The study of arterial supply of the carpal joint in one-humped camel (Camelus dromedrus)
|
|
|
- Dayna Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iranian Journal of Veterinary Medicine The study of arterial supply of the carpal joint in one-humped camel (Camelus dromedrus) Sajjadian, M. 1, Nazem, M.N. 2*, Radmehr, B. 3 1 Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman, Iran 2 Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman, Iran 3 Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Oloum tahghighat, Tehran, Iran. Key words: Dromedrus camel, carpal joint, radial artery, median artery, caudal interosseous artery Correspondence Nazem, M.N. Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman, Iran Tel: +98(343) Fax: +98(343) nnazem@mail.uk.ac.ir Received: 26 August 2014 Accepted: 19 November 2014 Introduction Carpal region is composed of several bones and their supportive structures, nerves and vessels. According to the importance of healthy of the forelimb, the purpose of this study was Abstract: BACKGROUND: There is little information about blood supply of the carpal joint in one- humped camel, while there is extensive data about cow and equine species. In order to perform surgeries and diagnostic techniques in carpal region, information about the elements of the joint such as its arteries is necessary. OBJECTIVES: This study aims at describing the origins, arrangements, and branches of the arterial supply of the carpal joint of the adult one-humped camel (Camelus dromedarius). METHODS: Twelve left forelimbs of camelus Dromedrus without any lameness history were divided into 3 equal groups randomly. The brachial artery, before the elbow joint, was injected with warm water containing red gelatin, red latex solution, and rodopas resin solution separately; then, the arterial supply of the carpal joint was studied. RESULTS: The results showed that the radial, median, and caudal interosseous arteries and their branches supplied the carpal joint. (Supplied the carpal joint) CONCLUSIONS: Our findings showed that radial artery and its branches such as dorsal and palmar carpal branches were the most important arteries that supply the carpal joint. Median and caudal interosseous arteries support supplying this joint too but the arterial branches supplying the carpal joint in the Bactrian camel are from the radial artery and dorsal interosseous antebrachium branches. In the cow, the common interosseous, median, collateral ulnar and radial arteries give off branches to supply the carpal joint while common interosseous, median, transverse cubital and radial arteries give off branches to supply the this joint in the horse. to describe the anatomy of the arterial supply of the carpal joint in one-humped camel and comparison results with cow and equine ones. Some researchers have been studied anatomical structures of bones (Soroori et al., 2007), tendons (Soroori et al., 2011) and digits 57
2 The study of arterial supply of the carpal... Sajjadian, M. / foot pad (Badawy, 2011) of the forelimb in one-humped camel by means different methods. The arterial supply of the forelimb of Bactrian camel has been studied previously (Jain et al., 1992; Jian-Lin et al., 1994; Jian-Lin et al.; 1998, Jian-Lin et al., 2000). Moreover arterial supply to the scapular, brachial and antebrachial regions of the llama has studied too (Arzone et al., 1995). Information about the arterial supply to the carpal joint in the one-humped camel (Camelus deromedrus) is lesser and also is rare comparing with than other species. Current study was conducted to describe the origins, arrangements and branches of the arterial supply of the carpal joint in the adult onehumped camel (Camelus dromedarius), where it gives anatomical information for researches and surgeons in the field of camel medicine. Materials and Methods Twelve left forelimbs of one-humped camel were divided in 3 equal groups. The samples were selected without regard to sex. Forelimbs were cut on the top of the elbow joint and the entrance of the brachial artery in the distal part of the forelimb was exposed to injecting fluid. In the first group, warm water containing red gelatin was infusion through into the brachial artery by syringe. Consequently skin of the forelimbs was removed and limbs were transferred to the 10% formalin solution. After ten days, arteries of the carpal joint were carefully described. This method helped to finding small arteries in this region. Process of the second group was similar to the first group but in this group, red latex solution was injected. Recent method allowed dissecting arteries easier than before technique but unlike it, couldn t expose small arteries. Rodopas resine solution was similarly injected. The samples were placed in cold water for a week. Then samples were placed in HCl acid (Merk, KgaA, German) for 2 days and after that carpal arteries were studied. In this method, muscles, nerves and other soft tissues around the arteries were removed by acid. Finally revealed anatomical structures were vigilantly explored. Results Camel carpal arterial branches were spread plexus under the dorsal carpal ligament. Several thin arteries of this plexus were supplied the carpal bones except the accessory carpal bone. Also some of these arteries entered the carpal capsules from the dorsal inter carpal ligaments and supplied them. Palmar arterial plexus placed under the palmar carpal ligament but didn t as broad as the dorsal carpal plexus. Also some arteries from this plexus were supplied the palmar capsule and ligaments of the palmar surface (Fig. 1). Distal forelimb arteries arrived from the brachial artery. The transverse cubital artery, collateral ulnar artery and common interosseous artery were derived from the brachial artery but didn t achieve to the carpal joint and thus couldn t supply this joint. The Cranial interosseous artery that was given off by the common interosseous artery didn t arrive to the carpal joint and thus couldn t supply this joint too (Fig. 1,3). The brachial artery became the median artery at the end of the distal fourth of the brachium after detachment of common interosseous artery. Median artery was the most artery of the antebrachium that was continued ventrally near the median vein and median nerve to the carpal joint. At the beginning, it passed ventrally between the flexor carpi radialis and radial head of the flexor digitrum profundus muscles at the medial border of the radius. At the palmar surface, it continued ventrally under the flexor carpi radialis muscle (next to the humeral and radial heads of the flexor digitrum profundus muscle) to the carpal joint. Median artery gave off several branches before arriv- 58
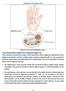
3 Sajjadian, M. Iranian Journal of Veterinary Medicine Figure 1. Dorsal carpal arteries and ligaments ( dorsal arterial plexus is seen ) (carpal joint capsule is removed). A) Radial bone. B) Metacarpal bone. C) Radial carpal bone. D) Intermediate carpal bone. E) Ulnar carpal bone. F) 3rd carpal bone. G) 4th carpal bone. H) Dorsal intercarpal bone ligaments. I) Deep part of collateral ligament. 1) Interosseous artery. 2) Dorsal carpal branch of palmar branch of radial artery. 3) Dorsal carpal branches of radial artery. 4) Dorsal metacarpal artery. ing to the carpal joint. These branches were supplied the muscles surrounding them. Then this artery gave off radial artery (the largest branch of this artery) at the final third of the radius. It extended ventrally between ligaments of the flexor digitrum superficial and flexor digitrum profundus muscles at the palmar surface. It passed from palmar part of carpal joint while surrounding by ligaments of the flexor digitrum superficial and flexor digitrum profundus muscles, median nerve and flexor retinaculum. It joined to palmar branch of the radial artery at palmar surface of metacarp and created the superficial palmar arc (Fig. 2,3). Radial artery, the most branch of the median artery, was the most artery that supplied the carpal joint which derived from median artery adjacent to ligament of flexor carpi radialis muscle at the final third of caudal surface of radius. This artery was passed under the flexor carpi radialis muscle near the humeral head of flexor digitrum superficialis and then changed its way to distal interosseous space and finally divided into two branches at the top of the distal interosseous space near the flexor digitrum Figure 2. Medial surface of the carpal joint. A) Flexor retinaculum. B) Tendon of flexor carpi radialis muscle. C) Median palmar nerve. 1) Median artery. 2) Radial artery. 3) Dorsal carpal branches of radial artery. 4) Superficial palmar branch of radial artery. 5) Radial vein. 6) Cephalic vein. 7) Median vein. profundus muscle: the thick branch was named palmar branch of radial artery and thin branch that was continuation of radial artery (Fig. 3). Palmar branch of radial artery with palmar branch of radial vein and lateral palmar nerve passed between ligaments of deep digital flexor muscle at the caudal surface of the antebrachium over the palmar ligament and entered the carpal canal at the medial surface of accessory carpal bone. Palmar branch of radial artery was divided into superficial and deep branches after crossing from carpal canal. Superficial branch was joined to medial artery over the suspensory ligament next to the fetlock and was accompanied in superficial palmar arc. Deep branch was passed between the suspensory ligament and metacarpal bone and was joined to deep palmar branch of radial artery and formed deep palmar arc. Deep palmar branch was given off palmar metacarpal artery (Fig. 3). Palmar branch of radial artery gave off several branches: interosseous, dorsal and palmar carpal branches. Interosseous artery of palmar branch of radial artery was resulting from palmar branch of radial artery near the distal interosseous space and after joining to the caudal interosseous artery was entered to distal interosseous space. 59
4 The study of arterial supply of the carpal... Sajjadian, M. Figure 3. Palmar carpal arteries and ligaments of the carpal joint. A) Median artery. B) Radial artery. C) Palmar branch of median artery. D) Interosseous artery. E) Caudal interosseous artery. F) Dorsal carpal branch of palmar branch of radial artery. G) Palmar carpal branches of palmar branch of radial artery. H) Dorsal carpal branches of radial artery. I) Palmar carpal branches of radial artery. J) Superficial palmar branch of radial artery. K) Deep palmar branch of radial artery. L) Deep palmar arc. 1) Suspensory ligament. 2) Superficial part of medial collateral ligament. 3) Deep parts of medial collateral ligament. 4) Palmar radiocarpal ligament. 5) Accessorioulnar carpal ligament. 6) Accessorioquartal ligament. 7) Accessoriometacarpal ligament. 8) Palmar intercarpal ligaments. 9) Palmar carpometacarpal ligaments. Figure 5. Schematically plan of arterial supply of the dorsal carpal joint. 1) Interosseous artery. 2) Dorsal carpal branch of radial artery. 3) Dorsal carpal branch of palmar branch of radial artery. 4) Dorsal carpal arterial plexus. 5) Dorsal metacarpal arteries. This artery continued at the dorsal surface of the radius, between the ligaments of extensor digitrum commonis and extensor carpi radialis muscles, to dorsal surface of carpal joint. 60 Figure 4. Schematically plan of arterial supply of the palmar carpal joint. 1) Median artery. 2) Dorsal carpal branch of radial artery. 3) Palmar carpal branch of radial artery. 4) Radial artery. 5) Superficial palmar branch of radial artery. 6) Deep palmar branch of radial artery. 7) Palmar branch of radial artery. 8) Interosseous artery. 9) Palmar carpal branch of palmar branch. 10) Dorsal carpal branch of palmar branch. 11) Superficial branch of palmar branch. 12) Deep branch of palmar branch. 13) Palmar metacarpal arteries. 14) Collateral radial artery. Interosseous artery gave off some branches to supply the extensor digitrum commonis and extensor carpi radialis muscles and connected to the dorsal carpal artery after the extensor carpi obliques muscle (Fig. 1,3). Dorsal carpal branch of palmar branch of radial artery was given off from radial artery before entering to carpal canal and was passed over the accessory ulnar ligament immediately. This arterial branch was turned round accessory ulnar ligament to arrive dorsal surface of carpal joint on the dorsal carpal ligament near the lateral surface of accessory carpal bone and was sent some branches to supply this carpal bone. This artery joined to the dorsal carpal arterial plexus finally (Fig. 1). Palmar carpal branches of palmar branch of radial artery included 2 or 3 branches that arose from radial artery in the carpal canal and were joined to palmar carpal arterial plexus (Fig. 1). After giving off this recently branch, radial artery continued adjacent the ligament of flexor carpi radialis muscle and passed from flexor retinaculum at the palmar surface of carpal joint and then divided into superficial
5 Sajjadian, M. palmar and deep palmar branches immediately after palmar carpal region. Superficial palmar branch connected to median artery at the proximal of the first third of metacarpal bone and corporate in superficial palmar arc formation. Deep palmar branch passed between suspensory ligament and metacarpal bone and joined to deep branch of palmar branch of radial artery to form deep palmar arc (Fig. 2,3). Lateral branches of radial artery were dorsal and palmar carpal branches. Dorsal carpal branches of radial artery were derived from radial artery at the flexor retinaculum and were passed between the deep and superficial parts of medial carpal collateral ligaments and were joined to dorsal carpal plexus. Palmar carpal branches of radial artery were given off by the radial artery at the flexor retinaculum too and were joined to palmar carpal artery (Fig. 3). Schematic plan of arterial supply of the carpal joint has been shown in figures 5 and 6 (Fig. 4,5). Arterial supply of the carpal joint are shown in the figures 5 and 6 schematically. Discussion Several studies were investigated the forelimb arteries in the camel (Smuth et al., 1987; Jian-Lin et al., 1994; Jian-Lin et al., 1998; Jian-Lin et al., 2000,). Smuts et al. (Smuth et al., 1987) reported that common interosseous, median and radial arteries are supply to the carpal joint, while our findings indicate that the caudal interosseous, median and radial arteries supply the carpal joint. In addition we showed that arterial plexus of the carpal joint in one humped camel, similar to the horse and cow ones (Budras et al., 2009; Dyce et al., 1996; Nickel et al., 1981) was below the dorsal and palmar carpal ligaments and composed of several arteries. Like to the horse, cow (Budras et al., 2009; Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981) and Bactrian camel (Jian-Lin et al., 2000), dorsal carpal plexus in Iranian Journal of Veterinary Medicine one humped camel was more developed than palmar arterial plexus. Distal branches of brachial artery in the one humped camel were transverse cubital, collateral ulnar and interosseous arteries, which have been reported with other researchers in dromedrus, Bactrian camel and llama (Arzone et al., 1995; Bego, 1960; Jain et al., 1992; Smuth et al., 1987; Jian-Lin et al., 2000). In our samples, transverse cubital artery was derived from the brachial artery before the collateral ulnar artery, while it originates from the brachial artery after the collateral ulnar artery in the horse and cow (Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981). Our results about transverse cubital artery were in agreement with Bactrian camel anatomical findings (Jian-Lin et al., 2000). Brachial artery was became median artery after detachment of the common interosseous artery. This artery was the most important artery of antebrachial and was continued to carpal joint. In this way it gave off some branches that named deep antebrachial arteries. This artery was anatomically similar to the Bactrian camel (Jian-Lin et al., 2000), cow (Dyce et al., 1996; Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981) and horse (Budras et al., 2009; Dyce et al., 1996; Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981) ones. Median artery continued about the final third of antebrachial and then gave off radial artery. Radial artery was the only branch of the median artery at the top of the carpal joint in the camel. It was like to cow ones (Dyce et al., 1996; Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981), while it gives off three branches in the horse (Budras et al., 2009; Nickel et al., 1981; Getty, 1975). This artery was passed from carpal canal to metacarpal region after detachment the radial artery. Findings in Bactrian camel have shown that this artery doesn t participate in supplying the carpal joint (Jian-Lin et al., 2000). Radial artery was the most important arterial supply to the carpal joint but its branches had basic differences with its counterparts in horse and cow (Budras et al., 2009; Dyce 61
6 The study of arterial supply of the carpal... Sajjadian, M. et al., 1996; Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981). In the cow the region of origin is located in the proximal but in the horse is in the distal third of the lower humerus. In the horse there is the small dorsal radialis artery at the first and then, immediately before the elbow joint, radial artery. Except in the horse, the radial artery runs caudomedially to the median artery along the caudomedial edge of the radius. Immediately proximal to the carpus it gives rise to the dorsal carpal artery which contributes to the formation of the dorsal and palmar rete carpal which goes to the palmar articular network. The radial artery then reaches the flexor retinaculum in a palmar position. In the horse the dorsal and palmar carpal rete do not come off the radial artery but arise by proximal radial artery. Therefore the radial artery, which arises far distally, divides immediately into the deep and superficial palmar branches. This artery doesn t participate in supplying the carpal joint in Bactrian camel (Jian-Lin et al., 2000). In the one - humped camel like to the Bactrian camel (Jian-Lin et al., 2000), the palmar branch was derived from the radial artery, while it is a branch of median artery in the horse and cow (Getty, 1975, Nickel et al., 1981). Palmar branch of radial artery in the camel was continued to lateral border of the carpal joint and was gave off interosseous artery at the distal interosseous space. These results were similar to findings in Bactrian camel and llama (Arzone et al., 1995; Jian-Lin et al., 2000). Interosseous artery joins to the dorsal carpal artery but doesn t supply the carpal joint in Bactrian camel (Jian-Lin et al., 2000). This artery wasn t detected in the horse (Budras et al., 2009; Nickel et al., 1981) while it is a branch of cranial interosseous artery in the cow (Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981). Common interosseous artery was the last branch of the brachial artery which stems from it at the dorsal common interosseous space. According to our findings, this artery doesn t supply the carpal joint. Smuts et al. (Smuth et al., 1987) have reported that common interosseous supplies the carpal joint. Some researchers have reported that collateral radial artery is the last branch of the brachial artery before the common interosseous artery (Jain et al., 1992), but we showed that common interosseous was the last branch of the brachial artery. It was similar to the cow and horse ones (Budras et al., 2009; Dyce et al., 1996; Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981). Branches of common interosseous were cranial and caudal interosseous arteries that were similar to other studies in Dromedarius (Bego, 1960; Jain et al., 1992; Smuth et al., 1987) and Bactrian camels (Jian-Lin et al., 2000). In some studies collateral radial artery was known as a branch of the common interosseous artery (Jain et al., 1992). We showed that cranial interosseous artery was short and was passed under the extensor digitrum commonis muscle but didn t arrive to carpal joint, while other researchers have reported this artery continues above the carpal joint and supplies it (Jain et al., 1992; Smuth et al., 1987). Jian-Lin has stated that this branch supplies the carpal joint in Bactrian camel (Jian-Lin et al., 2000), while Arzone didn t detect this artery in llama (Arzone et al., 1995). Our results indicate that caudal interosseous artery was the only branch of the common interosseous artery. This artery was relatively a thick artery at the caudal surface of the radial bone that continued above the distal interosseous space and joined to palmar branch of interosseous artery of radial artery. Other researchers reported that this artery divides into dorsal and palmar branches above the carpal joint and finally joins to dorsal and palmar carpal plexuses finally (Jain et al., 1992; Smuth et al., 1987). Arzone stated that this artery is short and can t supply the carpal joint in llama (Arzone et al., 1995). There is no report about supplying carpal joint by caudal interosseous artery in the Bactrian camel (Jian-Lin et al., 2000). 62
7 Sajjadian, M. Similar to the Bactrian camel (Jian-Lin et al., 2000) and llama (Arzone et al., 1995), Palmar carpal artery gave off dorsal carpal branch before entering the carpal canal. This branch wasn t reported in the horse and cow (Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981). Palmar carpal branch gave off several branches in the carpal canal and finally joined to palmar carpal arterial plexus. These branches weren t reported in the horse and cow (Dyce et al., 1996; Getty, 1975; Smuth et al., 1987). The continuation of palmar branch was similar to the ones in horse (Budras et al., 2009, Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981), cow (Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981) and was divided to superficial and deep branches. Continuation of radial artery after the palmar branch was similar to ones in the horse, cow and Bactrian camel (Dyce et al., 1996; Getty, 1975; Jian-Lin et al., 2000). It was passed from medial aspect of the flexor retinaculum and gave off some branches to dorsal and palmar carpal arterial plexus. These results are similar to the ones in cow (Nickel et al., 1981) and Bactrian camel (Jian-Lin et al., 2000). Radial artery doesn t have any branch during passage on the carpal joint in the horse (Dyce et al., 1996; Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981). Radial artery positioned at the proximal extremity of the metacarpal bones after passing from the carpal canal. It divided to superficial and deep deep palmar branches in horse (Budras et al., 2009; Dyce et al., 1996; Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981). Our findings showed that radial artery and its branches, median and caudal interosseous arteries supply this joint but the arteries supply the carpal joint in the Bactrian camel are radial artery and its branches and the dorsal interosseous antebrachium branches (Jian-Lin et al., 2000). In the cow, the common interosseous, median, collateral ulnar and radial arteries give off branches to supply the carpal joint but the common interosseous, median, transverse cubital and radial arteries give off branches to Iranian Journal of Veterinary Medicine supply the carpal joint in the horse (Budras et al., 2009; Dyce et al., 1996; Getty, 1975; Nickel et al., 1981). Acknowledgments This research was financially supported by the research council of Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman References Arzone, C.A., Calaudi, P., Casalonga, O., Valdes, V.A.(1995) Arterial irrigation of the scapular, brachial and antebrachial regions of the llama. Excreta camelida. 2: Badawy Adel, M. (2011) Computed tomographic anatomy of the fore foot in onehumped camel (Camelus dromedrus). Glob Vet. 6: Bego, U. (1960) Comparative anatomy of blood supply and nerves of the fore leg in the camel, llama, giraffe and cattle. Acta Anat. 42: 261. Budras Klaus Dieter, Sack, W.O., Rock, S. (2009) Anatomy of the Horse. (5 th ed.) Schlutersche. Frankfurt, Germany. p Dyce, K.M., Sack, W.D., Wensing, C.J.G. (1996) Text Book of Veterinary Anatomy. (2 nd ed.) W.B.Saunders company. Philadelphia, USA. Getty, R. (1975) Sisson and Grossman s. The Anatomy of the Domestic Animals. (5 th ed.) W.B.Saunders company. Philadelphia, USA. Jain, R.K., Dhingra, L.D. (1992) The brachial artery of camel. Indian J Anim Sci. 63: Jian-Lin Wang, Cui-Sheng, Gen-Xuan Wang, Hai-Yan, Li. (2000) The arterial supply of the carpal joint in the Bactrian camel (Camelus bactrianus). Vet Res Commun. 24: Jian-Lin Wang, Cui-Sheng, Zheng-Ming Xie. (1998) The arterial supply of the metacarpophalangeal joint in the Bactrian camel (Camelus bactrianus). Vet Res Commun. 22:
8 The study of arterial supply of the carpal... Sajjadian, M Jian-Lin Wang, Zheng-Ming, Xie. (1994) Arterial supply of the shoulder joint in the Bactrian camel (Camelus bactrianus). J Camel Pract Res. 2: Nickel, R., Schummer, A., Seiferle, E. (1981) The anatomy of the domestic animals. Vol. 3. Verlag Paul Parey. Berlin Humburg, Germany. Smuts, M.S., Bezuidenhout, A.J. (1987) Anatomy of the Dromedary. (1 st ed.) Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK. Soroori, S., Veshkini, A., Dehghan, M., Farhadian, O. (2007) Radiodraphic assessment of bone cortex to bone diameter ratio of manus and pes in camel. Iranian journal of veterinary surgery (IJVS). 2: Soroori, S., Masoudifard, M., Vajhi, A.R., Rostami, A., Salimi, M. (2011) Ultrasonography study of tendons and ligaments of metacarpal region in the camel (Camelus dromedarius). Int J Vet Res (University of Tehran). 5:
BRACHIAL PLEXUS 11/12/2014 كيف تتكون الضفيرة FORMATION ENLARGEMENT (INTUMESCENCE) OF THE SPINAL CORD. Grey matter. Cervical intumescence - C 6 - T 2
 BRACHIAL PLEXUS Prof. Fawzy Elnady ENLARGEMENT (INTUMESCENCE) OF THE SPINAL CORD Grey matter Cervical intumescence - C 6 - T 2 Lumbar intumescence - L 4 S 2 كيف تتكون الضفيرة FORMATION The ventral rami
BRACHIAL PLEXUS Prof. Fawzy Elnady ENLARGEMENT (INTUMESCENCE) OF THE SPINAL CORD Grey matter Cervical intumescence - C 6 - T 2 Lumbar intumescence - L 4 S 2 كيف تتكون الضفيرة FORMATION The ventral rami
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
divided by the bones ( redius and ulna ) and interosseous membrane into :
 fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Anatomic Review of Eleven Important Canine Acupuncture Points Part I: Thoracic Limb
 Review Anatomic Review of Eleven Important Canine Acupuncture Points Part I: Thoracic Limb Martha A. Littlefield DVM, MS, CVA ABSTRACT Two papers (Part I and Part II) review eleven commonly used acupuncture
Review Anatomic Review of Eleven Important Canine Acupuncture Points Part I: Thoracic Limb Martha A. Littlefield DVM, MS, CVA ABSTRACT Two papers (Part I and Part II) review eleven commonly used acupuncture
THE ANATOMY of the canine elbow has been fully
 Veterinary Surgery 38:135 143, 2009 INVITED REVIEW A Clinically Oriented Comprehensive Pictorial Review of Canine Elbow Anatomy GHEORGHE M. CONSTANTINESCU, DVM, PhD, mult Dr h c and ILEANA A. CONSTANTINESCU,
Veterinary Surgery 38:135 143, 2009 INVITED REVIEW A Clinically Oriented Comprehensive Pictorial Review of Canine Elbow Anatomy GHEORGHE M. CONSTANTINESCU, DVM, PhD, mult Dr h c and ILEANA A. CONSTANTINESCU,
Myologia Part II Objective: Students will examine the muscles of a canine in order to identify the musculature of the body.
 Okay Anatomy Anatomy I: Lesson 11 Myologia Part II Objective: Students will examine the muscles of a canine in order to identify the musculature of the body. Practical Tasks: 6) carpal flexors, pronators
Okay Anatomy Anatomy I: Lesson 11 Myologia Part II Objective: Students will examine the muscles of a canine in order to identify the musculature of the body. Practical Tasks: 6) carpal flexors, pronators
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
ANATOMY OF THE CARPAL ARTICULATION OF BUFFALO CALVES (BUBALUS BUBALIS)
 Original Article Buffalo Bulletin (October-December 2016) Vol.35 No.4 ANATOMY OF THE CARPAL ARTICULATION OF BUFFALO CALVES (BUBALUS BUBALIS) Supriya B. 1,*, T.S. Chandrasekhara Rao 2 and P. Jagapathi Ramayya
Original Article Buffalo Bulletin (October-December 2016) Vol.35 No.4 ANATOMY OF THE CARPAL ARTICULATION OF BUFFALO CALVES (BUBALUS BUBALIS) Supriya B. 1,*, T.S. Chandrasekhara Rao 2 and P. Jagapathi Ramayya
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader. Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS
 Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
ANATOMICAL DISPOSITION OF CARPAL BONES OF GOLDEN RETRIEVER DOG BY X-RAY EXPOSURE
 Explor. Anim. Exploratory Med. Res., Vol.2, Animal Issue and - 1, Medical 2012, p. Research, 76-80 Vol.2, Issue -1, July, 2012 ISSN 2277-470X ANATOMICAL DISPOSITION OF CARPAL BONES OF GOLDEN RETRIEVER
Explor. Anim. Exploratory Med. Res., Vol.2, Animal Issue and - 1, Medical 2012, p. Research, 76-80 Vol.2, Issue -1, July, 2012 ISSN 2277-470X ANATOMICAL DISPOSITION OF CARPAL BONES OF GOLDEN RETRIEVER
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Learning Objectives. 07 Aug 12. Article E-1. At the end of this section the learner will be able to:
 Module 1: Comparative Functional Anatomy and Biomechanics Article E-1 Learning Objectives At the end of this section the learner will be able to: Describe the bones of the equine thoracic Describe the
Module 1: Comparative Functional Anatomy and Biomechanics Article E-1 Learning Objectives At the end of this section the learner will be able to: Describe the bones of the equine thoracic Describe the
The Elbow and the cubital fossa. Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles
 Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity
 Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
forearm posterior compartment
 Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
EasyAnatomy s. Snapshot Guide to the Bones of the Canine Thoracic Limb. LlamaZOO Interactive facebook.
 Thoracic Limb The regions of the thoracic limb, or forelimb, are the shoulder, brachium (upper arm), antebrachium (lower arm), and the manus (forepaw). The manus is composed of the carpus, metacarpus,
Thoracic Limb The regions of the thoracic limb, or forelimb, are the shoulder, brachium (upper arm), antebrachium (lower arm), and the manus (forepaw). The manus is composed of the carpus, metacarpus,
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments
 Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
The Forearm 2. Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm
 The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5. September 30, 2011
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
Topographic Description of Metacarpal Tendons and Ligaments of Anatoly Donkey by Ultrasonography and Introducing a New Ligament
 November 2015, Volume 12, Number 4 Topographic Description of Metacarpal Tendons and Ligaments of Anatoly Donkey by Ultrasonography and Introducing a New Ligament Mohammad Naser Nazem 1*, Sayed Mohsen
November 2015, Volume 12, Number 4 Topographic Description of Metacarpal Tendons and Ligaments of Anatoly Donkey by Ultrasonography and Introducing a New Ligament Mohammad Naser Nazem 1*, Sayed Mohsen
BRACHIAL PLEXUS. DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae
 THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
MORPHOFUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS OF THE FOREARM MUSCLE AT SHEEP AND DOG
 MORPHOFUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS OF THE FOREARM MUSCLE AT SHEEP AND DOG Ştefănescu, S., G. Predoi, C. Belu, B. Georgescu, I. Dumitrescu, Carmen Biţoiu, Anca Şeicaru Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Bucharest,
MORPHOFUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS OF THE FOREARM MUSCLE AT SHEEP AND DOG Ştefănescu, S., G. Predoi, C. Belu, B. Georgescu, I. Dumitrescu, Carmen Biţoiu, Anca Şeicaru Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Bucharest,
Wrist and Hand Anatomy
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
The Arm and Cubital Fossa
 The Arm and Cubital Fossa Dr. Andrew Gallagher School of Anatomical Sciences University of the Witwatersrand Introduction The ARM (BRACHIUM) is the most proximal segment of the upper limb musculoskeletal
The Arm and Cubital Fossa Dr. Andrew Gallagher School of Anatomical Sciences University of the Witwatersrand Introduction The ARM (BRACHIUM) is the most proximal segment of the upper limb musculoskeletal
Proceedings of the 56th Annual Convention of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - AAEP -
 http://www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 56th Annual Convention of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - AAEP - December 4-8, 2010 Baltimore, Maryland, USA Next Meeting : Nov. 18-22, 2011 -
http://www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 56th Annual Convention of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - AAEP - December 4-8, 2010 Baltimore, Maryland, USA Next Meeting : Nov. 18-22, 2011 -
region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla.
 1 region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla. Inferiorly, a number of important structures pass between arm & forearm through cubital fossa. 2 medial
1 region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla. Inferiorly, a number of important structures pass between arm & forearm through cubital fossa. 2 medial
Case Studies. A. Kent Allen, DVM LAMENESS AND IMAGING IN THE SPORT HORSE
 Case Studies A. Kent Allen, DVM Author s address: Virginia Equine Imaging, 2716 Landmark School Road, The Plains, VA 20198; e-mail: vaequine@aol.com. 2007 AAEP. 1. Case Study #1: Medial Collateral Desmitis
Case Studies A. Kent Allen, DVM Author s address: Virginia Equine Imaging, 2716 Landmark School Road, The Plains, VA 20198; e-mail: vaequine@aol.com. 2007 AAEP. 1. Case Study #1: Medial Collateral Desmitis
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
8/25/2014. Radiocarpal Joint. Midcarpal Joint. Osteology of the Wrist
 Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Supplied in part by the musculocutaneous nerve. Forms the axis of rotation in movements of pronation and supination
 Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Cubital fossa and forearm
 Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Intrahepatic ramifications of the portal vein in the horse
 Intrahepatic ramifications of the portal vein in the horse Tadjalli, M. 1* and Moslemy, H. R. 2 1 Department of Anatomical Sciences, School of Veterinary Medicine, University of Shiraz, Shiraz, Iran; 2
Intrahepatic ramifications of the portal vein in the horse Tadjalli, M. 1* and Moslemy, H. R. 2 1 Department of Anatomical Sciences, School of Veterinary Medicine, University of Shiraz, Shiraz, Iran; 2
10/15/2014. Wrist. Clarification of Terms. Clarification of Terms cont
 Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Viorel Nacu. The clinical anatomy of the Hand
 Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Axilla and Brachial Region
 L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
compartments of the forearm
 " forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
" forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
Functional anatomy and variability of the blood vessels of the upper and lower limbs. Anastasia Bendelic Human Anatomy Departament
 Functional anatomy and variability of the blood vessels of the upper and lower limbs Anastasia Bendelic Human Anatomy Departament Plan: 1. Variations of the branching pattern of the aortic arch 2. Arterial
Functional anatomy and variability of the blood vessels of the upper and lower limbs Anastasia Bendelic Human Anatomy Departament Plan: 1. Variations of the branching pattern of the aortic arch 2. Arterial
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
MUSCLES. Anconeus Muscle
 LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
The Elbow 3/5/2015. The Elbow Scanning Sequence. * Anterior Joint (The anterior Pyramid ) * Lateral Epicondyle * Medial Epicondyle * Posterior Joint
 Scanning Sequence * Anterior Joint (The anterior Pyramid ) * Lateral Epicondyle * Medial Epicondyle * Posterior Joint Anterior Elbow Pyramid Courtesy of Jay Smith, MD. Vice chair PMR Mayo Clinic Rochester,
Scanning Sequence * Anterior Joint (The anterior Pyramid ) * Lateral Epicondyle * Medial Epicondyle * Posterior Joint Anterior Elbow Pyramid Courtesy of Jay Smith, MD. Vice chair PMR Mayo Clinic Rochester,
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Fracture and Dislocation of the Carpus ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
VARIANT ARTERIAL PATTERN IN THE FOREARM WITH ITS EMBRYOLOGICAL BASIS. Vaishnavi Joshi and Dr. Shaheen Sajid Rizvi
 Volume-8, Issue-3 July-Sept-2018 Coden:IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2018 ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 8 th June-2018 Revised: 15 th July-2018 Accepted: 16 th July-2018 DOI: 10.21276/Ijpaes http://dx.doi.org/10.21276/ijpaes
Volume-8, Issue-3 July-Sept-2018 Coden:IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2018 ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 8 th June-2018 Revised: 15 th July-2018 Accepted: 16 th July-2018 DOI: 10.21276/Ijpaes http://dx.doi.org/10.21276/ijpaes
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow
 Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
# Anatomy. Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla. Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil. Page 0 of 16
 #10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
#10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings
 Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings Poster No.: C-1779 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno, A. P. Pissarra,
Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings Poster No.: C-1779 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno, A. P. Pissarra,
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA November 2-5, 2011 Hyderabad, India Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission of WEVA Organizers
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the World Equine Veterinary Association WEVA November 2-5, 2011 Hyderabad, India Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission of WEVA Organizers
ANATOMY. Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date :
 ANATOMY Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date : Median nerve Meaian nerve to Pronator teres Course: Enter cubital fossa. Pierce Pronat. teres Between to FDS, FOP Below and lateral
ANATOMY Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date : Median nerve Meaian nerve to Pronator teres Course: Enter cubital fossa. Pierce Pronat. teres Between to FDS, FOP Below and lateral
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm
 Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락
 Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
VENOUS DRAINAGE O US F UPPER UPPER LIM B BY dr.fahad Ullah
 VENOUS DRAINAGE OF UPPER LIMB BY dr.fahad Ullah Venous drainage of the supper limb The venous system of the upper limb drains deoxygenated blood from the arm, forearm and hand It can anatomically be divided
VENOUS DRAINAGE OF UPPER LIMB BY dr.fahad Ullah Venous drainage of the supper limb The venous system of the upper limb drains deoxygenated blood from the arm, forearm and hand It can anatomically be divided
The Clavicle Right clavicle Deltoid tubercle: Conoid tubercle, conoid ligamen Impression for the
 The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
1/13/2013. Anatomy Guy Dissection Sheet Extensor Forearm and Hand. Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Anatomy - Hand. Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics. Osteology. Carpal Arch. Property of VOMPTI, LLC
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
The pectoral region. University of Babylon College of Medicine Dr.HaythemAli Alsayigh M.B.CH.B.-F.I.M.B.S. Surgical Clinical Anatomy
 The pectoral region University of Babylon College of Medicine Dr.HaythemAli Alsayigh M.B.CH.B.-F.I.M.B.S. Surgical Clinical Anatomy Objective Study the Bones and Joints A. Clavicle (collarbone) B. Scapula
The pectoral region University of Babylon College of Medicine Dr.HaythemAli Alsayigh M.B.CH.B.-F.I.M.B.S. Surgical Clinical Anatomy Objective Study the Bones and Joints A. Clavicle (collarbone) B. Scapula
Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY. Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES. The theme of the lesson The vessels of the upper limb.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 The theme of the lesson The vessels of the upper limb. Course Faculties І Medical
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 The theme of the lesson The vessels of the upper limb. Course Faculties І Medical
Morphological Variations in Lumbricals of Hand A Cadaveric Study
 IBIMA Publishing Plastic Surgery: An International Journal http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/psij/psij.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 821692, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.821692 Morphological Variations
IBIMA Publishing Plastic Surgery: An International Journal http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/psij/psij.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 821692, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.821692 Morphological Variations
Figure 27: The synovial membrane of the shoulder joint (anterior view)
 The coracoacromial ligament; is an accessory ligament that protects the superior aspect of the joint extending from the coracoid process to the acromion over the tendon of supraspinatus. The synovial membrane
The coracoacromial ligament; is an accessory ligament that protects the superior aspect of the joint extending from the coracoid process to the acromion over the tendon of supraspinatus. The synovial membrane
Forelimb Amputation. Indications. Pre operatively 11/12/2008. Technique Preparing for surgery. Bone neoplasia. Severe trauma/paralysis
 Forelimb Amputation January 10, 2007 Amy Bringardner Becky Pentecost Indications Bone neoplasia Osteosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Chondrosarcoma Severe trauma/paralysis Brachial plexus avulsion Infection Congenital
Forelimb Amputation January 10, 2007 Amy Bringardner Becky Pentecost Indications Bone neoplasia Osteosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Chondrosarcoma Severe trauma/paralysis Brachial plexus avulsion Infection Congenital
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful
 In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
Anatomy of the Upper Limb
 Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
MSK Imaging Conference. 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology
 MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
13 13/3/2012. Adel Muhanna
 13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
Introduction. The wrist contains eight small carpal bones, which as a group act as a flexible spacer between the forearm and hand.
 Wrist Introduction The wrist contains eight small carpal bones, which as a group act as a flexible spacer between the forearm and hand. Distal forearm Distal forearm 4 Distal end of the radius A. anterior
Wrist Introduction The wrist contains eight small carpal bones, which as a group act as a flexible spacer between the forearm and hand. Distal forearm Distal forearm 4 Distal end of the radius A. anterior
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides
 The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
The hand. it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand**
 Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
7) Digital flexors of the forelimb, pronators of the radioulnar joint
 Anatomy 1 - Lesson XI: Myologia- Part II Objective: Students will examine the muscles of a canine in order to identify the musculature of the body Practical Tasks 6-10: 6) Carpal flexors, pronators of
Anatomy 1 - Lesson XI: Myologia- Part II Objective: Students will examine the muscles of a canine in order to identify the musculature of the body Practical Tasks 6-10: 6) Carpal flexors, pronators of
Misc Anatomy. Upper Limb! 2. Lower Limb! 5. Venous Drainage! Head & neck! 8
 Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]
![[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]] [[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]](/thumbs/84/91174469.jpg) In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
G24: Shoulder and Axilla
 G24: Shoulder and Axilla Syllabus - Pg. 2 ANAT 6010- Medical Gross Anatomy David A. Morton, Ph.D. Objectives Upper limb Systemically: Bones (joints) Muscles Nerves Vessels (arteries/veins) Fascial compartments
G24: Shoulder and Axilla Syllabus - Pg. 2 ANAT 6010- Medical Gross Anatomy David A. Morton, Ph.D. Objectives Upper limb Systemically: Bones (joints) Muscles Nerves Vessels (arteries/veins) Fascial compartments
Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report
 SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity RADIUS AND ULNA right
 11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach.
 Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2228 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Muda, D. Orlandi, V. Prono, S. Migone,
Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2228 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Muda, D. Orlandi, V. Prono, S. Migone,
Practical 2 Worksheet
 Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
The Free Upper Limb. Bone of the Arm. aus: Platzer, Locomotor System (ISBN ), 2009 Georg Thieme Verlag KG
 : ones, Ligaments, Joints The Free The bones of the free upper limb are The humerus The radius and ulna The carpal bones The metacarpal bones The phalanges one of the Arm Humerus (A H) The humerus articulates
: ones, Ligaments, Joints The Free The bones of the free upper limb are The humerus The radius and ulna The carpal bones The metacarpal bones The phalanges one of the Arm Humerus (A H) The humerus articulates
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper
 Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Gross Anatomical Studies of the Bones of the Thoracic
 Gross Anatomical Studies of the Bones of the Thoracic Limbs of the Lion (Panthera leo) Nzalak, J.O; Eki, M.M; * Sulaiman, M.H; Umosen, A.D; Salami, S. O., Maidawa, S.M and Ibe, C.S Department of Veterinary
Gross Anatomical Studies of the Bones of the Thoracic Limbs of the Lion (Panthera leo) Nzalak, J.O; Eki, M.M; * Sulaiman, M.H; Umosen, A.D; Salami, S. O., Maidawa, S.M and Ibe, C.S Department of Veterinary
Joints of the upper limb II
 Joints of the upper limb II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Elbow joint The elbow joint is connecting the upper arm to the forearm. It is classed
Joints of the upper limb II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Elbow joint The elbow joint is connecting the upper arm to the forearm. It is classed
MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION
 MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION Dr Bronwen Ackermann COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulation WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney
MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION Dr Bronwen Ackermann COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulation WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney
CADAVERIC STUDY OF VARIANT FLEXOR CARPI ULNARIS
 IJCRR Vol 04 issue 23 Section: Heathcare Category: Research Received on: 26/10/12 Revised on: 05/11/12 Accepted on:22/11/12 CADAVERIC STUDY OF VARIANT FLEXOR CARPI ULNARIS MUSCLE Sharadkumar Pralhad Sawant,
IJCRR Vol 04 issue 23 Section: Heathcare Category: Research Received on: 26/10/12 Revised on: 05/11/12 Accepted on:22/11/12 CADAVERIC STUDY OF VARIANT FLEXOR CARPI ULNARIS MUSCLE Sharadkumar Pralhad Sawant,
Fracture and Dislocation of Metacarpal Bones, Metacarpophalangeal Joints, Phalanges, and Interphalangeal Joints ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
Chapter 8. The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb
 Chapter 8 The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb Pectoral Girdle pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle) supports the arm consists of two on each side of the body // clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade)
Chapter 8 The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb Pectoral Girdle pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle) supports the arm consists of two on each side of the body // clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade)
High-resolution ultrasound of the elbow - didactic approach.
 High-resolution ultrasound of the elbow - didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2358 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. M. Olchowy, M. Lasecki, U. Zaleska-Dorobisz; Wroclaw/PL Keywords:
High-resolution ultrasound of the elbow - didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2358 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. M. Olchowy, M. Lasecki, U. Zaleska-Dorobisz; Wroclaw/PL Keywords:
