How HIV Causes Disease Prof. Bruce D. Walker
|
|
|
- Amanda Jacobs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How HIV Causes Disease Howard Hughes Medical Institute Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School 1 The global AIDS crisis 60 million infections 20 million deaths 2 3 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 1
2 The level of virus in the blood predicts outcome RNA particles/ml plasma 10 million Rapid progression Slow progression Interquartile ranges 60,000 30,000 12,000 One year 4 Factors influencing HIV disease progression Viral Host Immunologic 5 New virus assembly 1-2 days 6 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 2
3 HIV-1 life cycle 4. Integration into host cell s nucleus 5. Transcription and translation 1. Attachment 2. Uncoating 3. Rev erse transcription 6. Assembly and release of new viruses 7 HIV genome vpu nef LTR gag pol vpr vif env tat rev LTR 8 9 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 3
4 Subtype distribution of collected HIV-1 sequences Variation within a subtype: up to 20% Variation among subtypes: up to 38% in some proteins 10 HIV genome vpu nef LTR gag pol vpr vif env tat rev LTR 11 HIV-1 life cycle 1. Attachment 4. Integration into host cell s nucleus 5. Transcription and translation 2. Uncoating 3. Rev erse transcription 6. Assembly and release of new viruses 12 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 4
5 Factors influencing HIV disease progression Viral Host Immunologic 13 Host factors Chemokine receptor polymorphisms 14 HIV-1 life cycle 4. Integration into host cell s nucleus 5. Transcription and translation 1. Attachment 2. Uncoating 3. Rev erse transcription 6. Assembly and release of new viruses 15 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 5
6 R5 virus X4 virus CCR5delta32 CD4 CCR5 CD4 CXCR4 16 Host factors Chemokine receptor polymorphisms Chemokine ligand gene duplications 17 R5 virus R5 virus CCL3L1 CD4 CCR5 32 CD4 CCR5 18 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 6
7 CCL3L1 Some gene segment duplications exist in the human genome, particularly related to immune response genes CCL3L1 is a potent anti-hiv chemokine Also known as MIP-1αP Low CCL3L1 copy number is associated with more rapid disease progression 19 Host factors Chemokine receptor polymorphisms Trim5α 20 HIV does not infect monkey cells Human cells Monkey cells 21 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 7
8 Trim5α HIV enters cells from Old World monkeys but does not establish a productive infection Trim5α is a monkey gene that makes a protein that blocks HIV Trim5α localizes in cytoplasmic bodies but the function is not known Stremlau et al., Science, 247: 848, Trim5α blocks reverse transcription by interacting with the viral capsid 1. Attachment 2. Uncoating 23 Host factors Chemokine receptor polymorphisms Trim5α APOBEC 3G 24 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 8
9 HIV genome LTR gag pol vpr vif vpu env tat rev nef LTR 25 Expression of the viral Vif protein is necessary for infection of some cell types Vif positive virus APOBEC Vif Vif negative virus APOBEC 26 APOBEC 3G APOBEC 3G is a natural antiviral defense mechanism Interacts with the virus to degrade it intracellularly Vif binds to APOBEC 3G and prevents this natural antiviral defense Can one block the Vif-APOBEC interaction as a therapeutic strategy? 27 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 9
10 Host factors Chemokine receptor polymorphisms APOBEC 3G Trim5 alpha HLA alleles 28 How is an infected cell recognized? 4. Integration into host cell s Presentation nucleus by HLA class I 5. Transcription and translation 1. Attachment 2. Uncoating 3. Rev erse transcription Assembly and 6. release Assembly and release of new viruses 29 K W I I L G L N R K HLA class I molecule 30 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 10
11 A2 B57 A3 B14 Cw6 Cw4 31 Relative hazard B*58 Cw*14 B*27 Cw*02 B*57 A*26 B*51 A*11 A*02 A*03 B*07 B*35 B*35px 32 Factors influencing HIV disease progression Viral Host Immunologic 33 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 11
12 The course of untreated HIV infection RNA particles/ml plasma 10 million 30,000 Months Years AIDS 34 What is the evolution of immune responses? Innate immunity TLR NK cells Adaptive immunity Cellular Humoral 35 Toll-like receptors on adaptive immunity 36 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 12
13 What role do TLR play in HIV infection? It has been recently demonstrated that ssrna derived from HIV-1 LTR can serve as a TLR7/8 ligand Heil, Science, 2004 Beignon, JCI, 2005 Does this drive immune activation and further destruction? Adaptive immune responses 39 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 13
14 New virus assembly Th B cell 40 Why do neutralizing antibodies fail to control infection? The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 14
15 Wei et al., 2003, Nature 422: 307 Richman et al., 2003, PNAS 100: What factors might modulate CTL efficacy? Viral peptides Quality of CTL HLA alleles 45 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 15
16 K W I I L G L N R K HLA class I molecule 46 What factors might modulate CTL efficacy? Viral peptides HLA alleles 47 K K T W W I I I I M L G G L L L N K R K HLA class I molecule 48 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 16
17 CTL responses and viral imprinting CTL 49 Genetics of immune control On a population level, there is evidence of viral evolution to escape dominant immune responses Persons with rare HLA alleles appear to have an advantage because mutations have not already been selected Moore et al., 2003, Science 296: 1439 Trachtenberg 2003, Nat. Med. 9: 928 Leslie et al., 2004, Nat. Med. 10: 282 Goulder et al., Nature, 2004 Kiepiela et al., Nature Medicine, HIV genome vpu nef LTR gag pol vpr vif env tat rev LTR 51 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 17
18 52 What factors might modulate CTL efficacy? Viral peptides Quality of CTL HLA alleles 53 Does lack of control relate to a functional defect in CTL? CTL CTL CTL CTL CTL CTL Proliferation 54 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 18
19 What could account for the loss of CTL proliferation? 55 CTLs Infected cells T helper cells Rosenberg et al., Science, 1997 Rosenberg et al., Nature, 2000 Douek et al., Nature, The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 19
20 Massive depletion of CD4 cells in acute SIV infection Monkeys infected with SIV Gut biopsies over the first few weeks of infection 30-60% of memory CD4 T cells are infected at peak viremia - many are resting! Most of these cells disappear within 4 days Authors suggest early treatment Mattapallil, J. J. et al., Nature, PD-1 is a negative regulator of CTL - engagement turns CTL off PD-1 Off PD-L1 59 Use of HLA class I tetramers to quantitate HIV-specific CD8 T cells CTL Tetramer 60 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 20
21 61 p< p= % PD HIV Total CD8 + Tetramer + (HIV + ) Total CD8 + (HIV - ) Day et al., Nature, Can one block the PD-1 pathway and restore function? Subjects 28 persons with untreated infection Methods Stimulate with cognate epitope in the presence or absence of anti-pdl1 Measure relative degree of expansion of the HIV-specific cells over 6 days 63 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 21
22 Blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 pathway increases expansion of HIV-specific CD8 T cells no peptide 1.2% anti-pd-l1 no peptide 1.2% + TL9 peptide 5.7% anti-pd-l1 + TL9 peptide 12.4% CD8 B*4201 TL9 64 Interpretation and implications 65 CTLs Infected cells T helper cells PD-1 PD-L1 66 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 22
23 CTL CTL CTL Conclusions HIV is an infection of the immune system and causes severe damage during acute infection Neutralizing antibody responses are poor due to genetic variation in the envelope and heavy glycosylation preventing contact CTL kill virus infected cells, but immune escape occurs Immune regulatory networks turn off the immune response to HIV over time The tremendous variability of HIV is a major challenge for vaccine development 69 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 23
24 70 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 24
Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. September 7, of 7 HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES
 1 of 7 I. Viral Origin. A. Retrovirus - animal lentiviruses. HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES 1. HIV is a member of the Retrovirus family and more specifically it is a member of the Lentivirus genus of this family.
1 of 7 I. Viral Origin. A. Retrovirus - animal lentiviruses. HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES 1. HIV is a member of the Retrovirus family and more specifically it is a member of the Lentivirus genus of this family.
, virus identified as the causative agent and ELISA test produced which showed the extent of the epidemic
 1 Two attributes make AIDS unique among infectious diseases: it is uniformly fatal, and most of its devastating symptoms are not due to the causative agent Male to Male sex is the highest risk group in
1 Two attributes make AIDS unique among infectious diseases: it is uniformly fatal, and most of its devastating symptoms are not due to the causative agent Male to Male sex is the highest risk group in
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM:
 RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Acquired Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen nonspecific) defense
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Acquired Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen nonspecific) defense
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM:
 RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Adaptive Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen - nonspecific) defense
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Adaptive Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen - nonspecific) defense
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Viruses and hosts Lentivirus from Latin lentis (slow), for slow progression of disease
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Viruses and hosts Lentivirus from Latin lentis (slow), for slow progression of disease
HIV Immunopathogenesis. Modeling the Immune System May 2, 2007
 HIV Immunopathogenesis Modeling the Immune System May 2, 2007 Question 1 : Explain how HIV infects the host Zafer Iscan Yuanjian Wang Zufferey Abhishek Garg How does HIV infect the host? HIV infection
HIV Immunopathogenesis Modeling the Immune System May 2, 2007 Question 1 : Explain how HIV infects the host Zafer Iscan Yuanjian Wang Zufferey Abhishek Garg How does HIV infect the host? HIV infection
Citation for published version (APA): Von Eije, K. J. (2009). RNAi based gene therapy for HIV-1, from bench to bedside
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) RNAi based gene therapy for HIV-1, from bench to bedside Von Eije, K.J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Von Eije, K. J. (2009). RNAi based
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) RNAi based gene therapy for HIV-1, from bench to bedside Von Eije, K.J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Von Eije, K. J. (2009). RNAi based
MID 36. Cell. HIV Life Cycle. HIV Diagnosis and Pathogenesis. HIV-1 Virion HIV Entry. Life Cycle of HIV HIV Entry. Scott M. Hammer, M.D.
 Life Cycle Diagnosis and Pathogenesis Scott M. Hammer, M.D. -1 Virion Entry Life Cycle of Entry -1 virion -1 Virus virion envelope Cell membrane receptor RELEASE OF PROGENY VIRUS REVERSE Co- TRANSCRIPTION
Life Cycle Diagnosis and Pathogenesis Scott M. Hammer, M.D. -1 Virion Entry Life Cycle of Entry -1 virion -1 Virus virion envelope Cell membrane receptor RELEASE OF PROGENY VIRUS REVERSE Co- TRANSCRIPTION
MedChem 401~ Retroviridae. Retroviridae
 MedChem 401~ Retroviridae Retroviruses plus-sense RNA genome (!8-10 kb) protein capsid lipid envelop envelope glycoproteins reverse transcriptase enzyme integrase enzyme protease enzyme Retroviridae The
MedChem 401~ Retroviridae Retroviruses plus-sense RNA genome (!8-10 kb) protein capsid lipid envelop envelope glycoproteins reverse transcriptase enzyme integrase enzyme protease enzyme Retroviridae The
HIV INFECTION: An Overview
 HIV INFECTION: An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ
HIV INFECTION: An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ
Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP
 Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP 1 Learning Objectives Recognize hazards associated with viral vectors in research and animal
Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP 1 Learning Objectives Recognize hazards associated with viral vectors in research and animal
Evidence of HIV-1 Adaptation to HLA- Restricted Immune Responses at a Population Level. Corey Benjamin Moore
 Evidence of HIV-1 Adaptation to HLA- Restricted Immune Responses at a Population Level Corey Benjamin Moore This thesis is presented for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy of Murdoch University, 2002 I
Evidence of HIV-1 Adaptation to HLA- Restricted Immune Responses at a Population Level Corey Benjamin Moore This thesis is presented for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy of Murdoch University, 2002 I
Adaptive Immunity. Lecture 14 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring Life is simple, but we insist on making it complicated CONFUCIUS
 Adaptive Immunity Lecture 14 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 Life is simple, but we insist on making it complicated CONFUCIUS Host defenses Intrinsic - Always present in the uninfected cell - Apoptosis,
Adaptive Immunity Lecture 14 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 Life is simple, but we insist on making it complicated CONFUCIUS Host defenses Intrinsic - Always present in the uninfected cell - Apoptosis,
HIV & AIDS: Overview
 HIV & AIDS: Overview UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR VJ TEMPLE 1 What
HIV & AIDS: Overview UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR VJ TEMPLE 1 What
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses
 Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 7: Cytokines Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research HHV-8 Discovered in the 1980 s at the
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 7: Cytokines Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research HHV-8 Discovered in the 1980 s at the
HIV acute infections and elite controllers- what can we learn?
 HIV acute infections and elite controllers- what can we learn? Thumbi Ndung u, BVM, PhD KwaZulu-Natal Research Institute for Tuberculosis and HIV (K-RITH) and HIV Pathogenesis Programme (HPP), Doris Duke
HIV acute infections and elite controllers- what can we learn? Thumbi Ndung u, BVM, PhD KwaZulu-Natal Research Institute for Tuberculosis and HIV (K-RITH) and HIV Pathogenesis Programme (HPP), Doris Duke
Retroviruses. ---The name retrovirus comes from the enzyme, reverse transcriptase.
 Retroviruses ---The name retrovirus comes from the enzyme, reverse transcriptase. ---Reverse transcriptase (RT) converts the RNA genome present in the virus particle into DNA. ---RT discovered in 1970.
Retroviruses ---The name retrovirus comes from the enzyme, reverse transcriptase. ---Reverse transcriptase (RT) converts the RNA genome present in the virus particle into DNA. ---RT discovered in 1970.
LESSON 4.6 WORKBOOK. Designing an antiviral drug The challenge of HIV
 LESSON 4.6 WORKBOOK Designing an antiviral drug The challenge of HIV In the last two lessons we discussed the how the viral life cycle causes host cell damage. But is there anything we can do to prevent
LESSON 4.6 WORKBOOK Designing an antiviral drug The challenge of HIV In the last two lessons we discussed the how the viral life cycle causes host cell damage. But is there anything we can do to prevent
Mina John Institute for Immunology and Infectious Diseases Royal Perth Hospital & Murdoch University Perth, Australia
 Mina John Institute for Immunology and Infectious Diseases Royal Perth Hospital & Murdoch University Perth, Australia AIDSvaccine conference, 14 th September 2011 IMGT HLA database July 2011 >5000 class
Mina John Institute for Immunology and Infectious Diseases Royal Perth Hospital & Murdoch University Perth, Australia AIDSvaccine conference, 14 th September 2011 IMGT HLA database July 2011 >5000 class
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Sui et al..7/pnas.997 Pre-CLP CM9 LA9 SL Tat# Pol Vif % Tetramer + CD + CD + Vac+IL- +IL- Vac Fig. S. Frequencies of six different CD + CD + Mamu-A*-tetramer + cells were measured
Supporting Information Sui et al..7/pnas.997 Pre-CLP CM9 LA9 SL Tat# Pol Vif % Tetramer + CD + CD + Vac+IL- +IL- Vac Fig. S. Frequencies of six different CD + CD + Mamu-A*-tetramer + cells were measured
NK mediated Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in HIV infections
 NK mediated Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in HIV infections Amy Chung Dr. Ivan Stratov Prof. Stephen Kent ADCC process consists of Target cell QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) FcγR decompressor
NK mediated Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in HIV infections Amy Chung Dr. Ivan Stratov Prof. Stephen Kent ADCC process consists of Target cell QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) FcγR decompressor
MID-TERM EXAMINATION
 Epidemiology 227 May 2, 2007 MID-TERM EXAMINATION Select the best answer for the multiple choice questions. There are 75 questions and 11 pages on the examination. Each question will count one point. Notify
Epidemiology 227 May 2, 2007 MID-TERM EXAMINATION Select the best answer for the multiple choice questions. There are 75 questions and 11 pages on the examination. Each question will count one point. Notify
Fig. 1: Schematic diagram of basic structure of HIV
 UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR HIV & AIDS: An Overview What is HIV?
UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR HIV & AIDS: An Overview What is HIV?
Micro 301 HIV/AIDS. Since its discovery 31 years ago 12/3/ Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) has killed >32 million people
 Micro 301 HIV/AIDS Shiu-Lok Hu hus@uw.edu December 3, 2012 Since its discovery 31 years ago Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) has killed >32 million people In 2011 34.0 million [31.4 35.9 million]
Micro 301 HIV/AIDS Shiu-Lok Hu hus@uw.edu December 3, 2012 Since its discovery 31 years ago Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) has killed >32 million people In 2011 34.0 million [31.4 35.9 million]
A VACCINE FOR HIV BIOE 301 LECTURE 10 MITALI BANERJEE HAART
 BIOE 301 LECTURE 10 MITALI BANERJEE A VACCINE FOR HIV HIV HAART Visit wikipedia.org and learn the mechanism of action of the five classes of antiretroviral drugs. (1) Reverse transcriptase inhibitors (RTIs)
BIOE 301 LECTURE 10 MITALI BANERJEE A VACCINE FOR HIV HIV HAART Visit wikipedia.org and learn the mechanism of action of the five classes of antiretroviral drugs. (1) Reverse transcriptase inhibitors (RTIs)
On an individual level. Time since infection. NEJM, April HIV-1 evolution in response to immune selection pressures
 HIV-1 evolution in response to immune selection pressures BISC 441 guest lecture Zabrina Brumme, Ph.D. Assistant Professor, Faculty of Health Sciences Simon Fraser University http://www3.niaid.nih.gov/topics/hivaids/understanding/biology/structure.htm
HIV-1 evolution in response to immune selection pressures BISC 441 guest lecture Zabrina Brumme, Ph.D. Assistant Professor, Faculty of Health Sciences Simon Fraser University http://www3.niaid.nih.gov/topics/hivaids/understanding/biology/structure.htm
Prokaryotic Biology. VIRAL STDs, HIV-1 AND AIDS
 Prokaryotic Biology VIRAL STDs, HIV-1 AND AIDS Prokaryotic Biology FROM THE CDC VIRAL STDs, HIV-1 AND AIDS VIRAL STDs & CONTACT VIRAL DISEASES A. GENITAL HERPES & COLD SORES 1. HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS-2 (HHV-2)
Prokaryotic Biology VIRAL STDs, HIV-1 AND AIDS Prokaryotic Biology FROM THE CDC VIRAL STDs, HIV-1 AND AIDS VIRAL STDs & CONTACT VIRAL DISEASES A. GENITAL HERPES & COLD SORES 1. HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS-2 (HHV-2)
5. Over the last ten years, the proportion of HIV-infected persons who are women has: a. Increased b. Decreased c. Remained about the same 1
 Epidemiology 227 April 24, 2009 MID-TERM EXAMINATION Select the best answer for the multiple choice questions. There are 60 questions and 9 pages on the examination. Each question will count one point.
Epidemiology 227 April 24, 2009 MID-TERM EXAMINATION Select the best answer for the multiple choice questions. There are 60 questions and 9 pages on the examination. Each question will count one point.
HIV/AIDS. Biology of HIV. Research Feature. Related Links. See Also
 6/1/2011 Biology of HIV Biology of HIV HIV belongs to a class of viruses known as retroviruses. Retroviruses are viruses that contain RNA (ribonucleic acid) as their genetic material. After infecting a
6/1/2011 Biology of HIV Biology of HIV HIV belongs to a class of viruses known as retroviruses. Retroviruses are viruses that contain RNA (ribonucleic acid) as their genetic material. After infecting a
HIV-1 SUBTYPE C MOTHER-TO-CHILD TRANSMISSION: GENETIC AND IMMUNOLOGIC CORRELATES. Elizabeth Susan Russell
 HIV-1 SUBTYPE C MOTHER-TO-CHILD TRANSMISSION: GENETIC AND IMMUNOLOGIC CORRELATES Elizabeth Susan Russell A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial
HIV-1 SUBTYPE C MOTHER-TO-CHILD TRANSMISSION: GENETIC AND IMMUNOLOGIC CORRELATES Elizabeth Susan Russell A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial
IAS 2015 Towards an HIV Cure symposium Vancouver Immune recognition following latency reversal
 IAS 2015 Towards an HIV Cure symposium Vancouver Immune recognition following latency reversal Marcus Altfeld Professor of Medicine Outline Immune recognition of HIV-1-infected cells Kinetics of antigen
IAS 2015 Towards an HIV Cure symposium Vancouver Immune recognition following latency reversal Marcus Altfeld Professor of Medicine Outline Immune recognition of HIV-1-infected cells Kinetics of antigen
LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK. How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome.
 Acquired immune deficiency syndrome 491 Acquired immune deficiency syndrome. The first cases of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) were reported in 1981 but it is now clear that cases of the disease
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome 491 Acquired immune deficiency syndrome. The first cases of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) were reported in 1981 but it is now clear that cases of the disease
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Rapid perforin upregulation directly ex vivo by CD8 + T cells is a defining characteristic of HIV elite controllers
 Rapid perforin upregulation directly ex vivo by CD8 + T cells is a defining characteristic of HIV elite controllers Adam R. Hersperger Department of Microbiology University of Pennsylvania Evidence for
Rapid perforin upregulation directly ex vivo by CD8 + T cells is a defining characteristic of HIV elite controllers Adam R. Hersperger Department of Microbiology University of Pennsylvania Evidence for
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Immunodeficiency. (2 of 2)
 Immunodeficiency (2 of 2) Acquired (secondary) immunodeficiencies More common Many causes such as therapy, cancer, sarcoidosis, malnutrition, infection & renal disease The most common of which is therapy-related
Immunodeficiency (2 of 2) Acquired (secondary) immunodeficiencies More common Many causes such as therapy, cancer, sarcoidosis, malnutrition, infection & renal disease The most common of which is therapy-related
Sequence Analysis of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1
 Sequence Analysis of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Stephanie Lucas 1,2 Mentor: Panayiotis V. Benos 1,3 With help from: David L. Corcoran 4 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Department
Sequence Analysis of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Stephanie Lucas 1,2 Mentor: Panayiotis V. Benos 1,3 With help from: David L. Corcoran 4 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Department
Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly
 FLU Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly October 23, 2008 Orthomyxoviruses Orthomyxo virus (ortho = true or correct ) Negative-sense RNA virus (complementary to mrna) Five different genera Influenza A, B, C Thogotovirus
FLU Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly October 23, 2008 Orthomyxoviruses Orthomyxo virus (ortho = true or correct ) Negative-sense RNA virus (complementary to mrna) Five different genera Influenza A, B, C Thogotovirus
HOST-PATHOGEN CO-EVOLUTION THROUGH HIV-1 WHOLE GENOME ANALYSIS
 HOST-PATHOGEN CO-EVOLUTION THROUGH HIV-1 WHOLE GENOME ANALYSIS Somda&a Sinha Indian Institute of Science, Education & Research Mohali, INDIA International Visiting Research Fellow, Peter Wall Institute
HOST-PATHOGEN CO-EVOLUTION THROUGH HIV-1 WHOLE GENOME ANALYSIS Somda&a Sinha Indian Institute of Science, Education & Research Mohali, INDIA International Visiting Research Fellow, Peter Wall Institute
Lecture 11. Immunology and disease: parasite antigenic diversity
 Lecture 11 Immunology and disease: parasite antigenic diversity RNAi interference video and tutorial (you are responsible for this material, so check it out.) http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow/3210/02.html
Lecture 11 Immunology and disease: parasite antigenic diversity RNAi interference video and tutorial (you are responsible for this material, so check it out.) http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow/3210/02.html
19 Viruses BIOLOGY. Outline. Structural Features and Characteristics. The Good the Bad and the Ugly. Structural Features and Characteristics
 9 Viruses CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV Lecture Presentation
9 Viruses CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV Lecture Presentation
Prevention of infection 2 : immunisation. How infection influences the host : viruses. Peter
 Prevention of infection 2 : immunisation How infection influences the host : viruses Peter Balfe, p.balfe@bham.ac.uk @pbalfeuk Let s have some LO s just for fun 1. Define the Immune response to viruses,
Prevention of infection 2 : immunisation How infection influences the host : viruses Peter Balfe, p.balfe@bham.ac.uk @pbalfeuk Let s have some LO s just for fun 1. Define the Immune response to viruses,
Clinical Education Initiative HIV CONTROLLERS: IMPLICATIONS FOR HIV CURE/REMISSION. Bruce Walker, MD
 Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org HIV CONTROLLERS: IMPLICATIONS FOR HIV CURE/REMISSION Bruce Walker, MD 6/23/2017 HIV Controllers: Implications for HIV Cure/Remission [video transcript]
Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org HIV CONTROLLERS: IMPLICATIONS FOR HIV CURE/REMISSION Bruce Walker, MD 6/23/2017 HIV Controllers: Implications for HIV Cure/Remission [video transcript]
Are we targeting the right HIV determinants?
 QuickTime et un décompresseur TIFF (non compressé) sont requis pour visionner cette image. AIDS Vaccine 2009 October 22 nd 2009 - Paris Are we targeting the right HIV determinants? Françoise BARRÉ-SINOUSSI
QuickTime et un décompresseur TIFF (non compressé) sont requis pour visionner cette image. AIDS Vaccine 2009 October 22 nd 2009 - Paris Are we targeting the right HIV determinants? Françoise BARRÉ-SINOUSSI
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Combining Pharmacology and Mutational Dynamics to Understand and Combat Drug Resistance in HIV
 Combining Pharmacology and Mutational Dynamics to Understand and Combat Drug Resistance in HIV A dissertation submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy by Max von Kleist, B.Sc., M.Sc. Supervisor:
Combining Pharmacology and Mutational Dynamics to Understand and Combat Drug Resistance in HIV A dissertation submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy by Max von Kleist, B.Sc., M.Sc. Supervisor:
HIV Diagnosis and Pathogenesis. HIV-1 Virion
 HIV Diagnosis and Pathogenesis Scott M. Hammer, M.D. HIV1 Virion Life Cycle of HIV HIV1 virion HIV1 Virus virion envelope Cell CD4membrane receptor VIRUS BINDING AND ENTRY RELEASE OF PROGENY VIRUS REVERSE
HIV Diagnosis and Pathogenesis Scott M. Hammer, M.D. HIV1 Virion Life Cycle of HIV HIV1 virion HIV1 Virus virion envelope Cell CD4membrane receptor VIRUS BINDING AND ENTRY RELEASE OF PROGENY VIRUS REVERSE
MID 36. Cell. HIV Life Cycle. HIV Diagnosis and Pathogenesis. HIV-1 Virion HIV Entry. Life Cycle of HIV HIV Entry. Scott M. Hammer, M.D.
 Life Cycle Diagnosis and Pathogenesis Scott M. Hammer, M.D. 1 Virion Entry Life Cycle of Entry 1 virion 1 Virus virion envelope Cell CD4membrane receptor RELEASE OF PROGENY VIRUS REVERSE Coreceptor TRANSCRIPTION
Life Cycle Diagnosis and Pathogenesis Scott M. Hammer, M.D. 1 Virion Entry Life Cycle of Entry 1 virion 1 Virus virion envelope Cell CD4membrane receptor RELEASE OF PROGENY VIRUS REVERSE Coreceptor TRANSCRIPTION
HIV-1 Dual Infection and Neurocognitive Impairment
 HIV-1 Dual Infection and Neurocognitive Impairment Gabriel Wagner, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Infectious Diseases & Global Public Health UC San Diego HIV-Associated End Organ Damage Antiretroviral
HIV-1 Dual Infection and Neurocognitive Impairment Gabriel Wagner, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Infectious Diseases & Global Public Health UC San Diego HIV-Associated End Organ Damage Antiretroviral
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 OCTOBER 31, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 OCTOBER 31, 2006
HIV and Challenges of Vaccine Development
 Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Institutes of Health HIV and Challenges of Vaccine Development Richard A. Koup, MD INTEREST
Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Institutes of Health HIV and Challenges of Vaccine Development Richard A. Koup, MD INTEREST
Anna de Goede HIV. host immunity and virus
 Anna de Goede HIV Immuno host immunity and virus therapy HIV Immunotherapy host immunity and virus evolution Anna de Goede HIV Immunotherapy host immunity and virus evolution HIV immuuntherapie gastheer-immuniteit
Anna de Goede HIV Immuno host immunity and virus therapy HIV Immunotherapy host immunity and virus evolution Anna de Goede HIV Immunotherapy host immunity and virus evolution HIV immuuntherapie gastheer-immuniteit
HIV 101: Fundamentals of HIV Infection
 HIV 101: Fundamentals of HIV Infection David H. Spach, MD Professor of Medicine University of Washington Seattle, Washington Learning Objectives After attending this presentation, learners will be able
HIV 101: Fundamentals of HIV Infection David H. Spach, MD Professor of Medicine University of Washington Seattle, Washington Learning Objectives After attending this presentation, learners will be able
Irina Maljkovic Berry
 Thesis for doctoral degree (Ph.D.) 2008 Thesis for doctoral degree (Ph.D.) 2008 Genetic aspects of HIV-1 evolution and transmission Irina Maljkovic Berry Genetic aspects of HIV-1 evolution and transmission
Thesis for doctoral degree (Ph.D.) 2008 Thesis for doctoral degree (Ph.D.) 2008 Genetic aspects of HIV-1 evolution and transmission Irina Maljkovic Berry Genetic aspects of HIV-1 evolution and transmission
HIV 1. Host Response to HIV-1 infection. Host - Parasite Relationships of HIV
 Organization of HIV-1Provirus Size 9kb Contains 9 genes encoding 15 proteins Early events of HIV- infection Membrane Receptor Complex Viral core 1 Binding of envelope gp120 prompts p41 to project 3 fusion
Organization of HIV-1Provirus Size 9kb Contains 9 genes encoding 15 proteins Early events of HIV- infection Membrane Receptor Complex Viral core 1 Binding of envelope gp120 prompts p41 to project 3 fusion
 CDC site UNAIDS Aids Knowledge Base http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/dhap.htm http://hivinsite.ucsf.edu/insite.jsp?page=kb National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases http://www.niaid.nih.gov/default.htm
CDC site UNAIDS Aids Knowledge Base http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/dhap.htm http://hivinsite.ucsf.edu/insite.jsp?page=kb National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases http://www.niaid.nih.gov/default.htm
Virological, immune and host genetics markers in the control of HIV infection
 Disease Markers 27 (2009) 105 120 105 DOI 10.3233/DMA-2009-0655 IOS Press Virological, immune and host genetics markers in the control of HIV infection Beatriz Mothe a, Javier Ibarrondo a, Anuska Llano
Disease Markers 27 (2009) 105 120 105 DOI 10.3233/DMA-2009-0655 IOS Press Virological, immune and host genetics markers in the control of HIV infection Beatriz Mothe a, Javier Ibarrondo a, Anuska Llano
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH THE IMMUNE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF HOST DEFENSES The human body contains three lines of against infectious agents (pathogens) 1. Mechanical and chemical boundaries (part of the innate immune system)
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF HOST DEFENSES The human body contains three lines of against infectious agents (pathogens) 1. Mechanical and chemical boundaries (part of the innate immune system)
Lecture 6. Burr BIO 4353/6345 HIV/AIDS. Tetramer staining of T cells (CTL s) Andrew McMichael seminar: Background
 Lecture 6 Burr BIO 4353/6345 HIV/AIDS Andrew McMichael seminar: Background Tetramer staining of T cells (CTL s) 1. Vβ 19: There are 52 T cell receptor (TCR) Vβ gene segments in germ line DNA (See following
Lecture 6 Burr BIO 4353/6345 HIV/AIDS Andrew McMichael seminar: Background Tetramer staining of T cells (CTL s) 1. Vβ 19: There are 52 T cell receptor (TCR) Vβ gene segments in germ line DNA (See following
VIRUSES. Biology Applications Control. David R. Harper. Garland Science Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON
 VIRUSES Biology Applications Control David R. Harper GS Garland Science Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON vii Chapter 1 Virus Structure and 2.2 VIRUS MORPHOLOGY 26 Infection 1 2.3 VIRAL CLASSIFICATION
VIRUSES Biology Applications Control David R. Harper GS Garland Science Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON vii Chapter 1 Virus Structure and 2.2 VIRUS MORPHOLOGY 26 Infection 1 2.3 VIRAL CLASSIFICATION
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1. Identification of the AIDS Virus a) opportunistic infections observed in homosexual men (all had T4 helper cell depletion) -> termed Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome;
Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1. Identification of the AIDS Virus a) opportunistic infections observed in homosexual men (all had T4 helper cell depletion) -> termed Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome;
levels of genes were separated by their expression levels; 2,000 high, medium, and low
 Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life
 Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity
 Innate & adaptive Immunity Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity Helen Horton PhD Seattle Biomedical Research Institute Depts of Global Health & Medicine, UW Cellular
Innate & adaptive Immunity Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity Helen Horton PhD Seattle Biomedical Research Institute Depts of Global Health & Medicine, UW Cellular
DEBATE ON HIV ENVELOPE AS A T CELL IMMUNOGEN HAS BEEN GAG-GED
 DEBATE ON HIV ENVELOPE AS A T CELL IMMUNOGEN HAS BEEN GAG-GED Viv Peut Kent Laboratory, University of Melbourne, Australia WHY ENVELOPE? Env subject to both humoral and cellular immune responses Perhaps
DEBATE ON HIV ENVELOPE AS A T CELL IMMUNOGEN HAS BEEN GAG-GED Viv Peut Kent Laboratory, University of Melbourne, Australia WHY ENVELOPE? Env subject to both humoral and cellular immune responses Perhaps
Mayo Clinic HIV ecurriculum Series Essentials of HIV Medicine Module 2 HIV Virology
 Mayo Clinic HIV ecurriculum Series Essentials of HIV Medicine Module 2 HIV Virology Eric M. Poeschla, MD Professor of Medicine College of Medicine Consultant, Division of Infectious Diseases Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic HIV ecurriculum Series Essentials of HIV Medicine Module 2 HIV Virology Eric M. Poeschla, MD Professor of Medicine College of Medicine Consultant, Division of Infectious Diseases Mayo Clinic
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY. CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells. Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation
 IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. September 7, of 7 RETROVIRUSES. 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
 1 of 7 I. Diseases Caused by Retroviruses RETROVIRUSES A. Human retroviruses that cause cancers 1. HTLV-I causes adult T-cell leukemia and tropical spastic paraparesis 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
1 of 7 I. Diseases Caused by Retroviruses RETROVIRUSES A. Human retroviruses that cause cancers 1. HTLV-I causes adult T-cell leukemia and tropical spastic paraparesis 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
Discovery of HIV and Early Findings
 Discovery of HIV and Early Findings Jay A. Levy, M.D. Professor of Medicine Director, Laboratory for Tumor and AIDS Virus Research University of California, San Francisco, CA Major Epidemics of the World
Discovery of HIV and Early Findings Jay A. Levy, M.D. Professor of Medicine Director, Laboratory for Tumor and AIDS Virus Research University of California, San Francisco, CA Major Epidemics of the World
HIV and drug resistance Simon Collins UK-CAB 1 May 2009
 HIV and drug resistance Simon Collins UK-CAB 1 May 2009 slides: thanks to Prof Clive Loveday, Intl. Clinical Virology Centre www.icvc.org.uk Tip of the iceberg = HIV result, CD4, VL Introduction: resistance
HIV and drug resistance Simon Collins UK-CAB 1 May 2009 slides: thanks to Prof Clive Loveday, Intl. Clinical Virology Centre www.icvc.org.uk Tip of the iceberg = HIV result, CD4, VL Introduction: resistance
Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses
 Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses 1. Overview of Animal Viruses 2. DNA Viruses 3. RNA Viruses 4. Prions 1. Overview of Animal Viruses Life Cycle of Animal Viruses The basic life cycle stages of animal viruses
Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses 1. Overview of Animal Viruses 2. DNA Viruses 3. RNA Viruses 4. Prions 1. Overview of Animal Viruses Life Cycle of Animal Viruses The basic life cycle stages of animal viruses
Defense Against Viruses/AIDS. Shomyseh Sanjabi, PhD Micro 204, 12/01/17
 Defense Against Viruses/AIDS Shomyseh Sanjabi, PhD Shomyseh.Sanjabi@gladstone.ucsf.edu Micro 204, 12/01/17 Recommended Reading: Textbook: Janeway chapter 13.22-13.38. Prof. V. Racaniello online material
Defense Against Viruses/AIDS Shomyseh Sanjabi, PhD Shomyseh.Sanjabi@gladstone.ucsf.edu Micro 204, 12/01/17 Recommended Reading: Textbook: Janeway chapter 13.22-13.38. Prof. V. Racaniello online material
Epidemiology 227 Mid-term Examination May 1, 2013
 Epidemiology 227 Mid-term Examination May 1, 2013 Select the best answer from the multiple choice questions. There are 78 questions and 12 pages on the examination. Notify your instructor if your examination
Epidemiology 227 Mid-term Examination May 1, 2013 Select the best answer from the multiple choice questions. There are 78 questions and 12 pages on the examination. Notify your instructor if your examination
Viral reproductive cycle
 Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Viral Genetics. BIT 220 Chapter 16
 Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
Mechanisms of CD8+ T Cell Mediated Virus Inhibition in HIV-1 Virus Controllers. Tamika L. Payne
 Mechanisms of CD8+ T Cell Mediated Virus Inhibition in HIV-1 Virus Controllers by Tamika L. Payne Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology Duke University Date: Approved: Georgia D. Tomaras, Supervisor
Mechanisms of CD8+ T Cell Mediated Virus Inhibition in HIV-1 Virus Controllers by Tamika L. Payne Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology Duke University Date: Approved: Georgia D. Tomaras, Supervisor
HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS
 Futuro promisorio de la terapia antirretroviral: Nuevos blancos terapéuticos. María José Míguez, M.D., PhD., Universidad de Miami, EE.UU. HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASA REPLICATION
Futuro promisorio de la terapia antirretroviral: Nuevos blancos terapéuticos. María José Míguez, M.D., PhD., Universidad de Miami, EE.UU. HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASA REPLICATION
Virology and HIV. Protease Inhibitors: Another Class of Drugs Against HIV
 Jones & Ba NOT FOR SAL Chapter 4 Jones & Ba NOT FOR SAL Virology and HIV Jones & Ba OT FOR SAL A General Introduction to Viruses What Are Viruses? How Does a Virus Infect a Host? rtlett Learning, A Typical
Jones & Ba NOT FOR SAL Chapter 4 Jones & Ba NOT FOR SAL Virology and HIV Jones & Ba OT FOR SAL A General Introduction to Viruses What Are Viruses? How Does a Virus Infect a Host? rtlett Learning, A Typical
Epitope Specific CD8 + T Cell Responses Predict Spontaneous Control of HIV Replication
 Epitope Specific CD8 + T Cell Responses Predict Spontaneous Control of HIV Replication Florencia Pereyra, MD Partners AIDS Research Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Background HIV -1 elicits HLA
Epitope Specific CD8 + T Cell Responses Predict Spontaneous Control of HIV Replication Florencia Pereyra, MD Partners AIDS Research Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Background HIV -1 elicits HLA
Mechanisms of antagonism of HIVspecific CD4+ T cell responses BSRI
 Mechanisms of antagonism of HIVspecific CD4+ T cell responses BSRI Problems Virus escape from immune recognition Antagonism of T cell responses Peptide-MHC-TCR interaction T cell antagonism Variants of
Mechanisms of antagonism of HIVspecific CD4+ T cell responses BSRI Problems Virus escape from immune recognition Antagonism of T cell responses Peptide-MHC-TCR interaction T cell antagonism Variants of
HIV Anti-HIV Neutralizing Antibodies
 ,**/ The Japanese Society for AIDS Research The Journal of AIDS Research : HIV HIV Anti-HIV Neutralizing Antibodies * Junji SHIBATA and Shuzo MATSUSHITA * Division of Clinical Retrovirology and Infectious
,**/ The Japanese Society for AIDS Research The Journal of AIDS Research : HIV HIV Anti-HIV Neutralizing Antibodies * Junji SHIBATA and Shuzo MATSUSHITA * Division of Clinical Retrovirology and Infectious
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
 The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
Development of Broadly Reactive HIV-1/AIDS Virus-like Particle Vaccines. Sean Patrick McBurney. B.S. Microbiology, University of Pittsburgh, 2004
 Development of Broadly Reactive HIV-1/AIDS Virus-like Particle Vaccines by Sean Patrick McBurney B.S. Microbiology, University of Pittsburgh, 2004 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of School of Medicine
Development of Broadly Reactive HIV-1/AIDS Virus-like Particle Vaccines by Sean Patrick McBurney B.S. Microbiology, University of Pittsburgh, 2004 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of School of Medicine
Alternate Antibody-Based Therapeutic Strategies To Purge the HIV Cell Reservoir
 Alternate Antibody-Based Therapeutic Strategies To Purge the HIV Cell Reservoir Giuseppe Pantaleo, M.D. Professor of Medicine Head, Division of Immunology and Allergy Executive Director, Swiss Vaccine
Alternate Antibody-Based Therapeutic Strategies To Purge the HIV Cell Reservoir Giuseppe Pantaleo, M.D. Professor of Medicine Head, Division of Immunology and Allergy Executive Director, Swiss Vaccine
Evolution of the Virulent Primary Isolate, SIV/DeltaB670, in vivo, Implications for Study Design and Antiviral Therapies
 Evolution of the Virulent Primary Isolate, SIV/DeltaB670, in vivo, Implications for Study Design and Antiviral Therapies by Rachel Taber Bachelors of Science, Western Washington University Bellingham,
Evolution of the Virulent Primary Isolate, SIV/DeltaB670, in vivo, Implications for Study Design and Antiviral Therapies by Rachel Taber Bachelors of Science, Western Washington University Bellingham,
Panther has new prey
 Raising the Bar for Performance Testing Panther has new prey The Aptima HIV-1 Quant Dx assay leads the hunt for HIV-1 diagnosis and viral load monitoring. Freedom to work the way you choose Run what assays
Raising the Bar for Performance Testing Panther has new prey The Aptima HIV-1 Quant Dx assay leads the hunt for HIV-1 diagnosis and viral load monitoring. Freedom to work the way you choose Run what assays
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection
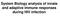 System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
227 28, 2010 MIDTERM EXAMINATION KEY
 Epidemiology 227 April 28, 2010 MIDTERM EXAMINATION KEY Select the best answer for the multiple choice questions. There are 64 questions and 9 pages on the examination. Each question will count one point.
Epidemiology 227 April 28, 2010 MIDTERM EXAMINATION KEY Select the best answer for the multiple choice questions. There are 64 questions and 9 pages on the examination. Each question will count one point.
Dynamics of lentiviral infection in vivo in the absence of adaptive immune responses
 Dynamics of lentiviral infection in vivo in the absence of adaptive immune responses Elissa J. Schwartz Associate Professor School of Biological Sciences Department of Mathematics & Statistics Washington
Dynamics of lentiviral infection in vivo in the absence of adaptive immune responses Elissa J. Schwartz Associate Professor School of Biological Sciences Department of Mathematics & Statistics Washington
HIV-1 acute infection: evidence for selection?
 HIV-1 acute infection: evidence for selection? ROLLAND Morgane University of Washington Cohort & data S6 S5 T4 S4 T2 S2 T1 S1 S7 T3 DPS (days post symptoms) 3 (Fiebig I) 7 (Fiebig I) 13 (Fiebig V) 14 (Fiebig
HIV-1 acute infection: evidence for selection? ROLLAND Morgane University of Washington Cohort & data S6 S5 T4 S4 T2 S2 T1 S1 S7 T3 DPS (days post symptoms) 3 (Fiebig I) 7 (Fiebig I) 13 (Fiebig V) 14 (Fiebig
CURRENT DEVELOMENTS AND FUTURE PROSPECTS FOR HIV GENE THERAPY USING INTERFERING RNA-BASED STRATEGIES
 [Frontiers in Bioscience 5, d527-555, May 1, 2000] CURRENT DEVELOMENTS AND FUTURE PROSPECTS FOR HIV GENE THERAPY USING INTERFERING RNA-BASED STRATEGIES Betty Lamothe, Sadhna Joshi Department of Medical
[Frontiers in Bioscience 5, d527-555, May 1, 2000] CURRENT DEVELOMENTS AND FUTURE PROSPECTS FOR HIV GENE THERAPY USING INTERFERING RNA-BASED STRATEGIES Betty Lamothe, Sadhna Joshi Department of Medical
Towards an HIV Cure. Steven G. Deeks Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco
 Towards an HIV Cure Steven G. Deeks Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Why are we now talking about a cure? Emerging recognition that HAART does not fully restore health and/or
Towards an HIV Cure Steven G. Deeks Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Why are we now talking about a cure? Emerging recognition that HAART does not fully restore health and/or
Chapter 10 (pages ): Differentiation and Functions of CD4+ Effector T Cells Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
Going Nowhere Fast: Lentivirus genetic sequence evolution does not correlate with phenotypic evolution.
 Going Nowhere Fast: Lentivirus genetic sequence evolution does not correlate with phenotypic evolution. Brian T. Foley, PhD btf@lanl.gov HIV Genetic Sequences, Immunology, Drug Resistance and Vaccine Trials
Going Nowhere Fast: Lentivirus genetic sequence evolution does not correlate with phenotypic evolution. Brian T. Foley, PhD btf@lanl.gov HIV Genetic Sequences, Immunology, Drug Resistance and Vaccine Trials
Inves)gación básica y curación del VIH- 1
 Inves)gación básica y curación del VIH- 1 Javier Mar)nez- Picado (jmpicado@irsicaixa.es) 23 rd Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunis5c Infec5ons February 22-25, 2016 Boston, Massachuse8s UNIVERSITAT
Inves)gación básica y curación del VIH- 1 Javier Mar)nez- Picado (jmpicado@irsicaixa.es) 23 rd Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunis5c Infec5ons February 22-25, 2016 Boston, Massachuse8s UNIVERSITAT
Structure of HIV. Virion contains a membrane envelope with a single viral protein= Env protein. Capsid made up of Gag protein
 Structure of HIV Virion contains a membrane envelope with a single viral protein= Env protein Important in receptor recognition Capsid made up of Gag protein (group-specific antigen) Icosahedral Interior
Structure of HIV Virion contains a membrane envelope with a single viral protein= Env protein Important in receptor recognition Capsid made up of Gag protein (group-specific antigen) Icosahedral Interior
19/06/2013. Viruses are not organisms (do not belong to any kingdom). Viruses are not made of cells, have no cytoplasm, and no membranes.
 VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
Medical and Immunological Interventions in HIV - 1 Infection
 Venhälsan and Stockholm Söder Hospital, Microbiology and Tumor Biology Center and Swedish Institute for Infectious Disease Control, Stockholm, Sweden Studies on Medical and Immunological Interventions
Venhälsan and Stockholm Söder Hospital, Microbiology and Tumor Biology Center and Swedish Institute for Infectious Disease Control, Stockholm, Sweden Studies on Medical and Immunological Interventions
