Histological Study of Halothane Effects on Lung in the Male White Mice
|
|
|
- Amice French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Histological Study of Halothane Effects on Lung in the Male White Mice Duaa Jasim Mohammad; Basim Abdullah Jasim. College Science Al-muthanna university/iraq Abstract: In order to study the side effect of halothane on the lung in the male white mice, the present work carried out (80) male white mice, which were divided into three groups. Each group was treated with halothane per 15 minutes through thirty days. The study designated to estimate the histological changes in three treated groups after exposure to three different concentrations of halothane in lung. The tissue section of lung that exposure to 1% concentration of halothane have some alveoli destruction and aggregation of inflammatory cells around the cystic dilation, so showed small aggregation of pulmonary alveolar macrophage (PAM ) in some of cystic dilation. The current results showed the third zones of bronchial tree filled with secretion, prominent emphysema, with proliferation of pneumocyte with blood spots and destruction in epithelial layer which lining the inner surface of the alveoli. The tissue section of lung after exposure to 2% concentration of halothane showed lung fibrosis, blood congestion in different locations of lung parenchyma with mild emphysema in wide regions of lung and some sections showed absent the alveolar sac and instead by cystic dilation. The tissue section of lung after exposure to 3% concentration of halothane showed completely degeneration of alveolar wall in different location of lung with proliferation of pneumocyte between the destruction alveoli, high aggregation of inflammatory cells as clusters around the affected alveoli and acute emphysema in some reigns of lung characterized by absent the alveolar sac and instead by very wide cystic dilation. INTRODUCTION: Each year in the United States, approximately three million Infants, children and adults receive anesthesia for surgical procedures, with many more receiving anesthesia for imaging studies or dental procedures [1]. The anesthetic agents have been used long ago and it is of great importance the appropriate anesthetic to possess properties like rapid onset, offset of action and predictable metabolism. Among currently used anesthetics are Inhalational anesthetic agents [2]. Inhalational anesthetics are the most commonly used agents for maintenance of general anesthesia in animals and human. The popularity of those drugs to establish anesthesia is based on a range of attractive, such as ease of administration, predictability of their effects, low cost. The most widely used volatile anesthetics cause a dose-dependent depression in respiration and thus have an irritable effect on the airway, and are effective bronchodilators [3]. However, there are also data that general anesthesia could lead to endothelial damage and pulmonary micro vascular injury, which phenomenon could result in respiratory complications after surgery [4]. The anesthetics agents that used at the present time, halothane, enflurane, isoflurane, sevoflurane, desflurane. The appropriate choice of anesthesia for patients, undergoing different type of long-durable surgery intervention requires minimal toxicity and accurate monitoring for patients at high risk for metabolic, cardiovascular and respiratory preoperative complications [2]. The elimination of anesthetic agents should avoid the metabolic breakdown and be independent from renal or hepatic function. Thus they should have minimum undesirable drug interaction, minimum side effects, or toxicity. Although the elimination of volatile anesthetics is primarily through the lung, a certain percent of the inhaled gases is metabolized. Some anesthetics' derivatives have been metabolized in the liver, with production of inorganic fluoride ions. The high tissue inorganic fluoride levels could lead to the nephrotoxic effect [5]. Other volatile halogenated hydrocarbons have been metabolized to trifluoroacetic acid. The latter interacts with hepatic proteins, induces an immune response in susceptible patients [6]. and lead to hepatotoxic effects. One commonly used inhalation anesthetic, with a known hepatotoxic effect is halothane [7]. Halothane has been used widely as a volatile anesthetic agent in clinical practice since 1957 [8]. It is well established that halothane is metabolized in the liver as a lipophilic xenobiotic to hepatotoxic intermediates [9]. Halothane have chemical structures, 2-bromo 2- chloro1,1,1-trifluoroethane [10]. Its many advantages, such as quick action, easy administration, non-inflammable, high potency and low cost, lead to its widespread use within a short time [11]. About 80% of inhaled halothane is taken by the body, is eliminated unchanged via the lungs, and about 20% of halothane, not eliminated in exhaled gas, is metabolized in the liver to its principal metabolite, trifluoro acetic acid (CF3COOH) [12]. Halothane is undesirable drug in humans, who risk developing lung disease because epithelial cell apoptosis may stimulate lung fibrosis, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), acute lung injury,destruction in alveolar wall and emphysema [13]. Halothane may provoke apoptosis in alveolar cells and thus may modulate respiratory function it is of great importance to assess the crucial role of apoptosis in the progression and pathogenesis of lung diseases, which is of value for clinical practice [14]. Aim of Study :1- Histological changes estimated in lung after exposure to halothane. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Experimental Animals: The present study carried out (80 ) male albino white mice from drug and healthy center in Baghdad province. The experimental animals were housed in animal house of college of science in Al- Muthanna university under controlling of temperature at 25-28ºC with feeding by used standard pellets. The average weight of experimental animals was 30 gm. The experimental animals were divided into four groups. Three treated groups (A,B and C ) 631
2 and the other (D) as control group. The experimental animals were left in labels separate cages. Each group composed of 20 mice, each group exposure to halothane with or by inhalation for 15 minutes daily during thirty days. The halothane concentration determined by vaporizer. The oxygen supplies for the vaporizer to mixed with the liquid halothane. The oxygen level for the exposure was 10% Group (A) : treated with 1 % concentration of halothane. Group ( B ) : treated with 2 % concentration of halothane. Group ( C ) : treated with 3 % concentration of halothane. Figure 1: Experimental animals that exposure to halothane anesthesia.e Histological technique: Fixation: The lung sample was laid in labeled container contain 10% formalin for 48 hours, Wishing: The sample was washed by using the tap water for (1 hr.), Dehydration: The sample was done to remove all extractable water by dehydrated diffusing through the tissue, alcohol was used, Clearing: This stage is considered as a middle step, it is obligatory because the used alcohol for dehydration will not dissolve or mix with molten paraffin, Embedding (Blocking): Paraffin wax that used is hard (melting point c), Cutting: cutting was done by using the rotary microtome. The thickness is (5 µm). the sample were put in hot water path with (52 c) for extending tissue, then the samples were carried on the slides which had a thin layer of Mayer egg albumin, the slide was put on the hot plate with (40 c) for overnight, Staining: Hematoxylin and Eosin stain: for demonstrating of the general structure of the tissue (15). RESULTS AND DISCUSSION: The Histological Result of The Control Group: The histological results of lung in the control group showed that the tissue sections of lung have normal pneumocyte with dark irregular nuclei centrally location. The tissue section of the lung showed that different generation of bronchial tree have normal wall line by normal epithelial layer. The upper branch of bronchial tree line by respiratory epithelia simple columnar epithelia. The present result of lung showed high amount of elastic fibers which distributed between the different generation of bronchial tree (figure 2). The current results of lung showed the upper generation of bronchial tree lined by different types of epithelia started with simple cuboidal epithelia, while in lower generation of bronchial tree lined by simple squamous epithelia. The alveolar sac have thin wall and line by simple squamous epithelia. The alveolar sac were surrounded by network of blood capillaries (figure 2). The Histological Results of Lung After Exposure to 1% Concentration of Halothane : The tissue section of lung that exposure to 1% concentration of halothane have some alveoli destruction and aggregation of inflammatory cells around the cystic dilation, so showed small aggregation of pulmonary alveolar macrophage (PAM ) in some of cystic dilation (figure 3). This result occur because toxicity of halothane which causes this changes,this findings agreement with [16] which said that The histological changes of halothane showed increase region of destruction, inflation and dilation of airway. The histological sections of lung showed that destruction in epithelial layer which lining the inner surface of the alveoli. The present result of the lung showed that small clusters of inflammatory cells between the alveoli. The present results of lung showed prominent emphysema, with proliferation of pneumocyte with blood spots. The alveolar sac characterized by disappeared the epithelial cell that lining the internal surface of alveolar sac (figure 3). The results showed bronchiole filled with secretion and blood (figure 3). This results noted that the halothane affected on the epithelial layer of bronchial tree and alveolar sac. The present results were similar to [17,18] which said that anesthesia have effects on the respiratory system, general anesthesia causes decrease in respiratory rate and respiratory complications by mismatch in alveolar breathing leading to the destruction of the alveolar wall and thus the occurrence of pulmonary complications after surgical operations. The Histological Results of Lung After Exposure to 2 % Concentration of Halothane : The histological results of lung section after treated with halothane 2% concentration showed blood congestion in different locations of lung parenchyma with mild emphysema in some reigns of lung characterized by absent the alveolar sac and instead by cystic dilation (figure 4). The high concentration of halothane which lead to acute histological destruction in the alveolar sac. This result were agreement with [14] which said that halothane may provoke apoptosis in alveolar cells and thus may modulate respiratory function it is of great importance to assess the crucial role of apoptosis in the progression and pathogenesis of lung diseases, which is of value for clinical practice. The most histological sections of the lung showed the alveoli and terminal bronchial tree have aggregation of RBCs (figure 4). The present result of lung showed separated the epithelial layer from basal line of bronchial tree, and some epithelial cells exfoliated and aggregation in the lumen of bronchial tree (figure 4). The present result showed blood hemorrhage in different location of the lung (figure 4). The results showed lung fibrosis in different regions of lung after treated with 2% concentration of 632
3 halothane (figure 4). This result similar to [13] which said that halothane is undesirable drug in humans, who risk developing lung disease because epithelial cell apoptosis may stimulate lung fibrosis, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), acute lung injury,destruction in alveolar wall and emphysema. Figure 2: cross section of lung in control group. H&E stain a: 10X, b: 40X. Figure 3: cross section of lung after exposure to 1% concentration of halothane. H&E stain a, b, c, d: 40X. 633
4 Figure 4: cross section of lung after exposure to 2% concentration of halothane. H&E stain a, b, c, d: 40X. Figure 5: cross section of lung after exposure to 3% concentration of halothane. H&E stain a, b, c, d: 40X. 634
5 Figure 6: cross section of lung after exposure to 3% concentration of halothane. H&E stain a, b, c, d: 40X. The Histological Results of Lung After Exposure to 3 % Concentration of Halothane : The lung of third groups which inhaled the halothane 3 % concentration showed completely degeneration of alveolar wall in different location of lung with blood congestion between the destruction alveoli (figure 5,6). The cross section of lung tissue after exposure to halothane, showed high aggregation of inflammatory cells as clusters around the effected alveoli. The current result of lung after treated showed the conduction zone of bronchial tree filled with thick secretion and have large aggregation of pulmonary alveolar macrophage inside the lumen of this zone (figure 5,6). This result agreement with [19] that said general anesthesia have side effects on the airway, this effect including relaxation of muscles and loss of cough reflex with full the airway with secretions causes in airway prevention, and dry gases effect of the function of respiratory system. The histological result of lung section after treated with halothane 3% concentration showed blood hemorrhage in different locations of lung parenchyma with acute emphysema in some reign of lung characterized by absent the alveolar sac and instead by cystic dilation (figure 5,6). This result agreement with [13] which said that halothane is undesirable drug in humans, who risk developing lung disease because epithelial cell apoptosis may stimulate lung fibrosis, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), acute lung injury, destruction in alveolar wall and emphysema. REFERENCES: [1] Sun LS, Li G, Dimaggio C, Byrne M, Rauh V, Brooks-Gunn J, Kakavouli A,Wood A. Coinvestigators of the Pediatric Anesthesia Neurodevelopment Assessment Research N: Anesthesia and neurodevelopment in children: time for an answer? Anesthesiology, 109: (2008). [2] Della Rocca G., Costa M.G., Bruno K., Coccia C., Pompei L., DiMarco P., Pretagostini R., Colonnello M., Rossi M., Pietropaoli P., Cortesini R. Pediatr. Surg. Int., 17 (2-3), (2001). [3] Kleinsasser A., Lindner K.H., Hoermann C., Schaefer A., Keller C., Loeckinger A. Anesthesiology, 95(6), (2001). [4] Gunaydin B., Karadenizli Y., Babacan A., Kaya K., Unlu M., Inanir S., Mahli A., Akcabay M., Yardim S. Respir. Med., 91(6), ( 1997 ). [5] O Keeffe. Pharmacol. Therap., 84, (1999). [6] Kitteringham N.R., Kenna J.G., Park B.K. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 40, (1995). [7] Kehlet H. Br. J. Anaesth., 78, (1997). [8] Topal, A., N, Gul, Y. Liool and OS, Gorgul. Hepatic effects of halothane, isoflurane or sevoflurane anesthesia in dogs. J. Vet. Med., 50: (2003). [9] Minoda, Y. and E. Kharasch. Halothane dependent lipid peroxidation in human liver microsomes is catalyzed by cytochrome p 4502A6 ( CYP2A6 ).Aneathesiology, 95: (2001). [10] McLain GE, Sipes IG, Brown BR. An animal model of halothane hepatotoxicity. Roles of enzyme induction and hypoxia. Anesthesiology 51: (1979). [11] D. Rosenak, A. Halevy and R. Orda. Halothane and liver damage. Postgraduate Medical Journal 65, (1989). [12] Mikhail MS, Murray MJ. Inhalation anaesthetics. In: Morgan GE, Mikhail MS, Murray MJ, (edi). Clinical anaesthesiology. 4th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 168. (2006). [13] Lu Q., Harrington E.O., Rounds S. Keio J Med, 54(4), (2005). [14] E. Stephanova, R. Valtcheva-Sarker, T. Topouzova-Hristova, Z. Lalchev. influence of volatile anaesthetics on lung cells and lung surfactant. biotechnol. & biotechnol. eq.(2007). [15] Luna L. C. Manual of histologic staining methods of Armed forces. Institute of pathology, 3 rd ed., Mc Graw-Hill Book. Newyork, London. 9: pp (1968). [16] Baxi V, Jain A, Dasgupta D: Anaesthesia for renal transplantation: an update. Indian J Anaesth; 53: (2009). [17] Hedenstierna G, Rothen HU. Respiratory function during anesthesia: Effects on gas exchange. Compr Physiol. 2: (2012). [18] Hartland BL, Newell TJ, Damico N. Alveolar recruitment maneuvers under general anesthesia: A systematic review of the literature. Respir Care. ;60: (2015). [19] Junqueira LC, Carneiro J. Basic Histology. Lange Medical Books Mc Grow-Hill (10th Edn.), India.(2003). 635
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals
 Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
7/12/2012. Respiratory system. Respiratory Response to Toxic Injury (Lung) Ninth Industrial Toxicology and Pathology Short Course.
 Ninth Industrial Toxicology and Pathology Short Course 23 27 July, 2012 Contemporary Concepts in Target Organ Toxicologic Pathology Respiratory system Respiratory Response to Toxic Injury (Lung) Eric Wheeldon
Ninth Industrial Toxicology and Pathology Short Course 23 27 July, 2012 Contemporary Concepts in Target Organ Toxicologic Pathology Respiratory system Respiratory Response to Toxic Injury (Lung) Eric Wheeldon
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Inhalational Anesthesia. Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine The University of Jordan February, 2018
 Inhalational Anesthesia School of Medicine The University of Jordan February, 2018 mgharaib@ju.edu.jo Inhalational Anesthesia n Gases or volatile liquids n Administration and Elimination is by the lungs
Inhalational Anesthesia School of Medicine The University of Jordan February, 2018 mgharaib@ju.edu.jo Inhalational Anesthesia n Gases or volatile liquids n Administration and Elimination is by the lungs
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Lec #2 histology. Bronchioles:
 Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing
 Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
General Anesthesia. Mohamed A. Yaseen
 General Anesthesia Mohamed A. Yaseen M.S,c Surgery Before Anesthesia General Anesthesia ( GA ) Drug induced absence of perception of all sensation allowing surgery or other painful procedure to be carried
General Anesthesia Mohamed A. Yaseen M.S,c Surgery Before Anesthesia General Anesthesia ( GA ) Drug induced absence of perception of all sensation allowing surgery or other painful procedure to be carried
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
The Respiratory System
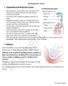 I. Organization of the Respiratory System The Respiratory System The respiratory system allows the circulation of air and the gas exchange between the body and the outside environment. It consists of the
I. Organization of the Respiratory System The Respiratory System The respiratory system allows the circulation of air and the gas exchange between the body and the outside environment. It consists of the
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
GAS EXCHANGE IB TOPIC 6.4 CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM. Terminal bronchiole Nasal cavity. Pharynx Left lung Alveoli.
 IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE
 IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
General anesthesia. No single drug capable of achieving these effects both safely and effectively.
 General anesthesia General anesthesia is essential to surgical practice, because it renders patients analgesic, amnesia, and unconscious reflexes, while causing muscle relaxation and suppression of undesirable
General anesthesia General anesthesia is essential to surgical practice, because it renders patients analgesic, amnesia, and unconscious reflexes, while causing muscle relaxation and suppression of undesirable
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
A. Incorrect! The alveolus is where gas exchange takes place. B. Correct! Surfactant is the lipid-rich material that permits lung inflation.
 Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
ISPUB.COM. Review Of Currently Used Inhalation Anesthetics: Part II. O Wenker SIDE EFFECTS OF INHALED ANESTHETICS CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 3 Number 3 O Wenker Citation O Wenker.. The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology. 1998 Volume 3 Number 3. Abstract SIDE EFFECTS OF INHALED ANESTHETICS
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 3 Number 3 O Wenker Citation O Wenker.. The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology. 1998 Volume 3 Number 3. Abstract SIDE EFFECTS OF INHALED ANESTHETICS
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
INHALATION AGENTS 2013/05/28 1
 INHALATION AGENTS 2013/05/28 1 2013/05/28 Isn t it romantic? 2 Administration 3 Physics Critical temperature Vapour vs. Gas Vapour pressure Blood Gas Partition Coefficient BGPC MAC 2013/05/28 4 Critical
INHALATION AGENTS 2013/05/28 1 2013/05/28 Isn t it romantic? 2 Administration 3 Physics Critical temperature Vapour vs. Gas Vapour pressure Blood Gas Partition Coefficient BGPC MAC 2013/05/28 4 Critical
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung
 Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Respiratory Toxicology
 Respiratory Toxicology Loch-Caruso ENVIRON 310 2017 1 Breathing Oxygen Carbon Dioxide http://www.webmd.com/lung/picture-of-the-lungs Loch-Caruso ENVIRON 310 2017 2 Breathing Enlarged view of the airways,
Respiratory Toxicology Loch-Caruso ENVIRON 310 2017 1 Breathing Oxygen Carbon Dioxide http://www.webmd.com/lung/picture-of-the-lungs Loch-Caruso ENVIRON 310 2017 2 Breathing Enlarged view of the airways,
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
-Tamara Wahbeh. -Razan Abu Rumman. Dr. Mohammed Al-Muhtaseb
 -2 -Tamara Wahbeh -Razan Abu Rumman Dr. Mohammed Al-Muhtaseb I tried to include everything the doctor mentioned in both the lecture and his slides in the simplest way possible, so hopefully there would
-2 -Tamara Wahbeh -Razan Abu Rumman Dr. Mohammed Al-Muhtaseb I tried to include everything the doctor mentioned in both the lecture and his slides in the simplest way possible, so hopefully there would
Restrictive lung diseases
 Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs
 The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
Inhalation anesthesia. Somchai Wongpunkamol,MD Anes., CMU
 Inhalation anesthesia Somchai Wongpunkamol,MD nes., CMU Inhalation anesthetics is agent that possess anaesthetic qualities that are administered by breathing through an anaesthesia mask or ET tube connected
Inhalation anesthesia Somchai Wongpunkamol,MD nes., CMU Inhalation anesthetics is agent that possess anaesthetic qualities that are administered by breathing through an anaesthesia mask or ET tube connected
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
Respiratory Physiology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Physiology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Functional respiratory anatomy Ventilation Mechanics of
Respiratory Physiology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Functional respiratory anatomy Ventilation Mechanics of
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Paramedic Rounds. Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
 Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
#8 - Respiratory System
 Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion
 Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiration Lesson 3. Respiration Lesson 3
 Respiration Lesson 3 and Airway Resistance (key factors affecting air flow) 1) What is the arterial blood pressure in a healthy 18 year old male? 2) What would his venous blood pressure be? 3) What is
Respiration Lesson 3 and Airway Resistance (key factors affecting air flow) 1) What is the arterial blood pressure in a healthy 18 year old male? 2) What would his venous blood pressure be? 3) What is
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
HISTO-PHYSIOLOGY HISTO-PHYSIOLOGY HISTO-PHYSIOLOGY. 09-Mar-15. Dr. Muhammad Tariq Javed. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Lec-1
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Lec-1 Dr. Muhammad Tariq Javed Professor Department of Pathology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk Web: http://www.geocities.ws/mtjaved 1 2 Conducting
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Lec-1 Dr. Muhammad Tariq Javed Professor Department of Pathology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk Web: http://www.geocities.ws/mtjaved 1 2 Conducting
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock. Dr Than Kyaw March 2012
 Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock Dr Than Kyaw March 2012 Special circulation (Coronary, Pulmonary, and Cerebral circulations) Introduction Special attention to circulation
Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock Dr Than Kyaw March 2012 Special circulation (Coronary, Pulmonary, and Cerebral circulations) Introduction Special attention to circulation
Volatile Anaesthetic Agents (Basic Principles)
 Volatile Anaesthetic Agents (Basic Principles) KSS School of Anaesthesia Basic Science Course South Coast Training Group Dr S M Walton Consultant Anaesthetist Eastbourne What do you need to know about
Volatile Anaesthetic Agents (Basic Principles) KSS School of Anaesthesia Basic Science Course South Coast Training Group Dr S M Walton Consultant Anaesthetist Eastbourne What do you need to know about
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Histology and development of the respiratory system
 Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
General anesthetics. Dr. Shamil AL-Noaimy Lecturer of Pharmacology Dept. of Pharmacology College of Medicine
 General anesthetics Dr. Shamil AL-Noaimy Lecturer of Pharmacology Dept. of Pharmacology College of Medicine Rationale General anesthesia is essential to surgical practice, because it renders patients analgesic,
General anesthetics Dr. Shamil AL-Noaimy Lecturer of Pharmacology Dept. of Pharmacology College of Medicine Rationale General anesthesia is essential to surgical practice, because it renders patients analgesic,
Development of Respiratory System. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra
 Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Diseases of the Lung and Respiratory Tract, Part I. William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU
 Diseases of the Lung and Respiratory Tract, Part I William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU Educational objectives: Distinguish the types of atelectasis and their etiologies Distinguish the
Diseases of the Lung and Respiratory Tract, Part I William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU Educational objectives: Distinguish the types of atelectasis and their etiologies Distinguish the
Chapter 25. General Anesthetics
 Chapter 25 1. Introduction General anesthetics: 1. Analgesia 2. Amnesia 3. Loss of consciousness 4. Inhibition of sensory and autonomic reflexes 5. Skeletal muscle relaxation An ideal anesthetic: 1. A
Chapter 25 1. Introduction General anesthetics: 1. Analgesia 2. Amnesia 3. Loss of consciousness 4. Inhibition of sensory and autonomic reflexes 5. Skeletal muscle relaxation An ideal anesthetic: 1. A
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESS TEMPLATE
 1 PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESS TEMPLATE DISEASE: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) DEFINITION: COPD can be defined as a disease in which there is a significant damage to the lungs thus reducing
1 PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESS TEMPLATE DISEASE: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) DEFINITION: COPD can be defined as a disease in which there is a significant damage to the lungs thus reducing
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING. Compiled by. Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives --()--
 IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
CYTOMORPHOLOGY MODULE 28.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 28.2 GENERAL GUIDELINES. Notes
 28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
Nasal Cavity. The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the. (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!)
 Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
Pharmacokinetics. Inhalational Agents. Uptake and Distribution
 Pharmacokinetics Inhalational Agents The pharmacokinetics of inhalational agents is divided into four phases Absorption Distribution (to the CNS Metabolism (minimal Excretion (minimal The ultimate goal
Pharmacokinetics Inhalational Agents The pharmacokinetics of inhalational agents is divided into four phases Absorption Distribution (to the CNS Metabolism (minimal Excretion (minimal The ultimate goal
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS
 FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water vapour Nitrogen
 1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
10.1 The Pulmonary-Circulatory System
 pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Overview. The Respiratory System. Chapter 18. Respiratory Emergencies 9/11/2012
 Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Particle Size and Dust Inhalation
 Pneumoconiosis A disease of the lungs characterized by fibrosis and caused by the chronic inhalation of mineral dusts, especially silica and asbestos. Helen Lang Dept. Geology & Geography West Virginia
Pneumoconiosis A disease of the lungs characterized by fibrosis and caused by the chronic inhalation of mineral dusts, especially silica and asbestos. Helen Lang Dept. Geology & Geography West Virginia
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION
 Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer
 Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Respiration. Functions Anatomy
 Respiration Functions Anatomy Major Functions Gas exchange: absorb O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate
Respiration Functions Anatomy Major Functions Gas exchange: absorb O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate
Gas exchange Regulate blood ph Voice production Olfaction Innate immunity
 Respiration Functions Gas exchange: Grab O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate immunity: physical protection
Respiration Functions Gas exchange: Grab O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate immunity: physical protection
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
The Respiratory System. Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb
 The Respiratory System Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb Objectives (lecture + practical) 1. Identify the conduction part of the respiratory tract and analyze the function of each segment 2. Identify
The Respiratory System Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb Objectives (lecture + practical) 1. Identify the conduction part of the respiratory tract and analyze the function of each segment 2. Identify
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE
 APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATION OF CHRONIC PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA. Citation Acta tuberculosea Japonica (1962),
 Title ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATION OF CHRONIC PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA Author(s) OKADA, Yoshio; SAGAWA, Yanosuke; IS DAIDO, Shigeo Citation Acta tuberculosea Japonica (1962), Issue Date 1962-03-30 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/51710
Title ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATION OF CHRONIC PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA Author(s) OKADA, Yoshio; SAGAWA, Yanosuke; IS DAIDO, Shigeo Citation Acta tuberculosea Japonica (1962), Issue Date 1962-03-30 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/51710
Respiration.notebook March 07, Unit 3. Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Hodgkin s Disease STSE
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Multi-center (5 centers); United States and Canada. September 10, 1992 to April 9, 1993
 vi STUDY SYNOPSIS Study Number: Title: Investigator: GHBA-534 A Phase III, Randomized, Open-Label Study To Compare The Safety, Tolerability And Recovery Characteristics of Sevoflurane Versus Halothane
vi STUDY SYNOPSIS Study Number: Title: Investigator: GHBA-534 A Phase III, Randomized, Open-Label Study To Compare The Safety, Tolerability And Recovery Characteristics of Sevoflurane Versus Halothane
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS
 Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
