Autophagy enhances the presentation of endogenous viralantigensonmhcclassimoleculesduring HSV-1 infection
|
|
|
- Stephany Nichols
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Autophagy enhanes the presentation of enogenous viralantigensonmhclassimoleulesuring V- infetion Lu English, Magali Chemali, Johanne Duron, Christiane Roneau, Annie Laplante, Diane Gingras, Diane Alexaner, Davi Leib, Christopher orbury 3, Roger Lippé & Mihel Desjarins,4,5 Viral proteins are usually proesse by the lassial major histoompatibility omplex (MHC) lass I presentation pathway. Here we showe that although marophages infete with herpes simplex virus type (V-) initially stimulate CD8 + T ells by this pathway, a seon pathway involving a vauolar ompartment was triggere later uring infetion. Morphologial an funtional analyses iniate that istint forms of autophagy failitate the presentation of V- antigens on MHC lass I moleules. One form of autophagy involve a previously unknown type of autophagosome that originate from the nulear envelope. Whereas interferon- stimulate lassial MHC lass I presentation, fever-like hyperthermia an the pyrogeni ytokine interleukin b ativate autophagy an the vauolar proessing of viral pepties. Viral pepties in autophagosomes were further proesse by the proteasome, whih suggests a omplex interation between the vauolar an MHC lass I presentation pathways. The elaboration of an effiient immune response against pathogens involves omplex intraellular antigen-proessing events. Enogenous antigens suh as viral proteins synthesize by infete host ells are egrae in the ytoplasm by the proteasome, an the resulting pepties are transloate into the enoplasmi retiulum, where they are loae onto major histoompatibility omplex (MHC) lass I moleules. In ontrast, exogenous antigens are proesse by hyrolases in lyti enovauolar ompartments an are loae on MHC lass II moleules that reah the ell surfae using reyling mahineries assoiate with these organelles. Although initially thought to be stritly segregate, these pathways are atually funtionally interonnete, as shown by the ability of ells to present exogenous antigens on MHC lass I moleules; this proess is referre to as ross-presentation. Autophagy, a proess that allows the transfer of enogenous ellular omponents into lyti vauolar ompartments, has been shown to be essential to both innate an aaptive immunity 4. This proess an be use to eliminate intraellular bateria an viruses 5. Furthermore, autophagy an failitate the presentation of enogenous antigens on MHC lass II moleules, thereby leaing to ativation of CD4 + T ells,3. The nature of the enovauolar membranes involve in the formation of autophagosomes is still a matter of ative investigation, but the enoplasmi retiulum is one potential soure of autophagosome membrane 4. As substantial amounts of viral membrane glyoproteins are synthesize in the enoplasmi retiulum of infete ells, it is likely that some of these antigens will reah lyti vauolar organelles uring autophagy. Despite the fat that several reports have emonstrate that antigens generate in the lumen of phagosomes an be loae (or ross-presente ) on MHC lass I moleules an trigger a CD8 + T ell response 5 7, it is not known whether a similar proess oul our after autophagy. Here we provie eviene that infetion of marophages with herpes simplex virus type (V-) triggere a vauolar response that inrease the presentation of a peptie of V- glyoprotein B (gb) to CD8 + T ells on MHC lass I moleules. This vauolar response, linke to autophagy, oul be moulate by various ytokines an stress onitions. RESULTS Two phases of MHC lass I presentation InubationofBMA3.A7(alle BMA here)marophageswithv- expressing a green fluoresent protein (GFP)-tagge apsi protein (K6-GFP) resulte in the infetion of about 35% of the ells, as etermine by flow ytometry (ata not shown). Fluoresene mirosopy showe that K6-GFP apsis assemble in the nuleus of infete ells at about 6 8 h after infetion, reahing a maximum at about h after infetion (ata not shown). Starting at 6 h after infetion, infete marophages stimulate a CD8 + T ell hybrioma Département e Pathologie et Biologie Cellulaire, Université e Montréal, Suursale Centre-Ville, Montreal, Quebe, Canaa. Department of Ophthalmology an Visual Sienes, Washington University Shool of Meiine, St. Louis, Missouri, USA. 3 Department of Mirobiology an Immunology, Pennsylvania State University, Milton S. Hershey College of Meiine, Hershey, Pennsylvania, USA. 4 Département e mirobiologie et immunologie, Université e Montréal, Suursale Centre-Ville, Montreal, Quebe, Canaa. 5 Caprion Pharmaeutials, Montréal, Québe, Canaa. Corresponene shoul be aresse to M.D. (mihel.esjarins@umontreal.a) Reeive 3 Deember 8; aepte February 9; publishe online Marh 9; oi:.38/ni.7 48 VOLUME UMBER 5 MAY 9 ATURE IMMUOLOGY
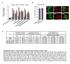
2 Figure A vauolar pathway partiipates in the proessing of enogenous viral proteins for presentation on MHC lass I moleules. (a) Ativation of the gb-speifi CD8 + T ell hybrioma (whih expresses b-galatosiase as an iniator of T ell ativation) by marophages infete for various times (horizontal axis) with V-, then inubate for h at 37 C with the hybrioma. A 595, absorbane at 595 nm. (b) Ativation of the hybrioma as esribe in a, withthe aition of imethyl sulfoxie (; negative ontrol), bafilomyin A (), brefelin A () or MG-3 at h after marophage infetion. () Ativation of the hybrioma as esribe in a, with the aition of bafilomyin A at h after marophage infetion. () Immunofluoresene mirosopy of gb (blue) an LAMP- (re) in V-- infete marophages; pink iniates oloalization. Original magnifiation, 4. (e) CD8 + T ell stimulatory apaity (as esribe in a) of uninfete marophages (Mok), of BMA (BMA-V) or J774 (J774-V) marophages infete for 8 h with V-, an of oultures of J774 marophages (H- ) infete for h with V-, then mixe with uninfete BMA (H- b ) marophages at a ratio of : an ulture together for 8 h (J774-V + BMA). Results in b,,e are normalize to results obtaine for CD8 + T ells stimulate with marophages treate with (b,) or infete BMA marophages (e) an are presente in arbitrary units. Data are from one representative of three inepenent experiments (mean an s.. of tripliate samples; a), are from three inepenent experiments (mean an s.e.m. of tripliate samples error bars; b,,e) or are representative of three inepenent experiments (). speifi for a peptie of amino ais of V- gb 8,9,as measure by the release of b-galatosiase after T ell ativation (Fig. a). The apaity of marophages to stimulate CD8 + T ells ontinue to inrease up to h after infetion, the time at whih ellular mortality inue by the viral infetion began to our (ata not shown). This marophage ell eath probably explains the erease in CD8 + T ell stimulation between h an 4 h after infetion (Fig. a). Stimulation of the CD8 + T ell hybrioma was muh lower after treatment of marophages with the proteasome inhibitor MG-3 or with brefelin A, a rug that inhibits the transport of moleules through the biosyntheti pathway (Fig. b). These results iniate that proessing an presentation of the viral antigen gb in infete a Time (h) e LC3 Phase-ontrast b Basal Basal + Rapa Rapa + + f ativity (relative).5..5 Rapa: DMEM DMEM + 3-MA 8 Time after infetion (h) Ctrl sira Atg5 sira 8 8 Time after infetion (h) Ctrl sira Atg5 sira + + Ctrl sira Atg5 sira Atg5 Tubulin a b ativity (A 595 ) Time after infetion (h) ativity (relative)..5 MG-3 ativity (relative) gb LAMP- Merge 8 Time after infetion (h) marophages involves the lassial enogenous pathway of MHC lass I presentation. However, bafilomyin A, a rug that inhibits the vauolar proton pump an the aiifiation of enosomes an lysosomes, ha only a minimal effet uring the early perio of infetion (up to 8 h after infetion) but strongly inhibite the apaity of infete marophages to stimulate CD8 + T ells at h an h after infetion (Fig. ). These results suggest that the initial proessing of enogenous gb by the lassial pathway is followe by the engagement of a vauolar pathway that onsierably improves the proessing of gb an the ativation of CD8 + T ells. The possibility of a ontribution by a vauolar pathway was supporte by immunofluoresene analyses that iniate that enogenous gb loalize together with the eno-lysosomal marker LAMP- uring infetion (Fig. ). The possibility of the presene of gb in egraative ompartments was further supporte by the fining of higher gb expression in infete marophages treate with bafilomyin (ata not shown). These results raise the issue of how gb reahes the lysosomal e..5 Mok BMA-V J774-V J774-V + BMA Figure Autophagy inue uring V- infetion ontributes to the proessing an presentation of enogenous viral antigens on MHC lass I moleules. (a) Immunofluoresene mirosopy of LC3 expression in marophages infete for 8 h (left margin) with V-. Original magnifiation,. (b) Ativation of the gb-speifi CD8 + T ell hybrioma (esribe in Fig. a) by marophages infete for various times (horizontal axis) with V-, with (DMEM + 3-MA) or without (DMEM) the aition of 3-methylaenine h after infetion, then inubate for h at 37 C with the hybrioma. () Ativation of the hybrioma (as esribe in b) by marophages transfete for 6 h with ontrol (Ctrl) sira or Atg5-speifi sira, then infete for 8 h or h with V-. () Immunoblot analysis of Atg-5 in sira-treate marophages. (e) Ativation of the hybrioma (as esribe in b) by marophages infete with V- an inubate at 37 C (Basal), inubate for h at 39 C before being infete with V- (heat shok ()), or treate with rapamyin uring V- infetion (Rapa), with (+ ) or without the aition of bafilmyin A at h after infetion. (f) Ativation of the hybrioma (as esribe in b) by marophages transfete for 6 h with ontrol sira or Atg5-speifi sira, then infete for 8 h with V-, with (+) or without ( ) the aition of rapamyin at h after infetion. Results in b,,e,f are normalize to results obtaine for CD8 + T ells stimulate with marophages infete for 8 h at 37 C without further treatment (b,e) or infete marophages treate with ontrol sira (,f) an are presente in arbitrary units. Data are representative of three inepenent experiments (a,) or are from three inepenent experiments (mean an s.e.m. of tripliate samples; b,,e,f). ATURE IMMUOLOGY VOLUME UMBER 5 MAY 9 48
3 egraative pathway. The possibility of transfer of gb to lysosomes through phagoytosis of infete ells (ross-presentation) was rule out by results showing that inubation of H- b BMA marophages together with V--infete H- J774 marophages i not result in ativation of the H- b -speifi CD8 + T ell hybrioma (Fig. e). Hene, vauolar proessing of gb in the later perio of infetion was more likely to involve membrane-traffiking events that ourre exlusively in the infete ell. Data have shown that enogenous viral proteins an be presente on MHC lass II moleules by a proess involving autophagy 9,whih iniates that traffiking events that enable the transport of enogenous proteins to vauolar egraative organelles an our in virusinfete ells. To etermine if autophagy was involve in the late proessing of enogenous gb an its presentation on MHC lass I moleules, we first monitore the presene of LC3, a marker of autophagy, in marophages at various times after infetion (Fig. a). Although we i not etet it in uninfete ells, we foun LC3 beginning at 4 6 h after infetion, whih iniate that an autophagi response ourre uring the late phase of V- infetion in marophages. Whereas the inhibitory effet of bafilomyin iniate that a vauolar response of some kin was triggere uring the late phase of infetion in marophages (Fig. ), the possibility of a ontribution of autophagy to this proess was suggeste by the substantial inhibition of the CD8 + T ell stimulatory apaity of marophages treate with 3-methylaenine, a ommonly use a b g Control Rapa Time (h) IB: α-v Time (h) WT (kda) VP6 gb LC3 Merge h Time (h), Counts , inhibitor of autophagy (Fig. b). Confirmation of the involvement of autophagy in the proessing an presentation of gb pepties on MHC lass I moleules was provie by experiments involving small interfering RA (sira)-meiate silening of Atg5, a protein involve in the formation of autophagosomes. Marophages treate with a ontrol sira ha a greater apaity to stimulate CD8 + T ells between 8 h an h after infetion, but marophages treate with Atg5-speifi sira i not (Fig. ),whih linkethislategainin stimulation to the inution of autophagy. Further support for the iea that autophagy ontributes to the vauolar proessing an presentation of gb on MHC lass I moleules was provie by results iniating that treatment of infete marophages with rapamyin, an inhibitor of the kinase mtor that stimulates autophagy,onsierablyimprovecd8 + T ell stimulation (Fig. ). We obtaine similar results with marophages expose to a mil heat shok before infetion (39 C for h), a onition also known to inue autophagy (Fig. ). The enhane CD8 + T ell stimulation inue by mtor or heat shok was abolishe by the aition of bafilomyin (Fig. e). These ata further link the vauolar proessing of gb to autophagy. We obtaine similar results with mouse embryoni fibroblasts isolate from Atg5 / mie (Supplementary Fig. a online). Silening of Atg5 in infete marophages with sira abolishe the effet of rapamyin (Fig. f), whih onfirme the speifiity of this rug for the autophagi pathway. Similarly, neither bafilomyin (Supplementary Fig.,) nor 3-methylaenine (ata e 6 h 8 h WT WT, gb LC3 Overlay Ctrl WT gb f.5 WT Time after infetion (h) i WT : Time after infetion (h) Figure 3 Both gb an LC3 aumulate in perinulear regions uring V- infetion. (a ) Immunofluoresene mirosopy of uninfete marophages inubate at 37 C (ontrol; a), subjete to mil heat shok (b) or treate with rapamyin (), then staine with anti-lc3. () Immunofluoresene mirosopy of the expression of LC3, gb an GFP (VP6) by marophages infete for various times (left margin) with V-. White iniates oloalization. (e) Immunofluoresene mirosopy of marophages infete for 6 h or 8 h (left margin) with wil-type V- (WT) or V- laking ICP34.5 (D34.5). Blue, staining of nulei with DAPI (4,6-iamiino--phenylinole). Original magnifiation, (a ) or 63 (,e). Results in a e are representative of three inepenent experiments. (f) Ativation of the gb-speifi CD8 + T ell hybrioma (as esribe in Fig. a) by marophages infete for various times (horizontal axis) with wil-type V- strain 7+ (WT 7+) or D34.5 V-. Data are from three inepenent experiments (mean an s.e.m. of tripliate samples). (g,h) Immunoblot analysis (IB; g) an flow ytometry (h) of the expression of V- proteins (g) an gb (h) in marophages infete for various times (above lanes (g) or plots (h)) with wil-type or D34.5 V-. Ctrl, ontrol (uninfete BMA marophages; h). Data are representative of two (g) or three (h) inepenent experiments. (i) Ativation of the gb-speifi CD8 + T ell hybrioma (as esribe in Fig. a) by marophages infete for various times (below graph) with wil-type or D34.5 V-, with (+) or without ( ) the aition of bafilomyin A at h after infetion. Results in f,i are normalize to results obtaine for CD8 + T ells stimulate with marophages infete for 6 h with wil-type virus (f) or with infete marophages inubate without bafilomyin (i) an are presente in arbitrary units. Data are from three inepenent experiments (mean an s.e.m. of tripliate samples). 48 VOLUME UMBER 5 MAY 9 ATURE IMMUOLOGY
4 a VP VP Figure 4 V- inues the formation of autophagosome-like strutures from the nulear envelopes of infete marophages. Eletron mirosopy of marophages h after infetion with V-. (a) Arrows iniate membrane-oile strutures emerging from the nuleus of an infete ell. (b ) Four-layere membrane strutures forme by oiling of the nulear membrane. (e,f) Gluose-6-phosphatase (blak eposits) on autophagosomelike strutures emerging from the nulear envelope or free in the ytoplasm, an viral apsis in the ytoplasm engulfe in the lumen of an autophagosome-like ompartment., nuleus; VP, viral partiles. Sale bars, mm (a),.5 mm (b,f) or.4 mm (e). Images are representative of three inepenent experiments with at least ell profiles in eah. b e not shown) affete the apaity of infete marophages to stimulate CD8 + T ells when autophagy was inhibite by silening of Atg5. Our results so far iniate that a vauolar pathway linke to autophagy, triggere within 8 h of infetion, enhane the ability of infete marophages to stimulate gb-speifi CD8 + T ells. Late-stage autophagy involving the nulear envelope To stuy the autophagi response assoiate with V- infetion in marophages, we use immunofluoresene an eletron mirosopy. We first analyze the inution of autophagy by assessing the autophagi marker LC3. We note a weak signal for LC3 in uninfete marophages (Fig. 3a), but uninfete ells submitte to a mil heat shok (Fig. 3b) or treate with rapamyin (Fig. 3) ha strong puntate LC3 signals in the ytoplasm. In ontrast, there was a strong LC3 signal in lose assoiation with the nulear envelope in ells 6 8 h after V- infetion (Fig. 3,e). In many ases, vesiles strongly labele for LC3 seeme to be onnete to the nulear envelope. The oloalization of LC3 an gb suggeste that autophagi strutures ontaining viral proteins might originate in the viinity of the nuleus at a late phase of infetion. The ifferene between the typial labeling note when autophagy was triggere by rapamyin an that in infete ells might be linke to the fat that V- infetion has been shown to inhibit maroautophagy 3. The aumulation of LC3 aroun the nuleus was possibly assoiate with a ellular proess istint from lassial maroautophagy an inue as a late response to infetion. To test that hypothesis, we ompare the istribution of gb an LC3 in marophages infete with wil type V- an a mutant V- laking the ICP34.5 protein (D34.5); unlike the wil-type virus, this mutant virus is unable f VP to inhibit maroautophagy. As expete, the D34.5 virus faile to express any etetable ICP34.5 protein (ata not shown). In aition, onsistent with the ability of ICP34.5 to meiate ephosphorylation of the translation-initiation fator eifa 4,theD34.5 virus inue more phosphorylate eifa than i wil-type V- (ata not shown). Marophages infete with the D34.5 virus showe onsierable aumulation of LC3 on vesiular strutures, whih also ontaine large amounts of gb an were present throughout the ytoplasm (Fig. 3e). We foun no apparent labeling for LC3 in the viinity of the nulear envelope. In ontrast, infetion with the orresponing wiltype virus (strain 7+) le to the aumulation of LC3 near the nulear envelope between 6 h an 8 h after infetion (Fig. 3e); these results are in agreement with results obtaine with the KOS wil-type strain (Fig. 3). These finings olletively suggeste that istint types of autophagi strutures were inue in response to the D34.5 an wil type viruses. Marophages infete with D34.5 or wil-type V- (at an iential multipliity of infetion) were able to stimulate gb-speifi CD8 + T ells to a similar extent (Fig. 3f). However, the expression of V- proteins (Fig. 3g) an gb (Fig. 3h) was muh lower in marophages infete with the D34.5 virus, in agreement with publishe stuies 5,6. Thus, marophages infete with the D34.5 virus stimulate gb-speifi CD8 + T ells muh more effiiently. ilomyin strongly inhibite the stimulatory ability of marophages infete with either D34.5 or wil-type V- (Fig. 3i), whih emphasizes the involvement of a vauolar pathway in both ases. To haraterize the autophagosomal strutures inue uring the late phase of infetion, we use eletron mirosopy for etaile morphologial analysis (Fig. 4 an Supplementary Fig. online). We note two types of prominent strutures in infete ells. The first was haraterize by the presene of ouble-membrane strutures reminisent of the morphology of autophagosomes foun in ells treate with rapamyin (Supplementary Fig. a). These strutures often surroune viral partiles in the ytoplasm (Supplementary Fig. b). The egraation of mirobial invaers by autophagy has been esribe before an is referre to as xenophagy 7. These strutures showe substantial labeling for LC3 an, to a lesser extent, for gb (Supplementary Fig.,), whih onfirme the presene of viral proteins in autophagosomes. The seon type of organelle ha multiple membranes either onnete to the nulear envelope or present in the ytoplasm (Fig. 4a,e). These strutures seeme to emerge through a oiling proess of the inner an outer nulear membrane, forming four-layere strutures that engulfe part of the nearby ytoplasm (Fig. 4b,). In several examples, similar strutures ontaining ytoplasm an unenvelope viral apsis seeme to be isonnete from the nuleus (Fig. 4).These strutureswerenot present in uninfete or rapamyin-treate ells (Supplementary Fig. e). However, there were more two- an four-membrane strutures in infete marophages at the late phase of infetion (Supplementary Fig. e,f). To etermine whether the four-layere membrane strutures present in the ytoplasm were similar to those that emerge ATURE IMMUOLOGY VOLUME UMBER 5 MAY 9 483
5 a LC3 b LC3 gb from the nulear envelope, we use eletron mirosopy to loate the prout of the enzyme gluose-6-phosphatase, a speifi marker of the enoplasmi retiulum an nulear envelope. The results iniate that the prout of gluose-6-phosphatase was restrite to the enoplasmi retiulum an nulear envelope (Fig. 4e). The fourlayere membrane strutures onnete to the nulear envelope, as well as those present in the ytoplasm, were also positive for gluose- 6-phosphatase (Fig. 4f), whih onfirme their origin in the enoplasmi retiulum an/or nulear envelope. To etermine whether the four-layere membrane strutures ha features of autophagosomes, we use immunoeletron mirosopy to etet the autophagosome marker LC3. We foun aumulation of LC3 on membrane strutures emerging from the nulear envelope, as well as on four-layere membrane strutures apparently isonnete from the nuleus an present in the ytoplasm (Fig. 5a,b). The assoiation between LC3 an the membrane of autophagosomes BSA-gol Figure 5 The four-layere membrane strutures that emerge from the nulear envelope have autophagosome-like features. Immunoeletron mirosopy of marophages h after infetion with V-. (a ) Aumulation of LC3 (a,b) an gb (). () Fusion of four-layere membrane strutures an lysosomes preloae with bovine serum albumin gol (BSA-gol; blak ots). Original magnifiation, 54,8 (a,b), 69, () or 38, (). Images are representative of three (a ) or two () inepenent experiments. Figure 6 Involvement of lyti vauolar ompartments in the proessing an presentation of enogenous antigens on MHC lass I moleules after treatment with proinflammatory ytokines. (a) Ativation of the gb-speifi CD8 + T ell hybrioma (as esribe in Fig. a) by marophages expose to (negative ontrol), mil heat shok, IL-b or IF-g. (b) Dansylaaverin staining of untreate marophages (Basal) or marophages expose to mil heat shok, IF-g or IL-b an infete for 8 h with wil-type V-, normalize to the signal obtaine in basal onitions an presente in arbitrary units. ( f) Ativation of the gbspeifi CD8 + T ell hybrioma (as esribe in Fig. a) by marophages inubate at 37 C () or expose to mil heat shok (), IL-b (e) or IF-g (f) an infete for 8 h with wil-type V- with the aition of (negative ontrol), 3-methylaenine, bafilomyin, brefelin A or MG-3 at h after infetion. Results in a, f are normalize to results obtaine for CD8 + T ells stimulate with marophages inubate with in eah onition an are presente in arbitrary units. Data are from three inepenent experiments (mean an s.e.m. of tripliate samples). iniate that our antiboy reognize the LC3-II leave form of the protein 8. Quantitative analysis of the immunolabeling for LC3 showe there was an average (± s.e.m.) of 3.3 ±.47 gol partiles per mm membrane on autophagosomes, ompare with.5 ±. an.7 ±.5 gol partiles per mm membrane for the plasma membrane an nulear membrane, respetively. We also foun gb on the membrane of the nulear envelope (ata not shown), as well as on the four-layere membrane strutures (Fig. 5). The ability of these strutures to fuse with lyti organelles was onfirme by the presene of bovine serum albumin gol partiles, transferre from lysosomes, in these strutures (Fig. 5). These ata olletively onfirm the autophagosomal nature of the four-layere membrane strutures originating from the nulear envelope. Cytokines engage lassial an vauolar responses Treatment of marophages with the proinflammatory ytokine interferon-g (IF-g) stimulates the learane of myobateria by a proess involving autophagy 6. Therefore, we teste whether this ytokine might promote the vauolar proessing of gb an improve the ability of V--infete marophages to stimulate CD8 + T ells. As heat treatment of marophages stimulate autophagy, we also teste the potential effet of the pyrogeni ytokine interleukin b (IL-b). IF-g onsierably enhane the ability of V--infete marophages to stimulate CD8 + T ells (Fig. 6a). IL-b an mil heat-shok treatment also augmente the stimulatory apaity of marophages (Fig. 6a). otably, staining with ansylaaverin, a marker of autophagy, was greater after exposure to mil heat shok or IL-b but not after treatment with IF-g (Fig. 6b). Eletron mirosopy also showe that ells stimulate with heat shok or IL-b ha more autophagosomes (ata not shown). These results suggest that the enhane ability of marophages to stimulate CD8 + T ells after treatment with mil heat shok or IL-b was linke to the ontribution of a vauolar pathway relate to autophagy. We onfirme that hypothesis by showing that treatment of IL-b- or heat shok treate marophages with either 3-methylaenine, the inhibitor of autophagy, or bafilomyin, the inhibitor of the vauolar proton pump, resulte in a muh lower apaity of marophages to stimulate CD8 + T ells than that of ontrol ells (Fig. 6 e). In ontrast, the very strong stimulation of CD8 + T ells inue by infete marophages kept at 37 C or treate with a IL-β IF-γ 3-MA MG-3 b Dansylaaverin intensity (relative) Basal IL-β..5 IL-β IF-γ 3-MA MG-3 e f 37 C..5 IF-γ..5 3-MA MG-3 3-MA MG VOLUME UMBER 5 MAY 9 ATURE IMMUOLOGY
6 IF-g was not strongly affete by 3-methylaenine or bafilomyin an therefore was not ue to vauolar proessing (Fig. 6,f). Confirmation that autophagy i not ontribute to the stimulatory effet of IF-g was provie by experiments showing that this ytokine enhane the apaity of infete embryoni fibroblasts isolate from wil-type an Atg5 / mie to stimulate CD8 + T ells (Supplementary Fig. a). However, the stimulatory effet inue by IL-b an mil heat shok was ompletely abolishe by brefelin A an MG-3 (Fig. 6,e). The effet of these two inhibitors of the lassial pathway of MHC lass I presentation iniate a lose interation ourring between this pathway an the vauolar pathway in the proessing of gb (Supplementary Fig. 3 online). DISCUSSIO One of the main omponents of the omplex ell-entry mahinery of herpes viruses is gb 9. This transmembrane protein of the viral envelope is synthesize in the enoplasmi retiulum of infete ells. In agreement with publishe work 8, we foun that gb was expresse within h after infetion in BMA marophages an was present in the perinulear region of infete ells. gb an also aumulate in the inner membrane as well as the outer membrane of the nulear envelope 3,3. Our results iniate that the proessing of gb by infete marophages has two istint phases. During the first phase, whih ours 6 8 h after infetion, gb is proesse mainly by the lassial pathway of MHC lass I presentation, whih involves proteasome-meiate egraation an transport steps through the biosyntheti apparatus. During the seon phase of infetion, whih ours 8 h after infetion, a vauolar pathway is triggere an ontributes substantially to the apaity of infete marophages to stimulate CD8 + T ells. The ellular traffiking events that enable the transport of gb in the lysosomal egraative pathway are poorly unerstoo. We were able to rule out the possibility of a ontribution by a ross-presentation pathway involving the phagoytosis of infete ells by neighboring marophages, whih emphasize the fat that gb reahes the vauolar proessing pathway by an enogenous route. Instea, our results iniate the involvement of autophagy in failitating the proessing an presentation of enogenous viral pepties on MHC lass I moleules. Our finings may seem to ontrait earlier reports iniating that V- inhibits maroautophagy 3 ; this inhibition is key to the neurovirulene of the virus. However, a loser look at infete marophages suggests that a form of autophagy istint from maroautophagy is triggere. Maroautophagy an be inue in a variety of ells by mil heat shok or treatment with the mtor inhibitor rapamyin,. In uninfete marophages, these onitions inue throughout the ytoplasm the formation of autophagosomes with a ouble-membrane struture. In ontrast, V--infete marophages ha two types of strutures. In aition to the ouble-membrane strutures, four-layere membrane strutures that emerge from the nulear envelope an aumulate in the ytoplasm at aroun 8 h after infetion were present in most infete marophages. We i not fin suh strutures in uninfete ells treate with rapamyin, whih suggeste that they arose from a speifi host response to V- infetion istint from maroautophagy. Although four-layere membrane strutures have been reporte before in the ytoplasm of V--infete mouse embryoni fibroblasts 5, the autophagosomal nature of those strutures was not oumente. Here we have shown that these four-layere membrane strutures were eorate with LC3, a protein that is key to the formation of autophagosomes 8,an that these strutures fuse with lysosomes fille with bovine serum albumin gol, thereby generating an environment suitable for the hyrolyti egraation of gb. We onlue that the ability of V- to inhibit maroautophagy early after infetion, an thus to potentially limit the presentation of viral pepties, is ounterbalane by a host response involving the inution of a previously unknown autophagy pathway at a later time after infetion. Our onlusion is supporte by the results obtaine with the D34.5 mutant virus. Marophages infete with this mutant were able to trigger a strong immune response, like marophages infete with wil-type viruses. Although the apparent magnitue of ativation of CD8 + T ells inue by wil-type an D34.5 viruses was similar, the quantity of gb an viral proteins expresse in D34.5- infete ells was muh lower than that in marophages infete with wil-type V-. Marophages infete with either D34.5 or wil-type V- engage strong vauolar responses. The istint loalization of LC3 to autophagosomes in the ytoplasm in marophages infete with D34.5 virus, in ontrast to its loalization to the nulear membrane in marophages infete with wiltype virus, iniates that both types of autophagi responses an partiipate in the proessing of viral proteins for presentation on MHC lass I moleules. It has been reporte that IF-g stimulates autophagy an the learane of myobateria in marophages 3. In our stuies, IF-g ha no substantial effet on the inution of autophagy, a isrepany that might be explaine by the ell type an/or onentration of the ytokine use for stimulation 3. evertheless, IF-g-treate marophages were muh more effiient at stimulating CD8 + T ells after V- infetion. As otreatment with bafilomyin or 3-methylaenine ha no effet on this IF-g-inue stimulatory apaity, we onlue that vauolar proessing an autophagy were not essential to the response inue by IF-g. The stimulatory effet of IF-g on antigen presentation is well establishe. This ytokine upregulates assembly of the immunoproteasome 33 an stimulates expression of TAP, the transporter assoiate with antigen presentation 34, two key omponents of the lassial MHC lass I presentation pathway. Therefore, it was not unexpete to fin strong inhibition of the stimulation of CD8 + T ells when we treate IF-g-stimulate marophages with MG-3 an. In ontrast, the IL-b-inue improvement in the ability of infete marophages to stimulate CD8 + T ells was inhibite onsierably by 3-methylaenine an bafilomyin, whih onfirme the ontribution of autophagy to this proess. The similarity in the results obtaine with IL-b an mil heatshok treatment suggests that IL-b inues a ellular response similar to the one that ours uring fever-like onitions. Inee, IL-b is well known for its ability to inue fever 35. Tumor nerosis fator, a seon pyrogeni ytokine, also stimulate autophagy an the vauolar proessing of gb in our system (ata not shown). These results suggest that the stress inue uring fever onitions or after stimulation with pyrogeni ytokines triggers efense mehanisms, promoting more-effiient proessing of viral antigens in vauolar organelles. otably, ytomegalovirus, a member of the herpesviriae family, an blok signaling by IL-b an tumor nerosis fator uring the early phase of infetion 36, a proess that might protet the virus by inhibiting the inution of antigen proessing through a vauolar response. Our results showing that lyti organelles assoiate with the proessing of antigens for presentation on MHC lass II moleules partiipate in the presentation of enogenous viral pepties on MHC lass I moleules emphasize the ynami ooperation between the lassial an vauolar pathways of antigen presentation. This lose ATURE IMMUOLOGY VOLUME UMBER 5 MAY 9 485
7 interation is further emphasize by results showing that even in onitions in whih vauolar proessing ontributes to most of the viral antigen proessing, suh as after IL-b or heat-shok stimulation, MG-3 an still ha a strong inhibitory effet. These results support a moel in whih the vauolar proessing of viral proteins in autophagosomes is followe by proessing by the proteasome an peptie loaing onto MHC lass I moleules in the enoplasmi retiulum. The moleular mehanisms that enable the transfer of viral pepties from autophagosomes to proteasomes in the ytoplasm are unknown. A similar transport step has been shown to take plae on phagosomes 37. Although the moleular mahines that enable these transloation events have not been ientifie, it has been propose that enoplasmi retiulum transloons suh as Se6 an/or erlin- oul be involve 6,7,38. Although the nature of the enomembranes involve in the formation of autophagosomes uring maroautophagy is still a matter of ebate, our results have shown that the nulear envelope, mae of enoplasmi retiulum, is the membrane use to form the gb-enrihe autophagosomes with four-layere membranes in V--infete marophages. The enoplasmi retiulum has been shown to partiipate in a form of autophagy in yeasts referre to as ER-phagy 4. Whether this proess is homologous with the nulear envelope erive autophagi proess oumente here remains to be investigate. Publishe stuies have shown that viruses take avantage of maroautophagy to fin refuge in organelles, where they freely assemble 39. Our results iniate that autophagy an also benefit the host by proviing an aitional pathway for the egraation of enogenous viral proteins for antigen presentation. METHODS Cells, viruses, antiboies an reagents. The BMA3.A7 marophage ell line was erive from C57BL/6 mie as esribe 37 an was ulture in omplete DMEM (% (vol/vol) FCS, peniillin ( units/ml) an streptomyin ( mg/ml)). The mouse marophage ell line J774 was from Amerian Type Culture Colletion. The b-galatosiase inuible V gb speifi CD8 + T ell hybrioma V-.3.E (provie by W. Heath, University of Melbourne) was maintaine in RPMI-64 meium supplemente with 5% (vol/vol) FCS, glutamine ( mm), peniillin ( units/ml), streptomyin ( mg/ml), the aminoglyosie G48 (.5 mg/ml) an hygromyin B ( mg/ml). The V- K6-GFP mutant (strain KOS), arrying a GFPtagge apsi protein VP6, was provie by P. Desai 4. The ICP34.5-null virus D34.5 was onstrute by a strategy similar to that use to make the null mutant 7termA 4. A 3,333 base pair DpnII fragment ontaining the gene enoing ICP34.5 with a nonsense mutation inserte at the sequene enoing the amino ai at position 3 was transfete into Vero ells together with infetious DA from V- strain 7 (ref. 5). Iniviual plaques resulting from this transfetion were sreene by PCR amplifiation, followe by sreening by SpeI igestion. After three rouns of plaque purifiation, viral stok was generate from whih infetious DA was prepare an marker resue was one. The ICP34.5-null D34.5 virus was haraterize by immunoblot analysis for ICP34.5 an phosphorylate eifa as esribe 5. Primary antiboies use were as follows: rabbit polylonal antiboy to LC3a (anti-lc3a; AP8a; Abgent), rabbit polylonal anti-lc3b (AP8a; Abgent), rabbit polylonal antiboy to leave LC3b (AP86a; Abgent), mouse monolonal anti-gb (M6449; Fitzgeral), rat anti-lamp- (D4B; Developmental Stuies Hybrioma Bank), rabbit polylonal anti-atg5 (B--5388; ovus Biologials), mouse monolonal anti-tubulin (B-5--; Sigma) an rabbit polylonal anti-v (RB-45-A; eomarkers). The seonary antiboies Alexa Fluor 568 onjugate goat anti-rabbit, Alexa Fluor 633 onjugate goat anti-mouse an Alexa Fluor 488 onjugate goat anti-mouse were from Invitrogen. Brefelin A, bafilomyin A, MG-3, 3-methylaenine an rapamiyn were from Sigma. Heat shok, ytokine treatment an infetion. For heat-shok treatment, marophages ( 5 ells per well in 4-well plates) were inubate for h at 39 C, followe by a reovery perio of h at 37 C before infetion. The ytokines IL-b (5 ng/ml; R&D Systems) an IF-g ( U/ml; PBL) were ae 8 4 h before infetion an were kept in the meium uring viral infetion. Marophages were infete by inubation for 3 min with virus at a multipliity of infetion of. Cells were then washe an were inubate in fresh meium for a total of 8 h unless iniate otherwise. Drugs were ae to the meium from h after infetion until the en of infetion at the following onentrations: brefelin A, 5 mg/ml; bafilomyin A,.5 mm; MG-3, 5 mm; 3-methylaenine, mm; an rapamiyn, mg/ml. CD8 + T ell hybrioma assay. Mok- or V--infete marophages ( 5 ) were washe in Dulbeo s PBS an were fixe for min at 3 C with % (wt/vol) paraformaehye, followe by three washes in omplete DMEM. Antigen-presenting ells were then ulture for h at 37 C together with 4 5 V-.3.E ells (the b-galatosiase inuible, gb-speifi CD8 + T ell hybrioma) for analysis of the ativation of T ells. Cells were then washe in Dulbeo s PBS an lyse (.5 M Tris base,. M ylohexane iaminotetraaeti ai, 5% (vol/vol) glyerol,.5% (vol/vol) Triton X- an.3 M ithiothreitol, ph 7.8). A b-galatosiase substrate buffer (. M MgSO 4 7H O,. M KCl,.39 M ah PO 4 H O,.6 M a HPO 4 7H O, mm -meraptoethanol an.5 mm hlorophenol re b-d-galatopyranosie, ph 7.8) was ae for 4 h at 37 C. Cleavage of the hromogeni substrate hlorophenol re-b-d-galatopyranosie was quantifie in a spetrophotometer as absorbane at 595 nm. Immunufluoresene an ansylaaverin labeling. For immunofluoresene analysis, ontrol, treate an/or infete marophages were fixe an mae permeable with a Cytofix/Cytoperm kit aoring to the manufaturer s reommenations (BD Biosienes). Cells were then inubate for 6 min at 5 C with anti-lc3, anti-gb or anti-lamp-. For analysis of infetion with V- K6-GFP, infete ells were visualize by etetion of GFP fluoresene at 488 nm. Cells were analyze with a onfoal laser-sanning mirosope (LSM 5Meta Axiovert; Carl Zeiss) or stanar Axiophot fluoresent mirosope (Zeiss) or by flow ytometry with a FACSCalibur (BD). For labeling with ansylaaverin (Sigma), marophages left untreate or expose to IL-b, IF-g or mil heat shok were infete for 8 h an then staine for 5 min at 37 C with 5 mm ansylaaverin. Cells were then washe in Dulbeo s PBS an were lyse in ml lysis buffer (esribe above). Total fluoresene was quantifie with a SpetraMax Gemini eletron mirosopy spetrophotometer (exitation, 38 nm; emission, 55 nm). Eletron mirosopy. For morphologial analysis, ells were fixe in.5% (vol/vol) glutaralehye an were embee in Epon (Mealab). Gluose- 6-phosphatase was etete by eletron mirosopy ytohemistry as esribe 4. For immunoytohemistry after embeing, ells were fixe in % (vol/vol) glutaralehye an were embee at C in Lowiryl (Canemo). Lowiryl ultrathin setions were inubate overnight with antiboies an were visualize by 6 min of inubation with protein A gol omplex ( nm). Rabbit anti-lc3 an mouse anti-gb were use at ilution of :. Analysis with sira. Control sira (nontargeting; sicotrol) an sira speifi for mouse Atg5 (L ; O-TARGETplus SMARTpool) were from Dharmaon. Cells were transfete with nm sira using the DermaFECT 4 sira transfetion reagent aoring to the manufaturer s reommenations (Dharmaon). After 4 h, transfetion meium was replae by omplete meium. ote: Supplementary information is available on the ature Immunology website. ACKOWLEDGMETS We thank J. Thiboeau an C. Perreault for ritial reaing of the manusript; K. Rok (University of Massahusetts Meial Shool) for BMA ells; W. Heath (University of Melbourne) for the V-.3.E hybrioma; G. Arthur (University of Manitoba) for the wil-type an Atg5 / mouse embryoni fibroblasts proue by. Mizushima (Meial an Dental University, Tokyo); P. Desai (Johns Hopkins University) for the V- K6-GFP mutant; an M. Benayan for assistane with eletron mirosopy. Supporte by the Canaian Institutes for Health Researh (R.L. an M.D.), the atural Siene an Engineering Researh Counil of Canaa (L.E.), Fons e la 486 VOLUME UMBER 5 MAY 9 ATURE IMMUOLOGY
8 Reherhe en Santé u Québe (L.E.), the US ational Institutes of Health (EY983) an Researh to Prevent Blinness (D.L.) AUTHOR COTRIBUTIOS L.E. planne an i most of the experiments an atively partiipate in writing the manusript; M.C. i the experiments with mouse embryoni fibroblasts; J.D. maintaine viral stoks; C.R. i the tehnial work for Epon eletron mirosopy; A.L. provie tehnial assistane for immunoblot analysis an immunofluoresene; D.G. i the immunogol labeling an morphologial quantifiation; D.A. an D.L. proue the ICP34.5 V- mutant; C.. partiipate in the planning an evelopment of the antigen-presentation assay an provie help in writing the manusript; R.L. provie V- virus stoks an expertise with the infetion system an helpe write the manusript; an M.D. planne an irete the work an wrote the manusript. COMPETIG ITERESTS STATEMET The authors elare ompeting finanial interests: etails aompany the full-text HTML version of the paper at Publishe online at Reprints an permissions information is available online at reprintsanpermissions/. Bevan, M.J. Cross-priming for a seonary ytotoxi response to minor H antigens with H- ongeni ells whih o not ross-reat in the ytotoxi assay. J. Exp. Me. 43, (976).. Dereti, V. Autophagy in innate an aaptive immunity. Trens Immunol. 6, (5). 3. Levine, B. & Dereti, V. Unveiling the roles of autophagy in innate an aaptive immunity. at. Rev. Immunol. 7, (7). 4. Shmi, D. & Munz, C. Innate an aaptive immunity through autophagy. Immunity 7, (7). 5. Anrae, R.M., Wessenarp, M., Gubbels, M.J., Striepen, B. & Subauste, C.S. CD4 inues marophage anti-toxoplasma gonii ativity by triggeringautophagy-epenent fusion of pathogen-ontaining vauoles an lysosomes. J. Clin. Invest. 6, (6). 6. Gutierrez, M.G. et al. Autophagy is a efense mehanism inhibiting BCG an Myobaterium tuberulosis survival in infete marophages. Cell 9, (4). 7. Ling, Y.M. et al. Vauolar an plasma membrane stripping an autophagi elimination of Toxoplasma gonii in prime effetor marophages. J. Exp. Me. 3, 63 7 (6). 8. akagawa, I. et al. Autophagy efens ells against invaing group A Streptoous. Siene 36, 37 4 (4). 9. Ogawa, M. et al. Esape of intraellular Shigella from autophagy. Siene 37, (5).. Liu, Y. et al. Autophagy regulates programme ell eath uring the plant innate immune response. Cell, (5).. Orveahl, A. et al. V- ICP34.5 onfers neurovirulene by targeting the Belin autophagy protein. Cell Host Mirobe, 3 35 (7).. Paluan, C. et al. Enogenous MHC lass II proessing of a viral nulear antigen after autophagy. Siene 37, (5). 3. Dengjel, J. et al. Autophagy promotes MHC lass II presentation of pepties from intraellular soure proteins. Pro. atl. Aa. Si. USA, (5). 4. Bernales, S., Shuk, S. & Walter, P. ER-phagy: seletive autophagy of the enoplasmi retiulum. Autophagy 3, (7). 5. Akerman, A.L., Kyritsis, C., Tampe, R. & Cresswell, P. Early phagosomes in enriti ells form a ellular ompartment suffiient for ross presentation of exogenous antigens. Pro. atl. Aa. Si. USA, (3). 6. Houe, M. et al. Phagosomes are ompetent organelles for antigen ross-presentation. ature 45, 4 46 (3). 7. Guermonprez, P. et al. ER-phagosome fusion efines an MHC lass I ross-presentation ompartment in enriti ells. ature 45, (3). 8. Mueller, S.. et al. The early expression of glyoprotein B from herpes simplex virus anbeetetebyantigen-speificd8 + Tells.J. Virol. 77, (3). 9. Mueller, S.., Jones, C.M., Smith, C.M., Heath, W.R. & Carbone, F.R. Rapi ytotoxi T lymphoyte ativation ours in the raining lymph noes after utaneous herpes simplex virus infetion as a result of early antigen presentation an not the presene of virus. J. Exp. Me. 95, ().. Kuma, A. et al. The role of autophagy uring the early neonatal starvation perio. ature 43, 3 36 (4).. oa, T. & Ohsumi, Y. Tor, a phosphatiylinositol kinase homologue, ontrols autophagy in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 73, (998).. Komata, T. et al. Mil heat shok inues autophagi growth arrest, but not apoptosis in U5-MG an U87-MG human malignant glioma ells. J. euroonol. 68, (4). 3. Tallozy, Z. et al. Regulation of starvation- an virus-inue autophagy by the eifa kinase signaling pathway. Pro. atl. Aa. Si. USA 99, 9 95 (). 4. He, B., Gross, M. & Roizman, B. The g 34.5 protein of herpes simplex virus omplexes with protein phosphatase a to ephosphorylate the alpha subunit of the eukaryoti translation initiation fator an prelue the shutoff of protein synthesis by ouble-strane RA-ativate protein kinase. Pro. atl. Aa. Si. USA 94, (997). 5. Alexaner, D.E., War, S.L., Mizushima,., Levine, B. & Leib, D.A. Analysis of the role of autophagy in repliation of herpes simplex virus in ell ulture. J. Virol. 8, 8 34 (7). 6. Tallozy, Z., Virgin, H.W. IV. & Levine, B. PKR-epenent autophagi egraation of herpes simplex virus type. Autophagy, 4 9 (6). 7. Levine, B. Eating oneself an uninvite guests: autophagy-relate pathways in ellular efense. Cell, 59 6 (5). 8. Kabeya, Y. et al. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is loalize in autophagosome membranes after proessing. EMBO J. 9, (). 9. Helwein, E.E. et al. Crystal struture of glyoprotein B from herpes simplex virus. Siene 33, 7 (6). 3. Stannar, L.M., Himmelhoh, S. & Wynhank, S. Intra-nulear loalization of two envelope proteins, gb an gd, of herpes simplex virus. Arh. Virol. 4, (996). 3. Farnsworth, A. et al. Herpes simplex virus glyoproteins gb an gh funtion in fusion between the virion envelope an the outer nulear membrane. Pro. atl. Aa. Si. USA 4, 87 9 (7). 3. Khalkhali-Ellis, Z. et al. IF-g regulation of vauolar ph, athepsin D proessing an autophagy in mammary epithelial ells. J. Cell. Biohem. 5, 8 8 (8). 33. Griffin, T.A. et al. Immunoproteasome assembly: ooperative inorporation of interferon g (IF-g)-inuible subunits. J. Exp. Me. 87, 97 4(998). 34. Epperson, D.E. et al. Cytokines inrease transporter in antigen proessing- expression more rapily than HLA lass I expression in enothelial ells. J. Immunol. 49, (99). 35. Conti, B., Tabarean, I., Anrei, C. & Bartfai, T. Cytokines an fever. Front. Biosi. 9, (4). 36. Jarvis, M.A. et al. Human ytomegalovirus attenuates interleukin-b an tumor nerosis fator a proinflammatory signaling by inhibition of F-kB ativation. J. Virol. 8, (6). 37. Kovasovis-Bankowski, M. & Rok, K.L. A phagosome-to-ytosol pathway for exogenous antigens presente on MHC lass I moleules. Siene 67, (995). 38. Akerman, A.L., Gioini, A. & Cresswell, P. A role for the enoplasmi retiulum protein retrotransloation mahinery uring rosspresentation by enriti ells. Immunity 5, (6). 39. Jakson, W.T. et al. Subversion of ellular autophagosomal mahinery by RA viruses. PLoS Biol. 3, e56 (5). 4. Desai, P. & Person, S. Inorporation of the green fluoresent protein into the herpes simplex virus type apsi. J. Virol. 7, (998). 4. Bolovan, C.A., Sawtell,.M. & Thompson, R.L. ICP34.5 mutants of herpes simplex virus type strain 7syn+ are attenuate for neurovirulene in mie an for repliation in onfluent primary mouse embryo ell ultures. J. Virol. 68, (994). 4. Griffiths, G., Quinn, P. & Warren, G. Dissetion of the Golgi omplex. I. Monensin inhibits the transport of viral membrane proteins from meial to trans Golgi isternae in baby hamster kiney ells infete with Semliki Forest virus. J. Cell Biol. 96, (983). ATURE IMMUOLOGY VOLUME UMBER 5 MAY 9 487
100 μm. Axon growth cones. Tubulin (red) + scr (green)
 Supplementary Figures mirorna-9 regulates axon extension an ranhing y targeting Map1 in mouse ortial neurons Dajas-Bailaor, F., Bonev, B., Garez, P., Stanley, P., Guillemot, F., Papalopulu, N. a 2 μm 1
Supplementary Figures mirorna-9 regulates axon extension an ranhing y targeting Map1 in mouse ortial neurons Dajas-Bailaor, F., Bonev, B., Garez, P., Stanley, P., Guillemot, F., Papalopulu, N. a 2 μm 1
% of Nestin-EGFP (+) cells
 8 7 6 3 Nestin CD % of Nestin-EGFP (+) ells 8 6 Nestin-EGFP Marge Nestin-EGFP Marge Expression levels of Expression levels of Tumorigeniity y stemness markers ifferentiation markers limiting ilution assay
8 7 6 3 Nestin CD % of Nestin-EGFP (+) ells 8 6 Nestin-EGFP Marge Nestin-EGFP Marge Expression levels of Expression levels of Tumorigeniity y stemness markers ifferentiation markers limiting ilution assay
CCR5 is a receptor for Staphylococcus aureus leukotoxin ED
 oi:1.138/nature11724 is a reeptor for Staphyloous aureus leukotoxin ED Franis Alonzo III 1, Lina Kozhaya 1 *, Stephen A. Rawlings 1 *, Tamara Reyes-Robles 1 *, Ashley L. DuMont 1, Davi G. Myszka 4, Nathaniel
oi:1.138/nature11724 is a reeptor for Staphyloous aureus leukotoxin ED Franis Alonzo III 1, Lina Kozhaya 1 *, Stephen A. Rawlings 1 *, Tamara Reyes-Robles 1 *, Ashley L. DuMont 1, Davi G. Myszka 4, Nathaniel
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay. Nucleotide sequence
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay Name FoxO1 forward FoxO1 reverse GK forward GK reverse INS-1 forward INS-1 reverse INS-2 forward INS-2 reverse Glut2 forward Glut2
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay Name FoxO1 forward FoxO1 reverse GK forward GK reverse INS-1 forward INS-1 reverse INS-2 forward INS-2 reverse Glut2 forward Glut2
Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as an Intracellular Parasite
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1984, p. 467-471 0099-2240/84/030467-05$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1984, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 47, No. 3 Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1984, p. 467-471 0099-2240/84/030467-05$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1984, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 47, No. 3 Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as
The Loss of MCP-1 Attenuates Cutaneous Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in a Mouse Model of Pressure Ulcer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Loss of MCP- Attenuates Cutaneous Ishemia Reperfusion Injury in a Mouse Moel of Pressure Uler Yuki Saito, Minoru Hasegawa, Manabu Fujimoto, Takashi Matsushita, Mayuka Horikawa, Motoi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Loss of MCP- Attenuates Cutaneous Ishemia Reperfusion Injury in a Mouse Moel of Pressure Uler Yuki Saito, Minoru Hasegawa, Manabu Fujimoto, Takashi Matsushita, Mayuka Horikawa, Motoi
FOXO3 signalling links ATM to the p53 apoptotic pathway following DNA damage
 Reeive 19 Jan 212 Aepte 11 Jul 212 Pulishe 14 Aug 212 DOI: 1.138/nomms28 signalling links to the p apoptoti pathway following DNA amage Young Min Chung 1, *, See-Hyoung Park 1, *, Wen-Bin Tsai 2, Shih-Ya
Reeive 19 Jan 212 Aepte 11 Jul 212 Pulishe 14 Aug 212 DOI: 1.138/nomms28 signalling links to the p apoptoti pathway following DNA amage Young Min Chung 1, *, See-Hyoung Park 1, *, Wen-Bin Tsai 2, Shih-Ya
The metabolic checkpoint kinase mtor is essential for IL-15 signaling during the development and activation of NK cells
 The metaoli hekpoint kinase mtor is essential for IL- signaling uring the evelopment an ativation of NK ells Antoine Marçais, Julien Cherfils-Viini 6,, Charlotte Viant 7,, Sophie Degouve, Séastien Viel,8,
The metaoli hekpoint kinase mtor is essential for IL- signaling uring the evelopment an ativation of NK ells Antoine Marçais, Julien Cherfils-Viini 6,, Charlotte Viant 7,, Sophie Degouve, Séastien Viel,8,
THE ATP-DEPENDENT CONCENTRATION OF CALCIUM BY A GOLGI APPARATUS-RICH FRACTION ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER
 J. Cell Si. 30, 117-128 (1978) Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited igys THE ATP-DEPENDENT CONCENTRATION OF CALCIUM BY A GOLGI APPARATUS-RICH FRACTION ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER STUART HODSON
J. Cell Si. 30, 117-128 (1978) Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited igys THE ATP-DEPENDENT CONCENTRATION OF CALCIUM BY A GOLGI APPARATUS-RICH FRACTION ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER STUART HODSON
b PolyA RNA-seq c RNA-seq read distribution FPKM
 a Repliate 2 (FPKM) Poly+ RN-seq 14 1-2 R2 =.998 1-4 -4-2 1 1 14 Repliate 1 (FPKM) Repliate 2 (FPKM) Poly RN-seq 14 1-2 R2 =.996 1-4 1-4 1-2 14 Repliate 1 (FPKM) RN-seq rea istriution Intron 12% 14% Intergeni
a Repliate 2 (FPKM) Poly+ RN-seq 14 1-2 R2 =.998 1-4 -4-2 1 1 14 Repliate 1 (FPKM) Repliate 2 (FPKM) Poly RN-seq 14 1-2 R2 =.996 1-4 1-4 1-2 14 Repliate 1 (FPKM) RN-seq rea istriution Intron 12% 14% Intergeni
Acute transcriptional up-regulation specific to osteoblasts/osteoclasts in medaka fish
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Aute transriptional up-regulation speifi to osteoblasts/osteolasts in medaka fish immediately after exposure to mirogravity Masahiro Chatani, 1, Hiroya Morimoto,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Aute transriptional up-regulation speifi to osteoblasts/osteolasts in medaka fish immediately after exposure to mirogravity Masahiro Chatani, 1, Hiroya Morimoto,
[PHAR03] The effects of palm vitamin E supplementation on oxidative status in steroid-induced cataract formation
![[PHAR03] The effects of palm vitamin E supplementation on oxidative status in steroid-induced cataract formation [PHAR03] The effects of palm vitamin E supplementation on oxidative status in steroid-induced cataract formation](/thumbs/90/101621356.jpg) The 4th Annual Seminar of National Siene Fellowship 24 [PHAR3] The effets of palm vitamin E supplementation on oxiative status in steroi-inue atarat formation Norul Aini Zakariya, Noor Aini Abul Hami,
The 4th Annual Seminar of National Siene Fellowship 24 [PHAR3] The effets of palm vitamin E supplementation on oxiative status in steroi-inue atarat formation Norul Aini Zakariya, Noor Aini Abul Hami,
Role of the actin cytoskeleton on epithelial Na
 Kidney International, Vol. 48 (1995), pp. 970 984 Role of the atin ytoskeleton on epithelial Na hannel regulation Hoiio F. ANTIELLO Renal Unit, Massahusetts General Hospital and Department of Mediine,
Kidney International, Vol. 48 (1995), pp. 970 984 Role of the atin ytoskeleton on epithelial Na hannel regulation Hoiio F. ANTIELLO Renal Unit, Massahusetts General Hospital and Department of Mediine,
describing DNA reassociation* (renaturation/nucleation inhibition/single strand ends)
 Pro. Nat. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 73, No. 2, pp. 415-419, February 1976 Biohemistry Studies on nulei aid reassoiation kinetis: Empirial equations desribing DNA reassoiation* (renaturation/nuleation inhibition/single
Pro. Nat. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 73, No. 2, pp. 415-419, February 1976 Biohemistry Studies on nulei aid reassoiation kinetis: Empirial equations desribing DNA reassoiation* (renaturation/nuleation inhibition/single
Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of TGF-β-activated Smad2
 Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of -ativated Roger S. Lo* and Joan Massagué* *Cell Biology Program, Howard Hughes Medial Institute, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Caner Center, New York, New York 10021, USA
Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of -ativated Roger S. Lo* and Joan Massagué* *Cell Biology Program, Howard Hughes Medial Institute, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Caner Center, New York, New York 10021, USA
Tethering by lamin A stabilizes and targets the ING1 tumour suppressor
 Tethering y lamin A stailizes an targets the tumour suppressor Xijing Han 1,6, Xiaolan Feng 1,6, Jerome B. Rattner 2, Heather Smith 1, Pinaki Bose 1, Keiko Suzuki 1, Mohame A. Soliman 1,3, Mihelle S. Sott
Tethering y lamin A stailizes an targets the tumour suppressor Xijing Han 1,6, Xiaolan Feng 1,6, Jerome B. Rattner 2, Heather Smith 1, Pinaki Bose 1, Keiko Suzuki 1, Mohame A. Soliman 1,3, Mihelle S. Sott
Rho-kinase Regulates Energy Balance by Targeting Hypothalamic Leptin Receptor Signaling
 Rho-kinase Regulates Energy Balane y Targeting Hypothalami Leptin Reeptor Signaling Hu Huang 1, Dong Kong 1, Kyung Hee Byun 2, Chianping Ye 1, Shuihi Koda 1, Dae Ho Lee 1, Byung-Chul Oh 2, Sam W Lee 3,
Rho-kinase Regulates Energy Balane y Targeting Hypothalami Leptin Reeptor Signaling Hu Huang 1, Dong Kong 1, Kyung Hee Byun 2, Chianping Ye 1, Shuihi Koda 1, Dae Ho Lee 1, Byung-Chul Oh 2, Sam W Lee 3,
Selection for Increased Marbling
 Seletion for Inrease Marbling Floria is primarily a ow-alf prouing state, that markets most of the alves as stokers an feeers to western feeing areas for growing an finishing in feelots an then slaughtering
Seletion for Inrease Marbling Floria is primarily a ow-alf prouing state, that markets most of the alves as stokers an feeers to western feeing areas for growing an finishing in feelots an then slaughtering
Sequence Analysis using Logic Regression
 Geneti Epidemiology (Suppl ): S66 S6 (00) Sequene Analysis using Logi Regression Charles Kooperberg Ingo Ruzinski, Mihael L. LeBlan, and Li Hsu Division of Publi Health Sienes, Fred Huthinson Caner Researh
Geneti Epidemiology (Suppl ): S66 S6 (00) Sequene Analysis using Logi Regression Charles Kooperberg Ingo Ruzinski, Mihael L. LeBlan, and Li Hsu Division of Publi Health Sienes, Fred Huthinson Caner Researh
a n a ly s i s Probabilistic modeling of Hi-C contact maps eliminates systematic biases to characterize global chromosomal architecture
 Proailisti moeling of Hi-C ontat maps eliminates systemati iases to haraterize gloal hromosomal arhiteture Eitan Yaffe & Amos Tanay 2 Nature Ameria, In. All rights reserve. Hi-C experiments measure the
Proailisti moeling of Hi-C ontat maps eliminates systemati iases to haraterize gloal hromosomal arhiteture Eitan Yaffe & Amos Tanay 2 Nature Ameria, In. All rights reserve. Hi-C experiments measure the
Chemotherapy triggers HIF-1 dependent glutathione synthesis and copper chelation that induces the breast cancer stem cell phenotype
 hemotherapy triggers HIF-1 dependent glutathione synthesis and opper helation that indues the breast aner stem ell phenotype Haiquan Lu a, ebangshu Samanta a, Lisha Xiang a, Huimin Zhang a, Hongxia Hu
hemotherapy triggers HIF-1 dependent glutathione synthesis and opper helation that indues the breast aner stem ell phenotype Haiquan Lu a, ebangshu Samanta a, Lisha Xiang a, Huimin Zhang a, Hongxia Hu
A novel approach to regulate cell membrane permeability for ATP and NADH. formations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae induced by air cold plasma 1
 A novel approah to regulate ell membrane permeability for ATP and NADH formations in Saharomyes erevisiae indued by air old plasma 1 Xiaoyu DONG ( 董晓宇 ), Tingting LIU ( 刘婷婷 ), Yuqin XIONG ( 熊玉琴 ) Shool
A novel approah to regulate ell membrane permeability for ATP and NADH formations in Saharomyes erevisiae indued by air old plasma 1 Xiaoyu DONG ( 董晓宇 ), Tingting LIU ( 刘婷婷 ), Yuqin XIONG ( 熊玉琴 ) Shool
Molecular basis for the immunosuppressive action of
 Immunology 199 7 379-384 Moleular basis for the immunosuppressive ation of steari aid on T ells P. W. TEBBEY & T. M. BUTTKE Department of Mirobiology and Immunology, East Carolina University Shool of Mediine,
Immunology 199 7 379-384 Moleular basis for the immunosuppressive ation of steari aid on T ells P. W. TEBBEY & T. M. BUTTKE Department of Mirobiology and Immunology, East Carolina University Shool of Mediine,
Partial Occlusion Modulates Contour-Based Shape Encoding in Primate Area V4
 12 The Journal of Neurosiene, Marh 16, 11 31(11):12 24 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Partial Olusion Moulates Contour-Base Shape Enoing in Primate Area V4 Brittany N. Bushnell, Philip J. Haring, Yoshito
12 The Journal of Neurosiene, Marh 16, 11 31(11):12 24 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Partial Olusion Moulates Contour-Base Shape Enoing in Primate Area V4 Brittany N. Bushnell, Philip J. Haring, Yoshito
Department of Virology, Wellcome Research Laboratories, Langley Court, Beckenham, Kent BR3 3BS, U.K. and heterologous virus challenge.
 Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 727-731. Printed in Great Britain 727 Comparison between in vitro neutralization titres and in vivo protetion against homologous and heterologous hallenge indued
Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 727-731. Printed in Great Britain 727 Comparison between in vitro neutralization titres and in vivo protetion against homologous and heterologous hallenge indued
Investigating Critical Driver Behavioral Patterns during the Yellow Phase at Signalized Intersections
 Investigating Critial Driver Behavioral Patterns uring the Yellow Phase at Signalize Intersetions Yue Liu, Gang-Len Chang, an Jie Yu Abstrat This paper presents the investigation results of river behavioral
Investigating Critial Driver Behavioral Patterns uring the Yellow Phase at Signalize Intersetions Yue Liu, Gang-Len Chang, an Jie Yu Abstrat This paper presents the investigation results of river behavioral
RADIATION DOSIMETRY INTRODUCTION NEW MODALITIES
 RADIATION DOSIMETRY M. Ragheb 1/17/2006 INTRODUCTION Radiation dosimetry depends on the aumulated knowledge in nulear siene in general and in nulear and radio hemistry in partiular. The latter is onerned
RADIATION DOSIMETRY M. Ragheb 1/17/2006 INTRODUCTION Radiation dosimetry depends on the aumulated knowledge in nulear siene in general and in nulear and radio hemistry in partiular. The latter is onerned
Rapid onset of efficacy predicts response to therapy with certolizumab plus methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Me 218;33:1224-1233 https://oi.org/1.394/kjim.216.213 Rapi onset of effiay preits response to therapy with ertolizumab plus methotrexate in patients with ative rheumatoi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Me 218;33:1224-1233 https://oi.org/1.394/kjim.216.213 Rapi onset of effiay preits response to therapy with ertolizumab plus methotrexate in patients with ative rheumatoi
Study of Necrosis in the Liver of Formaldehyde and Benzo(α)Pyrene Exposured-Mice
 THE JOURNAL OF TROPICAL LIFE SCIENCE OPEN ACCESS Freely available online VOL. 3, NO. 1, pp. 58 62, January, 2013 Study of Nerosis in the Liver of Formaldehyde and Benzo(α)Pyrene Exposured-Mie Ahmad Soni,
THE JOURNAL OF TROPICAL LIFE SCIENCE OPEN ACCESS Freely available online VOL. 3, NO. 1, pp. 58 62, January, 2013 Study of Nerosis in the Liver of Formaldehyde and Benzo(α)Pyrene Exposured-Mie Ahmad Soni,
Use of Parents, Sibs, and Unrelated Controls for Detection of Associations between Genetic Markers and Disease
 Am. J. Hum. Genet. 63:492 506, 998 Use of Parents, Sibs, an Unrelate Controls for Detetion of Assoiations between Geneti Markers an Disease Daniel J. Shai,2 an Charles Rowlan Departments of Health Sienes
Am. J. Hum. Genet. 63:492 506, 998 Use of Parents, Sibs, an Unrelate Controls for Detetion of Assoiations between Geneti Markers an Disease Daniel J. Shai,2 an Charles Rowlan Departments of Health Sienes
Role of b3-adrenergic receptors in the action of a tumour lipid mobilizing factor
 British Journal of Caner (22) 86, 424 428 ª 22 The Caner Researh Campaign All rights reserve 7 92/2 $25. www.bjaner.om Role of b3-arenergi reeptors in the ation of a tumour lipi mobilizing fator ST Russell
British Journal of Caner (22) 86, 424 428 ª 22 The Caner Researh Campaign All rights reserve 7 92/2 $25. www.bjaner.om Role of b3-arenergi reeptors in the ation of a tumour lipi mobilizing fator ST Russell
phosphatidylcholine by high performance liquid chromatography: a partial resolution of molecular species
 A large-sale purifiation of phosphatidylethanolamine, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylholine by high performane liquid hromatography: a partial resolution of moleular speies R. S. Fager,
A large-sale purifiation of phosphatidylethanolamine, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylholine by high performane liquid hromatography: a partial resolution of moleular speies R. S. Fager,
Translocation of a hydrocarbon fluorescent probe between Epstein-Barr virus and lymphoid cells: An assay for
 Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 75, No. 1, pp. 576-58, Otober 1978 ell Biology Transloation of a hydroarbon fluoresent probe between Epstein-Barr virus and lymphoid ells: An assay for early events in viral
Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 75, No. 1, pp. 576-58, Otober 1978 ell Biology Transloation of a hydroarbon fluoresent probe between Epstein-Barr virus and lymphoid ells: An assay for early events in viral
Expression and Significance of p53, Rb, p21/waf-1, p16/ink-4a, and PTEN Tumor Suppressors in Canine Melanoma
 Vet Pathol 39:458 472 (2002) Expression and Signifiane of p53, Rb, p21/waf-1, p16/ink-4a, and PTEN Tumor Suppressors in Canine Melanoma A. KOENIG, S. R. BIANCO, S. FOSMIRE, J. WOJCIESZYN, AND J. F. MODIANO
Vet Pathol 39:458 472 (2002) Expression and Signifiane of p53, Rb, p21/waf-1, p16/ink-4a, and PTEN Tumor Suppressors in Canine Melanoma A. KOENIG, S. R. BIANCO, S. FOSMIRE, J. WOJCIESZYN, AND J. F. MODIANO
Correspondence should be addressed to Ali Mobasheri,
 Evidene-Based Complementary and Alternative ediine Volume 2012, Artile ID 509383, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2012/509383 Researh Artile Botanial Extrats from Rosehip (Rosaanina), Willow Bark (Salix alba), and
Evidene-Based Complementary and Alternative ediine Volume 2012, Artile ID 509383, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2012/509383 Researh Artile Botanial Extrats from Rosehip (Rosaanina), Willow Bark (Salix alba), and
Messenger RNA in HeLa Cells :
 ur. J. Biohem. 17 (1970) 296-318 Messenger RNA in HeLa Cells : An nvestigation of Free and Polyribosome-Bound Cytoplasmi Messenger Ribonuleoprotein Partiles by Kineti Labelling and letron Mirosopy Georges
ur. J. Biohem. 17 (1970) 296-318 Messenger RNA in HeLa Cells : An nvestigation of Free and Polyribosome-Bound Cytoplasmi Messenger Ribonuleoprotein Partiles by Kineti Labelling and letron Mirosopy Georges
a-4/b-1 and a-l/b-2 integrins mediate cytokine induced lung leukocyte-epithelial adhesion and injury
 British Journal of Pharmaology (27) 152, 915 929 & 27 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/7 $3. www.brjpharmaol.org RESEARCH PAPER a-4/b-1 and a-l/b-2 integrins mediate ytokine indued lung
British Journal of Pharmaology (27) 152, 915 929 & 27 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/7 $3. www.brjpharmaol.org RESEARCH PAPER a-4/b-1 and a-l/b-2 integrins mediate ytokine indued lung
LETTER. Journal Club. Pathogen-induced human T H 17 cells produce IFN-c or IL-10 and are regulated by IL-1b. Markus Geuking April 27 th, 2012
 Journal Clu LETTER oi:1.138/nature1957 Pathogen-inue human T H 17 ells proue IFN- or IL-1 an are regulate y IL-1 Christina E. Zielinski 1, Feerio Mele 1, Dominik Ashenrenner 1, Davi Jarrossay 1, Franesa
Journal Clu LETTER oi:1.138/nature1957 Pathogen-inue human T H 17 ells proue IFN- or IL-1 an are regulate y IL-1 Christina E. Zielinski 1, Feerio Mele 1, Dominik Ashenrenner 1, Davi Jarrossay 1, Franesa
Supplementary Material for. Inflammation induced repression of Foxp3-bound chromatin in regulatory T cells
 Supplementary Material for Inflammation inue repression of -oun hromatin in regulatory T ells Aaron Arvey 1,2, Joris van er Veeken 1,2, Roert M. Samstein 1,2, Yongqiang Feng 1,2, John A. Stamatoyannopoulos
Supplementary Material for Inflammation inue repression of -oun hromatin in regulatory T ells Aaron Arvey 1,2, Joris van er Veeken 1,2, Roert M. Samstein 1,2, Yongqiang Feng 1,2, John A. Stamatoyannopoulos
Original Articles. Experimental disciform edema and necrotizing keratitis in the rabbit. Joseph F. Metcalf, James I. McNeill, and Herbert E.
 Original Artiles Experimental disiform edema and nerotizing keratitis in the rabbit Joseph F. Metalf, James I. MNeill, and Herbert E. Kaufman The development of experimental disiform edema and nerotizing
Original Artiles Experimental disiform edema and nerotizing keratitis in the rabbit Joseph F. Metalf, James I. MNeill, and Herbert E. Kaufman The development of experimental disiform edema and nerotizing
Module 6. Traveller's Diarrhea
 Moule 6 Traveller's Diarrhea What an ause traveller s iarrhoea1 7 ways to avoi traveller s iarrhoea1 1 Break the seals on bottle rinks yourself 2 Use water that has been boile for at least 5 minutes when
Moule 6 Traveller's Diarrhea What an ause traveller s iarrhoea1 7 ways to avoi traveller s iarrhoea1 1 Break the seals on bottle rinks yourself 2 Use water that has been boile for at least 5 minutes when
cholerae Non-Ol and Comparison with a Protease of V. cholerae 01
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 1989, p. 2799-283 Vol. 57, No. 9 19-9567/89/92799-4$2./ Copyright C) 1989, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Purifiation and Charaterization of a Protease Produed by Vibrio holerae
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 1989, p. 2799-283 Vol. 57, No. 9 19-9567/89/92799-4$2./ Copyright C) 1989, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Purifiation and Charaterization of a Protease Produed by Vibrio holerae
ALX4, an epigenetically down regulated tumor suppressor, inhibits breast cancer progression by interfering Wnt/β-catenin pathway
 Yang et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinial Caner Researh (2017) 36:170 DOI 10.1186/s13046-017-0643-9 RESEARCH Open Aess ALX4, an epigenetially own regulate tumor suppressor, inhiits reast aner progression
Yang et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinial Caner Researh (2017) 36:170 DOI 10.1186/s13046-017-0643-9 RESEARCH Open Aess ALX4, an epigenetially own regulate tumor suppressor, inhiits reast aner progression
Unexpected subcellular distribution of a specific isoform of the Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor, CAR-SIV, in human pancreatic beta cells
 Diaetologia (2018) 61:2344 2355 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-018-4704-1 ARTICLE Unexpeted suellular distriution of a speifi isoform of the Coxsakie and adenovirus reeptor, CAR-SIV, in human panreati
Diaetologia (2018) 61:2344 2355 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-018-4704-1 ARTICLE Unexpeted suellular distriution of a speifi isoform of the Coxsakie and adenovirus reeptor, CAR-SIV, in human panreati
Retraction Retracted: Study of Effect of Salvianolic Acid B on Motor Function Recovery in Rats with Spinal Cord Injury
 Hindawi BioMed Researh International Volume 217, Artile ID 8234878, 1 page https://doi.org/1.1155/217/8234878 Retration Retrated: Study of Effet of Salvianoli Aid B on Motor Funtion Reovery in Rats with
Hindawi BioMed Researh International Volume 217, Artile ID 8234878, 1 page https://doi.org/1.1155/217/8234878 Retration Retrated: Study of Effet of Salvianoli Aid B on Motor Funtion Reovery in Rats with
Homotypic Cell Cannibalism and Cannibalism Index-A Four Year Study in In ltrating Ductal Carcinoma Breast 1* 1 1
 ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Homotypi Cell Cannibalism and Cannibalism Index-A Four Year Study in In ltrating Dutal Carinoma Breast 1* 1 1 Alok Mohan, Pradeep Kr. Sharma, R.K. Thakral 1 Department of
ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Homotypi Cell Cannibalism and Cannibalism Index-A Four Year Study in In ltrating Dutal Carinoma Breast 1* 1 1 Alok Mohan, Pradeep Kr. Sharma, R.K. Thakral 1 Department of
and jejunal fluid immunoglobulins in adult coeliac
 Gut, 1974, 15, 371-376 Jejunal muosal immunoglobulin-ontaining ells and jejunal fluid immunoglobulins in adult oelia disease and dermatitis herpetiformis M. LANCASTR-SMITH, PARVN KUMAR, R. MARKS, M. L.
Gut, 1974, 15, 371-376 Jejunal muosal immunoglobulin-ontaining ells and jejunal fluid immunoglobulins in adult oelia disease and dermatitis herpetiformis M. LANCASTR-SMITH, PARVN KUMAR, R. MARKS, M. L.
Mechanism of Action of Phenethyl Alcohol: Breakdown of the Cellular Permeability Barrier
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Feb., 1967, p. 56-566 Vol. 93, No. 2 Copyright @ 1967 Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Printed In U.S.A. Mehanism of Ation of Phenethyl Alohol: Breakdown of the Cellular Permeability
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Feb., 1967, p. 56-566 Vol. 93, No. 2 Copyright @ 1967 Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Printed In U.S.A. Mehanism of Ation of Phenethyl Alohol: Breakdown of the Cellular Permeability
Dexamethasone modulation of tumour necrosis factor-a (cachectin) release by activated normal human alveolar macrophages
 ur Resplr J 1992, 5, 67-72 Dexamethasone modulation of tumour nerosis fator-a (ahetin) release by ativated normal human alveolar marophages N. Martinet, P. Vaillant, Th. Charles, J. Lambert, Y. Martinet*
ur Resplr J 1992, 5, 67-72 Dexamethasone modulation of tumour nerosis fator-a (ahetin) release by ativated normal human alveolar marophages N. Martinet, P. Vaillant, Th. Charles, J. Lambert, Y. Martinet*
Binding and Transport of Thiamine by Lactobacillus casei
 JOURNAL OF BACTRIOLOGY, Mar. 1978, P. 119-1196 21-9193/78/133-1 19$2./ Copyright 1978 Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 133, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Binding and Transport of Thiamine by Latobaillus asei
JOURNAL OF BACTRIOLOGY, Mar. 1978, P. 119-1196 21-9193/78/133-1 19$2./ Copyright 1978 Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 133, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Binding and Transport of Thiamine by Latobaillus asei
Confinement-optimized three-dimensional T cell amoeboid motility is modulated via myosin IIA regulated adhesions
 Confinement-optimize three-imensional T ell amoeoi motility is moulate via myosin IIA regulate ahesions Joran Jaoelli 1, Rahel S Frieman 1, Mary Anne Conti 2, Ana-Maria Lennon-Dumenil 3, Matthieu Piel
Confinement-optimize three-imensional T ell amoeoi motility is moulate via myosin IIA regulate ahesions Joran Jaoelli 1, Rahel S Frieman 1, Mary Anne Conti 2, Ana-Maria Lennon-Dumenil 3, Matthieu Piel
Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillance by human γδ T cell receptor binding to Endothelial Protein C Receptor
 Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillane y human γδ T ell reeptor inding to Endothelial Protein C Reeptor Carrie R. Willox, Vinent Pitard, Sonia Netzer, Lionel Couzi, Mahoo Salim, Toias Silerzahn,
Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillane y human γδ T ell reeptor inding to Endothelial Protein C Reeptor Carrie R. Willox, Vinent Pitard, Sonia Netzer, Lionel Couzi, Mahoo Salim, Toias Silerzahn,
Nature Publishing Group
 Vol 453 29 May 28 doi:1.138/nature6928 Funtional genomi sreen reveals genes involved in lipid-droplet formation and utilization Yi Guo 1,4, Toias C.Walther 1,5, Meghana Rao 4, Nio Stuurman 2, Gohta Goshima
Vol 453 29 May 28 doi:1.138/nature6928 Funtional genomi sreen reveals genes involved in lipid-droplet formation and utilization Yi Guo 1,4, Toias C.Walther 1,5, Meghana Rao 4, Nio Stuurman 2, Gohta Goshima
Spleen VAT FMO. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Ki67 DX5 CD27. CD11b 2B4 KLRG1 CD69 NKG2D CXCR3 CD44 NKG2A/C/E CD62L CD103 CD94 CD48.
 IFN (% of ells) CD7 Marophages Medium NCR LPS PMA/Ionomyin CD IFN (% of ells) T ells Marophages B ells DX CD9 KLRG NKGD B CDL CD CD CXCR CD9 CD NKGA/C/E NCR Ly9h Ly9G Ly9d Ly9i Ly9/i/h FMO CD7 CD9a CD7
IFN (% of ells) CD7 Marophages Medium NCR LPS PMA/Ionomyin CD IFN (% of ells) T ells Marophages B ells DX CD9 KLRG NKGD B CDL CD CD CXCR CD9 CD NKGA/C/E NCR Ly9h Ly9G Ly9d Ly9i Ly9/i/h FMO CD7 CD9a CD7
Measurement of Dose Rate Dependence of Radiation Induced Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1
 Measurement of Dose Rate Dependene of Radiation Indued Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1 D. Dorfan, T. Dubbs, A. A. Grillo, W. Rowe, H. F.-W. Sadrozinski, A. Seiden, E. Spener, S. Stromberg,
Measurement of Dose Rate Dependene of Radiation Indued Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1 D. Dorfan, T. Dubbs, A. A. Grillo, W. Rowe, H. F.-W. Sadrozinski, A. Seiden, E. Spener, S. Stromberg,
Supplemental Information. Autophagy in Oncogenic K-Ras. Promotes Basal Extrusion. of Epithelial Cells by Degrading S1P. Current Biology, Volume 24
 Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Autophagy in Oncogenic K-Ras Promotes Basal Extrusion of Epithelial Cells by Degrading S1P Gloria Slattum, Yapeng Gu, Roger Sabbadini, and Jody Rosenblatt
Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Autophagy in Oncogenic K-Ras Promotes Basal Extrusion of Epithelial Cells by Degrading S1P Gloria Slattum, Yapeng Gu, Roger Sabbadini, and Jody Rosenblatt
In vivo covalent cross-linking of photon-converted rare-earth nanostructures for tumour localization and theranostics
 Reeived 27 May 2015 Aepted 7 De 2016 Published 20 Jan 2016 DOI: 10.1038/nomms10432 OPE In vivo ovalent ross-linking of photon-onverted rare-earth nanostrutures for tumour loalization and theranostis Xiangzhao
Reeived 27 May 2015 Aepted 7 De 2016 Published 20 Jan 2016 DOI: 10.1038/nomms10432 OPE In vivo ovalent ross-linking of photon-onverted rare-earth nanostrutures for tumour loalization and theranostis Xiangzhao
original article Chao-Lien Liu 1, Peiqing Ye 1, Benjamin C Yen 1 and Carol H Miao 1,2
 The Amerian Soiety of Gene & Cell Therapy original artile In Vivo Expansion of Regulatory T ells With IL-2/IL-2 mab Complexes Prevents Anti-fator VIII Immune Responses in Hemophilia A Mie Treated With
The Amerian Soiety of Gene & Cell Therapy original artile In Vivo Expansion of Regulatory T ells With IL-2/IL-2 mab Complexes Prevents Anti-fator VIII Immune Responses in Hemophilia A Mie Treated With
World Journal of Gastroenterology
 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) Worl Journal of Gastroenterology Worl J Gastroenterol 2018 Feruary 21; 24(7): 767-876 Pulishe y Baishieng Pulishing Group In S Contents Weekly Volume 24 Numer
ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) Worl Journal of Gastroenterology Worl J Gastroenterol 2018 Feruary 21; 24(7): 767-876 Pulishe y Baishieng Pulishing Group In S Contents Weekly Volume 24 Numer
Competition for priority in processing increases prefrontal cortex s involvement in top-down control: an event-related fmri study of the stroop task
 Cognitive Brain Researh 17 (2003) 212 222 www.elsevier.om/ loate/ ogbrainres Researh report Competition for priority in proessing inreases prefrontal ortex s involvement in top-own ontrol: an event-relate
Cognitive Brain Researh 17 (2003) 212 222 www.elsevier.om/ loate/ ogbrainres Researh report Competition for priority in proessing inreases prefrontal ortex s involvement in top-own ontrol: an event-relate
General information. Cell mediated immunity. 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon. Anytime after class.
 General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
See related commentary on pg 10
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE See related ommentary on pg 1 The Small Heat-Shok Protein Undergoes ERK-Dependent Phosphorylation and Redistribution to the Cytoskeleton in Response to Dual Leuine Zipper-Bearing Kinase
ORIGINAL ARTICLE See related ommentary on pg 1 The Small Heat-Shok Protein Undergoes ERK-Dependent Phosphorylation and Redistribution to the Cytoskeleton in Response to Dual Leuine Zipper-Bearing Kinase
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death
 www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death Supplementary
www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death Supplementary
Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice
 Inativation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers aute renal failure in mie Jose Pero Friemann Angeli 1, Manuela Shneier 2, Bettina Proneth 1, Yulia Y. Tyurina 3, Vlaimir A. Tyurin 3, Vitoria J. ammon
Inativation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers aute renal failure in mie Jose Pero Friemann Angeli 1, Manuela Shneier 2, Bettina Proneth 1, Yulia Y. Tyurina 3, Vlaimir A. Tyurin 3, Vitoria J. ammon
In Vitro Culture of Ovules and Embryos from Seedless Grapes (Vitis vinifera L.)
 In Vitro Culture of vules and Embryos from Seedless Grapes (Vitis vinifera L.) P. Burger and P.. Goussard" 1) Nietvoorbij Researh Institute for Vitiulture and enology, Agriultural Researh Counil, Private
In Vitro Culture of vules and Embryos from Seedless Grapes (Vitis vinifera L.) P. Burger and P.. Goussard" 1) Nietvoorbij Researh Institute for Vitiulture and enology, Agriultural Researh Counil, Private
Chapter III. Efficacy of promising agents/combinations in preventing vaginal/cervical inflammation caused by infection with T. vaginalis Introduction
 Chapter III Effiay of promising agents/ombinatio in preventing vaginal/ervial inflammation aused by infetion with T. vaginalis Introdution A ontraeptive mirobiide is supposed to be in ontat with the erviovaginal
Chapter III Effiay of promising agents/ombinatio in preventing vaginal/ervial inflammation aused by infetion with T. vaginalis Introdution A ontraeptive mirobiide is supposed to be in ontat with the erviovaginal
Differentiation-Associated Expression of the Epstein-Barr Virus
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 1991, p. 2868-2874 0022-538X/91/062868-07$02.00/0 Copyright 1991, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 65, No. 6 Differentiation-Assoiated Expression of the Epstein-Barr Virus
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 1991, p. 2868-2874 0022-538X/91/062868-07$02.00/0 Copyright 1991, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 65, No. 6 Differentiation-Assoiated Expression of the Epstein-Barr Virus
Evolutionary Control of an Autonomous Field
 Evolutionary Control of an Autonomous Fiel Mar W. wen SPAWAR System Center San Diego Coe D7 San Diego, CA, U.S.A. mowen@spawar.navy.mil Dale M. Klamer & Barbara Dean rinon Corporation San Diego, CA, U.S.A.
Evolutionary Control of an Autonomous Fiel Mar W. wen SPAWAR System Center San Diego Coe D7 San Diego, CA, U.S.A. mowen@spawar.navy.mil Dale M. Klamer & Barbara Dean rinon Corporation San Diego, CA, U.S.A.
Journal of Equine Veterinary Science
 Journal of Equine Veterinary Siene 31 (2011) 645-649 Journal of Equine Veterinary Siene journal homepage: www.j-evs.om Original Researh Comparison of Insulin Sensitivity of Horses Aapte to Different Exerise
Journal of Equine Veterinary Siene 31 (2011) 645-649 Journal of Equine Veterinary Siene journal homepage: www.j-evs.om Original Researh Comparison of Insulin Sensitivity of Horses Aapte to Different Exerise
Herpesviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION In format provided by JAATTELA (NOVEMBER 2005)
 Box S1: Methods for studying lysosomal function and integrity Volume and distribution of the acidic compartment. Acridine orange is a metachromatic fluorochrome and a weak base that accumulates in the
Box S1: Methods for studying lysosomal function and integrity Volume and distribution of the acidic compartment. Acridine orange is a metachromatic fluorochrome and a weak base that accumulates in the
Supporting information
 Supporting information Evolution of Hollow TiO 2 Nanostrutures via the Kirkendall Effet Driven y Cation Exhange with Enhaned Photoeletrohemial Performane Yanhao Yu, 1 Xin Yin, 1 Alexander Kvit, 1,2 Xudong
Supporting information Evolution of Hollow TiO 2 Nanostrutures via the Kirkendall Effet Driven y Cation Exhange with Enhaned Photoeletrohemial Performane Yanhao Yu, 1 Xin Yin, 1 Alexander Kvit, 1,2 Xudong
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Every Flex is Quite Complex
 Name Class Date Every Flex is Quite Complex Struture and Funtion in a Chiken Wing Investigative Lab 27 8 Question How do the tissues of a hiken wing work together during movement? Lab Overview In this
Name Class Date Every Flex is Quite Complex Struture and Funtion in a Chiken Wing Investigative Lab 27 8 Question How do the tissues of a hiken wing work together during movement? Lab Overview In this
Opening and Closing Transitions for BK Channels Often Occur in Two
 72 Biophysial Journal Volume 65 August 1993 72-714 Opening and Closing Transitions for BK Channels Often Our in Two Steps via Sojourns through a Brief ifetime Subondutane State William B. Ferguson, Owen
72 Biophysial Journal Volume 65 August 1993 72-714 Opening and Closing Transitions for BK Channels Often Our in Two Steps via Sojourns through a Brief ifetime Subondutane State William B. Ferguson, Owen
Stefan D Anker, Stephan von Haehling
 464 See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Dr Stefan D Anker, National Heart and Lung Institute, Department of Clinial Cardiology, Dovehouse Street, London SW3 6LY, UK; s.anker@imperial.a.uk
464 See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Dr Stefan D Anker, National Heart and Lung Institute, Department of Clinial Cardiology, Dovehouse Street, London SW3 6LY, UK; s.anker@imperial.a.uk
Supplementary Figure 1. Verification of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative
 Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
ARTICLE Oncolytic herpes simplex virus kills stem-like tumor-initiating colon cancer cells
 Citation: Moleular Therapy Onolytis (216) 3, 1613; doi:1.138/mto.216.13 www.nature.om/mto ARLE Onolyti herpes simplex virus kills stem-like tumor-initiating olon aner ells Susanne G Warner 1, Dana Haddad
Citation: Moleular Therapy Onolytis (216) 3, 1613; doi:1.138/mto.216.13 www.nature.om/mto ARLE Onolyti herpes simplex virus kills stem-like tumor-initiating olon aner ells Susanne G Warner 1, Dana Haddad
Prime, Repair, Restore: The Active Role of Chromatin in the DNA Damage Response
 Prime, Repair, Restore: The Ative Role of Chromatin in the DNA Damage Response Gaston Soria, 1,2,3 Sophie E. Polo, 1,2,3 and Geneviève Almouzni 1,2, * 1 Laboratory of Chromatin Dynamis, Institut Curie
Prime, Repair, Restore: The Ative Role of Chromatin in the DNA Damage Response Gaston Soria, 1,2,3 Sophie E. Polo, 1,2,3 and Geneviève Almouzni 1,2, * 1 Laboratory of Chromatin Dynamis, Institut Curie
Comparative in Vitro Cytotoxicity Study of Silver Nanoparticle on Two Mammalian Cell Lines
 Dublin Institute of Tehnology ARROW@DIT Artiles Shool of Physis 28 Comparative in Vitro Cytotoxiity Study of Silver Nanopartile on Two Mammalian Cell Lines Gordon Chambers Dublin Institute of Tehnology,
Dublin Institute of Tehnology ARROW@DIT Artiles Shool of Physis 28 Comparative in Vitro Cytotoxiity Study of Silver Nanopartile on Two Mammalian Cell Lines Gordon Chambers Dublin Institute of Tehnology,
Supplementary Figure 1. Implants derived from human embryoid body preparations contain non-cardiac structures. In early studies, infarcted hearts
 a Supplementary Figure 1. Implants derived from human emryoid ody preparations ontain non-ardia strutures. In early studies, infarted hearts reeived ell preparations of low ardia purity (
a Supplementary Figure 1. Implants derived from human emryoid ody preparations ontain non-ardia strutures. In early studies, infarted hearts reeived ell preparations of low ardia purity (
Epigenetic and transcriptional signatures of stable versus plastic differentiation of proinflammatory
 Epigeneti and transriptional signatures of stable versus plasti differentiation of proinflammatory gd T ell subsets Nina Shmolka,5, Karine Serre,5, Ana R Grosso, Margarida Rei,2, Daniel J Pennington 2,
Epigeneti and transriptional signatures of stable versus plasti differentiation of proinflammatory gd T ell subsets Nina Shmolka,5, Karine Serre,5, Ana R Grosso, Margarida Rei,2, Daniel J Pennington 2,
Coupled feedback loops maintain synaptic long-term. potentiation: A computational model of PKMzeta
 1 Draft version 28, 2018-04-30. This paper has not been peer reviewed. Please do not opy or ite without author's permission. Coupled feedbak loops maintain synapti long-term potentiation: omputational
1 Draft version 28, 2018-04-30. This paper has not been peer reviewed. Please do not opy or ite without author's permission. Coupled feedbak loops maintain synapti long-term potentiation: omputational
M E Guicciardi, G J Gores
 1024 RECENT ADVANCES IN BASIC SCIENCE APOPTOSIS: A MECHANISM OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC LIVER INJURY See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Dr G J Gores, Mayo Clini College of Mediine,
1024 RECENT ADVANCES IN BASIC SCIENCE APOPTOSIS: A MECHANISM OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC LIVER INJURY See end of artile for authors affiliations Correspondene to: Dr G J Gores, Mayo Clini College of Mediine,
Pentoxifylline and Other Protein. Gene Expression. HIV-LTR NF-KB Induced. Kinase C Inhibitors Down-Regulate
 Pentoxifylline and Other Protein Kinase C Inhibitors DownRegulate HIVLTR NFKB Indued Gene Expression Debajit K. Biswas,* Christoph M. Ahlers,t Brue J. Dezube,t and Arthur B. Pardeet *Division of Cell Growth
Pentoxifylline and Other Protein Kinase C Inhibitors DownRegulate HIVLTR NFKB Indued Gene Expression Debajit K. Biswas,* Christoph M. Ahlers,t Brue J. Dezube,t and Arthur B. Pardeet *Division of Cell Growth
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT METHODS OF PRESERVATION ON THE QUALITY OF CATTLE AND GOAT MEAT. Abstract
 Bang. J. Anim. Si. 2009, 38(1&2) : 86 91 ISSN 0003-3588 EFFECT OF DIFFERENT METHODS OF PRESERVATION ON THE QUALITY OF CATTLE AND GOAT MEAT S. Bin. Faisal, S. Akhter 1 and M. M. Hossain Abstrat The study
Bang. J. Anim. Si. 2009, 38(1&2) : 86 91 ISSN 0003-3588 EFFECT OF DIFFERENT METHODS OF PRESERVATION ON THE QUALITY OF CATTLE AND GOAT MEAT S. Bin. Faisal, S. Akhter 1 and M. M. Hossain Abstrat The study
Estimation of Glomerular Podocyte Number: A Selection of Valid Methods
 Estimation of Glomerular Podoyte Number: A Seletion of Valid Methods Kevin V. Lemley,* John F. Bertram, Susanne B. Niholas, and Kathryn White *Division of Nephrology, Children s Hospital Los Angeles, Los
Estimation of Glomerular Podoyte Number: A Seletion of Valid Methods Kevin V. Lemley,* John F. Bertram, Susanne B. Niholas, and Kathryn White *Division of Nephrology, Children s Hospital Los Angeles, Los
Pharmaceutical care of stroke patients. Course activities
 Pharmaeutial are of stroke patients Course ativities Pharmaeutial are of stroke patients Course ativities page 2 Case Stuy 1 4 Case Stuy 2 6 Case Stuy 3 8 Multiple Choie Questionnaire Case Stuy 1 Mr Ferguson
Pharmaeutial are of stroke patients Course ativities Pharmaeutial are of stroke patients Course ativities page 2 Case Stuy 1 4 Case Stuy 2 6 Case Stuy 3 8 Multiple Choie Questionnaire Case Stuy 1 Mr Ferguson
constituent amino acids in man'
 Gut, 197, 11, 25-254 Intestinal absorption of arnosine and its onstituent amino aids in man' A. M. ASATOOR, J. K. BANDOH2, A. F. LANT, M. D. MILN, AND F. NAVAB From the Medial Unit of the Westminster Hospital,
Gut, 197, 11, 25-254 Intestinal absorption of arnosine and its onstituent amino aids in man' A. M. ASATOOR, J. K. BANDOH2, A. F. LANT, M. D. MILN, AND F. NAVAB From the Medial Unit of the Westminster Hospital,
Effect of Dietary Astaxanthin and Background Color on Pigmentation and Growth of Red Cher r y Shr imp, Neocaridina heteropoda
 KASETSART UNIVERSITY FISHERIES RESEARCH BULLETIN 04, VOLUME 38 () Effet of Dietary and Color on Pigmentation and Growth of Red Cher r y Shr imp, Neoaridina heteropoda Nongnuh Laohavisuti * and Usharee
KASETSART UNIVERSITY FISHERIES RESEARCH BULLETIN 04, VOLUME 38 () Effet of Dietary and Color on Pigmentation and Growth of Red Cher r y Shr imp, Neoaridina heteropoda Nongnuh Laohavisuti * and Usharee
American Orthodontics Exhibit 1001 Page 1 of 6. US 6,276,930 Bl Aug. 21,2001 /IIIII
 (12) United States Patent Pozzi /IIIII 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006276930Bl (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,276,930 Bl Aug. 21,2001 (54) ORTHODONTIC AID
(12) United States Patent Pozzi /IIIII 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006276930Bl (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,276,930 Bl Aug. 21,2001 (54) ORTHODONTIC AID
Methylglyoxal impairs insulin signalling and insulin action on glucose-induced insulin secretion in the pancreatic beta cell line INS-1E
 Diabetologia () 5:9 95 DOI.7/s5--8-8 ARTICLE Methylglyoxal impairs insulin signalling and insulin ation on gluose-indued insulin seretion in the panreati beta ell line INS-E F. Fiory & A. Lombardi & C.
Diabetologia () 5:9 95 DOI.7/s5--8-8 ARTICLE Methylglyoxal impairs insulin signalling and insulin ation on gluose-indued insulin seretion in the panreati beta ell line INS-E F. Fiory & A. Lombardi & C.
polymorphonuclear neutrophil release of granular
 Br. J. Pharma. (1985), 86, 533-537 Phorbol myristate aetate enhanes human polymorphonulear neutrophil release of granular enzymes but inhibits hemokinesis J.R.S. Hoult & Sussan Nourshargh Department of
Br. J. Pharma. (1985), 86, 533-537 Phorbol myristate aetate enhanes human polymorphonulear neutrophil release of granular enzymes but inhibits hemokinesis J.R.S. Hoult & Sussan Nourshargh Department of
Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Study on Phthalimide Derivatives as HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
 SieneAsia 27 (2001) : 245-250 Quantitative Struture-Ativity Relationship Study on Phthalimide Derivatives as HIV-1 Reverse Transriptase Inhibitors Jiraporn Ungwitayatorn a, *, Chutima Matayatsuk a, Pathanakarn
SieneAsia 27 (2001) : 245-250 Quantitative Struture-Ativity Relationship Study on Phthalimide Derivatives as HIV-1 Reverse Transriptase Inhibitors Jiraporn Ungwitayatorn a, *, Chutima Matayatsuk a, Pathanakarn
Recent advances in basic science BACTERIAL INTERACTIONS WITH CELLS OF THE INTESTINAL MUCOSA: TOLL- LIKE RECEPTORS AND NOD2
 1182 Reent advanes in basi siene BACTERIAL INTERACTIONS WITH CELLS OF THE INTESTINAL MUCOSA: TOLL- LIKE RECEPTORS AND NOD2 Published online first 19 April 2005 Correspondene to: Dr E Cario, University
1182 Reent advanes in basi siene BACTERIAL INTERACTIONS WITH CELLS OF THE INTESTINAL MUCOSA: TOLL- LIKE RECEPTORS AND NOD2 Published online first 19 April 2005 Correspondene to: Dr E Cario, University
EXCRETION RATE ON PLASMA NICOTINE DURING
 Br. J. lin. Pharma. (1978), 5, 293-297 EFFECT OF URINARYpH AND NICOTINE EXCRETION RATE ON PLASMA NICOTINE DURING CIGARETTE SMOKING AND CHEWING NICOTINE GUM C. FEYERABEND & 1M.A.H. RUSSELL Poisons Unit,
Br. J. lin. Pharma. (1978), 5, 293-297 EFFECT OF URINARYpH AND NICOTINE EXCRETION RATE ON PLASMA NICOTINE DURING CIGARETTE SMOKING AND CHEWING NICOTINE GUM C. FEYERABEND & 1M.A.H. RUSSELL Poisons Unit,
