Supplemental Figure 1. Small RNA size distribution from different soybean tissues.
|
|
|
- Cory Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Figure 1. Small RNA size distribution from different soybean tissues. The size of small RNAs was plotted versus frequency (percentage) among total sequences (A, C, E and G) or distinct sequences (B, D, F, and H). Library codes and detailed information about each library are indicated in Supplemental Data set 1A. A B C D E F G H 1
2 Supplemental Figure 2. Leaf small RNA size distributions in Arabidopsis and soybean. Size distribution of total small RNAs ([A], [C]) and distinct small RNAs ([B], [D]) in Arabidopsis and soybean. The bottom panels of [C] and [D] provide details of the categories of 21-nt small RNAs in soybean, in the form of a pie chart. A Arabidopsis thaliana B Arabidopsis thaliana Frequency (%) Abundance Leaf-PCt1 Frequency (%) Distinct Leaf-PCt1 Small RNA length (nt) Small RNA length (nt) C Glycine max D Glycine max Frequency (%) Abundance Leaf-WW3023_1 Frequency (%) Distinct Leaf-WW3023_1 Small RNA length (nt) Small RNA length (nt) 2
3 Supplemental Figure 3. Examples of mirbase-annotated mirnas in our four categories of assessment. The mirbase-annotated mirna of interest is circled in red, with a red arrowhead for additional emphasis. One example of each type that we identified is shown, including the following: (A) Weaklyexpressed loci. (B) sirna-like mirna loci. (C) Marginal mirna loci. (D) Typical mirna loci. A B gma-mir1522 C gma-mir1520a D gma-mir4345 gma-mir156b 3
4 Supplemental Figure 4. The pipeline for the identification of novel mirna and mirna variants. 69 small RNA libraries 1 st Filter Set 1) Genome matched excluding t/r/sn/snornas 2) Abundance 50 TP5M in at least one library 3) Size between nt 4) Hits to soybean genome between 1 and 20 2 nd Filter Set 1) Select two most abundant sequences 2) Modified mireap 3 rd Filter Set 1) Strand bias: sense/total 0.9 2) Abundance bias: (top1+top2)/total 0.7 3) Within or nearby (50 nt) to known t/r/sn/snorna 4 th Filter Set Stem-loop structure prediction (CentroidFold) 5 th Filter Set Exclude known mirnas Candidates : 124,526,447 Known mirnas: 370 Candidates : 29,133 Known mirnas: 198 Candidates : 2,523 (4,074 precursors) Known mirnas: 120 Candidates : 180 (361 precursors) Known mirnas: 71 Candidates : 151 (332 precursors) Known mirnas: novel mirnas (33 precursors) 44 new variants of known mirnas 4
5 Supplemental Figure 5. Abundance profiles of the mir171 family. The log2-transformed values of normalized read abundance (TP5M) in flower, leaf and nodule tissues are displayed as a heat map. The mirna members with the same sequences were collapsed into one row. Log2 transformation:
6 Supplemental Figure 6. Secondary structures for the stem-loop region of precursors of the soybean mirnas that are triggers of PHAS loci. Sequences highlighted in red are the mature mirna sequence. (A) mirna triggers with asymmetric bulges in the precursors; the asymmetric bulge in the stem-loop is indicated by a purple arrow, combined with a zoomed-in view of the nucleotides found at the bulge. (B next page) mirna triggers lacking an asymmetric bulge in the precursor. 6
7 Supplemental Figure 6. (continued) 7
8 Supplemental Figure 7. PhasiRNAs from the ARF4 locus are triggered by tasiarfs. Small RNA and PARE data demonstrate that like ARF3/ETT (Figure 4), the ARF4 locus is targeted by 21-nt tasiarfs at both cleaved and non-cleaved sites, triggering secondary sirnas biogenesis via the two-hit mechanism. At the top, the cleavage position is indicated with a black arrow in the tasiarf-arf4 sequence alignment. See the legend of Figure 4 for a full description of the images and symbols. 204/248 Glyma12g AAGGUCUUGCAAGGUCAAGAA 3 ARF4 o SCORE: UUCCAGAAUGUUCCAGUUCUU 5 tasiarf Cleaved target Chr.12: Non-cleaved target Chr.12: Phasing Score 198bp Small RNA abundances PARE RNA abundances Small RNA data tasiarf target site PARE data 8
9 Supplemental Figure 8. Several soybean loci related to arogenate dehydrogenase-encoding transcripts are abundant sources of 21-nt phasirnas. (A) An intergenic (unannotated) region on chromosome 14 approximately between positions 15,772,000 and 15,775,000 generates an abundant set of secondary sirnas (blue dots are 21-mers, green are 22- mers). This sequence is predicted to form a long hairpin structure (data not shown); this is recognizable by the presence of an inverted repeat at the loop region (orange box). The blue boxes in the center indicate tandem repeats. Other features are as described in the legend of Figure 4. (B) Two arogenate dehydrogenase-encoding genes in soybean are PHAS loci. (C) A tree of the arogenate dehydrogenase proteins encoded in the soybean genome, with gene identifiers at right. The clade highlighted in pink contains the two loci producing phasirnas. The tree was produced using from the alignment generated by CLUSTALW. A Chr.14:15,772,000; Arogenate dehydrogenase-like B Glyma17g13150; Arogenate dehydrogenase Glyma05g07870; Arogenate dehydrogenase C 0.01 Glyma17g13150 Glyma05g07870 Glyma13g01050 Glyma15g06340 Glyma14g05990 Glyma11g35760 Glyma18g
10 Supplemental Figure 9. Seed-specific PHAS loci from MYB5 genes. Small RNA plots and phasing scores of MYB5 phasirna precursors ([A] is Glyma05g04900, [B] is Glyma17g15270). The target binding sites for the mirna triggers are indicated with green triangles and the cleavage positions are indicated with black arrows in the sequence alignment at the top. In the lower panels, the green and red bars show the levels of normalized read abundances for phasirnas and mirna triggers, respectively, in different tissues for these two MYB5 genes. A Glyma05g UGGAAUUCUCAUUUGUGCAAAA 3 MYB5 SCORE: ACCUUAUGAGUAAACUCGUUCU 5 mir828 Cleaved target Chr.5: B Glyma17g UGGAAUUCUCAUUUGUGCAAAA 3 MYB5 SCORE: ACCUUAUGAGUAAACUCGUUCU 5 mir828 Cleaved target Chr.17: Small RNA abundances Small RNA abundances Phasing Score Phasing Score Glyma05g04900 Glyma17g
11 Supplemental Figure 10. Decrease of mir390 and TAS3a and TAS3b read abundances during nodule development. Normalized read abundances of mir390 and 21-nt phasirnas generated from TAS3a and TAS3b in developing nodules, from 10 to 30 days after inoculation, measured over an interval of five days Reads abundance (TP5M) TAS3a TAS3b mir Stage of nodule development (in days-post-inoculation) (Day) 11
12 Supplemental Figure 11. Co-localization of legume anther- or flower-specific PHAS loci and their mirna triggers. (A) Small RNA abundances of mir4392 and phasirnas generated from the adjacent PHAS locus; both sets of small RNAs accumulate exclusively in soybean flower tissues, particularly in anthers. The RNA-seq read abundances of the mirna and PHAS precursors confirm the exclusive expression of both loci in flower tissues. (B) The target site of mir4392 on the soybean chromosome is indicated with brown lines, and the position of the mir4392 locus and the mature mirna is indicated with a red arrow. (C) The target site of mir5754 on Medicago chromosome 4 is indicated in brown. The locus generating mir5754 is nearby, with the mature mirna indicated with a red arrow. A B Glycine max gma-mir4392 target gma-mir4392 C Medicago truncatula Medtr4g Medtr4g mtr-mir5754 target mtr-mir5754 target mtr-mir
13 Supplemental Figure 12. A model of transposable element control in legume pollen by pollenspecific phasirnas. The MIRNA gene and the PHAS genes localized in the adjacent region are shown as blue and green horizontal bars, respectively. The long black line represents a portion of chromosome region. The MIRNA gene transcribes a mirna precursor, which will be subsequently processed to the 22-nt mirna by a dicer-like protein (DCL, normally DCL1). The 22-nt mirna will bind to an Argonaute (AGO), targeting the transcript produced from the PHAS gene. A set of 21-nt phasirnas will then be generated from the PHAS gene transcript. These phasirnas, mediated by AGO, will target hundreds of transposable elements (TEs) genome-widely and probably control those TEs via transcription (TGS) or posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS) mechanisms. The twenty soybean chromosomes are shown in green vertical bars and the locations of predicted TE targets are indicated as red triangles. 13
MicroRNAs as master regulators of the plant NB-LRR defense gene family via the production of phased, trans-acting sirnas
 RESOURCE/METHODOLOGY MicroRNAs as master regulators of the plant NB-LRR defense gene family via the production of phased, trans-acting sirnas Jixian Zhai, 1,2 Dong-Hoon Jeong, 1,2 Emanuele De Paoli, 1,2,7
RESOURCE/METHODOLOGY MicroRNAs as master regulators of the plant NB-LRR defense gene family via the production of phased, trans-acting sirnas Jixian Zhai, 1,2 Dong-Hoon Jeong, 1,2 Emanuele De Paoli, 1,2,7
RNA-Seq Atlas of Glycine max: A guide to the Soybean Transcriptome
 RNA-Seq Atlas of Glycine max: A guide to the Soybean Transcriptome How do novel structures or functions evolve? A more relevant example Symbiosis and Nitrogen Fixation Limpens & Bisseling (23) Curr. Opin.
RNA-Seq Atlas of Glycine max: A guide to the Soybean Transcriptome How do novel structures or functions evolve? A more relevant example Symbiosis and Nitrogen Fixation Limpens & Bisseling (23) Curr. Opin.
ANALYSIS OF SOYBEAN SMALL RNA POPULATIONS HLAING HLAING WIN THESIS
 ANALYSIS OF SOYBEAN SMALL RNA POPULATIONS BY HLAING HLAING WIN THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Bioinformatics in the Graduate College
ANALYSIS OF SOYBEAN SMALL RNA POPULATIONS BY HLAING HLAING WIN THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Bioinformatics in the Graduate College
Eukaryotic small RNA Small RNAseq data analysis for mirna identification
 Eukaryotic small RNA Small RNAseq data analysis for mirna identification P. Bardou, C. Gaspin, S. Maman, J. Mariette, O. Rué, M. Zytnicki INRA Sigenae Toulouse INRA MIA Toulouse GenoToul Bioinfo INRA MaIAGE
Eukaryotic small RNA Small RNAseq data analysis for mirna identification P. Bardou, C. Gaspin, S. Maman, J. Mariette, O. Rué, M. Zytnicki INRA Sigenae Toulouse INRA MIA Toulouse GenoToul Bioinfo INRA MaIAGE
Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples.
 Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
High-resolution identification and abundance profiling of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) micrornas
 Khatabi et al. BMC Genomics (216) 17:85 DOI 1.1186/s12864-16-2391-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE High-resolution identification and abundance profiling of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) micrornas Behnam Khatabi
Khatabi et al. BMC Genomics (216) 17:85 DOI 1.1186/s12864-16-2391-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE High-resolution identification and abundance profiling of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) micrornas Behnam Khatabi
Supplemental Figure 1. Genes showing ectopic H3K9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study.
 mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003)
 MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
Identification of mirnas in Eucalyptus globulus Plant by Computational Methods
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 2 Issue 5 May 2013 PP.70-74 Identification of mirnas in Eucalyptus globulus Plant by Computational
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 2 Issue 5 May 2013 PP.70-74 Identification of mirnas in Eucalyptus globulus Plant by Computational
Improved annotation of C. elegans micrornas by deep sequencing reveals structures associated with processing by Drosha and Dicer
 BIOINFORMATICS Improved annotation of C. elegans micrornas by deep sequencing reveals structures associated with processing by Drosha and Dicer M. BRYAN WARF, 1 W. EVAN JOHNSON, 2 and BRENDA L. BASS 1
BIOINFORMATICS Improved annotation of C. elegans micrornas by deep sequencing reveals structures associated with processing by Drosha and Dicer M. BRYAN WARF, 1 W. EVAN JOHNSON, 2 and BRENDA L. BASS 1
Small RNA and PARE sequencing in flower bud reveal the involvement of srnas in endodormancy release of Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia 'Kosui')
 Bai et al. BMC Genomics (2016) 17:230 DOI 10.1186/s12864-016-2514-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Small RNA and PARE sequencing in flower bud reveal the involvement of srnas in endodormancy release of Japanese
Bai et al. BMC Genomics (2016) 17:230 DOI 10.1186/s12864-016-2514-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Small RNA and PARE sequencing in flower bud reveal the involvement of srnas in endodormancy release of Japanese
Cross species analysis of genomics data. Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets
 02-716 Cross species analysis of genomics data Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets Outline Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Why Computational Methods? Computational Methods
02-716 Cross species analysis of genomics data Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets Outline Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Why Computational Methods? Computational Methods
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Genome-Wide Analysis of leafbladeless1-regulated and Phased Small RNAs Underscores the Importance of the TAS3 ta-sirna Pathway to Maize Development
 Genome-Wide Analysis of leafbladeless1-regulated and Phased Small RNAs Underscores the Importance of the TAS3 ta-sirna Pathway to Maize Development Marcela C. Dotto 1, Katherine A. Petsch 1, Milo J. Aukerman
Genome-Wide Analysis of leafbladeless1-regulated and Phased Small RNAs Underscores the Importance of the TAS3 ta-sirna Pathway to Maize Development Marcela C. Dotto 1, Katherine A. Petsch 1, Milo J. Aukerman
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Transcriptome-wide analysis of microrna expression in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae
 Biryukova et al. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:557 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Transcriptome-wide analysis of microrna expression in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae Inna Biryukova 1*, Tao Ye 2 and Elena
Biryukova et al. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:557 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Transcriptome-wide analysis of microrna expression in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae Inna Biryukova 1*, Tao Ye 2 and Elena
sirna count per 50 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand Repeat length (bp) per 50 kb repeats in the chromosome
 Qi et al. 26-3-2564C Qi et al., Figure S1 sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the complementary strand Repeat length (bp) per 5 kb repeats
Qi et al. 26-3-2564C Qi et al., Figure S1 sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the complementary strand Repeat length (bp) per 5 kb repeats
Differentially expressed microrna cohorts in seed development may contribute to poor grain filling of inferior spikelets in rice
 Peng et al. BMC Plant Biology 2014, 14:196 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Differentially expressed microrna cohorts in seed development may contribute to poor grain filling of inferior spikelets in rice
Peng et al. BMC Plant Biology 2014, 14:196 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Differentially expressed microrna cohorts in seed development may contribute to poor grain filling of inferior spikelets in rice
Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
Obstacles and challenges in the analysis of microrna sequencing data
 Obstacles and challenges in the analysis of microrna sequencing data (mirna-seq) David Humphreys Genomics core Dr Victor Chang AC 1936-1991, Pioneering Cardiothoracic Surgeon and Humanitarian The ABCs
Obstacles and challenges in the analysis of microrna sequencing data (mirna-seq) David Humphreys Genomics core Dr Victor Chang AC 1936-1991, Pioneering Cardiothoracic Surgeon and Humanitarian The ABCs
Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of lincrnas acting as mirna targets or decoys in maize
 Fan et al. BMC Genomics (2015) 16:793 DOI 10.1186/s12864-015-2024-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of lincrnas acting as mirna targets or decoys in maize
Fan et al. BMC Genomics (2015) 16:793 DOI 10.1186/s12864-015-2024-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of lincrnas acting as mirna targets or decoys in maize
Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein
 Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein Objective: To review transcription, translation, reading frames, mutations, and reading files from GenBank, and to review some of the bioinformatics tools, such
Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein Objective: To review transcription, translation, reading frames, mutations, and reading files from GenBank, and to review some of the bioinformatics tools, such
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2419
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF SMALL RNAs IN MAIZE MUTANTS WITH DEFECTS IN DEVELOPMENT AND PARAMUTATION. Reza Hammond
 COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF SMALL RNAs IN MAIZE MUTANTS WITH DEFECTS IN DEVELOPMENT AND PARAMUTATION by Reza Hammond A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment
COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF SMALL RNAs IN MAIZE MUTANTS WITH DEFECTS IN DEVELOPMENT AND PARAMUTATION by Reza Hammond A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing
 Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing Jakub Orzechowski Westholm (1) Long- term bioinforma=cs support, Science For Life Laboratory Stockholm (2) Department of Biophysics and Biochemistry,
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing Jakub Orzechowski Westholm (1) Long- term bioinforma=cs support, Science For Life Laboratory Stockholm (2) Department of Biophysics and Biochemistry,
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
In silico identification of mirnas and their targets from the expressed sequence tags of Raphanus sativus
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(2) In silico identification of mirnas and their targets from the expressed sequence tags of Raphanus sativus Charuvaka Muvva 1 *, Lata Tewari 2, Kasoju Aruna
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(2) In silico identification of mirnas and their targets from the expressed sequence tags of Raphanus sativus Charuvaka Muvva 1 *, Lata Tewari 2, Kasoju Aruna
A putative MYB35 ortholog is a candidate for the sex-determining genes in Asparagus
 Supplementary figures for: A putative MYB35 ortholog is a candidate for the sex-determining genes in Asparagus officinalis Daisuke Tsugama, Kohei Matsuyama, Mayui Ide, Masato Hayashi, Kaien Fujino, and
Supplementary figures for: A putative MYB35 ortholog is a candidate for the sex-determining genes in Asparagus officinalis Daisuke Tsugama, Kohei Matsuyama, Mayui Ide, Masato Hayashi, Kaien Fujino, and
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Prediction of micrornas and their targets
 Prediction of micrornas and their targets Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Computational Methods Mature and precursor mirna prediction mirna target gene prediction Summary micrornas? RNA can
Prediction of micrornas and their targets Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Computational Methods Mature and precursor mirna prediction mirna target gene prediction Summary micrornas? RNA can
RIP-seq of BmAgo2-associated small RNAs reveal various types of small non-coding RNAs in the silkworm, Bombyx mori
 Nie et al. BMC Genomics 2013, 14:661 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access RIP-seq of BmAgo2-associated small RNAs reveal various types of small non-coding RNAs in the silkworm, Bombyx mori Zuoming Nie 1, Fang
Nie et al. BMC Genomics 2013, 14:661 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access RIP-seq of BmAgo2-associated small RNAs reveal various types of small non-coding RNAs in the silkworm, Bombyx mori Zuoming Nie 1, Fang
A WIDESPREAD IMPACT ON SMALL RNAS AND GENE NETWORKS IN RICE MSP1/OSTDL1A MUTANTS, PARTNERS WITH KEY ROLES IN ANTHER DEVELOPMENT.
 A WIDESPREAD IMPACT ON SMALL RNAS AND GENE NETWORKS IN RICE MSP1/OSTDL1A MUTANTS, PARTNERS WITH KEY ROLES IN ANTHER DEVELOPMENT by Qili Fei A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware
A WIDESPREAD IMPACT ON SMALL RNAS AND GENE NETWORKS IN RICE MSP1/OSTDL1A MUTANTS, PARTNERS WITH KEY ROLES IN ANTHER DEVELOPMENT by Qili Fei A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware
mir2118-triggered phased sirnas are differentially expressed during the panicle development of wild and domesticated African rice species
 Ta et al. Rice (2016) 9:10 DOI 10.1186/s12284-016-0082-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE mir2118-triggered phased sirnas are differentially expressed during the panicle development of wild and domesticated African rice
Ta et al. Rice (2016) 9:10 DOI 10.1186/s12284-016-0082-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE mir2118-triggered phased sirnas are differentially expressed during the panicle development of wild and domesticated African rice
Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.32 PCOS locus after conditioning for the lead SNP rs10993397;
Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.32 PCOS locus after conditioning for the lead SNP rs10993397;
Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma
 Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma Justin Chen, Christopher S. Hackett, Shile Zhang, Young K. Song, Robert J.A. Bell, Annette M. Molinaro, David A. Quigley, Allan Balmain,
Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma Justin Chen, Christopher S. Hackett, Shile Zhang, Young K. Song, Robert J.A. Bell, Annette M. Molinaro, David A. Quigley, Allan Balmain,
genomics for systems biology / ISB2020 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq)
 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
Introduction. Introduction
 Introduction We are leveraging genome sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to more accurately define mutated and stable genes and dysregulated metabolic pathways in solid tumors. These efforts
Introduction We are leveraging genome sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to more accurately define mutated and stable genes and dysregulated metabolic pathways in solid tumors. These efforts
Zhao et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2017) 18:180 DOI /s
 Zhao et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2017) 18:180 DOI 10.1186/s12859-017-1601-4 SOFTWARE QuickMIRSeq: a pipeline for quick and accurate quantification of both known mirnas and isomirs by jointly processing
Zhao et al. BMC Bioinformatics (2017) 18:180 DOI 10.1186/s12859-017-1601-4 SOFTWARE QuickMIRSeq: a pipeline for quick and accurate quantification of both known mirnas and isomirs by jointly processing
Transcriptome profiling of the developing male germ line identifies the mir-29 family as a global regulator during meiosis
 RNA BIOLOGY 2017, VOL. 14, NO. 2, 219 235 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1270002 RESEARCH PAPER Transcriptome profiling of the developing male germ line identifies the mir-29 family as a global
RNA BIOLOGY 2017, VOL. 14, NO. 2, 219 235 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1270002 RESEARCH PAPER Transcriptome profiling of the developing male germ line identifies the mir-29 family as a global
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing
 Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing RNA-seq Course November 8th 2017 Marc Friedländer ComputaAonal RNA Biology Group SciLifeLab / Stockholm University Special thanks to Jakub Westholm for
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing RNA-seq Course November 8th 2017 Marc Friedländer ComputaAonal RNA Biology Group SciLifeLab / Stockholm University Special thanks to Jakub Westholm for
Figure S1 Expression of AHL gene family members in diploid (Ler Col) and triploid (Ler
 Supplemental material Supplemental figure legends Figure S Expression of AHL gene family members in diploid (Ler ) and triploid (Ler osd) seeds. AHLs from clade B are labelled with (I), and AHLs from clade
Supplemental material Supplemental figure legends Figure S Expression of AHL gene family members in diploid (Ler ) and triploid (Ler osd) seeds. AHLs from clade B are labelled with (I), and AHLs from clade
MicroRNAs and Their Regulatory Roles in Plants
 Annu. Rev. lant Biol. 2006. 57:19 53 The Annual Review of lant Biology is online at plant.annualreviews.org doi: 10.1146/ annurev.arplant.57.032905.105218 opyright c 2006 by Annual Reviews. All rights
Annu. Rev. lant Biol. 2006. 57:19 53 The Annual Review of lant Biology is online at plant.annualreviews.org doi: 10.1146/ annurev.arplant.57.032905.105218 opyright c 2006 by Annual Reviews. All rights
V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs
 What are micrornas? V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs How can one identify micrornas? What is the function of micrornas? Elisa Izaurralde, MPI Tübingen Huntzinger, Izaurralde, Nat. Rev. Genet. 12,
What are micrornas? V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs How can one identify micrornas? What is the function of micrornas? Elisa Izaurralde, MPI Tübingen Huntzinger, Izaurralde, Nat. Rev. Genet. 12,
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION GO term analysis of differentially methylated SUMIs. GO term analysis of the 458 SUMIs with the largest differential methylation between human and chimp shows that they are more
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION GO term analysis of differentially methylated SUMIs. GO term analysis of the 458 SUMIs with the largest differential methylation between human and chimp shows that they are more
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures. for. pirna-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional
 Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a Location of GUUUCA motif relative to RNA position 4e+05 3e+05 Reads 2e+05 1e+05 0e+00 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 Distance upstream b 1: Egg 2: L3 3: Adult 4: HES 4e+05 3e+05 2e+05 start
Supplementary Figure 1 a Location of GUUUCA motif relative to RNA position 4e+05 3e+05 Reads 2e+05 1e+05 0e+00 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 Distance upstream b 1: Egg 2: L3 3: Adult 4: HES 4e+05 3e+05 2e+05 start
BWA alignment to reference transcriptome and genome. Convert transcriptome mappings back to genome space
 Whole genome sequencing Whole exome sequencing BWA alignment to reference transcriptome and genome Convert transcriptome mappings back to genome space genomes Filter on MQ, distance, Cigar string Annotate
Whole genome sequencing Whole exome sequencing BWA alignment to reference transcriptome and genome Convert transcriptome mappings back to genome space genomes Filter on MQ, distance, Cigar string Annotate
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Genome-Wide Identification of mirnas Responsive to Drought in Peach (Prunus persica) by High-Throughput Deep Sequencing
 Genome-Wide Identification of mirnas Responsive to Drought in Peach (Prunus persica) by High-Throughput Deep Sequencing Vahap Eldem 1,2, Ufuk Çelikkol Akçay 3, Esma Ozhuner 1, Yakup Bakır 4, Serkan Uranbey
Genome-Wide Identification of mirnas Responsive to Drought in Peach (Prunus persica) by High-Throughput Deep Sequencing Vahap Eldem 1,2, Ufuk Çelikkol Akçay 3, Esma Ozhuner 1, Yakup Bakır 4, Serkan Uranbey
Research Article Base Composition Characteristics of Mammalian mirnas
 Journal of Nucleic Acids Volume 2013, Article ID 951570, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/951570 Research Article Base Composition Characteristics of Mammalian mirnas Bin Wang Department of Chemistry,
Journal of Nucleic Acids Volume 2013, Article ID 951570, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/951570 Research Article Base Composition Characteristics of Mammalian mirnas Bin Wang Department of Chemistry,
CRS4 Seminar series. Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4. Biomedicine. Bioinformatics. Paolo Uva July 11, 2012
 CRS4 Seminar series Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4 Biomedicine Bioinformatics Paolo Uva July 11, 2012 Partners Pharmaceutical company Fondazione San Raffaele,
CRS4 Seminar series Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4 Biomedicine Bioinformatics Paolo Uva July 11, 2012 Partners Pharmaceutical company Fondazione San Raffaele,
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA AGING, July 2014, Vol. 6 No. 7
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Figure S1. Muscle mass changes in different anatomical regions with age. (A) The TA and gastrocnemius muscle showed a significant loss of weight in aged mice (24 month old) compared to
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Figure S1. Muscle mass changes in different anatomical regions with age. (A) The TA and gastrocnemius muscle showed a significant loss of weight in aged mice (24 month old) compared to
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II
 MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
mirnas involved in the development and differentiation of fertile and sterile flowers in Viburnum macrocephalum f. keteleeri
 Li et al. BMC Genomics (2017) 18:783 DOI 10.1186/s12864-017-4180-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access mirnas involved in the development and differentiation of fertile and sterile flowers in Viburnum macrocephalum
Li et al. BMC Genomics (2017) 18:783 DOI 10.1186/s12864-017-4180-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access mirnas involved in the development and differentiation of fertile and sterile flowers in Viburnum macrocephalum
IDENTIFICATION OF IN SILICO MIRNAS IN FOUR PLANT SPECIES FROM FABACEAE FAMILY
 Original scientific paper 10.7251/AGRENG1803122A UDC633:34+582.736.3]:577.2 IDENTIFICATION OF IN SILICO MIRNAS IN FOUR PLANT SPECIES FROM FABACEAE FAMILY Bihter AVSAR 1*, Danial ESMAEILI ALIABADI 2 1 Sabanci
Original scientific paper 10.7251/AGRENG1803122A UDC633:34+582.736.3]:577.2 IDENTIFICATION OF IN SILICO MIRNAS IN FOUR PLANT SPECIES FROM FABACEAE FAMILY Bihter AVSAR 1*, Danial ESMAEILI ALIABADI 2 1 Sabanci
Genome-wide identification of non-coding RNAs interacted with micrornas in soybean
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE published: 23 December 2014 doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00743 Genome-wide identification of non-coding RNAs interacted with micrornas in soybean Chu-Yu Ye 1,HaoXu 2, Enhui Shen 1,YangLiu
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE published: 23 December 2014 doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00743 Genome-wide identification of non-coding RNAs interacted with micrornas in soybean Chu-Yu Ye 1,HaoXu 2, Enhui Shen 1,YangLiu
Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities
 Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities Gábor Boross,2, Katalin Orosz,2 and Illés J. Farkas 2, Department of Biological Physics,
Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities Gábor Boross,2, Katalin Orosz,2 and Illés J. Farkas 2, Department of Biological Physics,
Open Flower. Juvenile leaf Flowerbud. Carpel 35 NA NA NA NA 61 NA 95 NA NA 15 NA 41 3 NA
 PaxDB Root Juvenile leaf Flowerbud Open Flower Carpel Mature Pollen Silique Seed Sec3a Sec3b Sec5a Sec5b Sec6 Sec8 Sec10a/b Sec15a Sec15b Exo84a Exo84b Exo84c Exo70A1 Exo70A2 Exo70A3 49 47 8 75 104 79
PaxDB Root Juvenile leaf Flowerbud Open Flower Carpel Mature Pollen Silique Seed Sec3a Sec3b Sec5a Sec5b Sec6 Sec8 Sec10a/b Sec15a Sec15b Exo84a Exo84b Exo84c Exo70A1 Exo70A2 Exo70A3 49 47 8 75 104 79
Identification of novel and candidate mirnas in rice by high throughput sequencing. and J-K Zhu,
 Identification of novel and candidate mirnas in rice by high throughput sequencing Ramanjulu Sunkar 1,4*, Xuefeng Zhou 2* Yun Zheng 2, Weixiong Zhang 2, and Jian-Kang Zhu, 3,4 1 Department of Biochemistry
Identification of novel and candidate mirnas in rice by high throughput sequencing Ramanjulu Sunkar 1,4*, Xuefeng Zhou 2* Yun Zheng 2, Weixiong Zhang 2, and Jian-Kang Zhu, 3,4 1 Department of Biochemistry
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf. Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016
 Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016 What does H3K4 methylation do? Plant of interest: Vitis vinifera Culturally important
Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016 What does H3K4 methylation do? Plant of interest: Vitis vinifera Culturally important
Genome-Wide Profiling and Analysis of Arabidopsis sirnas
 Genome-Wide Profiling and Analysis of Arabidopsis sirnas PLoS BIOLOGY Kristin D. Kasschau 1,2, Noah Fahlgren 1,2,3, Elisabeth J. Chapman 1,2,3, Christopher M. Sullivan 1,2, Jason S. Cumbie 1,2, Scott A.
Genome-Wide Profiling and Analysis of Arabidopsis sirnas PLoS BIOLOGY Kristin D. Kasschau 1,2, Noah Fahlgren 1,2,3, Elisabeth J. Chapman 1,2,3, Christopher M. Sullivan 1,2, Jason S. Cumbie 1,2, Scott A.
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
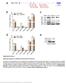 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
ONLINE SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 1 ONLINE SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Small trna-derived RNAs are increased and more abundant than micrornas in chronic hepatitis B and C Sara R. Selitsky 1-3, Jeanette Baran-Gale 1,2, Masao Honda 4, Daisuke
1 ONLINE SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Small trna-derived RNAs are increased and more abundant than micrornas in chronic hepatitis B and C Sara R. Selitsky 1-3, Jeanette Baran-Gale 1,2, Masao Honda 4, Daisuke
Host Double Strand Break Repair Generates HIV-1 Strains Resistant to CRISPR/Cas9
 Host Double Strand Break Repair Generates HIV-1 Strains Resistant to CRISPR/Cas9 Kristine E. Yoder, a * and Ralf Bundschuh b a Department of Molecular Virology, Immunology and Medical Genetics, Center
Host Double Strand Break Repair Generates HIV-1 Strains Resistant to CRISPR/Cas9 Kristine E. Yoder, a * and Ralf Bundschuh b a Department of Molecular Virology, Immunology and Medical Genetics, Center
Santosh Patnaik, MD, PhD! Assistant Member! Department of Thoracic Surgery! Roswell Park Cancer Institute!
 Santosh Patnaik, MD, PhD Assistant Member Department of Thoracic Surgery Roswell Park Cancer Institute MicroRNA biology, techniques and applications History Biogenesis Nomenclature Tissue specificity Mechanisms
Santosh Patnaik, MD, PhD Assistant Member Department of Thoracic Surgery Roswell Park Cancer Institute MicroRNA biology, techniques and applications History Biogenesis Nomenclature Tissue specificity Mechanisms
VirusDetect pipeline - virus detection with small RNA sequencing
 VirusDetect pipeline - virus detection with small RNA sequencing CSC webinar 16.1.2018 Eija Korpelainen, Kimmo Mattila, Maria Lehtivaara Big thanks to Jan Kreuze and Jari Valkonen! Outline Small interfering
VirusDetect pipeline - virus detection with small RNA sequencing CSC webinar 16.1.2018 Eija Korpelainen, Kimmo Mattila, Maria Lehtivaara Big thanks to Jan Kreuze and Jari Valkonen! Outline Small interfering
Small RNA Sequencing. Project Workflow. Service Description. Sequencing Service Specification BGISEQ-500 SERVICE OVERVIEW SAMPLE PREPARATION
 BGISEQ-500 SERVICE OVERVIEW Small RNA Sequencing Service Description Small RNAs are a type of non-coding RNA (ncrna) molecules that are less than 200nt in length. They are often involved in gene silencing
BGISEQ-500 SERVICE OVERVIEW Small RNA Sequencing Service Description Small RNAs are a type of non-coding RNA (ncrna) molecules that are less than 200nt in length. They are often involved in gene silencing
RNA-seq Introduction
 RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
MODULE 4: SPLICING. Removal of introns from messenger RNA by splicing
 Last update: 05/10/2017 MODULE 4: SPLICING Lesson Plan: Title MEG LAAKSO Removal of introns from messenger RNA by splicing Objectives Identify splice donor and acceptor sites that are best supported by
Last update: 05/10/2017 MODULE 4: SPLICING Lesson Plan: Title MEG LAAKSO Removal of introns from messenger RNA by splicing Objectives Identify splice donor and acceptor sites that are best supported by
STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells
 CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
Genome-Wide Identification and Comparative Analysis of Conserved and Novel MicroRNAs in Grafted Watermelon by High-Throughput Sequencing
 Genome-Wide Identification and Comparative Analysis of Conserved and Novel MicroRNAs in Grafted Watermelon by High-Throughput Sequencing Na Liu 1,2, Jinghua Yang 1,2, Shaogui Guo 3, Yong Xu 3 *, Mingfang
Genome-Wide Identification and Comparative Analysis of Conserved and Novel MicroRNAs in Grafted Watermelon by High-Throughput Sequencing Na Liu 1,2, Jinghua Yang 1,2, Shaogui Guo 3, Yong Xu 3 *, Mingfang
Figure S2. Distribution of acgh probes on all ten chromosomes of the RIL M0022
 96 APPENDIX B. Supporting Information for chapter 4 "changes in genome content generated via segregation of non-allelic homologs" Figure S1. Potential de novo CNV probes and sizes of apparently de novo
96 APPENDIX B. Supporting Information for chapter 4 "changes in genome content generated via segregation of non-allelic homologs" Figure S1. Potential de novo CNV probes and sizes of apparently de novo
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
Dicer-2 Processes Diverse Viral RNA Species
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Biology) Department of Biology 2-12-2013 Dicer-2 Processes Diverse Viral RNA Species Leah R Sabin University of Pennsylvania Qi Zheng University
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Biology) Department of Biology 2-12-2013 Dicer-2 Processes Diverse Viral RNA Species Leah R Sabin University of Pennsylvania Qi Zheng University
MicroRNAs and Cancer
 MicroRNAs and Cancer MicroRNAs are an abundant class of small (20-25 nucleotides) non-protein coding RNAs that function as negative gene regulators. The human genome contains up to 1000 micrornas which
MicroRNAs and Cancer MicroRNAs are an abundant class of small (20-25 nucleotides) non-protein coding RNAs that function as negative gene regulators. The human genome contains up to 1000 micrornas which
Variant Classification. Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc.
 Variant Classification Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc. Overview Sequencing pipelines are able to identify rare variants not found in catalogs such as dbsnp. As a result, variants in these datasets
Variant Classification Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc. Overview Sequencing pipelines are able to identify rare variants not found in catalogs such as dbsnp. As a result, variants in these datasets
Cloning and characterization of small RNAs from Medicago truncatula reveals four novel legume-specific microrna families
 Research Cloning and characterization of small RNAs from Blackwell Oxford, NPH New 0028-646X 1469-8137 2915 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02915.x June 085??? 98??? Original XXThe Phytologist Authors UK Article
Research Cloning and characterization of small RNAs from Blackwell Oxford, NPH New 0028-646X 1469-8137 2915 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02915.x June 085??? 98??? Original XXThe Phytologist Authors UK Article
Criteria for Annotation of Plant MicroRNAs
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 20: 3186 3190, December 2008, www.plantcell.org ª 2008 American Society of Plant Biologists Criteria for Annotation of Plant MicroRNAs Blake C. Meyers, a,1 Michael J. Axtell, b,1 Bonnie
The Plant Cell, Vol. 20: 3186 3190, December 2008, www.plantcell.org ª 2008 American Society of Plant Biologists Criteria for Annotation of Plant MicroRNAs Blake C. Meyers, a,1 Michael J. Axtell, b,1 Bonnie
Figure S1. Analysis of endo-sirna targets in different microarray datasets. The
 Supplemental Figures: Figure S1. Analysis of endo-sirna targets in different microarray datasets. The percentage of each array dataset that were predicted endo-sirna targets according to the Ambros dataset
Supplemental Figures: Figure S1. Analysis of endo-sirna targets in different microarray datasets. The percentage of each array dataset that were predicted endo-sirna targets according to the Ambros dataset
Identifying mirnas in RNA viruses
 1 / 13 Identifying mirnas in RNA viruses Kevin Lamkiewicz Friedrich Schiller Universität Jena 16.02.2017 32nd TBI Winterseminar Bled 2 / 13 mirnas and their function U C A C A G G U C A A G C G U U G G
1 / 13 Identifying mirnas in RNA viruses Kevin Lamkiewicz Friedrich Schiller Universität Jena 16.02.2017 32nd TBI Winterseminar Bled 2 / 13 mirnas and their function U C A C A G G U C A A G C G U U G G
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins.
 Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4439
 Figure S1. Overview of the variant calling and verification process. This figure expands on Fig. 1c with details of verified variants identification in 547 additional validation samples. Somatic variants
Figure S1. Overview of the variant calling and verification process. This figure expands on Fig. 1c with details of verified variants identification in 547 additional validation samples. Somatic variants
Arabidopsis thaliana small RNA Sequencing. Report
 Arabidopsis thaliana small RNA Sequencing Report September 2015 Project Information Client Name Client Company / Institution Macrogen Order Number Order ID Species Arabidopsis thaliana Reference UCSC hg19
Arabidopsis thaliana small RNA Sequencing Report September 2015 Project Information Client Name Client Company / Institution Macrogen Order Number Order ID Species Arabidopsis thaliana Reference UCSC hg19
MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome
 Supplementary Information: MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome Jianrong Wang, Cristina Vicente-García, Davide Seruggia, Eduardo Moltó, Ana Fernandez- Miñán, Ana Neto, Elbert
Supplementary Information: MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome Jianrong Wang, Cristina Vicente-García, Davide Seruggia, Eduardo Moltó, Ana Fernandez- Miñán, Ana Neto, Elbert
Evidence for the biogenesis of more than 1,000 novel human micrornas
 Friedländer et al. Genome Biology 2014, 15:R57 RESEARCH Open Access Evidence for the biogenesis of more than 1,000 novel human micrornas Marc R Friedländer 1,2,3,4*, Esther Lizano 1,2,3,4, Anna JS Houben
Friedländer et al. Genome Biology 2014, 15:R57 RESEARCH Open Access Evidence for the biogenesis of more than 1,000 novel human micrornas Marc R Friedländer 1,2,3,4*, Esther Lizano 1,2,3,4, Anna JS Houben
Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first
 Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first intron IGLL5 mutation depicting biallelic mutations. Red arrows highlight the presence of out of phase
Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first intron IGLL5 mutation depicting biallelic mutations. Red arrows highlight the presence of out of phase
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Pirna Sequence Variants Associated With Prostate Cancer In African Americans And Caucasians
 Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Public Health Theses School of Public Health January 2015 Pirna Sequence Variants Associated With Prostate Cancer In African
Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Public Health Theses School of Public Health January 2015 Pirna Sequence Variants Associated With Prostate Cancer In African
Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation
 Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation Hang Yu, 1, 2, a) Wei Han, 1, 3, b) Wen Ma, 1, 2 1, 2, 3, c) and Klaus Schulten 1) Beckman
Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation Hang Yu, 1, 2, a) Wei Han, 1, 3, b) Wen Ma, 1, 2 1, 2, 3, c) and Klaus Schulten 1) Beckman
Characterization and comparison of flower bud micrornas from yellow-horn species
 Characterization and comparison of flower bud micrornas from yellow-horn species Y. Ao 1,2 1 Key Laboratory for Silviculture and Conservation, Ministry of Education, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing,
Characterization and comparison of flower bud micrornas from yellow-horn species Y. Ao 1,2 1 Key Laboratory for Silviculture and Conservation, Ministry of Education, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing,
mirna regulation in the early development of barley seed
 Curaba et al. BMC Plant Biology 2012, 12:120 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access mirna regulation in the early development of barley seed Julien Curaba, Andrew Spriggs, Jen Taylor, Zhongyi Li and Chris Helliwell
Curaba et al. BMC Plant Biology 2012, 12:120 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access mirna regulation in the early development of barley seed Julien Curaba, Andrew Spriggs, Jen Taylor, Zhongyi Li and Chris Helliwell
Gene silencing pathways found in the green alga Volvox carteri reveal insights into evolution and origins of small RNA systems in plants
 Dueck et al. BMC Genomics (2016) 17:853 DOI 10.1186/s12864-016-3202-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Gene silencing pathways found in the green alga Volvox carteri reveal insights into evolution and origins
Dueck et al. BMC Genomics (2016) 17:853 DOI 10.1186/s12864-016-3202-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Gene silencing pathways found in the green alga Volvox carteri reveal insights into evolution and origins
Mature microrna identification via the use of a Naive Bayes classifier
 Mature microrna identification via the use of a Naive Bayes classifier Master Thesis Gkirtzou Katerina Computer Science Department University of Crete 13/03/2009 Gkirtzou K. (CSD UOC) Mature microrna identification
Mature microrna identification via the use of a Naive Bayes classifier Master Thesis Gkirtzou Katerina Computer Science Department University of Crete 13/03/2009 Gkirtzou K. (CSD UOC) Mature microrna identification
The Cornucopia of Small RNAs in Plant Genomes
 Rice (2008) 1:52 62 DOI 10.1007/s12284-008-9008-5 REVIEW The Cornucopia of Small RNAs in Plant Genomes Stacey A. Simon & Jixian Zhai & Jia Zeng & Blake C. Meyers Received: 10 June 2008 /Accepted: 3 July
Rice (2008) 1:52 62 DOI 10.1007/s12284-008-9008-5 REVIEW The Cornucopia of Small RNAs in Plant Genomes Stacey A. Simon & Jixian Zhai & Jia Zeng & Blake C. Meyers Received: 10 June 2008 /Accepted: 3 July
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3731
 Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
