STUDY ON MYCOTIC DISSEMINATION AND PATHOLOGICAL FINDINGS ASSOCIATED WITH EXPERIMENTAL CANDIDA ALBICANS INFECTION IN BALB/C MICE
|
|
|
- Clare Lynch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STUDY ON MYCOTIC DISSEMINATION AND PATHOLOGICAL FINDINGS ASSOCIATED WITH EXPERIMENTAL CANDIDA ALBICANS INFECTION IN BALB/C MICE Khalil H. Al- Jeboori & Saja A. H. Al- Harreery Dept of pathology, College of Vet. Medicine, Univ. of Baghdad, Iraq ABSTRACT Candidiasis is a one of zoonotic disease and a public health importance. To identify dissemination of Candida albicans and pathological findings associated with the experimental mycotic infection model. C. albicans strain were obtained from public health laboratory and reidentified, the dose were increased to 25% of LD50 ( 5x10 5 CFu/ml) to become 6.25 x10 5 CFu/ml and 0.25 ml were injected intraperitoneally in group of mice (40), every 3 days 3 mice were sacrificed for a period of 30 days. C. albicans isolation were done from the different organs of mice and were found that C. albicans were persisted for days in different organs of mice except that it persisted for 21 days in kidneys, liver and spleen. Different pathological lesions were recorded in the mice organs during the period of infection with C. albicans. Kidney showed interstitial nephritis with perivascular leukocytes Cuffing, microabscesses and purulent granuloma in liver hyperplasia of white pulp and red pulp with amyloidosis in spleen, interstitial pneumonic lesion with peribronchial lymphoid tissue hyperplasia, focal myocarditis and epicarditis. Microglia cell proliferation in brain, focal peritonitis, hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue of peyers patches and intestinal wall thickening and endometrial hyperplasia and endometritis and mucupurulent vaginitis. KEYWORDS: C. albicans, zoonotic disease, balb/c mice, Candidiasis. INTRODUCTION Candida albicans is an opportunistic yeast pathogen that was frequently isolated from the mucosal surfaces, of normal individuals and it is capable to initiating variety of recurring diseases especially in the vagina, oral and gastrointestinal mucosa, it also can affect different systemic organs in the body [1,2]. Infections with C. albicans increased prodominently in the patients with immunodeficiency, following the using broad spectrum antibiotics and cancer therapy and after surgical operation and tissue transplantation [3,4]. Candidiasis is a common infection in man and animals. It affect poultry causing high mortality also, it affect cattle and associated with abortion and mastitis and affect most of different animals and even laboratory animals and it sure that candidiasis is one of zoonotic diseases [5,6] and so the importance of this diseases, this study aimed to identify the dissemination of C. albicans in the body organs of mice and to identify pathological findings associated with experimental infection of this laboratory animal with this microbial infection. MATERIALS & METHODS Candida albicans obtained from the central public health laboratories and to ensure its purification, the following diagnostic methods had done including, cultural characteristics, microbiological examination, Germ tube formation chlamyolospores formation test. API candida Biomerieuxs, France). After determination LD50 for C. albicans [7] it is found that mice sensitive to lethal dose fifty 5x10 5 CFU/ml ) for this reason we increase the dose with 25% to become 6.25 x 10 5 CFU/ml, then 0.25 % of C. albicans were taken and injected intraperitoneally in 40 mice ( Balb / c white mice ) and 3 mice infected were killed at 3 days interval for 30 days, then isolation of C. albicans from different organs were done and pieces from different organs were taken in 10% formalin for fixation, then after processing routinely in histokinette, cut at 5 thickness and stained with hematoxyline and eosin and examined under light microscope [8]. RESULTS & DISCUSSION 1- The dissemination of C. albicans in the different body organs of experimental intraperitoneally infected mice. During the experimental term (30 days), there is individual differences in appear and disappear of the infection in different body organs (Table 1), It persist in liver, spleen and kidney for 21 days whereas in brain and other organ persist for days post inoculation. 534
2 Mycotic dissemination with experimental Candida albicans infection in Balb/C Mice Table 1: Spread of C. albicans in different body organs of experimental intraperitoneally infected mice - Total No. of mice : 40 mouse - Killed mice (4) each days including dead animals. - Dose 0.25 ml of 6.25 x 10 5 cfu/ml to each mouse. - ( + ) C. albicans isolated from organs of killed and dead mice. - ( - ) No isolation of C. albicans from body organs. These results agree with [9], they mentioned that C. albicans can affect liver, kidney, spleen, lung, brain, intestine in addition to uterus and vagina, when yeast inoculated intraperitoneally in mice and spread through blood stream and cause systemic candidiasis [10] which is evident in this study. C. albicans began to disappear from most of body organs such as liver, kidney, spleen & lung after days post inoculation, these results agree with [11] whom mentioned that the clearance of these organ from C. albicans is related to developing the immune response against this microbial infection during this period of infection [12]. Histopathological changes Kidneys The main lesions were consisted of infiltration of interstitial tissue with neutrophils and mononuclear cells ( lymphocytes, macrophages and plasma cells ) between renal tubules and adjacent glomeruli ( Fig.1) and around blood vessels in addition to dilatation of Bowman capsule. FIGURE 1: kidney interstitial nephritis characterized by extensive infiltration of lymphocytes and macrophages between renal tubules and glomeruli ( arrow ) ( H& E ) x 200 Liver There is congestion, hydropic degeneration with vaccuolation of hepatocytes and multifocal aggregation of neutrophils and edema in the adjacent area to central vein and in portal area, these cellular reactions cause a microabscess which gradually transform into suppurative granuloma especially in advance cases, with a central necrosis surrounded by neutrophils, mononuclear cells and giant cells with fibroblasts proliferation FIGURE 2 : liver : Cirrhosis, early suppurative granulomatous reaction with central caseasion surrounded by neutrophils, mononuclear cells (MNC) infiltration and fibroblast proliferation ( arrow ), in addition to congestion of blood vessels ( H&E)x200 Spleen There is extensive hyperplasia of the white pulp region in per arteriolar sheath region (T cell region) and in the remainder area of the pulp (B cell region) (Fig- 3). Also there is reticuloendothelial cell hyperplasia in the red pulp and thickening of spleen trabecnlae. In certain section extensive amyloid deposition enclosing the white pulp. 535
3 FIGURE 3: spleen Amyloid, sago spleen type amyloidosis inclosing the white pulp (arrow) ( H&E) x 200 Lungs There is extensive interstitial pneumonic lesion characterize by thickening of alveolarwalls due to congestion of alveolar capillaries and infiltration of mononuclear cells (Fig 4 ) causing narrowing of alveolar FIGURE 4 : lung peribronchial lymphoid tissue, hyperplasia (arrow) ( H&E)x200) Lumina, also there are a peribronchial lymphoid tissue hyperplasia and in advance cases a pulmonary fibrosis. Heart In the most sections there is infiltration of neutrophils and mononuclear cells between muscle fibers and on the epicardium FIGURE 5: Heart Myocarditis, infiltraton of inflammatory cells between myocardial muscles fibers also congestion of blood vessels ( arrow ) ( H&E) x 200) Brain There is focal aggregate of neutrophils and mononuclear cells around blood vessels (perivasculor leukocyte cuffing) in addition to focal gliosis with focal proliferation of microglia cells (Fig 6). In certain sections focal meningitis characterized by infiltration of meanings with neutrophils FIGURE 6: Brain focal gliosis characterized by focal proliferation of microglial cells with focal area of edematous liquification (arrow). ( H&E) x 200 and mononuclear cells and congestion of Blood vessels and edema. Peritoneum There is extensive infiltration of neutrophils and mononuclear cells in the adipose tissue and around the blood vessels of the peritoneal tissue (Fig -7) FIGURE 7: peritoneum Adipose tissue infiltration of lymphocytes and macrophage on the peritoneal surfaces ( arrow ) ( H&E)x200 FIGURE 8: Intestine Reactive hyperplasia of peyer's pataches with germinal center formation (arrow). ( H&E) x
4 Mycotic dissemination with experimental Candida albicans infection in Balb/C Mice Intestine There is extensive hyperplasia of the lymphoid tissue in the peyer's patch region causing thickening of intestinal wall (Fig 8) Uterus There is extensive endometrial epithelial hyperplasia and infiltration of neutrophils and mononuclear cells in subendometrial region leading to thickening of uterus (Fig- 9). In other sections there is sloughing of epithelia lining of endometrium and presence of the inflammatory cellular exudates and mucus in the uterine lumen. FIGURE 9 : Uterus endometrium sloughing of epithelial lining of endometrium and mucus exudates in addition to subendometrial inflammatory infiltration ( arrow ). ( H&E)x200 Vagina There is extensive infiltration of neutrophils and mononuclear cells and congestion of blood vessels in vaginal wall and sloughing of mucosal epithelial lining with mucopurulent exudate in the vaginal lumen (Fig 10). This study revealed that the renal tissue is the one of the organs sensitive to C. albicans infection with production of different lesions due to proliferation of this microbial agent in renal tissue and as a result of less presence of phagocytic cells in renal tissue [13]. Liver is considered to be the 2 nd target organ infected with C. albicans and associated with degenerative changes, abscessation and supportive granuloma formation, similar finding were observed by [9] due to proliferation of this microbe in liver tissue. Spleen showed extensive hyperplasia of white pulp and reticuloendothelal hyperplasia of Red pulp in addition to amyloid enclosing white pulp, similar finding in spleen were reported by [14] but with less degree and explained on the basis of the dose and virulence of the C. albicans, similar lesion in the lungs were reported by [15], they considered that the lung is one of the target organs affected by C. albicans. similar findings were reported in the heart and brain of mice [14] with a focal inflammatory cellular reaction between myocardial fibers but with less degree and in brain of mice with microglia cell proliferation and perivascular leukocyte cuffing depending on dose and virulent of C. albicans [14]. Similar lesions were reported in periton (focal peritonitis) this agree with [16] and in intestine, hyperplasia of peyer's patches and intestinal wall thichenining due to inflammatory cell infiltration and goblet cell proliferation. This result agree with [17] who explained this lesion in intestine due irritation of mucosal surface by C. albicons. this study revealed that the endometrial hyperplasia, sloughing of their epithelial lining together with mucopurulent vaginitis and mucopurulent exudate filling the vaginal and uterine lumena occurred as a result of proliferation of yeast like FIGURE 10: Vagina : Mucoperulent vaginitis : suppurative exudates ( arrow) mixed with mucus secretion with sloughing of their epithelial lining, also some inflammatory cell infiltration in the vaginal wall and hyperplasia of their epithelial lining ( double arrow ), ( H&E)x200 cells of C. albicans which is more evident as a white patches in vaginal mucosa, this result agree with [18]. REFERENCES [1]. Yuthika, H. Samaranayake, P, and samaranayake, L. (2001) Experimental oral candidiasis in animal models. Clin. Microbial Review, 14(2): [2]. Waltimo, T. M. T, Sen, B. H., Meuman, J. H., Qrestavik, D. and Haapasolo, M.P.P.(2003)yeast apical periodontitis crit. Rev. oral. Biol. Med. 14(2) [3]. Ruhnke, M. (2002) skin and mucous membrane infection In. R.A. Calderone (ed) Candida and candidiasis. American society for microbiology, Washington D.C., P [4]. Ryan, K. J. and Ray, C. G. (2004) Sherries medical microbiology 4 th ed. Chapter 48, Candida albicans, Pp [5]. Hormandorfer, S. and Bauer, J yeast infection in veterinary medicine contrib. microbial, 2000, 5, [6]. Al Baker, S. M. A. (2005) study of some immunological aspects for some antigens of Candida albicans isolated from vaginal infection Ph. D. thesis, college of medicine university of Al- Mustansiriyah, 2005). [7]. Reed. L. J. and muench. H. (1938) Asimple method of estimating fifty percent and end points Am. J. Hygiene, 24, [8]. Luna, H. T. and Lee, G. Manual histological staining methods of the armed forces institute and pathology 3 rd. ed the Blakis. Mc Graw Hillbook Co. New yourk.usa, [9]. Cole, G. T., Iynn, K. T. seshan, K. R. and pope, L. M. (1989) Gastrointestinal and systemic candidiasis in immunocompromised mice. J. Med. Vet. mycol., 27(6)
5 [10]. Gillen, D. and Emerson, S. (2002) Drug resistance in pathogenic fungi school of public health and community medicine university of Washington SPHCM on research Issue,9. [11]. Chores, G. M., Cavalcanti, M. A., Carneiro, A. M. and Lopes, S.L. (2004) mode of experimental infection in healthy and immunosuppressed Swiss albino mice using Candida albicans strains with different pattern of enzymatic activity. Braz. J. microbial. 35(4). [12]. Johnson, A. G and Clarke, B. L. Highyield Immunology, 2 nd ed. 2005, P 7-8. [13]. Mugge, A., Daniel, W. G., Nonnast Daniel, B., Schroder, E., Torlschel, H. and Lichten, P. (2005) Renal infarction with fatal bleeding an unusual complication of Candida albicans endocarditis J. Mol. Med., 65 (24) [14]. Al Thwani, A. Nand Hassan F. K. pathological effect and immune response of Candida albicans and C. Krusi in mice M. Sc thesis college of vet. Med. University of Baghdad, [15]. Cannon, R. R. French, S. W., Johnston, D., Edwards, J. E and Filler, S. G. (2002) Candida albicans stimulate local expression leukocyte adhesion molecules and cytokinesin vivo J. Infect. Dis., 186, [16]. Bibashi, E., Menmos, D., Koklina, E., Tsakiris, D., Sofianon, D. and Papadimitriou, M. (2003) fungal peritonitis complicating peritoneal Dialysis on 11- year period : Report of 46 cases. clin. infect. Dis., 36, [17]. Arsani, R. K. (1993) Experimental candidiasis in Japanese quail. mycopath.121, (2) [18]. Hopfer, R. L. (1985) Mycology of Canida albicans, Book of candidiasis cited by G.P. Bodey and V. Fenstein. Ravan press New Your,
Figure 2: Lymph node Cortical follicular (F) and paracortical (PC) atrophy, with narrowing of the cortex relative to the medulla (M).
 Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
PATHOLOGY OF PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA INFECTION IN CHICKENS
 Indian J. Anim. Res., 40 (1): 15-19, 2006 PATHOLOGY OF PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA INFECTION IN CHICKENS Shilpa Sood 1 and P.C. Verma CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar - 125 004, India ABSTRACT The
Indian J. Anim. Res., 40 (1): 15-19, 2006 PATHOLOGY OF PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA INFECTION IN CHICKENS Shilpa Sood 1 and P.C. Verma CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar - 125 004, India ABSTRACT The
Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology
 2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
PATHOLOGICAL STUDY ON SOME RENAL LESION IN SHEEP AND GOATS IN DIYALA PROVINCE
 I.J.S.N., VOL.8 (3) 2017: 611-615 ISSN 2229 6441 PATHOLOGICAL STUDY ON SOME RENAL LESION IN SHEEP AND GOATS IN DIYALA PROVINCE Noura N. Ali & Khalil H. Aljeboori Department of Pathology, college of Vet,
I.J.S.N., VOL.8 (3) 2017: 611-615 ISSN 2229 6441 PATHOLOGICAL STUDY ON SOME RENAL LESION IN SHEEP AND GOATS IN DIYALA PROVINCE Noura N. Ali & Khalil H. Aljeboori Department of Pathology, college of Vet,
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR
 Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Study the physiological and histological changes in mice liver that infected with Candida albicans and the role of camel's milk to treatment
 Study the physiological and histological changes in mice liver that infected with Candida albicans Sura Saad Abdulazeez Ali Dep. of Basic Nursing seinces, College of Nursing, Univ. of Tikrit, Iraq Abstract
Study the physiological and histological changes in mice liver that infected with Candida albicans Sura Saad Abdulazeez Ali Dep. of Basic Nursing seinces, College of Nursing, Univ. of Tikrit, Iraq Abstract
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Histopathology: pulmonary pathology
 Histopathology: pulmonary pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: pulmonary pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Annals of RSCB Vol. XIV, Issue 1
 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF POSTWEANING MULTISYSTEMIC WASTING SYNDROME D. Cadar 1, V. Miclăuş 2, Marina Spînu 1, V. Rus 2, A. Cságola 3, T. Tuboly 3 1 UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AND VETERINARY
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF POSTWEANING MULTISYSTEMIC WASTING SYNDROME D. Cadar 1, V. Miclăuş 2, Marina Spînu 1, V. Rus 2, A. Cságola 3, T. Tuboly 3 1 UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AND VETERINARY
Opportunistic Mycoses
 CANDIDIASIS SOFYAN LUBIS DEPARTEMEN MIKROBIOLOGI FAK.KEDOKTERAN USU MEDAN 2009 Opportunistic Mycoses Opportunistic mycoses are fungal infections that do not normally cause disease in healthy people, but
CANDIDIASIS SOFYAN LUBIS DEPARTEMEN MIKROBIOLOGI FAK.KEDOKTERAN USU MEDAN 2009 Opportunistic Mycoses Opportunistic mycoses are fungal infections that do not normally cause disease in healthy people, but
1) Mononuclear phagocytes : 2) Regarding acute inflammation : 3) The epithelioid cells of follicular granulomas are :
 Pathology Second 1) Mononuclear phagocytes : - Are the predominant cells in three day old wounds - Are common in liver, spleen and pancreasd - Produce fibroblast growth factor - Secrete interferon-g -
Pathology Second 1) Mononuclear phagocytes : - Are the predominant cells in three day old wounds - Are common in liver, spleen and pancreasd - Produce fibroblast growth factor - Secrete interferon-g -
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #3 KEY
 2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification
 Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~ 1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~ 1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Chronic inflammation. 07-Dec-15. Macrophage Tissue destruction
 Chronic inflammation DR. M. TARIQ JAVED PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY FACULTY OF VETERINARY SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE, FAISALABAD. Other types of cells present B & T lymphocytes (antibody and
Chronic inflammation DR. M. TARIQ JAVED PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY FACULTY OF VETERINARY SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE, FAISALABAD. Other types of cells present B & T lymphocytes (antibody and
Anatomy. Lymph: Tissue fluid that enters a lymphatic capillary (clear fluid that surrounds new piercings!)
 Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification. Taxonomic Systems for Identification of the Anamorphs of Conidiogenous Fungi
 Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.
 المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Histopathological Evaluation of Pulmonary Effects of Sodium Dichromate Cr VI in Rats
 IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 9, Issue 4 Ver. II (Apr. 2016), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Histopathological Evaluation of
IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 9, Issue 4 Ver. II (Apr. 2016), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Histopathological Evaluation of
Cellular Injury. Intracellular degeneration. By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall /20/2018 1
 Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Avian Pathology. Bacterial diseases: histo slides. ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN
 Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
Extracellular degeneration
 Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
3/17/2014. The Lymphatic System. Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs
 The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes
 CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic Pathways. Lymphatic Capillaries. network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids
 Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Scottish Surveillance of Healthcare Associated Infection Programme (SSHAIP) Health Protection Scotland (HPS) SSI Surveillance Protocol 7th Edition
 1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Fourth Practical Pathology. Circulatory disturbances
 Fourth Practical Pathology Circulatory disturbances 12.12.2018 1 Organ: Lung (40X, low power) 1) The blood capillaries within the alveolar septa are engorged with blood 2) Pinkish proteinaceous fluid,
Fourth Practical Pathology Circulatory disturbances 12.12.2018 1 Organ: Lung (40X, low power) 1) The blood capillaries within the alveolar septa are engorged with blood 2) Pinkish proteinaceous fluid,
Chapter 1. Full file at
 Chapter 1 1. Which is the best definition of immunity? Answer: B A. The state of having been exposed to a pathogen repeatedly B. The state of being resistant to reinfection with a pathogen C. When an individual
Chapter 1 1. Which is the best definition of immunity? Answer: B A. The state of having been exposed to a pathogen repeatedly B. The state of being resistant to reinfection with a pathogen C. When an individual
2014 SEVPAC Case #63 (Slide ID: #1)
 2014 SEVPAC Case #63 (Slide ID: #1) Tuskegee University College of Veterinary Medicine Dr. Ebony Gilbreath Tissues submitted to TUSVM diagnostic services for histopathology Puppies 4 weeks of age From
2014 SEVPAC Case #63 (Slide ID: #1) Tuskegee University College of Veterinary Medicine Dr. Ebony Gilbreath Tissues submitted to TUSVM diagnostic services for histopathology Puppies 4 weeks of age From
Nyamdolgor.U, Usuhgerel.S, Baatarjargal.P, others, Journal of agricultural sciences 15 (02): 51-55, 2015
 51 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY FOR USING OF POX INACTIVATED VACCINE IN GOATS Nyamdolgor.U 1*, Usuhgerel.S 2, Baatarjargal.P 1, Altanchimeg.A 1, Odbileg.R 1 1-Institute of Veterinary Medicine, MULS, Mongolia
51 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY FOR USING OF POX INACTIVATED VACCINE IN GOATS Nyamdolgor.U 1*, Usuhgerel.S 2, Baatarjargal.P 1, Altanchimeg.A 1, Odbileg.R 1 1-Institute of Veterinary Medicine, MULS, Mongolia
Immunology - Problem Drill 04: Structure and Functions of the Immune System
 Immunology - Problem Drill 04: Structure and Functions of the Immune System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which one of the following is non-encapsulated and less organized secondary lymphoid organ? Question
Immunology - Problem Drill 04: Structure and Functions of the Immune System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which one of the following is non-encapsulated and less organized secondary lymphoid organ? Question
AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY
 AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY 1. Hallmark lesions of infection with polytropic strains of mouse hepatitis virus include: A. Lymphocytic syncytia in mesenteric lymph nodes B.
AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY 1. Hallmark lesions of infection with polytropic strains of mouse hepatitis virus include: A. Lymphocytic syncytia in mesenteric lymph nodes B.
Inflammation Laboratory 1
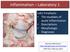 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL
 EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL INFECTION PRODUCED IN GUINEA PIGS' SAMUEL B. FORMAL, GUSTAVE J. DAMMIN, E. H. LABREC, AND H. SCHNEIDER Walter Reed Army Institute of Research,
EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL INFECTION PRODUCED IN GUINEA PIGS' SAMUEL B. FORMAL, GUSTAVE J. DAMMIN, E. H. LABREC, AND H. SCHNEIDER Walter Reed Army Institute of Research,
I.J.A.B.R, VOL. 4(2) 2014: ISSN
 I.J.A.B.R, VOL. 4(2) 2014: 190-195 ISSN 2250 3579 ROLE OF BCG VACCINE IN BACTERIAL DISSEMINATION, PATHOLOGY AND IMMUNIZATION AGAINST ENTEROPATHOGENIC ESCHERICHIA COLI AND THERE CHALLENGE INFECTION IN WHITE
I.J.A.B.R, VOL. 4(2) 2014: 190-195 ISSN 2250 3579 ROLE OF BCG VACCINE IN BACTERIAL DISSEMINATION, PATHOLOGY AND IMMUNIZATION AGAINST ENTEROPATHOGENIC ESCHERICHIA COLI AND THERE CHALLENGE INFECTION IN WHITE
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues
 The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Case Of The Month.(interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis): An Article From: Skin & Allergy News [HTML] [Digital] By Sherry Boschert READ ONLINE
![Case Of The Month.(interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis): An Article From: Skin & Allergy News [HTML] [Digital] By Sherry Boschert READ ONLINE Case Of The Month.(interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis): An Article From: Skin & Allergy News [HTML] [Digital] By Sherry Boschert READ ONLINE](/thumbs/81/83039326.jpg) Case Of The Month.(interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis): An Article From: Skin & Allergy News [HTML] [Digital] By Sherry Boschert READ ONLINE If you are looking for a ebook Case of the month.(interstitial
Case Of The Month.(interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis): An Article From: Skin & Allergy News [HTML] [Digital] By Sherry Boschert READ ONLINE If you are looking for a ebook Case of the month.(interstitial
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features.
 Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Histopathology Description:
 2013-2-1 CANINE HEART Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION : The Royal Veterinary college, Dept. of Pathology and Biology Signalment: 11-month-old male Border Collie dog (Canis familiaris)
2013-2-1 CANINE HEART Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION : The Royal Veterinary college, Dept. of Pathology and Biology Signalment: 11-month-old male Border Collie dog (Canis familiaris)
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome
 Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease
 Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Inflammatory pulp conditions DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY
 Inflammatory pulp conditions DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY Inflammation is the single most important disease process affecting the dental pulp. Pulpitis
Inflammatory pulp conditions DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY Inflammation is the single most important disease process affecting the dental pulp. Pulpitis
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review
 Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System
 Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
This is Learning Component 6 in Learning Module 1. We will show examples of features ( things ) including mineral deposits, urates, pigments, dust,
 This is Learning Component 6 in Learning Module 1. We will show examples of features ( things ) including mineral deposits, urates, pigments, dust, plant material, and amyloid. 1 Calcium salts are the
This is Learning Component 6 in Learning Module 1. We will show examples of features ( things ) including mineral deposits, urates, pigments, dust, plant material, and amyloid. 1 Calcium salts are the
(JPC ) Caprine lungs
 2011-7-2 (JPC 3133973) Caprine lungs Bat Otgontugs Bovine Pathology Contributor: Natoinal Institute Animal Health, Tsukuba, Japan Signalment: 5-year 3-month old female Japanese native breed goat, (Capra
2011-7-2 (JPC 3133973) Caprine lungs Bat Otgontugs Bovine Pathology Contributor: Natoinal Institute Animal Health, Tsukuba, Japan Signalment: 5-year 3-month old female Japanese native breed goat, (Capra
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY FOLLOWING RUSSELL'S VIPER (VIPERA RUSSELLI) BITE
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY FOLLOWING RUSSELL'S VIPER (VIPERA RUSSELLI) BITE Soe ~oe', May Mya win2, Than Than Htwe', Myint win', Swe Swe ~het* and Wynn Wynn Kyawl 'Department of Medical Research No. 5. Ziwaka
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY FOLLOWING RUSSELL'S VIPER (VIPERA RUSSELLI) BITE Soe ~oe', May Mya win2, Than Than Htwe', Myint win', Swe Swe ~het* and Wynn Wynn Kyawl 'Department of Medical Research No. 5. Ziwaka
09-Mar-15 PNEUMONIA RESPIRATORY SYSTEM L-3
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM L-3 Professor Department of Pathology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk Web: https://sites.geocities.ws/mtjaved PNEUMONIA The pulmonary inflammatory response
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM L-3 Professor Department of Pathology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk Web: https://sites.geocities.ws/mtjaved PNEUMONIA The pulmonary inflammatory response
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE INVLOLVEMENT OF INFECTIOUS DENTAL DISEASES INTO THE MAXILLARY SINUS INFLAMMATION SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. UNIV. DR. ELENA IONIŢĂ PhD: DR. MARINA OLIMPIA
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE INVLOLVEMENT OF INFECTIOUS DENTAL DISEASES INTO THE MAXILLARY SINUS INFLAMMATION SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. UNIV. DR. ELENA IONIŢĂ PhD: DR. MARINA OLIMPIA
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Firm Texture. (chronic) Cut surface: purulent exudate in bronchi Sequels: Abscesses,
 2008 Classification of Pneumonias in Domestic Animals There is no universal classification! Based on texture, distribution of lesions and type of exudate, pneumonias in domestic animals are currently classified
2008 Classification of Pneumonias in Domestic Animals There is no universal classification! Based on texture, distribution of lesions and type of exudate, pneumonias in domestic animals are currently classified
Histopathology: healing
 Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Influenza A virus infection predisposes hosts to secondary infection with different
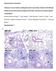 Supplementary information Influenza A virus infection predisposes hosts to secondary infection with different Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes with similar outcome but serotype-specific manifestation.
Supplementary information Influenza A virus infection predisposes hosts to secondary infection with different Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes with similar outcome but serotype-specific manifestation.
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART. I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine
 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine Acute myocardial infarction coagulative necrosis subendocardialy 2 hyperemic layer 3 normal myocard 4 epicard Acute myocardial
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine Acute myocardial infarction coagulative necrosis subendocardialy 2 hyperemic layer 3 normal myocard 4 epicard Acute myocardial
Chapter10 Immune system
 Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor
 Vet. Pathol. 12: 1-5 (1975) Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor C.H. LAMAR and D.C. VAN SICKLE School of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University,
Vet. Pathol. 12: 1-5 (1975) Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor C.H. LAMAR and D.C. VAN SICKLE School of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University,
CELLS & ORGANS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM
 17 CHAPTER - 3 CELLS & ORGANS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Carried within the blood and lymphoid organs are various white blood cells, or leukocytes, that participate in the immune response. Thus, make up cells of
17 CHAPTER - 3 CELLS & ORGANS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Carried within the blood and lymphoid organs are various white blood cells, or leukocytes, that participate in the immune response. Thus, make up cells of
Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome
 J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
Menigitidis. Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline
 Menigitidis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Review Normal Microanatomy Image Ref: www.histology-world.com
Menigitidis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Review Normal Microanatomy Image Ref: www.histology-world.com
HISTO-PHYSIOLOGY HISTO-PHYSIOLOGY HISTO-PHYSIOLOGY. 09-Mar-15. Dr. Muhammad Tariq Javed. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Lec-1
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Lec-1 Dr. Muhammad Tariq Javed Professor Department of Pathology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk Web: http://www.geocities.ws/mtjaved 1 2 Conducting
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Lec-1 Dr. Muhammad Tariq Javed Professor Department of Pathology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk Web: http://www.geocities.ws/mtjaved 1 2 Conducting
HISTOLOGICAL PARAMETERS
 HISTOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ADDITIONAL FILE FOR THE MANUSCRIPT: Peritoneal Negative Pressure Therapy Prevents Multiple Organ Injury in a Chronic Porcine Sepsis and Ischemia/Reperfusion model Brian D. Kubiak
HISTOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ADDITIONAL FILE FOR THE MANUSCRIPT: Peritoneal Negative Pressure Therapy Prevents Multiple Organ Injury in a Chronic Porcine Sepsis and Ischemia/Reperfusion model Brian D. Kubiak
[General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology
![[General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology [General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology](/thumbs/73/69585662.jpg) Introduction to Pathology Pathology: Literally translated, pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos, suffering). It involves the investigation of the causes of disease and the associated changes
Introduction to Pathology Pathology: Literally translated, pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos, suffering). It involves the investigation of the causes of disease and the associated changes
HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c
 Research Article HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c a* Ex-Professor & Head of Pharmacology (Pharmacy), presently Officer-In-Charge of Rinder
Research Article HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c a* Ex-Professor & Head of Pharmacology (Pharmacy), presently Officer-In-Charge of Rinder
Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I
 BIOL 4849 Medical Mycology Summer 2006 Histoplasmosis Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I u Most common endemic mycotic disease in the United States u Two different varieties (actually
BIOL 4849 Medical Mycology Summer 2006 Histoplasmosis Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I u Most common endemic mycotic disease in the United States u Two different varieties (actually
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d
 هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one
 Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
Fungi More or Less Obligately Associated with Humans. Requirements for Designating a Mycosis*
 P Fungi More or Less Obligately Associated with Humans a. a few dermatophytes (the anthropophilic species ) b. Malassezia furfur c. Candida albicans d. + Lacazia (Loboa) loboi*p e. + Pneumocystis jirovecii*p
P Fungi More or Less Obligately Associated with Humans a. a few dermatophytes (the anthropophilic species ) b. Malassezia furfur c. Candida albicans d. + Lacazia (Loboa) loboi*p e. + Pneumocystis jirovecii*p
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
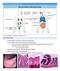 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology
 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue. nur
 8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
Genetics. Environment. You Are Only 10% Human. Pathogenesis of IBD. Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function IBD
 Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Bacterial, viral, protoozal and fungal infections of the CNS
 Bacterial, viral, protoozal and fungal infections of the CNS Prof. Isidro Ferrer, Institut Neuropatologia, Servei Anatomia Patològica, IDIBELL-Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge, Universitat de Barcelona,
Bacterial, viral, protoozal and fungal infections of the CNS Prof. Isidro Ferrer, Institut Neuropatologia, Servei Anatomia Patològica, IDIBELL-Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge, Universitat de Barcelona,
Respiratory Pathology. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response. Physiology Unit 3
 INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system
 phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system 2006-2007 1) recognizing the presence of an infection; 2) containing the infection and working to eliminate it; 3) regulating
phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system 2006-2007 1) recognizing the presence of an infection; 2) containing the infection and working to eliminate it; 3) regulating
