ASPECTE HISTOPATOLOGICE ÎN AFECÞIUNILE GRANULOMATOASE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF GRANULOMATOUS DISEASES
|
|
|
- Jessica Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REFERATE GENERALE GENERAL REPORTS ASPECTE HISTOPATOLOGICE ÎN AFECÞIUNILE GRANULOMATOASE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF GRANULOMATOUS DISEASES OLGUÞA ANCA ORZAN*, IRINA TUDOSE** Bucureºti Rezumat Afecþiunile granulomatoase reprezintã un grup de boli cu etiologie ºi cu manifestãri clinice variate care au în comun formarea de granuloame (la nivel cutanat sau al altor organe), evidenþiabile la examenul histopatologic. Denumirea de granulom provine din limba latinã granulum (granula) +oma (rezultatul unei acþiuni), iar din punct de vedere histopatologic se defineºte ca o colecþie organizatã de histiocite. În funcþie de aspectul histopatologic, þinându-se cont de tipul celular predominant, aranjamentul histiocitelor, absenþa/prezenþa ºi tipul necrozei, precum ºi cantitatea, distribuþia ºi compoziþia infiltratului inflamator, afecþiunile granulomatoase pot fi împãrþite în cinci categorii: granuloame epitelioide, cunoscute ºi sub denumirea de naked granuloma, granuloame tuberculoide, granuloame în palisadã, granuloame supurative ºi granuloame de corp strãin. Cuvinte cheie: granulom epitelioid, naked granuloma, granulom tuberculoid, granulom în palisadã, granulom supurativ, granulom de corp strãin, reacþie granulomatoasã. Summary Granulomatous diseases are a group of various disorders, having different etiology and clinical findings, but with the same histopathological features (cutaneous or other organ granulomas). The term granuloma comes form the latine granulum (grain) +oma (the result of an action), and it is defined as a collection of histiocytes. Based on histological features, taking into account the main cellular type, the histiocyte arrangement, the absence/ presence and type of necrosis, as well as the amount, the distribution and composition of the inflammatory infiltrate, the granulomatous disorders can be divided into five categories: epithelioid granuloma ( naked granuloma ), tuberculoid granuloma, palisade granuloma, suppurative granuloma and foreign body granuloma. Key word: epithelioid granuloma, naked granuloma, tuberculoid granuloma, palisade granuloma, suppurative granuloma, foreign body granuloma, granulomatous reaction. DermatoVenerol. (Buc.), 56: * Spitalul Clinic Universitar de Urgenþã Elias, Bucureºti ** Spitalul Clinic de Dermato-venerologie Scarlat Longhin, Bucureºti 79
2 Descrierea elementelor celulare conþinute în infiltratul granulomatos Histiocitele, denumite ºi macrofage, îºi au originea în mãduva osoasã de unde sunt eliberate în circulaþia sangvinã îndreptându-se cãtre þesuturi sub formã de monocite. În condiþiile unei stimulãri corespunzatoare, monocitele se transformã în macrofage care se pot prezenta sub forma celulelor epitelioide ºi a celulelor gigante multinucleate. (1) Macrofagele îndeplinesc un rol extrem de important în procesul de fagocitozã, fiind capabile sã ingere particule mari (microorganisme, detritusuri celulare, etc.), cât ºi în reacþiile imunologice mediate celular ºi umoral, prin procesarea ºi prezentarea antigenului ºi secreþia unor molecule bioactive (citokine, factori de creºtere, factori chemotactici, de coagulare, enzime, fracþiuni ale complementului, etc). Din punct de vedere histopatologic, monocitele sunt, în general, greu de diferenþiat de limfocite deoarece ambele tipuri celulare au caracteristici similare: nucleu hipercrom, rotund ºi citoplasmã redusã cantitativ. (1) Macrofagele sau histiocitele, au dimensiuni mai mari decât monocitele, au citoplasma mai palid coloratã, nucleul rotund-ovalar ºi membrana nuclearã bine vizibilã. Existã situaþii în care macrofagele nu pot fi diferenþiate morfologic de fibroblaste sau de celulele endoteliale, situaþii în care este utilã efectuarea de teste imunohistochimice. Markerii imunohistochimici pozitivi pentru macrofage sunt KiM1p ºi KP (CD68). (2) Celulele epitelioide sau histiocitele epitelioide se dezvoltã din macrofage, în special, în urma reacþiilor de hipersensibilitate întârziatã. Sunt denumite astfel datoritã asemãnãrii cu celulele epiteliale: au nucleul rotund-ovalar, central situat ºi citoplasma abundentã, eozinofilã. Se gãsesc fie grupate sub forma granuloamelor epitelioide, fie amestecate printre limfocite, macrofage ºi celule gigante de corp strãin. (1) Celulele (histiocite) gigante sunt celule mari, multinucleate. Existã mai multe tipuri de celule gigante, dar niciunul nu este specific unei anumite afecþiuni. Se descriu astfel: 1. Celule gigante de corp strãin care conþin numeroºi nuclei neregulat distribuiþi la Main cells of the granulomatous reaction Histiocytes, also called macrophages have their origin in the bone marrow. They are released into the blood flow and travel to the tissues as monocytes. On proper stimulation monocytes develop into macrophages which are epithelioid and foreign body giant cells (1). The macrophages have an important role both in the phagocytosis process, being able to ingest large particles (microorganisms, cellular detritus, etc), and in the cellular and humoral immunological reactions, processing and presenting the antigen and releasing bioactive molecules (cytokines, growth, chemotactic and coagulation factors, enzymes, fractions of the complement, etc). Accordingly to the histological features, the monocytes are, in general, difficult to distinguish by the lymphocytes as both cells have similar features: a rounded, dark nucleus and scanty cytoplasm. (1) Macrophages or histiocytes are larger cells than the monocytes, with a lightly stained cytoplasm, a rounded nucleus with a well visible nuclear membrane. There are cases when the macrophages cannot be morphological differentiated by fibroblasts or endothelial cells. In these situations the immunohistochemical exams could be helpful since the macrophages are positive for KiM1p and KP (CD68). (2) The epithelioid cells or histiocytes develop from macrophages, especially secondary to delayed hypersensitivity reactions. They are termed epithelioid because of their resemblance to epithelial cells: rounded, central placed nucleus and an eosinophilic cytoplasm. These histiocytes can be found either in groups, forming the epithelioid granulomas, or among lymphocytes, macrophages and foreign body giant cells. (1) Giant cells (histiocytes) are large, multinucleate cells. There are several types of giant cells, but none is specific for a certain disease: 1. Foreign body giant cells contain numerous nuclei, uneven distributed in the cytoplasm. They are found in all foreign body reactions and several tumors; 80
3 nivelul citoplasmei. Se întâlnesc în toate reacþiile de corp strãin ºi în unele tumori; 2. Celule gigante Langhans în care nucleii sunt aranjaþi sub formã de potcoavã la periferie. Apar în procese infecþioase, inclusiv TBC; 3. Celule gigante de tip Touton în care existã numeroºi nuclei situaþi în jurul unei citoplasme centrale, condensate, iar între nuclei ºi membrana celularã se gãsesc incluzii lipidice. Aceste incluzii nu pot fi evidenþiate pe secþiunile la parafinã, pentru vizualizarea acestora fiind necesarã efectuarea de secþiuni la gheaþã si coloratii special Sudan III si Scharlac. Celulele gigante de tip Touton sunt întâlnite în xantoame, xantogranulom juvenil, dermatofibrom xantomatos ºi reacþii de corp strãin. (3) Clasificarea histopatologicã a afecþiunilor granulomatoase În funcþie de aspectul histopatologic, þinându-se cont de tipul celular predominant, aranjamentul histiocitelor, absenþa/prezenþa ºi tipul necrozei, precum ºi cantitatea, distribuþia ºi compoziþia infiltratului inflamator, afecþiunile granulomatoase pot fi împãrþite în cinci categorii: 1. granuloame epitelioide, cunoscute ºi sub denumirea de naked granuloma 2. granuloame tuberculoide 3. granuloame în palisadã 4. granuloame supurative 5. granuloame de corp strãin 1. Granulomul epitelioid (fig.1, 2, 3) este alcãtuit din celule epitelioide grupate în derm, cu un infiltrat inflamator minim sau absent ( naked granuloma ). Întrucât modificarea histopatologicã specificã din sarcoidozã este consideratã ca fiind granuloamul epitelioid, acesta a mai fost denumit ºi granulom sarcoidal. Cu toate acestea, el nu este specific sarcoidozei, mai putând fi întâlnit ºi în alte dermatite granulomatoase, de exemplu ca rãspuns la un corp strãin (beriliu, zirconiu, siliciu, pigment din tatuaje) (4), la un agent 2. Langhans giant cells have the nuclei arranged as a horseshoe at the periphery of the cell. They are found in infectious conditions, including tuberculosis; 3. Touton giant cells have numerous nuclei placed around a central and condensate cytoplasm, and between the nuclei and the membrane cell there are inclusions with lipids. The lipids are dissolved by usual fixation and tissue preparation (paraffin sections). They can be identified on frozen sections using Sudan III and Scharlac stains. Touton giant cells are found in xanthomas, juvenil xanthogranuloma, xantomatous dermatofibroma and foreign body reactions. (3) Histopathological classification of granulomatous diseases Based on histological features, taking into account the main cellular type, the histiocyte arrangement, the absence/ presence and type of necrosis, as well as the amount, the distribution and composition of the inflammatory infiltrate, the granulomatous disorders can be divided into five categories: 1. epithelioid granuloma ( naked granuloma ) 2. tuberculoid granuloma 3. palisading granuloma 4. suppurative granuloma 5. foreign body granuloma. 1. Epithelioid granuloma (fig. 1, 2, 3) is a collection of epithelioid cells throughout the dermis, without or with minimal associated lymphocyte infiltrate ( naked granuloma ). Because the specific histopathological changes in sarcoidosis were considered to be the epithelioid granulomas, they were also called sarcoidal granulomas. However, these are not specific for sarcoidosis, as they can be also found in several granulomatous dermatitis as a response to a foreign material (beryllium, zirconium, silica, tattoo pigments) (4), to infectious agents (5), in immunodeficiency disorders (6), 81
4 Fig. 1. Multiple granuloame de tip epitelioid (HEx40). Multiple epithelioid granulomas (HEx40). Fig. 1. Multiple epithelioid granulomas type (HEx40). Multiple epithelioid granulomas (HEx40). Fig. 2. Granuloame epitelioide care nu conflueazã (HEx100). Non-coalescing epithelioid granulomas (HEx100). Fig. 2. Epithelioid granulomas not confluence (HEx100). Non-coalescing epithelioid granulomas (HEx100). Fig. 3. Granulom epitelioid înconjurat de infiltrat inflamator limfocitar ºi fãrã necrozã fibrinoidã sau de cazeificare (HEx200). Epithelioid granuloma surrounded by a lymphocytic infiltrate with neither fibrinoid nor caseation necrosis (HEx200). Fig. 3. Epithelioid granuloma surrounded by lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate without fibrinoid necrosis or cazeificare (HEx200). Epithelioid granuloma Surrounded by a lymphocytic infiltration with fibrinoid cloud neither caseation necrosis (HEx200). infecþios (5), în sindroame de imunodeficienþã (6), boli limfoproliferative (7) ºi erupþii postmedicamentoase (8). 2. Granulomul tuberculoid se formeazã prin gruparea histiocitelor (multinucleate de tip Langhans ºi epitelioide), înconjurate de o coroanã limfocitarã, iar în centru, uneori, de o zonã de necrozã de cazeificare. Cu ajutorul coloraþiei Ziehl- Neelson pot fi identificaþi bacilii (de culoare roz pe fond albastru deschis, bacili cu lungimea de 4 nm), mai ales în zona centralã de necrozã de cazeificare. Granuloamele de tip tuberculoid apar în infecþiile cu Mycobacterium tuberculosis sau alte mycobacterii atipice. Granulymphoproliferative disorders (7) and drug eruptions (8). 2. Tuberculoid granuloma is a collection of histiocytes (multinucleate Langhans type and epithelioid histiocytes) surrounded by a dense lymphocytic infiltrate and sometimes with a central caseation necrosis. Ziehl-Neelson stain identifies acid fast bacilli, especially in the zone of necrosis (the bacilli are colored in pink on a light blue background and they are 4 nm in diameter). The tuberculoid granulomas are seen in infections with Mycobacterium tuberculosis or atypical mycobacteria. In leprosy, the granulomas are perivascular and along the 82
5 loamele din leprã sunt mai alungite, cu dispoziþie, mai ales, perivascularã ºi perineuralã. Se mai pot dezvolta ºi dupã vaccinarea BCG ºi dupã imunoterapie, în sifilis secundar tardiv (asociazã numeroase plasmocite), dermatita perioralã, rozaceea granulomatoasã, boala Crohn cutanatã ºi cheilita granulomatoasã (sindrom Melkerson-Rosenthal). 3. Granulomul în palisadã (fig. 4, 5) este alcãtuit dintr-o zonã centralã de degenerescenþã a colagenului ºi/sau necrozã înconjuratã de histiocite epitelioide ºi celule gigante. Pot fi clasificate în granuloame albastre datoritã depozitelor de mucinã (granulom inelar) (fig. 6, 7) sau datoritã prafului nuclear neutrofilic (dermatitã granulomatoasã ºi neutrofilicã în palisadã sau granulomul Churg- Strauss) ºi roºii datoritã hialinizãrii colagenului (necrobiozã lipoidicã, xantogranulom necrobiotic) (fig. 8), depozitelor de fibrinã (noduli reumatoizi) sau eozinofilelor degradate (sindrom Wells ºi sindrom Churg-Strauss). 4. Granuloamul supurativ (fig. 9, 10) conþine pe lângã celule gigante numeroase neutrofile ºi o zonã de necrozã tisularã. perineurovascular bundels. These granulomas can also occur after BCG vaccination and after immunotherapy, in late secondary syphilis (numerous plasmocytes associated), perioral dermatitis, granulomatous rosacea, cutaneous Crohn disease and granulomatous cheilitis (Melkerson-Rosenthal syndrome). 3. Palisading granuloma (fig. 4, 5) is characterized by a central zone of altered collagen and/or necrosis, surrounded by epithelioid and giant multinucleate histiocytes. They can be classified in blue granulomas due to mucin (granuloma annulare) (fig. 6, 7) or due to neutrophilic nuclear dust (palisading granulomatous and neutrophilc dermatitis or Churg-Strauss dermatitis), and red granuloma due to degenerated collagen (necrobiosis lipoidica, necrobiotic xanthogranuloma), (fig. 8) deposits of fibrin (rheumatoid nodules) or altered eosinophils (Wells syndrome and Churg- Strauss syndrome). 4. Suppurative granuloma (fig. 9, 10) contains in addition to histiocytes, numerous neutrophils and, possible, a Fig. 4. Granulom în palisadã -fibre de colagen îngroºate ºi degenerate (HEx40). Palisading granuloma -degenerated collagen fibers (HEx40). Fig. 4. Granuloma in the palisade-thick collagen fibers and degenerated (HEx40). Granuloma-degenerated collagen Palisading Fibers (HEx40). Fig. 5. Granulom în palisadã (HEX100). Palisading granuloma (HEx100). Fig. 5. Granuloma in the palisade (HEX100). Palisading granuloma (HEx100). 83
6 Fig. 6. Granulom inelar -depozite centrale de mucinã cu histiocite dispuse în palisadã în periferie (AAx100). Granuloma annulare - central deposits of mucin (AAx100). Fig. 6. Granuloma annular-central mucin deposits with histiocite arranged in the peripheral palisade (AAx100). Annular granuloma-central deposits of mucin (AAx100). Fig. 7. Granulom inelar -depozite de mucinã (AAx200). Granuloma annulare -deposits of mucin (AAx200). Fig. 7. Granuloma annular-mucin deposits (AAx200). Annular granuloma-deposits of mucin (AAx200). Fig. 8. Granulom în palisadã -fibre de colagen îngroºate ºi fragmentate (PASx200). Palisading granulomma -thickened and altered collagen fibers (PASx200). Fig. 8. Granuloma in the palisade-thickened and fragmented collagen fibers (PASx200). Palisading granulommathickened and altered collagen Fibers (PASx200). Fig. 9. Granulom supurativ (HEx100). Suppurative granuloma (HEx100). Fig. 9. Suppurative granuloma (HEx100). Suppurative granuloma (HEx100). Cele mai frecvente situaþii în care apar reacþii granulomatoase supurative cutanate sunt datorate agenþilor infecþioºi (micoze profunde, boala ghearelor de pisicã, etc) ºi corpilor strãini (cel mai adesea conþinutul unui chist rupt). (9) 5. Granulomul de corp strãin (fig. 11, 12, 13) apare ca reacþie la materiale exogene central necrosis. The two most common causes of suppurative granulomantous reaction in the skin are infectious agents (deep fungi, cat scratch disease, etc) and foreign body (most commonly the contents of a ruptured cyst).(9) 5. Foreign body granuloma (fig. 11, 12, 13) is developed as a reaction to exogenous 84
7 Fig. 10. Granulom supurativ (HEx200). Suppurative granuloma (HEx200). Fig. 10. Granulom suppurative (HEx200). Suppurative granuloma (HEx200). Fig. 11. Reacþie de corp strãin în jurul unor fragmente de keratinã de la nivelul tijei foliculului pilos (HEx200). Foreign body reaction around fragments of keratin from a hair follicle (HEx200). Fig. 11. Foreign body reaction around the fragments of keratin from hair follicle stem (HEx200). Foreign body reaction around fragments of keratin from the hair follicle (HEx200). Fig. 12. Reacþie de corp strãin -celule gigante multinucleate cu resturi de keratinã intracitoplasmaticã (HEx200). Foreign body reaction - multinucleate giant cells with intracytoplasmic fragments of keratin (HEx200). Fig. 12. Foreign-body reaction with multinucleated giant cells and intracytoplasmic keratin debris (HEx200). Foreignbody reaction with multinucleated giant cells intracytoplasmic fragments of keratin (HEx200). Fig. 13. Celule gigante de corp strãin cu resturi de keratinã intracitoplasmatic (HEx400). Multinucleate giant cells with intracytoplasmic fragments of keratin (HEx400). Fig. 13. Foreign body giant cells with intracytoplasmic keratin debris (HEx400). Multinucleated giant cells with intracytoplasmic fragments of keratin (HEx400). (aºchii, materiale de suturã, siliciu, sticlã) sau materiale endogene (uraþi, calciu, keratinã, pãr). Din punct de vedere histopatologic poate avea aspect de granulom epidelioid, în palisadã sau supurativ. material (splinters, sutures, mouthparts of a tick) and to endogenous material (hair, keratin, calcium, etc). It must be noted that foreign bodies can induce any type of granuloma formation, i.e. sarcoidal, tuberculoid, palisading and suppurative. 85
8 Tabel 1. Clasificarea afecþiunilor granulomatoase Granuloame Granuloame Granuloame Granuloame epitelioide tuberculoide Granuloame în palisadã supurative de corp strãin - sarcoidozã - TBC Granuloame Granuloame "roºii" - infecþii - materiale exogene - reacþii de corp - infecþii cu "albastre" - colagen hialinizat: - chiste foliculare (aºchii, materiale strãin (tatuaje, mycobacterii - mucinã: necrobioza rupte de suturã, siliciu, siliciu, etc) atipice granulom inelar lipoidicã - corpi exogeni sticlã) - leprã - neutrofile: - depozite de fibrinã: - corpi endogeni - materiale - sifilis tertiar granulomatoza nodul reumatoid endogene (uraþi, - rozacee Wegener - eozinofile de calciu, keratinã, granulomatoasã generate: pãr). - boala Crohn sindrom Well's cutanatã sindrom Churg- - cheilita Strauss granulomatoasã - leishmania Table 1. Classification of granulomatous diseases Epithelioid Tuberculoid Suppurative Foreign body granuloma granuloma Palisading granuloma granuloma granuloma - sarcoidosis - tuberculosis Blue granulomas: Red granuloamas: - infections - exogenous - foreign body - infections with - mucin: granuloma - degenerated - ruptured materials reactions atypical annulare collagen infundibular cysts (splinters, sutures, (tattoo, sillicca, mycobacteria - neutrophils: necrobiosis foreign bodies etc) etc) - leprosy Wegener lipoidicã - endogenous - tertiary sifilis granulomatosis - deposits of fibrin materials (hair - granulomatous rheumatoid follicles, keratin). rozacea nodule - cutaneous Crohn - altered eosinophils disease Well s syndrome - granulomatous Churg-Strauss cheilitis syndrome - leishmania În ultima perioada, date din literaturã fac referire din ce în ce mai frecvent la un tip particular de granulom de corp strãin, ºi anume granulomul apãrut secundar injectãrii unei substanþe de tip filler. Utilizarea acestor fillere a crescut semnificativ în ultimul deceniu, crescând ºi incidenþa complicaþiilor asociate utilizãrii acestei proceduri dermato-cosmetice. O trãsãturã caracteristicã a acestor reacþii patologice este inflamaþia excesivã care cel mai adesea este granulomatoasã, dar poate fi ºi supurativã sau Lately, there are more and more reports in the literature about a special type of foreign body granuloma, namely, the granuloma secondary to injection of a dermal filler agent. Along with the significant increased of using of dermal fillers, the number of complications associated to this technique has increased as well. A characteristic feature of these pathological reactions is the heavy inflammation which often it is a granulomatous one. There are cases when the type of the inflammatory infiltrate helps 86
9 limfo-plasmocitarã. Existã situaþii în care tipul infiltratului inflamator ajutã la identificarea compoziþiei agentului cosmetic utilizat. Înþelegerea caracteristicilor histopatologice ale fillerelor este importantã pentru stabilirea unui diagnostic corect ºi pentru adoptarea une conduite terapeutice corespunzãtoare. Intrat în redacþie: identifying the type of the used cosmetic agent. Understanding of the histopathological features of the fillers used is important for a correct diagnosis, as well as for a correct therapeutic strategy. (10) Received: Bibliografie/Bibliography 1. Lever W.F., Schamburg-Lever G. Histopathology of the Skin 6 th Edition. J.B. Lippincott Company, p 51-53; 2. Lu K.Q. Granulomatosis in Clinical and Basic Immunodermatology by Gaspari A.A, Tyring S.K; Springer-Verlag London 2008, p ; 3. Simmons J.R. Granulomas in Dermatopathology by Sanchez R.L, Raimer SS; Landes Bioscience 2001, p ; 4. Callen J.P. The presence of foreign bodies does not exclude the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol 2001; p ; 5. Ferrara G., Cannone M., Scalvenzi M., et al. Facial granulomatous diseases. A study of four cases tested for the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA using nested polymerase chain reaction. Am J Dermatopathol 2001; p 23-28; 6. Levine T.S., Price A.B., Boyle S., Webster ADB. Cutaneous sarcoid-like granulomas in primary immunodeficiency disorders. Br J Dermatol 1994; p ; 7. Scarabello A., Leinweber B., Ardigo M., et al. Cutaneous lymphomas with prominent granulomatous reaction: a potential pitfall in the histopathologic diagnosis of cutaneous T and B-cell lymphomas. Am J Surg Pathol 2002; p ; 8. Wendling J., Descamps V., Grossin M., et al. Sarcoidosis during combined interferon alpha and ribavirin therapy in two patients with chronic hepatitis C. Arch Dermatol 2002; p ; 9. Stander S., Boer A., Ackerman B. Rudiments: Granulomatous inflammation and granuloma: definitions and a critique of them. Dermatopat: Practical & Conceptual Oct-Dec 2003; 10. Mercer S.E., Kleinerman R., Goldenberg G., et al. Histopathologic identification of dermal filler agents. J Drugs in Dermatol 2010; p Adresã de corespondenþã: Correspondence adress: Dr. Olguþa Anca Orzan olguta@gmail.com 87
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis
 Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123
 BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
Histopathology: chronic inflammation
 Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Avian Pathology. Bacterial diseases: histo slides. ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN
 Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Electroencephalography (EEG) alteration in Autism Spectum Disorder (ASD)
 Electroencephalography (EEG) alteration in Autism Spectum Disorder (ASD) FLORINA RAD 1, CAMELIA CIOBANU 2, GIANINA ANGHEL 3, IULIANA DOBRESCU 4 ABSTRACT There is a controversial relationship between Autism
Electroencephalography (EEG) alteration in Autism Spectum Disorder (ASD) FLORINA RAD 1, CAMELIA CIOBANU 2, GIANINA ANGHEL 3, IULIANA DOBRESCU 4 ABSTRACT There is a controversial relationship between Autism
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
More Non-infectious Granulomatous Diseases! Karolyn Wanat, MD Assistant Professor, Dermatology & Pathology University of Iowa
 More Non-infectious Granulomatous Diseases! Karolyn Wanat, MD Assistant Professor, Dermatology & Pathology University of Iowa Conflicts of Interest/Disclosure None Classification/Overview 1) Necrobiotic/Palisading
More Non-infectious Granulomatous Diseases! Karolyn Wanat, MD Assistant Professor, Dermatology & Pathology University of Iowa Conflicts of Interest/Disclosure None Classification/Overview 1) Necrobiotic/Palisading
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR
 Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
الفتوي الاصفر الحبيبوم = Xanthogranuloma_Juvenile JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9
 JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
2/18/19. Case 1. Question
 Case 1 Which of the following can present with granulomatous inflammation? A. Sarcoidosis B. Necrobiotic xanthogranulma C. Atypical mycobacterial infection D. Foreign Body Reaction E. All of the above
Case 1 Which of the following can present with granulomatous inflammation? A. Sarcoidosis B. Necrobiotic xanthogranulma C. Atypical mycobacterial infection D. Foreign Body Reaction E. All of the above
Inflammation. Part II
 Inflammation Part II Inflammatory phases: Alteration damage (dystrophy and necrosis) Exudation the reaction of microcirculation, formation of liquid exudate, migration of leukocytes and phagocytosis Proliferation
Inflammation Part II Inflammatory phases: Alteration damage (dystrophy and necrosis) Exudation the reaction of microcirculation, formation of liquid exudate, migration of leukocytes and phagocytosis Proliferation
number Done by Corrected by Doctor موسى العبادي
 number 12 Done by Corrected by Doctor موسى العبادي Morphology of Granulomatous Inflammations The first image (left) shows a lung alveolus in which necrosis is taking place. The image below it shows the
number 12 Done by Corrected by Doctor موسى العبادي Morphology of Granulomatous Inflammations The first image (left) shows a lung alveolus in which necrosis is taking place. The image below it shows the
Necrotizing granulomatous inflammation: what does it mean if your special stains are negative?
 & 2012 USCAP, Inc. All rights reserved 0893-3952/12 $32.00 S31 : what does it mean if your special stains are negative? Marie-Christine Aubry Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic,
& 2012 USCAP, Inc. All rights reserved 0893-3952/12 $32.00 S31 : what does it mean if your special stains are negative? Marie-Christine Aubry Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic,
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma presented with annular erythematous patches over the face and cheek in a Chinese lady
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2009) 17, 151-155 Case Report Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma presented with annular erythematous patches over the face and cheek in a Chinese lady SKF Loo, LY
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2009) 17, 151-155 Case Report Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma presented with annular erythematous patches over the face and cheek in a Chinese lady SKF Loo, LY
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
ASSESSING KPs ARLT S TRIANGLE
 Understanding Granulomatous Disease in Optometric Practice Thomas F. Freddo, O.D., Ph.D., F.A.A.O. Adjunct Professor of Optometry MCP Health Sciences University ASSESSING KPs ARLT S TRIANGLE 1 Types of
Understanding Granulomatous Disease in Optometric Practice Thomas F. Freddo, O.D., Ph.D., F.A.A.O. Adjunct Professor of Optometry MCP Health Sciences University ASSESSING KPs ARLT S TRIANGLE 1 Types of
Clinicopathologic Self- Assessment S003 AAD 2017
 Clinicopathologic Self- Assessment S003 AAD 2017 Clay J. Cockerell, M.D. Director, Cockerell Dermatopathology Director, Division of Dermatopathology UT Southwestern Medical Center July 2017 No relevant
Clinicopathologic Self- Assessment S003 AAD 2017 Clay J. Cockerell, M.D. Director, Cockerell Dermatopathology Director, Division of Dermatopathology UT Southwestern Medical Center July 2017 No relevant
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2).
 22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
Interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis -A Case Report Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis -A Case Report Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Wen-Yu Chang Gwo-Shing Chen Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis is a rare entity first described by Ackerman
Interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis -A Case Report Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Wen-Yu Chang Gwo-Shing Chen Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis is a rare entity first described by Ackerman
Elsevier B.V.; この論文は出版社版でありま Right 引用の際には出版社版をご確認ご利用ください This is
 Title Refractory cutaneous lichenoid sarc tranilast. Author(s) Nakahigashi, Kyoko; Kabashima, Kenj Utani, Atsushi; Miyachi, Yoshiki Citation Journal of the American Academy of 63(1): 171-172 Issue Date
Title Refractory cutaneous lichenoid sarc tranilast. Author(s) Nakahigashi, Kyoko; Kabashima, Kenj Utani, Atsushi; Miyachi, Yoshiki Citation Journal of the American Academy of 63(1): 171-172 Issue Date
Clinico-Pathological Study of Cutaneous Granulomatous Lesions- a 5 yr Experience in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India
 54 Original Article Iran J Pathol. 2016; 11(1): 54-60 http://www.ijp.iranpath.org/ Clinico-Pathological Study of Cutaneous Granulomatous Lesions- a 5 yr Experience in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India
54 Original Article Iran J Pathol. 2016; 11(1): 54-60 http://www.ijp.iranpath.org/ Clinico-Pathological Study of Cutaneous Granulomatous Lesions- a 5 yr Experience in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Chronic inflammation. 07-Dec-15. Macrophage Tissue destruction
 Chronic inflammation DR. M. TARIQ JAVED PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY FACULTY OF VETERINARY SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE, FAISALABAD. Other types of cells present B & T lymphocytes (antibody and
Chronic inflammation DR. M. TARIQ JAVED PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY FACULTY OF VETERINARY SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE, FAISALABAD. Other types of cells present B & T lymphocytes (antibody and
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS
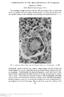 CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY
 CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
An institution-based observational study to identify sensitive histopathological parameters in leprosy
 Research Article An institution-based observational study to identify sensitive histopathological parameters in leprosy Amit S Mistry, Santoshdev P Rathod, Pooja Agarwal Department of Dermatology, AMC-MET
Research Article An institution-based observational study to identify sensitive histopathological parameters in leprosy Amit S Mistry, Santoshdev P Rathod, Pooja Agarwal Department of Dermatology, AMC-MET
Anaphylactic response in rabbit Part II
 Anaphylactic response in rabbit Part II Introduction Four types of hypersensitivity reactions: Type I: allergy Type II: antibodies Type III: immune complex Type IV: T-cells Type I Hypersensitivity ALLERGY
Anaphylactic response in rabbit Part II Introduction Four types of hypersensitivity reactions: Type I: allergy Type II: antibodies Type III: immune complex Type IV: T-cells Type I Hypersensitivity ALLERGY
Mast cells in leprosy
 Original article: Mast cells in leprosy *Dr. Navdeep Kaur, 1 Dr. S.S. Hiremath, 2 Dr. Suresh K.K. 3 1Post Graduate, 2 Professor, 3 Professor, Department of Pathology, JJM Medical College, Davangere, Karnataka,
Original article: Mast cells in leprosy *Dr. Navdeep Kaur, 1 Dr. S.S. Hiremath, 2 Dr. Suresh K.K. 3 1Post Graduate, 2 Professor, 3 Professor, Department of Pathology, JJM Medical College, Davangere, Karnataka,
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes.
 DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes. What is pathology? Pathology is the branch of medical sciences that treats the essential nature of disease, especially the changes
DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes. What is pathology? Pathology is the branch of medical sciences that treats the essential nature of disease, especially the changes
21/07/2017. Hobnail endothelial cells are not the same as epithelioid endothelial cells
 UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
Patology. Inflammation (1) inflammations. Inflammations, regeneration, repair, and scarring. lecture 2
 Patology Inflammations, regeneration, repair, and scarring lecture 2 prof dr hab. n. med. Andrzej Marszałek Inflammation (1) inflammations is a complex reaction to injurious agents such as microbes, chemical
Patology Inflammations, regeneration, repair, and scarring lecture 2 prof dr hab. n. med. Andrzej Marszałek Inflammation (1) inflammations is a complex reaction to injurious agents such as microbes, chemical
Spectrum of granulomatous lesions in a tertiary care hospital
 Original Research Article DOI: 10.5958/2394-6792.2016.00113.7 Spectrum of lesions in a tertiary care hospital R. Vimal Chander 1,*, P. Jayaganesh 2, Tejaswini Punuru Reddy 3, Chitra Srinivasan 4 1 Assistant
Original Research Article DOI: 10.5958/2394-6792.2016.00113.7 Spectrum of lesions in a tertiary care hospital R. Vimal Chander 1,*, P. Jayaganesh 2, Tejaswini Punuru Reddy 3, Chitra Srinivasan 4 1 Assistant
IMMUNE EFFECTOR MECHANISMS. Cell-Mediated Reactions
 IMMUNE EFFECTOR MECHANISMS Cell-Mediated Reactions T-Cell Cytoxicity Definition - cytotoxicity involving direct contact between CTLs and target cells, resulting in target cell lysis or apoptosis Mechanisms
IMMUNE EFFECTOR MECHANISMS Cell-Mediated Reactions T-Cell Cytoxicity Definition - cytotoxicity involving direct contact between CTLs and target cells, resulting in target cell lysis or apoptosis Mechanisms
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases
 Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Granulomatous dermatitis. Philip E. LeBoit, M.D. Depts. of Pathology and Dermatology University of California, San Francisco
 Granulomatous dermatitis Philip E. LeBoit, M.D. Depts. of Pathology and Dermatology University of California, San Francisco Granulomatous dermatitis refers to inflammatory skin diseases in which histiocytes
Granulomatous dermatitis Philip E. LeBoit, M.D. Depts. of Pathology and Dermatology University of California, San Francisco Granulomatous dermatitis refers to inflammatory skin diseases in which histiocytes
GRANULOMUL FACIAL: OBSERVAÞII ASUPRA UNUI CAZ
 CAZURI CLINICE GRANULOMUL FACIAL: OBSERVAÞII ASUPRA UNUI CAZ A. OANÞÃ*, S. ROGOZ**, M. IRIMIE* Braºov Rezumat Introducere: Granulomul facial este o afecþiune rarã, caracterizatã clinic prin una sau mai
CAZURI CLINICE GRANULOMUL FACIAL: OBSERVAÞII ASUPRA UNUI CAZ A. OANÞÃ*, S. ROGOZ**, M. IRIMIE* Braºov Rezumat Introducere: Granulomul facial este o afecþiune rarã, caracterizatã clinic prin una sau mai
A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months
 A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months GMS- Neg AFB-Neg Fite stain - neg HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS CASEOUS GRANULOMA INFECTION -MYCOBACTERIUM
A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months GMS- Neg AFB-Neg Fite stain - neg HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS CASEOUS GRANULOMA INFECTION -MYCOBACTERIUM
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies
 My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies P A U L H A U N, MD, MS, F A A D A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E R M A T O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O P A T H O L O G Y D E P A R T M E N T O F D E R M
My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies P A U L H A U N, MD, MS, F A A D A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E R M A T O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O P A T H O L O G Y D E P A R T M E N T O F D E R M
Arthritis and Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Skin: A Diagnostic Dilemma
 Arthritis and Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Skin: A Diagnostic Dilemma Introduction Pages with reference to book, From 280 To 282 Irshad Nabi Soomro ( Department of Pathology, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
Arthritis and Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Skin: A Diagnostic Dilemma Introduction Pages with reference to book, From 280 To 282 Irshad Nabi Soomro ( Department of Pathology, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
LYMPHOID ORGANS. Dr. Iram Tassaduq
 LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
LEIOMIOAME CUTANATE MULTIPLE. PREZENTARE DE CAZ MULTIPLE CUTANEOUS LEIOMYOMAS. CASE PRESENTATION
 CAZURI CLINICE CLINICAL CASES LEIOMIOAME CUTANATE MULTIPLE. PREZENTARE DE CAZ MULTIPLE CUTANEOUS LEIOMYOMAS. CASE PRESENTATION SIMONA-ROXANA GEORGESCU*, MARIA-ISABELA SÂRBU*, CRISTINA-IULIA MITRAN**, MÃDÃLINA-IRINA
CAZURI CLINICE CLINICAL CASES LEIOMIOAME CUTANATE MULTIPLE. PREZENTARE DE CAZ MULTIPLE CUTANEOUS LEIOMYOMAS. CASE PRESENTATION SIMONA-ROXANA GEORGESCU*, MARIA-ISABELA SÂRBU*, CRISTINA-IULIA MITRAN**, MÃDÃLINA-IRINA
Contents. vii. Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii
 Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Granulomatous Lesions: A Diagnostic Challenge To Dermatopathologists
 Original Research Article Granulomatous Lesions: A Diagnostic Challenge To Dermatopathologists Karuna Gupta 1, Anita Kumari 2, Kalpana Mangal 3* 1 Professor, 2 PG Resident (3rd year), 3* Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article Granulomatous Lesions: A Diagnostic Challenge To Dermatopathologists Karuna Gupta 1, Anita Kumari 2, Kalpana Mangal 3* 1 Professor, 2 PG Resident (3rd year), 3* Assistant Professor,
Sheet #7. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheet #7 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Connective tissue The differences between epithelial and connective tissue - Epithelial cells are tightly packed (no or minimal spaces
Sheet #7 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Connective tissue The differences between epithelial and connective tissue - Epithelial cells are tightly packed (no or minimal spaces
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION
 Original Article Abstract : A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION 2 4 3 3 Harish S. Permi, Jayaprakash Shetty K., Shetty K. Padma, Teerthanath S., 3 2 1 5 Michelle Mathias, Sunil Kumar
Original Article Abstract : A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION 2 4 3 3 Harish S. Permi, Jayaprakash Shetty K., Shetty K. Padma, Teerthanath S., 3 2 1 5 Michelle Mathias, Sunil Kumar
QJM Advance Access published January 21, 2015 BIG LIPS. M. Reveillon, V. Eble, H. Levesque, I. Marie
 QJM Advance Access published January 21, 2015 BIG LIPS M. Reveillon, V. Eble, H. Levesque, I. Marie Mathilde Reveillon, MD; Vincent Eble, MD; Hervé Levesque MD, PhD; Isabelle Marie, MD, PhD. Department
QJM Advance Access published January 21, 2015 BIG LIPS M. Reveillon, V. Eble, H. Levesque, I. Marie Mathilde Reveillon, MD; Vincent Eble, MD; Hervé Levesque MD, PhD; Isabelle Marie, MD, PhD. Department
المركب النموذج--- سبيتز وحمة = Type Spitz's Nevus, Compound SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7
 SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Liver: Hepatitis, necrotizing, multifocal to coalescing, severe, with numerous trichomonads. (3 pt)
 Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL) from the field to the cellular and the subcellular levels
 Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL) from the field to the cellular and the subcellular levels A M EL Hassan Institute of Endemic Diseases University of Khartoum Introduction PKDL is a VL related
Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL) from the field to the cellular and the subcellular levels A M EL Hassan Institute of Endemic Diseases University of Khartoum Introduction PKDL is a VL related
Granulomatous reaction - a histopathological study: a retrospective and prospective study of 5 years
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20150136 Granulomatous reaction - a histopathological
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20150136 Granulomatous reaction - a histopathological
Introduction. 23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology. FLUIDS, Part 1. Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT
 23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT FLUIDS, Part 1 "Blue walls", Claudia Hansen, 2009 Introduction o Challenging to everyone o Almost any benign or malignant process
23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT FLUIDS, Part 1 "Blue walls", Claudia Hansen, 2009 Introduction o Challenging to everyone o Almost any benign or malignant process
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis
 Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Figure 7.1 Figure 7.2 Figure 7.3
 CASE 7 Patient: A 63 year-old Thai female from Pathumthani Chief Complaint: Progressive facial eruption in 1 month Present Illness: The lesions involved only facial area without itching or pain. No associated
CASE 7 Patient: A 63 year-old Thai female from Pathumthani Chief Complaint: Progressive facial eruption in 1 month Present Illness: The lesions involved only facial area without itching or pain. No associated
Case 16.1 A 67-year-old Thai man from Nontaburi Chief complaint: Asymptomatic erythematous papules and plaques for 2 months Present illness: Two
 Case 16.1 A 67-year-old Thai man from Nontaburi Chief complaint: Asymptomatic erythematous papules and plaques for 2 months Present illness: Two months, he developed asymptomatic multiple erythematous
Case 16.1 A 67-year-old Thai man from Nontaburi Chief complaint: Asymptomatic erythematous papules and plaques for 2 months Present illness: Two months, he developed asymptomatic multiple erythematous
Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity
 Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
Lupus Vulgaris of Elbow A Case Report
 Lupus Vulgaris of Elbow A Case Report Surendra Prakash Vyas 1, Dharm Chand Kothari 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Sardar Patel Medical College, Bikaner, India 2, Resident, Department
Lupus Vulgaris of Elbow A Case Report Surendra Prakash Vyas 1, Dharm Chand Kothari 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Sardar Patel Medical College, Bikaner, India 2, Resident, Department
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Heyam Awad
 number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
The Immune System. A macrophage. ! Functions of the Immune System. ! Types of Immune Responses. ! Organization of the Immune System
 The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
Dermatopathology Workshop Summary, Berlin 2004
 Dermatopathology Workshop Summary, Berlin 2004 David A. Whiting and Rolf Hoffmannw Baylor Hair Research and Treatment Center, Dallas, Texas, USA; wdermatology Practice, Freiburg, Germany Figure 1 Case
Dermatopathology Workshop Summary, Berlin 2004 David A. Whiting and Rolf Hoffmannw Baylor Hair Research and Treatment Center, Dallas, Texas, USA; wdermatology Practice, Freiburg, Germany Figure 1 Case
Disseminated cutaneous BCG infection following BCG immunotherapy in patients with lepromatous leprosy
 Lepr Rev (2015) 86, 180 185 CASE REPORT Disseminated cutaneous BCG infection following BCG immunotherapy in patients with lepromatous leprosy GEETI KHULLAR*, TARUN NARANG*, KUSUM SHARMA**, UMA NAHAR SAIKIA***
Lepr Rev (2015) 86, 180 185 CASE REPORT Disseminated cutaneous BCG infection following BCG immunotherapy in patients with lepromatous leprosy GEETI KHULLAR*, TARUN NARANG*, KUSUM SHARMA**, UMA NAHAR SAIKIA***
Cellular Neurothekeoma
 Cellular Neurothekeoma Scott W Binder, MD Pritzker Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Sr. Vice Chair Director, Pathology Clinical Services Chief, Dermatopathology Geffen/UCLA School of Medicine Clinical
Cellular Neurothekeoma Scott W Binder, MD Pritzker Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Sr. Vice Chair Director, Pathology Clinical Services Chief, Dermatopathology Geffen/UCLA School of Medicine Clinical
Original Article Morphological study of different granulomatous lesions of the skin M Naved Uz Zafar, Saleem Sadiq*, M Arif Memon**
 Original Article Morphological study of different granulomatous lesions of the skin M Naved Uz Zafar, Saleem Sadiq*, M Arif Memon** Pathology Department, Sindh Medical College/Dow University of Health
Original Article Morphological study of different granulomatous lesions of the skin M Naved Uz Zafar, Saleem Sadiq*, M Arif Memon** Pathology Department, Sindh Medical College/Dow University of Health
Connective Tissue (CT)
 Connective Tissue (CT) YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Introduction of CT 1. Origin 2. Compositions
Connective Tissue (CT) YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Introduction of CT 1. Origin 2. Compositions
VALOAREA ªI UTILITATEA MICROSCOPIEI CONFOCALE DE REFLECTANÞÃ ÎN DERMATOLOGIE THE VALUE AND UTILITY OF REFLECTANCE CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY IN DERMATOLOGY
 REFERATE GENERALE GENERAL REPORTS VALOAREA ªI UTILITATEA MICROSCOPIEI CONFOCALE DE REFLECTANÞÃ ÎN DERMATOLOGIE THE VALUE AND UTILITY OF REFLECTANCE CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY IN DERMATOLOGY DANIELA ªERBAN*, MARIA
REFERATE GENERALE GENERAL REPORTS VALOAREA ªI UTILITATEA MICROSCOPIEI CONFOCALE DE REFLECTANÞÃ ÎN DERMATOLOGIE THE VALUE AND UTILITY OF REFLECTANCE CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY IN DERMATOLOGY DANIELA ªERBAN*, MARIA
STRUCTURE OF FOOD CONSUMPTION IN ROMANIA DURING , COMPARED TO THE E.U.
 Lucrări ştiinţifice Zootehnie şi Biotehnologii, vol. 40(2), (2007), Timişoara. STRUCTURE OF FOOD CONSUMPTION IN ROMANIA DURING 1990-2002, COMPARED TO THE E.U. STRUCTURA CONSUMULUI ALIMENTAR ÎN ROMÂNIA
Lucrări ştiinţifice Zootehnie şi Biotehnologii, vol. 40(2), (2007), Timişoara. STRUCTURE OF FOOD CONSUMPTION IN ROMANIA DURING 1990-2002, COMPARED TO THE E.U. STRUCTURA CONSUMULUI ALIMENTAR ÎN ROMÂNIA
A Retrospective Histological Evaluation of Non-neoplastic Superficial Lymphadenopathy
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 1 A Retrospective Histological Evaluation of Non-neoplastic Superficial Lymphadenopathy S Chhabra, H Mohan, A Bal Citation S Chhabra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 1 A Retrospective Histological Evaluation of Non-neoplastic Superficial Lymphadenopathy S Chhabra, H Mohan, A Bal Citation S Chhabra,
1) Mononuclear phagocytes : 2) Regarding acute inflammation : 3) The epithelioid cells of follicular granulomas are :
 Pathology Second 1) Mononuclear phagocytes : - Are the predominant cells in three day old wounds - Are common in liver, spleen and pancreasd - Produce fibroblast growth factor - Secrete interferon-g -
Pathology Second 1) Mononuclear phagocytes : - Are the predominant cells in three day old wounds - Are common in liver, spleen and pancreasd - Produce fibroblast growth factor - Secrete interferon-g -
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 Academic lectures for general medicine Summer course 3rd year Updated 2001-2016 GENERAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CHRONIC INFLAMMATION R. A- Benacka, MD, PhD Department of Pathophysiology Medical faculty, Safarik
Academic lectures for general medicine Summer course 3rd year Updated 2001-2016 GENERAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CHRONIC INFLAMMATION R. A- Benacka, MD, PhD Department of Pathophysiology Medical faculty, Safarik
Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Misdiagnosed as Leprosy. Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature
 Indian J Lepr 2016, 88 : 177-183 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Case Report Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Misdiagnosed as Leprosy. Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature 1 2 3
Indian J Lepr 2016, 88 : 177-183 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Case Report Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Misdiagnosed as Leprosy. Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature 1 2 3
INDEX. surgpath.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. diffuse pleural fibrosis, pleural plaques,
 INDEX Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenocarcinoma, minimally invasive. See Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA). Airway-centered interstitial fibrosis, 183 184 ALK (anaplastic
INDEX Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenocarcinoma, minimally invasive. See Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA). Airway-centered interstitial fibrosis, 183 184 ALK (anaplastic
Etiology. Extreme temperature, electric shock, ionization, physical injury, etc. Metabolic substances, acids, alkalis drugs, tissue necrosis
 INFLAMMATION Inflammation Protective response that is intended to eliminate the initial cause of injury Innate and acquired mechanisms Local or generalized (sepsis) processes Terminology: ~ itis ending
INFLAMMATION Inflammation Protective response that is intended to eliminate the initial cause of injury Innate and acquired mechanisms Local or generalized (sepsis) processes Terminology: ~ itis ending
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Type III Hypersensitivity. Immune Complex Mediated Reaction
 Type III Hypersensitivity Immune Complex Mediated Reaction Type III: Immune Complex Mediated Reaction *When antibodies (Ig G or Ig M) and antigen coexist immune complexes are formed *Immune complexes are
Type III Hypersensitivity Immune Complex Mediated Reaction Type III: Immune Complex Mediated Reaction *When antibodies (Ig G or Ig M) and antigen coexist immune complexes are formed *Immune complexes are
Agenda. Components of blood. Blood is Fluid Connective Tissue. Blood: General functions
 Agenda Chapter 19: Blood Major functions Major Components Structure of RBCs and WBCs ABO Blood Types, and Rh Factor Lab 34.1 and Blood Typing Blood: General functions Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients,
Agenda Chapter 19: Blood Major functions Major Components Structure of RBCs and WBCs ABO Blood Types, and Rh Factor Lab 34.1 and Blood Typing Blood: General functions Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients,
Extracellular degeneration
 Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Histological Spectrum of Pure Neuritic Leprosy:
 Department of Histopathology Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education & Research Chandigarh,India Histological Spectrum of Pure Neuritic Leprosy: Experience at Tertiary Care Centre Dr Uma Nahar INTRODUCTION
Department of Histopathology Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education & Research Chandigarh,India Histological Spectrum of Pure Neuritic Leprosy: Experience at Tertiary Care Centre Dr Uma Nahar INTRODUCTION
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania
 Tropical Medicine and International Health VOLUME I NO. 2 PP 243-250 APRIL 1996 Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania major infections A. Gaafar r, A. Ismai13, A. Y. El Kadaro4, Elsir
Tropical Medicine and International Health VOLUME I NO. 2 PP 243-250 APRIL 1996 Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania major infections A. Gaafar r, A. Ismai13, A. Y. El Kadaro4, Elsir
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and. Specific. (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell
 There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
Connective tissue Histology lab 6 Notes by Omar Sami
 Connective tissue Histology lab 6 Notes by Omar Sami The connective tissue is composed of: 1- Cells. 2- Extra Cellular Matrix; fibers & ground substance. Ground substance is where you find both Cells &
Connective tissue Histology lab 6 Notes by Omar Sami The connective tissue is composed of: 1- Cells. 2- Extra Cellular Matrix; fibers & ground substance. Ground substance is where you find both Cells &
In our paper, we suggest that tuberculosis and sarcoidosis are two ends of the same spectrum. Given the pathophysiological and clinical link between
 In our paper, we suggest that tuberculosis and sarcoidosis are two ends of the same spectrum. Given the pathophysiological and clinical link between the two, we also propose a classification system for
In our paper, we suggest that tuberculosis and sarcoidosis are two ends of the same spectrum. Given the pathophysiological and clinical link between the two, we also propose a classification system for
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference
 www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
Connective tissue CONNECTIVE TISSUE Part I
 Connective tissue CONNECTIVE TISSUE Part I Part 1 Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body (app. 50% of body weight) Includes the most abundant and widely distributed tissues General features of
Connective tissue CONNECTIVE TISSUE Part I Part 1 Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body (app. 50% of body weight) Includes the most abundant and widely distributed tissues General features of
Case Presentation VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Vasculitis
 Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
