sirna count per 50 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand Repeat length (bp) per 50 kb repeats in the chromosome
|
|
|
- Vivian Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Qi et al C Qi et al., Figure S1 sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the complementary strand Repeat length (bp) per 5 kb repeats in the chromosome pericentromeric Position (bp) on chlomosome 1
2 Qi et al C Figure S1. Chromosome-wide density analysis of the AGO4-associated small RNAs on Chromosome 1. The non-redundant set of small RNAs was screened against the Arabidopsis genome using WU-BLAST. The density of small RNAs with perfect matches to the direct strand (upper panel) or the complementary strand (middle panel) of Chromosome 1, and the density of repeats (lower panel) on Chromosome 1 were plotted in a 5 Kb sliding window. The position of the pericentromeric region is marked.
3 Qi et al C Qi et al., Figure S2 sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the complementary strand Repeat length (bp) per 5 kb repeats in the chromosome pericentromeric Position (bp) on chlomosome 2
4 Qi et al C Figure S2. Chromosome-wide density analysis of the AGO4-associated small RNAs on Chromosome 2. The non-redundant set of small RNAs was screened against the Arabidopsis genome using WU-BLAST. The density of small RNAs with perfect matches to the direct strand (upper panel) or the complementary strand (middle panel) of Chromosome 2, and the density of repeats (lower panel) on Chromosome 2 were plotted in a 5 Kb sliding window. The position of the pericentromeric region is marked. 2
5 Qi et al C Qi et al., Figure S3 sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the complementary strand Repeat length (bp) per 5 kb repeats in the chromosome pericentromeric Position (bp) on chlomosome 3
6 Qi et al C Figure S3. Chromosome-wide density analysis of the AGO4-associated small RNAs on Chromosome 3. The non-redundant set of small RNAs was screened against Arabidopsis genome using WU-BLAST. The density of small RNAs with perfect matches to the direct strand (upper panel) or the complementary strand (middle panel) of Chromosome 3, and the density of repeats (lower panel) on Chromosome 3 were plotted in a 5 Kb sliding window. The position of the pericentromeric region is marked. 3
7 Qi et al C Qi et al., Figure S4 sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the complementary strand Repeat length (bp) per 5 kb repeats in the chromosome pericentromeric Position (bp) on chlomosome 5
8 Qi et al C Figure S4. Chromosome-wide density analysis of the AGO4-associated small RNAs on Chromosome 5. The non-redundant set of small RNAs was screened against the Arabidopsis genome using WU-BLAST. The density of small RNAs with perfect matches to the direct strand (upper panel) or the complementary strand (middle panel) of Chromosome 5, and the density of repeats (lower panel) on Chromosome 5 were plotted in a 5 Kb sliding window. The position of the pericentromeric region is marked. 4
9 Qi et al C a 6 Qi et al., Figure S Total AGO1 AGO4 2 1 b mir159 mir16 mir161 mir164 mir166 mir167 mir168 mir172 mir319 mir39
10 Qi et al C Figure S5 Preferential association of a subset of micrornas with AGO4. a. Data obtained from 454 sequencing were used to quantify levels of individual mirnas, relative to total mirna content, in AGO1 and AGO4 complexes and in total RNA. Percent contribution for a subset of micrornas with preferential association with either AGO1 or AGO4 is shown graphically. b. Northen analysis of mir172, mir163, mir39, and mir173 confirm patterns of AGO1 and AGO4 binding discerned from sequencing. sirnas from AtSN1 and tasirna48 are shown as controls for AGO4 and AGO1-bound species, respectively. 5
11 La-er Col La-er Col La-er Col La-er Col La-er Col Qi et al C Qi et al., Figure S6 a Total RNA Control TAPAGO4 b 3 nt La-er Col dcl3-1 rdr2-1 AtREP2 3 nt 2 nt AtREP2 3 nt 2 nt SIMPLEHAT2 3 nt 2 nt 3 nt SIMPLEHAT2 mir171 2 nt 2 nt c Percentage of methylated cytosine AtREP CpG CpNpG CpHpH dcl3-1 rdr dcl3-1 rdr dcl3-1 rdr2-1 SIMPLEHAT2 Percentage of methylated cytosine CpG dcl3-1 rdr CpHpH dcl3-1 rdr2-1
12 Qi et al C Figure S6 Identification of AGO4-regulated loci through small RNA sequencing. a, Northern analysis of small RNAs in total RNA and in RNAs isolated from TAPAGO4 and control purifications were performed using the indicated probes. Radioactive RNAs of known sizes were included as size markers. b, Northern analysis of AtREP1/2 and SIMPLEHAT2 sirnas were performed on RNA from the indicated plants. mir171 serves as a loading control. c, Analysis of CpG (left), CpNpG (center), and CpHpH (right) methylation at ATREP2 and SIMPLEHAT2 loci was carried out by bisulfite sequencing of genomic DNA prepared from the indicated plants. The methylation level is shown by the percentage of methylated cytosine in all sequenced clones. Data in Table S6 were used to generate the histograms. 6
13 Qi et al C Qi et al., Figure S7 Control AGO4 D66A D742A H874A
14 Qi et al C Figure S7. Accumulation of AGO4 wild-type and DDH mutant proteins in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Total proteins were extracted from pooled samples of ~3 T1 transgenic lines for each constructs. Western blot analysis was performed using anti-myc antibody. The position of myc-ago4 is indicated by the arrow. The lower band is a cross-reacting species seen in all samples. 7
15 Qi et al C Qi et al., Figure S8 Input RNA Control IP AGO4 IP Input RNA Control IP AGO4 IP Substrate 5 cleavage product TAS3 (mir39) AP2 (mir172)
16 Qi et al C Figure S8. AGO4-mediated cleavage of mirna targets. AGO4 complexes or control immunoprecipitates were mixed with labeled, synthetic target RNAs for two AGO-4 associated micrornas, mir39 and mir172 (TAS3 and AP2 mrna, respectively). Cleavage was monitored by electrophoresis of reaction products. 8
17 Qi et al C Qi et al., Figure S9 CpG CpNpG CpHpH Percentage of methylated cytosine SUP AtMu1 Percentage of methylated cytosine MEA-ISR Percentage of methylated cytosine AtREP2 Percentage of methylated cytosine clk-st Control#L1 Control#L2 AGO4#L2 AGO4#L3 D66A#L8 D66A#L12 D742A#L1 D742A#L2 H874A#L2 H874A#L3 clk-st Control#L1 Control#L2 AGO4#L2 AGO4#L3 D66A#L8 D66A#L12 D742A#L1 D742A#L2 H874A#L2 H874A#L3 clk-st Control#L1 Control#L2 AGO4#L2 AGO4#L3 D66A#L8 D66A#L12 D742A#L1 D742A#L2 H874A#L2 H874A#L3
18 Qi et al C Figure S9. Analysis of CpG (left), CpNpG (middle), and CpHpH (right) methylation at SUP, AtMu1, MEA-ISR and ATREP2 loci in T2 transgenic lines. Bisulfite sequencing data from two biological replicates were combined. Methylation levels are shown by the percentage of methylated cytosines in all sequenced clones. Data from Table S8 were used to generate the histograms. 9
19 Control#L1 Control#L2 AGO4#L2 AGO4#L3 D66A#L8 D66A#L12 D742A#L1 D742A#L2 H874A#L2 H874A#L3 Qi et al C Qi et al., Figure S1 clk-st 3 nt MEA-ISR 2 nt Relative levels to clk-st nt 2 nt Relative levels to clk-st nt 2 nt AtREP2 AtSN1 Relative levels to clk-st nt 2 nt mir171
20 Qi et al C Figure S1. Northern blot analysis of sirnas derived from MEA-ISR, AtSN1, and ATREP2 in RNAs prepared from the indicated T2 plants. mir171 was used as a loading control. The sirna signals were normalized relative to mir171 and the relative levels were calculated by comparison to those in clk-st (see text, arbitrarily set to 1). 1
Supplemental Figure 1. Genes showing ectopic H3K9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study.
 mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples.
 Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
SUVR2 is involved in transcriptional gene silencing by associating with SNF2-related chromatin-remodeling proteins in Arabidopsis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2014) :1-21. 2014 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/14 www.nature.com/cr npg SUVR2 is involved in transcriptional gene silencing by associating with SNF2-related
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2014) :1-21. 2014 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/14 www.nature.com/cr npg SUVR2 is involved in transcriptional gene silencing by associating with SNF2-related
SC-L-H shared(37) Specific (1)
 A. Brain (total 2) Tissue-specific (2) Brain-heart shared (8) Specific (2) CNS-heart shared(68) Specific () Heart (total 4) Tissue-specific () B-L-H shared (37) specific () B. Brain (total 2) Tissue-specific
A. Brain (total 2) Tissue-specific (2) Brain-heart shared (8) Specific (2) CNS-heart shared(68) Specific () Heart (total 4) Tissue-specific () B-L-H shared (37) specific () B. Brain (total 2) Tissue-specific
Genome-Wide Profiling and Analysis of Arabidopsis sirnas
 Genome-Wide Profiling and Analysis of Arabidopsis sirnas PLoS BIOLOGY Kristin D. Kasschau 1,2, Noah Fahlgren 1,2,3, Elisabeth J. Chapman 1,2,3, Christopher M. Sullivan 1,2, Jason S. Cumbie 1,2, Scott A.
Genome-Wide Profiling and Analysis of Arabidopsis sirnas PLoS BIOLOGY Kristin D. Kasschau 1,2, Noah Fahlgren 1,2,3, Elisabeth J. Chapman 1,2,3, Christopher M. Sullivan 1,2, Jason S. Cumbie 1,2, Scott A.
reads observed in trnas from the analysis of RNAs carrying a 5 -OH ends isolated from cells induced to express
 Supplementary Figure 1. VapC-mt4 cleaves trna Ala2 in E. coli. Histograms representing the fold change in reads observed in trnas from the analysis of RNAs carrying a 5 -OH ends isolated from cells induced
Supplementary Figure 1. VapC-mt4 cleaves trna Ala2 in E. coli. Histograms representing the fold change in reads observed in trnas from the analysis of RNAs carrying a 5 -OH ends isolated from cells induced
Supplemental Figure 1. Small RNA size distribution from different soybean tissues.
 Supplemental Figure 1. Small RNA size distribution from different soybean tissues. The size of small RNAs was plotted versus frequency (percentage) among total sequences (A, C, E and G) or distinct sequences
Supplemental Figure 1. Small RNA size distribution from different soybean tissues. The size of small RNAs was plotted versus frequency (percentage) among total sequences (A, C, E and G) or distinct sequences
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
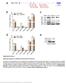 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Cross species analysis of genomics data. Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets
 02-716 Cross species analysis of genomics data Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets Outline Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Why Computational Methods? Computational Methods
02-716 Cross species analysis of genomics data Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets Outline Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Why Computational Methods? Computational Methods
Benchmark study: Exiqon mircury LNA microrna arrays vs. Supplier A s DNA based capture probes. Includes comparison of:
 Benchmark study: Exiqon mircury LNA microrna arrays vs. Supplier A s DNA based capture probes Includes comparison of: I. II. III. Signal levels Relative quantification False differences For complete experimental
Benchmark study: Exiqon mircury LNA microrna arrays vs. Supplier A s DNA based capture probes Includes comparison of: I. II. III. Signal levels Relative quantification False differences For complete experimental
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003)
 MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
MicroRNAs and Their Regulatory Roles in Plants
 Annu. Rev. lant Biol. 2006. 57:19 53 The Annual Review of lant Biology is online at plant.annualreviews.org doi: 10.1146/ annurev.arplant.57.032905.105218 opyright c 2006 by Annual Reviews. All rights
Annu. Rev. lant Biol. 2006. 57:19 53 The Annual Review of lant Biology is online at plant.annualreviews.org doi: 10.1146/ annurev.arplant.57.032905.105218 opyright c 2006 by Annual Reviews. All rights
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf. Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016
 Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016 What does H3K4 methylation do? Plant of interest: Vitis vinifera Culturally important
Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016 What does H3K4 methylation do? Plant of interest: Vitis vinifera Culturally important
Understanding the interaction between RNA-directed DNA methylation and DNA demethylases and its role in Fusarium oxysporum
 Understanding the interaction between RNA-directed DNA methylation and DNA demethylases and its role in Fusarium oxysporum disease response in Arabidopsis thaliana Joanne R.M. Lee, B. Biotech (Hons.) A
Understanding the interaction between RNA-directed DNA methylation and DNA demethylases and its role in Fusarium oxysporum disease response in Arabidopsis thaliana Joanne R.M. Lee, B. Biotech (Hons.) A
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES
 EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
ARGONAUTE10 and ARGONAUTE1 Regulate the Termination of Floral Stem Cells Through Two MicroRNAs in Arabidopsis
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge Plant and Soil Sciences Faculty Publications Plant and Soil Sciences 3-31-2011 ARGONAUTE10 and ARGONAUTE1 Regulate the Termination of Floral Stem Cells Through Two MicroRNAs
University of Kentucky UKnowledge Plant and Soil Sciences Faculty Publications Plant and Soil Sciences 3-31-2011 ARGONAUTE10 and ARGONAUTE1 Regulate the Termination of Floral Stem Cells Through Two MicroRNAs
Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor RAV2 to Block RNA Silencing
 Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor RAV2 to Block RNA Silencing Matthew W. Endres 1, Brian D. Gregory 2,3, Zhihuan Gao 1, Amy Wahba Foreman
Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor RAV2 to Block RNA Silencing Matthew W. Endres 1, Brian D. Gregory 2,3, Zhihuan Gao 1, Amy Wahba Foreman
MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation
 MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation Tao Li 1 *, Michael J. Morgan 1 *, Swati Choksi 1, Yan Zhang 1, You-Sun Kim 2#, Zheng-gang
MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation Tao Li 1 *, Michael J. Morgan 1 *, Swati Choksi 1, Yan Zhang 1, You-Sun Kim 2#, Zheng-gang
Small RNAs and Cross-Kingdom RNAi in Plant-Microbial Interaction Hailing Jin
 Small RNAs and Cross-Kingdom RNAi in Plant-Microbial Interaction Hailing Jin Department of Plant Pathology & Microbiology Institute for Integrative Genome Biology micrornas (mirnas) Small RNAs PolII PolIV
Small RNAs and Cross-Kingdom RNAi in Plant-Microbial Interaction Hailing Jin Department of Plant Pathology & Microbiology Institute for Integrative Genome Biology micrornas (mirnas) Small RNAs PolII PolIV
Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor RAV2 to Block RNA Silencing
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Biology) Department of Biology 1-15-2010 Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Biology) Department of Biology 1-15-2010 Two Plant Viral Suppressors of Silencing Require the Ethylene-Inducible Host Transcription Factor
Supplemental Figure 1
 1 Supplemental Figure 1 Effects of DATE shortening on HGF promoter activity. The HGF promoter region (-1037 to +56) containing wild-type (30As) or truncated DATE (26As, 27As, 28A, 29As) from breast cancer
1 Supplemental Figure 1 Effects of DATE shortening on HGF promoter activity. The HGF promoter region (-1037 to +56) containing wild-type (30As) or truncated DATE (26As, 27As, 28A, 29As) from breast cancer
Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012 Vol. 8(4): Journal of Agricultural
 Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012 Vol. 8(4): 1389-1395 Journal of Agricultural Available Technology online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com 2012, Vol. 8(4): 1389-1395 ISSN 1686-9141 The effect of the decreased
Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012 Vol. 8(4): 1389-1395 Journal of Agricultural Available Technology online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com 2012, Vol. 8(4): 1389-1395 ISSN 1686-9141 The effect of the decreased
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq
 Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice
 Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing. Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM
 MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
ANALYSIS OF SOYBEAN SMALL RNA POPULATIONS HLAING HLAING WIN THESIS
 ANALYSIS OF SOYBEAN SMALL RNA POPULATIONS BY HLAING HLAING WIN THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Bioinformatics in the Graduate College
ANALYSIS OF SOYBEAN SMALL RNA POPULATIONS BY HLAING HLAING WIN THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Bioinformatics in the Graduate College
Supplementary materials and methods.
 Supplementary materials and methods. Microarray printing and data analysis. The LNA-modified oligonucleotide probe set for all annotated mirnas from mouse (Mus musculus) and human (Homo sapiens) in the
Supplementary materials and methods. Microarray printing and data analysis. The LNA-modified oligonucleotide probe set for all annotated mirnas from mouse (Mus musculus) and human (Homo sapiens) in the
Assignment 5: Integrative epigenomics analysis
 Assignment 5: Integrative epigenomics analysis Due date: Friday, 2/24 10am. Note: no late assignments will be accepted. Introduction CpG islands (CGIs) are important regulatory regions in the genome. What
Assignment 5: Integrative epigenomics analysis Due date: Friday, 2/24 10am. Note: no late assignments will be accepted. Introduction CpG islands (CGIs) are important regulatory regions in the genome. What
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Improved annotation of C. elegans micrornas by deep sequencing reveals structures associated with processing by Drosha and Dicer
 BIOINFORMATICS Improved annotation of C. elegans micrornas by deep sequencing reveals structures associated with processing by Drosha and Dicer M. BRYAN WARF, 1 W. EVAN JOHNSON, 2 and BRENDA L. BASS 1
BIOINFORMATICS Improved annotation of C. elegans micrornas by deep sequencing reveals structures associated with processing by Drosha and Dicer M. BRYAN WARF, 1 W. EVAN JOHNSON, 2 and BRENDA L. BASS 1
Use Case 9: Coordinated Changes of Epigenomic Marks Across Tissue Types. Epigenome Informatics Workshop Bioinformatics Research Laboratory
 Use Case 9: Coordinated Changes of Epigenomic Marks Across Tissue Types Epigenome Informatics Workshop Bioinformatics Research Laboratory 1 Introduction Active or inactive states of transcription factor
Use Case 9: Coordinated Changes of Epigenomic Marks Across Tissue Types Epigenome Informatics Workshop Bioinformatics Research Laboratory 1 Introduction Active or inactive states of transcription factor
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance.! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014
 Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical
 Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical representation using all SNPs (n= 13,515,798) including the region on chromosome 1 including SORT1 which was previously
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical representation using all SNPs (n= 13,515,798) including the region on chromosome 1 including SORT1 which was previously
Gene silencing pathways found in the green alga Volvox carteri reveal insights into evolution and origins of small RNA systems in plants
 Dueck et al. BMC Genomics (2016) 17:853 DOI 10.1186/s12864-016-3202-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Gene silencing pathways found in the green alga Volvox carteri reveal insights into evolution and origins
Dueck et al. BMC Genomics (2016) 17:853 DOI 10.1186/s12864-016-3202-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Gene silencing pathways found in the green alga Volvox carteri reveal insights into evolution and origins
Results. Abstract. Introduc4on. Conclusions. Methods. Funding
 . expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
. expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Meta-analysis of IDH-mutant cancers identifies EBF1 as a novel interaction partner for
 Meta-analysis of IDH-mutant cancers identifies EBF1 as a novel interaction partner for TET2 Paul Guilhamon 1, Malihe Eskandarpour 2, Dina Halai 3, Gareth A. Wilson 1, Andrew Feber 1, Andrew E. Teschendorff
Meta-analysis of IDH-mutant cancers identifies EBF1 as a novel interaction partner for TET2 Paul Guilhamon 1, Malihe Eskandarpour 2, Dina Halai 3, Gareth A. Wilson 1, Andrew Feber 1, Andrew E. Teschendorff
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Eukaryotic small RNA Small RNAseq data analysis for mirna identification
 Eukaryotic small RNA Small RNAseq data analysis for mirna identification P. Bardou, C. Gaspin, S. Maman, J. Mariette, O. Rué, M. Zytnicki INRA Sigenae Toulouse INRA MIA Toulouse GenoToul Bioinfo INRA MaIAGE
Eukaryotic small RNA Small RNAseq data analysis for mirna identification P. Bardou, C. Gaspin, S. Maman, J. Mariette, O. Rué, M. Zytnicki INRA Sigenae Toulouse INRA MIA Toulouse GenoToul Bioinfo INRA MaIAGE
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin
 Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Precursors of trnas are stabilized by methylguanosine cap structures Takayuki Ohira and Tsutomu Suzuki Department of Chemistry and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Engineering,
Supplementary Information Precursors of trnas are stabilized by methylguanosine cap structures Takayuki Ohira and Tsutomu Suzuki Department of Chemistry and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Engineering,
Fragile X Syndrome. Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype
 Fragile X Syndrome Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype A loss of function of the FMR-1 gene results in severe learning problems, intellectual disability
Fragile X Syndrome Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype A loss of function of the FMR-1 gene results in severe learning problems, intellectual disability
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT ACTB AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT LCOR
 Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF SMALL RNAs IN MAIZE MUTANTS WITH DEFECTS IN DEVELOPMENT AND PARAMUTATION. Reza Hammond
 COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF SMALL RNAs IN MAIZE MUTANTS WITH DEFECTS IN DEVELOPMENT AND PARAMUTATION by Reza Hammond A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment
COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF SMALL RNAs IN MAIZE MUTANTS WITH DEFECTS IN DEVELOPMENT AND PARAMUTATION by Reza Hammond A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment
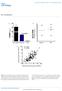 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen
 Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Epigenetic programming in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
 Epigenetic programming in chronic lymphocytic leukemia Christopher Oakes 10 th Canadian CLL Research Meeting September 18-19 th, 2014 Epigenetics and DNA methylation programming in normal and tumor cells:
Epigenetic programming in chronic lymphocytic leukemia Christopher Oakes 10 th Canadian CLL Research Meeting September 18-19 th, 2014 Epigenetics and DNA methylation programming in normal and tumor cells:
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Table S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample
 Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a Location of GUUUCA motif relative to RNA position 4e+05 3e+05 Reads 2e+05 1e+05 0e+00 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 Distance upstream b 1: Egg 2: L3 3: Adult 4: HES 4e+05 3e+05 2e+05 start
Supplementary Figure 1 a Location of GUUUCA motif relative to RNA position 4e+05 3e+05 Reads 2e+05 1e+05 0e+00 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 Distance upstream b 1: Egg 2: L3 3: Adult 4: HES 4e+05 3e+05 2e+05 start
Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics. DNA methylation in prostate cancer
 Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics DNA methylation in prostate cancer Overarching theme Epigenetic regulation allows the genome to be responsive to the environment Sets the tone for
Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics DNA methylation in prostate cancer Overarching theme Epigenetic regulation allows the genome to be responsive to the environment Sets the tone for
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice
 An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models. Yu Wu
 Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Scaffold function of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in protein ubiquitination
 Yoon et al, page Scaffold function of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in protein ubiquitination Je-Hyun Yoon,, Kotb Abdelmohsen, Jiyoung Kim, Xiaoling Yang, Jennifer L. Martindale, Kumiko Tominaga-Yamanaka,
Yoon et al, page Scaffold function of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in protein ubiquitination Je-Hyun Yoon,, Kotb Abdelmohsen, Jiyoung Kim, Xiaoling Yang, Jennifer L. Martindale, Kumiko Tominaga-Yamanaka,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic
 Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
Eukaryotic transcription (III)
 Eukaryotic transcription (III) 1. Chromosome and chromatin structure Chromatin, chromatid, and chromosome chromatin Genomes exist as chromatins before or after cell division (interphase) but as chromatids
Eukaryotic transcription (III) 1. Chromosome and chromatin structure Chromatin, chromatid, and chromosome chromatin Genomes exist as chromatins before or after cell division (interphase) but as chromatids
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature23267 Discussion Our findings reveal unique roles for the methylation states of histone H3K9 in RNAi-dependent and - independent heterochromatin formation. Clr4 is the sole S. pombe enzyme
doi:10.1038/nature23267 Discussion Our findings reveal unique roles for the methylation states of histone H3K9 in RNAi-dependent and - independent heterochromatin formation. Clr4 is the sole S. pombe enzyme
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information HBV maintains electrostatic homeostasis by modulating negative charges from phosphoserine and encapsidated nucleic acids Authors: Pei-Yi Su 1,2,3, Ching-Jen Yang 2, Tien-Hua Chu
Supplementary Information HBV maintains electrostatic homeostasis by modulating negative charges from phosphoserine and encapsidated nucleic acids Authors: Pei-Yi Su 1,2,3, Ching-Jen Yang 2, Tien-Hua Chu
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing
 Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing Jakub Orzechowski Westholm (1) Long- term bioinforma=cs support, Science For Life Laboratory Stockholm (2) Department of Biophysics and Biochemistry,
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing Jakub Orzechowski Westholm (1) Long- term bioinforma=cs support, Science For Life Laboratory Stockholm (2) Department of Biophysics and Biochemistry,
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna
 Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Appendix. Table of Contents
 Appendix Table of Contents Appendix Figures Figure S1: Gp78 is not required for the degradation of mcherry-cl1 in Hela Cells. Figure S2: Indel formation in the MARCH6 sgrna targeted HeLa clones. Figure
Appendix Table of Contents Appendix Figures Figure S1: Gp78 is not required for the degradation of mcherry-cl1 in Hela Cells. Figure S2: Indel formation in the MARCH6 sgrna targeted HeLa clones. Figure
Evidence of a Pathway of Reduction in Bacteria: Reduced Quantities of Restriction Sites Impact trna Activity in a Trial Set
 Evidence of a of Reduction in Bacteria: Reduced Quantities of Restriction Sites Impact trna Activity in a Trial Set Oliver Bonham-Carter, Lotfollah Najjar, Dhundy Bastola School of Interdisciplinary Informatics
Evidence of a of Reduction in Bacteria: Reduced Quantities of Restriction Sites Impact trna Activity in a Trial Set Oliver Bonham-Carter, Lotfollah Najjar, Dhundy Bastola School of Interdisciplinary Informatics
Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes
 Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
Genome-Wide Analysis of leafbladeless1-regulated and Phased Small RNAs Underscores the Importance of the TAS3 ta-sirna Pathway to Maize Development
 Genome-Wide Analysis of leafbladeless1-regulated and Phased Small RNAs Underscores the Importance of the TAS3 ta-sirna Pathway to Maize Development Marcela C. Dotto 1, Katherine A. Petsch 1, Milo J. Aukerman
Genome-Wide Analysis of leafbladeless1-regulated and Phased Small RNAs Underscores the Importance of the TAS3 ta-sirna Pathway to Maize Development Marcela C. Dotto 1, Katherine A. Petsch 1, Milo J. Aukerman
supplementary information
 DOI:.38/ncb1963 a wild 5.3kb 11.2kb targeting vector stop PCR primer KKpn NNhe targeted allele 5.7kb 6.8kb probe b d (g) 35 3 25 2 genomic Southern blot Kpn I digest Nhe I digest / / / / / / 11.2 kb 5.7
DOI:.38/ncb1963 a wild 5.3kb 11.2kb targeting vector stop PCR primer KKpn NNhe targeted allele 5.7kb 6.8kb probe b d (g) 35 3 25 2 genomic Southern blot Kpn I digest Nhe I digest / / / / / / 11.2 kb 5.7
Phenomena first observed in petunia
 Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1 33,312. Aire rep 1. Aire rep 2 # 44,325 # 44,055. Aire rep 1. Aire rep 2.
 a 33,312 b rep 1 rep 1 # 44,325 rep 2 # 44,055 [0-84] rep 2 [0-84] 1810043G02Rik Pfkl Dnmt3l Icosl rep 1 [0-165] rep 2 [0-165] Rps14 Cd74 Mir5107 Tcof1 rep 1 [0-69] rep 2 [0-68] Id3 E2f2 Asap3 rep 1 [0-141]
a 33,312 b rep 1 rep 1 # 44,325 rep 2 # 44,055 [0-84] rep 2 [0-84] 1810043G02Rik Pfkl Dnmt3l Icosl rep 1 [0-165] rep 2 [0-165] Rps14 Cd74 Mir5107 Tcof1 rep 1 [0-69] rep 2 [0-68] Id3 E2f2 Asap3 rep 1 [0-141]
