Imaging Criteria (CT findings) Inflammatory changes localized to appendix +/- appendiceal dilation +/- contrast non-filling
|
|
|
- Rafe Merritt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table 1. Data Dictionaries for Grading System for EGS Conditions A. Acute Appendicitis I Description Acutely inflamed appendix, intact Gangrenous appendix, intact Perforated appendix with local contamination Perforated appendix with periappendiceal phlegmon or Perforated appendix with generalized Clinical Criteria Pain, leukocytosis and right lower quadrant (RLQ) tenderness Pain, leukocytosis and RLQ tenderness Pain, leukocytosis and RLQ tenderness Pain, leukocytosis and RLQ tenderness; may have palpable mass (CT findings) Inflammatory changes localized to appendix +/- appendiceal dilation +/- contrast non-filling Appendiceal wall necrosis with contrast nonenhancement +/- air in appendiceal wall Above with local periappendiceal fluid +/- contrast extravasation Regional soft tissue inflammatory changes, phlegmon or Generalized Diffuse abdominal or pelvic inflammatory changes +/- free intraperitoneal fluid or air Acutely inflamed appendix, intact Gangrenous appendix, intact Above, with evidence of local contamination Above, with or phlegmon in region of appendix Above, with addition of generalized purulent contamination away from appendix Presence of neutrophils at the base of crypts, submucosa +/- in muscular wall Mucosa and muscular wall digestion; not identifiable on hematoxylin and eosin stain (H & E) Gross or focal dissolution of muscular wall Gross Gross 1 P a g e
2 B. Breast Infections Description Clinical Criteria (US or CT findings) I Breast cellulitis Erythema, induration, edema, pain, tenderness Simple Single, small without loculations; not involving the nipple/areolar complex Complex Large with multiple loculations, multiple es, or involving nipple/areola complex; lymphadenopathy Breast with axillary extension Breast with ipsilateral lymphadenopathy, thrombophlebitis, lymphangitis Inflammation without fluid collection Single well circumscribed fluid collection within breast tissue, not involving nipple/areolar complex Multiple separate fluid collections or single large collection with multiple loculations within breast tissue or involvement of nipple/areola complex Fascial plane thickening with enhancement; evidence of lymphadenopathy on US or CT Operative Criteria Single, well circumscribed fluid collection within breast tissue, not involving nipple/ areola complex Multiple separate fluid collections or single large collection with multiple loculations within breast tissue, or involvement of nipple/areola complex; enlarged lymph nodes Above, plus axillary fluid collections, extension of inflammatory changes well beyond the es Pathologic Criteria limited to breast tissue limited to breast tissue with cultures positive for organism if available of breast tissue and axillary lymph nodes with cultures positive for 2 P a g e
3 Breast with chest wall involvement Above, plus erosion into chest wall muscles or ribs or pleural space, or necrotizing fasciitis Above, plus inflammatory changes in the chest wall muscles, ribs or pleural space Above, with erosion into chest wall muscles or ribs or pleural space, or necrotizing fasciitis involving chest wall, fascia, muscles or ribs with or without necrosis and cultures positive for 3 P a g e
4 C. Acute Cholecystitis Description Clinical Criteria (CT/US/HIDA findings) I Acute cholecystitis GB empyema or gangrenous cholecystitis or emphysematous cholecystitis GB with local contamination GB with pericholecystic or gastrointestinal fistula Right upper quadrant (RUQ) or epigastric pain; Murphy s Sign; leukocytosis RUQ or epigastric pain; Murphy s Sign; leukocytosis Localized in RUQ Localized at multiple locations; abdominal distention with symptoms of bowel obstruction Wall thickening; distention; gallstones or sludge; pericholecystic fluid; non-visualization of gallbladder (GB) on hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan Above, plus air in GB lumen, wall or in the biliary tree; focal mucosal defects without frank HIDA with focal transmural defect, extraluminal fluid collection or radiotracer but limited to RUQ Abscess in RUQ outside GB; bilio-enteric fistula; gallstone ileus Inflammatory changes localized to GB; wall thickening; distention; gallstones Distended GB with pus or hydrops; necrosis or gangrene of wall; not perforated Perforated GB wall (non-iatrogenic) with bile outside the GB but limited to RUQ Pericholecystic ; bilio-enteric fistula; gallstone ileus Acute inflammatory changes in the GB wall without necrosis or pus Above, plus pus in the GB lumen; necrosis of GB wall; intramural ; epithelial sloughing; no Necrosis with of the GB wall (non-iatrogenic) Necrosis with of the GB wall (non-iatrogenic) GB with generalized Above, with generalized Free intra-peritoneal bile Above, plus generalized Necrosis with of the GB wall (non-iatrogenic) 4 P a g e
5 D. Acute Diverticulitis of the Colon I Description Clinical Criteria (CT findings) Colonic Pain; leukocytosis; Mesenteric stranding; inflammation minimal or no colon wall thickening tenderness Colon micro or pericolic phlegmon without Localized pericolic Distant and/or multiple es Free colonic with generalized Local tenderness (single or multiple areas) without Pericolic phlegmon; foci of air (single or multiple); no Operative Criteria Pericolic phlegmon with no Pathologic Criteria Inflamed colon with microscopic Localized Pericolic Pericolic Inflamed colon with Localized at multiple locations Abscess or phlegmon away from the colon Generalized Free air and free fluid Abscess or phlegmon away from the colon generalized fecal and purulent contamination Inflamed colon with Inflamed colon with 5 P a g e
6 E. Esophageal Perforation Operative Criteria Pathologic criteria Description Clinical Criteria Imaging and/or endoscopic criteria I Mucosal tear Dysphagia; chest pain, upper abdominal pain or back pain; breathing problems No abnormality or possible intramural air Preservation of normal anatomy with dissection required to identify inflammation Partial thickness or mucosal tear Full thickness tear with minimal inflammation Full thickness tear with localized Esophageal wall necrosis Empyema; ; mediastinitis Above, with subcutaneous emphysema Above, with vomiting and ill-appearing Esophageal thickening Obvious inflammation Full thickness with minimal inflammation without mediastinitis or Air in prevertebral planes Presence of inflammation and stigmata of with contained collection As above Mediastinal widening Inflammation; necrosis of the esophageal wall with localized contamination As above Pleural effusion disseminated contamination; erosion into adjacent structures (chest, mediastinum, or abdomen) Mediastinal inflammation or emphysema Severe mediastinal necrosis Pleural invasion or empyema 6 P a g e
7 F. Hernias (Internal or Abdominal wall) Description Clinical Criteria I Reducible hernia Palpable, reducible hernia without fever or leukocytosis Incarcerated hernia without bowel ischemia Incarcerated with bowel ischemic but viable Incarcerated hernia with gangrenous bowel or with local spillage Incarcerated with and diffuse peritoneal contamination Local tenderness with non-reducible palpable hernia. No fever of leukocytosis. Local tenderness with non-reducible palpable hernia; may be associated with fever, tachycardia, or leukocytosis Local tenderness with guarding, non-reducible palpable hernia with associated skin changes such as erythema Diffuse abdominal tenderness with guarding or rebound; non-reducible palpable hernia with associated skin changes such as erythema (CT findings) Hernia visible on CT Hernia visible on CT Hernia visible on CT with local stranding or inflammatory changes Hernia visible on CT with local stranding or inflammatory changes as well as contained fluid collection Hernia visible on CT with local stranding or inflammatory changes as well as diffuse fluid collections and inflammation Abdominal wall defect present Abdominal wall defect present with abdominal contents lodged in defect; healthy appearing viscera Abdominal wall defect present with abdominal contents lodged in defect; visibly inflamed but viable appearing viscera Abdominal wall defect present with abdominal contents lodged in defect; gangrenous or perforated abdominal contents Abdominal wall defect present with abdominal contents lodged in defect; gangrenous or perforated abdominal contents with diffuse contamination Local necrosis or Local necrosis or 7 P a g e
8 G. Infectious Colitis Description Clinical Criteria ( CT findings) I Mucosal disease with positive cultures or other confirmatory laboratory testing Diarrhea and/or abdominal pain with positive stool cultures or toxin assays; inflamed mucosa on endoscopy Normal CT Normal colon Mucosal inflammatory changes on biopsy, positive stool cultures or toxin assays Colon wall thickening by cross-sectional imaging or pseudomembranes on endoscopy Colon wall thickening with ascites or diffuse colonic dilation or diffuse coalescing pseudomembranes Diarrhea and/or abdominal pain, and/or abdominal tenderness with pseudomembranes on endoscopy Abdominal pain and tenderness and/or distension; coalescing pseudomembranes by endoscopy Localized colonic wall thickening Diffuse colonic thickening or localized thickening and free intraabdominal fluid Localized thickened but otherwise normal colon Diffusely thickened colon or localized thickening with free intra-abdominal fluid Transmural colonic inflammation Transmural colonic inflammation 8 P a g e
9 Description Clinical Criteria Localized colonic necrosis, with or without Diffuse transmural colonic necrosis, with or without Abdominal pain with and mucosal necrosis by endoscopy Abdominal pain with mucosal necrosis by endoscopy ( CT findings) Colonic thickening with free fluid +/- evidence of or Colonic thickening with free fluid +/- evidence of or Colonic thickening with localized or discontinuous transmural necrosis or ischemia with or without or Diffuse colonic necrosis with or without or Transmural colonic inflammation with areas of necrosis Transmural colonic inflammation with areas of full thickness necrosis 9 P a g e
10 H. Intestinal Obstruction Due to Adhesions Description Clinical Criteria (CT findings) I Partial SBO Some flatus; normal or Normal imaging or hypoactive bowel minimal intestinal sounds; minor distension abdominal distention Complete SBO; bowel viable and not compromised Complete SBO with compromised but viable bowel Complete SBO with non-viable bowel or with localized spillage SB with diffuse peritoneal contamination Minimal to no flatus; hypoactive bowel sounds; distension without generalized tenderness No flatus; absent bowel sounds; abdominal distension with localized tenderness Obstipation; abdominal distension with diffuse tenderness, rebound, guarding Abdominal distension with evidence of Intestinal distension with transition point; delayed contrast flow with some distal contrast; no evidence of bowel compromise Intestinal distension with transition point and no distal contrast flow; evidence of complete obstruction or impending bowel compromise Evidence of localized or free air; bowel distension with free air or free fluid Bowel with free air and free fluid Operative Criteria Minimal intestinal distension with no evidence of bowel obstruction Intestinal distention with transition point; no evidence of bowel compromise Intestinal distention with impending bowel compromise Intestinal distension with localized or free fluid Intestinal distension with, free fluid and evidence of diffuse Pathologic criteria Bowel gangrene or Bowel gangrene or 10 P a g e
11 I. Intestinal Arterial Ischemia of the Bowel Description Clinical Criteria (CT findings) I Bowel ischemia without tissue loss Bowel ischemia with mucosal ulceration only, without transmural infarction Segmental transmural bowel infarction without Segmental transmural bowel infarction with Anorexia with abdominal pain Abdominal pain out of proportion to exam; no Abdominal pain and tenderness without Abdominal pain and tenderness with Wall thickening and mucosal edema with enhancement. Wall thickening and edema without enhancement; mesenteric vessel occlusion Wall thickening without mucosal or intestinal wall enhancement; intramural, portal, or mesenteric pneumatosis Pneumoperitoneum, contrast extravasation, Normal appearing bowel Normal serosa, mucosal ischemia and ulceration Transmural necrosis without Transmural necrosis with and Ischemia without ulceration Mucosal ulceration Transmural necrosis without Transmural necrosis with Pan-intestinal infarction Abdominal pain and tenderness with or above with involvement of both Superior Mesenteric Artery and Inferior Mesenteric Artery distributions Pan-intestinal infarction and necrosis with or without Transmural infarction with 11 P a g e
12 J. Acute Pancreatitis Description Clinical Criteria (CT findings) I Acute edematous pancreatitis Midepigastric abdominal pain and tenderness; elevated amylase and/or lipase Pancreatitis without phlegmon, necrosis, peripancreatic fluid collection or Edematous pancreas Pancreatic phlegmon or peripancreatic fluid collection or hemorrhage Sterile pancreatic necrosis Midepigastric abdominal pain and tenderness; elevated amylase and/or lipase Midepigastric abdominal pain and tenderness; elevated amylase and/or lipase Phlegmon or peripancreatic fluid collection or hemorrhage Pancreatic necrosis without extraluminal air or Pancreatic phlegmon or peripancreatic fluid collection Pancreatic necrosis without purulence or Gram stain and culture of necrosis negative for Infected pancreatic necrosis or Severe midepigastric abdominal pain and tenderness; elevated amylase and/or lipase Pancreatic necrosis with extraluminal air or Pancreatic necrosis with purulence or Gram stain and culture of necrosis or positive for Extra-pancreatic extension of pancreatic necrosis involving adjacent organs, such as colonic necrosis Severe diffuse midepigastric abdominal pain and tenderness; elevated amylase and/or lipase Extra-pancreatic extension of necrosis involving adjacent organs, such as colonic necrosis Involvement or necrosis of adjacent organs Involvement or necrosis of resected adjacent organs 12 P a g e
13 K. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease I Description Inflammation of the cervix Purulent cervical drainage Inflammation of the tubes, ovaries, and/or entire uterus Tubo-ovarian, pyometra Clinical Criteria (CT or US findings) None None OR vaginal discharge, vaginal irritation, pelvic discomfort Above, plus pelvic pain or discomfort; fever Severe pelvic pain; fever None or positive cervical cultures for Inflammation of pelvic organ or organs Inflammation and of pelvic organ or organs None, or purulent pelvic fluid on laparoscopy Drainage of tuboovarian or pyometra None or positive cervical cultures for None, or positive cervical or pelvic cultures for Generalized pelvic sepsis Generalized Single or multiple es, widespread inflammation Drainage of fluid collections, complications related to es, such as interloop es causing bowel obstruction; hysterectomy None, or positive cervical or pelvic cultures for 13 P a g e
14 L. Perforated Peptic Ulcer Disease (Gastric or Duodenal) Description Clinical Criteria (CT findings) I Micro without Contained with localized localized and localized fluid collection in lesser sac or RUQ Free with duodenal destruction ± penetration into adjacent organs and generalized Discomfort in the epigastric region Tenderness confined to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) Tenderness confined to the RUQ Diffuse Diffuse Extraluminal gas with no associated inflammatory changes Extraluminal gas contained in a walled off collection or the retroperitoneum associated collection that is not contained in a anatomic space or but not disseminated disseminated air and fluid disseminated air and fluid with loss of local anatomic planes at the site of Preservation of normal anatomy with dissection required to identify the Presence of inflammation and stigmata of with contained collection Inflammation and contamination of peritoneal cavity confined to the RUQ disseminated succus or purulent disseminated succus or purulent and erosion into adjacent structures minimal bowel wall inflammation bowel wall inflammation bowel wall inflammation bowel wall inflammation Destructive erosion of involved structures 14 P a g e
15 M. Perirectal Abscess Description Clinical Criteria I Perianal Anal pain and swelling, erythema, tenderness Drainage of localized pus Intersphincteric or ischiorectal Horseshoe Supralevator Necrotizing soft tissue infection of the perineum, buttocks, etc., AKA Fournier s gangrene Fever; perineal pain; diffuse swelling; pain with defecation; palpable fluctuant area on digital examination Pain with defecation; palpable fluctuant area on digital examination Fever; may present with sepsis or perineal discomfort; may have no localized clinical signs Systemic signs of sepsis, perineal pain and swelling, cellulitis, crepitus, necrotic skin changes Endorectal ultrasound localization; CT may localize collection but MRI preferable Endorectal ultrasound localization; CT may localize collection but MRI preferable Endorectal ultrasound not useful; CT demonstrating collection X-ray or CT may demonstrate air in soft tissues. CT or MRI may demonstrate intraabdominal or retroperitoneal source of infection. Drainage of localized pus Drainage of localized pus Drainage of localized pus Necrotic skin and soft tissue of perianal, perineal, and genitalia Culture of positive for Culture of positive for Culture of positive for Above, plus necrotic skin and soft tissue of perianal, perineal, and genitalia 15 P a g e
16 N. Pleural Space Infection Description Clinical Criteria I Retained hemothorax or pleural effusion with positive pleural fluid cultures Leukocytosis, fever, chest pain Pleural fluid consistent with blood or infected fluid no evidence of loculations Retained blood, blood clot, or other nonpurulent fluid without lung trapping. Culture of fluid positive for Purulent, freeflowing pleural effusion or hemothorax by imaging Fibrinopurulent stage with loculated areas of effusion or hemothorax Organizing stage with evidence for restricted lung expansion and pulmonary mechanics Respiratory failure, leukocytosis, fever, chest pain Respiratory failure, leukocytosis, fever, chest pain Severe respiratory failure, leukocytosis, fever, chest pain Pleural fluid consistent with blood or infected fluid; no evidence of loculation Pleural fluid consistent with blood or infected fluid, with evidence of loculation Pleural fluid consistent with blood or infected fluid with evidence of loculation; significantly decreased lung volumes Retained blood, blood clot, with purulent areas OR completely purulent fluid. Retained blood, blood clot or other purulent fluid with limited lung trapping Retained blood, blood clot or other purulent fluid with diffuse pleural inflammation and lung trapping Culture of fluid positive for Culture of fluid positive for with areas of fibrous peel Culture of fluid positive for with areas of fibrous peel Spontaneous external drainage or spreading extra-thoracic Severe respiratory failure, leukocytosis, fever, chest pain Above, plus severe inflammatory changes of adjacent abdominal, Above, with external drainage or necrotizing soft tissue infection of mediastinum, Above, with necrotic soft tissue from mediastinum, or subcutaneous space 16 P a g e
17 necrotizing soft tissue infection mediastinal or subcutaneous tissue diaphragm or subcutaneous tissues 17 P a g e
18 O. Soft Tissue Infections Description Clinical Criteria I Cellulitis Folliculitis, erysipelas, impetigo, simple cellulitis Superficial necrosis or liquefaction Subcutaneous Abscess Necrotizing, blistering or bullous cellulitis or skin necrosis Subcutaneous (CT findings) Superficial inflammation with no subcutaneous stranding Subcutaneous stranding, but no Well defined (walled off) subcutaneous fluid collection with surrounding inflammation Fasciitis Fasciitis Inflammation extending to fascia; likely air along fascia margins Myonecrosis Myonecrosis Air deep to fascia; likely poor perfusion of muscle Well defined subcutaneous fluid collection Clear involvement of fascia with healthy, viable muscle underneath. Extension of necrosis into muscle and deeper tissue involving epidermis only involving epidermis and dermis involving epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fat with cultures positive for if available involving epidermis, dermis, sub-cutaneous fat, and muscular fascia with cultures positive for if available involving epidermis, dermis, sub- cutaneous fat, muscular fascia, adjacent tissue (muscle, etc.) with cultures positive for if available 18 P a g e
19 P. Surgical Site Infections Description Clinical Criteria I Infection involving skin only Infection involving subcutaneous tissue Infection involving fascia or muscle layer Infection involving body cavity or deep space that was opened or manipulated One or more of the following: periincisional erythema, warmth, pain, swelling without induration, exudate, or wound separation One or more of the following: periincisional erythema warmth, pain, swelling plus induration or exudate confined to subcutaneous tissues Subcutaneous or phlegmon extending to muscle or fascia Above, plus separation of fascia or subfascial (CT findings) Soft tissue inflammatory changes, phlegmon or in subcutaneous tissues Regional soft tissue inflammatory changes, phlegmon or involving muscle or fascia Phlegmon or extending deep to muscle or fascia OR fascial dehiscence at surgical site Phlegmon or in subcutaneous tissues Phlegmon or involving muscle or fascia Phlegm on or extending deep to muscle or fascia OR facial wound dehiscence limited to subcutaneous tissues involving muscle or fascia with cultures positive for organism if available involving fascia and underlying tissues with cultures positive 19 P a g e
20 during the surgery for organism if available Infection involving body cavity or deep space away from the site that was opened or manipulated during surgery Purulent drainage in a body cavity away from the operative site Phlegmon or in body cavity or deep space extending deeper than the fascia/deep muscle incision Phlegmon or in body cavity or deep space extending deeper than the fascial/deep muscle incision in body cavity or deep space away extending deeper than the fascial/deep muscle incision with cultures positive for if available 20 P a g e
Table 0: Description of Grading System for Anatomic Severity of Disease in Emergency. Local disease confined to the organ with minimal abnormality
 Table 0: of Grading System for Anatomic Severity of Disease in Emergency Local disease confined to the organ with minimal Local disease confined to the organ with severe Local extension Table 1: Universal
Table 0: of Grading System for Anatomic Severity of Disease in Emergency Local disease confined to the organ with minimal Local disease confined to the organ with severe Local extension Table 1: Universal
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum. Elective Student S. C.
 Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients).
 Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
of Trauma Assembly 28 th Page 1
 Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 28 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 12 Disease Grading Systemss in Emergency General Surgery January 16, 2015 Disney s Contemporary Resort Lake
Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 28 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 12 Disease Grading Systemss in Emergency General Surgery January 16, 2015 Disney s Contemporary Resort Lake
General Data. 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性
 General Data 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性 Chief Complaint Vomiting twice this early morning Fever up to 38.9ºC was noted Present Illness (1) Old CVA with left side weakness for more than 10 years and with bed ridden
General Data 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性 Chief Complaint Vomiting twice this early morning Fever up to 38.9ºC was noted Present Illness (1) Old CVA with left side weakness for more than 10 years and with bed ridden
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
Plain Radiographs in Non-Traumatic Abdominal Pain. Plain Radiographs in Non-Traumatic Abdominal Pain
 Jake Block, MD Associate Professor Associate Vice-Chairman for Clinical Operations Director, Musculoskeletal and Emergency Radiology Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences Vanderbilt University
Jake Block, MD Associate Professor Associate Vice-Chairman for Clinical Operations Director, Musculoskeletal and Emergency Radiology Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences Vanderbilt University
Characteristic. Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils
 ACUTE INFLAMMATION Characteristic Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils TYPES Serous Inflammation Fibrinous Inflammation
ACUTE INFLAMMATION Characteristic Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils TYPES Serous Inflammation Fibrinous Inflammation
LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL
 SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
General surgery department of SGMU Lecturer ass. Khilgiyaev R.H. Anaerobic infection. Gas gangrene
 Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
Acute Abdomen. Nirav Patel MD, FACS Banner University Medical Center - Phoenix
 Acute Abdomen Nirav Patel MD, FACS Banner University Medical Center - Phoenix ? Diffuse periumbilical with localization to RLQ + Nausea, anorexia, fevers - Diarrhea, emesis Exacerbated by movement, bumps
Acute Abdomen Nirav Patel MD, FACS Banner University Medical Center - Phoenix ? Diffuse periumbilical with localization to RLQ + Nausea, anorexia, fevers - Diarrhea, emesis Exacerbated by movement, bumps
... Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment.
 Definition Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment. " Epidemiology Humans represent the main reservoir of Clostridium difficile, which is not part of the
Definition Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment. " Epidemiology Humans represent the main reservoir of Clostridium difficile, which is not part of the
ACUTE ABDOMEN IN OLDER CHILDREN. Carlos J. Sivit M.D.
 ACUTE ABDOMEN IN OLDER CHILDREN Carlos J. Sivit M.D. ACUTE ABDOMEN Clinical condition characterized by severe abdominal pain developing over several hours ACUTE ABDOMINAL PAIN Common childhood complaint
ACUTE ABDOMEN IN OLDER CHILDREN Carlos J. Sivit M.D. ACUTE ABDOMEN Clinical condition characterized by severe abdominal pain developing over several hours ACUTE ABDOMINAL PAIN Common childhood complaint
Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen
 Prof. András Palkó MD, PhD Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen Faculty of General Medicine University of Szeged Hungary 1 Definition Sudden onset of severe symptoms requiring emergency
Prof. András Palkó MD, PhD Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen Faculty of General Medicine University of Szeged Hungary 1 Definition Sudden onset of severe symptoms requiring emergency
Abdominal ultrasound:
 Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research 11/16/2017. Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument 11/16/2017
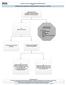 Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument Approximately 139 Potentially relevant guidelines identified in various resources* 59
Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument Approximately 139 Potentially relevant guidelines identified in various resources* 59
Surgical Management of IBD. Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003
 Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology
 Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
FHS Appendicitis US Protocol
 FHS Appendicitis US Protocol Reviewed By: Shireen Khan, MD; Sarah Farley, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: May 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible
FHS Appendicitis US Protocol Reviewed By: Shireen Khan, MD; Sarah Farley, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: May 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible
General'Surgery'Service'
 General'Surgery'Service' Patient Care Goals and Objectives 1)! Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric 2)! Interpret the results of clinical evaluations (history, physical examination) performed on patients being
General'Surgery'Service' Patient Care Goals and Objectives 1)! Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric 2)! Interpret the results of clinical evaluations (history, physical examination) performed on patients being
MANAGEMENT OF PYOGENIC LIVER ABSCESS BOYOUNG SONG, M.D. SUNY DOWNSTATE SURGERY 11/7/13
 MANAGEMENT OF PYOGENIC LIVER ABSCESS BOYOUNG SONG, M.D. SUNY DOWNSTATE SURGERY 11/7/13 CASE THE PATIENT IS A 79 YEAR OLD MALE WITH 3 DAY HISTORY OF LOWER ABDOMINAL PAIN, NAUSEA WITHOUT VOMITING, CHILLS
MANAGEMENT OF PYOGENIC LIVER ABSCESS BOYOUNG SONG, M.D. SUNY DOWNSTATE SURGERY 11/7/13 CASE THE PATIENT IS A 79 YEAR OLD MALE WITH 3 DAY HISTORY OF LOWER ABDOMINAL PAIN, NAUSEA WITHOUT VOMITING, CHILLS
Esophageal Perforation
 Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Always keep it in the differential
 Acute Appendicitis Lissa C. Sakata and Lindsey Perea 2 Always keep it in the differential Learning Objectives 1. The learner should be able to describe the etiology of acute appendicitis. 2. The learner
Acute Appendicitis Lissa C. Sakata and Lindsey Perea 2 Always keep it in the differential Learning Objectives 1. The learner should be able to describe the etiology of acute appendicitis. 2. The learner
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology. Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update
 Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學
 Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Chapter 24 - Abdominal_Emergencies
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 24.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. 13, 15, 18, 20 22 24.2 Describe the location, structure, and function of the organs in the abdominal
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 24.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. 13, 15, 18, 20 22 24.2 Describe the location, structure, and function of the organs in the abdominal
Cholecystitis is defined as nonspecific inflammation of the gallbladder with or without cholelithiasis. Types: calculous and acalculous.
 Cholecystitis is defined as nonspecific inflammation of the gallbladder with or without cholelithiasis. Types: calculous and acalculous. Anatomy of the gallbladder The gallbladder, a pear-shaped reservoir
Cholecystitis is defined as nonspecific inflammation of the gallbladder with or without cholelithiasis. Types: calculous and acalculous. Anatomy of the gallbladder The gallbladder, a pear-shaped reservoir
General Surgery Service
 General Surgery Service Patient Care Goals and Objectives Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric assessed for a) Obesity surgery b) Treatment of i) Adenocarcinoma of the stomach ii) GIST iii) Carcinoid 2) Optimize
General Surgery Service Patient Care Goals and Objectives Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric assessed for a) Obesity surgery b) Treatment of i) Adenocarcinoma of the stomach ii) GIST iii) Carcinoid 2) Optimize
Gastroenterology. Certification Examination Blueprint. Purpose of the exam
 Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies. V.Stoynova
 Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
Emergency MDCT in case of right lower quadrant pain
 Emergency MDCT in case of right lower quadrant pain Poster No.: C-0563 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Lisitskaya, V. Sinitsyn; Moscow/RU Keywords: Abdomen, Emergency, Gastrointestinal
Emergency MDCT in case of right lower quadrant pain Poster No.: C-0563 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Lisitskaya, V. Sinitsyn; Moscow/RU Keywords: Abdomen, Emergency, Gastrointestinal
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Gastrointestinal Disorders. Disorders of the Esophagus 3/7/2013. Congenital Abnormalities. Achalasia. Not an easy repair. Types
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain
 Peptic Ulcer Disease 58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain Has had dyspepsia in the past for which he took Tums, but this is much worse and only partially relieved
Peptic Ulcer Disease 58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain Has had dyspepsia in the past for which he took Tums, but this is much worse and only partially relieved
Case Discussion Splenic Abscess
 Case Discussion Splenic Abscess Personal Data Gender: male Birth Date: 1928/Mar/06th Allergy: Mefenamic Smoking: 0.5 PPD for 55 years Alcohol: negative (?) 4 Months Ago Abdominal pain: epigastric area
Case Discussion Splenic Abscess Personal Data Gender: male Birth Date: 1928/Mar/06th Allergy: Mefenamic Smoking: 0.5 PPD for 55 years Alcohol: negative (?) 4 Months Ago Abdominal pain: epigastric area
Radiology. Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions
 Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
The Acute Abdomen New Mexico Nurse Practitioner Council Annual Conference, 2012
 The Acute Abdomen New Mexico Nurse Practitioner Council Annual Conference, 2012 Darra D. Kingsley, MD Associate Professor, Surgery, University of New Mexico School of Medicine Associate Chief of Staff,
The Acute Abdomen New Mexico Nurse Practitioner Council Annual Conference, 2012 Darra D. Kingsley, MD Associate Professor, Surgery, University of New Mexico School of Medicine Associate Chief of Staff,
Historical perspective
 Raj Santharam, MD GI Associates, LLC Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical College of Wisconsin Historical perspective FFS first widespread use in the early 1970 s Expansion of therapeutic techniques
Raj Santharam, MD GI Associates, LLC Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical College of Wisconsin Historical perspective FFS first widespread use in the early 1970 s Expansion of therapeutic techniques
Abdominal Complications After Bone Marrow Transplantation in Children: Sonographic and CT Findings
 1023 Pictorial Essay Abdominal Complications After Bone Marrow Transplantation in Children: Sonographic and CT Findings Ellen C. Benya,1 2 Carlos J. Sivit, 2 and Ralph R. Quinones2 3 Bone marrow transplantation
1023 Pictorial Essay Abdominal Complications After Bone Marrow Transplantation in Children: Sonographic and CT Findings Ellen C. Benya,1 2 Carlos J. Sivit, 2 and Ralph R. Quinones2 3 Bone marrow transplantation
Safe Answers For The American Board of Surgery Certifying Exam & Recertifying Exam
 Safe Answers For The American Board of Surgery Certifying Exam & Recertifying Exam By Sarmad Aji, MD., FACS. A comprehensive review of the most commonly asked questions on the American Board of Surgery
Safe Answers For The American Board of Surgery Certifying Exam & Recertifying Exam By Sarmad Aji, MD., FACS. A comprehensive review of the most commonly asked questions on the American Board of Surgery
Abdominal Examination Benchmarks
 Abdominal Examination Benchmarks Preparation and Positioning: Stand on the right side of the patient. The patient should be supine and double draped so only the abdomen is exposed o To relax the abdominal
Abdominal Examination Benchmarks Preparation and Positioning: Stand on the right side of the patient. The patient should be supine and double draped so only the abdomen is exposed o To relax the abdominal
elical CT plays an important role
 bdominal Imaging Yu et al. Helical CT of cute RLQ Pain Pictorial Essay Jinxing Yu 1 nn S. Fulcher Mary nn Turner Robert. Halvorsen Yu J, Fulcher S, Turner M, Halvorsen R Helical CT Evaluation of cute Right
bdominal Imaging Yu et al. Helical CT of cute RLQ Pain Pictorial Essay Jinxing Yu 1 nn S. Fulcher Mary nn Turner Robert. Halvorsen Yu J, Fulcher S, Turner M, Halvorsen R Helical CT Evaluation of cute Right
What s Your Diagnosis?
 What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: 5 year old MC Belgian Malinois Presenting Complaint: Perineal hernia as well as not eating or defecating History: The patient presented to the KSU VHC on 7/28/2018 for
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: 5 year old MC Belgian Malinois Presenting Complaint: Perineal hernia as well as not eating or defecating History: The patient presented to the KSU VHC on 7/28/2018 for
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Chapter 14: Training in Radiology. DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12
 DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
ACUTE ABDOMEN. Dr. M Asadi. Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS. Assistant Professor of General Surgery
 ACUTE ABDOMEN Dr. M Asadi Assistant Professor of General Surgery Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS Definition I. The term Acute Abdomen refers to signs & symptoms of abdominal pain and tenderness,
ACUTE ABDOMEN Dr. M Asadi Assistant Professor of General Surgery Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS Definition I. The term Acute Abdomen refers to signs & symptoms of abdominal pain and tenderness,
Abdominal Assessment
 Abdominal Assessment Mary Marian, MS,RD,CSO University of AZ, Tucson, AZ Neha Parekh, MS,RD,LD,CNSC Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Objectives: 1. Outline the steps in performing an abdominal examination.
Abdominal Assessment Mary Marian, MS,RD,CSO University of AZ, Tucson, AZ Neha Parekh, MS,RD,LD,CNSC Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Objectives: 1. Outline the steps in performing an abdominal examination.
Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
3/22/2011. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Appendicitis. Lemone and Burke Chapter 26
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Lemone and Burke Chapter 26 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Discuss etiology, patho and clinical manifestations of Appendicitis Peritonitis Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Lemone and Burke Chapter 26 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Discuss etiology, patho and clinical manifestations of Appendicitis Peritonitis Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s
12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery
 12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery 34. A 40-year-old female has been referred to you for a recent ER and hospital admission, from which she was given a diagnosis of acute diverticulitis. Treatment at that
12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery 34. A 40-year-old female has been referred to you for a recent ER and hospital admission, from which she was given a diagnosis of acute diverticulitis. Treatment at that
, may spread caudally to present as a perianal abscess, laterally across the external sphincter to form an ischiorectal abscess or, rarely,
 ANORECTAL ABSCESSES , may spread caudally to present as a perianal abscess, laterally across the external sphincter to form an ischiorectal abscess or, rarely, superiorly above the anorectal junction
ANORECTAL ABSCESSES , may spread caudally to present as a perianal abscess, laterally across the external sphincter to form an ischiorectal abscess or, rarely, superiorly above the anorectal junction
EFSUMB EUROPEAN FEDERATION OF SOCIETIES FOR ULTRASOUND IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY Building a European Ultrasound Community
 MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography
MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography
Gastrointestinal Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%)
 Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS
 INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY
 LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY WHAT IS THE APPENDIX? The appendix is a small, fingerlike pouch of the intestinal tract located where the small and large join. It has no known use. It is postulated that the
LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY WHAT IS THE APPENDIX? The appendix is a small, fingerlike pouch of the intestinal tract located where the small and large join. It has no known use. It is postulated that the
USMLE and COMLEX II. CE / CK Review. General Surgery. 1. Northwestern Medical Review
 USMLE and COMLEX II CE / CK Review General Surgery 1. Northwestern Medical Review Northwestern Medical Review www.northwesternmedicalreview.com Lansing, Michigan 2014-2015 Acute Abdomen 1. Your patient
USMLE and COMLEX II CE / CK Review General Surgery 1. Northwestern Medical Review Northwestern Medical Review www.northwesternmedicalreview.com Lansing, Michigan 2014-2015 Acute Abdomen 1. Your patient
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently
 Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Which Blunt Trauma Patients Should Be Studied by Abdominal CT?
 MDCT of Bowel and Mesenteric Injury: How Findings Influence Management 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology
MDCT of Bowel and Mesenteric Injury: How Findings Influence Management 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology
NCD for Fecal Occult Blood Test
 NCD for Fecal Occult Blood Test Applicable CPT Code(s): 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal
NCD for Fecal Occult Blood Test Applicable CPT Code(s): 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen. Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university
 US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
Case Scenario 1. The patient has now completed his neoadjuvant chemoradiation and has been cleared for surgery.
 Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases
 Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases Hsiu-Po Wang Department of Emergency Medicine National Taiwan University Hospital Real-time ultrasound has become a standard
Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases Hsiu-Po Wang Department of Emergency Medicine National Taiwan University Hospital Real-time ultrasound has become a standard
GENERAL SURGERY FOR SMART PEOPLE JOE NOLD MD, FACS WICHITA SURGICAL SPECIALISTS
 GENERAL SURGERY FOR SMART PEOPLE JOE NOLD MD, FACS WICHITA SURGICAL SPECIALISTS CONFLICTS/DECLARATIONS I have no financial conflicts or declarations I AM always willing to see a consult for you TEXT TOPICS
GENERAL SURGERY FOR SMART PEOPLE JOE NOLD MD, FACS WICHITA SURGICAL SPECIALISTS CONFLICTS/DECLARATIONS I have no financial conflicts or declarations I AM always willing to see a consult for you TEXT TOPICS
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS:
 CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
QUESTIONS for the examination in surgery for 4 th -year students of the Faculty of foreign students
 QUESTIONS for the examination in surgery for 4 th -year students of the Faculty of foreign students 1. The main principles of surgical deontology and its founders. 2. Acute appendicitis. Anatomico-physiological
QUESTIONS for the examination in surgery for 4 th -year students of the Faculty of foreign students 1. The main principles of surgical deontology and its founders. 2. Acute appendicitis. Anatomico-physiological
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Chapter 8: Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Abdominal Injuries Abdomen is major body cavity extending from to pelvis. Contains organs that make up digestive, urinary, and genitourinary systems.
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Chapter 8: Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Abdominal Injuries Abdomen is major body cavity extending from to pelvis. Contains organs that make up digestive, urinary, and genitourinary systems.
Esophageal Disorders. Gastrointestinal Diseases. Peptic Ulcer Disease. Wireless capsule endoscopy. Diseases of the Small Intestine 7/24/2010
 Esophageal Disorders Gastrointestinal Diseases Fernando Vega, MD HIHIM 409 Dysphagia Difficulty Swallowing and passing food from mouth via the esophagus Diagnostic aids: Endoscopy, Barium x ray, Cineradiology,
Esophageal Disorders Gastrointestinal Diseases Fernando Vega, MD HIHIM 409 Dysphagia Difficulty Swallowing and passing food from mouth via the esophagus Diagnostic aids: Endoscopy, Barium x ray, Cineradiology,
INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC
 INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 16 S. Amjad Hussain, Chinda Suriyapa, Karl Grubaugh ( Depts. of Surger and
INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 16 S. Amjad Hussain, Chinda Suriyapa, Karl Grubaugh ( Depts. of Surger and
Hemorrhoids. Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery
 Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
Scottish Surveillance of Healthcare Associated Infection Programme (SSHAIP) Health Protection Scotland (HPS) SSI Surveillance Protocol 7th Edition
 1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
What s Your Diagnosis? Jessica Eisenbarth. Signalment: Jazz is a female intact 2 year old German Shorthaired Pointer.
 What s Your Diagnosis? Jessica Eisenbarth Signalment: Jazz is a female intact 2 year old German Shorthaired Pointer. Presenting complaint: Jazz was presented to the K-State emergency service on August
What s Your Diagnosis? Jessica Eisenbarth Signalment: Jazz is a female intact 2 year old German Shorthaired Pointer. Presenting complaint: Jazz was presented to the K-State emergency service on August
Peritonitis SUPPURATIVE DISEASES OF SEROUS CAVITY
 Peritonitis SUPPURATIVE DISEASES OF SEROUS CAVITY peritonitis A special feature of peritonitis is the spread of infection and the intensive absorption by the peritoneum of toxic products - bacterial toxins,
Peritonitis SUPPURATIVE DISEASES OF SEROUS CAVITY peritonitis A special feature of peritonitis is the spread of infection and the intensive absorption by the peritoneum of toxic products - bacterial toxins,
Surgical Education Series
 Surgical Education Series The Acute Abdomen Ahmad kachooei, MD MPH Assistant Professor Division of General Surgery Department of Surgery University of Qom Outline Definitions What causes an acute abdomen
Surgical Education Series The Acute Abdomen Ahmad kachooei, MD MPH Assistant Professor Division of General Surgery Department of Surgery University of Qom Outline Definitions What causes an acute abdomen
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2016; 2:1
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2016; 2:1 Editor-in-Chief: Olufemi E. Idowu. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria. MANAGEMENT OF APPENDICITIS Ibrahim NA, Njokanma
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2016; 2:1 Editor-in-Chief: Olufemi E. Idowu. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria. MANAGEMENT OF APPENDICITIS Ibrahim NA, Njokanma
Causes of abdominal pain Doctors in the ED spend lots of time and money diagnosing abdominal pain. They still often do not know the exact cause
 1 2 3 What's Going On in There? EMS and Abdominal Pain Kevin McFarlane BSN,RN,CEN,CPEN,EMT Southwest Emergency Education and Consulting What is going on in there Acute Abdomen Sudden onset of pain within
1 2 3 What's Going On in There? EMS and Abdominal Pain Kevin McFarlane BSN,RN,CEN,CPEN,EMT Southwest Emergency Education and Consulting What is going on in there Acute Abdomen Sudden onset of pain within
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O
 ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
Abdominopelvic Actinomycosis: spectrum of Imaging Findings and common mimickers.
 Abdominopelvic Actinomycosis: spectrum of Imaging Findings and common mimickers. Poster No.: C-1375 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Giannila, A. J. Van Der Molen, P. Maniatis,
Abdominopelvic Actinomycosis: spectrum of Imaging Findings and common mimickers. Poster No.: C-1375 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Giannila, A. J. Van Der Molen, P. Maniatis,
QUESTIONS IN SURGERY General Surgery (3rd year) Surgery nr.1 (4th year)
 QUESTIONS IN SURGERY General Surgery (3 rd year) 1. Bleeding: definition, classification. Physiological mechanisms of compensation and pathological mechanisms of decompensation in case of hemorrhage. Physiologic
QUESTIONS IN SURGERY General Surgery (3 rd year) 1. Bleeding: definition, classification. Physiological mechanisms of compensation and pathological mechanisms of decompensation in case of hemorrhage. Physiologic
Chapter 18 - Gastrointestinal & Urologic Emergencies
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Chapter 18 Gastrointestinal and Urologic National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 4) Medicine Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Chapter 18 Gastrointestinal and Urologic National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 4) Medicine Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation
Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis
 1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno. Objectives. Why?
 Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno Objectives Discuss the goals of point-of-care biliary ultrasound Review the
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno Objectives Discuss the goals of point-of-care biliary ultrasound Review the
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 20 Caring for Clients with Bowel Disorders Diarrhea Pathophysiology Result from impaired water absorption
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 20 Caring for Clients with Bowel Disorders Diarrhea Pathophysiology Result from impaired water absorption
CT Evaluation of Bowel Wall Thickening. Dr: Adel El Badrawy; M.D. Lecturer of Radio Diagnosis Faculty of Medicine Mansoura University.
 CT Evaluation of Bowel Wall Thickening By Dr: Adel El Badrawy; M.D. Lecturer of Radio Diagnosis Faculty of Medicine Mansoura University. The CT findings of bowel wall thickening includes 1 Degree of thickening.
CT Evaluation of Bowel Wall Thickening By Dr: Adel El Badrawy; M.D. Lecturer of Radio Diagnosis Faculty of Medicine Mansoura University. The CT findings of bowel wall thickening includes 1 Degree of thickening.
HCPCS Codes (Alphanumeric, CPT AMA) ICD-9-CM Codes Covered by Medicare Program
 HCPCS s (Alphanumeric, CPT AMA) 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal neoplasm screening ICD-9-CM
HCPCS s (Alphanumeric, CPT AMA) 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal neoplasm screening ICD-9-CM
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina
 Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System
 USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A surgeon is planning to remove a patient s gallbladder endoscopically. During the procedure, the endoscope will traverse
USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A surgeon is planning to remove a patient s gallbladder endoscopically. During the procedure, the endoscope will traverse
U Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology. Lecture Objectives. MDCT in Acute Pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis: Etiologies
 Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Lecture Objectives MDCT in Acute Pancreatitis Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology niversity Hospital Zurich, Switzerland To describe the role of
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Lecture Objectives MDCT in Acute Pancreatitis Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology niversity Hospital Zurich, Switzerland To describe the role of
1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive abdominal distension 3 months Failure
 Dr Rajasree S Dr Srinivas S, Dr Bagdi RK, Dr Satheesh C Apollo Childrens Hospital, Chennai 1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive
Dr Rajasree S Dr Srinivas S, Dr Bagdi RK, Dr Satheesh C Apollo Childrens Hospital, Chennai 1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive
GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT
 GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT Name & Title Of Author: Dr Linda Jewes, Consultant Microbiologist Date Amended: December 2016 Approved by Committee/Group: Drugs & Therapeutics
GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT Name & Title Of Author: Dr Linda Jewes, Consultant Microbiologist Date Amended: December 2016 Approved by Committee/Group: Drugs & Therapeutics
DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS
 DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS YASHODAMMAL 70 YRS OD LADY had C/o diffuse lower abdominal pain 20 days h/o blood in stools 4 days h/o vomiting 2 days h/o burning micturation
DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS YASHODAMMAL 70 YRS OD LADY had C/o diffuse lower abdominal pain 20 days h/o blood in stools 4 days h/o vomiting 2 days h/o burning micturation
Appendicitis. I. Background & Significance: Algorithm Definitions 1. CASE
 I. Background & Significance: Appendicitis Appendicitis is one of the most common acquired surgical conditions of childhood. Diagnosis of appendicitis remains difficult. Much work has been done on validation
I. Background & Significance: Appendicitis Appendicitis is one of the most common acquired surgical conditions of childhood. Diagnosis of appendicitis remains difficult. Much work has been done on validation
