Relationship between UV-irradiated HaCaT cell cytokines and Th1/Th2 imbalance
|
|
|
- Harvey Chambers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Relationship between UV-irradiated HaCaT cell cytokines and Th1/Th2 imbalance H.Y. Li 1,2, F.R. Zhang 1,3 and D.Q. Deng 4 1 Shandong Provincial Hospital for Skin Diseases, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China 2 Department of Dermatology, The Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou, Shandong, China 3 Shandong Provincial Institute of Dermatology and Venereology, Jinan, Shandong, China 4 Department of Dermatology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, Yunnan, China Corresponding author: D.Q. Deng lihaiying_l@163.com Genet. Mol. Res. 14 (3): (2015) Received September 30, 2014 Accepted April 28, 2015 Published July 17, 2015 DOI ABSTRACT. We have previously found that an imbalance of Tc1/Tc2 T cell subtypes in vivo impacts the development of photodermatitis. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between cytokines derived from keratinocytes exposure to UV and the imbalance of Th subgroups. We used different doses of UVA and UVB to irradiate HaCaT cells. Twelve hours after irradiation, the expression of IL- 10R, IL-4R, IL-12R, and IFN-γR proteins was observed using the S-P method, and the percentage of positive cells calculated. Protein levels of the respective ligands in the supernatant was measured by ELISA. Our results showed low levels of expression of the interrogated proteins in unirradiated HaCaT cells, and little or no expression could be detected in the supernatant. Little or no expression was also observed for IL-12R
2 UV-irradiated HaCaT cell cytokines and Th1/Th and IFN-γR 12 h after UVA or UVB irradiation. However, the expression of IL-10R and IL-10 was upregulated 12 h following UVB irradiation, as well as following lower dose UVA irradiation. In contrast, higher dose UVA decreased the expression of IL-10R and IL-10. The expression of IL-4R was increased following high doses of UVA and UVB irradiation, whereas no expression was observed after lower dose UV exposure. There was no change in IL-4 secretion into the supernatant. Our results demonstrate that the effects of UV exposure on keratinocyte-derived cytokines are different according to the doses of irradiation and the types of cytokines, and suggest that keratinocyte-derived cytokines after UV exposure might cause an imbalance of Th1/Th2. Key words: Irradiation; HaCaT cells; Cytokines; Th cells INTRODUCTION The immune system of the skin is constituted of various immunocytes; among these, the keratinocyte is of particular importance, as it can secrete various cytokines, thus participating in immunoregulation. Keratinocytes have a primary role in the amplification of skin inflammation during immune-mediated skin diseases. Over the last 10 years, a large number of studies have focused on the effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on keratinocyte-derived cytokines and have reported that the relationship between keratinocyte-derived cytokines and the imbalance of T helper cell subtype (Th1/Th2) ratio had some impact on the occurrence and development of certain skin diseases (Mozzanica et al., 1995; Teraki et al., 2000). Our previous research in vivo indicated that the infiltrating monocytes isolated from patient epidermis and dermis were primarily composed of CD8+ T cells expressing IFN-γ and IL-12 receptors. At the same time, the IFN-γ and IL-12 levels detected in patient serum were higher compared to those of normal controls, which indicated that the imbalance of the T cell subtype (Tc1/Tc2) ratio had some impact on the development of photo-dermatitis. Based on our previous study, we used UVA and UVB to irradiate human immortal epidermis (HaCaT) cells, and then detected the expression of IL-10R, IL-4R, IL-12R, and IFN-γR in the cells and the secretion of IL-10, IL-4, IL-12, and IFN-γ in the serum 12 h after irradiation to investigate the impact of UV irradiation on keratinocyte-derived cytokines and the relevance of the cytokines to the imbalance of T cell subgroups. These studies will provide theoretical and experimental evidence for further research into the pathogenesis of photo-dermatitis. MATERIAL AND METHODS Radiation sources In this study, we utilized ultraviolet phototherapy apparatus models SS-01 (spectrum nm, peak 370 nm) and SS-01B (spectrum 312 ± 10 nm) (Sigmar High-tech Limited, Shanghai, China). By fixing the irradiation distance, the irradiation intensity was also fixed. We could obtain different irradiation doses according to different irradiation times. In this study, we irradiated cells with UVA for 62 and 128 s, and the corresponding irradiation doses
3 H.Y. Li et al were 2.00 and 4.00 J/cm 2, respectively. Similarly, the irradiation times for UVB were 10, 20, and 40 s, and the corresponding irradiation doses were 30.00, 60.00, and mj/cm 2. Before irradiation, the cell culture medium (Dulbecco s modified Eagle s medium, DMEM) was replaced with phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Cell lines, antibodies, and reagents The HaCaT cell line was purchased from China Type Culture Conserve Center at Wuhan College, Wuhan, China. For immunohistochemical staining, rabbit polyclonal antihuman IL-10R (SC-984), IL-12Rβ1 (SC-658), IL-4R (SC-684), and IFN-γR (SC-700) antibodies were used (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA). ELISA kits for IL-10, IL-12, IL-4, and IFN-γ were also used (JingMei Biotechnology Company, Beijing, China). Cell culture medium, supplements, and fetal bovine serum (FBS) were obtained from GIBCO (Gaithersburg, MD, USA) In vitro UV irradiation of HaCaT cells The HaCaT cell line was grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS. When the desired cell number was reached, the cells were dissociated and the suspensions were added to 40-mm culture dishes at 2.5 x 10 5 /ml in 2 ml DMEM with 10% FBS and cultured at 37 C, 5% CO 2. When 70-75% confluence was achieved, the medium was removed and the cells were rinsed three times with PBS and overlain with 0.1 ml PBS. The HaCaT cells were irradiated with different doses of UVA and UVB. After irradiation, the cells were cultured in DMEM with 10% FBS at 37 C with 5% CO 2. At 12 h following irradiation, the supernatant fluid was removed and centrifuged for 10 min at 4000 rpm, and stored at -70 C for later use. The cells were dissociated and spotted onto slides. The slides were dehydrated in 95% alcohol, rinsed with PBS, and air dried at room temperature. The cells on the slides were fixed with 4 C acetone for 10 min for later use. Immunohistochemistry In preparation for immunohistochemical analysis, fixed sample slides were rinsed with PBS and dried at room temperature. They were treated with endogenous peroxidase inhibitor for 10 min to quench endogenous peroxidase activity, and rinsed three times with PBS for 3 min each. Slides were subsequently treated with normal animal serum for 10 min, following which the serum was dispelled without additional rinsing. The slides were incubated with anti-il-10r, anti-il-12r, anti-il-4r, and anti-ifn-γr separately for 2 h at room temperature, and then rinsed with three times with PBS for 3 min each. Biotin-labeled secondary- Abs were applied for 10 min, and then the slides were subjected to another PBS rinse series. Samples were treated with streptavidin-peroxidase at room temperature for 10 min (Maixin Biotechnology Development Company in Fuzhou), followed by PBS rinses as before. Staining was performed with DAB for 10 min. Slides were re-stained with hematoxylin for 2 min, differentiated with hydrochloric acid-alcohol for 2 s, and rinsed with water. The slides were covered with neutral gum for preservation and visualization. For the negative controls, primary Abs were omitted and replaced with PBS.
4 UV-irradiated HaCaT cell cytokines and Th1/Th ELISA UV induced IL-10, IL-12, IL-4, and IFN-γ were assayed using ELISA. According to the manufacturer protocol (JingMei Biotechnology Company). The plates were analyzed in an ELISA microplate reader (BIO-RAD model 550, Berkeley, CA, USA). DMEM was used as the zero standard. Cultures were conducted in triplicate for each condition. Ascertainment of results For immunohistochemistry, brown-yellow staining was taken as positive. To ascertain the percentage of positive cells, we counted three high-power fields per slide and conducted the same process for each condition. For ELISA, results were given as pg/ml directly from the ELISA microplate reader. Statistical analysis Comparisons were done by one-way ANOVA if the values were normally distributed and with homogenous variance. If not, the Kruskal-Wallis rank test was used. P value < 0.05 was considered to reflect statistical significance, and then the Mann-Whitney rank test was used to compare the difference between the experimental and control groups. RESULTS Morphological changes The cell connections were loosened after UV irradiation. Refraction was weakened. Some lethality was observed. Changes in groups receiving higher doses of UV (UVA 4.00 J/cm 2, UVB mj/cm 2 ) were more distinct (Figures 1 and 2). Figure 1. Twelve hours after UVA 4.00 J/cm 2 irradiation.
5 H.Y. Li et al Figure 2. Twelve hours after UVB mj/cm 2 irradiation. Immunohistochemistry Twelve hours after UV irradiation, most HaCaT cell membranes and/or plasma stained positive by immunohistochemical assessment. The expression of IL-12R and IFN-γR was feebly positive (Figures 3A-E and 4A-E). The percentages of positive cells for these markers are listed in Table 1. HaCaT cell membranes and/or plasma were stained slightly brown-yellow in the non-irradiated group, and the expression of IL-4R was weakly positive. At 12 h after UV irradiation, the expression of IL-4R was intensified, especially in the groups receiving higher doses of UV irradiation (UVA 4.00 J/cm 2, UVB mj/cm 2 (Figure 5A-E). The expression of IL-10R was strongly positive after UVB and 2.00 J/cm 2 UVA irradiation, and weakly positive expression was seen in the 4.00 J/cm 2 UVA irradiation group (Figure 6A-E). The percentages of positive cells for these markers are listed in Table 2. Figure 3. IFN-γR (S-P method x 400 times). Representative images are shown for each group: A. UVA 2.00 J/cm 2 ; B. UVA 4.00 J/cm 2 ; C. UVB mj/cm 2 ; D. UVB mj/cm 2 ; and E. UVB mj/cm 2. Figure 4. IL-12R (S-P method x 400 times). Representative images are shown for each group: A. UVA 2.00 J/cm 2 ; B. UVA 4.00 J/cm 2 ; C. UVB mj/cm 2 ; D. UVB mj/cm 2 ; and E. UVB mj/cm 2.
6 UV-irradiated HaCaT cell cytokines and Th1/Th Table 1. Percentages of IFN-γR and IL-12R positive HaCaT cells 12 h after UV irradiation. Irradiation group IFN-γR IL-12R Means ± SD P value Means ± SD P value UVA 2 J/cm ± ± UVA 4 J/cm ± ± UVB 30 mj/cm ± ± UVB 60 mj/cm ± ± UVB 120 mj/cm ± ± N group ± ± P > 0.05: no significant difference between trial and control groups. Figure 5. IL-4R (S-P immunohistochemical method x 400 times). Representative images are shown for each group: A. UVA 2.00 J/cm 2 ; B. UVA 4.00 J/cm 2 ; C. UVB mj/cm 2 ; D. UVB mj/cm 2 ; and E. UVB mj/cm 2. Figure 6. IL-10R (S-P immunohistochemical method x 400 times). Representative images are shown for each group: A. UVA 2.00 J/cm 2 ; B. UVA 4.00 J/cm 2 ; C. UVB mj/cm 2 ; D. UVB mj/cm 2 ; and E. UVB mj/cm 2. Table 2. Percentages of IL-4R and IL-10R positive cells in HaCaT cells 12 h after UV irradiation. Irradiation group IL-4R IL-10R*** ELISA Means ± SD P value Means ± SD P value UVA 2 J/cm ± ± UVA 4 J/cm ± 6.073* 0.020* ± UVB 30 mj/cm ± ± UVB 60 mj/cm ± ± UVB 120 mj/cm ± 4.102** 0.020** ± N group ± ± *P = 0.02 < 0.05, significant difference between UVA 4 J/cm 2 and non-irradiated groups. **P = 0.02 < 0.05, significant difference between UVB 120 mj/cm 2 and non-irradiated groups. ***Using the rank test, significant difference between the trial and control groups. There was no or little secreted IL-12 and IFN-γ in the supernatant at 12 h after UV irradiation. The Kruskal-Wallis rank test was used to compare the secretion of IL-12 and IFN-γ. c 2 values were and 4.697, respectively, and P values were and 0.454, respectively. There was no significant difference in the total distribution among the trial and control groups. Levels of secreted IL-4 and IL-10 at 12 h after UV irradiation are shown in Table 3.
7 H.Y. Li et al Table 3. Concentrations of IL-10 and IL-4 in the supernatant at 12 h after UV irradiation (pg/ml). Irradiation group IL-4* IL-10 Means ± S Means ± S UVA 2 J/cm ± ± UVA 4 J/cm ± ± 3.007** UVB 30 mj/cm ± ± 0.003*** UVB 60 mj/cm ± ± 2.605** UVB 120 mj/cm ± ± 2.605*** N group ± ± *Using the rank test, c 2 = 5.532, P = 0.352; no significant difference among the total distribution. **P = < 0.05; significant difference between UVA4 J/cm 2 and non-irradiated groups. ***P = < 0.05; significant difference between UVB30 mj/cm 2 and non-irradiated groups. DISCUSSION Photo-dermatitis is a spectrum disease caused by exposure to sunlight or other rays on the skin. Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) and chronic actinic dermatitis are the most common manifestations and are characterized by an intense infiltrate of monocytes in the dermis. The pathogenesis of these diseases is not clear. Recently, researchers have posited the hypothesis that delayed type hypersensitivity (DTH) is caused by skin induction exposure to sunlight. The majority of the human epidermis, approximately 80%, is composed of keratinocytes. These can secrete various cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and TNF-γ among others, and thus participate in immunoregulation. Several studies have reported that keratinocyte-derived cytokines following exposure to UV lead to pathophysiological changes by affecting the balance of Th1/Th2; however, most studies have focused on the immunosuppression aspect of cytokine production (Schmitt et al., 2000; Aubin, 2003). The study regarding diseases related to the imbalance of Th1/Th2 focused primarily on atopic dermatitis (Th1 type skin disease) and psoriasis (Th2 type skin disease). The relationship between keratinocyte-derived cytokines following exposure to UV and the Th1/Th2 imbalance has not been reported. Comparatively, our previous studies have suggested that the development of photo-dermatitis might be related to the excess expression of Tc1 and the suppression of Tc2 expression (Chen et al., 2005). We used UVA and UVB to irradiate HaCaT cells to investigate the effects of UV irradiation on keratinocyte-derived cytokines and the relationship between cytokines and the imbalance of Th1/Th2, and to provide experimental and theoretical evidence for future studies. The HaCaT cell line consists of transfected human epidermal cells, and has the differentiation characteristics of basal layer cells. Mee et al. (2000) suggested that the effect of culture condition should be considered when discussing the cell biology in vitro. Our experiments indicated that if HaCaT cells were seeded at 2 x 10 5 /ml, when the cells reached 70% confluence (the time at which they would be exposed to UV), 12 h later the cells of the non-irradiated group would have reached a confluence in excess of 95%. Therefore, we examined the effect of UV irradiation on keratinocyte-derived cytokines at 12 h after irradiation. Different effects of UVA and UVB on HaCaT cells UV has been shown without question to be the important inducer in the pathogenesis of photo-dermatitis. Previous studies regarding photo-dermatitis have focused primarily on the effects of UVB on keratinocyte-derived immunomodulating cytokines and adhesive mol-
8 UV-irradiated HaCaT cell cytokines and Th1/Th ecules (Grundmann et al., 2001). Although the biological activity of UVA is not as strong as that of UVB, it has a higher ratio in sunlight and deeper penetration. Accordingly, researchers have begun to consider the effects of UVA on photo-dermatitis (Krutmann, 2000). Our results indicated that the effects on keratinocyte-derived cytokines after UV exposure differed according to the dose of irradiation and the type of cytokines analyzed. For Th1s, the effect of 2.00 J/cm 2 UVA on HaCaT derived IL-10 was similar to that of UVB whereas the opposite effect was seen for 4.00 J/cm 2 UVA irradiation; the effect of UVA on HaCaT-derived IL-4 was similar to that of UVB. For Th2-type cytokines, the effects of UVA and UVB were similar. Current research results considering the photobiology of UVA are not entirely consistent, and a few are incompatible. Some scholars think that UVA might strengthen UVB. Serre et al. (1997) reported that covering the skin with sunscreen could adversely affect the contact hypersensitivity after UV exposure, and they therefore conjectured that UVA might cooperate with UVB. On the other hand, Kondo and Jimbow (1998) reported that keratinocytes could produce IL-12 after exposure to UVA, and suggested that IL-12 might inhibit the immunological suppression induced by exposure to UVB characterized by production of IL-10. Our results might be considered to reflect the former conclusions from some perspectives. Our analysis showed that different effects were produced in the course of keratinocyte-derived cytokine release, according to the different doses and the different composition of UV applied. Kondo and Jimbow (1998) also thought that the different UV composition primarily determined the balance of cytokine production between Th1 type and Th2 types. Effect of UV on keratinocyte-derived Th1 type cytokines Our previous research indicated that the infiltrating T cells in lesions from photodermatitis patients primarily expressed IL-12R and IFN-γR and that the secretion of IL-12 and IFN-γ was higher than that of controls. Based on this result, to clarify the pathobiological change of keratinocytes after exposure to UV irradiation, we detected the effect of UV on HaCaT cell-derived Th1-type cytokines IL-12 and IFN-γ. Our results indicated that there was no or little expression of IL-12R and IFN-γR in the HaCaT cells and the same result was seen in the supernatant 12 h after UVA and UVB irradiation. Although in our experiment we could not detect the secretion of IL-12 and IFN-γ, this did not exclude the possibility of other mechanisms preventing secretion of these cytokines, or that they might have been stored in the cells. In addition, the keratinocyte itself might secrete many kinds of cytokines in vivo; in turn they are also the target cells of different immunomodulators serving various functions toward influencing the cytokines and modulators secreted by themselves and other cells, allowing them to participate in the process of immunomodulation (Maas-Szabowski et al., 2003) Under our experimental conditions, we used HaCaT cells as the research objective, which could deviate the entire immune environment in vivo, and which therefore might cause it to not be directly applicable to understanding the biology behavior of keratinocytes (Tsuda et al., 2003). Effect of UV on keratinocyte-derived Th2 type cytokines On the basis of the previous conclusion, we detected the effect of UV on the HaCaT cell-derived Th1 type cytokines IL-4 and IL-10. Our results indicated that prior to irradiation, only weakly positive IL-10R expression and slight spontaneously secreted IL-10 could be detected, whereas, and with UVB irradiation, an up-regulation of both IL-10R and IL-10 could
9 H.Y. Li et al be detected 12 h after irradiation. A similar finding was observed in following lower dose UVA irradiation. Some studies have demonstrated that UV exposure can induce a systematic immunosuppression reaction, and that this reaction is related to keratinocyte-derived IL-10 (Rivas and Ullrich, 1992). It indicated that without stimulation, keratinocytes spontaneously secrete minute amounts of IL-10, and that the secretion is up-regulated after stimulation such as UV irradiation or allergic contact, and IL-10 negatively acts on the local immunoreaction. The observation that IL-10 gene knock-out mice are usually hypersensitive to allergens indicates that keratinocyte-derived IL-10 has some effect on sustaining the stabilization of the skin immune-environment (Rivas and Ullrich, 1992). IL-10 up-regulation can inhibit the occurrence of DTH and this inhibition is related to photo-carcinogenesis; this finding is consistent with our experimental results. Furthermore, our experiment indicates that keratinocytes might self-regulate their expression of IL-10R and IL-10. We suggest that the effects of the culture condition itself on keratinocytes should not be excluded when discussing the biology of keratinocytes in vitro. In addition, the lamp-housing of UV equipment and the doses of irradiation also impact the experimental results, which might be an important aspect to consider in the former, differing sets of results. IL-4 is another important Th2 cytokine. Our results suggested that the expression of IL-4R in HaCaT cells was up-regulated by cells exposed to higher dose of UVA and UVB; however, there was no change in IL-4 secretion into the supernatant and no IL-4R expression could be detected after lower dose UV exposure. It is generally thought that IL-4 is produced mainly from other epidermal or infiltrating inflammatory cells. However, keratinocytes express IL-4 mrna and protein, and act as the target cells of IL-4 (Xiao et al., 2003). Our results are consistent with this conclusion. In conclusion, Th1 and Th2 cytokines function oppositely in immunomodulation. In a pathological situation, keratinocytes up-regulate the local Th1 or Th2 in the skin by selectively secreting different functional cytokines. An imbalance of Th1/Th2 occurs in skin inflammatory disease. Our results suggest that HaCaT cells give priority to expression of Th2 cytokines at 12 h after UVB and 2.00 J/cm 2 UVA irradiation, up-regulate IL-4 and downregulate IL-10, and that there is no significant impact on Th1 cytokines after 4.00 J/cm 2 UVA irradiation. This model seems to be the opposite of our research results obtained in vivo. Our former result (Li et al., 2007) suggests that the secretion of IL-12 and IFN-γ in patient serum is higher than that in the normal control, and that there is no significant change in the secretion of IL-4 and IL-10. Our analysis of the result shows that there are all positive expression of IL-12R, IFN-γR, IL-10R, and IL-4R in HaCaT cells regardless of UV irradiation exposure, suggesting that keratinocytes play an important role in local immunity. While different UV compositions have different consequences for the various keratinocyte-derived cytokines, the different composition and doses of UV might have the net effect of balancing out the Th1/ Th2 cytokines. Our previous result was obtained in vivo and the research was done using infiltrating T lymphocytes in the dermis. This study used the HaCaT cell line and further discusses the pathogenesis of photo-dermatitis from the point of view of keratinocytes. These two phenomena, keratinocyte-mediated Th2 reaction following UV irradiation in vitro and lymphocyte-mediated Th1 reaction in vivo, might be spatially distinct, but might perhaps reflect a concerted result on the whole. We can assume that following UV irradiation, if priority was given to the keratinocyte-mediated Th2 reaction, it would induce immunosuppression which might lead to photo-carcinogenesis; on the other hand, if priority was given to the lymphocytemediated Th1 reaction, it would induces DTH which might lead to photo-dermatitis. These consequences are not contradictory. The present report about keratinocyte-derived cytokines
10 UV-irradiated HaCaT cell cytokines and Th1/Th is primarily based on results in vitro with the HaCaT cell line or on keratinocytes cultured in vitro. The conclusion drawn from in vitro studies might be different from that drawn from in vivo studies because of the difference of experimental conditions and the factors that affect each condition. Further study would be needed to determine whether this supposition is correct. Our study investigated the relationship between cytokines derived from keratinocyte exposure to UV radiation and an imbalance of T helper cell subgroups. These results could provide experimental support for further studies on the pathogenesis of photo-dermatitis. Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. REFERENCES Aubin F (2003). Mechanisms involved in ultraviolet light-induced immunosuppression. Eur. J. Dermatol. 13: Chen H, Deng DQ, Zhou XH, Fan YY, et al. (2005). Imbalance of Tc cell in the pathogenesis of chronic actinic dermatitis. Chin. J. Dermatol. 38: Grundmann JU, Böckelmann R, Bonnekoh B and Gollnick HP (2001). UV erythema reducing capacity of mizolastine compared to acetylsalicylic acid or both combined in comparison to indomethacin. Photochem. Photobiol. 74: Kondo S and Jimbow K (1998). Dose-dependent induction of IL-12 but not IL-10 from human keratinocytes after exposure to ultraviolet light A. J. Cell Physiol. 177: Krutmann J (2000). Ultraviolet A radiation-induced biological effects in human skin: relevance for photoaging and photodermatosis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 23: S22-S26. Li HY, Deng DQ, Wang JH and Fan YJ (2007). Effects of UV on IL-12 and IFN-γ derived from HaCaT cells. China J. Lepr. Skin Dis. 23: 1-3. Maas-Szabowski N, Stärker A and Fusenig NE (2003). Epidermal tissue regeneration and stromal interaction in HaCaT cells is initiated by TGF-alpha. J. Cell Sci. 116: Mee JB, Alam Y and Groves RW (2000). Human keratinocytes constitutively produce but do not process interleukin-18. Br. J. Dermatol. 143: Mozzanica N, Cattaneo A, Trabattoni D, Finzi AF, et al. (1995). Production of type 1 and type 2 cytokines by peripheral blood mononuclear cells of psoriatic patients. Immunology 86: Rivas JM and Ullrich SE (1992). Systemic suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity by supernatants from UVirradiated keratinocytes. An essential role for keratinocyte-derived IL-10. J. Immunol. 149: Schmitt DA, Walterscheid JP and Ullrich SE (2000). Reversal of ultraviolet radiation-induced immune suppression by recombinant interleukin-12: suppression of cytokine production. Immunology 101: Serre I, Cano JP, Picot MC, Meynadier J, et al. (1997). Immunosuppression induced by acute solar-simulated ultraviolet exposure with a sun protection factor of 15 and high UVA protection. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 37: Teraki Y, Hotta T and Shiohara T (2000). Increased circulating skin homing cutaneous lymphocyte associated antigen (CLA)+ type 2 cytokine producing cells, and decreased CLA+ type 1 cytokine producing cells in atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 143: Tsuda T, Tohyama M, Yamasaki K, Shirakata Y, et al. (2003). Lack of evidence for TARC/CCL17 production by normal human keratinocytes in vitro. J. Dermatol. Sci. 3: Xiao T, Kagami S, Saeki H, Sugaya M, et al. (2003). Both IL-4 and IL-13 inhibit the TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma enhanced MDC production in a human keratinocyte cell line, HaCaT cells. J. Dermatol. Sci. 31:
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY
 THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY Joanna Narbutt Department of Dermatology Medical University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland Photoimmunosuppression ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION DNA
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY Joanna Narbutt Department of Dermatology Medical University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland Photoimmunosuppression ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION DNA
Repeated Doses of UVR Cause Minor Alteration in Cytokine Serum Levels in Humans
 Mediators of Inflammation 2005:5 (2005) 298 303 PII: S0962935105507014 DOI: 10.1155/MI.2005.298 RESEARCH COMMUNICATION Repeated Doses of UVR Cause Minor Alteration in Cytokine Serum Levels in Humans Joanna
Mediators of Inflammation 2005:5 (2005) 298 303 PII: S0962935105507014 DOI: 10.1155/MI.2005.298 RESEARCH COMMUNICATION Repeated Doses of UVR Cause Minor Alteration in Cytokine Serum Levels in Humans Joanna
Skin Photoallergy Test 皮肤光变态反应试验方法. China Food and Drug Administration. Translated by Chemlinked
 Skin Photoallergy Test 皮肤光变态反应试验方法 China Food and Drug Administration Translated by Chemlinked Date of Publication: Aug. 15, 2017 Date of Implementation:Aug. 15, 2017 Disclaimer This is an unofficial document
Skin Photoallergy Test 皮肤光变态反应试验方法 China Food and Drug Administration Translated by Chemlinked Date of Publication: Aug. 15, 2017 Date of Implementation:Aug. 15, 2017 Disclaimer This is an unofficial document
Mechanism of Macrophage-Derived Chemokine/CCL22 Production by HaCaT Keratinocytes
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 27, No. 2, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2015.27.2.152 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mechanism of Macrophage-Derived Chemokine/CCL22 Production by HaCaT Keratinocytes Chizuko Yano, Hidehisa Saeki
Ann Dermatol Vol. 27, No. 2, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2015.27.2.152 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mechanism of Macrophage-Derived Chemokine/CCL22 Production by HaCaT Keratinocytes Chizuko Yano, Hidehisa Saeki
Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory, T-cell mediated
 Narrowband UVB Treatment Increases Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels in Patients With Chronic Plaque Psoriasis Seyamak Saleky, MD; Işıl Bulur, MD; Zeynep Nurhan Saraçoğlu, MD PRACTICE POINTS The 25-hydroxyvitamin
Narrowband UVB Treatment Increases Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels in Patients With Chronic Plaque Psoriasis Seyamak Saleky, MD; Işıl Bulur, MD; Zeynep Nurhan Saraçoğlu, MD PRACTICE POINTS The 25-hydroxyvitamin
CHAPTER 2. Is severity eruption assessment possible? in polymorphous light
 CHAPTER 2 Is severity assessment in polymorphous light Is severity eruption assessment possible? in polymorphous light Ines Schornagel, eruption Kees Guikers, possible? Huib van Weelden, Carla Bruijnzeel-Koomen
CHAPTER 2 Is severity assessment in polymorphous light Is severity eruption assessment possible? in polymorphous light Ines Schornagel, eruption Kees Guikers, possible? Huib van Weelden, Carla Bruijnzeel-Koomen
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients
 Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
SUN HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES
 SUN HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES CORRELATION BETWEEN VITAMIN D, UVB, AND MS Researchers are finding a strong association between vitamin D levels, UVB exposure and multiple sclerosis (MS). According to the Mayo
SUN HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES CORRELATION BETWEEN VITAMIN D, UVB, AND MS Researchers are finding a strong association between vitamin D levels, UVB exposure and multiple sclerosis (MS). According to the Mayo
Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL) from the field to the cellular and the subcellular levels
 Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL) from the field to the cellular and the subcellular levels A M EL Hassan Institute of Endemic Diseases University of Khartoum Introduction PKDL is a VL related
Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL) from the field to the cellular and the subcellular levels A M EL Hassan Institute of Endemic Diseases University of Khartoum Introduction PKDL is a VL related
McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells
 Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Radiation-induced Bystander Effect in Immune Response 1
 BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 17, 40-46 (2004) Radiation-induced Bystander Effect in Immune Response 1 SHU-ZHENG LIU 2, SHUN-ZI JIN, AND XIAO-DONG LIU Department of Radiation Biology, Jilin University
BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 17, 40-46 (2004) Radiation-induced Bystander Effect in Immune Response 1 SHU-ZHENG LIU 2, SHUN-ZI JIN, AND XIAO-DONG LIU Department of Radiation Biology, Jilin University
Invited Re vie W. Antinuclear antibody-keratinocyte interactions in photosensitive cutaneous lupus erythematosus
 Histol Histopathol (1 999) 14: 627-633 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Invited Re vie W Antinuclear antibody-keratinocyte interactions in photosensitive cutaneous lupus
Histol Histopathol (1 999) 14: 627-633 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Invited Re vie W Antinuclear antibody-keratinocyte interactions in photosensitive cutaneous lupus
Chloroquine inhibits cell growth and induces cell death in A549 lung cancer cells
 Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 14 (2006) 3218 3222 Chloroquine inhibits cell growth and induces cell death in A549 lung cancer cells Chuandong Fan, a,c Weiwei Wang, a,c Baoxiang Zhao, b, Shangli Zhang
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 14 (2006) 3218 3222 Chloroquine inhibits cell growth and induces cell death in A549 lung cancer cells Chuandong Fan, a,c Weiwei Wang, a,c Baoxiang Zhao, b, Shangli Zhang
Activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) expression is increased in erythema multiforme and is regulated by IFN-c in human keratinocytes
 DOI:1.1111/j.16-625.29.18.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/exd Activating transcription factor 3 () expression is increased in erythema multiforme and is regulated by IFN-c in human keratinocytes Brian P.
DOI:1.1111/j.16-625.29.18.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/exd Activating transcription factor 3 () expression is increased in erythema multiforme and is regulated by IFN-c in human keratinocytes Brian P.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Invest Dermatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 February 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2014 August ; 134(8): 2071 2074. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.141. A possible role for IL-17A in establishing Th2 inflammation
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2014 August ; 134(8): 2071 2074. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.141. A possible role for IL-17A in establishing Th2 inflammation
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy
 Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on
 Supplemental Methods Immunohistochemical Analyses Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on prostatectomy sections obtained post-study. Briefly,
Supplemental Methods Immunohistochemical Analyses Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on prostatectomy sections obtained post-study. Briefly,
DermaPep A530. Multifunctional anti-inflammatory peptide for irritated and sensitive skin. Experience The Magic of Science
 Experience The Magic of Science DermaPep A53 Multifunctional anti-inflammatory peptide for irritated and sensitive skin DermaP ep Experience the magic of science Anti-aging DermaPep A35 DermaPep A42 DermaPep
Experience The Magic of Science DermaPep A53 Multifunctional anti-inflammatory peptide for irritated and sensitive skin DermaP ep Experience the magic of science Anti-aging DermaPep A35 DermaPep A42 DermaPep
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
ab Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
DNA vaccine, peripheral T-cell tolerance modulation 185
 Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia
 Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia YOSHINOBU ASANO, SHOICHIRO SHIBATA, SHINJI KOBAYASHI, SEIICHI OKAMURA, YOSHIYUKI NIHO First Department
Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia YOSHINOBU ASANO, SHOICHIRO SHIBATA, SHINJI KOBAYASHI, SEIICHI OKAMURA, YOSHIYUKI NIHO First Department
Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage
 Trace Nutrients Research 26 : 88 92 (2009) Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage Amy TOMITA, Tomoyo KAJIURA and Shuichi KIMURA Showa
Trace Nutrients Research 26 : 88 92 (2009) Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage Amy TOMITA, Tomoyo KAJIURA and Shuichi KIMURA Showa
Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet
 Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet IL-2 is an interleukin, a type of cytokine immune system signaling molecule. IL-2 is a T cell stimulatory cytokine best known for inducing T cell proliferation, the
Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet IL-2 is an interleukin, a type of cytokine immune system signaling molecule. IL-2 is a T cell stimulatory cytokine best known for inducing T cell proliferation, the
Experience The Magic of Science. DermaPep UL. Multi-functional whitening active. Experience the magic of science
 Experience The Magic of Science Multi-functional whitening active DermaP ep Experience the magic of science Anti-aging DermaPep A35 DermaPep A42 DermaPep A44 DermaPep A53 Whitening DermaPep A35 DermaPep
Experience The Magic of Science Multi-functional whitening active DermaP ep Experience the magic of science Anti-aging DermaPep A35 DermaPep A42 DermaPep A44 DermaPep A53 Whitening DermaPep A35 DermaPep
Measuring PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer Cell Lines with AlphaLISA
 APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Author: Jeanine Hinterneder, PhD PerkinElmer Inc. Hopkinton, MA Measuring PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer Cell Lines with AlphaLISA Introduction In the tumor microenvironment,
APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Author: Jeanine Hinterneder, PhD PerkinElmer Inc. Hopkinton, MA Measuring PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer Cell Lines with AlphaLISA Introduction In the tumor microenvironment,
Summary. Introduction. Materials and methods
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 277 281 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/02/040277+05 $22.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2001.0509, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 277 281 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/02/040277+05 $22.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2001.0509, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA)
 Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet on the Use of Sunbeds Introduction A sunbed, also known as a tanning bed or sun tanning bed, is a device that emits ultraviolet radiation (typically
Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet on the Use of Sunbeds Introduction A sunbed, also known as a tanning bed or sun tanning bed, is a device that emits ultraviolet radiation (typically
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet
 colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human IL5 in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants and urine. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human IL5 in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants and urine. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
Project manager. Dr. Nicola Zerbinati. Therapeutic protocols of monochromatic source 355 nm λ
 Project manager Therapeutic protocols of monochromatic source 355 nm λ INTRODUCTION Artificial ultraviolet rays (UV) such as sunbeds, lamps, solar panels, are used both in the beauty and medical field,
Project manager Therapeutic protocols of monochromatic source 355 nm λ INTRODUCTION Artificial ultraviolet rays (UV) such as sunbeds, lamps, solar panels, are used both in the beauty and medical field,
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, psoriasis
 IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Goedkoop, A.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Goedkoop, A.
A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes
 A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes Hiroaki Mizukami, Takeharu Kanazawa, Takashi Okada, and Keiya Ozawa Division of Genetic Therapeutics, Center for Molecular Medicine,
A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes Hiroaki Mizukami, Takeharu Kanazawa, Takashi Okada, and Keiya Ozawa Division of Genetic Therapeutics, Center for Molecular Medicine,
Inhibition of cisplatin-resistant tumor cells on activated CD4+ T cells in ovarian cancer and its mechanism
 Pharmaceutical Inhibition of cisplatin-resistant tumor cells on activated CD4+ T cells in ovarian cancer and its mechanism Objective: To investigate the inhibition of cisplatin-resistant tumor cells on
Pharmaceutical Inhibition of cisplatin-resistant tumor cells on activated CD4+ T cells in ovarian cancer and its mechanism Objective: To investigate the inhibition of cisplatin-resistant tumor cells on
Sun Safety and Skin Cancer Prevention. Maryland Skin Cancer Prevention Program
 Sun Safety and Skin Cancer Prevention Maryland Skin Cancer Prevention Program Do You Know the Facts About Skin Cancer? Skin cancer is the most common cancer but also the most preventable Childhood sunburn
Sun Safety and Skin Cancer Prevention Maryland Skin Cancer Prevention Program Do You Know the Facts About Skin Cancer? Skin cancer is the most common cancer but also the most preventable Childhood sunburn
NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254)
 Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
ACTIVE.LITE. Patent-Pending Technology + Visibly Perceivable Results in Less than 14 Days. Tomorrow s Vision Today!
 ACTIVE.LITE Patent-Pending Technology + Visibly Perceivable Results in Less than 14 Days Tomorrow s Vision Today! AESTHETIC PERFECTION IS THE STANDARD Aesthetic skin perfection is now the consumer standard
ACTIVE.LITE Patent-Pending Technology + Visibly Perceivable Results in Less than 14 Days Tomorrow s Vision Today! AESTHETIC PERFECTION IS THE STANDARD Aesthetic skin perfection is now the consumer standard
Supplemental Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Quantikine ELISA. Mouse IL-13 Immunoassay. Catalog Number M1300CB Catalog Number SM1300CB Catalog Number PM1300CB
 Quantikine ELISA Mouse IL-13 Immunoassay Catalog Number M1300CB Catalog Number SM1300CB Catalog Number PM1300CB For the quantitative determination of mouse Interleukin 13 (IL-13) concentrations in cell
Quantikine ELISA Mouse IL-13 Immunoassay Catalog Number M1300CB Catalog Number SM1300CB Catalog Number PM1300CB For the quantitative determination of mouse Interleukin 13 (IL-13) concentrations in cell
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Kit. purified polyclonal antibody raised against the full length recombinant p24 is used.
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Kit 80-001 1 kit 96 assays This kit can measure the amount of HIV-1 Gag p24 antigen in cell culture medium handily by a sandwich ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) method. p24 antigen
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Kit 80-001 1 kit 96 assays This kit can measure the amount of HIV-1 Gag p24 antigen in cell culture medium handily by a sandwich ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) method. p24 antigen
Summary. lymphoma/myeloma, regulatory T cells (T reg) Introduction. Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi: /cei.
 bs_bs_banner Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:1.1111/cei.1273 Increased frequency of skin-infiltrating FoxP3 + regulatory T cells as a diagnostic indicator of severe atopic dermatitis
bs_bs_banner Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:1.1111/cei.1273 Increased frequency of skin-infiltrating FoxP3 + regulatory T cells as a diagnostic indicator of severe atopic dermatitis
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet
 colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
Assessment of the in vitro skin irritation of chemicals using the Vitrolife-Skin human skin model
 AATEX 14, Special Issue, 417-423 Proc. 6th World Congress on Alternatives & Animal Use in the Life Sciences August 21-25, 2007, Tokyo, Japan Assessment of the in vitro skin irritation of chemicals using
AATEX 14, Special Issue, 417-423 Proc. 6th World Congress on Alternatives & Animal Use in the Life Sciences August 21-25, 2007, Tokyo, Japan Assessment of the in vitro skin irritation of chemicals using
Modulation of the immune system by UV radiation: more than just the effects of vitamin D?
 Modulation of the immune system by UV radiation: more than just the effects of vitamin D? Prue H. Hart*, Shelley Gorman* and John J. Finlay-Jones Abstract Humans obtain most of their vitamin D through
Modulation of the immune system by UV radiation: more than just the effects of vitamin D? Prue H. Hart*, Shelley Gorman* and John J. Finlay-Jones Abstract Humans obtain most of their vitamin D through
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE EPITHELIAL PRECANCEROUS LESIONS PRECURSORS OF
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE EPITHELIAL PRECANCEROUS LESIONS PRECURSORS OF
Recent insights into atopic dermatitis and implications for management of infectious complications
 Mark Boguniewicz, MD Professor, Division of Allergy-Immunology Department of Pediatrics National Jewish Health and University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver, Colorado USA Recent insights into atopic
Mark Boguniewicz, MD Professor, Division of Allergy-Immunology Department of Pediatrics National Jewish Health and University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver, Colorado USA Recent insights into atopic
e n ta d i n e Photoprotection Anti-photoaging the most natural way to reinforce skin natural defenses against outdoor and indoor radiations
 eno p r e se rvativ e n ta d i n e Photoprotection Anti-photoaging the most natural way to reinforce skin natural defenses against outdoor and indoor radiations Anti-oxidation Anti-inflammation Anti-immunosuppression
eno p r e se rvativ e n ta d i n e Photoprotection Anti-photoaging the most natural way to reinforce skin natural defenses against outdoor and indoor radiations Anti-oxidation Anti-inflammation Anti-immunosuppression
Key words: Photodermatosis, Plant sensitivity, Airborne contact dermatitis
 Original Article Occurrence of plant sensitivity among patients of photodermatoses: A control-matched study of 156 cases from New Delhi Hemanta Kumar Kar, Sonali Langar, Tarlok Chand Arora, Pankaj Sharma,
Original Article Occurrence of plant sensitivity among patients of photodermatoses: A control-matched study of 156 cases from New Delhi Hemanta Kumar Kar, Sonali Langar, Tarlok Chand Arora, Pankaj Sharma,
HUMAN PHOTOTOXICITY AND PHOTOALLERGENICITY TEST. April, 2006
 HUMAN PHOTOTOXICITY AND PHOTOALLERGENICITY TEST April, 2006 Protocol Number: Title: Objective: Human Phototoxicity and Photoallergenicity Test The objective of the test is to assess the potential of a
HUMAN PHOTOTOXICITY AND PHOTOALLERGENICITY TEST April, 2006 Protocol Number: Title: Objective: Human Phototoxicity and Photoallergenicity Test The objective of the test is to assess the potential of a
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Narrow-band UVB PHOTOTHERAPY for Skin Diseases
 Narrow-band UVB PHOTOTHERAPY for Skin Diseases By Dr. Manal Bosseila Cairo University, Egypt HISTORICAL ASPECT In 1978: Irradiation cabin with broad band UVB tubes was introduced for psoriasis & uremic
Narrow-band UVB PHOTOTHERAPY for Skin Diseases By Dr. Manal Bosseila Cairo University, Egypt HISTORICAL ASPECT In 1978: Irradiation cabin with broad band UVB tubes was introduced for psoriasis & uremic
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
Biologic Therapies for Atopic Dermatitis and Beyond
 Biologic Therapies for Atopic Dermatitis and Beyond Jonathan Corren, M.D. Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Disclosures Genentech - research Medimmune/AZ -
Biologic Therapies for Atopic Dermatitis and Beyond Jonathan Corren, M.D. Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Disclosures Genentech - research Medimmune/AZ -
Sunlight-Induced Immunosuppression in Humans Is Initially Because of UVB, Then UVA, Followed by Interactive Effects
 Sunlight-Induced Immunosuppression in Humans Is Initially Because of UVB, Then UVA, Followed by Interactive Effects Terence S. C. Poon, Ross St. C. Barnetson, and Gary M. Halliday Discipline of Medicine
Sunlight-Induced Immunosuppression in Humans Is Initially Because of UVB, Then UVA, Followed by Interactive Effects Terence S. C. Poon, Ross St. C. Barnetson, and Gary M. Halliday Discipline of Medicine
SCIENTIFIC PAPER ABSTRACT
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER ABSTRACT Vitiligo Treatment with Monochromatic Excimer Light and Tacrolimus: Results of an Open Randomized Controlled Study Nistico` S., Chiricozzi A., M.D., Rosita Saraceno R., Schipani
SCIENTIFIC PAPER ABSTRACT Vitiligo Treatment with Monochromatic Excimer Light and Tacrolimus: Results of an Open Randomized Controlled Study Nistico` S., Chiricozzi A., M.D., Rosita Saraceno R., Schipani
Toxic responses of the immune system
 Toxic responses of the immune system Dr.Bushra Hassan Marouf University of Sulaimani-College of Pharmacy Lec 3,4 1 Immune system Immunity is a homeostatic process, a series of delicately balanced, complex,
Toxic responses of the immune system Dr.Bushra Hassan Marouf University of Sulaimani-College of Pharmacy Lec 3,4 1 Immune system Immunity is a homeostatic process, a series of delicately balanced, complex,
Immunohistochemical Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Psoriasis Vulgaris
 Immunohistochemical Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Psoriasis Vulgaris Amina Gamal el Din 1 *, Hanan M Saleh 2, Nermeen Abdel Fattah 2 and Abdel Maksoud A 3 1.Pathology Department, Medical Research
Immunohistochemical Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Psoriasis Vulgaris Amina Gamal el Din 1 *, Hanan M Saleh 2, Nermeen Abdel Fattah 2 and Abdel Maksoud A 3 1.Pathology Department, Medical Research
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Foreseen Shield Nopal
 Foreseen Shield Nopal A STORY The Nopal Opuntia ficus indica, Cactaceae A Mexican legendary cactus Born in the centre of Mexico, that cactus with an original shape caracterized by its organization with
Foreseen Shield Nopal A STORY The Nopal Opuntia ficus indica, Cactaceae A Mexican legendary cactus Born in the centre of Mexico, that cactus with an original shape caracterized by its organization with
Human IL-2. Pre-Coated ELISA Kit
 Human IL-2 (Interleukin 2) Pre-Coated ELISA Kit Catalog No: 90-2083 1 96 well Format (96 tests) Detection Range: 31.2 2000 pg/ml Sensitivity: < 18.75 pg/ml This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro
Human IL-2 (Interleukin 2) Pre-Coated ELISA Kit Catalog No: 90-2083 1 96 well Format (96 tests) Detection Range: 31.2 2000 pg/ml Sensitivity: < 18.75 pg/ml This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro
VITAMIN D AND THE SKIN JOYCE FARAH MD MS FAAD FARAH DERMATOLOGY AND COSMETICS, LLC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE AND ENT UPSTATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
 VITAMIN D AND THE SKIN JOYCE FARAH MD MS FAAD FARAH DERMATOLOGY AND COSMETICS, LLC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE AND ENT UPSTATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY VIT D RECEPTORS ROLE IN MAINTAINING NORMAL FOLLICULAR
VITAMIN D AND THE SKIN JOYCE FARAH MD MS FAAD FARAH DERMATOLOGY AND COSMETICS, LLC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE AND ENT UPSTATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY VIT D RECEPTORS ROLE IN MAINTAINING NORMAL FOLLICULAR
To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of. PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell cycle analysis To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell cycle analysis To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
EVOLUTIONARY STUDY OF CHRONIC CUTANEOUS MODIFICATIONS CAUSED BY EXPOSURE TO ULTRAVIOLET RADIATIONS IN HAIRLESS MICE
 Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula: Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară Vol. XII/B, 2013 EVOLUTIONARY STUDY OF CHRONIC CUTANEOUS MODIFICATIONS CAUSED BY EXPOSURE TO
Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula: Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară Vol. XII/B, 2013 EVOLUTIONARY STUDY OF CHRONIC CUTANEOUS MODIFICATIONS CAUSED BY EXPOSURE TO
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
The role of interleukin-36 in inflammatory skin diseases
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI NAPOLI FEDERICO II DOTTORATO DI RICERCA IN MEDICINA CLINICA E SPERIMENTALE CURRICULUM IN SCIENZE IMMUNOLOGICHE E DERMATOLOGICHE XXIX Ciclo Coordinatore: Prof. Gianni Marone TESI
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI NAPOLI FEDERICO II DOTTORATO DI RICERCA IN MEDICINA CLINICA E SPERIMENTALE CURRICULUM IN SCIENZE IMMUNOLOGICHE E DERMATOLOGICHE XXIX Ciclo Coordinatore: Prof. Gianni Marone TESI
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN
 YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
Study the Effects of Exposing the Skin and Eyes of Mice to Ultraviolet-C Radiation
 International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 4, Issue 11, November 2016, PP 8-14 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0365.0411002
International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 4, Issue 11, November 2016, PP 8-14 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0365.0411002
Th17 Pathway Research By Bio-Plex
 Th17 Pathway Research By Bio-Plex Zhiyang Shen, Senior Product Manager Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc 2011 年 6 月 28 日星期二 T helper cell research Timeline: advances on T helper research. Figure depicts some of
Th17 Pathway Research By Bio-Plex Zhiyang Shen, Senior Product Manager Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc 2011 年 6 月 28 日星期二 T helper cell research Timeline: advances on T helper research. Figure depicts some of
CHAPTER 3. Diagnostic phototesting in polymorphous. Diagnostic phototesting in polymorphous light eruption: the optimal number of irradiations
 CHAPTER 3 Diagnostic phototesting in polymorphous light eruption: the optimal number of irradiations Diagnostic phototesting in polymorphous light eruption: Ines Schornagel, Edward the optimal Knol, Huib
CHAPTER 3 Diagnostic phototesting in polymorphous light eruption: the optimal number of irradiations Diagnostic phototesting in polymorphous light eruption: Ines Schornagel, Edward the optimal Knol, Huib
Comparison of the narrow band UVB versus systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of lichen planus: A randomized clinical trial
 Received: 10.7.2011 Accepted: 5.12.2011 Original Article Comparison of the narrow band UVB versus systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of lichen planus: A randomized clinical trial Fariba Iraji, 1
Received: 10.7.2011 Accepted: 5.12.2011 Original Article Comparison of the narrow band UVB versus systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of lichen planus: A randomized clinical trial Fariba Iraji, 1
HTRF MEASUREMENT OF CYTOKINE RELEASE FROM FRESH BLOOD SAMPLES
 HTRF MEASUREMENT OF CYTOKINE RELEASE FROM FRESH BLOOD SAMPLES APPLICATION NOTE ABSTRACT Cisbio offers a comprehensive line of HTRF cytokine assays to investigate the functional response of immune cells.
HTRF MEASUREMENT OF CYTOKINE RELEASE FROM FRESH BLOOD SAMPLES APPLICATION NOTE ABSTRACT Cisbio offers a comprehensive line of HTRF cytokine assays to investigate the functional response of immune cells.
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-10. Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald,
 Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-1 Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald, James A. Dromey, Bo Han Lee, Junyan Qian, Ralph M Böhmer and Leonard
Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-1 Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald, James A. Dromey, Bo Han Lee, Junyan Qian, Ralph M Böhmer and Leonard
Human LDL ELISA Kit. Innovative Research, Inc.
 Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
Anti-diabetic Activity of a Polyphenol-rich Extract from Phellinus. igniarius in KK-Ay Mice with Spontaneous Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Anti-diabetic Activity of a Polyphenol-rich Extract from Phellinus igniarius in KK-Ay Mice
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Anti-diabetic Activity of a Polyphenol-rich Extract from Phellinus igniarius in KK-Ay Mice
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet
 colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of rat TNF-alpha concentrations in cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of rat TNF-alpha concentrations in cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
Internationales Journal für angewandte Wissenschaft
 Internationales Journal für angewandte Wissenschaft Kosmetik Haushalt Spezialprodukte Sonderdruck aus 7-23 D. Schmid, C. Schürch, F. Zülli, H.-P. Nissen, H. Prieur: Mycosporine-like amino acids: Natural
Internationales Journal für angewandte Wissenschaft Kosmetik Haushalt Spezialprodukte Sonderdruck aus 7-23 D. Schmid, C. Schürch, F. Zülli, H.-P. Nissen, H. Prieur: Mycosporine-like amino acids: Natural
Osteopathic Dermatology
 Osteopathic Dermatology Teodor Huzij, DO, FACN Reagan Anderson, DO, FAOCD, FASMS, Certificate of Added Qualification for Mohs Surgery, MPH, MCS, Program Director for RVU/CDI Dermatology Residency Program
Osteopathic Dermatology Teodor Huzij, DO, FACN Reagan Anderson, DO, FAOCD, FASMS, Certificate of Added Qualification for Mohs Surgery, MPH, MCS, Program Director for RVU/CDI Dermatology Residency Program
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice
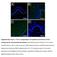 Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
TNF-alpha ELISA. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
 TNF-alpha ELISA For the quantitative determination of TNF-alpha in serum, plasma, buffered solution or cell culture medium. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number:
TNF-alpha ELISA For the quantitative determination of TNF-alpha in serum, plasma, buffered solution or cell culture medium. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number:
Skin Pigmentation Kinetics After UVB Exposure
 Acta Derm Venereol 2008; 88: 223 228 INVESTIGATIVE REPORT Skin Pigmentation Kinetics After UVB Exposure Mette H. Ravnbak, Peter A. Philipsen, Stine R. Wiegell and Hans C. Wulf Department of Dermatology,
Acta Derm Venereol 2008; 88: 223 228 INVESTIGATIVE REPORT Skin Pigmentation Kinetics After UVB Exposure Mette H. Ravnbak, Peter A. Philipsen, Stine R. Wiegell and Hans C. Wulf Department of Dermatology,
Animal Models of Atopic Dermatitis
 Skin Diseases Animal Models of Atopic Dermatitis JMAJ 47(11): 51 57, 24 Hitoshi MIZUTANI*, Takeshi NISHIGUCHI**, and Takaaki MURAKAMI*** *** Professor, Department of Dermatology, Mie University, Faculty
Skin Diseases Animal Models of Atopic Dermatitis JMAJ 47(11): 51 57, 24 Hitoshi MIZUTANI*, Takeshi NISHIGUCHI**, and Takaaki MURAKAMI*** *** Professor, Department of Dermatology, Mie University, Faculty
GSI Canine IL-5 ELISA Kit-2 Plates DataSheet
 Interleukin5 (IL5) is a secreted glycoprotein that belongs to the α-helical group of cytokines (1, 2, 3). Unlike other family members, it is present as a covalently linked antiparallel dimer (4, 5). IL-5
Interleukin5 (IL5) is a secreted glycoprotein that belongs to the α-helical group of cytokines (1, 2, 3). Unlike other family members, it is present as a covalently linked antiparallel dimer (4, 5). IL-5
IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES
 13 13 IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES Yanni Yu, a Binjie Meng a Guizhou, China SUMMARY: Chondrocytes of rib-cage cartilage from Wistar rats
13 13 IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES Yanni Yu, a Binjie Meng a Guizhou, China SUMMARY: Chondrocytes of rib-cage cartilage from Wistar rats
CELL MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE
 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE Chapter IV - CELL MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE Sujatha, M. 2013. Evaluation of Immunological changes in Fish, Catla catla administered with bacterial pathogen, Aeromonas hydrophila,
CELL MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE Chapter IV - CELL MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE Sujatha, M. 2013. Evaluation of Immunological changes in Fish, Catla catla administered with bacterial pathogen, Aeromonas hydrophila,
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: , 2014
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 769-774, 2014 Helicobacter pylori infection promotes the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer through increasing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 769-774, 2014 Helicobacter pylori infection promotes the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer through increasing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase
Comparison of the efficacy of PUVA versus BBUVB in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris
 IJMAMR 5 (2017) 1-6 ISSN 2053-1834 Comparison of the efficacy of PUVA versus BBUVB in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris Tran Hau Khang* and Le Huu Doanh National Hospital of Dermatology and Venereology,
IJMAMR 5 (2017) 1-6 ISSN 2053-1834 Comparison of the efficacy of PUVA versus BBUVB in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris Tran Hau Khang* and Le Huu Doanh National Hospital of Dermatology and Venereology,
data for the processes that occur
 THE JOURNAL O INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright l 1965 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 63, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECT OF ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT ON ISOLATED CUTANEOUS BLOOD VESSELS* W. MITCHELL
THE JOURNAL O INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright l 1965 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 63, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECT OF ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT ON ISOLATED CUTANEOUS BLOOD VESSELS* W. MITCHELL
BMP6 and BMP4 expression in patients with cancer-related anemia and its relationship with hepcidin and s-hjv
 BMP6 and BMP4 expression in patients with cancer-related anemia and its relationship with hepcidin and s-hjv Y.J. Shi and X.T. Pan Affiliated Taicang Hospital of Suzhou University, Taicang, Jiangsu, China
BMP6 and BMP4 expression in patients with cancer-related anemia and its relationship with hepcidin and s-hjv Y.J. Shi and X.T. Pan Affiliated Taicang Hospital of Suzhou University, Taicang, Jiangsu, China
Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and PUVA therapy in the treatment of early-stage mycosis fungoides: a right left comparative study
 Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2005; 21: 281 286 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and therapy in the treatment of early-stage
Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2005; 21: 281 286 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and therapy in the treatment of early-stage
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Protein-Mediated Anti-Adhesion Surface against Oral Bacteria
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Protein-Mediated Anti-Adhesion Surface against Oral Bacteria Xi Liu a,b,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Protein-Mediated Anti-Adhesion Surface against Oral Bacteria Xi Liu a,b,
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
