For more information about how to cite these materials visit
|
|
|
- Derrick Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Author(s): Matthew Velkey, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how you may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this material should contact with any questions, corrections, or clarification regarding the use of content. For more information about how to cite these materials visit Any medical information in this material is intended to inform and educate and is not a tool for self-diagnosis or a replacement for medical evaluation, advice, diagnosis or treatment by a healthcare professional. Please speak to your physician if you have questions about your medical condition. Viewer discretion is advised: Some medical content is graphic and may not be suitable for all viewers.
2 Citation Key for more information see: Use + Share + Adapt { Content the copyright holder, author, or law permits you to use, share and adapt. } Public Domain Government: Works that are produced by the U.S. Government. (USC ) Public Domain Expired: Works that are no longer protected due to an expired copyright term. Public Domain Self Dedicated: Works that a copyright holder has dedicated to the public domain. Creative Commons Zero Waiver Creative Commons Attribution License Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike License Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike License GNU Free Documentation License Make Your Own Assessment { Content Open.Michigan believes can be used, shared, and adapted because it is ineligible for copyright. } Public Domain Ineligible: Works that are ineligible for copyright protection in the U.S. (USC (b)) *laws in your jurisdiction may differ { Content Open.Michigan has used under a Fair Use determination. } Fair Use: Use of works that is determined to be Fair consistent with the U.S. Copyright Act. (USC ) *laws in your jurisdiction may differ Our determination DOES NOT mean that all uses of this 3rd-party content are Fair Uses and we DO NOT guarantee that your use of the content is Fair. To use this content you should do your own independent analysis to determine whether or not your use will be Fair.
3 Lymphatic Histology M1 Immunology Sequence J. Matthew Velkey, Ph.D. Winter 2009
4 Learning Objectives Text: Ross, 5 th ed., pp Atlas: Wheater s, 5 th ed., pp Understand the distinction between PRIMARY and SECONDARY lymphoid organs 2. Be able to describe the organization and function of: Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue Diffuse and nodular lymphoid tissue, also including regions of extensive lymphoid infiltration such as Peyer s patches, appendix, and tonsils. lymph nodes Spleen Thymus 3. Be able to identify the regions rich in B and T lymphocytes in each organ and explain the cellular processes, relevant to immune functions, that are taking place in these regions. 4. Know the homing patterns of B & T lymphocytes.
5 Functions of the Lymphatic System 1. Monitor body surfaces and fluid compartments (e.g. epidermis, mucosae*, interstitium) 2. React to the presence of potentially harmful antigens recognized as non-self 3. Autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, type I diabetes, etc.) Lymphatic System consists of: A. Cells 1. Lymphocytes (B,T, natural killer) 2. Antigen-presenting cells (dendritic cells, Langerhans cells & macrophages) B. Lymphatic tissue diffuse and nodular C. Lymphatic organs (lymph nodes, spleen, thymus) D. Lymphatic vessels that carry the cells and fluid *Mucosae refers to lining tissue of the body cavities, e.g. GI tract, respiratory tract, genitourinary tract
6 Lymphoid organs are classified as: Primary lymphoid organs Thymus Bone marrow Lymphatic nodules of the distal intestinal tract (e.g. ileum and appendix) Secondary (effector) lymphoid organs/tissue Spleen & lymph nodes (organs) Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), e.g. lymphocytes and lymphatic nodules in the lamina propria Ross, Fig. 14.1
7 Primary Lymphoid Organs: The bone marrow and the thymus and the Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (e.g. appendix, terminal ileum) are the initial education centers of the immune system In these organs, lymphocytes (T cells in the thymus, B cells in bone marrow and gut) differentiate into immunocompetent cells (i.e. they can recognize self vs. nonself ) This differentiation is said to be antigen-independent The lymphocytes then enter the blood and lymph to populate: epidermis and mucosae connective tissue secondary lymphoid organs
8 Secondary Lymphoid Organs: The lymph nodes, lymphatic nodules, tonsils, spleen are the secondary education centers of the immune system In these organs, immunocompetent lymphocytes differentiate into immune effector and memory cells that undergo antigendependent activation and proliferation in these organs. These lymphocytes then carry out their functions in the: connective tissue secondary lymphoid organs mucosal surfaces lining epithelia They participate in: Cell mediated immunity (mostly cytotoxic T cells) Humoral responses (production of antibody) (B cells, also requires helper T cells.
9 Lymphocytes in peripheral blood smear lymphocyte Mizobuti histology slide set These are B and T-cells that have undergone antigen-independent differentiation and are trafficking through the bloodstream on their way to lymphoid organs/tissue.
10 Source Undetermined
11 Diapedesis: it s not just for the Normans and the Saxons Cytokines and chemokines (along with selectins and integrins) mediate EXTRAvasation of lymphocytes into tissues. Tether Roll Arrest Migrate blood flow cytokines chemokines L. Stoolman APCs and other cells
12 MALT: intraepithelial lymphocytes: γδt-cells (neither helper nor cytotoxic): first to see antigens U-M Histology Collection
13 Intraepithelial lymphocytes Shown here in resp. epith. Homing mediated by addressins (a sort of lymphocyte GPS ) U-M Histology Collection
14 LYMPHOCYTES IN CONNECTIVE TISSUE: MALT = mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue LN Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas Diffuse lymphoid tissue Lamina propria (LP) of gut shown here, but can be found associated with mucosae anywhere in the gut, respiratory, and genitourinary tracts. U-M Histology Collection Primary lymphatic nodule/follicle (LN) Aggregation of lymphocytes in lamina propria or submucosa
15 Secondary follicles/nodules Contain germinal centers Arise when B-lymphocytes are presented with appropriate antigen, receive T-cell help, and then begin proliferating as lymphoblasts Lymphoblasts differentiate into plasma cells or memory cells; aberrant lymphoblasts undergo apoptosis. Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas
16 Microfold, or M CELLS Modified intestinal epithelial cells that assist in antigen presentation by conveying macromolecules from the intestinal lumen to underlying compartments housing lymphocytes and macrophages. Source Undetermined
17 Source Undetermined M cells: TEM
18 After antigen presentation and T-cell help, activated B-cells set up germinal centers in secondary follicles Secondary follicle germinal centers Arise when B-lymphocytes are presented with appropriate antigen, receive T-cell help, and then begin proliferating as lymphoblasts Lymphoblasts differentiate into plasma cells or memory cells; aberrant lymphoblasts undergo apoptosis. Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas
19 Germinal center: high magnification U-M Histology Collection. Slide 175.
20 Lymphoblast viewed by transmission electron microscopy Source Undetermined
21 Source Undetermined
22 Plasma Cells are mature B lymphocytes U-M Histology Collection Black arrows indicate several plasma cells Junquiera and Carneiro. Basic Histology. Tenth Ed White arrows = Golgi regions
23 EM of Plasma Cells Source Undetermined Source Undetermined
24 So, associated with just about any mucosa (GI, respiratory, genitourinary), you may see: Intraepithelial lymphocytes (T-cells) Diffuse lymphoid tissue: B-cells T-cells APCs Primary nodules Secondary nodules Germinal center with lymphoblasts and mphages Source Undetermined
25 Regions of extensive lymphoid infiltration: Peyer s patches Aggregates of lymphoid follicles in the ileum. Source Undetermined
26 Appendix Blind sac extending from the caecum primary and secondary follicles in lamina propria and submucosa So, clearly a secondary lymphoid organ However, also a site of antigen-independent differentiation (similar to Bursa of Fabriscus is birds) So, also a primary lymphoid organ Sorry about the various primary and secondary nomenclature; that s just the way it is Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas
27 Tonsils: MALT of the oropharynx United States Federal Government
28 TONSILS Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas The palatine tonsils are paired structures made of dense accumulations of lymphatic tissue located in the mucous membrane of the junction of the oropharynx and oral cavity. The tonsils dip down into the underlying CT, forming crypts. There are also lingual tonsils and pharyngeal tonsils (under the roof of the nasopharynx and around the opening of the Eustachian tubes). Key features: crypts, abundant nodules, stratified squamous epithelium
29 Wanderlust: lymphocytes don t just stay in one place From the MALT, lymphocytes can squeeze into lymph vessels S.K. Kim. U-M Histology Collection
30 ..go through larger lymphatic channels in the mesentery U-M Histology Collection
31 ..and end up at a LYMPH NODE. U-M Histology Collection
32 Lymph Nodes Main functions: 1. Filter lymph, thereby promoting lymphocyte contact with antigen 2. Provides necessary microenvironment for antigen-dependent differentiation Ross, Fig. 14.1
33 Lymphoid circulation in the body takes place in both the blood stream and the lymphatic vessels, a separate vessel system that carries cells of the lymphoid system and their products (cytokines, antibodies, etc.). United States Federal Government
34 Lymphatic drainage: anatomy Image of lymphatic drainage anatomy removed Original Image:
35 Lymph node structure Image of lymph node structure removed Original Image: herbrandsonc/bio201_mckinley/ f24-10a_lymph_node_and c.jpg Ross Textbook of Histology
36 Lymphatic Circulation Through a Lymph Node Lymph nodes filter lymph 1. Afferent lymphatic vessels drain lymph into the Subcapsular Sinus 2. Lymph then passes to the Trabecular sinuses 3. From there, the lymph goes to the Medullary sinuses. Image of lymph node circulation removed 4. Lymphocytes and macrophages pass easily between these sinuses and the tissue of the lymph node. 5. Macrophages in sinuses monitor the fluids. Macs phagocytose the antigenic material and present it to T- and B-cells Original Image:
37 Lymph Node Structure - Capsule & subcapsular sinus - Trabeculae & trabecular sinuses sinuses contain lymph, macrophages, and reticular cells - Cortex: superficial cortex (B-cells) -primary follicles/nodules -secondary follicles/nodules (i.e. with germinal centers) deep cortex (T-cells, dendritic cells) - Medulla: medullary cords (B-cells, plasma cells) medullary sinuses (lymph, more macrophages, plasma cells, and reticular cells) U-M Histology Collection
38 High magnification view of a sinus (subcapsular sinus shown here) U-M Histology Collection M=macrophage, Ly=lymphocytes, RF/RC=reticular fiber (and associated reticular cell)
39 From the sub-capsular sinus, lymph percolates through trabecular sinuses, and finally into medullary sinuses U-M Histology Collection
40 Reticular (Reticulin) Fibers Form a delicate supporting framework for highly cellular tissues (endocrine glands, lymph nodes, liver, bone marrow, spleen, smooth muscle). Composed mainly of Type III collagen, with a carbohydrate moiety that reduces Ag+ to metallic sliver = argyrophilic. Special stain: silver impregnation to visualize. Thinner than type I collagen (Type III fibrils are nm diameter; type I fibrils are ~200 nm diameter) Source Undetermined
41 Reticular Fibers (type III collagen) made by reticular cells (specialized fibroblasts) Top left: Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas. Others: Sources Undetermined
42 Medullary sinuses drain into EFFERENT lymphatics that exit from the hilum of the lymph node U-M Histology Collection
43 Blood Circulation Through a Lymph Node 1. Blood enters through an artery at the hilus 2. Arterioles branch from hilar artery to feed into capillary beds 3. Capillary beds are drained by high endothelial venules* Image of lymph node blood circulation removed 4. HEVs drain into hilar vein Original Image: Ross, fig *HEVs are sites where lymphocytes can leave blood stream to enter the lymph node tissue bed.
44 U-M Histology Collection capsule
45 U-M Histology Collection
46 High Endothelial Venules Site of: Fluid absorption (via aquaporin-1 channels), which causes lymph flow EXIT of lymphocytes from bloodstream via diapedesis Source Undetermined
47 Source Undetermined
48 Source Undetermined
49 Source Undetermined
50 Summary of lymphocyte traffic in a lymph node Solvent drag caused by caused by HEV fluid transport draws lymph in via afferent vessels ~10% of lymphocytes enter this way; mostly memory cells Image of lymphocyte trafficking in lymph node removed HEV endothelial cells express selectins and other receptors for antigen-primed lymphocytes that stimulate them to EXIT bloodstream via diapedesis ~90% enter this way; mostly naïve lymphocytes T-cells move to deep cortex; B-cells migrate to superficial cortex; differentiated plasma cells move to medullary cords and secrete IgG into lymph Lymphocytes may leave lymph node via EFFERENT lymph vessels (can rejoin bloodstream via thoracic duct, jugular vein, etc.)
51 The Spleen Filters the blood Destroys old red blood cells Serves as an immune organ Divided into Red Pulp (RBC/ hemoglobin recycling) White Pulp (responsible for immune functions) Ross, Fig. 14.1
52 Monitoring antigens in blood Proliferation of lymphocytes Production of humoral antibodies Immune Functions Of the Spleen Hematopoietic Functions Of the Spleen Formation of blood cells in fetal life Removal and destruction of RBCs & platelets Retrieval of iron from RBC hemoglobin Storage of RBCs and platelets (more so in non-human species)
53 Spleen: anatomy Gray s Anatomy
54 Spleen: anatomy Cancer.gov, Wikipedia,
55 ORGANIZATION OF THE SPLEEN Ross, 14.29
56 Splenic Circulation 1. Blood enters via splenic artery at hilus 2. Splenic artery branches into trabecular arteries (which travel within connective tissue trabeculae). 3. Trabecular arteries give off branches known as central arteries which leave the trabecula and enter the substance of the spleen (covered by a peri-arterial lymphatic sheath). 4. Central arteries branch into penicillar arterioles that piece through the lymphatic sheath and spill into splenic cords. 5. Blood percolates through splenic cords and across walls of splenic sinuses. 6. Splenic sinuses drain into pulp veins. 7. Pulp veins drain into trabecular veins. 8. Trabecular veins drain into splenic vein at the hilus.
57 Circulation in the human spleen is primarily OPEN: blood pours into the red pulp, percolates through red pulp cords, and re-enters the bloodstream at splenic sinuses Image of splenic circulation removed Original Image: NOTE: NO afferent lymph vessels not necessary because lymphocytes can easily enter splenic parenchyma via open circulation pattern.
58 Wheater s, Functional Histology, Fifth Edition, 2006
59 Organization of the spleen: white pulp and red pulp White pulp: lymphatic aggregations around central arteries: periarterial lymphatic sheath (PALS): T-cells lymph nodules: B-cells Red pulp: cords and sinuses U-M Histology Collection
60 White pulp function Blood and antigens pour into red pulp (more on that later) Antigen presentation takes place in MARGINAL ZONE T-cells (from PALS) provide help to activate mphages and B-cells activated mphages stimulated to destroy ingested material (e.g. bacteria) activated B-cells set up proliferative germinal centers U-M Histology Collection
61 As the body is exposed to antigens and the immune system mounts an immune response in the form of antibody production, lymph nodules (w/ germinal centers) appear in the white pulp of the spleen. U-M Histology Collection
62 PALS w/ secondary follicle Shown here with central artery cut in cross section note that the CA has been pushed off to the side by the rapid expansion of cells in the germinal center (GC) RP= red pulp MZ= marginal zone (antigen presentation) dashed circle = T-cell rich zone Ross, plate 35-3
63 Scanning EM of a Splenic Sinus (SS) and Cord of Billroth The cords contain, RBCs, neutrophils (N), macrophages (M), blood platelets (P) A reticular cell framework (RC) supports the cord. The sinus is bounded by the epithelial cells that form the basket-like structure of the sinus (VS) Ross 14.30a
64 Spleen (red pulp) at high power (40x) sinus cord cord sinus U-M Histology Collection
65 Percolation of blood into splenic sinuses Here, you are inside the sinus looking through to the cord, where both a macrophage (M) and a neutrophil (N) are outside the sinus. Note that the endothelial cells have a rodlike appearance. Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas; Source Undetermined
66 A B Splenic sinuses and cords A. red pulp B. higher mag of venous sinus and cords of Billroth C. silver-stained section D. diagram C discontinuous basement membrane D Image of splenic sinuses and cords removed Original Image: Lymphoid%20System.files/UntiHE20.jpeg Ross and Pawlina. Histology: A Text and Atlas, Plate 36. Figure 1, 2, 3.
67 SPLEEN: venous sinus showing rodlike endothelial cells Source Undetermined
68 SPLENIC CIRCULATION Sinuses drain into splenic pulp veins, which, in turn, drain into trabecular veins. Trabecular veins travel within trabeculae and drain into splenic vein at the hilus. red pulp white pulp U-M Histology Collection
69 The Thymus T-cell education Self vs. nonself distinctions Cell-mediated immune functions Populates effector organs Lymph nodes Lymphatic nodules Spleen Tonsils Ross, Fig. 14.1
70 The Thymus is a Primary Lymphoid (Immune) Organ Responsible For the Education of T-Cells Located over the great vessels of the heart in the area of the body called the mediastinum Develops from an invagination of EPITHELIUM of the 3 rd pharyngeal pouch, so an endodermal organ. Specialized epithelial cells (called epithioreticular cells) that are joined to one another by long processes with desmosomes on the extremities of the cells (like starfish joined together at the tips) make up the bag-like support for: Lymphocytes that, when the organ is young, fill this bag. NOTE: There are generally no B cells in the Thymus.
71 The Young Thymus Surrounded by a CT capsule; cortex has a lot of lymphocytes, fewer in the medulla THERE ARE NO GERMINAL CENTERS IN THE THYMUS! Gray s Anatomy Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas
72 Source Undetermined
73 The Thymus undergoes a process called THYMIC INVOLUTION, as T cells leave the thymus to populate other lymphoid effector organs, the organ shrinks, leaving only the epithelioretucular cells U-M Histology Collection The young thymus Thymus at puberty U-M Histology Collection
74 Overview of T-cell education Image of T cell education removed Original Image: nri/journal/v6/n2/images/nri1781-f4.jpg 1. Naïve T-cells enter medulla via diapedesis across venules 2. Pass into cortex to undergo POSITIVE selection: Presented with MHC molecules and self or non-self antigens by ERCs T-cells that recognize MHCs and self/nonself antigens pass this selection process and survive (those that don t undergo apoptosis) 3. Move into medulla to undergo NEGATIVE selection: T-cells that recognize SELF antigens displayed by self MHCs (i.e. are :autoreactive ) are eliminated 4. Differentiate into helper (CD4+) or cytotoxic (CD8+) T-cells and leave medulla via diapedesis across venules
75 Arterioles & capillaries in the thymic cortex are ensheathed by epithelioreticular cells forming a blood-thymus barrier. Image of thymic cortex removed Image of thymic cortex removed
76 Blood-Thymus Barrier Education of T-cells must occur in a very controlled environment such that antigens are ONLY presented by epithelial reticular cells. To ensure that no other cells or free antigens are present, there is a very tight BLOOD-THYMUS BARRIER consisting of: 1. The blood capillary wall endothelial cells endothelial cell basal laminae pericytes 2. Perivascular connective tissue type III collagen macrophages 3. Epithelioreticular cell layer basal lamina of the epithelial reticular cells (type I ERCs) epithelial reticular cells (NOTE: T-cells can enter thymus ONLY via bloodstream NO AFFERENT LYMPH VESSELS!)
77 Source Undetermined Macrophage
78 Source Undetermined
79 Source Undetermined
80 Source Undetermined
81 Source Undetermined
82 High mag view of medulla Source Undetermined T-cells that survive selection process allowed to cross venule endothelium (INTRAvasation) to enter circulation.
83 Hassall s corpuscles Type VI ERCs; function not very well known, but produce interleukins (such as IL-4 and IL-7) and so likely influence T-cell differentiation Source Undetermined
84 In the medulla, epithelioreticular cells form onionized structures called Hassall s corpuscles quite prevalent in older thymus LM view EM view Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas
85 Source Undetermined
86 Slide 6: Ross, Fig Slide 9: Mizobuti histology slide set Slide 10: Source Undetermined Slide 11: Dr. Lloyd Stoolman Slide 12: U-M Histology Collection Slide 13:U-M Histology Collection Slide 14: Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas; U-M Histology Collection Slide 15: Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas Slide 16: Source Undetermined Slide 17: Source Undetermined Slide 18: Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas Slide 19: U-M Histology Collection. Slide 175. Slide 20: Source Undetermined Slide 21: Source Undetermined Slide 22: U-M Histology Collection; Junquiera and Carneiro. Basic Histology. Tenth Ed Slide 23: Source Undetermined; Source Undetermined Slide 24: Source Undetermined Slide 25: Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas Slide 26: Source Undetermined Slide 27: United States Federal Government Slide 28: Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas Slide 29: Dr. S.K. Kim Slide 30: U-M Histology Collection Slide 31: U-M Histology Collection Additional Source Information for more information see: Slide 32: Ross, Fig Slide 33: United States Federal Government Slide 34: Original Image from Slide 35: Original Image: c.jpg; Ross Textbook of Histology Slide 36: Original Image:
87 Slide 37: U-M Histology Collection Slide 38: U-M Histology Collection Slide 39: U-M Histology Collection Slide 40: Source Undetermined Slide 41: Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas; Source Undetermined (Rest of Images) Slide 42: U-M Histology Collection Slide 43: Original Image: Ross, fig Slide 44: U-M Histology Collection Slide 45: U-M Histology Collection Slide 46: Source Undetermined Slide 47: Source undetermined Slide 48: Source Undetermined Slide 49: Source Undetermined Slide 51: Ross, fig Slide 53: Gray s Anatomy Slide 54: Cancer.gov, Wikipedia, Slide 55: Ross Slide 57: Original Image: Slide 58: Wheater s, Functional Histology, Fifth Edition, 2006 Slide 59: U-M Histology Collection Slide 60: U-M Histology Collection Slide 61: U-M Histology Collection Slide 62: Ross. Plate 35-3 Slide 63: Ross 14.30a Slide 64: U-M Histology Collection Slide 65: Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas; Source Undetermined Slide 66: Ross and Pawlina. Plate 36. Figure 1, 2, 3.; Original Image Slide 67: Source Undetermined Slide 68: U-M Histology Collection Slide 69: Ross Fig Slide 71: Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas; Gray s Anatomy Slide 72: Source Undetermined Slide 73: U-M Histology Collection; U-M Histology Collection Slide 74: Original Image from Slide 77: Source Undetermined Slide 78: Source Undetermined Slide 79: Source Undetermined Slide 80: Source Undetermined Slide 81: Source Undetermined Slide 82: Source Undetermined
88 Slide 83: Source Undetermined Slide 84: Source Undetermined Slide 84: Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas; Ross and Pawlina, Histology: A Text and Atlas Slide 85: Source Undetermined
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues
 The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System
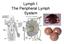 Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
LYMPHOID ORGANS. Dr. Iram Tassaduq
 LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
Chapter10 Immune system
 Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue. nur
 8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
Immune - lymphatic system
 Immune system - organisation: Immune - lymphatic system - histology & embryology organised lymphoid structures cell components lymphocytes event. lymphatic follicles accessory cells monocytes-macrophages
Immune system - organisation: Immune - lymphatic system - histology & embryology organised lymphoid structures cell components lymphocytes event. lymphatic follicles accessory cells monocytes-macrophages
The Lymphoid System Pearson Education, Inc.
 23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Overview of the Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Protects us against disease Lymphatic system cells respond to: Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells,
Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Overview of the Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Protects us against disease Lymphatic system cells respond to: Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells,
Flow Cytometry. Hanan Jafar (2017)
 1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
2/19/2018. Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues. What is Lymph?
 Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Lymphoid tissue. 1. Central Lymphoid tissue. - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus.
 1. Central Lymphoid tissue Lymphoid tissue - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus. Bone Morrow - The major site of hematopoiesis in humans. - Hematopoiesis
1. Central Lymphoid tissue Lymphoid tissue - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus. Bone Morrow - The major site of hematopoiesis in humans. - Hematopoiesis
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB. BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 21 Part 1 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Lymphatic system Main function
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 21 Part 1 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Lymphatic system Main function
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa!
 A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
the liver and spleen. There they will proliferate and differentiate along the various leucocyte lines. Later, bone marrow becomes the predominant
 Chapter 10 Lymphatic System 10.1. General Comments The primary functions of lymphoid organs are protective or immunologic in nature. They are the source of immunocompetent cells which are capable of neutralizing
Chapter 10 Lymphatic System 10.1. General Comments The primary functions of lymphoid organs are protective or immunologic in nature. They are the source of immunocompetent cells which are capable of neutralizing
Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and Tissues of the Immune System. Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
3/17/2014. The Lymphatic System. Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs
 The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
3- Antigen-presenting cells, which are found, in addition to lymphoid tissue, in skin.
 Lymphoid System Dr.firdous It consists of organs, whose tissues and cells play an important role in immunity; a protective response of the internal environment of the body against microorganisms and foreign
Lymphoid System Dr.firdous It consists of organs, whose tissues and cells play an important role in immunity; a protective response of the internal environment of the body against microorganisms and foreign
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Goals 1. Discuss the organization of the lymphatic system, including the vessels, principal lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen 2. Explain the relationship between
Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Goals 1. Discuss the organization of the lymphatic system, including the vessels, principal lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen 2. Explain the relationship between
Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout. Secondary lymphoid organs. Dr H Awad
 Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout Secondary lymphoid organs Dr H Awad INTRODUCTION So far we discussed the cells of the immune system and how they recognize their antigens and get stimulated. The number
Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout Secondary lymphoid organs Dr H Awad INTRODUCTION So far we discussed the cells of the immune system and how they recognize their antigens and get stimulated. The number
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
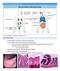 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
Overview of the Lymphoid System
 Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System
 Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
The Lymphatic System
 الكلية االسالمية الجامعة قسم تقنيات التحليالت المرضية االسم التدريسي: ا.د.عبد الهادي صالل المرحلة الثانية المادة : التشريح / النظري 2018-2017 م. م. عباس حسين عبيد The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system
الكلية االسالمية الجامعة قسم تقنيات التحليالت المرضية االسم التدريسي: ا.د.عبد الهادي صالل المرحلة الثانية المادة : التشريح / النظري 2018-2017 م. م. عباس حسين عبيد The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts
 Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems
 Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Lymphatic and Immune www.vastaccess.com 2 Specialized component of circulatory system Lymphatic system functions: Maintenance of internal fluid balance Immunity Lymph derived from blood and tissue fluid
Lymphatic and Immune www.vastaccess.com 2 Specialized component of circulatory system Lymphatic system functions: Maintenance of internal fluid balance Immunity Lymph derived from blood and tissue fluid
LIVER & SPLEEN. Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra..
 LIVER & SPLEEN Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: 1. The histological structure of liver with special emphasis
LIVER & SPLEEN Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: 1. The histological structure of liver with special emphasis
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Paper No.: 10: Immunology Module : 04: Phylogeny and Ontogeny of immune system: Organization and structure of immune system.
 Paper No.: 10: Module : 04: Phylogeny and Ontogeny of immune system: Organization and Development Team Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer: Content Reviewer:
Paper No.: 10: Module : 04: Phylogeny and Ontogeny of immune system: Organization and Development Team Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer: Content Reviewer:
Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students
 University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
GENERAL ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 GENERAL ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM - A SYSTEM WHICH CONTROLS PRESERVE GENETIC INTEGRITY OF THE ORGANISM. BODILY FUNCTIONS PROTECTION OF ANTIGENS CALLED IMMUNITY (FROM THE LATIN WORD
GENERAL ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM - A SYSTEM WHICH CONTROLS PRESERVE GENETIC INTEGRITY OF THE ORGANISM. BODILY FUNCTIONS PROTECTION OF ANTIGENS CALLED IMMUNITY (FROM THE LATIN WORD
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY
 KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic Pathways. Lymphatic Capillaries. network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids
 Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Lymphoid Organs and Lymphocyte Trafficking. Dr. Issa Abu-Dayyeh
 Lymphoid Organs and Lymphocyte Trafficking Dr. Issa Abu-Dayyeh Invader recognition Where does invader recognition take place?? Secondary lymphoid organs: Lymph nodes Spleen Mucosal-associated lymphoid
Lymphoid Organs and Lymphocyte Trafficking Dr. Issa Abu-Dayyeh Invader recognition Where does invader recognition take place?? Secondary lymphoid organs: Lymph nodes Spleen Mucosal-associated lymphoid
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about pathogens is true? Question #01 (A) Both viruses and bacteria need to infect
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about pathogens is true? Question #01 (A) Both viruses and bacteria need to infect
Chapter 22. The Lymphatic System. AP2 Chapter 22 1
 Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System AP2 Chapter 22 1 Chapter 22 Outline I. Lymphatic System II. Immunity III. Innate Immunity IV. Adaptive Immunity V. Immune Interactions VI. Immunotherapy VII. Acquired Immunity
Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System AP2 Chapter 22 1 Chapter 22 Outline I. Lymphatic System II. Immunity III. Innate Immunity IV. Adaptive Immunity V. Immune Interactions VI. Immunotherapy VII. Acquired Immunity
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Michael Hortsch, Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Michael Hortsch, Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Lymphatic System and Immune System. Blood capillaries. Lymphatic vessels/ lymph nodes. Then, identify by labeling these specific structures in part B.
 Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
CELLS, ORGANS, AND MOLECULES: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE CELLS OF THE BLOOD FROM AN IMMUNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE.
 CELLS, ORGANS, AND MOLECULES: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE CELLS OF THE BLOOD FROM AN IMMUNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE. Erythrocytes: Red blood cells (~5 x 10 6 / L) (~5 x 10 12 /L) of blood.
CELLS, ORGANS, AND MOLECULES: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE CELLS OF THE BLOOD FROM AN IMMUNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE. Erythrocytes: Red blood cells (~5 x 10 6 / L) (~5 x 10 12 /L) of blood.
Introduction to Immunology Part 2 September 30, Dan Stetson
 Introduction to Immunology Part 2 September 30, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #2 Slide 1 of 26 CLASS ANNOUNCEMENT PLEASE NO TREE NUTS IN CLASS!!! (Peanuts, walnuts, almonds, cashews, etc)
Introduction to Immunology Part 2 September 30, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #2 Slide 1 of 26 CLASS ANNOUNCEMENT PLEASE NO TREE NUTS IN CLASS!!! (Peanuts, walnuts, almonds, cashews, etc)
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
Chapter 14. Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
Lymphatic System. Chapter 14. Introduction. Main Channels of Lymphatics. Lymphatics. Lymph Tissue. Major Lymphatic Vessels of the Trunk
 Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
2/28/18. Lymphatic System and Immunity. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 27. Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Immunology - Problem Drill 04: Structure and Functions of the Immune System
 Immunology - Problem Drill 04: Structure and Functions of the Immune System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which one of the following is non-encapsulated and less organized secondary lymphoid organ? Question
Immunology - Problem Drill 04: Structure and Functions of the Immune System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which one of the following is non-encapsulated and less organized secondary lymphoid organ? Question
- Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body. - Has disease-fighting functions - Helps maintain homeostasis
 Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Prachi Agarwal M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Prachi Agarwal M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
OBJECTIVES. The Amazing Immune System
 The Amazing Immune System Graphic source: (l) Jeanne Kelly, NIAID; (r) Wikimedia Commons OBJECTIVES Describe at least three components of the immune system Describe the role in our immune response of at
The Amazing Immune System Graphic source: (l) Jeanne Kelly, NIAID; (r) Wikimedia Commons OBJECTIVES Describe at least three components of the immune system Describe the role in our immune response of at
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Putting it Together. Stephen Canfield Secondary Lymphoid System. Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s
 Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS. during postnatal period and to provide elasticity during prenatal and early
 CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50%
 BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 7 Lymphatic System & Immune System Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions and Structure of the lymphatic
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 7 Lymphatic System & Immune System Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions and Structure of the lymphatic
Lymphatic System. Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph. Organs and structures involved. similar to interstitial fluid
 Lymphatic System Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph similar to interstitial fluid Organs and structures involved red bone marrow thymus spleen lymph nodes diffuse lymphatic tissue tonsils, adenoids
Lymphatic System Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph similar to interstitial fluid Organs and structures involved red bone marrow thymus spleen lymph nodes diffuse lymphatic tissue tonsils, adenoids
CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Lymphatic System: Lymphatic System which consists of vessels and organs plays two vital roles in our lives: 1) The vessels
CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Lymphatic System: Lymphatic System which consists of vessels and organs plays two vital roles in our lives: 1) The vessels
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology. Robin Lorenz
 Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Lymphatic System Lymphatic capillaries reabsorb excessive tissue fluid and transport the fluid through the lymphatic pathway, and ultimately dispose
The Lymphatic System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Lymphatic System Lymphatic capillaries reabsorb excessive tissue fluid and transport the fluid through the lymphatic pathway, and ultimately dispose
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Immunity- ability to resist infection and disease through the activation of specific defenses These defenses can be found in the lymphatic system Lymphatic
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Immunity- ability to resist infection and disease through the activation of specific defenses These defenses can be found in the lymphatic system Lymphatic
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces
 Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces Department of Biologic & Materials Sciences School of Dentistry University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109-1078 1 Image quality
Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces Department of Biologic & Materials Sciences School of Dentistry University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109-1078 1 Image quality
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Arno Kumagai, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Arno Kumagai, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
General Biology. A summary of innate and acquired immunity. 11. The Immune System. Repetition. The Lymphatic System. Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.
 A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Michael Heung, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Michael Heung, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Immunity or Resistance Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Ability to ward off damage or disease through our defenses 2 types of immunity Innate or nonspecific immunity present at birth No specific
Immunity or Resistance Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Ability to ward off damage or disease through our defenses 2 types of immunity Innate or nonspecific immunity present at birth No specific
Lymphatic Vessels & Lymph lymphatic vessels. 20 The Lymphatic System. They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System. Keeps us healthy!
 They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System: 1. lymphatic vessels 2. lymph 3. irculation, P, Supports immune & clotting, etc... cardiovascular system! Lymphoid Organs & Tissues:
They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System: 1. lymphatic vessels 2. lymph 3. irculation, P, Supports immune & clotting, etc... cardiovascular system! Lymphoid Organs & Tissues:
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Jonathan Trobe, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Author: Jonathan Trobe, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
