Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012 Vol. 8(4): Journal of Agricultural
|
|
|
- Monica Riley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012 Vol. 8(4): Journal of Agricultural Available Technology online , Vol. 8(4): ISSN The effect of the decreased expression of dicer-like proteins 2 and 4 on cyclic viral titer, and short interference RNA in Cucumber mosaic virus infected tobacco plants Sunpapao, A. 1,2*, Mochizuki, T 1. and Ohki T. S 1. 1 Graduate School of Life and Environmental Sciences, Osaka Prefecture University, 1-1, Gakuen-cho, Naka-ku, Sakai, Osaka , Japan, 2 Present address: Department of Pest Management, Faculty of Natural Resources, Prince of Songkla University, P.O. Box 6, Kor Hong, Hatyai, Songkla 90112, Thailand Sunpapao, A. Mochizuki, T. and Ohki T.S. (2012) The effect of the decreased expression of dicer-like proteins 2 and 4 on cyclic viral titer, and short interference RNA in Cucumber mosaic virus infected tobacco plants. Journal of Agricultural Technology 8(4): When infected with Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), infected tobacco plants developed cyclic patterns of mosaic and mottle symptoms interspersed with symptomless leaves along the stem of individual plants. To determine the virus-plant interaction, the CMV viral coat protein (CP) and short interference RNA (sirna) in CMV-infected tobacco were analyzed. A cyclical accumulation of CP was detected in young developing leaves of non-transgenic plants, but not in DCL2/4i transgenic plants. Northern blot analysis showed that CMV-specific sirna of young developing leaves varied based on leaf position, and was not related to symptom severity in fully expanded leaves. Key words: Coat protein, Cucumber mosaic virus, mosaic, RNA silencing Introduction Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) is a member of the genus Cucumovirus in the family Bromoviridae. CMV is widespread around the world and causes serious yield losses in important crops. This virus has a wide range of hosts (Palukaitis and Gracia-Arenal, 2003) and attacks a greater number of vegetable varieties, ornamentals, weeds, and other plants than do other viruses. Most characteristic among the symptoms induced by CMV are foliar mosaic, leaf deformation, and varying degrees of stunting (Palukaitis et al., 1992). Previously, the kinetics of infection by the wild-type CMV (Pepo) during leaf morphogenesis i.e. the infection of leaf primordia (LP) and the developing stages of non-transgenic tobacco plants were examined. The distribution of CMV in fully expanded symptomless leaves and leaves bearing the mosaic * Corresponding author: Anurag Sunpapao; anurag.su@psu.ac.th 1389
2 symptom during the late infection period was determined at the LP stage (Sunpapao et al., 2011). It was found that the 2b protein of CMV was required to establish a CMV infection of meristem tissues and to induce cyclic symptoms on the infected non-transgenic tobacco plants (Sunpapao et al., 2009). Plants have no immune system to battle viral infections as animals do, but they have a special defensive system. Virus infections in plant hosts activate an antiviral mechanism known as RNA silencing, which is based on sequencespecific degradation of RNA (Ding and Voinnet, 2007). This is an adaptive defense mechanism that is triggered by double stranded RNA (dsrna) corresponding to the invading viral RNA. Subsequently, the dsrna is cleaved into small fragments called short interference RNA (sirna) by RNase III-like enzymes such as dicer and dicer-like protein (DCL) (Voinnet, 2005). It is known that the Arabidopsis thaliana genome encodes four DCL enzymes, six RNA dependent RNA polymerases (RDRs) and other components of the silencing machinery in plants and the Nicotiana tabacum genome encodes four DCL and six RDR homologues. To counteract this host defense mechanism, many RNA and DNA plant viruses encode suppressor proteins (Roth et al., 2004) including CMV 2b protein (Brigneti et al., 1998). Although the only available strategy beyond classical plant breeding for the control of virus diseases in crops is the use of virus-tolerant varieties, study of the interaction between RNA silencing and viral distribution in the occurrence of symptoms is valuable. The present study compared viral titer and sirna amounts in young developing leaves and the pattern of symptoms in CMV-infected non-transgenic and DCL2/4i transgenic plants. Materials and methods Plant materials, virus and inoculation The tobacco plants used in this study were bred from plants provided by Dr. T. Meshi of the Division of Plant Sciences, National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, Tsukuba. The tobacco plants were down-regulated by using inverted-repeat constructs, which is an RNA silencing based mechanism. The RNA interference (RNAi) knock-down tobacco plants, double mutant DCL2/4i were then used as plant materials. The Pepo strain of CMV was originally obtained from Cucurbita pepo (Osaki et al., 1973). The largest leaves of the five-to seven-leaf-stage of transgenic and non-transgenic tobacco plants were mechanically inoculated with purified CMV (25 µg/ml). The inoculated leaf was defined as leaf position 0 (L0), while the leaves above the inoculated leaf were sequentially numbered. The inoculated plants were grown under 1390
3 Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012, Vol. 8(4): greenhouse conditions, and then symptoms in the fully expanded leaves were observed for a month. Western blot analysis Total protein was extracted from young developing leaf tissues samples with homogenate buffer (250 mm Tris-HCl ph 7.5, 2.5 mm EDTA, 0.1% ascorbic acid, 1mM phenylmethylsulphonylfluoride). The extracted protein samples were separated in 10% SDS-acrylamide separating gel and stacking gel and were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The procedures for detecting the immuno-method and signal were performed as described previously (Sunpapao et al., 2011). Northern blot analysis Total RNA was extracted from young developing leaves (1 to 2cm) by using Tripure Isolation Reagent (Roche Diagnostics, Tokyo, Japan) according to the manufacturer s instructions. For sirna detection, 20µg total RNA was dissolved in an equal volume of 100% formamide and loaded onto a 15% acrylamide gel containing 7 M urea. The low-molecular-mass RNAs were transferred onto a Hybond-NX membrane (GE Healthcare Biosciences) by electroblotting. Hybridization was performed using DIG-labelled, full length CMV RNAs complementary to the CMV negative-sense RNAs transcribed from Pepo CMV clones (Saitoh et al., 1999). The procedures for hybridization and the detection of signals were performed as described previously (Mochizuki et al., 2004). Results Cyclic symptom patterns of CMV-infected tobacco To analyze the pattern of mosaic symptoms, non-transgenic and DCL2/4i tobacco plants were inoculated with CMV and the symptoms were then observed 30 days post-inoculation. The results showed that all the plants developed cyclic mosaic patterns (Table. 1). 1391
4 Table 1. Pattern of symptoms in non-trnasgenic (Nt) and DCL2/4i transgenic tobacco plants infected with CMV Plants Leaf positions (L) Patterns L5 L6 L7 L8 L9 L10 L11 L12 L13 L14 Nt - - M M Mo S S S M M Cyclic DCL2/4i Mo Mo Mo S Mo M Mo M - - Cyclic M = mosaic, Mo = mottle, S = symptomless Cyclical accumulation of viral titer Because the expression of mosaic symptoms has been implicated in the distribution of the virus in young developing leaves, the study focused on the viral coat protein (CP) in such leaves, 1 to 2cm in length, at all leaf positions in the CMV-infected non-transgenic and DCL2/4i tobacco plants. The viral CP in young developing leaves was established by western blot analysis. In the nontransgenic plants, the cyclical accumulation of viral CP varied based on leaf position (Fig. 1). High levels of CP were detected at L7 and L8, reduced levels at L9-L11, restored high levels at L12 and L13 which decreased again at L14. No cyclical accumulation of CMV CP was detected in DCL2/4i. This result suggested that double down regulation of both DCL2 and DCL4 might break the cyclical accumulation of viral titer in DCL2/4i transgenic plants. Fig. 1. Accumulation of CMV CP in young developing leaves, 1 to 2cm in length in CMV infected tobacco plants. The numbers indicate leaf positions above the inoculated leaf (L0). The amounts of viral CP were analyzed by western blot analysis. CMV CP was detected. with an anti-cmv IgG antibody. Total proteins were stained with coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) to ensure equal loading. H: healthy plant. 1392
5 Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012, Vol. 8(4): Accumulation of CMV-specific sirna CMV-specific sirna can be used as a general indicator of RNA silencing against viral infection, therefore the amounts of sirna derived from CMV viral RNA were analyzed. After inoculation with CMV, three young developing leaves were sampled from different plants. The amounts of sirna in the leaf tissues were examined by northern blot analysis (Fig. 2). In the nontransgenic tobacco plants, sirna peaked at L7-L9, and L11-L13. In the DCL2/4i transgenic tobacco plants, sirna was detected from L5-L12 which peaked at L11 and L12. These results suggest that the amounts of sirna in young developing leaves are not related to the mosaic patterns in the expanded leaves of either non-transgenic or transgenic tobacco plants. Fig. 2. Northern blot analysis of CMV-specific sirna corresponding to RNA extracted from young developing leaves of CMV-inoculated tobacco plants, 10, 15, 20 and 25 days post-inoculation. Total RNA was extracted from three young developing leaves and 20µg total RNA was analyzed to detect sirna. sirna was detected based on full-length negative-sense CMV RNA. MB: methylene blue staining. Discussion Following CMV infection, some fully expanded tobacco leaves display mosaicism, whereas other leaves recover and are symptomless (Ohki et al., 1990), and this is known as cyclic symptom expression. Previous studies conducted by the present researchers showed that viral CP and viral RNA in young developing leaves shifted with leaf position and was related to symptom severity on the fully expanded leaves in non-transgenic tobacco plants 1393
6 (Sunpapao et al., 2011). In this study the viral titer and the amounts of sirna were compared between non-transgenic and double down-regulated transgenic (DCL2/4i) plants. The symptom pattern of both the non-transgenic and DCL2/4i transgenic plants was not significantly changed (Table. 1). Although there was not a complete loss-of function, the lower expression of both genes might have been sufficient for cyclic symptom expression. The double down regulation of both DCL2 and DCL4 broke the cyclical accumulation of viral CP (Fig.1). A previous study (unpublished data) showed that the low expression of DCL2, DCL4 and RDR1 does not affect viral titer, and there was no difference between non-transgenic and transgenic plants. To establish RNA silencing against CMV infection, CMV-specific sirna in CMV-infected tobacco plants was detected as a general indicator of RNA silencing. Thus viral CP in young developing leaves seemed to be mostly paralleled by the symptom severity in expanded leaves, while sirna was not. Further, CMV has been to known to encode RNA silencing suppressor protein (2b protein) which interferes with several steps in the antiviral RNA silencing pathway resulting in varying amounts of sirna in young developing leaves. CMV 2b protein might disrupt the amount of sirna in the RNA silencing mechanism. However, if there is no completed down regulation of DCL2 and DCL4, the silencing components of other genes such as DCL1 and DCL3 may work hierarchically causing cyclic mosaic patterns in the CMV-infected plant host. In this study it was shown that a reduction of both DCL2 and DCL4 mrna influenced the cyclical accumulation of CMV titer in DCL2/4i transgenic tobacco plants, but had no impact on the amount of sirna and the cyclic mosaic patterns. Acknowledgement We are grateful to Dr. T. Meshi of Division of Plant Sciences, National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, Tsukuba, for the kindly providing RNA-down regulated tobacco plants. References Brigneti, G., Voinnet, O. Li, W.-X. Ji, L.H., Ding S.W. and Baulcombe D.C. (1998). Viral pathogenicity determinants are suppressors of transgene silencing in Nicotiana benthamiana. EMBO J 17: Ding, S.W. and Voinnet, O. (2007). Antiviral immunity directed by small RNAs., Cell 130: Mochizuki, T. and Ohki S.T. (2004). Shoot meristem tissue of tobacco inoculated with Cucumber mosaic virus is infected with the virus and subsequently recovers from the infection by RNA silencing. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 70:
7 Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012, Vol. 8(4): Ohki, S.T., Takami Y. and Inoue T. (1990). Accumulation of double-stranded RNAs 3 and 4 in the symptomless leaves and green areas of mosaic-affected leaves of tobacco plants infected with cucumber mosaic virus. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 56: Osaki, T., Shobara K. and Takahashi, T. (1973). A strain of cucumber mosaic virus isolated from Cucurbita pepo. Kansai Pl. Prot. 15: (in Japanese). Palukaitis, P. and Gracia-Arenal, F. (2003). Cucumovirus, Adv. Virus Res. 62: Palukaitis, P., Roossinck, M.J., Dietzgen R.G. and Francki, R.I.B. (1992). Cucumber mosaic virus. Adv. Virus Res. 41: Roth, B.M., Pruss G.J. and Vance, V.B. (2004). Plant viral suppressors of RNA silencing. Virus Res. 102: Saitoh, H., Fujiwara, M., Ohki S.T. and Osaki T. (1999). The coat protein gene is essential for the systemic infection of cucumber mosaic virus in Cucumis figarei at high temperature. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 65: Sunpapao, A., Mochizuki, T. and Ohki, S.T. (2011). Relationship between viral distribution in the leaf primordial/young developing leaves and symptom severity in the fully expanded leaves of tobacco plants infected with Cucumber mosaic virus. Australasian Plant Pathol. 40: Sunpapao, A., Nakai, T., Mochizuki T. and Ohki, S.T. (2009). The 2b protein of Cucumber mosaic virus is essential for viral infection of the shoot apical meristem and for efficient invasion of leaf primordia in infected tobacco plants. J. Gen. Virol. 90: Voinnet, O. (2005). Induction and suppression of RNA silencing; insight from viral detections. Nat. Rev. Gene. 6: (Published in July 2012) 1395
Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 36 (1), 21-26, Jan. - Feb Original Article. Anurag Sunpapao*, Tomofumi Mochizuki, and Satoshi T.
 Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 36 (1), 21-26, Jan. - Feb. 2014 http://www.sjst.psu.ac.th Original Article Effect of dicer-like proteins2 and 4 and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase1 as RNA silencing components
Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 36 (1), 21-26, Jan. - Feb. 2014 http://www.sjst.psu.ac.th Original Article Effect of dicer-like proteins2 and 4 and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase1 as RNA silencing components
Anurag Sunpapao, Takashi Nakai, Fang Dong, Tomofumi Mochizuki and Satoshi T. Ohki INTRODUCTION
 Journal of General Virology (2009), 90, 3015 3021 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.013219-0 The 2b protein of cucumber mosaic virus is essential for viral infection of the shoot apical meristem and for efficient invasion
Journal of General Virology (2009), 90, 3015 3021 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.013219-0 The 2b protein of cucumber mosaic virus is essential for viral infection of the shoot apical meristem and for efficient invasion
MINIREVIEW. Activation and Suppression of RNA Silencing by Plant Viruses
 Virology 281, 1 5 (2001) doi:10.1006/viro.2000.0812, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on MINIREVIEW Activation and Suppression of RNA Silencing by Plant Viruses James C. Carrington, 1 Kristin
Virology 281, 1 5 (2001) doi:10.1006/viro.2000.0812, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on MINIREVIEW Activation and Suppression of RNA Silencing by Plant Viruses James C. Carrington, 1 Kristin
Leaves turn yellow: small RNAs from viruses silence plant genes such as those involved in photosynthesis. Vitantonio Pantaleo IPSP-CNR
 Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche Di.S.Ba Conferenza del Dipartimento di Scienze Bio-agroalimentari del CNR Accademia dei Georgofili, Firenze 24-25 Ottobre 2016 Accademia dei Georgofili Leaves turn yellow:
Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche Di.S.Ba Conferenza del Dipartimento di Scienze Bio-agroalimentari del CNR Accademia dei Georgofili, Firenze 24-25 Ottobre 2016 Accademia dei Georgofili Leaves turn yellow:
Phenomena first observed in petunia
 Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Plasmid vector for cloning infectious cdnas from plant RNA viruses: high infectivity of cdna clones of tomato aspermy cucumovirus
 Journal of General Virology (1997), 78, 1181 1185. Printed in Great Britain...... SHORT COMMUNICATION Plasmid vector for cloning infectious cdnas from plant RNA viruses: high infectivity of cdna clones
Journal of General Virology (1997), 78, 1181 1185. Printed in Great Britain...... SHORT COMMUNICATION Plasmid vector for cloning infectious cdnas from plant RNA viruses: high infectivity of cdna clones
Pseudorecombination between Two Distinct Strains of Cucumber mosaic virus Results in Enhancement of Symptom Severity
 Plant Pathol. J. 30(3) : 316-322 (2014) http://dx.doi.org/10.5423/ppj.nt.04.2014.0031 pissn 1598-2254 eissn 2093-9280 Note Open Access The Plant Pathology Journal The Korean Society of Plant Pathology
Plant Pathol. J. 30(3) : 316-322 (2014) http://dx.doi.org/10.5423/ppj.nt.04.2014.0031 pissn 1598-2254 eissn 2093-9280 Note Open Access The Plant Pathology Journal The Korean Society of Plant Pathology
Virus-host interactions
 Virus-host interactions - Strategies viruses use to replicate their genomes in susceptible host cells replication - Strategies viruses use to move their genomes throughout susceptible host plants cell-to-cell
Virus-host interactions - Strategies viruses use to replicate their genomes in susceptible host cells replication - Strategies viruses use to move their genomes throughout susceptible host plants cell-to-cell
Satellite RNA reduces expression of the 2b suppressor protein resulting in the attenuation of symptoms caused by Cucumber mosaic virus infection
 DOI: 10.1111/J.1364-3703.2010.00696.X Satellite RNA reduces expression of the 2b suppressor protein resulting in the attenuation of symptoms caused by Cucumber mosaic virus infection WEI-NA HOU 1,2,, CHENG-GUO
DOI: 10.1111/J.1364-3703.2010.00696.X Satellite RNA reduces expression of the 2b suppressor protein resulting in the attenuation of symptoms caused by Cucumber mosaic virus infection WEI-NA HOU 1,2,, CHENG-GUO
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Attenuated Isolates of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Produced by Satellite RNA and Cross Protection between Attenuated Isolates and Virulent Ones
 Attenuated Isolates of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Produced by Satellite RNA and Cross Protection between Attenuated Isolates and Virulent Ones Kouji YOSHIDA*, Tadanori GOTO* and Norio IIZUKA* Key Words: attenuated
Attenuated Isolates of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Produced by Satellite RNA and Cross Protection between Attenuated Isolates and Virulent Ones Kouji YOSHIDA*, Tadanori GOTO* and Norio IIZUKA* Key Words: attenuated
Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor RAV2 to Block RNA Silencing
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Biology) Department of Biology 1-15-2010 Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Biology) Department of Biology 1-15-2010 Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor
Biological Character of Cucumber Mozaic Virus (CMV) Isolates from Bali
 Biological Character of Cucumber Mozaic Virus (CMV) Isolates from Bali Ni Putu Pandawani a, Cokorda Javandira b,farida Hanum c.* a,b,c Universitas Mahasaraswati Denpasar, Jalan Kamboja 11A Denpasar, Post
Biological Character of Cucumber Mozaic Virus (CMV) Isolates from Bali Ni Putu Pandawani a, Cokorda Javandira b,farida Hanum c.* a,b,c Universitas Mahasaraswati Denpasar, Jalan Kamboja 11A Denpasar, Post
Evolutionary History of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Deduced by Phylogenetic Analyses
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2002, p. 3382 3387 Vol. 76, No. 7 0022-538X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.76.7.3382 3387.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evolutionary
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2002, p. 3382 3387 Vol. 76, No. 7 0022-538X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.76.7.3382 3387.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evolutionary
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Identification of new resistance sources for Cucumber mosaic virus new isolate-p1 (CMV-P1) in Capsicum spp.
 Absorbance at 405nm Absorbance at 405nm Absorbance at 405nm College of Agriculture and Life Sciences Identification of new resistance sources for Cucumber mosaic virus new isolate-p1 (CMV-P1) in Capsicum
Absorbance at 405nm Absorbance at 405nm Absorbance at 405nm College of Agriculture and Life Sciences Identification of new resistance sources for Cucumber mosaic virus new isolate-p1 (CMV-P1) in Capsicum
Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor RAV2 to Block RNA Silencing
 Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor RAV2 to Block RNA Silencing Matthew W. Endres 1, Brian D. Gregory 2,3, Zhihuan Gao 1, Amy Wahba Foreman
Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor RAV2 to Block RNA Silencing Matthew W. Endres 1, Brian D. Gregory 2,3, Zhihuan Gao 1, Amy Wahba Foreman
RNA-Based Plant Protection
 RNA-Based Plant Protection Host-Induced Gene Silencing to Engineer Resistance to FHB Karl-Heinz Kogel Phytopathologie, Gießen RNA-Based Plant Protection Is there an agronomic potential for application?
RNA-Based Plant Protection Host-Induced Gene Silencing to Engineer Resistance to FHB Karl-Heinz Kogel Phytopathologie, Gießen RNA-Based Plant Protection Is there an agronomic potential for application?
ACCEPTED. Juan Jovel, Melanie Walker, and Hélène Sanfaçon*
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on August 00 J. Virol. doi:0./jvi.0-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved. 0 0 0 Recovery
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on August 00 J. Virol. doi:0./jvi.0-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved. 0 0 0 Recovery
Biological Properties of Pseudorecombinant and Recombinant Strains Created with Cucumber Mosaic Virus and Tomato Aspermy Virus
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 1997, p. 3597 3602 Vol. 71, No. 5 0022-538X/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Biological Properties of Pseudorecombinant and Recombinant Strains Created
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 1997, p. 3597 3602 Vol. 71, No. 5 0022-538X/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Biological Properties of Pseudorecombinant and Recombinant Strains Created
RNAi Restricts Virus Infections
 RNAi Restricts Virus Infections RNA silencing is a new immunity mechanism that protects fruit flies, mosquitoes, and nematodes as well as plants against viral infections Shou-Wei Ding Shou-Wei Ding is
RNAi Restricts Virus Infections RNA silencing is a new immunity mechanism that protects fruit flies, mosquitoes, and nematodes as well as plants against viral infections Shou-Wei Ding Shou-Wei Ding is
Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 16207 Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 16207 Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases
 Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 67-73) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 113-117), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 119), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 75-77).
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 67-73) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 113-117), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 119), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 75-77).
sirna count per 50 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand Repeat length (bp) per 50 kb repeats in the chromosome
 Qi et al. 26-3-2564C Qi et al., Figure S1 sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the complementary strand Repeat length (bp) per 5 kb repeats
Qi et al. 26-3-2564C Qi et al., Figure S1 sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the complementary strand Repeat length (bp) per 5 kb repeats
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
VirusDetect pipeline - virus detection with small RNA sequencing
 VirusDetect pipeline - virus detection with small RNA sequencing CSC webinar 16.1.2018 Eija Korpelainen, Kimmo Mattila, Maria Lehtivaara Big thanks to Jan Kreuze and Jari Valkonen! Outline Small interfering
VirusDetect pipeline - virus detection with small RNA sequencing CSC webinar 16.1.2018 Eija Korpelainen, Kimmo Mattila, Maria Lehtivaara Big thanks to Jan Kreuze and Jari Valkonen! Outline Small interfering
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases
 Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 69-75) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 115-119), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 121), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 77-79).
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 69-75) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 115-119), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 121), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 77-79).
PLANT VIRUS SATELLITE AND DEFECTIVE INTERFERING RNAS: New Paradigms for a New Century
 Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004. 42:415 37 doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.42.040803.140402 Copyright c 2004 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved PLANT VIRUS SATELLITE AND DEFECTIVE INTERFERING RNAS: New Paradigms
Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004. 42:415 37 doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.42.040803.140402 Copyright c 2004 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved PLANT VIRUS SATELLITE AND DEFECTIVE INTERFERING RNAS: New Paradigms
Induced biochemical changes in the CMV infected cucurbit plants
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2012, 3 (2):863-870 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Induced biochemical
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2012, 3 (2):863-870 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Induced biochemical
reads observed in trnas from the analysis of RNAs carrying a 5 -OH ends isolated from cells induced to express
 Supplementary Figure 1. VapC-mt4 cleaves trna Ala2 in E. coli. Histograms representing the fold change in reads observed in trnas from the analysis of RNAs carrying a 5 -OH ends isolated from cells induced
Supplementary Figure 1. VapC-mt4 cleaves trna Ala2 in E. coli. Histograms representing the fold change in reads observed in trnas from the analysis of RNAs carrying a 5 -OH ends isolated from cells induced
Turnip crinkle virus coat protein mediates suppression of RNA silencing in Nicotiana benthamiana
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com R Virology 306 (2003) 33 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/yviro Turnip crinkle virus coat protein mediates suppression of RNA silencing in Nicotiana benthamiana Carole
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com R Virology 306 (2003) 33 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/yviro Turnip crinkle virus coat protein mediates suppression of RNA silencing in Nicotiana benthamiana Carole
ESTABLISHMENT OF SOME VIRUSES POLYPHAGUES ON ECONOMICALLY IMPORTANT ESSENTIAL OIL BEARING AND MEDICINAL PLANTS IN BULGARIA
 ESTABLISHMENT OF SOME VIRUSES POLYPHAGUES ON ECONOMICALLY IMPORTANT ESSENTIAL OIL BEARING AND MEDICINAL PLANTS IN BULGARIA B. Dikova Plant Protection Institute, 2230, Kostinbrod, Bulgaria Correspondence
ESTABLISHMENT OF SOME VIRUSES POLYPHAGUES ON ECONOMICALLY IMPORTANT ESSENTIAL OIL BEARING AND MEDICINAL PLANTS IN BULGARIA B. Dikova Plant Protection Institute, 2230, Kostinbrod, Bulgaria Correspondence
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life
 Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Human Genome: Mapping, Sequencing Techniques, Diseases
 Human Genome: Mapping, Sequencing Techniques, Diseases Lecture 4 BINF 7580 Fall 2005 1 Let us review what we talked about at the previous lecture. Please,... 2 The central dogma states that the transfer
Human Genome: Mapping, Sequencing Techniques, Diseases Lecture 4 BINF 7580 Fall 2005 1 Let us review what we talked about at the previous lecture. Please,... 2 The central dogma states that the transfer
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Virology Papers Virology, Nebraska Center for 2002 Efficient Infection of Nicotiana benthamiana by Tomato bushy stunt virus
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Virology Papers Virology, Nebraska Center for 2002 Efficient Infection of Nicotiana benthamiana by Tomato bushy stunt virus
The Inactivation of Virus in Cultured Shoot Tips of Nicotiana rustica L.
 J. gen. ViroL (1969), 5, 237-24I With I plate Printed in Great Britain 237 The Inactivation of Virus in Cultured Shoot Tips of Nicotiana rustica L. By D. G. A. WALKEY, JANET FITZPATRICK JUDITH M. G. WOOLFITT
J. gen. ViroL (1969), 5, 237-24I With I plate Printed in Great Britain 237 The Inactivation of Virus in Cultured Shoot Tips of Nicotiana rustica L. By D. G. A. WALKEY, JANET FITZPATRICK JUDITH M. G. WOOLFITT
Viral Counter Defense X Antiviral Immunity in Plants: Mechanisms for Survival
 Chapter 11 Viral Counter Defense X Antiviral Immunity in Plants: Mechanisms for Survival Alessandra Tenório Costa, Juliana Pereira Bravo, Rodrigo Kazuo Makiyama, Alessandra Vasconcellos Nunes and Ivan
Chapter 11 Viral Counter Defense X Antiviral Immunity in Plants: Mechanisms for Survival Alessandra Tenório Costa, Juliana Pereira Bravo, Rodrigo Kazuo Makiyama, Alessandra Vasconcellos Nunes and Ivan
Project Title: Development of a method for conducting tests for resistance to tombusviruses and lettuce dieback in the greenhouse.
 I. Abstract. Project Title: Development of a method for conducting tests for resistance to tombusviruses and lettuce dieback in the greenhouse. Project Investigators: Drs. William M. Wintermantel and Ivan
I. Abstract. Project Title: Development of a method for conducting tests for resistance to tombusviruses and lettuce dieback in the greenhouse. Project Investigators: Drs. William M. Wintermantel and Ivan
Viral suppressors of RNA silencing
 Review Viral suppressors of RNA silencing József Burgyán 1,2 and Zoltán Havelda 2 1 Istituto di Virologia Vegetale, CNR, Strada Delle Cacce 73, Torino, Italy 2 Agricultural Biotechnology Center, Szent-Gyorgyi
Review Viral suppressors of RNA silencing József Burgyán 1,2 and Zoltán Havelda 2 1 Istituto di Virologia Vegetale, CNR, Strada Delle Cacce 73, Torino, Italy 2 Agricultural Biotechnology Center, Szent-Gyorgyi
Viruses 101., and concluded that living organisms do not crystallize. In other words,.
 Viruses 101 In 1897, Dutch scientist called tiny particles in the liquid extracted from a plant disease, which is the Latin word for. In 1935, American biochemist isolated crystals of, and concluded that
Viruses 101 In 1897, Dutch scientist called tiny particles in the liquid extracted from a plant disease, which is the Latin word for. In 1935, American biochemist isolated crystals of, and concluded that
Genetic Analysis of Cucumber Mosaic, Peanut Stunt and Chrysanthemum Mild Mottle Viruses
 Ann. Phytopath. Soc. Japan 46: 159-168 (1980) Genetic Analysis of Cucumber Mosaic, Peanut Stunt and Chrysanthemum Mild Mottle Viruses Kaoru HANADA* and Hiroshi TOCHIHARA* Abstract Four strains of cucumber
Ann. Phytopath. Soc. Japan 46: 159-168 (1980) Genetic Analysis of Cucumber Mosaic, Peanut Stunt and Chrysanthemum Mild Mottle Viruses Kaoru HANADA* and Hiroshi TOCHIHARA* Abstract Four strains of cucumber
Characterization of Cucumber mosaic virus infecting Indian long pepper (Piper longum L.) and betel vine (Piper betle L.) in India
 n Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 5, January 2006, pp 89-93 Characterization of Cucumber mosaic virus infecting n long pepper (Piper longum L.) and betel vine (Piper betle L.) in P S Hareesh, R Madhubala
n Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 5, January 2006, pp 89-93 Characterization of Cucumber mosaic virus infecting n long pepper (Piper longum L.) and betel vine (Piper betle L.) in P S Hareesh, R Madhubala
Tomato Cell Death Mediated By Complementary Plant Viral Satellite RNA Sequences
 MPMI Vol. 11, No. 12, 1998, pp. 1214 1222. Publication no. M-1998-0928-01R. 1998 The American Phytopathological Society Tomato Cell Death Mediated By Complementary Plant Viral Satellite RNA Sequences Michael
MPMI Vol. 11, No. 12, 1998, pp. 1214 1222. Publication no. M-1998-0928-01R. 1998 The American Phytopathological Society Tomato Cell Death Mediated By Complementary Plant Viral Satellite RNA Sequences Michael
MPMI Vol. 18, No. 5, 2005, pp DOI: / MPMI The American Phytopathological Society
 MPMI Vol. 18, No. 5, 2005, pp. 428 434. DOI: 10.1094 / MPMI -18-0428 2005 The American Phytopathological Society Salicylic Acid-Induced Resistance to Cucumber mosaic virus in Squash and Arabidopsis thaliana:
MPMI Vol. 18, No. 5, 2005, pp. 428 434. DOI: 10.1094 / MPMI -18-0428 2005 The American Phytopathological Society Salicylic Acid-Induced Resistance to Cucumber mosaic virus in Squash and Arabidopsis thaliana:
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH CONSIDERATIONS FOR WORK WITH VIRAL VECTORS
 OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH CONSIDERATIONS FOR WORK WITH VIRAL VECTORS GARY R. FUJIMOTO, M.D. PALO ALTO MEDICAL FOUNDATION ADJUNCT ASSOCIATE CLINICAL PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES AND GEOGRAPHIC
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH CONSIDERATIONS FOR WORK WITH VIRAL VECTORS GARY R. FUJIMOTO, M.D. PALO ALTO MEDICAL FOUNDATION ADJUNCT ASSOCIATE CLINICAL PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES AND GEOGRAPHIC
Isolation of an Arabidopsis thaliana Mutant in Which the Multiplication of both Cucumber Mosaic Virus and Turnip Crinkle Virus Is Affected
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 1998, p. 8731 8737 Vol. 72, No. 11 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Isolation of an Arabidopsis thaliana Mutant in
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 1998, p. 8731 8737 Vol. 72, No. 11 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Isolation of an Arabidopsis thaliana Mutant in
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer. Application Note
 Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Identifying mirnas in RNA viruses
 1 / 13 Identifying mirnas in RNA viruses Kevin Lamkiewicz Friedrich Schiller Universität Jena 16.02.2017 32nd TBI Winterseminar Bled 2 / 13 mirnas and their function U C A C A G G U C A A G C G U U G G
1 / 13 Identifying mirnas in RNA viruses Kevin Lamkiewicz Friedrich Schiller Universität Jena 16.02.2017 32nd TBI Winterseminar Bled 2 / 13 mirnas and their function U C A C A G G U C A A G C G U U G G
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
VIRUS VIROID PRION. Ms.Tanyaratana Dumkua Biology Department, Mahidolwittayanusorn School
 VIRUS VIROID PRION Ms.Tanyaratana Dumkua Biology Department, Mahidolwittayanusorn School What is virus? Living? Need food? Reproduction? Cell? Cytoplasm? Cell membrane? Metabolism? Size? Component? Adenovirus
VIRUS VIROID PRION Ms.Tanyaratana Dumkua Biology Department, Mahidolwittayanusorn School What is virus? Living? Need food? Reproduction? Cell? Cytoplasm? Cell membrane? Metabolism? Size? Component? Adenovirus
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
A Viral Movement Protein Prevents Spread of the Gene Silencing Signal in Nicotiana benthamiana
 Cell, Vol. 103, 157 167, September 29, 2000, Copyright 2000 by Cell Press A Viral Movement Protein Prevents Spread of the Gene Silencing Signal in Nicotiana benthamiana Olivier Voinnet, Carsten Lederer,
Cell, Vol. 103, 157 167, September 29, 2000, Copyright 2000 by Cell Press A Viral Movement Protein Prevents Spread of the Gene Silencing Signal in Nicotiana benthamiana Olivier Voinnet, Carsten Lederer,
Small RNAs and Cross-Kingdom RNAi in Plant-Microbial Interaction Hailing Jin
 Small RNAs and Cross-Kingdom RNAi in Plant-Microbial Interaction Hailing Jin Department of Plant Pathology & Microbiology Institute for Integrative Genome Biology micrornas (mirnas) Small RNAs PolII PolIV
Small RNAs and Cross-Kingdom RNAi in Plant-Microbial Interaction Hailing Jin Department of Plant Pathology & Microbiology Institute for Integrative Genome Biology micrornas (mirnas) Small RNAs PolII PolIV
Emergence of a resistance breaking strain of Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) in California
 Emergence of a resistance breaking strain of Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) in California Maria R. Rojas Department of Plant Pathology University of California Davis A diversity of viruses affect processing
Emergence of a resistance breaking strain of Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) in California Maria R. Rojas Department of Plant Pathology University of California Davis A diversity of viruses affect processing
Viral Genetics. BIT 220 Chapter 16
 Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
Replication of Recombinant Flock House Virus RNA Encapsidated by Turnip Yellow Mosaic Virus Coat Proteins in Nicotiana benthamiana
 Journal of Bacteriology and Virology 2017. Vol. 47, No. 2 p.87 95 http://dx.doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2017.47.2.87 Original Article Replication of Recombinant Flock House Virus RNA Encapsidated by Turnip Yellow
Journal of Bacteriology and Virology 2017. Vol. 47, No. 2 p.87 95 http://dx.doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2017.47.2.87 Original Article Replication of Recombinant Flock House Virus RNA Encapsidated by Turnip Yellow
Complete Nucleotide Sequence of RNA1 of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Y Strain and Evolutionary Relationships among Genome RNAs of the Virus Strains
 Complete Nucleotide Sequence of RNA1 of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Y Strain and Evolutionary Relationships among Genome RNAs of the Virus Strains Jiro KATAOKA*, Chikara MASUTA* and Yoichi TAKANAMI* Abstract
Complete Nucleotide Sequence of RNA1 of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Y Strain and Evolutionary Relationships among Genome RNAs of the Virus Strains Jiro KATAOKA*, Chikara MASUTA* and Yoichi TAKANAMI* Abstract
Analysis of Genetic Bottlenecks during Horizontal Transmission of Cucumber Mosaic Virus
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 2006, p. 8345 8350 Vol. 80, No. 17 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00568-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Analysis of Genetic
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 2006, p. 8345 8350 Vol. 80, No. 17 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00568-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Analysis of Genetic
Host-Specific Cell-to-Cell and Long-Distance Movements of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Are Facilitated by the Movement Protein of Groundnut Rosette Virus
 Virology 260, 98 108 (1999) Article ID viro.1999.9806, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Host-Specific Cell-to-Cell and Long-Distance Movements of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Are Facilitated
Virology 260, 98 108 (1999) Article ID viro.1999.9806, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Host-Specific Cell-to-Cell and Long-Distance Movements of Cucumber Mosaic Virus Are Facilitated
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Chapter 18. Viral Genetics. AP Biology
 Chapter 18. Viral Genetics 2003-2004 1 A sense of size Comparing eukaryote bacterium virus 2 What is a virus? Is it alive? DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat Viruses are not cells Extremely tiny electron
Chapter 18. Viral Genetics 2003-2004 1 A sense of size Comparing eukaryote bacterium virus 2 What is a virus? Is it alive? DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat Viruses are not cells Extremely tiny electron
Supplemental Figure 1. Small RNA size distribution from different soybean tissues.
 Supplemental Figure 1. Small RNA size distribution from different soybean tissues. The size of small RNAs was plotted versus frequency (percentage) among total sequences (A, C, E and G) or distinct sequences
Supplemental Figure 1. Small RNA size distribution from different soybean tissues. The size of small RNAs was plotted versus frequency (percentage) among total sequences (A, C, E and G) or distinct sequences
19 Viruses BIOLOGY. Outline. Structural Features and Characteristics. The Good the Bad and the Ugly. Structural Features and Characteristics
 9 Viruses CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV Lecture Presentation
9 Viruses CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV Lecture Presentation
PL PA 601 Plant Defenses and Viral Counterstrategies 30 March & 1 April, 2004 S. Lazarowitz
 PL PA 601 Plant Defenses and Viral Counterstrategies 30 March & 1 April, 2004 S. Lazarowitz A. Virus Definitions and Basic Principles (Lazarowitz 2001). 1. Unique properties of viruses a. Obligate intracellular
PL PA 601 Plant Defenses and Viral Counterstrategies 30 March & 1 April, 2004 S. Lazarowitz A. Virus Definitions and Basic Principles (Lazarowitz 2001). 1. Unique properties of viruses a. Obligate intracellular
REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION-POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (RT- PCR) FOR DIRECT DETECTION OF CUCUMBER MOSAIC VIRUS (CMV) IN GLADIOLUS
 Vol. 44, No. 1, January 1998 BIOCHEMISTRY and MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges 89-95 REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION-POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (RT- PCR) FOR DIRECT DETECTION OF CUCUMBER MOSAIC VIRUS (CMV) IN
Vol. 44, No. 1, January 1998 BIOCHEMISTRY and MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges 89-95 REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION-POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (RT- PCR) FOR DIRECT DETECTION OF CUCUMBER MOSAIC VIRUS (CMV) IN
Application of Real Time PCR for Detection And Identification of Soybean Pests in Michigan
 Application of Real Time PCR for Detection And Identification of Soybean Pests in Michigan Project Number: Team Leader: GR03-004 Patrick Hart, Michigan State University Department of Plant Pathology Objectives
Application of Real Time PCR for Detection And Identification of Soybean Pests in Michigan Project Number: Team Leader: GR03-004 Patrick Hart, Michigan State University Department of Plant Pathology Objectives
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Lecture 2: Virology. I. Background
 Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Project Title: Evaluating the Distribution and Potential Impacts of Soybean Vein Necrosis Virus in Delaware
 Delaware Soybean Board Report for Kleczewski, 2014 Project Title: Evaluating the Distribution and Potential Impacts of Soybean Vein Necrosis Virus in Delaware Background and Objectives: Soybeans are susceptible
Delaware Soybean Board Report for Kleczewski, 2014 Project Title: Evaluating the Distribution and Potential Impacts of Soybean Vein Necrosis Virus in Delaware Background and Objectives: Soybeans are susceptible
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Reverse Genetics of RNA Viruses
 Reverse Genetics of RNA Viruses Reverse Genetics (RG) he creation of a virus with a fulllength copy of the viral genome he most powerful tool in modern virology RG of RNA viruses Generation or recovery
Reverse Genetics of RNA Viruses Reverse Genetics (RG) he creation of a virus with a fulllength copy of the viral genome he most powerful tool in modern virology RG of RNA viruses Generation or recovery
Plant Vira1 Synergism: The Potyviral Genome Encodes a Broad-Range Pathogenicity Enhancer That Transactivates Replication of Heterologous Viruses
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 9, 859-868, June 1997 O 1997 American Society of Plant Physiologists Plant Vira1 Synergism: The Potyviral Genome Encodes a Broad-Range Pathogenicity Enhancer That Transactivates Replication
The Plant Cell, Vol. 9, 859-868, June 1997 O 1997 American Society of Plant Physiologists Plant Vira1 Synergism: The Potyviral Genome Encodes a Broad-Range Pathogenicity Enhancer That Transactivates Replication
New Insights in Freesia Leaf Necrosis Disease
 New Insights in Freesia Leaf Necrosis Disease E.T.M. Meekes 1 and M. Verbeek 2 1 Naktuinbouw, P.O. Box 40, 2370 AA Roelofarendsveen, The Netherlands 2 Plant Research International, P.O. Box 69, 6700 AB
New Insights in Freesia Leaf Necrosis Disease E.T.M. Meekes 1 and M. Verbeek 2 1 Naktuinbouw, P.O. Box 40, 2370 AA Roelofarendsveen, The Netherlands 2 Plant Research International, P.O. Box 69, 6700 AB
Do First: Answer in your DFAD
 Do First: Answer in your DFAD Answer each question with a short answer. Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card 1. What body system does HIV attack? 2. What cells does HIV attack? 3. Is HIV a virus or
Do First: Answer in your DFAD Answer each question with a short answer. Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card 1. What body system does HIV attack? 2. What cells does HIV attack? 3. Is HIV a virus or
Certificate of Analysis
 Certificate of Analysis Catalog No. Amount Lot Number 631987 10 μg Specified on product label. Product Information plvx-ef1α-ires-mcherry is a bicistronic lentiviral expression vector that can be used
Certificate of Analysis Catalog No. Amount Lot Number 631987 10 μg Specified on product label. Product Information plvx-ef1α-ires-mcherry is a bicistronic lentiviral expression vector that can be used
In Situ Localization and Tissue Distribution of the Replication-Associated Proteins of Cucumber Mosaic Virus in Tobacco and Cucumber
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2002, p. 10654 10664 Vol. 76, No. 21 0022-538X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.76.21.10654 10664.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. In Situ
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2002, p. 10654 10664 Vol. 76, No. 21 0022-538X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.76.21.10654 10664.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. In Situ
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections
 Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections Zohreh Sharifi,ph.D Blood Transfusion Research Center, High Institute for Research and Education in Transfusion Medicine Hepatitis B-laboratory diagnosis Detection
Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections Zohreh Sharifi,ph.D Blood Transfusion Research Center, High Institute for Research and Education in Transfusion Medicine Hepatitis B-laboratory diagnosis Detection
Cell-to-Cell, but Not Long-Distance, Spread of RNA Silencing That Is Induced in Individual Epidermal Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 2004, p. 3149 3154 Vol. 78, No. 6 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.6.3149 3154.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cell-to-Cell,
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 2004, p. 3149 3154 Vol. 78, No. 6 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.6.3149 3154.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cell-to-Cell,
VIRUSES RECORDED IN PORTUGAL IN TOMATO PROTECTED CROPS. J. C. Sequeira Estaçâo Agronómica Nacional INIA 2780 OEIRAS Portugal
 VIRUSES RECORDED IN PORTUGAL IN TOMATO PROTECTED CROPS M. Lourdes V. Borges Estaçâo Agronómica Nacional INIA 2780 OEIRAS Portugal J. C. Sequeira Estaçâo Agronómica Nacional INIA 2780 OEIRAS Portugal Abstract
VIRUSES RECORDED IN PORTUGAL IN TOMATO PROTECTED CROPS M. Lourdes V. Borges Estaçâo Agronómica Nacional INIA 2780 OEIRAS Portugal J. C. Sequeira Estaçâo Agronómica Nacional INIA 2780 OEIRAS Portugal Abstract
Genetic Diversity in RNA Virus Quasispecies Is Controlled by Host-Virus Interactions
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 2001, p. 6566 6571 Vol. 75, No. 14 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.14.6566 6571.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Genetic
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 2001, p. 6566 6571 Vol. 75, No. 14 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.14.6566 6571.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Genetic
Characterization of Double-Stranded RNA Satellites Associated with the Trichomonas vaginalis Virus
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 1995, p. 6892 6897 Vol. 69, No. 11 0022-538X/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Characterization of Double-Stranded RNA Satellites Associated with the
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 1995, p. 6892 6897 Vol. 69, No. 11 0022-538X/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Characterization of Double-Stranded RNA Satellites Associated with the
Islamic University Faculty of Medicine
 Islamic University Faculty of Medicine 2012 2013 2 RNA is a modular structure built from a combination of secondary and tertiary structural motifs. RNA chains fold into unique 3 D structures, which act
Islamic University Faculty of Medicine 2012 2013 2 RNA is a modular structure built from a combination of secondary and tertiary structural motifs. RNA chains fold into unique 3 D structures, which act
Science & Technologies CELERY MOSAIC VIRUS ON FOENICULUM VULGARE IN BULGARIA. 7 Shosse Bankya Str., 1080 Sofia, Bulgaria, E mail:
 CELERY MOSAIC VIRUS ON FOENICULUM VULGARE IN BULGARIA Bistra Dikova 1 and Hristo Lambev 2 1 Nikola Poushkarov Institute for Soil Science, Agrotechnologies and Plant Protection 7 Shosse Bankya Str., 1080
CELERY MOSAIC VIRUS ON FOENICULUM VULGARE IN BULGARIA Bistra Dikova 1 and Hristo Lambev 2 1 Nikola Poushkarov Institute for Soil Science, Agrotechnologies and Plant Protection 7 Shosse Bankya Str., 1080
Cucumber Green Mottle Mosaic Virus on Cucumber and Watermelon and Melon Necrotic Spot Virus on Muskmelon
 Cucumber Green Mottle Mosaic Virus on Cucumber and Watermelon and Melon Necrotic Spot Virus on Muskmelon By YASUO KOMURO Chief, Laboratory of Virus Taxonomy, Institute for Plant Virus Research There are
Cucumber Green Mottle Mosaic Virus on Cucumber and Watermelon and Melon Necrotic Spot Virus on Muskmelon By YASUO KOMURO Chief, Laboratory of Virus Taxonomy, Institute for Plant Virus Research There are
NS1 Protein Expression in the JaOArS982 Strain of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Does Not Enhance Virulence in Mice
 Tropical Medicine and Health Vol. 43 No.4, 2015, 233 237 doi: 10.2149/tmh.2015-27 Copyright 2015 by The Japanese Society of Tropical Medicine 233 Short Communications NS1 Protein Expression in the JaOArS982
Tropical Medicine and Health Vol. 43 No.4, 2015, 233 237 doi: 10.2149/tmh.2015-27 Copyright 2015 by The Japanese Society of Tropical Medicine 233 Short Communications NS1 Protein Expression in the JaOArS982
Tubular Inclusion Bodies in Plants Infected with Viruses of the NEPO Type
 J. gen. Virol. (I97O), 7, I59-166 Printed in Great Britain I59 Tubular Inclusion Bodies in Plants Infected with Viruses of the NEPO Type By D. G. A. WALKEY AND M. J. W. WEBB National Vegetable Research
J. gen. Virol. (I97O), 7, I59-166 Printed in Great Britain I59 Tubular Inclusion Bodies in Plants Infected with Viruses of the NEPO Type By D. G. A. WALKEY AND M. J. W. WEBB National Vegetable Research
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology
 علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
Host-Induced Gene Silencing in the Fusarium-Wheat interaction. Wanxin Chen and Patrick Schweizer
 Host-Induced Gene Silencing in the Fusarium-Wheat interaction Wanxin Chen and Patrick Schweizer What is Host-Induced Gene Silencing (HIGS)? Fungus Bgh Trujillo et al. (2004) MPMI HIGS: HI reduced GAME
Host-Induced Gene Silencing in the Fusarium-Wheat interaction Wanxin Chen and Patrick Schweizer What is Host-Induced Gene Silencing (HIGS)? Fungus Bgh Trujillo et al. (2004) MPMI HIGS: HI reduced GAME
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Chapter 18 Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences
Chapter 18 Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences
Framework for the evaluation of. and scientific impacts of plant viruses. technologies.
 Framework for the evaluation of biosecurity, commercial, regulatory and scientific impacts of plant viruses and viroids identified by NGS technologies. Sebastien Massart, Thierry Candresse, José Gil, Christophe
Framework for the evaluation of biosecurity, commercial, regulatory and scientific impacts of plant viruses and viroids identified by NGS technologies. Sebastien Massart, Thierry Candresse, José Gil, Christophe
Use of Capto ViralQ for the removal of genomic DNA from influenza virus produced in MDCK cells
 GE Healthcare Application note 28-9769-69 AA Vaccines Use of Capto ViralQ for the removal of genomic DNA from influenza virus produced in MDCK cells We have developed a chromatographic method to remove
GE Healthcare Application note 28-9769-69 AA Vaccines Use of Capto ViralQ for the removal of genomic DNA from influenza virus produced in MDCK cells We have developed a chromatographic method to remove
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression. (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs)
 Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Cellular MicroRNA and P Bodies Modulate Host-HIV-1 Interactions. 指導教授 : 張麗冠博士 演講者 : 黃柄翰 Date: 2009/10/19
 Cellular MicroRNA and P Bodies Modulate Host-HIV-1 Interactions 指導教授 : 張麗冠博士 演講者 : 黃柄翰 Date: 2009/10/19 1 MicroRNA biogenesis 1. Pri mirna: primary mirna 2. Drosha: RNaseIII 3. DCR 1: Dicer 1 RNaseIII
Cellular MicroRNA and P Bodies Modulate Host-HIV-1 Interactions 指導教授 : 張麗冠博士 演講者 : 黃柄翰 Date: 2009/10/19 1 MicroRNA biogenesis 1. Pri mirna: primary mirna 2. Drosha: RNaseIII 3. DCR 1: Dicer 1 RNaseIII
Gene Vaccine Dr. Sina Soleimani
 Gene Vaccine Dr. Sina Soleimani Human Viral Vaccines Quality Control Laboratory (HVVQC) Titles 1. A short Introduction of Vaccine History 2. First Lineage of Vaccines 3. Second Lineage of Vaccines 3. New
Gene Vaccine Dr. Sina Soleimani Human Viral Vaccines Quality Control Laboratory (HVVQC) Titles 1. A short Introduction of Vaccine History 2. First Lineage of Vaccines 3. Second Lineage of Vaccines 3. New
INSTRUCTION MANUAL. RNA Clean & Concentrator -5 Catalog Nos. R1015 & R1016. Highlights. Contents
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog Nos. R1015 & R1016 Highlights Quick (5 minute) method for cleaning and concentrating RNA. Ideal for purification of RNA from aqueous phase following an acid phenol extraction.
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog Nos. R1015 & R1016 Highlights Quick (5 minute) method for cleaning and concentrating RNA. Ideal for purification of RNA from aqueous phase following an acid phenol extraction.
Supporting Information
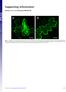 Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses
 Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 7: Cytokines Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research HHV-8 Discovered in the 1980 s at the
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 7: Cytokines Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research HHV-8 Discovered in the 1980 s at the
