows most human characteris-cs are polygenic (controlled by mul-ple genes, not merely one dominant or two recessive genes) Virtual Field Trip: Reading Your DNA Most serious gene-c disorders are not transmiued by dominant genes. Why? realworldpsychology Most people understand that genes affect our health, such as poten-al for heart disease, diabetes, and cancer Genes also affect our personality traits, behavioral habits, sexual orienta-on, and psychological disorders Q1 Can our genes influence whom we vote for in presidenaal elecaons? Genes can even influence which poli-cal party we side with, and our views on death penalty, unemployment, and abor-on (Hatemi & McDermoU, 2012) Video: Lifespan Gene Video: Genome ABCs Gene- Environment Interaction Environmental factors both physical and psychological also influence our characteris-cs Malnourished children may not reach their full poten-al gene-c height or maximum intelligence Video: Gene Therapy Safety Tutorial Video: The InteracAon of Genes and Environment 2
3 Genes vs. Environment Iden-cal twins share all their genes, How can fraternal twins share about half of their psychologists genes (just like non- twin siblings) separate gene-c Twins raised together by birth parents causes from share the same environment environmental Iden-cal twins should be more alike than causes? fraternal twins (such as in intelligence) Research on adop-ve children can trace characteris-cs to birth parents vs. adop-ve parents Research shows many psychological traits (and disorders) run in biological families Heritability Heritability = the percentage of varia-on in a popula-on auributable to heredity If no gene-c influence, heritability would be 0% If no environmental influence, heritability would be 100% Heritability does NOT apply to INDIVIDUALS Heritability does not trump environment Evolutionary Psychology Many behaviors emerged and s-ll exist because they helped our ancestors survive Natural selecaon = par-cular gene-c trait gives an organism a reproduc-ve advantage Reproduc-on of the fiuest, not survival of the fiuest Video: What Sex Is Your Brain? 3
4 NEURAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR The Basics Building blocks of brain and nervous system: Neurons = responsible for receiving, processing, and transmihng electrochemical informa-on Glial cells = provide structure, nutri-on and other support to neurons Video: Stem Cell Shakes Parts of a Neuron Dendrites = branching fibers that receive impulses from other neurons and send them to the cell body Cell body = AKA soma, contains cell nucleus Axon = long, tube- like structure that sends impulses away from cell body to other neurons (or to muscles, glands) Video: Cell Scouts 4
5 Action Potential Action Potential Sequence of depolariza-on and repolariza-on moves the ac-on poten-al from the cell body to the axon terminal buuons like the wave Electricity moves 36 million meters/second Nerve impulses move 10 meters/second Nerve impulses move 10x faster through axons with myelin sheath Q2 Speed of Thought Why can spending the first few months of life in an orphanage lead to long- term problems in cogniave funcaoning? Social isola-on during early weeks/months of life (as for babies in orphanage) prevents proper growth of myelin, leading to long- term cogni-ve impairment 5
6 Communication Between Communica-on WITHIN neuron is electrical, but communica-on BETWEEN neurons is chemical Sending neuron gets close to receiving neuron at synapac gap, where neurotransmi[ers (chemicals) cross the gap to deliver the message How Neurotransmitters Work Reuptake Lock and Key 6
7 Common Neurotransmitters Endorphins Common neurotransmiuer elevate mood, reduce pain Opium- based drugs mimic the body s natural endorphins Q3 How can a chemical in the brain lead rats to binge- eat M&Ms? Endorphins affect memory, learning, appe-te, and sexual ac-vity. Rats injected with endorphins ate 5% of their body weight in M&Ms! Video: Brain Viagara Hormones & the Endocrine System Endocrine system = network of glands located throughout the body that secretes hormones into the bloodstream Neurons send messages to certain receptors; hormone messages are carried by the blood to any cell that will listen Regulates and maintains long- term body processes, such as growth, sexual characteris-cs, diges-on, and elimina-on Controls response to emergencies: adrenal glands release cor-sol, epinephrine, and norepinephrine 7
8 NERVOUS SYSTEM ORGANIZATION Central Nervous System (CNS) CNS is powerful, but fragile NeuroplasAcity = brain can reorganize its func-onal structure due to usage and experience Q4 How can stem cell injecaons lead to restored vision and improved recovery from strokes? Neurogenesis = lost cells can be replaced by neural stem cells (rare immature cells that can migrate and grow into any type of cell). No cell transplant for spinal cord injuries in humans, but animal research shows stem cell treatment leads to improvement in paralyzed limbs Video: Mending Broken Hearts 8
9 Spinal Cord Relays AND ini-ates vital informa-on to other parts of the body Reflexes = automa-c behavior in response to s-muli Allows immediate ac-on without delay of rou-ng through brain What is the evolu-onary benefit of the reflex arc? Newborn ReLlexes A B C RooAng reflex Lightly stroke the cheek and watch how the infant automa-cally (reflexively) turns toward the s-mula-on and auempts to suck Grasping Reflex Place your finger or an object in the infant s palm and note the automa-c grasp Babinski Reflex Lightly stroke the sole of the foot, and the big toe will move toward the top, while the other toes fan out. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) The part of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord Carries informa-on to and from the CNS Links brain and spinal cord to body s sense receptors, muscles and glands SomaAc nervous system (SNS): carries sensory informa-on to the brain and instruc-ons back to skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): responsible for involuntary tasks like heart rate, diges-on, and breathing 9
10 Autonomic Nervous System SympatheAc division: mobilizes energy to respond to stressor (fight or flight) ParasympatheAc division: calms body to conserve energy, returns body to normal func-oning ater stress A TOUR THROUGH THE BRAIN Biological Tools for Research Virtual Field Trip: Neuroimaging 10
11 Biological Tools for Research (cont.) Forebrain Limbic System The interconnected group of forebrain structures involved with emoaons, drives, and memory, as well as major physiological funcaons Cerebral Cortex The thin surface layer that regulates most complex behavior (i.e. sensaaons, motor control). AnimaAon: The Brain Limbic System Hippocampus Seahorse shaped part of the limbic system involved in forming and retrieving memories Amygdala Part of the limbic system that controls emoaons, like aggression and fear. 11
12 realworldpsychology Cerebral cortex = surface layer of the brain Responsible for most complex behaviors and higher mental processes Damage to cerebral cortex linked to substance abuse, demen-a, and suicide Q5 Why are former NFL athletes at increased risk of depression, demenaa, and suicide? Trauma is par-cularly common in contact sports, like football, ice hockey, boxing, and soccer Lobes Tutorial Video: Build a Brain Learning AcAvity Tutorial Video: DissecAng the Brain realworldpsychology In 1848, 25- year- old railroad worker Phineas Gage had a metal rod accidentally blown through the front of his face, destroying much of his brain s frontal lobe Experienced dras-c personality changes; became impa-ent and lacked concern for coworkers He eventually obtained a job driving a stagecoach, which required high motor, cogni-ve, and interpersonal skills Video: Kid Concussions What does modern research about neuroplas-city tell us about Gage s possible recovery? 12
13 Two Brains in One? Each hemisphere controls the opposite site of the body Corpus callosum = thick band of nerves, connects the two hemispheres Although each side of the brain might have a specialty (like Broca s area for speech in the let hemisphere), when specific regions of the brain are injured or destroyed their func-ons can be assumed by neighboring region or even opposite hemisphere realworldpsychology Popular myth says let brain is analy-cal and right brain manages crea-vity Research shows both hemispheres work together in an integrated manner, like teammates playing soccer; each area might have special-es, but everyone knows what the other is doing and can help when needed Video: Watching Living Brains 13
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Biological Psychology
 Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Nervous System. Lesson 11
 Nervous System Lesson 11 Reflex Arcs 1. Patellar reflex Causes leg to kick up 2. Achilles reflex Causes foot to jerk forward 3. Triceps reflex Causes arm to straighten 4. Babinski reflex 4. Pupil Dilation
Nervous System Lesson 11 Reflex Arcs 1. Patellar reflex Causes leg to kick up 2. Achilles reflex Causes foot to jerk forward 3. Triceps reflex Causes arm to straighten 4. Babinski reflex 4. Pupil Dilation
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
35-2 The Nervous System
 1 of 38 Do Now Finish the matching quiz. You may use your brain hat to help you. 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous
1 of 38 Do Now Finish the matching quiz. You may use your brain hat to help you. 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous
Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2
 NAME PER DATE Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2 Matching: 1. afferent nerves 2. autonomic nervous system 3. cell body 4. central nervous system (CNS) 5. dendrites 6. efferent nerves 7. myelin sheath
NAME PER DATE Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2 Matching: 1. afferent nerves 2. autonomic nervous system 3. cell body 4. central nervous system (CNS) 5. dendrites 6. efferent nerves 7. myelin sheath
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
 Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Structure of the Cortex
 Structure of the Cortex Introduction Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Structure of the Cortex Glial cells ( glue cells ) Lobes Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Occipital lobes Temporal lobes Structure of the Cortex
Structure of the Cortex Introduction Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Structure of the Cortex Glial cells ( glue cells ) Lobes Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Occipital lobes Temporal lobes Structure of the Cortex
Biological Psychology. Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!!
 Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
The Nervous System II Neurons
 The Nervous System II Neurons Review Nervous System What is it? The system that receives, processes, stores and transmits information that comes from various parts of the body and the external world. Composed
The Nervous System II Neurons Review Nervous System What is it? The system that receives, processes, stores and transmits information that comes from various parts of the body and the external world. Composed
Week 2 Psychology. The Brain and Behavior
 Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Biological Process 9/7/10. (a) Anatomy: Neurons have three basic parts. 1. The Nervous System: The communication system of your body and brain
 Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
 Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Bio11: The Nervous System. Body control systems. The human brain. The human brain. The Cerebrum. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Chapter 8. The Nervous System
 Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior. Definitions
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
Neural and Hormonal Systems
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
Unit 3 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism
 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
The Nervous System IN DEPTH
 The Nervous System IN DEPTH The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Note taking tips Make sure that you have written
The Nervous System IN DEPTH The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Note taking tips Make sure that you have written
Vocabulary. Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold
 Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
How We Grow & Change
 How We Grow & Change Neural Development What makes up nerves? Neurons! (single cells) Interesting Facts About Neurons: Average brain has approx 100 billion neurons and we only use 10% (10 billion neurons)!
How We Grow & Change Neural Development What makes up nerves? Neurons! (single cells) Interesting Facts About Neurons: Average brain has approx 100 billion neurons and we only use 10% (10 billion neurons)!
Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior. Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed)
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
AP PSYCH Unit 3A Biological Basis Of Behavior Neural Processing & The Endocrine System
 AP PSYCH Unit 3A Biological Basis Of Behavior Neural Processing & The Endocrine System 1. Everything psychological is simultaneously biological 2. What are neurons and how do they communicate? 3. How do
AP PSYCH Unit 3A Biological Basis Of Behavior Neural Processing & The Endocrine System 1. Everything psychological is simultaneously biological 2. What are neurons and how do they communicate? 3. How do
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD
 Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain
 Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain What does the Brain do? Stand up Walk around every person you pass tell them a different function the brain performs Do this until you are told to stop
Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain What does the Brain do? Stand up Walk around every person you pass tell them a different function the brain performs Do this until you are told to stop
Body control systems. Nervous system. Organization of Nervous Systems. The Nervous System. Two types of cells. Organization of Nervous System
 Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (QUESTIONS) Start at:
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (QUESTIONS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (QUESTIONS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON
 UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON CHARACTERISTICS COMPLEXITY: nerve cells connecting allow you to do EVERYTHING you will ever do INTEGRATION: brain pulls all information you get together
UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON CHARACTERISTICS COMPLEXITY: nerve cells connecting allow you to do EVERYTHING you will ever do INTEGRATION: brain pulls all information you get together
Neuroscience. Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior.
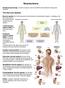 Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior. The Nervous System: Nervous system: the body s speedy electrochemical communication network, consisting of
Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior. The Nervous System: Nervous system: the body s speedy electrochemical communication network, consisting of
Neuroscience. Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior 1/11/2010. The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biological Bases of Behavior
 Biological Bases of Behavior What do neurons look like? I These are the basic parts Types of Neurons What do neurons (really) look like? What do neurons do? Collect inputs on their If sufficient input
Biological Bases of Behavior What do neurons look like? I These are the basic parts Types of Neurons What do neurons (really) look like? What do neurons do? Collect inputs on their If sufficient input
The Nervous System. The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind.
 The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
Chapter Two: Biology and Psychology
 Chapter Two: Biology and Psychology The Nervous System: On Being Wired Phineas (1) had a tamping rod shoot through the (2) lobe of his brain. He (3) but his (4) changed significantly. The nervous system
Chapter Two: Biology and Psychology The Nervous System: On Being Wired Phineas (1) had a tamping rod shoot through the (2) lobe of his brain. He (3) but his (4) changed significantly. The nervous system
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
netw rks Guided Reading Activity Body and Behavior Lesson 1 The Basics of the Nervous System Review Questions: Outlining
 Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 The Basics of the Nervous System Review Questions: Outlining Directions: Read the lesson and complete the outline below. Refer to your textbook to fill in the blanks. I.
Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 The Basics of the Nervous System Review Questions: Outlining Directions: Read the lesson and complete the outline below. Refer to your textbook to fill in the blanks. I.
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Chapter 4. The Brain
 Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems. Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers
 Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How Do Genetic Factors Affect Behavior? II. Does Our Evolutionary Heritage Influence Current Behavior? III. How is the Nervous
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How Do Genetic Factors Affect Behavior? II. Does Our Evolutionary Heritage Influence Current Behavior? III. How is the Nervous
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s
 Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s movements, sends and carries signals to and from the different
Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s movements, sends and carries signals to and from the different
Copyright 2017 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 1
 1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test
 AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
Unit Six The Nervous System
 Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
-The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment
 -The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to maintain an organism
-The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to maintain an organism
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Why does the writer above love running so much? One of the reasons. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure. Reader s Guide. Exploring Psychology
 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Reader s Guide Main Idea Learning about the nervous system helps us know how messages that are sent to the brain cause behavior. Vocabulary central nervous system
The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Reader s Guide Main Idea Learning about the nervous system helps us know how messages that are sent to the brain cause behavior. Vocabulary central nervous system
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1
 Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
THE CONTROL SYSTEMS NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE
 THE CONTROL SYSTEMS NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE Introduction to nervous system There are 3 main parts to your Nervous System 1. Your Nerves 2. Your Brain 3. Your Spinal Cord Your Nerves Your nerves are made
THE CONTROL SYSTEMS NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE Introduction to nervous system There are 3 main parts to your Nervous System 1. Your Nerves 2. Your Brain 3. Your Spinal Cord Your Nerves Your nerves are made
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY
 Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY 1. Describe, in correct order, the events that occur during the transmission of a nerve impulse (action potential) as it travels from point X to point Y.
Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY 1. Describe, in correct order, the events that occur during the transmission of a nerve impulse (action potential) as it travels from point X to point Y.
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology
 PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Neural and Hormonal Systems
 Neural and Hormonal Systems Explains why we feel strong, sad, happy & nervous. Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that transmit signals throughout the body Soma The cell body of a neuron,
Neural and Hormonal Systems Explains why we feel strong, sad, happy & nervous. Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that transmit signals throughout the body Soma The cell body of a neuron,
The Nervous System & Nervous tissue. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Nervous System & Nervous tissue Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of the Nervous System 1. Nervous system and endocrine system are the chief control centers in maintaining body homeostasis. 2. Nervous
The Nervous System & Nervous tissue Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of the Nervous System 1. Nervous system and endocrine system are the chief control centers in maintaining body homeostasis. 2. Nervous
Body control systems. Let s start at the top: the human brain. The Cerebrum. The human brain. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
The Nervous System. Nerves, nerves everywhere!
 The Nervous System Nerves, nerves everywhere! Purpose of the Nervous System The information intake and response system of the body. Coordinates all body functions, voluntary and involuntary! Responds to
The Nervous System Nerves, nerves everywhere! Purpose of the Nervous System The information intake and response system of the body. Coordinates all body functions, voluntary and involuntary! Responds to
Chapter 2. An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology
 Page 1 Chapter 2 An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology One-Dimensional vs. Multidimensional Models One-Dimensional Models Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach Could mean an emphasis
Page 1 Chapter 2 An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology One-Dimensional vs. Multidimensional Models One-Dimensional Models Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach Could mean an emphasis
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
From Implantation to Neural Tube
 By 28 weeks after conception, brain has virtually all the neurons it will ever have. At birth, the brain weighs about.75lb (25% of adult weight) At 3 years of age, 80% of adult weight. At 5 years of age,
By 28 weeks after conception, brain has virtually all the neurons it will ever have. At birth, the brain weighs about.75lb (25% of adult weight) At 3 years of age, 80% of adult weight. At 5 years of age,
Meyers' A&P February 15, Unit 7. The Nervous System. I. Functions of the Nervous System. Monitors body's internal and external enviornments
 Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
What two body systems work together to carry Out regulation?
 What is regulation? -The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to
What is regulation? -The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to
Fig Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
Biological Basis of Behavior. Chapter 2
 Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
[RG online edits added ; updated ] Unit 3: The Nervous System. Introduction
![[RG online edits added ; updated ] Unit 3: The Nervous System. Introduction [RG online edits added ; updated ] Unit 3: The Nervous System. Introduction](/thumbs/79/79754305.jpg) [RG online edits added 6-23-04; updated 6-30-04] Unit 3: The Nervous System Introduction Everything you do, everything you feel, every thought that you have, every sensation that you experience, involves
[RG online edits added 6-23-04; updated 6-30-04] Unit 3: The Nervous System Introduction Everything you do, everything you feel, every thought that you have, every sensation that you experience, involves
Warm-Up. Label the parts of the neuron below.
 Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
Biopsychology. Biological Bases of Behaviour. Miss. Paslawski Psychology 40S 2017
 Biopsychology Biological Bases of Behaviour Miss. Paslawski Psychology 40S 2017 http://fundersandfounders.com/9-types-of-intelligence/#naturalist How does your brain process information? Naturalist Intelligence
Biopsychology Biological Bases of Behaviour Miss. Paslawski Psychology 40S 2017 http://fundersandfounders.com/9-types-of-intelligence/#naturalist How does your brain process information? Naturalist Intelligence
Workings of the Mind and Body. Mr. Mattingly Psychology
 Workings of the Mind and Body Mr. Mattingly Psychology The Nervous System: Two Parts: Central Nervous System (CNS) = brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) = nerves throughout your body
Workings of the Mind and Body Mr. Mattingly Psychology The Nervous System: Two Parts: Central Nervous System (CNS) = brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) = nerves throughout your body
Human Nervous System. The nervous system has three functions
 Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
