Elastic tissue textus connectivus elasticus:
|
|
|
- Derick Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Connective tissue 2 1. Connective tissue with special properties: elastic and reticular tissues embryonic connective tissues adipose tissue 2. Supporting connective tissues: cartilage hyaline, elastic and fibrous bone 3. Chondrogenesis 4. Bone tissue: bone cells bone matrix 5.Types of bone tissue 6. Histogenesis of bone
2 Elastic tissue textus connectivus elasticus: vocal folds, ligg. flava et lig. suspensorium penis cells and extracellular matrix: protein fibers: thin collagen thick, parallel elastic fibers reticular fibers amorphous ground substance Cells: flattened fibroblasts and fibrocytes Properties: typical yellow color great elasticity Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 2
3 Reticular tissue textus connectivus reticularis: architectural framework of the myeloid (bone marrow) and lymphoid (lymph nodes, spleen) hematopoietic organs Cells: specialized fibroblasts (reticular cells) cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Properties and functions: branched reticular fibers form a delicate structural network precursor for fibroblasts phagocytic properties Extracellular matrix: protein fibers: reticular fibers (type III collagen) nm in diameter PAS-positive and argyrophilic amorphous ground substance Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 3
4 derived from all three germ layers prominent ground substance matrix loose network of collagen or reticular fibers Embryonic connective tissues mesenchymal connective tissue (mesenchyme): between and within the developing tissues and organs in adult humans, only found in the dental pulp mesenchymal cells stem cell properties capable of developing into connective tissue, bone, cartilage, the lymphatic and the circulatory system Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 4
5 Embryonic connective tissues mucous connective tissue: found during fetal development umbilical cord (Wharton s jelly), pulp of young teeth structural very similar to mesenchyme lower capability to differentiate less plastic cells: mainly fibroblasts collagen fibers and a few elastic or reticular fibers abundance of amorphous ground substance (primarily hyaluronic acid) Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 5
6 Adipose tissue textus adiposus (Lat. adeps, fat): 15-20% of body weight in men; 20-25% in women cells (lipocytes, adipocytes) and extracellular matrix histogenesis from mesenchymally derived lipoblasts Functions: largest repository of energy helps to shape the surface of the body acts as shock absorbers contributes to the thermal insulation of the body helps to keep some organs in place secretes various types of molecules has a rich blood supply Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 6
7 Location: hypoderimis(panniculus adiposus) omentum, mesentery retroperitoneal space, around kidneys breast Structure: subdivided into incomplete lobules unilocular adipose cells: spherical or polyhedral cells large ( µm) cells one large central droplet of fat eccentric and flattened nuclei a thin ring of cytoplasm signet ring cells reticular fibers form a fine interwoven network a rich vascular bed and network of nerves Functions: mechanical cushion of vital organs thermoregulatory role, heat insulation a large depot of energy and water for the organism a secretory organ leptin Unilocular adipose tissue common (white) adipose tissue: its color varies from white to dark yellow (carotenoids dissolved in fat) found throughout the human body except for the eyelids, penis and scrotum Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 7
8 Location a more limited distribution: in hibernating animals hibernating gland in rodents and small mammals around the shoulder girdle in human embryo and newborn 2-5% of the body weight: on the back, along the upper half of the spine and toward the shoulders Structure: multilocular adipose cells: polygonal cells smaller (10 folds = up to 60 µm) cells a large number of lipid droplets a spherical and central nucleus numerous brown mitochondria with abundant long cristae subdivided into lobules richly vascularized tissue cells receive direct sympathetic innervation Functions: important mainly in the first months of postnatal life, greatly reduced in adulthood thermoregulation source of heat and lipid resembles an endocrine gland Multilocular adipose tissue brown adipose tissue: its color is due to both the large number of blood capillaries and the numerous mitochondria (containing colored cytochromes) Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 8
9 textus cartilagineus: Cartilage tissue Gr. chondros, cartilage cells chondroblasts and chondrocytes extracellular matrix 95% peculiarities: specialized cells an extensive extracellular matrix with a firm consistency avascular tissue lack of proper blood supply has no lymphatic vessels devoid of nerves low regeneration capacity NB: main function to support soft tissues Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 9
10 Cartilage cells Chondroblasts origin: undifferentiated mesenchymal cells chondrogenic cells Chondrocytes µm: synthesize and secrete fibers (collagen and elastic) and ground substance their synthesis is accelerated by growth hormone, thyroxine and testosterone, and by vitamin A, C and D located in matrix cavities, lacunae, appearing in isogenous groups (Gr. isos, equal + genos, family) low metabolic activity their mitotic and synthetic activity decline with age Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 10
11 Cartilage matrix extracellular matrix: highly hydrated 60-70% water amorphous substance: glycosaminoglycans hyaluronic acid chondroitin sulfates keratan sulfate ptoteoglycans aggrecan structural glycoproteins chondronectin protein fibers: collagen 20 nm type I and ІІ collagen elastic fibers Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 11
12 Types of cartilage Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 12
13 Gr. hyalos, glass cells: chondroblasts chondrocytes embedded in the lacunae of matrix isogenous groups 2-8 chondrocytes matrix 40% of the dry weight: collagen fibers collagen type ІІ proteoglycan aggregates (4 µm), contain 70-80% water territorial (capsular) matrix 50 µm basophilic, metachromasia PAS-positive + isogenous groups = chondron pericellular capsule 1-3 µm interterritorial matrix articular cartilage (2-5 mm) 4 zones: superficial (tangential zone) up to 10% middle (transitional) layer deep (radial) layer largest part calcified layer partly mineralized perichondrium two layers: stratum fibrosum collagen І fibers stratum cellulare chondrogenic cells nourishes and regenerates the cartilage Hyaline cartilage wide distibuted temporary skeleton (embryo), ribs, articular surfaces, the walls of larger respiratory passages (adults) Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 13
14 Elastic cartilage yellowish color (elastin) not normally calcified, less susceptible to degenerative processes cells: chondroblasts chondrocytes lacunae isogenous groups 1-2 chondrocytes matrix: abundant network of fine elastic fibers collagen type II fibrils proteoglycans perichondrium: appositional growth distribution: auricle and external auditory canal auditory (Eustachian) tube cartilages in the larynx (epiglottis) Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 14
15 Fibrocartilage flexible, though and elastic associated with dense connective tissue cells: chondroblasts in columns chondrocytes arranged in long rows singly small isogenous groups (2 cells) matrix acidophilic: parallel collagen fibrils type I collagen less abundant basophilic amorphous matrix sulfated glycosaminoglycans no identifiable perichondrium distribution: synchondroses in intervertebral disks symphysis pubis, articular menisci some articular surfaces in attachments of certain ligaments to the cartilaginous surface of bones Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 15
16 Histogenesis of cartilage mesenchymal cells chondroblasts chondrofication centers chondroblasts amorphous matrix chondrocytes isogenous groups growth of cartilage: interstitial growth mitotic division of preexisting chondrocytes only during the early phases of cartilage formation appositional growth differentiation of perichondrial cells in the epiphyseal plates of long bones and within articular cartilage Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 16
17 Gr. osteon, bone textus osseus: cells: osteoblasts (Gr. blastos, germ) osteocytes (Gr. kytos, cell) osteoclasts (Gr. klastos, broken) intercellular calcified material (bone matrix) peculiarities: one of the hardest tissues of the human body richly vascularized main constituent of adult skeleton reservoir of calcium (99%), phosphorus main function defense: protection of vital organs in the cranial and thoracic cavities support of freshly structures forms a system of levers to enhance body movements good regeneration capacity Bone (osseous) tissue Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 17
18 osteoprogenitor (osteogenic) cells in periosteum, endosteum and bone canals derived from mesenchymal stem cells develop into osteoblasts or chondroblasts in avascular zones, respectively osteoblasts (20-30 µm) basophilic type I collagen proteoglycans and glycoproteins located at the surfaces of bone tissue osteocytes µm: cell bodies lie in the lacunae, cytoplasmic processes in the bone matrix canaliculi Bone cells involved in the maintenance of the bony matrix synthetic activity completed derive from osteoblasts, do not divide osteoclasts µm: multinucleated 5-50 (100) nuclei acidophilic cytoplasm lie within enzymatically etched Howship s lacunae remove bone tissue (bone resorption) members of the mononuclear phagocyte system Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 18
19 Intercellular material bone matrix: organic matter (35% of the dry weight) elasticity: type I collagen 90% glycosaminoglycans hyaluronic acid chondroitin sulfates keratan sulfate proteoglycans specific glycoproteins osteocalcin and osteospondin inorganic (mineral) matter (65%) rigidity: hydroxyapatite crystals calcium phosphate 85% calcium carbonate 6-10% magnesium phosphate up to 1.5% calcium fluoride traces Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 19
20 primary (immature) bone tissue: nonlamellar (woven) bone temporary higher proportion of osteocytes irregular array of fine collagen fibers secondary (mature) bone tissue: lamellar bone: spongy (cancellous) bone compact bone: outer circumferential lamellae interstitial (intermediate) lamellae inner circumferential lamellae osteon (Haversian system): concentric lamellae of bone 3-20 Haversian canal µm Volkmann s canal periosteum: stratum fibrosum outer layer collagen (Sharpey s) fibers stratum osteogenicum inner layer osteoblasts and osteoclasts endosteum osteoprogenitor cells Types of bone tissue Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 20
21 Bone histogenesis Desmal (direct) osteogenesis condensation of mesenchymal tissue: intramembranous ossification: flat bones skull vault, clavicle begin ~ 8 weeks, mesenchymal cells primary ossification centers Chondral (indirect) osteogenesis deposition of bone matrix on a preexisting cartilage matrix: perichondral ossification: in the diaphysis of the long bones primary ossification centers osteoblasts bone lamella calcification of the cartilage matrix degeneration of chondrocytes sprouting of blood vessels osteoprogenitor cells osteoblasts osteoid fusion of the ossification centers endochondral ossification: in the epiphyseal and diaphyseal cartilage bone collar degeneration of chondrocytes penetration of blood vessels mesenchymal cells osteoblasts osteoid deposition of calcium salts Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 21
22 stimulation: STH calcitonin vitamin D 3 deficiency rachitis inhibition: corticosteroids Bone growth growth plate, epiphyseal cartilage, cartilago epiphysialis cartilage growth zones: resting zone proliferative zone hypertrophic zone calcified cartilage zone ossification zone Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 22
23 Bone fracture: localized hemorrhage formation of a blood clot destruction of bone matrix and death of bone cells Bone remodeling Fracture repair: immature mature bone tissue areas of cartilage primary bone formation endochondral ossification intramembranous ossification formation of bone callus replacement by secondary bone restoration of the original bone structure Bone hypertrophy Bone artrophy (osteoporosis) Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 23
24 Thank you... Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 24
Chapter 4. Cartilage and Bone. Li Shu-Lei instructor. Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University
 Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Cartilage. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cartilage Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology 1 Cartilage is a specialized type of connective tissue designed to give support, bear weight and withstand tension, torsion and
Cartilage Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology 1 Cartilage is a specialized type of connective tissue designed to give support, bear weight and withstand tension, torsion and
Cartilage. - Cartilage together with long bone form the skeleton and support the body.
 Cartilage - Cartilage is a special type of CT has a firm pliable matrix that can resist mechanical stress, act as a shock absorber. - Cartilage together with long bone form the skeleton and support the
Cartilage - Cartilage is a special type of CT has a firm pliable matrix that can resist mechanical stress, act as a shock absorber. - Cartilage together with long bone form the skeleton and support the
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim The cartilage General characteristics: 1. Cartilage is a specialized type of connective tissue (supporting connective tissue). 2. Consists, like other connective tissues, of
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim The cartilage General characteristics: 1. Cartilage is a specialized type of connective tissue (supporting connective tissue). 2. Consists, like other connective tissues, of
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Quiz 6. Cartilage and Bone
 Quiz 6 Cartilage and Bone MCQs X type (true or false): 1. Cartilage tissue: a. Has a rich blood supply. b. Develops from mesenchyme. c. Has ability for a quick regeneration. d. Has chondrocytes as precursor
Quiz 6 Cartilage and Bone MCQs X type (true or false): 1. Cartilage tissue: a. Has a rich blood supply. b. Develops from mesenchyme. c. Has ability for a quick regeneration. d. Has chondrocytes as precursor
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
Blood. Hematopoietic Tissue
 Blood Hematopoietic Tissue Is a type of connective tissue in which its cells are suspended in a circulating fluid. Erythrocytes+ leukocytes + platelets (thrombocytes) =formed elements of blood. These formed
Blood Hematopoietic Tissue Is a type of connective tissue in which its cells are suspended in a circulating fluid. Erythrocytes+ leukocytes + platelets (thrombocytes) =formed elements of blood. These formed
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Cartilage & bone. Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File
 Cartilage & bone Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES describe the microscopic structure, distribution and growth of the different types of Cartilage
Cartilage & bone Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES describe the microscopic structure, distribution and growth of the different types of Cartilage
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
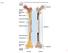 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
physical properties depend on: electrostatic bonds between collagen/elastic fibers and GAGs water bound to negatively charged sulfated GAG chains
 connective/supporting tissue bears mechanical stress without distortion -> shock absorption smooth surface -> facilitates movements of joints guides development of bones chondrocytes extracellular matrix
connective/supporting tissue bears mechanical stress without distortion -> shock absorption smooth surface -> facilitates movements of joints guides development of bones chondrocytes extracellular matrix
5.3. The Nature of Cartilage Matrix The components of cartilage matrix include a high component of fibers, and proteoglycans. Proteoglycans are a
 Chapter 5 Supportive Tissues Support in Animals is carried out by Cartilage and Bone. A. Cartilage 5.1. Nature of Cartilage Cartilage is a highly resilient c..t that provides strength and support in areas
Chapter 5 Supportive Tissues Support in Animals is carried out by Cartilage and Bone. A. Cartilage 5.1. Nature of Cartilage Cartilage is a highly resilient c..t that provides strength and support in areas
Connective Tissue. Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment.
 Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment. Connective Tissue Functions Binding and support Protection Insulation Transportation
Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment. Connective Tissue Functions Binding and support Protection Insulation Transportation
CARTILAGE. Dr. Emad I Shaqoura M.D, M.Sc. Anatomy Faculty of Medicine, Islamic University-Gaza October, 2015
 CARTILAGE Dr. Emad I Shaqoura M.D, M.Sc. Anatomy Faculty of Medicine, Islamic University-Gaza October, 2015 Introduction Hyaline Cartilage Elastic Cartilage Fibrocartilage Cartilage Formation, Growth,
CARTILAGE Dr. Emad I Shaqoura M.D, M.Sc. Anatomy Faculty of Medicine, Islamic University-Gaza October, 2015 Introduction Hyaline Cartilage Elastic Cartilage Fibrocartilage Cartilage Formation, Growth,
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Mast Cell. Mast Cells. James W. Truman, Ph.D. Howard Hughes Medical Institute Chevy Chase, Maryland
 5 th ANNUAL SINAUER ASSOCIATES DISTINGUISHED SCIENTIST LECTURE James W. Truman, Ph.D. Howard Hughes Medical Institute Chevy Chase, Maryland Neuronal Lineages in the CNS of Drosophila: Units of Development,
5 th ANNUAL SINAUER ASSOCIATES DISTINGUISHED SCIENTIST LECTURE James W. Truman, Ph.D. Howard Hughes Medical Institute Chevy Chase, Maryland Neuronal Lineages in the CNS of Drosophila: Units of Development,
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Lecture Overview. Connective Tissues. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Connective Tissues Lecture 10
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Connective Tissues Lecture 10 Lecture Overview General composition and function of connective tissue Components of
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Connective Tissues Lecture 10 Lecture Overview General composition and function of connective tissue Components of
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Module 2:! Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A! Semester 1! !!! !!!! Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb!
 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
Practical Histology. Lab 3: Connective tissue
 Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as
 Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
BONE AND CARTILAGE LIA DAMAYANTI. Department of Histology - FMUI
 1 BONE AND CARTILAGE LIA DAMAYANTI Department of Histology - FMUI Agenda 2 Introduction Cartilage Development of cartilage Growth and repair Components of cartilage Type of Cartilage Agenda 3 Bone Components
1 BONE AND CARTILAGE LIA DAMAYANTI Department of Histology - FMUI Agenda 2 Introduction Cartilage Development of cartilage Growth and repair Components of cartilage Type of Cartilage Agenda 3 Bone Components
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Compact bone; Many parallel Haversian canals contain: small blood vessels. very small nerve. Interconnected by Volkmann s canals.
 Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes
 HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance?
 1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
b. Adult bones produce 2.5 million RBCs each second.
 Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
contains an antiangiogenesis factor
 CARTILAGE & BONE Cartilage and Bone objectives Student must learn :. What is the meaning of cartilage, and their function, location in human body.. To distinguish the 3 types of cartilage. And their cells,
CARTILAGE & BONE Cartilage and Bone objectives Student must learn :. What is the meaning of cartilage, and their function, location in human body.. To distinguish the 3 types of cartilage. And their cells,
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Connective Tissue. Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix
 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the matrix (wandering) Macrophages:
Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the matrix (wandering) Macrophages:
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix 1 True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the
Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix 1 True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Saba Alfayoumi. Heba Kalbouneh
 11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Chapter 6 Skeletal System
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
Growth and repair: Cartilage is a vascular tissues that receives nutrients by diffusion through its matrix, cartilage grow by 2 mechanisms:
 Skeletal connective tissues: (cartilage and bone): Cartilage and bone are specialized connective tissues both adapted to serve as skeletal framework in most vertebrates the presence of solid inter cellular
Skeletal connective tissues: (cartilage and bone): Cartilage and bone are specialized connective tissues both adapted to serve as skeletal framework in most vertebrates the presence of solid inter cellular
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (Refer to pp for specific characteristics of each) VAN (**Be familiar with exceptions**)
 CONNECTIVE TISSUE CHARACTERISTICS: *Most abundant tissue type; Composed of ECM (GS & Protein Fibers) + Cells (Refer to pp.129-131 for specific characteristics of each) *Highly equipped with VAN assists
CONNECTIVE TISSUE CHARACTERISTICS: *Most abundant tissue type; Composed of ECM (GS & Protein Fibers) + Cells (Refer to pp.129-131 for specific characteristics of each) *Highly equipped with VAN assists
The Tissue Level of Organization
 Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Car$lage and Bone. Kris$ne Kra0s, M.D.
 Car$lage and Bone Kris$ne Kra0s, M.D. Car$lage and Bone Lecture Objec$ves Describe the general func$ons of car$lage and bone. Compare the func$on and composi$on of the three types of car$lage. Describe
Car$lage and Bone Kris$ne Kra0s, M.D. Car$lage and Bone Lecture Objec$ves Describe the general func$ons of car$lage and bone. Compare the func$on and composi$on of the three types of car$lage. Describe
Derived copy of Bone *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Cartilage Cartilage is a special form of connective tissue; it has the same origin of connective tissue (embryonic mesenchyme). It contains cells
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Cartilage Cartilage is a special form of connective tissue; it has the same origin of connective tissue (embryonic mesenchyme). It contains cells
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Tissues organs system organism. pg151
 Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
Sheets 16&17. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheets 16&17 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ossification (formation of bone) - Osteoblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix of the bone and these osteoblasts
Sheets 16&17 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ossification (formation of bone) - Osteoblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix of the bone and these osteoblasts
Anatomy & Physiology
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
4 Types of Tissue. Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural
 Connective Tissue 4 Types of Tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural Connective Tissue Fills internal spaces Supports & binds other tissues Transports materials Stores energy Classification of Connective
Connective Tissue 4 Types of Tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural Connective Tissue Fills internal spaces Supports & binds other tissues Transports materials Stores energy Classification of Connective
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal System Functions
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue 6-1 Skeletal System Functions Support. Bone is hard and rigid; cartilage is flexible yet strong. Cartilage in nose, external ear, thoracic cage and trachea.
Chapter 6 Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue 6-1 Skeletal System Functions Support. Bone is hard and rigid; cartilage is flexible yet strong. Cartilage in nose, external ear, thoracic cage and trachea.
4 Types of Tissue. Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural
 Connective Tissue 4 Types of Tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural Connective Tissue Fills internal spaces Supports & binds other tissues Transports materials Stores energy Classification of Connective
Connective Tissue 4 Types of Tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural Connective Tissue Fills internal spaces Supports & binds other tissues Transports materials Stores energy Classification of Connective
Types of Bones. 5 basic types of bones: Sutural bones - in joint between skull bones
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
Dr.Heba Kalbouneh. Ragad Alhawi. Dr.Heba Kalbouneh
 9 Dr.Heba Kalbouneh Ragad Alhawi Dr.Heba Kalbouneh "Cartilage" Cartilage is a special form of connective tissue; it has the same origin of connective tissue (embryonic mesenchyme). It contains cells and
9 Dr.Heba Kalbouneh Ragad Alhawi Dr.Heba Kalbouneh "Cartilage" Cartilage is a special form of connective tissue; it has the same origin of connective tissue (embryonic mesenchyme). It contains cells and
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Connective tissues. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Connective tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Connective tissue (CT) Connective tissue is a term applied to a basic type of tissue of mesodermal origin, which is sparsely populated
Connective tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Connective tissue (CT) Connective tissue is a term applied to a basic type of tissue of mesodermal origin, which is sparsely populated
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue. Functions of Bone. Bones
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
The purpose of this practical session is to demonstrate cartilage and bone as specialized connective tissues to the student.
 1 CARTILAGE AND BONE The purpose of this practical session is to demonstrate cartilage and bone as specialized connective tissues to the student. 1. Hyaline cartilage Slide 73 This is a cross section through
1 CARTILAGE AND BONE The purpose of this practical session is to demonstrate cartilage and bone as specialized connective tissues to the student. 1. Hyaline cartilage Slide 73 This is a cross section through
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS. These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore.
 BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
Chapter 6. Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6 Bone Tissue Functions of the Skeleton support hold the body up, supports muscles, mandible and maxilla support teeth protection brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs movement limb movements, breathing,
Chapter 6 Bone Tissue Functions of the Skeleton support hold the body up, supports muscles, mandible and maxilla support teeth protection brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs movement limb movements, breathing,
Connective Tissue (CT)
 Connective Tissue (CT) YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Introduction of CT 1. Origin 2. Compositions
Connective Tissue (CT) YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Introduction of CT 1. Origin 2. Compositions
Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Skeletal System. Bio 105
 Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline. Skeletal System. Tendons link the skeletal and the muscular systems.
 Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
HISTOLOGY Lecture 2 Connective tissue, muscle and bone tissue PCL Prof. P. Kyamanywa DoS-FACMED NUR
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 2 Connective tissue, muscle and bone tissue PCL1 2012 Prof. P. Kyamanywa DoS-FACMED NUR 4: Connective Tissue nur General function and composition providing structural support for the
HISTOLOGY Lecture 2 Connective tissue, muscle and bone tissue PCL1 2012 Prof. P. Kyamanywa DoS-FACMED NUR 4: Connective Tissue nur General function and composition providing structural support for the
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
Copy and Return to Teacher. The Skeletal System
 Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Outline. Skeletal System. Functions of Bone. Bio 105: Skeletal System 3/17/2016. The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam
 Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Epithelia of Coverings and Linings. Tissues. Tissue
 Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
