Car$lage and Bone. Kris$ne Kra0s, M.D.
|
|
|
- Brett Booker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Car$lage and Bone Kris$ne Kra0s, M.D.
2 Car$lage and Bone Lecture Objec$ves Describe the general func$ons of car$lage and bone. Compare the func$on and composi$on of the three types of car$lage. Describe the two methods of car$lage forma$on. Describe the cells and extracellular matrix of bone. Compare and contrast immature and mature bone. Describe the two methods of bone forma$on.
3 Car$lage and Bone Lecture Outline Car$lage Func$on and characteris$cs of car$lage Composi$on of car$lage Three types of car$lage Forma$on of car$lage Bone Func$on and characteris$cs of bone Composi$on of bone Two (okay, four) types of bone Forma$on of bone
4 Car$lage and Bone Lecture Outline Car$lage Func$on and characteris$cs of car$lage
5 Func$ons and Characteris$cs of Car$lage Car$lage is strong and sort of rigid but also flexible. It can withstand force but it can also bend. It s made of cells (chondroblasts and chondrocytes) and extracellular matrix. Forms the suppor$ng framework of some organs. Lines the surface of ar$cula$ng bones. Forms the template for growth and development of long bones.
6 Metabolic facts that will make you feel sorry for car$lage Bone is very metabolically ac$ve. Car$lage is not. Bone has a good blood supply. Car$lage does not. Bone usually heals well. Car$lage does not.
7 Car$lage and Bone Lecture Outline Car$lage Func$on and characteris$cs of car$lage Composi$on of car$lage
8 Car$lage is a specialized, suppor$ng connec$ve $ssue composed of cells and extracellular matrix. Car$lage Cells Chondroblasts Precursor cells that differen$ate into chondrocytes. Chondrocytes Mature car$lage cells that lie in linle ar$factual lacunae.
9 Car$lage Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Car$lage ECM is composed of: Collagen and/or elas$c fibers Lots of GAGs and proteoglycans Nice choices! These substances make the ECM firm and resistant to mechanical forces.
10 Composi$on of ECM in Car$lage
11 Perichondrium Perichondrium covers the surface of hyaline and elas$c car$lage (but not fibrocar$lage). Dense connec$ve $ssue composed of fibroblasts and type I collagen fibers. Contains blood vessels.
12 Car$lage is avascular. So what? Car$lage itself has no blood vessels or nerves in its extracellular matrix (bone is a different story). Nutrients must diffuse from perichrondrium through extracellular matrix to chondrocytes. This means metabolic ac$vity is low, the width of car$lage is limited, and car$lage heals poorly.
13 Car$lage and Bone Lecture Outline Car$lage Func$on and characteris$cs of car$lage Composi$on of car$lage Three types of car$lage
14 The fibers of the extracellular matrix determine the type of car$lage. Hyaline car$lage Elas$c car$lage Fibrocar$lage Type II collagen fibers Type II collagen fibers and elas$c fibers Type I collagen fibers
15 Three Types of Car$lage Hyaline car$lage Most common. Ar$cular surfaces of joints, large respiratory passages (nose, larynx, trachea, bronchi), ribsternum junc$on, and epiphyseal plate. Func$ons: support so0 $ssue, line joints, growth of long bones.
16 Hyaline Car$lage: Histologic Features Perichondrium Chondroblasts Extracellular matrix Chondrocytes
17 Hyaline ar$cular car$lage
18 Three Types of Car$lage Hyaline car$lage Elas$c car$lage Located in areas that are pliable and flexible Pinna of ear, external auditory canal, auditory (eustachian) tube, epiglo\s, larynx
19 Elas$c car$lage: perichondrium
20 Elas$c car$lage: chondrocytes and matrix
21 Three Types of Car$lage Hyaline car$lage Elas$c car$lage Fibrocar$lage Located in areas subjected to pulling forces Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, and anachments of tendons and ligaments
22 Fibrocar$lage: collagen fibers
23 Fibrocar$lage: chondrocytes
24 Fibrocar$lage: matrix
25 Car$lage and Bone Lecture Outline Car$lage Func$on and characteris$cs of car$lage Composi$on of car$lage Three types of car$lage Forma$on of car$lage
26 Two Methods of Car$lage Forma$on Inters$$al growth: growth from within car$lage. Chondrocytes divide and secrete matrix. Apposi$onal growth: growth along the outside of car$lage. Chondroblasts secrete matrix and differen$ate into chondrocytes.
27 Car$lage and Bone Lecture Outline Car$lage Func$on and characteris$cs of car$lage Composi$on of car$lage Three types of car$lage Forma$on of car$lage Bone Func$on and characteris$cs of bone
28 Func$ons of Bone Support and protec$on of so0 $ssues ANachment of muscles for movement Loca$on of hematopoie$c bone marrow where blood cells are produced Stores and releases calcium, phosphate and other ions
29 Characteris$cs of Bone Bone is highly vascularized and very metabolically ac$ve. Bone remodels (turns over) constantly throughout life. Ideally, bone removal occurs at same rate as bone produc$on. Inhibi$on of bone turnover leads to poor quality, unhealthy bone.
30 Car$lage and Bone Lecture Outline Car$lage Func$on and characteris$cs of car$lage Composi$on of car$lage Three types of car$lage Forma$on of car$lage Bone Func$on and characteris$cs of bone Composi$on of bone
31 Composi$on of Bone Cells Osteoblasts: produce bone matrix Osteocytes: lie in lacunae Osteoclasts: resorb bone Extracellular matrix Organic matrix: osteoid, composed of type I collagen fibers and ground substance Inorganic (mineralized) matrix: hydroxyapa$te
32 Osteoblasts Found along edge of bone, with osteoid underneath. Ac$ve osteoblasts are cuboidal-columnar with abundant RER, Golgi and secretory granules; inac$ve osteoblasts are flanened.
33 Make bone! Osteoblast Func$ons Produce osteoid (organic bone matrix) with type I collagen fibers, proteoglycans and glycoproteins. Deposit inorganic hydroxyapa$te crystals: Ca 10 (PO 4 ) 6 (OH) 2 Bone forma$on promoted by testosterone, estrogen, growth hormone, weight-bearing exercise and muscle use.
34 Osteocytes are involved in maintenance of bone matrix. Their death results in resorp$on of matrix. Each osteocyte sits in its own lacuna. Osteocytes have small, dark, flanened nuclei with minimal rough ER and Golgi. Osteocytes
35 Mul$nucleated giant cells ( μm). Lie in Howship s lacunae. Arise from fusion of blood monocytes. Numerous lysosomes. Ac$vely resorbing osteoclasts adjacent to bone have cytoplasmic membrane branching ( ruffled border ). Osteoclasts
36 How do osteoclasts resorb bone? Clear zone: an area of cytoplasm that seals off an acidic micro-environment containing lysosomal enzymes. This is where bone resorp$on occurs.
37 How do osteoclasts resorb bone? The osteoclast transfers collagenase and protons into this microenvironment, breaking down collagen fibers and calcium salts. Then, the osteoclast phagocy$zes the remnants of bone resorp$on.
38 Bone Matrix Inorganic 50% of dry weight of bone Mostly calcium Organic Type I collagen Ground substance (proteoglycans and glycoproteins)
39 Serum Calcium and Bone Resorp$on When serum calcium is low, parathyroid hormone is released, which tells osteoblasts to make osteoclast s$mula$ng factor. Osteoclasts then resorb bone, which increases serum calcium. Cool! When serum calcium is high, calcitonin is released, which inhibits osteoclas$c resorp$on of bone, leading to decreased serum calcium.
40 Car$lage and Bone Lecture Outline Car$lage Func$on and characteris$cs of car$lage Composi$on of car$lage Three types of car$lage Forma$on of car$lage Bone Func$on and characteris$cs of bone Composi$on of bone Two (okay, four) types of bone
41 Two Gross Types of Bone Compact bone Very dense, solid structure. Spongy bone Open, loose structure.
42 Compact Bone and Spongy Bone Compact bone Spongy bone
43 Two Microscopic Types of Bone Immature (primary, woven) bone The first bone laid down. Formed quickly. Later replaced by mature bone. Mature (secondary, lamellar) bone Arranged in osteons: layers (lamellae) of bone around linle canals.
44 Immature vs. Mature Bone Immature bone Mature bone Gross structure Always spongy Compact (outside) and spongy (inside) Collagen fiber arrangement Random Parallel Number of osteocytes Lots Rela$vely few
45 Two Microscopic Types of Bone Immature (primary, woven) bone The first bone laid down. Formed quickly. Later replaced by mature bone.
46 Immature bone: super low-power view
47 Immature bone: high-power view
48 Two Microscopic Types of Bone Immature (primary, woven) bone The first bone laid down. Formed quickly. Later replaced by mature bone. Mature (secondary, lamellar) bone Arranged in osteons: layers (lamellae) of bone around linle canals.
49
50 Central canal Osteocytes Lamellae Osteon (Haversian system)
51 Volkmann (perfora$ng) canals connect osteons
52 Periosteum and Endosteum Periosteum lines the outer surface of compact bone. Two layers: outer dense connec$ve $ssue layer and inner layer of osteoprogenitor cells. Sharpey s fibers are collagen fibers which $ghtly anach the periosteum to the bone matrix. Contains blood vessels for nutri$on of bone. Contains osteoblasts for bone growth, repair and remodeling.
53 central canal osteon external lamellae Periosteum inner layer outer layer perfora$ng fibers inters$$al lamellae trabeculae of spongy bone
54 Periosteum and Endosteum Periosteum lines the outer surface of compact bone. Endosteum lines the inner surface of compact bone. Also lines the surface of bony trabeculae of spongy bone, and the Haversian canals. Contains osteoblasts for bone growth, repair and remodeling.
55 Endosteum
56 Car$lage and Bone Lecture Outline Car$lage Func$on and characteris$cs of car$lage Composi$on of car$lage Three types of car$lage Forma$on of car$lage Bone Func$on and characteris$cs of bone Composi$on of bone Two types of bone Forma$on of bone
57 Bone Development (Osteogenesis) Bone can be formed in two ways: Intramembranous ossifica$on Occurs in flat bones (most of skull, including maxilla and mandible). Endochondral ossifica$on Occurs in long bones and irregular bones.
58 Eight Steps in Intramembranous Ossifica$on 1. Capillaries grow into mesenchyme & release oxygen. 2. Surrounding mesenchymal cells round up, differen$ate into osteoblasts and form osteoid. 3. Osteoid mineralizes. Osteoblasts become osteocytes. 4. Bone spicules form and enlarge to form trabeculae of immature bone. 5. A single plate (table) of bone is formed. 6. Immature bone is replaced by mature bone. 7. Remodeling con$nues, and 2 tables of bone are formed. 8. The two tables are separated by diploe: Tables = compact bone Diploe = spongy bone with marrow
59 Intramembranous Ossifica$on
60 Intramembranous Ossifica$on
61 Intramembranous Ossifica$on
62 Intramembranous Ossifica$on
63 Six Steps in Endochondral Ossifica$on 1. Fetal hyaline car$lage develops. 2. Car$lage calcifies, and a periosteal bone collar forms around the diaphysis (long part of the bone). 3. A primary ossifica$on center forms in the diaphysis. 4. Secondary ossifica$on centers form in the epiphyses (ends of the bone). 5. Bone replaces car$lage (except the ar$cular car$lage and epiphyseal plates). 6. Epiphyseal plates ossify.
64 Endochondral Ossifica$on
65 Endochondral Ossifica$on
66 Endochondral Ossifica$on Epiphysis: the end of a long bone. Consists primarily of spongy bone, with a layer of compact bone on the outside. Diaphysis: the sha0 of a long bone. Consists of compact bone on the outside and a marrow cavity inside.
67 Endochondral bone forma$on: super low-power view
68 Endochondral bone forma$on: zones of matura$on
69 Endochondral bone forma$on: res$ng zone
70 Endochondral bone forma$on: prolifera$ve zone
71 Endochondral bone forma$on: zone of hypertrophy
72 Endochondral bone forma$on: zone of calcifica$on
73 Endochondral bone forma$on: zone of ossifica$on
74 Epiphyseal plate in endochondral ossifica$on
75 Synovial joint (diarthrosis)
76 Synovial Membrane
77 Ar$cular car$lage Joint cavity Synovial membrane
78 Car$lage and Bone Lecture Outline Car$lage Func$on and characteris$cs of car$lage Composi$on of car$lage Three types of car$lage Forma$on of car$lage Bone Func$on and characteris$cs of bone Composi$on of bone Two types of bone Forma$on of bone
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 4. Cartilage and Bone. Li Shu-Lei instructor. Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University
 Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
Cartilage & bone. Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File
 Cartilage & bone Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES describe the microscopic structure, distribution and growth of the different types of Cartilage
Cartilage & bone Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES describe the microscopic structure, distribution and growth of the different types of Cartilage
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Module 2:! Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A! Semester 1! !!! !!!! Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb!
 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Chapter 6 Skeletal System
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Cartilage. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cartilage Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology 1 Cartilage is a specialized type of connective tissue designed to give support, bear weight and withstand tension, torsion and
Cartilage Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology 1 Cartilage is a specialized type of connective tissue designed to give support, bear weight and withstand tension, torsion and
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
b. Adult bones produce 2.5 million RBCs each second.
 Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
5.3. The Nature of Cartilage Matrix The components of cartilage matrix include a high component of fibers, and proteoglycans. Proteoglycans are a
 Chapter 5 Supportive Tissues Support in Animals is carried out by Cartilage and Bone. A. Cartilage 5.1. Nature of Cartilage Cartilage is a highly resilient c..t that provides strength and support in areas
Chapter 5 Supportive Tissues Support in Animals is carried out by Cartilage and Bone. A. Cartilage 5.1. Nature of Cartilage Cartilage is a highly resilient c..t that provides strength and support in areas
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Saba Alfayoumi. Heba Kalbouneh
 11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
Quiz 6. Cartilage and Bone
 Quiz 6 Cartilage and Bone MCQs X type (true or false): 1. Cartilage tissue: a. Has a rich blood supply. b. Develops from mesenchyme. c. Has ability for a quick regeneration. d. Has chondrocytes as precursor
Quiz 6 Cartilage and Bone MCQs X type (true or false): 1. Cartilage tissue: a. Has a rich blood supply. b. Develops from mesenchyme. c. Has ability for a quick regeneration. d. Has chondrocytes as precursor
Sheets 16&17. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheets 16&17 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ossification (formation of bone) - Osteoblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix of the bone and these osteoblasts
Sheets 16&17 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ossification (formation of bone) - Osteoblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix of the bone and these osteoblasts
Derived copy of Bone *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
Skeletal System Functions
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue 6-1 Skeletal System Functions Support. Bone is hard and rigid; cartilage is flexible yet strong. Cartilage in nose, external ear, thoracic cage and trachea.
Chapter 6 Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue 6-1 Skeletal System Functions Support. Bone is hard and rigid; cartilage is flexible yet strong. Cartilage in nose, external ear, thoracic cage and trachea.
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
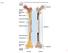 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Blood. Hematopoietic Tissue
 Blood Hematopoietic Tissue Is a type of connective tissue in which its cells are suspended in a circulating fluid. Erythrocytes+ leukocytes + platelets (thrombocytes) =formed elements of blood. These formed
Blood Hematopoietic Tissue Is a type of connective tissue in which its cells are suspended in a circulating fluid. Erythrocytes+ leukocytes + platelets (thrombocytes) =formed elements of blood. These formed
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS. These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore.
 BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
Compact bone; Many parallel Haversian canals contain: small blood vessels. very small nerve. Interconnected by Volkmann s canals.
 Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
physical properties depend on: electrostatic bonds between collagen/elastic fibers and GAGs water bound to negatively charged sulfated GAG chains
 connective/supporting tissue bears mechanical stress without distortion -> shock absorption smooth surface -> facilitates movements of joints guides development of bones chondrocytes extracellular matrix
connective/supporting tissue bears mechanical stress without distortion -> shock absorption smooth surface -> facilitates movements of joints guides development of bones chondrocytes extracellular matrix
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Bone Special connective tissue. Cartilages + Bones = Skeleton. Osseous = refers to bone. Functions of the bone: 1. Support: It forms the framework
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Bone Special connective tissue. Cartilages + Bones = Skeleton. Osseous = refers to bone. Functions of the bone: 1. Support: It forms the framework
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Mast Cell. Mast Cells. James W. Truman, Ph.D. Howard Hughes Medical Institute Chevy Chase, Maryland
 5 th ANNUAL SINAUER ASSOCIATES DISTINGUISHED SCIENTIST LECTURE James W. Truman, Ph.D. Howard Hughes Medical Institute Chevy Chase, Maryland Neuronal Lineages in the CNS of Drosophila: Units of Development,
5 th ANNUAL SINAUER ASSOCIATES DISTINGUISHED SCIENTIST LECTURE James W. Truman, Ph.D. Howard Hughes Medical Institute Chevy Chase, Maryland Neuronal Lineages in the CNS of Drosophila: Units of Development,
Chapter 6. Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6 Bone Tissue Functions of the Skeleton support hold the body up, supports muscles, mandible and maxilla support teeth protection brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs movement limb movements, breathing,
Chapter 6 Bone Tissue Functions of the Skeleton support hold the body up, supports muscles, mandible and maxilla support teeth protection brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs movement limb movements, breathing,
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
Oral Histology. Alveolar bone or process: Functions of alveolar bone: Chemical composition: Development of the alveolar process: Dr.
 Oral Histology Lec.12 Alveolar bone or process: Dr. Nada Al-Ghaban Alveolar bone is a specialized part of the mandibular and maxillary bones that forms the primary support structure for teeth. Although
Oral Histology Lec.12 Alveolar bone or process: Dr. Nada Al-Ghaban Alveolar bone is a specialized part of the mandibular and maxillary bones that forms the primary support structure for teeth. Although
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Ossification = Osteogenesis
 Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1)
 NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
Anatomy & Physiology
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Do Now: 1. Where, specifically, is blood created? Which part of the long bone? 2. Which structures are primarily associated with growth? 3.
 Do Now: 1. Where, specifically, is blood created? Which part of the long bone? 2. Which structures are primarily associated with growth? 3. How could damage to these areas impact bone growth? WRITE AND
Do Now: 1. Where, specifically, is blood created? Which part of the long bone? 2. Which structures are primarily associated with growth? 3. How could damage to these areas impact bone growth? WRITE AND
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
BONE AND CARTILAGE LIA DAMAYANTI. Department of Histology - FMUI
 1 BONE AND CARTILAGE LIA DAMAYANTI Department of Histology - FMUI Agenda 2 Introduction Cartilage Development of cartilage Growth and repair Components of cartilage Type of Cartilage Agenda 3 Bone Components
1 BONE AND CARTILAGE LIA DAMAYANTI Department of Histology - FMUI Agenda 2 Introduction Cartilage Development of cartilage Growth and repair Components of cartilage Type of Cartilage Agenda 3 Bone Components
Copy and Return to Teacher. The Skeletal System
 Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Gross Anatomy. Landmarks on a typical long bone. Membranes. Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes. Periosteum Endosteum
 BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
Cartilage. - Cartilage together with long bone form the skeleton and support the body.
 Cartilage - Cartilage is a special type of CT has a firm pliable matrix that can resist mechanical stress, act as a shock absorber. - Cartilage together with long bone form the skeleton and support the
Cartilage - Cartilage is a special type of CT has a firm pliable matrix that can resist mechanical stress, act as a shock absorber. - Cartilage together with long bone form the skeleton and support the
Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Bone. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44789 1 Bone OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
OpenStax-CNX module: m44789 1 Bone OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
OpenStax-CNX module: m Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin. Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance?
 1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Chapter 5. The Skeletal System. Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Types of Bones. 5 basic types of bones: Sutural bones - in joint between skull bones
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
contains an antiangiogenesis factor
 CARTILAGE & BONE Cartilage and Bone objectives Student must learn :. What is the meaning of cartilage, and their function, location in human body.. To distinguish the 3 types of cartilage. And their cells,
CARTILAGE & BONE Cartilage and Bone objectives Student must learn :. What is the meaning of cartilage, and their function, location in human body.. To distinguish the 3 types of cartilage. And their cells,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 ( ) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST 3 2011 1. If calcium levels in the extracellular fluid are too low, parathyroid hormone secretion would and osteoclast activity
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST 3 2011 1. If calcium levels in the extracellular fluid are too low, parathyroid hormone secretion would and osteoclast activity
The purpose of this practical session is to demonstrate cartilage and bone as specialized connective tissues to the student.
 1 CARTILAGE AND BONE The purpose of this practical session is to demonstrate cartilage and bone as specialized connective tissues to the student. 1. Hyaline cartilage Slide 73 This is a cross section through
1 CARTILAGE AND BONE The purpose of this practical session is to demonstrate cartilage and bone as specialized connective tissues to the student. 1. Hyaline cartilage Slide 73 This is a cross section through
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim The cartilage General characteristics: 1. Cartilage is a specialized type of connective tissue (supporting connective tissue). 2. Consists, like other connective tissues, of
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim The cartilage General characteristics: 1. Cartilage is a specialized type of connective tissue (supporting connective tissue). 2. Consists, like other connective tissues, of
Connective tissues. All forms of connective tissue share some common structural features and a common embryonic origin.
 Connective tissues Connective tissue forms a framework upon which epithelial tissue rests and within which nerve tissue and muscle tissue are embedded. Blood vessels and nerves travel through connective
Connective tissues Connective tissue forms a framework upon which epithelial tissue rests and within which nerve tissue and muscle tissue are embedded. Blood vessels and nerves travel through connective
Outline. Skeletal System. Functions of Bone. Bio 105: Skeletal System 3/17/2016. The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam
 Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (Refer to pp for specific characteristics of each) VAN (**Be familiar with exceptions**)
 CONNECTIVE TISSUE CHARACTERISTICS: *Most abundant tissue type; Composed of ECM (GS & Protein Fibers) + Cells (Refer to pp.129-131 for specific characteristics of each) *Highly equipped with VAN assists
CONNECTIVE TISSUE CHARACTERISTICS: *Most abundant tissue type; Composed of ECM (GS & Protein Fibers) + Cells (Refer to pp.129-131 for specific characteristics of each) *Highly equipped with VAN assists
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling
 Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation)
Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation)
The Tissue Level of Organization
 Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides. Chapter 6
 Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Skeletal System. Bio 105
 Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline. Skeletal System. Tendons link the skeletal and the muscular systems.
 Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Practical Histology. Lab 3: Connective tissue
 Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue. Functions of Bone. Bones
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes
 HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
Growth and repair: Cartilage is a vascular tissues that receives nutrients by diffusion through its matrix, cartilage grow by 2 mechanisms:
 Skeletal connective tissues: (cartilage and bone): Cartilage and bone are specialized connective tissues both adapted to serve as skeletal framework in most vertebrates the presence of solid inter cellular
Skeletal connective tissues: (cartilage and bone): Cartilage and bone are specialized connective tissues both adapted to serve as skeletal framework in most vertebrates the presence of solid inter cellular
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Epithelia of Coverings and Linings. Tissues. Tissue
 Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58082 1 Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure * Willy Cushwa Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58082 1 Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure * Willy Cushwa Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
