Received 15 April 2004/Returned for modification 7 June 2004/Accepted 8 September 2004
|
|
|
- Gordon Page
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Jan. 2005, p Vol. 73, No /05/$ doi: /iai Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Interleukin-17/Interleukin-17 Receptor-Mediated Signaling Is Important for Generation of an Optimal Polymorphonuclear Response against Toxoplasma gondii Infection Michelle N. Kelly, 1 Jay K. Kolls, 2 Kyle Happel, 3 Joseph D. Schwartzman, 4 Paul Schwarzenberger, 5 Crescent Combe, 1 Magali Moretto, 1 and Imtiaz A. Khan 1 * Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Parasitology, 1 Department of Pulmonary Medicine, 3 and Division of Gene Therapy, 5 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, Louisiana; Department of Pediatrics, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 2 ;and Department of Pathology, Dartmouth Medical School, Lebanon, New Hampshire 4 Received 15 April 2004/Returned for modification 7 June 2004/Accepted 8 September 2004 We investigated the role of interleukin-17 (IL-17)/IL-17 receptor (IL-17R)-mediated signaling in the protective immunity against Toxoplasma gondii. IL-17R / mice developed a normal adaptive immunity against the parasite. However, increased mortality in the knockout animals can be attributed to a defect in the migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to infected sites during early infection. * Corresponding author. Mailing address: Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Parasitology, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, LA Phone: (504) Fax: (504) ikhan@lsuhsc.edu. While the induction of a cell-mediated response is essential for protection against Toxoplasma gondii, the initial innate immune response led by neutrophils has also been reported to be critical for successful resolution of the infection (1, 6, 13). Depletion studies have shown that their loss leads to exacerbation of infection (3, 13). The factors involved in the development of this neutrophil response against infection have not been well studied. Recently, interleukin 17 (IL-17) has been shown to be one of the major cytokines involved in the development and recruitment of neutrophils (18). In the present study, the role of IL-17 receptor (IL-17R)-mediated signaling in the generation of protective immunity against an intracellular parasite was evaluated for the first time. IL-17R / mice are more susceptible to T. gondii than are parental wild types. To determine if a lack of IL-17 signaling can alter the susceptibility to T. gondii infection, 5- to 6-weekold female IL-17R / mice (Amgen Inc., Thousand Oaks, Calif.) and parental C57BL/6 mice (Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, Maine) were challenged perorally with 15 cysts of the 76K strain of T. gondii. As seen in Fig. 1A, nearly 80% of the knockout mice succumbed to infection by day 22 postinfection (p.i.). Conversely, none of the wild-type mice died or exhibited any signs of clinical sickness, and they survived until the termination of the experiment. When the inoculum was increased to 30 cysts, parental control animals survived longer (P 0.001) but ultimately succumbed to the infection (Fig. 1B). To determine if the susceptibility of IL-17R / mice was due to increased parasite burden, tissues from both knockout and parental mice were analyzed by quantitative PCR as already described (4). The relative abundance of the B1 gene, a genetic marker for T. gondii, was determined at day 14 p.i. in the animals receiving the low dose (15 cysts) and at day 7 p.i. in those infected with a higher dose (30 cysts). As shown in Fig. 1C, a low-dose infection resulted in an approximately 2 log increase of parasite burden in the tissues (spleen, liver, gut, and brain) of knockout animals compared to wild-type mice (P 0.05). The levels in the parental controls were close to uninfected levels, indicating that they were able to resolve the infection. Similarly, when the mice were infected with a higher parasite dose, tissues of the knockout mice had a significantly higher parasite burden than the parental strain, with the liver displaying the largest difference (P 0.05) (Fig. 1D). IL-17R / mice display less severe tissue damage in response to T. gondii infection. Previous studies have reported that C57BL/6 mice infected orally with a high dose of T. gondii cysts develop a severe inflammatory response (8, 15). To determine if lack of IL-17R can alter the inflammatory response, tissues from mice at day 7 p.i were subjected to histopathological analysis as previously described (4). As expected, the liver from parental C57BL/6 mice showed extensive fatty change in hepatocytes (Fig. 2A), while IL-17R-knockout mice had slightly less severe changes (Fig. 2B). As shown in Fig. 2C, the small intestine of the wild-type animals exhibited extensive necrosis and hemorrhage as previously described (10), but the IL-17R / animals showed much less mucosal damage (Fig. 2D). T. gondii tachyzoites were evident in the lamina propria of the IL-17R / mice (Fig. 2, insert), while the multiple fields from the wild-type mice did not show any presence of parasites. PMN influx into tissues is inhibited in IL-17R / mice. Our present studies demonstrated that although IL-17R / mice exhibit increased mortality from toxoplasma infection, they develop a normal antigen-specific T-cell immunity and NK-cell 617
2 618 NOTES INFECT. IMMUN. FIG. 1. IL-17R / mice are susceptible to oral T. gondii infection and display a high parasite burden. Survival of IL-17R / mice infected with different doses of cysts (15 [A] or 30 [B] cysts/mouse) is shown. Data are represented as the cumulative percentage of two experiments (n 10). The statistical analysis was performed using the Kaplan-Meier test (16). Shown is the number of parasites per microgram of tissue DNA in the organs of IL-17R / mice infected with 15 (C) or 30 (D) cysts of T. gondii (n 3). Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired Student s t test as already described (12).
3 VOL. 73, 2005 NOTES 619 FIG. 2. Photomicrographs of the liver and ileum from IL-17R / and wild-type mice infected with 30 cysts of T. gondii at day 7 p.i. (A) Wild-type (WT) liver: extensive fatty change is seen in hepatocytes with small foci of mixed PMN and lymphocytic infiltration. Bar, 10 M. (B) IL17R / liver: less severe fatty change is seen in hepatocytes with lymphocytic inflammation similar to that seen in the parental animals, including some PMNs. Bar, 10 M. (C) WT small intestine: extensive necrosis and hemorrhage, with loss of the superficial mucosa and blood and cellular debris in bowel lumen (star). Small foci of mixed inflammatory cells including PMNs are seen in the lamina propria (arrow). Bar, 75 M. (D) IL 17R / small intestine: the superficial mucosa is preserved (star), and a mixed inflammatory infiltrate including PMNs is evident within the lamina propria (arrow). Bar, 75 M. (Inset) Close-up with arrow pointing to tachyzoites in lamina propria of a knockout animal. response against the parasite (data not shown). As neutrophils are important in host defense to T. gondii (1, 13) and IL-17 has been implicated in polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) granulopoeisis and recruitment (9, 11, 18), we were interested in evaluating the trafficking of PMNs to the tissues of animals infected with 30 cysts of the 76K strain of T. gondii. Hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of liver and intestine were examined, and relative PMN indices were determined by examination under an Olympus Van Ox microscope. Multiple sections of each tissue were counted in a blinded manner (7). At days 2 and 4 p.i., a decreased PMN index was observed in both tissues in the IL-17R / mice (Table 1). This difference was more pronounced in the intestine, but the number of PMNs began to increase in both tissues by day 6 p.i. Neutrophil migration into the peritoneal cavity is significantly decreased in IL-17R / mice after T. gondii infection. In order to assess the ability of IL-17R / mice to recruit neutrophils, wild-type and knockout animals were injected intraperitoneally with RH strain tachyzoites. Four hours later, peritoneal exudate cells were collected ( /sample) and cytospun (700 rpm for 5 min) onto glass microscope slides (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, Pa.) pretreated with Vectabond (Vector Lab, Burlingame, Calif.) by using cytofunnels (Thermo Shandon, Pittsburgh, Pa.). To determine the number of neutrophils, differential counts (300 cells/slide) were performed using a Diff-Quick stain (IMEB, San Marco, Calif.) (5). Previous studies (2) have shown that intraperitoneal infection of mice with tachyzoites of T. gondii results in a rapid recruitment of PMNs into the peritoneal cavity. As shown in Fig. 3, the number of neutrophils in the peritoneum of the wild-type mice as a result of T. gondii infection was significantly higher than that of the IL-17R / mice 4 h p.i. (P 0.05). To determine if a defect in neutrophil recruitment is accompanied by decreased macrophage inflammatory protein 2 (MIP-2) levels, serum from the infected animals was evaluated for the chemokine at days 0, 2, 4, and 6 p.i. by using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit (R&D Systems) according to the manufacturer s protocol (14, 17). As shown in Fig. 4, there was no difference between control and knockout mice in the initial chemokine level (day 0). However, at days 2 and 4 p.i., levels of MIP-2 in the control animals increased significantly (P 0.02) over those in the knockout mice, which remained at concentrations similar to those of uninfected animals (Fig. 4). By day 6, the level of MIP-2 in the knockout TABLE 1. Relative PMN indices in the tissues of T. gondii-infected mice PMN index a at day p.i.: Tissue Mouse 1 Mouse 2 Mouse 1 Mouse 2 Mouse 1 Mouse 2 Mouse 1 Mouse 2 Wild-type liver IL-17R / liver Wild-type gut IL-17R / gut a, no, or rare, single PMN within inflammatory nodules;, few, or less than one-third, of the cells in the inflammatory nodules are PMNs;, moderate, or one- to two-thirds of the cells in the nodule are PMNs;, two-thirds or more of the cells are PMNs.
4 620 NOTES INFECT. IMMUN. FIG. 3. Defective PMN influx in IL-17R / mice early after T. gondii infection. The number of neutrophils was determined by differential counting. *, P The results are representative of two experiments. mice began to increase but was still significantly less than in the parental control animals (P 0.05). In summary, as stated above, PMNs appear to play an important role during early T. gondii infection (5). The mechanism of rapid induction of neutrophil response during T. gondii infection has not been described. The present study demonstrates for the first time that early neutrophil induction during T. gondii infection is dependent on IL-17-mediated signaling. A diminished response in IL-17R / mice was associated with failure to produce the chemokine MIP-2 early in infection. Based on our findings, we hypothesize that T. gondii infection induces a strong and early neutrophil response. The neutrophils clear the parasites during initial stages of infection so that adaptive immunity, which is induced later, is not overburdened. In the presence of suboptimal levels of neutrophils, parasite load is not efficiently reduced and adaptive immunity is unable to handle this elevated burden, which ultimately leads to increased mortality. We are thankful to Joseph Chaiban for his help in phenotypic studies. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant A awarded to I.A.K. REFERENCES 1. Alexander, J., T. M. Scharton-Kersten, G. Yap, C. W. Roberts, F. Y. Liew, and A. Sher Mechanisms of innate resistance to Toxoplasma gondii infection. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B 352: Bliss, S. K., B. A. Butcher, and E. Y. Denkers Rapid recruitment of neutrophils containing prestored IL-12 during microbial infection. J. Immunol. 165: Bliss, S. K., L. C. Gavrilescu, A. Alcaraz, and E. Y. Denkers Neutrophil depletion during Toxoplasma gondii infection leads to impaired immunity and lethal systemic pathology. Infect. Immun. 69: Casciotti, L., K. H. Ely, M. E. Williams, and I. A. Khan CD8 -T-cell immunity against Toxoplasma gondii can be induced but not maintained in mice lacking conventional CD4 T cells. Infect. Immun. 70: Del Rio, L., S. Bennouna, J. Salinas, and E. Y. Denkers CXCR2 deficiency confers impaired neutrophil recruitment and increased susceptibility during Toxoplasma gondii infection. J. Immunol. 167: Gazzinelli, R., S. Heiny, T. A. Wynn, S. Wolf, and A. Sher Interleukin 12 is required for the T-lymphocyte-independent induction of interferon FIG. 4. Defective chemokine production in IL-17R / mice infected with T. gondii. IL-17R / mice (three mice/group) were infected with 15 cysts of T. gondii. Data are presented as means standard deviations of individual mice. Significant differences between treatment pairs are indicated by lines. **, P 0.02; *, P The assay was performed twice with similar results.
5 VOL. 73, 2005 NOTES 621 gamma by an intracellular parasite and induces resistance in T-cell deficient hosts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: Khan, I. A., P. M. Murphy, L. Casciotti, J. D. Schwartzman, J. Collins, J.-L. Gao, and G. R. Yeaman Mice lacking the chemokine receptor CCR1 show increased susceptibility to Toxoplasma gondii infection. J. Immunol. 166: Khan, I. A., J. D. Schwartzman, T. Matsuura, and L. H. Kasper A dichotomous role for nitric oxide during acute Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: Laan, M., Z.-H. Cui, H. Hoshino, J. Lotvall, M. Sjostrand, D. C. Gruenert, B.-E. Skoogh, and A. Linden Neutrophil recruitment by human IL-17 via C-X-C chemokine release in the airways. J. Immunol. 162: Liesenfeld, O., J. Kosek, J. Remington, and Y. Suzuki Association of CD4 T cell-dependent, interferon-gamma-mediated necrosis of the small intestine with genetic susceptibility of mice to peroral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J. Exp. Med. 184: Miyamoto, M., O. Prause, M. Sjostrand, M. Laan, J. Lotvall, and A. Linden Endogenous IL-17 as a mediator of neutrophil recruitment caused by endotoxin exposure in mouse airways. J. Immunol. 170: Neter J., W. Wasserman, and M. H. Kutner Applied linear statistical models, 2nd ed. R.D. Irwin, Homewood, Ill. 13. Sayles, P. C., and L. L. Johnson Exacerbation of toxoplasmosis in neutrophil-depleted mice. Nat. Immun. 15: Standiford, T., S. Kunkel, M. Greenberger, L. Laichalk, and R. Strieter Expression and regulation of chemokines in bacterial pneumonia. J. Leukoc. Biol. 59: Suzuki, Y., A. Sher, G. Yap, D. Park, L. E. Neyer, O. Liesenfeld, M. Fort, H. Kang, and E. Gufwoli IL-10 is required for prevention of necrosis in the small intestine and mortality in both genetically resistant BALB/c and susceptible C57BL/6 mice following peroral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 164: Tanino, Y., H. Makita, K. Miyamoto, T. Betsuyaku, Y. Ohtsuka, J. Nishihira, and M. Nishimura Role of macrophages migration inhibitory factor in bleomycin-induced lung injury and fibrosis in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 283:L156 L Xue, M.-L., A. Thakur, and M. Willcox Macrophage inflammatory protein-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor regulate corneal neovascularization induced by infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. Immunol. Cell Biol. 80: Ye, P., F. H. Rodriguez, S. Kanaly, K. L. Stocking, J. Schurr, P. Schwarzenberger, P. Oliver, W. Huang, P. Zhang, J. Zhang, J. E. Shellito, G. J. Bagby, S. Nelson, K. Charrier, J. J. Peschon, and J. K. Kolls Requirement of interleukin 17 receptor signaling for lung CXC chemokine and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor expression, neutrophil recruitment, and host defense. J. Exp. Med. 194: Editor: S. H. E. Kaufmann
Experimental Ocular Toxoplasmosis in Genetically Susceptible and Resistant Mice
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2005, p. 5160 5165 Vol. 73, No. 8 0019-9567/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.73.8.5160 5165.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Experimental
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2005, p. 5160 5165 Vol. 73, No. 8 0019-9567/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.73.8.5160 5165.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Experimental
CD8 -T-Cell Immunity against Toxoplasma gondii Can Be Induced but Not Maintained in Mice Lacking Conventional CD4 T Cells
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Feb. 2002, p. 434 443 Vol. 70, No. 2 0019-9567/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.2.434 443.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. CD8 -T-Cell
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Feb. 2002, p. 434 443 Vol. 70, No. 2 0019-9567/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.2.434 443.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. CD8 -T-Cell
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals. Taniawati Supali. Department of Parasitology
 Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
Felix Yarovinsky. Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center. Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii
 Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
Recruitment of Gr-1 monocytes is essential for control of acute toxoplasmosis
 Published Online: 31 May, 2005 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20050054 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on June 28, 2018 ARTICLE Recruitment of Gr-1 monocytes is essential for control of acute toxoplasmosis
Published Online: 31 May, 2005 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20050054 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on June 28, 2018 ARTICLE Recruitment of Gr-1 monocytes is essential for control of acute toxoplasmosis
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
NOTES. Received 24 January 2003/Returned for modification 21 February 2003/Accepted 6 June 2003
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 2003, p. 5355 5359 Vol. 71, No. 9 0019-9567/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5355 5359.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. NOTES
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 2003, p. 5355 5359 Vol. 71, No. 9 0019-9567/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5355 5359.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. NOTES
Supplementary Figures
 Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
Interleukin-17 enhances the removal of respiratory syncytial virus in mice by promoting neutrophil migration and reducing interferon-gamma expression
 Interleukin-17 enhances the removal of respiratory syncytial virus in mice by promoting neutrophil migration and reducing interferon-gamma expression G. Zhang 1, K.F. Zhou 2 and Z.H. Lu 1 1 Department
Interleukin-17 enhances the removal of respiratory syncytial virus in mice by promoting neutrophil migration and reducing interferon-gamma expression G. Zhang 1, K.F. Zhou 2 and Z.H. Lu 1 1 Department
Coccidia. Eucoccidioside
 Coccidia Kingdom Sub-Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Protista Protozoa Apicomplexa Sporozoasida Eucoccidioside Sarcocystidae Toxoplasma gondii 1 Toxoplasma gondii (life cycle) Sexual cycle
Coccidia Kingdom Sub-Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Protista Protozoa Apicomplexa Sporozoasida Eucoccidioside Sarcocystidae Toxoplasma gondii 1 Toxoplasma gondii (life cycle) Sexual cycle
Lung Disease in Pediatrics: is it all in the Genes?
 Lung Disease in Pediatrics: is it all in the Genes? Jay K. Kolls, M.D. Chair, Department of Genetics LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans, LA Children s s Hospital of Pittsburgh Severe combined immunodeficiency
Lung Disease in Pediatrics: is it all in the Genes? Jay K. Kolls, M.D. Chair, Department of Genetics LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans, LA Children s s Hospital of Pittsburgh Severe combined immunodeficiency
Subject Index. Bcl-2, apoptosis regulation Bone marrow, polymorphonuclear neutrophil release 24, 26
 Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Supplemental Information. Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection. Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15
 Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15 Supplemental Information Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection Arya Khosravi, Alberto Yáñez, Jeremy G. Price, Andrew Chow, Miriam Merad, Helen
Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15 Supplemental Information Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection Arya Khosravi, Alberto Yáñez, Jeremy G. Price, Andrew Chow, Miriam Merad, Helen
Xisheng Wang, 1 Hoil Kang, 2,3 Takane Kikuchi, 1 and Yasuhiro Suzuki 1,2,3 *
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2004, p. 4432 4438 Vol. 72, No. 8 0019-9567/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.8.4432 4438.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Gamma Interferon
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2004, p. 4432 4438 Vol. 72, No. 8 0019-9567/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.8.4432 4438.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Gamma Interferon
Genetics. Environment. You Are Only 10% Human. Pathogenesis of IBD. Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function IBD
 Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Memory NK cells during mousepox infection. Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science
 Memory NK cells during mousepox infection Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science Infectious Diseases are a Major Cause of Death Worldwide May 14 th 1796 Prevalence
Memory NK cells during mousepox infection Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science Infectious Diseases are a Major Cause of Death Worldwide May 14 th 1796 Prevalence
4. Th1-related gene expression in infected versus mock-infected controls from Fig. 2 with gene annotation.
 List of supplemental information 1. Graph of mouse weight loss during course of infection- Line graphs showing mouse weight data during course of infection days 1 to 10 post-infections (p.i.). 2. Graph
List of supplemental information 1. Graph of mouse weight loss during course of infection- Line graphs showing mouse weight data during course of infection days 1 to 10 post-infections (p.i.). 2. Graph
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Chapter 3, Part A (Pages 37-45): Leukocyte Migration into Tissues
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Supporting Information
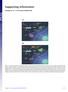 Supporting Information Aldridge et al. 10.1073/pnas.0900655106 Fig. S1. Flow diagram of sublethal (a) and lethal (b) influenza virus infections. (a) Infection of lung epithelial cells by influenza virus
Supporting Information Aldridge et al. 10.1073/pnas.0900655106 Fig. S1. Flow diagram of sublethal (a) and lethal (b) influenza virus infections. (a) Infection of lung epithelial cells by influenza virus
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells. Part II: Cells (aka the Sentinels)
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Exercise Alters Stress and Inflammatory Response in Lungs of Mice
 Exercise Alters Stress and Inflammatory Response in Lungs of Mice Joseph Sevcik1, Shibani Naik2, Marian L Kohut1,2 1Department of Kinesiology, Iowa State University, Ames, IA 2Immunobiology Department,
Exercise Alters Stress and Inflammatory Response in Lungs of Mice Joseph Sevcik1, Shibani Naik2, Marian L Kohut1,2 1Department of Kinesiology, Iowa State University, Ames, IA 2Immunobiology Department,
Accepted Manuscript. Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development. Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo
 Accepted Manuscript Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo PII: S0016-5085(18)34974-6 DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.057 Reference: YGAST 62119 To appear
Accepted Manuscript Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo PII: S0016-5085(18)34974-6 DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.057 Reference: YGAST 62119 To appear
Animal Models to Understand Immunity
 Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
IFNg. IFNg IL-5 IL-13 IL-17 IL-22. LTi NCR+ ILC3. IL-17 IL-22 IFNg
 Group 1 ILC T-Bet Eomes Nkp46 NK1.1 NK cells IFNg T-Bet ILC1 IFNg low RORgt Group 2 ILC RORa CD127 ILC2 IL-5 IL-13 Group 3 ILC RORc CD127 AhR T-Bet AhR LTi c-kit; CD4+/- NCR+ ILC3 c-kit; Nkp46 IL-17 IL-22
Group 1 ILC T-Bet Eomes Nkp46 NK1.1 NK cells IFNg T-Bet ILC1 IFNg low RORgt Group 2 ILC RORa CD127 ILC2 IL-5 IL-13 Group 3 ILC RORc CD127 AhR T-Bet AhR LTi c-kit; CD4+/- NCR+ ILC3 c-kit; Nkp46 IL-17 IL-22
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Product Datasheet. Ly-6G6C Antibody (NIMP-R14) NB Unit Size: 0.05 mg. Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 23
 Product Datasheet Ly-6G6C Antibody (NIMP-R14) NB600-1387 Unit Size: 0.05 mg Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 23 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at:
Product Datasheet Ly-6G6C Antibody (NIMP-R14) NB600-1387 Unit Size: 0.05 mg Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 23 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at:
Immune CD8 T Cells Prevent Reactivation of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in the Immunocompromised Host
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Nov. 1999, p. 5869 5876 Vol. 67, No. 11 0019-9567/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Immune CD8 T Cells Prevent Reactivation of
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Nov. 1999, p. 5869 5876 Vol. 67, No. 11 0019-9567/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Immune CD8 T Cells Prevent Reactivation of
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
IL-12 family members in experimental colitis. Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany
 IL-12 family members in experimental colitis Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany IBD - Pathogenesis Genetic Predisposition Bacterial Antigens Activation of
IL-12 family members in experimental colitis Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany IBD - Pathogenesis Genetic Predisposition Bacterial Antigens Activation of
Lack of Interleukin-12 in p40-deficient Mice Leads to Poor CD8 T-Cell Immunity against Encephalitozoon cuniculi Infection
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, June 2010, p. 2505 2511 Vol. 78, No. 6 0019-9567/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/iai.00753-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Lack of Interleukin-12
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, June 2010, p. 2505 2511 Vol. 78, No. 6 0019-9567/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/iai.00753-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Lack of Interleukin-12
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Supplementary Figure 1. NOS2 -/- mice develop an analogous Ghon complex after infection in the ear dermis and show dissemination of Mtb to the lung. (A) WT and NOS2 -/- mice were
Supplementary Material Supplementary Figure 1. NOS2 -/- mice develop an analogous Ghon complex after infection in the ear dermis and show dissemination of Mtb to the lung. (A) WT and NOS2 -/- mice were
Neutrophil Depletion during Toxoplasma gondii Infection Leads to Impaired Immunity and Lethal Systemic Pathology
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2001, p. 4898 4905 Vol. 69, No. 8 0019-9567/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.8.4898 4905.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Neutrophil
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2001, p. 4898 4905 Vol. 69, No. 8 0019-9567/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.8.4898 4905.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Neutrophil
Received 9 September 2005/Returned for modification 14 October 2005/Accepted 20 December 2005
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 2006, p. 1846 1856 Vol. 74, No. 3 0019-9567/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.74.3.1846 1856.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Role of
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 2006, p. 1846 1856 Vol. 74, No. 3 0019-9567/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.74.3.1846 1856.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Role of
Murine polymorphonuclear neutrophils produce interferon- in response to pulmonary infection with Nocardia asteroides
 Murine polymorphonuclear neutrophils produce interferon- in response to pulmonary infection with Nocardia asteroides Terri N. Ellis and Blaine L. Beaman Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunology,
Murine polymorphonuclear neutrophils produce interferon- in response to pulmonary infection with Nocardia asteroides Terri N. Ellis and Blaine L. Beaman Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunology,
17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012
 17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012 The Sagamore Resort, Bolton Landing, NY, USA The following report includes highlights
17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012 The Sagamore Resort, Bolton Landing, NY, USA The following report includes highlights
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Nutrition & Gut Immunity
 Nutrition & Gut Immunity Kenneth A. Kudsk, MD FACS Professor of Surgery University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, Wisconsin No conflicts of interest to disclose % Survival Survival vs. Malnutrition (after
Nutrition & Gut Immunity Kenneth A. Kudsk, MD FACS Professor of Surgery University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, Wisconsin No conflicts of interest to disclose % Survival Survival vs. Malnutrition (after
Fc receptors, phagocytosis role 128
 Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL
 EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL INFECTION PRODUCED IN GUINEA PIGS' SAMUEL B. FORMAL, GUSTAVE J. DAMMIN, E. H. LABREC, AND H. SCHNEIDER Walter Reed Army Institute of Research,
EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL INFECTION PRODUCED IN GUINEA PIGS' SAMUEL B. FORMAL, GUSTAVE J. DAMMIN, E. H. LABREC, AND H. SCHNEIDER Walter Reed Army Institute of Research,
As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the
 3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases
 محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
Impaired Resistance to the Development of Toxoplasmic Encephalitis in Interleukin-6-Deficient Mice
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, June 1997, p. 2339 2345 Vol. 65, No. 6 0019-9567/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Impaired Resistance to the Development of Toxoplasmic Encephalitis
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, June 1997, p. 2339 2345 Vol. 65, No. 6 0019-9567/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Impaired Resistance to the Development of Toxoplasmic Encephalitis
Supplementary Figure 1. ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons
 Supplementary Figure 1 ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons a pstat3 controls Pos Neg ETBF 1 2 3 4 b pstat1 pstat2 pstat3 pstat4 pstat5 pstat6 Actin Figure Legend: (a) ETBF induce predominantly
Supplementary Figure 1 ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons a pstat3 controls Pos Neg ETBF 1 2 3 4 b pstat1 pstat2 pstat3 pstat4 pstat5 pstat6 Actin Figure Legend: (a) ETBF induce predominantly
Methodology Prevalence:
 Context of Research Free ranging domestic fowl are very susceptible to parasitic infections owing to their exposure to parasites during their roaming in the backyards in search of food. Heterakis gallinarum
Context of Research Free ranging domestic fowl are very susceptible to parasitic infections owing to their exposure to parasites during their roaming in the backyards in search of food. Heterakis gallinarum
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Stegbauer et al. 10.1073/pnas.0903602106 SI Methods Analysis of Plasma Renin Activity (PRA) and ACE Activity. PRA and serum ACE activity levels were determined by RIA (RENCTK, DiaSorin;
Supporting Information Stegbauer et al. 10.1073/pnas.0903602106 SI Methods Analysis of Plasma Renin Activity (PRA) and ACE Activity. PRA and serum ACE activity levels were determined by RIA (RENCTK, DiaSorin;
Ch 12. Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses
 Ch 12 Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity. Define and explain PRRs and PAMPs Differentiate physical from chemical factors, and list examples of
Ch 12 Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity. Define and explain PRRs and PAMPs Differentiate physical from chemical factors, and list examples of
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 NLRP12 is downregulated in biopsy samples from patients with active ulcerative colitis (UC). (a-g) NLRP12 expression in 7 UC mrna profiling studies deposited in NCBI GEO database.
Supplementary Figure 1 NLRP12 is downregulated in biopsy samples from patients with active ulcerative colitis (UC). (a-g) NLRP12 expression in 7 UC mrna profiling studies deposited in NCBI GEO database.
Immunologically Induced and Elicited Local
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 1970, p. 757-761 Copyright 1970 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 2, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Immunologically Induced and Elicited Local Resistance to Staphylococcus aureus
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 1970, p. 757-761 Copyright 1970 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 2, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Immunologically Induced and Elicited Local Resistance to Staphylococcus aureus
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Supplemental Methods: Histopathology scoring of individual components of Valentino
 Supplementary Materials Online: Supplemental Methods: Histopathology scoring of individual components of Valentino synovitis grade and Mankin cartilage pathology scale Hemophilic synovitis was graded 0-10
Supplementary Materials Online: Supplemental Methods: Histopathology scoring of individual components of Valentino synovitis grade and Mankin cartilage pathology scale Hemophilic synovitis was graded 0-10
Suppression of CD4 + T-Cells in the Spleen of Mice Infected with Toxoplasma gondii KI-1 Tachyzoites
 ISSN (Print) 0023-4001 ISSN (Online) 1738-0006 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Korean J Parasitol. Vol. 48, No. 4: 325-329, December 2010 DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2010.48.4.325 Suppression of CD4 + T-Cells in the Spleen of
ISSN (Print) 0023-4001 ISSN (Online) 1738-0006 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Korean J Parasitol. Vol. 48, No. 4: 325-329, December 2010 DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2010.48.4.325 Suppression of CD4 + T-Cells in the Spleen of
Supplementary Figures for TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disorder by Linnan Zhu et al
 Supplementary Figures for TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disorder by Linnan Zhu et al Suppl. Fig. 1 Tissue DN C Proteins kd TSC1-17 TSC 1 loxp bp -48-285 ctin PEMs Neutrophils
Supplementary Figures for TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disorder by Linnan Zhu et al Suppl. Fig. 1 Tissue DN C Proteins kd TSC1-17 TSC 1 loxp bp -48-285 ctin PEMs Neutrophils
CD8α + dendritic cells are the critical source of interleukin-12 that controls acute infection by Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites
 Published as: Immunity. 2011 August 26; 35(2): 249 259. CD8α + dendritic cells are the critical source of interleukin-12 that controls acute infection by Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites Mona Mashayekhi 1,
Published as: Immunity. 2011 August 26; 35(2): 249 259. CD8α + dendritic cells are the critical source of interleukin-12 that controls acute infection by Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites Mona Mashayekhi 1,
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with
 Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland Approved for public release; distribution unlimited
 AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry W. Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry W. Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
The Case of the Spring Break Consequences
 The Case of the Spring Break Consequences Hazel reluctantly opened her eyes when her alarm went off. Spring Break was over, and she was definitely NOT ready for the second half of the semester. However,
The Case of the Spring Break Consequences Hazel reluctantly opened her eyes when her alarm went off. Spring Break was over, and she was definitely NOT ready for the second half of the semester. However,
 SUMMARY Coeliac disease is a common food intolerance in Western populations, in which it has a prevalence of about 1%. In early infancy, when the transition is made to a gluten-containing diet (particularly
SUMMARY Coeliac disease is a common food intolerance in Western populations, in which it has a prevalence of about 1%. In early infancy, when the transition is made to a gluten-containing diet (particularly
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties
 Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties neutrophils---acute inflammation monocytes---subacute/chronic inflammation eosinophils---parasitic or allergic inflammation natural
Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties neutrophils---acute inflammation monocytes---subacute/chronic inflammation eosinophils---parasitic or allergic inflammation natural
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 A LN Cell count (1 ) 1 3 1 CD+ 1 1 CDL lo CD hi 1 CD+FoxP3+ 1 1 1 7 3 3 3 % of cells 9 7 7 % of cells CD+ 3 1 % of cells CDL lo CD hi 1 1 % of CD+ cells CD+FoxP3+ 3 1 % of CD+ T
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 A LN Cell count (1 ) 1 3 1 CD+ 1 1 CDL lo CD hi 1 CD+FoxP3+ 1 1 1 7 3 3 3 % of cells 9 7 7 % of cells CD+ 3 1 % of cells CDL lo CD hi 1 1 % of CD+ cells CD+FoxP3+ 3 1 % of CD+ T
Sponsored document from Microbes and Infection / Institut Pasteur
 Sponsored document from Microbes and Infection / Institut Pasteur The Syk/CARD9-coupled receptor Dectin-1 is not required for host resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice Mohlopheni J. Marakalala
Sponsored document from Microbes and Infection / Institut Pasteur The Syk/CARD9-coupled receptor Dectin-1 is not required for host resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice Mohlopheni J. Marakalala
ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung
 IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
Review Article Understanding the Role of Chemokines and Cytokines in Experimental Models of Herpes Simplex Keratitis
 Hindawi Immunology Research Volume 2017, Article ID 7261980, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7261980 Review Article Understanding the Role of Chemokines and Cytokines in Experimental Models of Herpes
Hindawi Immunology Research Volume 2017, Article ID 7261980, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7261980 Review Article Understanding the Role of Chemokines and Cytokines in Experimental Models of Herpes
Overview of Immunology: Mucosal Immunology- the guardian of oral health
 Overview of Immunology: Mucosal Immunology- the guardian of oral health Jacqueline Mays, DDS, MHSc, PhD April 6, 2017 AAOM Annual Conference Statement of Disclosure: I have no actual or potential conflict
Overview of Immunology: Mucosal Immunology- the guardian of oral health Jacqueline Mays, DDS, MHSc, PhD April 6, 2017 AAOM Annual Conference Statement of Disclosure: I have no actual or potential conflict
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Putting it Together. Stephen Canfield Secondary Lymphoid System. Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s
 Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Defining the Helper T Cell Contribution to Helicobacter pylori Gastritis. Brian M. Gray
 Defining the Helper T Cell Contribution to Helicobacter pylori Gastritis by Brian M. Gray A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Microbiology
Defining the Helper T Cell Contribution to Helicobacter pylori Gastritis by Brian M. Gray A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Microbiology
Supplementary Information. Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania. through collective production of nitric oxide
 Supplementary Information Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania through collective production of nitric oxide Romain Olekhnovitch, Bernhard Ryffel, Andreas J. Müller and Philippe Bousso Supplementary
Supplementary Information Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania through collective production of nitric oxide Romain Olekhnovitch, Bernhard Ryffel, Andreas J. Müller and Philippe Bousso Supplementary
Received 6 February 2007/Returned for modification 22 May 2007/Accepted 3 June 2007
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 2007, p. 4608 4620 Vol. 75, No. 9 0019-9567/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00198-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Relative Importance
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 2007, p. 4608 4620 Vol. 75, No. 9 0019-9567/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00198-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Relative Importance
Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of EPO and EPOR during self-limited versus delayed
 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of EPO and EPOR during self-limited versus delayed inflammation resolution. a: Flow cytometry analysis showing the electronic gating strategy used to identify peritoneal
Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of EPO and EPOR during self-limited versus delayed inflammation resolution. a: Flow cytometry analysis showing the electronic gating strategy used to identify peritoneal
Differential Infectivity and Division of Toxoplasma gondii in Human Peripheral Blood Leukocytes
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2000, p. 4822 4826 Vol. 68, No. 8 0019-9567/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Differential Infectivity and Division of Toxoplasma
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2000, p. 4822 4826 Vol. 68, No. 8 0019-9567/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Differential Infectivity and Division of Toxoplasma
PATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PULIC HEALTH PATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS Yaowalark Sukthana 1, Phuangphet Waree 1, Emsri Pongponratn 2, Urai Chaisri 2 and Mario Riganti 2
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PULIC HEALTH PATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS Yaowalark Sukthana 1, Phuangphet Waree 1, Emsri Pongponratn 2, Urai Chaisri 2 and Mario Riganti 2
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
Corso di Laurea Specialistica in Biotecnologie Molecolari aa 2006/2007 Presentazione di Immunologia Molecolare INTERFERON GAMMA.
 Corso di Laurea Specialistica in Biotecnologie Molecolari aa 2006/2007 Presentazione di Immunologia Molecolare INTERFERON GAMMA Valentina Grosso The Inteferons 1957: Isaacs and Lindenmann discovered a
Corso di Laurea Specialistica in Biotecnologie Molecolari aa 2006/2007 Presentazione di Immunologia Molecolare INTERFERON GAMMA Valentina Grosso The Inteferons 1957: Isaacs and Lindenmann discovered a
Potential Rebalancing of the Immune System by Anti-CD52 Therapy
 Potential Rebalancing of the Immune System by Anti-CD52 Therapy Johanne Kaplan, PhD VP Neuroimmunology Research Genzyme March 26, 2013 RESTRICTED USE SEE TRAINING MEMO 2011 DO Genzyme NOT 1COPY Corporation
Potential Rebalancing of the Immune System by Anti-CD52 Therapy Johanne Kaplan, PhD VP Neuroimmunology Research Genzyme March 26, 2013 RESTRICTED USE SEE TRAINING MEMO 2011 DO Genzyme NOT 1COPY Corporation
IL-22 mediates mucosal host defense against gram negative bacterial pneumonia
 IL-22 mediates mucosal host defense against gram negative bacterial pneumonia Shean J. Aujla, Yvonne R. Chan, Mingquan Zheng, Mingjian Fei, David J. Askew, Derek A. Pociask,Todd A. Reinhart, Florencia
IL-22 mediates mucosal host defense against gram negative bacterial pneumonia Shean J. Aujla, Yvonne R. Chan, Mingquan Zheng, Mingjian Fei, David J. Askew, Derek A. Pociask,Todd A. Reinhart, Florencia
Basis of Immunology and
 Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Innate Immunity. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Phagocytosis: An Evolutionarily Conserved Mechanism to Remove Apoptotic Bodies and Microbial Pathogens
 Phagocytosis of IgG-coated Targets by s Phagocytosis: An Evolutionarily Conserved Mechanism to Remove Apoptotic Bodies and Microbial s 3 min 10 min Mast Cells Can Phagocytose Too! Extension of an F-actin-rich
Phagocytosis of IgG-coated Targets by s Phagocytosis: An Evolutionarily Conserved Mechanism to Remove Apoptotic Bodies and Microbial s 3 min 10 min Mast Cells Can Phagocytose Too! Extension of an F-actin-rich
ulcer healing role 118 Bicarbonate, prostaglandins in duodenal cytoprotection 235, 236
 Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Regulation and Function of T-Cell-Mediated Immunity during Toxoplasma gondii Infection
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 1998, p. 569 588 Vol. 11, No. 4 0893-8512/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Regulation and Function of T-Cell-Mediated
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 1998, p. 569 588 Vol. 11, No. 4 0893-8512/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Regulation and Function of T-Cell-Mediated
Mass Histology Service
 Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
Part III Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction
 Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Host Response to Disease Resistance- ability
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Host Response to Disease Resistance- ability
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 Concepts. MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally!
 MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
Interleukin-20 is associated with delayed healing in diabetic wounds
 Interleukin-20 is associated with delayed healing in diabetic wounds Phillip Finley, PhD Integrated and Applied Sciences Program Biology and Statistics/Research Methodology Normal Healing Body s natural
Interleukin-20 is associated with delayed healing in diabetic wounds Phillip Finley, PhD Integrated and Applied Sciences Program Biology and Statistics/Research Methodology Normal Healing Body s natural
Immune Surveillance. Immune Surveillance. Immune Surveillance. Neutrophil granulocytes Macrophages. M-cells
 he immune system is everywhere Some organs have developed strategies towards the immune system to keep it out or to put it under control Immune privileged organs: Brain Eye estis hyroid gland Humoral immunity
he immune system is everywhere Some organs have developed strategies towards the immune system to keep it out or to put it under control Immune privileged organs: Brain Eye estis hyroid gland Humoral immunity
Immunology sheet. Done by: rasha rakan. Lecture: Introduction to medical immunology
 Immunology sheet Done by: rasha rakan Lecture: Introduction to medical immunology Second line of defense First line of defense RBCs Platelets Phagocytosis Blood In tissue Plasma cells are b cells that
Immunology sheet Done by: rasha rakan Lecture: Introduction to medical immunology Second line of defense First line of defense RBCs Platelets Phagocytosis Blood In tissue Plasma cells are b cells that
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Evaluation of Type-Specific and Non-Type-Specific Pseudomonas Vaccine for Treatment of Pseudomonas Sepsis During Granulocytopenia
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1976, p. 1139-1143 Copyright 1976 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 4 Printed in USA. Evaluation of Type-Specific and Non-Type-Specific Pseudomonas Vaccine for
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1976, p. 1139-1143 Copyright 1976 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 4 Printed in USA. Evaluation of Type-Specific and Non-Type-Specific Pseudomonas Vaccine for
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
