ARDS with septic shock due to Legionella longbeachae pneumonia in a patient with polymyalgia rheumatica
|
|
|
- Franklin Gilmore
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASE REPORT Heart, Lung and Vessels. 2014; 6(2): ARDS with septic shock due to Legionella longbeachae pneumonia in a patient with polymyalgia rheumatica T. Reynaldos Canton Migotto 1, S. Györik Lora 2, V. Gaia 3, A. Pagnamenta 1 1 Department of Intensive Care, Regional Hospital of Mendrisio, Switzerland; 2 Department of Internal and Respiratory Medicine, Regional Hospital of Bellinzona, Switzerland; 3 Swiss National Reference Centre for Legionella, Cantonal Institute of Microbiology, Bellinzona, Switzerland Heart, Lung and Vessels. 2014; 6(2): ABSTRACT Legionella longbeachae is a very uncommon cause of community acquired pneumonia in Western countries. L. longbeachae does not grow on blood agar media and is usually not detected by sputum gram stain or blood culture. Furthermore Legionella urinary antigen testing fails to detect it. In this report we described a 79-yearold man with polymyalgia rheumatica under systemic corticosteroid treatment without other additional risk factors who developed a cultured-proven L. longbeachae community-acquired pneumonia complicated by an acute respiratory distress syndrome with septic shock. This case report demonstrates that non-pneumophila Legionella species must be taken into account as casual agents of community acquired pneumonia even in mild immunosuppressed patients, and empiric anti-legionella antimicrobial coverage might be indicated until Legionella has definitively been rule out by adequate testing. Keywords: Legionella longbeachae, community-acquired pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock. INTRODUCTION Corresponding author: Alberto Pagnamenta, MD Department of Intensive Care Regional Hospital of Mendrisio Via Turconi, 23 CH-6850 Mendrisio, Switzerland alberto.pagnamenta@eoc.ch In most outpatients with suspected community acquired pneumonia microbial diagnosis is not mandatory since empiric antibiotic treatment is usually succesful. Clinical features and radiologic findings usually fail to identify the etiologic pathogen. Immunosuppressed patients deserve special attention and invasive procedures are compulsory in order to obtain sputum to make specific diagnosis. Empiric antimicrobial coverage should be tailored to treat the most likely pathogen in accordance to individual patient characteristics. CASE REPORT A 79-year-old man presented to the emergency department of the Regional Hospital of Bellinzona, Switzerland with a 2-day history of fever and unproductive cough as well as dyspnea on exertion. Previous history was remarkable for chronic corticosteroid use (10 mg daily of prednisone for eight months to treat polymyalgia rheumatica without giant cell arteritis). He was a non-smoker and did not have pre-existing pulmonary diseases. He had not travelled
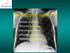
2 ARDS by Legionella longbeachae 20 mg/d four days later. He was then transferred to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) of the regional hospital of Mendrisio, Switzerland due to lack of free beds in Bellinzona. On admission the patient was ventilated on pressure-controlled mode with an fraction of inspired oxygen (FIO 2 ) of 80%, a peak airway pressure <30 cm H 2 O, and a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) between 8-10 cm H 2 O in order to maintain oxygen saturation (SaO 2 ) >92%. The pao 2 /FIO 2 ratio was <200 mmhg. The hemodynamic was supported with norepinephrine (doses between mcg/min). A chest computer tomography revealed an airspace consolidation of the left lower lobe and bilateral infiltrates (Figure 1). A transthoracic echocardiography excluded a left ventricular dysfunction, and mitral and aortic valves appeared normal. A bronchoalveolar lavage sample showed a neutrophil predominance (>50%). Despite regression of the inflammatory parameters (CRP from 350 to 129 mg/l and procalcitoabroad recently, but was gardening during the last week before hospital admission. On initial presentation, his temperature was 38.5 C, heart rate was 95 beats/min, blood pressure was 128/64 mmhg and his respiratory rate was 18 breaths/min. Physical examination revealed fine crackles of the left lower lobe whereas other findings were normal. Initial oxygen saturation was 94% while breathing room air. Laboratory values were remarkable for anemia (9.1 g/dl, normal range g/dl) elevated C-reactive protein (CRP 373 mg/l, normal <5 mg/l) and elevated creatinine (141 µmol/l, normal <106 µmol/l). White blood cell count was cell/l with a differential showing 83% neutrophils and 8.5% lymphocytes. Pneumococcal and legionella urinary antigen tests were negative. Cultures of blood showed no growth. Chest radiographs did not show focal consolidations. He initiated antibiotic therapy with intravenous ceftriaxone (2 g/24 h). Thereafter he developed a highly productive cough requiring a cough-assist (CoughAssist CM-3200, Megamed, Cham, Switzerland) to successfully clear the bronchial tree. Two days later he developed a rapid progressive respiratory failure with an impending hemodynamic instability. A chest radiograph revealed an opacification of the left lung suggesting a nearly complete atelectasis; therefore, he underwent intubation. A bronchoscopy did not detect any endobronchial obstruction and on ultrasonography only a minimal left side pleural effusion was visible. After obtaining secretions from the left upper and lower lobes with mini lavage for culture antibiotic treatment was changed to intravenous imipenem-cilastatin (500 mg/6 h) plus clarithromycin (500 mg/12 h). Prednisone dosage was increased up to 50 mg daily in order to prevent adrenal insufficiency and reduced to Figure 1 - Computed tomography of the chest one day after admission to the intensive care unit showing bilateral infiltrates and airspace consolidation of the left lower lobe. 115
3 T. Reynaldos Canton Migotto, et al. 116 nin from 6.3 to 2.2 µg/l in three days) high fever persisted with abundant tracheal secretion requiring frequent aspirations and therefore we replaced clarithromycin with intravenous levofloxacin (500 mg/12 h). The bronchial sample obtained on the day of intubation was cultured on buffered charcoal-yeast extract agar medium on which Legionella surprisingly grew longbeachae. Cultures for other bacteria (including mycobacteria) respiratory viruses and fungi remained negative. These results allowed us to make a definitive diagnosis of L. longbeachae communityacquired pneumonia (CAP) complicated by acute respiratory distress syndrome with septic shock. The clinical course was characterized by a progressive improvement until the sixth day after admission to the ICU. Thereafter, we observed a new worsening of the respiratory parameters without an apparent cause requiring higher FIO 2 and PEEP levels. In the absence of clinical signs of ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP) further bronchial samples were not obtained and antibiotic coverage remained unchanged. Despite higher FIO 2 and PEEP levels the patient remained hypoxemic and, to protect the right ventricle from high intrathoracic pressure and to maintain an open-lung ventilation protective strategy (tidal volume of 6 ml per kg ideal body weight and peak airway pressure <30 cm H 2 O), with a transient moderate permissive hypercapnia we decided to prone the patient with a consistent improvement allowing us to progressively reduce the respiratory support. On day thirteen after admission to the ICU the patient developed again high fever with worsening respiratory parameters and hemodynamic instability consistent with a suspected impending VAP. After discussion with the family members and in accordance with the patient s wishes, we decided not to perform the diagnostic evaluation of a suspected VAP and to withhold further support and the patient died shortly after. An autopsy was not performed. DISCUSSION The patient described herein with polymyalgia rheumatica represents a sporadic CAP case with ARDS and septic shock due to L. longbeachae infection, diagnosed by culture from bronchial secretions. In accordance with the BAL cultures, and sample with a neutrophil predominance excluding an acute eosinophilic pneumonia and a cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, a contamination seems very unlikely (1). The delay between the onset of the symptoms and appropriate antibiotic coverage is probably responsible for the development of the ARDS diagnosed in accordance with the Berlin definition (2). By admission to our ICU the patient presented criteria for early prone positioning (3). Under standard of care supine low tidal volume ventilation the patient progressively improved rendering prone ventilation initially no more indicated. The only risk factor for Legionella pneumonia that we could identify was the longterm systemic steroids treatment (10 mg daily of prednisone) associated with depression of-cell mediated immunity. The four days transient increase of prednisone dosage in order to prevent adrenal insufficiency seems unlikely to be responsible for the poor patient s outcome. To the best of our knowledge this case represents the first report of a L. longbeachae CAP complicated by ARDS with septic shock in a patient with corticosteroid-dependent polymyalgia rheumatica. Furthermore, this is the first description of a L. longbeachae infection in Switzerland. L. longbeachae was first described as a cause of pneumonia in two Californian patients
4 ARDS by Legionella longbeachae (4). This infection is very uncommon in the United States and Europe (5) but it accounts for approximately 50% of all cases of Legionnaires disease in Australia and New Zealand (6), and it is far more prevalent than L. pneumophila in Southeast Asia (7). L. longbeachae is one of the soil-dwelling pathogenetic Legionella species and its transmission has been linked to gardening and exposure to potting soil (8). The present case was notified to the Regional Public Health authorities, but because it was a sporadic case of non-pneumophila Legionella infection, no additional epidemiological investigations were undertaken. L. longbeachae is not only less prevalent than L. pneumophila but also probably less virulent (9). This could be an explanation of its nearly exclusive occurrence in immunosuppressed hosts. Pneumonia cases due to L. longbeachae reported from outside Australia occurred in immunocompromized patients: those undergone splenectomy, under immunosuppressive drugs for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or in transplant recipients (10). Garcia and coll. reported a fatal case of community-acquired pneumonia due to L. longbeachae in Spain (11). Their young patient with SLE was also under corticosteroid treatment, but in contrast to our patient she had one important additional risk factor for Legionella pneumonia: cigarettes smoking (12). Moreover despite severe hypoxemia this patient did not fulfill all the criteria for ARDS diagnosis because hydrostatic pulmonary edema was formally not excluded (eg echocardiography). The widespread introduction of Legionella urinary antigen testing into many hospital laboratories has resulted in a decreasing use of cultures and serology studies (13). Although urinary antigen test remains positive even during administration of empiric anti-legionella antibiotics, it is helpful in patients with unproductive cough and the test-result is usually available within hours permitting an early diagnosis, it is only specific for L. pneumophila serogroup 1 (14, 15). Therefore it is likely that many infections caused by non-pneumophila species remain undiagnosed, as in our patient at hospital admission. Legionella spp. does not grow on blood agar media, and are usually not detected by sputum Gram stain or blood culture. The standard media for Legionella isolation is buffered charcoal-yeast extract agar (BCYE) eventually supplemented with anisomycin, dyes, polymycin and vancomycin to reduce sample contamination. Our findings support the importance of examining sputum for Legionella spp. by cultural methods when pneumonia is suspected, especially in the immunocompromized host, where early recognition of the responsible pathogen and appropriate antibiotic therapy are crucial for the patient s survival (16). Furthermore, the sensitivity of Legionella urinary antigen test depends on clinical severity of pneumonia, so that a mild pneumonia or an early-onset pneumonia may go undiagnosed if the test is used alone (14, 15). In summary, this culture-proven case of L. longbeachae infection demonstrates that non-pneumophila Legionella species must be considered as casual agents of pneumonia even in mild immunosuppressed patients. It should be noted that non-pneumophila Legionella infections are probably underreported because urinary antigen testing and serology fail to detect these pathogens and because sputum culture on appropriate media is not always standard practice in the CAP diagnosis. A delay in diagnosis and in appropriate antibiotic treatment could significantly affect patients outcome, especially in the immunocompromized hosts. 117
5 T. Reynaldos Canton Migotto, et al. 118 Since sputum cultures take several days, empiric anti-legionella antibiotic coverage and real-time PCR testing should be considered in high-risk patients. Finally, we suggest to administer anti-legionella antibiotics in severe CAPs if the urinary antigen test is negative, unless another pathogen has been detected as the causal agent and the involvement of Legionella has, definitively, been ruled out. REFERENCES 1. Schwarz MI, Albert RK. «Imitators» of the ARDS: implications for diagnosis and treatment. Chest 2004; 125: ARDS Definition Task Force, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ferguson ND, Caldwell E, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012; Guérin C, Reignier J, Richard JC, Beuret P, Gacouin A, Boulain T, al. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 2013; 368: McKinney RM, Porschen RK, Edelstein PH, Bissett ML, Harris PP, Bondell SP, et al. Legionella longbeachae species nova, another etiologic agent of human pneumonia. Ann Intern Med 1981; 94: Fields BS, Benson RF, Besser RE. Legionella and Legionnaires disease: 25 years of investigation. Clin Microbiol Rev 2002; 15: Yohannes K, Roche PW, Roberts A, Liu C, Firestone SM, Bartlett M, et al. Australia s notifiable diseases status, 2004, annual report of the National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System. Commun Dis Intell 2006; 30: Phares CR, Wangroongsarb P, Chantra S, Paveenkitiporn W, Tondella ML, Benson RF, et al. Epidemiology of severe pneumonia caused by Legionella longbeachae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Chlamydia pneumoniae: 1-year,population-based surveillance for severe pneumonia in Thailand. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 45: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Legionnaires disease associated with potting soil-california, Oregon and Washington, May-June MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2000; 49: Terry Ali OA; Zink S, von Lackum NK, Abu-Kwaik Y. Comparative assessment of virulence Traits in Legionella spp. Microbiology 2003; 149: Kümpers P, Tiede A, Kirschner P, Girke J, Ganser A, Peest D. Legionnaires disease in immunocompromised patients: a case report of Legionella longbeachae pneumonia and review of the literature. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2008; 57: García C, Ugalde E, Campo AB, Miñambres E, Kovács N. Fatal case of community-acquired pneumonia caused by Legionella longbeachae in a patient with sistemic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2004; 23: Den Boer JW, Nijhof J, Friesema I. Risk factors for sporadic community-acquired Legionnaires disease. A 3-year national case-control study. Public Health 2006; 120: Benin A, Benson RF, Besser RE. Trends in legionnaires disease, : decliningmortality and new pattern of diagnosis. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 35: von Baum H, Ewig S, Marre R, Suttorp N, Gonschior S, Welte T, et al. Community-acquired Legionella pneumonia: New insights from the German competence network for community acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 46: Shimada T, Noguchi Y, Jackson JL, Miyashita J, Hayashino Y, Kamiya T, et al. Systemic review and metaanalysis. Urinary antigen tests for Legionellosis. Chest 2009; 136: Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A, Bartlett JG, Campbell GD, Dean NC, et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired Pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 44 (Suppl. 2): Cite this article as: Reynaldos Canton Migotto T, Györik Lora S, Gaia V, Pagnamenta A. ARDS with septic shock due to Legionella longbeachae pneumonia in a patient with polymyalgia rheumatic. Heart, Lung and Vessels. 2014; 6(2): Source of Support: Nil. Conflict of interest: None declared. Acknowledgement: We acknowledge Orlando Petrini PhD, ECPM, Director of the Cantonal Institute of Microbiology, Bellinzona, Switzerland, for providing editorial assistance.
Community-Acquired Pneumonia OBSOLETE 2
 Community-Acquired Pneumonia OBSOLETE 2 Clinical practice guidelines serve as an educational reference, and do not supersede the clinical judgment of the treating physician with respect to appropriate
Community-Acquired Pneumonia OBSOLETE 2 Clinical practice guidelines serve as an educational reference, and do not supersede the clinical judgment of the treating physician with respect to appropriate
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update
 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update Prof. A.S.M. Areef Ahsan FCPS(Medicine) MD(Critical Care Medicine) MD ( Chest) Head, Dept. of Critical Care Medicine BIRDEM General Hospital INTRODUCTION
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update Prof. A.S.M. Areef Ahsan FCPS(Medicine) MD(Critical Care Medicine) MD ( Chest) Head, Dept. of Critical Care Medicine BIRDEM General Hospital INTRODUCTION
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia
 Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics
 Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics Nicole Wolter Centre for Respiratory Diseases and Meningitis (CRDM) National Institute for Communicable Diseases nicolew@nicd.ac.za 7 th FIDSSA Conference, Cape
Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics Nicole Wolter Centre for Respiratory Diseases and Meningitis (CRDM) National Institute for Communicable Diseases nicolew@nicd.ac.za 7 th FIDSSA Conference, Cape
Community acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila in a tertiary care hospital
 101 Research article Community acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila in a tertiary care hospital Abstract BN Dissanayake 1,, DE Jayawardena 2, CG Senevirathna 1, TM Gamage 1 Sri Lankan Journal
101 Research article Community acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila in a tertiary care hospital Abstract BN Dissanayake 1,, DE Jayawardena 2, CG Senevirathna 1, TM Gamage 1 Sri Lankan Journal
Community Acquired Pneumonia. Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP
 Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
UPDATE IN HOSPITAL MEDICINE
 UPDATE IN HOSPITAL MEDICINE FLORIDA CHAPTER ACP MEETING 2016 Himangi Kaushal, M.D., F.A.C.P. Program Director Memorial Healthcare System Internal Medicine Residency DISCLOSURES None OBJECTIVES Review some
UPDATE IN HOSPITAL MEDICINE FLORIDA CHAPTER ACP MEETING 2016 Himangi Kaushal, M.D., F.A.C.P. Program Director Memorial Healthcare System Internal Medicine Residency DISCLOSURES None OBJECTIVES Review some
Lecture Notes. Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia
 Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Making the Right Call With. Pneumonia. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a. Community-Acquired. What exactly is CAP?
 Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Torres A, Sibila O, Ferrer M, et al. Effect of corticosteroids on treatment failure among hospitalized patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia and high inflammatory
Supplementary Online Content Torres A, Sibila O, Ferrer M, et al. Effect of corticosteroids on treatment failure among hospitalized patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia and high inflammatory
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Blum CA, Nigro N, Briel M, et al. Adjunct prednisone
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Blum CA, Nigro N, Briel M, et al. Adjunct prednisone
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids
 Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
COPD exacerbation. Dr. med. Frank Rassouli
 Definition according to GOLD report: - «An acute event - characterized by a worsening of the patients respiratory symptoms - that is beyond normal day-to-day variations - and leads to a change in medication»
Definition according to GOLD report: - «An acute event - characterized by a worsening of the patients respiratory symptoms - that is beyond normal day-to-day variations - and leads to a change in medication»
Landmark articles on ventilation
 Landmark articles on ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity ARDS AECC DEFINITION-1994 ALI Acute onset Bilateral chest infiltrates PCWP
Landmark articles on ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity ARDS AECC DEFINITION-1994 ALI Acute onset Bilateral chest infiltrates PCWP
NOSOCOMIAL LEGIONELLA SEPTICEMIA IN PATIENT WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW
 NOSOCOMIAL LEGIONELLA SEPTICEMIA IN PATIENT WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW Theerawat Naksanguan and Pakpoom Phoompoung Division of Infectious Diseases and Tropical
NOSOCOMIAL LEGIONELLA SEPTICEMIA IN PATIENT WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW Theerawat Naksanguan and Pakpoom Phoompoung Division of Infectious Diseases and Tropical
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum
 The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 25, 2018 0800 EDT NH-HAN 20180825 Cluster of Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia (Legionnaire
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 25, 2018 0800 EDT NH-HAN 20180825 Cluster of Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia (Legionnaire
Trial protocol - NIVAS Study
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Trial protocol - NIVAS Study METHODS Study oversight The Non-Invasive Ventilation after Abdominal Surgery
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Trial protocol - NIVAS Study METHODS Study oversight The Non-Invasive Ventilation after Abdominal Surgery
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
DAILY SCREENING FORM
 DAILY SCREENING FORM Patient s initials: Date of admission: Time of admission: Gender: M F Year of Birth: Type of admission: Medical/Surgical/Postoperative (elective) Days Date Mechanical ventilation Lung
DAILY SCREENING FORM Patient s initials: Date of admission: Time of admission: Gender: M F Year of Birth: Type of admission: Medical/Surgical/Postoperative (elective) Days Date Mechanical ventilation Lung
Best of Pulmonary Jennifer R. Hucks, MD University of South Carolina School of Medicine
 Best of Pulmonary 2012-2013 Jennifer R. Hucks, MD University of South Carolina School of Medicine Topics ARDS- Berlin Definition Prone Positioning For ARDS Lung Protective Ventilation In Patients Without
Best of Pulmonary 2012-2013 Jennifer R. Hucks, MD University of South Carolina School of Medicine Topics ARDS- Berlin Definition Prone Positioning For ARDS Lung Protective Ventilation In Patients Without
New respiratory symptoms and lung imaging findings in a woman with polymyositis
 Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
To develop guidelines for the use of appropriate antibiotics for adult patients with CAP and guidance on IV to PO conversion.
 Page 1 of 5 TITLE: COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA (CAP) EMPIRIC MANAGEMENT OF ADULT PATIENTS AND IV TO PO CONVERSION GUIDELINES: These guidelines serve to aid clinicians in the diagnostic work-up, assessment
Page 1 of 5 TITLE: COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA (CAP) EMPIRIC MANAGEMENT OF ADULT PATIENTS AND IV TO PO CONVERSION GUIDELINES: These guidelines serve to aid clinicians in the diagnostic work-up, assessment
MAJOR ARTICLE. Atypical Pneumonia in Thailand CID 2007:45 (15 December) e147
 MAJOR ARTICLE Epidemiology of Severe Pneumonia Caused by Legionella longbeachae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Chlamydia pneumoniae: 1-Year, Population- Based Surveillance for Severe Pneumonia in Thailand
MAJOR ARTICLE Epidemiology of Severe Pneumonia Caused by Legionella longbeachae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Chlamydia pneumoniae: 1-Year, Population- Based Surveillance for Severe Pneumonia in Thailand
Does proning patients with refractory hypoxaemia improve mortality?
 Does proning patients with refractory hypoxaemia improve mortality? Clinical problem and domain I selected this case because although this was the second patient we had proned in our unit within a week,
Does proning patients with refractory hypoxaemia improve mortality? Clinical problem and domain I selected this case because although this was the second patient we had proned in our unit within a week,
Pneumonia. Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine
 Pneumonia Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine Definition Pneumonia is an acute respiratory illness caused by an infection of the lung parenchyma, associated with recently developed
Pneumonia Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine Definition Pneumonia is an acute respiratory illness caused by an infection of the lung parenchyma, associated with recently developed
New Surveillance Definitions for VAP
 New Surveillance Definitions for VAP 2012 Critical Care Canada Forum Toronto Dr. John Muscedere Associate Professor of Medicine, Queen s University Kingston, Ontario Presenter Disclosure Dr. J. G. Muscedere
New Surveillance Definitions for VAP 2012 Critical Care Canada Forum Toronto Dr. John Muscedere Associate Professor of Medicine, Queen s University Kingston, Ontario Presenter Disclosure Dr. J. G. Muscedere
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Angel Coz MD, FCCP, DCE Assistant Professor of Medicine UCSF Fresno November 4, 2017 No disclosures OBJECTIVES Identify current trends and risk factors of ARDS Describe
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Angel Coz MD, FCCP, DCE Assistant Professor of Medicine UCSF Fresno November 4, 2017 No disclosures OBJECTIVES Identify current trends and risk factors of ARDS Describe
Trends in Legionnaires Disease, : Declining Mortality and New Patterns of Diagnosis
 MAJOR ARTICLE Trends in Legionnaires Disease, 1980 1998: Declining Mortality and New Patterns of Diagnosis Andrea L. Benin, a Robert F. Benson, and Richard E. Besser Respiratory Diseases Branch, Division
MAJOR ARTICLE Trends in Legionnaires Disease, 1980 1998: Declining Mortality and New Patterns of Diagnosis Andrea L. Benin, a Robert F. Benson, and Richard E. Besser Respiratory Diseases Branch, Division
WORKSHOP. The Multiple Facets of CAP. Community acquired pneumonia (CAP) continues. Jennifer s Situation
 Practical Pointers pointers For for Your your Practice practice The Multiple Facets of CAP Dr. George Fox, MD, MSc, FRCPC, FCCP Community acquired pneumonia (CAP) continues to be a significant health burden
Practical Pointers pointers For for Your your Practice practice The Multiple Facets of CAP Dr. George Fox, MD, MSc, FRCPC, FCCP Community acquired pneumonia (CAP) continues to be a significant health burden
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in
 Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Pneumonia in the Hospitalized
 Pneumonia in the Hospitalized Patient: Use of Steroids Nicolette Myers, MD Pulmonary/Sleep/Critical Care November 9, 2018 Park Nicollet Clinic Facts About Pneumonia CAP is the 8 th most common cause of
Pneumonia in the Hospitalized Patient: Use of Steroids Nicolette Myers, MD Pulmonary/Sleep/Critical Care November 9, 2018 Park Nicollet Clinic Facts About Pneumonia CAP is the 8 th most common cause of
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA
 KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Methodology: Expert opinion Issue Date: 8-97 Champion: Pulmonary Medicine Most Recent Update: 6-08, 7-10, 7-12 Key Stakeholders: Pulmonary Medicine,
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Methodology: Expert opinion Issue Date: 8-97 Champion: Pulmonary Medicine Most Recent Update: 6-08, 7-10, 7-12 Key Stakeholders: Pulmonary Medicine,
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
Necrotising pneumonia
 Necrotising pneumonia TASNIM HASAN INFECTIOUS DISEASE ADVANCE TRAINEE 29 TH SEPTEMBER 2017 Background 57 year old male Background Rheumatoid arthritis On adalimumab and methotrexate Ischaemic heart disease
Necrotising pneumonia TASNIM HASAN INFECTIOUS DISEASE ADVANCE TRAINEE 29 TH SEPTEMBER 2017 Background 57 year old male Background Rheumatoid arthritis On adalimumab and methotrexate Ischaemic heart disease
Care Guideline DRAFT for review cycle 08/02/17 CARE OF THE ADULT PNEUMONIA PATIENT
 Care Guideline DRAFT for review cycle 08/02/17 CARE OF THE ADULT PNEUMONIA PATIENT Target Audience: All MHS employed providers within Primary Care, Urgent Care, and In-Hospital Care. The secondary audience
Care Guideline DRAFT for review cycle 08/02/17 CARE OF THE ADULT PNEUMONIA PATIENT Target Audience: All MHS employed providers within Primary Care, Urgent Care, and In-Hospital Care. The secondary audience
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1).
 PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1). 1 Inform Consent Date: / / dd / Mmm / yyyy 2 Patient identifier: Please enter the 6 digit Patient identification number from your site patient log
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1). 1 Inform Consent Date: / / dd / Mmm / yyyy 2 Patient identifier: Please enter the 6 digit Patient identification number from your site patient log
What is the next best step?
 Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
VAP Are strict diagnostic criteria advisable?
 VAP Are strict diagnostic criteria advisable? Javier Garau, MD, PhD 18th Infection and Sepsis Symposium, Porto, 27th February 2013 Limitations of current definitions Alternatives -Streamlined definition
VAP Are strict diagnostic criteria advisable? Javier Garau, MD, PhD 18th Infection and Sepsis Symposium, Porto, 27th February 2013 Limitations of current definitions Alternatives -Streamlined definition
HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA: EPIDEMIOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA: EPIDEMIOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY David Jay Weber, M.D., M.P.H. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, & Epidemiology Associate Chief Medical Officer, UNC Health
HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA: EPIDEMIOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY David Jay Weber, M.D., M.P.H. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, & Epidemiology Associate Chief Medical Officer, UNC Health
The IDSA/ATS consensus guidelines on the management of CAP in adults
 The IDSA/ATS consensus guidelines on the management of CAP in adults F. Piffer F. Tardini R. Cosentini U.O. Medicina d'urgenza, Gruppo NIV, Fondazione Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Mangiagalli e Regina
The IDSA/ATS consensus guidelines on the management of CAP in adults F. Piffer F. Tardini R. Cosentini U.O. Medicina d'urgenza, Gruppo NIV, Fondazione Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Mangiagalli e Regina
Surgery Grand Rounds. Non-invasive Ventilation: A valuable tool. James Cromie, PGY 3 8/24/09
 Surgery Grand Rounds Non-invasive Ventilation: A valuable tool James Cromie, PGY 3 8/24/09 History of mechanical ventilation 1930 s: use of iron lung 1940 s: First NIV system (Bellevue Hospital) 1950 s:
Surgery Grand Rounds Non-invasive Ventilation: A valuable tool James Cromie, PGY 3 8/24/09 History of mechanical ventilation 1930 s: use of iron lung 1940 s: First NIV system (Bellevue Hospital) 1950 s:
Steroids in ARDS: if, when, how much? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Dept. of Emergency Medicine Kent Hospital, İzmir, Türkiye
 Steroids in ARDS: if, when, how much? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Dept. of Emergency Medicine Kent Hospital, İzmir, Türkiye Steroids in ARDS: conclusion Give low-dose steroids if indicated for another problem
Steroids in ARDS: if, when, how much? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Dept. of Emergency Medicine Kent Hospital, İzmir, Türkiye Steroids in ARDS: conclusion Give low-dose steroids if indicated for another problem
ARDS and Ventilators PG26 Update in Surgical Critical Care October 9, 2013
 ARDS and Ventilators PG26 Update in Surgical Critical Care October 9, 2013 Pauline K. Park MD, FACS, FCCM University of Michigan School of Medicine Ann Arbor, MI OVERVIEW New Berlin definition of ARDS
ARDS and Ventilators PG26 Update in Surgical Critical Care October 9, 2013 Pauline K. Park MD, FACS, FCCM University of Michigan School of Medicine Ann Arbor, MI OVERVIEW New Berlin definition of ARDS
Community acquired pneumonia
 Community acquired pneumonia definition Symptoms of an acute LRTI New focal signs on chest examination At least one systemic feature New radiographic shadow Defination{Crofton} IT IS A SYNDROME CAUSED
Community acquired pneumonia definition Symptoms of an acute LRTI New focal signs on chest examination At least one systemic feature New radiographic shadow Defination{Crofton} IT IS A SYNDROME CAUSED
Clinical Outcomes for Hospitalized Patients with Legionella Pneumonia in the Antigenuria Era: The Influence of Levofloxacin Therapy
 MAJOR ARTICLE Clinical Outcomes for Hospitalized Patients with Legionella Pneumonia in the Antigenuria Era: The Influence of Levofloxacin Therapy Analía Mykietiuk, 1 Jordi Carratalà, 1 Núria Fernández-Sabé,
MAJOR ARTICLE Clinical Outcomes for Hospitalized Patients with Legionella Pneumonia in the Antigenuria Era: The Influence of Levofloxacin Therapy Analía Mykietiuk, 1 Jordi Carratalà, 1 Núria Fernández-Sabé,
CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement
 CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement Evidence-Based Assessment of Diagnostic Tests for Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia* Executive Summary Ronald F. Grossman, MD, FCCP; and Alan Fein, MD,
CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement Evidence-Based Assessment of Diagnostic Tests for Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia* Executive Summary Ronald F. Grossman, MD, FCCP; and Alan Fein, MD,
Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
 Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Robin Jump, MD, PhD Cleveland Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center Case Western Reserve University
Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Robin Jump, MD, PhD Cleveland Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center Case Western Reserve University
Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated
 Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated Edwin Yu Clin Infect Dis 2007;44(S2):27-72 Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 171:388-416 IDSA / ATS Guidelines Microbiology Principles and Practice of Infectious
Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated Edwin Yu Clin Infect Dis 2007;44(S2):27-72 Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 171:388-416 IDSA / ATS Guidelines Microbiology Principles and Practice of Infectious
Sub-category: Intensive Care for Respiratory Distress
 Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Intensive Care for Respiratory Distress Topic: Acute Respiratory Distress
Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Intensive Care for Respiratory Distress Topic: Acute Respiratory Distress
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
CARE OF THE ADULT PNEUMONIA PATIENT
 Care Guideline CARE OF THE ADULT PNEUMONIA PATIENT Target Audience: The target audience for this Care Guideline is all MultiCare providers and staff, including those associated with our clinically integrated
Care Guideline CARE OF THE ADULT PNEUMONIA PATIENT Target Audience: The target audience for this Care Guideline is all MultiCare providers and staff, including those associated with our clinically integrated
CASE PRESENTATION VV ECMO
 CASE PRESENTATION VV ECMO Joshua Huelster, MD Fellow in Critical Care Medicine Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center Disclosure There are no conflicts of interest
CASE PRESENTATION VV ECMO Joshua Huelster, MD Fellow in Critical Care Medicine Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center Disclosure There are no conflicts of interest
Pneumonia (Ventilator-associated [VAP] and non-ventilator-associated Pneumonia [PNEU]) Event
![Pneumonia (Ventilator-associated [VAP] and non-ventilator-associated Pneumonia [PNEU]) Event Pneumonia (Ventilator-associated [VAP] and non-ventilator-associated Pneumonia [PNEU]) Event](/thumbs/86/94095894.jpg) Pneumonia (Ventilator-associated [VAP] and non-ventilator-associated Pneumonia []) Event Introduction: In 2011, an estimated 157,000 healthcare-associated pneumonias occurred in acute care hospitals in
Pneumonia (Ventilator-associated [VAP] and non-ventilator-associated Pneumonia []) Event Introduction: In 2011, an estimated 157,000 healthcare-associated pneumonias occurred in acute care hospitals in
Community Acquired & Nosocomial Pneumonias
 Community Acquired & Nosocomial Pneumonias IDSA/ATS 2007 & 2016 Guidelines José Luis González, MD Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Intro - Definitions & Diagnosing CAP treatment VAP & HAP
Community Acquired & Nosocomial Pneumonias IDSA/ATS 2007 & 2016 Guidelines José Luis González, MD Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Intro - Definitions & Diagnosing CAP treatment VAP & HAP
Exam 1 Review. Cardiopulmonary Symptoms Physical Examination Clinical Laboratory Studies
 Exam 1 Review Cardiopulmonary Symptoms Physical Examination Clinical Laboratory Studies WBC Count Differential A patient had been admitted to the hospital for acute shortness of breath. A CXR examination
Exam 1 Review Cardiopulmonary Symptoms Physical Examination Clinical Laboratory Studies WBC Count Differential A patient had been admitted to the hospital for acute shortness of breath. A CXR examination
PNEUMONIA. I. Background 6 th most common cause of death in U.S. Most common cause of infection related mortality
 Page 1 of 8 September 4, 2001 Donald P. Levine, M.D. University Health Center Suite 5C Office: 577-0348 dlevine@intmed.wayne.edu Assigned reading: pages 153-160; 553-563 PNEUMONIA the most widespread and
Page 1 of 8 September 4, 2001 Donald P. Levine, M.D. University Health Center Suite 5C Office: 577-0348 dlevine@intmed.wayne.edu Assigned reading: pages 153-160; 553-563 PNEUMONIA the most widespread and
The new ARDS definitions: what does it mean?
 The new ARDS definitions: what does it mean? Richard Beale 7 th September 2012 METHODS ESICM convened an international panel of experts, with representation of ATS and SCCM The objectives were to update
The new ARDS definitions: what does it mean? Richard Beale 7 th September 2012 METHODS ESICM convened an international panel of experts, with representation of ATS and SCCM The objectives were to update
ARDS: an update 6 th March A. Hakeem Al Hashim, MD, FRCP SQUH
 ARDS: an update 6 th March 2017 A. Hakeem Al Hashim, MD, FRCP SQUH 30M, previously healthy Hx: 1 week dry cough Gradually worsening SOB No travel Hx Case BP 130/70, HR 100/min ph 7.29 pco2 35 po2 50 HCO3
ARDS: an update 6 th March 2017 A. Hakeem Al Hashim, MD, FRCP SQUH 30M, previously healthy Hx: 1 week dry cough Gradually worsening SOB No travel Hx Case BP 130/70, HR 100/min ph 7.29 pco2 35 po2 50 HCO3
Advance Pathology Services, P.C Professional Drive, Suite 3 Cadillac, MI Phone: Fax:
 Advance Pathology Services, P.C. 8865 Professional Drive, Suite 3 Cadillac, MI 49601 Phone: 231-468-2346 Fax: 231-468-2349 Pathology Analysis: Pneumonia and Pulmonary Hemorrhage Cause Death; Clinically
Advance Pathology Services, P.C. 8865 Professional Drive, Suite 3 Cadillac, MI 49601 Phone: 231-468-2346 Fax: 231-468-2349 Pathology Analysis: Pneumonia and Pulmonary Hemorrhage Cause Death; Clinically
Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics)
 Page 1 of 8 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2014 UpToDate Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics) Authors Thomas J Marrie, MD Thomas M File, Jr, MD Section Editor John
Page 1 of 8 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2014 UpToDate Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics) Authors Thomas J Marrie, MD Thomas M File, Jr, MD Section Editor John
Research & Reviews of. Pneumonia
 Chapter Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of VAP in Adult ICU Patients Priyam Batra * ; Purva Mathur Research & Reviews of Department of Laboratory Medicine, AIIMS, Trauma Centre, New Delhi, India. *
Chapter Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of VAP in Adult ICU Patients Priyam Batra * ; Purva Mathur Research & Reviews of Department of Laboratory Medicine, AIIMS, Trauma Centre, New Delhi, India. *
ECMO for Severe Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure: Pro-Con Debate. Carolyn Calfee, MD MAS Mark Eisner, MD MPH
 ECMO for Severe Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure: Pro-Con Debate Carolyn Calfee, MD MAS Mark Eisner, MD MPH June 3, 2010 Case Presentation Setting: Community hospital, November 2009 29 year old woman with
ECMO for Severe Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure: Pro-Con Debate Carolyn Calfee, MD MAS Mark Eisner, MD MPH June 3, 2010 Case Presentation Setting: Community hospital, November 2009 29 year old woman with
A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough
 Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
The ARDS is characterized by increased permeability. Incidence of ARDS in an Adult Population of Northeast Ohio*
 Incidence of ARDS in an Adult Population of Northeast Ohio* Alejandro C. Arroliga, MD, FCCP; Ziad W. Ghamra, MD; Alejandro Perez Trepichio, MD; Patricia Perez Trepichio, RRT; John J. Komara Jr., BA, RRT;
Incidence of ARDS in an Adult Population of Northeast Ohio* Alejandro C. Arroliga, MD, FCCP; Ziad W. Ghamra, MD; Alejandro Perez Trepichio, MD; Patricia Perez Trepichio, RRT; John J. Komara Jr., BA, RRT;
The use of proning in the management of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
 Case 3 The use of proning in the management of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Clinical Problem This expanded case summary has been chosen to explore the rationale and evidence behind the use of proning
Case 3 The use of proning in the management of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Clinical Problem This expanded case summary has been chosen to explore the rationale and evidence behind the use of proning
MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTING IN PICU
 MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTING IN PICU This is a guideline for the taking of microbiological samples in PICU to diagnose or exclude infection. The diagnosis of infection requires: Ruling out non-infectious causes
MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTING IN PICU This is a guideline for the taking of microbiological samples in PICU to diagnose or exclude infection. The diagnosis of infection requires: Ruling out non-infectious causes
Radiological syndroms. Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome
 Radiological syndroms Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome Alveolar syndrome Pulmonary architecture : Morphological unit is the lobule 15-25mm
Radiological syndroms Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome Alveolar syndrome Pulmonary architecture : Morphological unit is the lobule 15-25mm
Two Cases of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome with High Values of Chlamydophila pneumoniae-specific Antibodies
 CASE REPORT Two Cases of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome with High Values of Chlamydophila pneumoniae-specific Antibodies Ryotaro Igusa 1, Atsushi Nakamura 1, Sachiko Kawana 1, Taizou Shibahara 2,
CASE REPORT Two Cases of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome with High Values of Chlamydophila pneumoniae-specific Antibodies Ryotaro Igusa 1, Atsushi Nakamura 1, Sachiko Kawana 1, Taizou Shibahara 2,
Polmoniti: Steroidi sì, no, quando. Alfredo Chetta Clinica Pneumologica Università degli Studi di Parma
 Polmoniti: Steroidi sì, no, quando Alfredo Chetta Clinica Pneumologica Università degli Studi di Parma Number of patients Epidemiology and outcome of severe pneumococcal pneumonia admitted to intensive
Polmoniti: Steroidi sì, no, quando Alfredo Chetta Clinica Pneumologica Università degli Studi di Parma Number of patients Epidemiology and outcome of severe pneumococcal pneumonia admitted to intensive
Relationships and Emerging Pathogens: Microbiology, Infection Prevention and Public Health Working Together
 Relationships and Emerging Pathogens: Microbiology, Infection Prevention and Public Health Working Together Objectives Using the M. chimaera outbreak as the discussion scenario, explore communication roles
Relationships and Emerging Pathogens: Microbiology, Infection Prevention and Public Health Working Together Objectives Using the M. chimaera outbreak as the discussion scenario, explore communication roles
Evaluation of the Oxoid Xpect Legionella test kit for Detection of Legionella
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 6 May 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00397-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 6 May 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00397-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Eosinophilic lung diseases
 Eosinophilic lung diseases Chai Gin Tsen Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital The eyes do not see what the mind does not know Not very common A high index of suspicion
Eosinophilic lung diseases Chai Gin Tsen Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital The eyes do not see what the mind does not know Not very common A high index of suspicion
and localized ground glass opacities, or bronchiolar focal or multifocal micronodules;
 E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN. IAP UG Teaching slides
 PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN 1 INTRODUCTION 156 million new episodes / yr. worldwide 151 million episodes developing world 95% in developing countries 19% of all deaths in children
PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN 1 INTRODUCTION 156 million new episodes / yr. worldwide 151 million episodes developing world 95% in developing countries 19% of all deaths in children
Sample Case Study. The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on
 Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Uranga A, España, Bilbao A, et al. Duration of antibiotic treatment in communityacquired pneumonia: a multicenter randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. ublished online
Supplementary Online Content Uranga A, España, Bilbao A, et al. Duration of antibiotic treatment in communityacquired pneumonia: a multicenter randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. ublished online
To Study The Cinico-Radiological Features And Associated Co-Morbid Conditions
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 16 (July. 2018), PP 58-62 www.iosrjournals.org To study the clinico-radiological features
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 16 (July. 2018), PP 58-62 www.iosrjournals.org To study the clinico-radiological features
Prone ventilation revisited in H1N1 patients
 International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research ISSN: 2393-8870 www.ijarm.com DOI: 10.22192/ijamr Volume 5, Issue 10-2018 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijamr.2018.05.10.005 Prone
International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research ISSN: 2393-8870 www.ijarm.com DOI: 10.22192/ijamr Volume 5, Issue 10-2018 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijamr.2018.05.10.005 Prone
Pneumonia. Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial
 Pneumonia Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial Epidemiology of pneumonia Commonest infectious cause of death in the UK and USA Incidence - 5-11 per 1000 per year Worse
Pneumonia Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial Epidemiology of pneumonia Commonest infectious cause of death in the UK and USA Incidence - 5-11 per 1000 per year Worse
Difficult Ventilation in ARDS Patients
 Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as submitted by the author.
Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as submitted by the author.
DOI: /
 DOI:10.23873/2074-0506-2018-10-2-105-109 Specific features of respiratory and intensive therapy for pulmonary infectious complications of acute and chronic kidney graft rejection F.G. Nazyrov, R.A. Ibadov,
DOI:10.23873/2074-0506-2018-10-2-105-109 Specific features of respiratory and intensive therapy for pulmonary infectious complications of acute and chronic kidney graft rejection F.G. Nazyrov, R.A. Ibadov,
Over the last several years various national and
 Recommendations for the Management of COPD* Gary T. Ferguson, MD, FCCP Three sets of guidelines for the management of COPD that are widely recognized (from the European Respiratory Society [ERS], American
Recommendations for the Management of COPD* Gary T. Ferguson, MD, FCCP Three sets of guidelines for the management of COPD that are widely recognized (from the European Respiratory Society [ERS], American
Objectives. Pneumonia. Pneumonia. Epidemiology. Prevalence 1/7/2012. Community-Acquired Pneumonia in infants and children
 Objectives Community-Acquired in infants and children Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America - 2011 Sabah Charania,
Objectives Community-Acquired in infants and children Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America - 2011 Sabah Charania,
Pneumonia Severity Scores:
 Pneumonia Severity Scores: Are they Accurate Predictors of Mortality? JILL McEWEN, MD FRCPC Clinical Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC Canada President,
Pneumonia Severity Scores: Are they Accurate Predictors of Mortality? JILL McEWEN, MD FRCPC Clinical Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC Canada President,
Accurate Diagnosis Of Postoperative Pneumonia Requires Objective Data
 Accurate Diagnosis Of Postoperative Pneumonia Requires Objective Data David Ebler, MD David Skarupa, MD Andrew J. Kerwin, MD, FACS Jhun de Villa, MD Michael S. Nussbaum, MD, FACS J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS
Accurate Diagnosis Of Postoperative Pneumonia Requires Objective Data David Ebler, MD David Skarupa, MD Andrew J. Kerwin, MD, FACS Jhun de Villa, MD Michael S. Nussbaum, MD, FACS J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS
PULMONARY EMERGENCIES
 EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
Is ARDS Important to Recognize?
 Is ARDS Important to Recognize? Lorraine B. Ware MD Vanderbilt University Financial Disclosures: research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim, Global Blood Therapeutics Why diagnose ARDS? -initiate specific
Is ARDS Important to Recognize? Lorraine B. Ware MD Vanderbilt University Financial Disclosures: research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim, Global Blood Therapeutics Why diagnose ARDS? -initiate specific
PNEUMONIA. Patient Case: Chief Complaint: I have been short of breath and have been coughing up rust-colored phlegm for the past 3 days.
 PNEUMONIA Relevant Guidelines: 2008 IDSA CAP guidelines: http://www.idsociety.org/guidelines/patient_care/idsa_practice_guidelines/infections_by_org an_system/lower/upper_respiratory/community-acquired_pneumonia_(cap)/
PNEUMONIA Relevant Guidelines: 2008 IDSA CAP guidelines: http://www.idsociety.org/guidelines/patient_care/idsa_practice_guidelines/infections_by_org an_system/lower/upper_respiratory/community-acquired_pneumonia_(cap)/
Critical Care Nursing Theory. Pneumonia. - Pneumonia is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma
 - is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma - is a common infection encountered by critical care nurses when it complicates the course of a serious illness or leads to acute respiratory distress.
- is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma - is a common infection encountered by critical care nurses when it complicates the course of a serious illness or leads to acute respiratory distress.
Steroids for ARDS. Clinical Problem. Management
 Steroids for ARDS James Beck Clinical Problem A 60 year old lady re-presented to ICU with respiratory failure. She had previously been admitted for fluid management and electrolyte correction having presented
Steroids for ARDS James Beck Clinical Problem A 60 year old lady re-presented to ICU with respiratory failure. She had previously been admitted for fluid management and electrolyte correction having presented
MRSA pneumonia mucus plug burden and the difficult airway
 Case report Crit Care Shock (2016) 19:54-58 MRSA pneumonia mucus plug burden and the difficult airway Ann Tsung, Brian T. Wessman An 80-year-old female with a past medical history of chronic obstructive
Case report Crit Care Shock (2016) 19:54-58 MRSA pneumonia mucus plug burden and the difficult airway Ann Tsung, Brian T. Wessman An 80-year-old female with a past medical history of chronic obstructive
Surviving Sepsis Campaign. Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock. An Overview
 Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock An Overview Mechanical Ventilation of Sepsis-Induced ALI/ARDS ARDSnet Mechanical Ventilation Protocol Results: Mortality
Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock An Overview Mechanical Ventilation of Sepsis-Induced ALI/ARDS ARDSnet Mechanical Ventilation Protocol Results: Mortality
Pneumonia 2017 OMAR PIRZADA
 Pneumonia 2017 OMAR PIRZADA Pneumonia Pneumonia is common 0.5-1% of adults per year, 5-12% presenting to GP with LRTi 22-42% will be admitted to hospital Symptoms and signs Case 1 26 year old man Sudden
Pneumonia 2017 OMAR PIRZADA Pneumonia Pneumonia is common 0.5-1% of adults per year, 5-12% presenting to GP with LRTi 22-42% will be admitted to hospital Symptoms and signs Case 1 26 year old man Sudden
Outcomes From Severe ARDS Managed Without ECMO. Roy Brower, MD Johns Hopkins University Critical Care Canada Forum Toronto November 1, 2016
 Outcomes From Severe ARDS Managed Without ECMO Roy Brower, MD Johns Hopkins University Critical Care Canada Forum Toronto November 1, 2016 Severe ARDS Berlin Definition 2012 P:F ratio 100 mm Hg Prevalence:
Outcomes From Severe ARDS Managed Without ECMO Roy Brower, MD Johns Hopkins University Critical Care Canada Forum Toronto November 1, 2016 Severe ARDS Berlin Definition 2012 P:F ratio 100 mm Hg Prevalence:
The Effect of Tidal Volume on Pulmonary Complications following Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: A Randomized and Controlled Study
 The Effect of Tidal Volume on Pulmonary Complications following Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: A Randomized and Controlled Study Yaxing Shen, MD, Ming Zhong, MD, Lijie Tan, MD Zhongshan Hospital,Fudan
The Effect of Tidal Volume on Pulmonary Complications following Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: A Randomized and Controlled Study Yaxing Shen, MD, Ming Zhong, MD, Lijie Tan, MD Zhongshan Hospital,Fudan
