RECAP FROM MONDAY AND TUESDAY LECTURES
|
|
|
- Leslie Banks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RECAP FROM MONDAY AND TUESDAY LECTURES Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport factors: interact with the target macromolecule (signal recognition) interact with the NPC (nucleoporin Phe - Gly repeats) NPC cytoplasmic fibers nuclear basket Nucleocytoplasmic transport factors: Karyopherins (importins/exportins) import proteins / export trna, snrna, rrna regulated by the GTPase Ran NTF2 import Ran
2 Cytoplasm Nucleus translation Search for mrna export factors yeast genetics: poly(a+) accumulation interaction with nucleoporin - Mex67p Segref et al., 97 -Dbp5p Snay-Hodge et al., 98 - Gle2p/Rae1 Murphy et al., 96; Brown et al., 95 nuclear export pre-mrna processing m 7 G m 7 G AAAA retroviruses: -Crm1 (exportin) -HIV-1 Fornerod et al., 97 -TAP (Mex67p homologue) -SRV (CTE RNA) Grüter et al., 98
3 RNA export receptor binding in the nucleus trna Xpo-t U snrna HIV-Rev Crm1 cargo release in the cytosol SRV-CTE mrna TAP-p15
4 Both TAP and p15 are essential for bulk mrna export Knockdown of D.melanogaster TAP or p15 results in nuclear accumulation of bulk polyadenylated RNAs control TAP ds RNAi p15 ds RNAi oligo(dt) in situ hybridization poly-(a) + DNA nucleoporins
5 The TAP subunit of the mrna export receptor is conserved (human NXF1 and yeast Mex67) cargo binding NPC binding p15 binding The p15 subunit of the mrna export receptor is not conserved (human p15 / yeast Mtr2) How does it recognize RNA cargoes? How does it recognize nuclear pore complexes? What is the function of p15? Mtr2?
6 TAP C-terminal portion: interacts with nucleoporins and p15 NTF2-like UBA-like p15 TAP p15 NTF2 NTF2 1.9Å resolution Rfree 22.5 % TAP-p15 heterodimer NTF2-NTF2 homodimer FG-repeat (Fribourg et al., 2001) Bayliss et al., (Stewart (1999). JMB et al., 293: )
7 Structural similarity of NTF2-like domains insertion NTF2 p15 TAP 22% seq.id. with NTF2 rmsd 1.9Å (113 Cα) 13% seq.id. with NTF2 rmsd 2.5 Å (95 Cα)
8 NTF2-like UBA-like p15 UBA-like domain function: NPC binding UBA-like domain: 10% export activity NTF2-like domain: no export activity NTF2-like domain: function???? Extrapolate functional similarity from structural similarity? NTF2 is the Ran import factor binds RanGDP binds nucleoporins RanGDP NTF2 Ran regulator to most transport pathways?mrna export pathway?
9 TAP structure is incompatible with Ran binding insertion NTF2 TAP
10 p15 structure is incompatible with Ran binding Ran switch II NTF2 p15
11 The Ran-binding pocket of NTF2 is occluded in p15 Ran switch II F61 F101 R107 W41 L121 W47 F135 NTF2 p15
12 TAP NTF2-like domain binds Phe-Gly repeat nucleoporins 2.8 Å Rfree 26.9% TAP p15
13 TAP:p15 directly interact with Phe-Gly containing nucleoporins via two structurally unrelated domains p15 NTF2-like scaffold Fribourg et al UBA-like domain Grant et al FG-peptide FG-peptide Recognition of nucleoporins: Phe residue: hydrophobic interactions Gly residue: conformational flexibility
14 TAP has two nucleoporin binding sites NTF2-like Mutation of nucleoporin-binding sites: nuclear envelope localization TAP-GFP wt mut in NTF2 mut in UBA double mut GFP-TAP Double mutant overexpression: inhibition of bulk poly(a) + RNA poly(a) +
15 p15 is recruited to the NPC by TAP Nuclear envelope localization GFP-TAP zz-p15 wt wt wt R134D D482R R134D salt bridge swap the function of p15 is structural
16 TAP is conserved from lower to higher eukaryotes Human TAP and yeast Mex67 (NXF) The smaller subunit of the mrna export factor is not conserved Human p15 and yeast Mtr2: functional homologues no sequence homology 2.8 Å Rf 26.2% p15 TAP H.s. NXF Mtr2 Mex67 S.c. NXF Fribourg and Conti, 2003 Human p15 and yeast Mtr2: structural homology
17 TAP N-terminal portion: cargo binding Cellular mrna (indirect binding via adaptors) Viral CTE RNA (direct binding to human TAP) cargo binding RBD domain RNA-binding NPC binding LRR domain conserved human/yeast Å resolution Rfree 27.8 % Liker et al
18 RNA binding domain of TAP: canonical structure, non canonical sequence
19 LRR binding domain of TAP: structural homology to U2A 4 leucine-rich-repeats in TAP 5 leucine-rich-repeats in U2A (Price et al., 1998)
20 Structural homology TAP RNP-LRR domains RNP-LRR domains binding to U2 snrna (Price et al., 1998)
21 TAP RNP and LRR domains bind a viral RNA directly Viral CTE RNA +TAP +TAP CTE-RNA: TAP: RNP and LRR domains required (in cis) mapped the surface by mutagenesis TAP Spliceosomal complex (Price et al., 98) Cellular mrna TAP: RNP not strictly required (not conserved) conserved LRR domain as an adaptor?
22 mrna export receptor TAP:p15 heterodimer TAP: conserved and essential LRR, NTF2-like and UBA-like domains recognizes Phe-Gly nucleoporin repeats at two sites The function of p15 is structural in maintaining a proper fold (Mtr2?) It is not regulated by Ran mrna release? mrna binding? Adaptor proteins?
23 mrna nuclear export mrna processing mrnp assembly hnrnps mrnp cargo binding TAP-p15 NPC docking + translocation nuclear pore complex (NPC) Translation NMD/localization
24 Adaptors: the exon-exon junction complex? EJC: protein complex deposited upstream of splice junctions EJC proteins in mrna metabolism: splicing, export, NMD, localization
25 ago and Y14: at the core of the EJC form a complex in vitro and in vivo from sequence: Y14 contains an RBD involved in oskar mrna localization involved in nonsense mediated mrna decay Normal case: displacement of EJC proteins: no NMD, stable mrna Aberrant case (PTC): recruitment of NMD factors: mrna degradation
26 Mago-Y14 complex N C RNP2 RNP1 C N Y14 Mago Mago is sandwiched between two domains of Y14
27 The RBD of Y14 binds the protein Mago tight interaction interface L136 L L118 L K114 D128
28 How does it contact RNA?
29 How does it work in nonsense-mediated mrna decay?
30
31
32
33
34 Both Y14 and Mago are required for nonsense mediated mrna decay Provide a binding platform for recruitment of the NMD machinery Same surface is involved in both NMD and oskar mrna localization
35 Current view of mrna export
36 Elena Conti Sebastien Fribourg Genaro Pimienta Fulvia Bono Erika Liker Elena Fernandez Elisa Izaurralde Isabelle Braun David Gatfield Thanks to: N. Gerhing, A. Kulozik, M. Hentze
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression. (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs)
 Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
MCB Chapter 11. Topic E. Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes. Reading :
 MCB Chapter 11 Topic E Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes Reading : 419-449 Topic E Michal Linial 14 Jan 2004 1 Self-splicing group I introns were the first examples of catalytic
MCB Chapter 11 Topic E Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes Reading : 419-449 Topic E Michal Linial 14 Jan 2004 1 Self-splicing group I introns were the first examples of catalytic
Ageneral paradigm for nuclear transport was established primarily through studies of
 CHAPTER 10 The Molecular Mechanisms of mrna Export Tetsuya Taura, Mikiko C. Siomi and Haruhiko Siomi Ageneral paradigm for nuclear transport was established primarily through studies of protein import
CHAPTER 10 The Molecular Mechanisms of mrna Export Tetsuya Taura, Mikiko C. Siomi and Haruhiko Siomi Ageneral paradigm for nuclear transport was established primarily through studies of protein import
Genetics. Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA
 Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA 1 3.4 A 2 Expression of Genetic information DNA Double stranded In the nucleus Transcription mrna Single stranded Translation In the cytoplasm
Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA 1 3.4 A 2 Expression of Genetic information DNA Double stranded In the nucleus Transcription mrna Single stranded Translation In the cytoplasm
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about gene expression control in eukaryotes is correct? Question #1 (A)
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about gene expression control in eukaryotes is correct? Question #1 (A)
The Nonsense-Mediated Decay RNA Surveillance Pathway
 Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007. 76:51 74 First published online as a Review in Advance on March 12, 2007 The Annual Review of Biochemistry is online at biochem.annualreviews.org This article s doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.050106.093909
Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007. 76:51 74 First published online as a Review in Advance on March 12, 2007 The Annual Review of Biochemistry is online at biochem.annualreviews.org This article s doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.050106.093909
REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER
 REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER RNA Splicing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice
REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER RNA Splicing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control
 Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
RECAP (1)! In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas.! What was first evidence for this precursorproduct
 RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone
 Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone mrna is coated and compacted by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), forming large messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mrnps). RBPs assemble on nascent and mature mrnas.
Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone mrna is coated and compacted by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), forming large messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mrnps). RBPs assemble on nascent and mature mrnas.
Abstract. comment reviews reports deposited research refereed research interactions information
 http://genomebiology.com/2002/3/3/reviews/1006.1 Minireview Integration of splicing, transport and translation to achieve mrna quality control by the nonsense-mediated decay pathway Thomas Schell*, Andreas
http://genomebiology.com/2002/3/3/reviews/1006.1 Minireview Integration of splicing, transport and translation to achieve mrna quality control by the nonsense-mediated decay pathway Thomas Schell*, Andreas
Retroviral RNA Processing and stability
 Retroviral RN Processing and stability m 7 gag pol env src Karen Beemon Johns Hopkins niversity m 7 env src m 7 src Retroviruses hijack host cell gene expression machinery to generate progeny virions Simple
Retroviral RN Processing and stability m 7 gag pol env src Karen Beemon Johns Hopkins niversity m 7 env src m 7 src Retroviruses hijack host cell gene expression machinery to generate progeny virions Simple
Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes
 Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes biologiemoleculara.usmf.md pass.: bmgu e.usmf.md 1 DNA in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria biologiemoleculara.usmf.md e.usmf.md pass.: bmgu
Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes biologiemoleculara.usmf.md pass.: bmgu e.usmf.md 1 DNA in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria biologiemoleculara.usmf.md e.usmf.md pass.: bmgu
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
The mrna Nuclear Export Machinery is Targeted by Influenza Virus and Antivirals
 University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Dissertations Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2009-02-17 The mrna Nuclear Export Machinery is Targeted by Influenza Virus and Antivirals Neal Gilpin
University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Dissertations Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2009-02-17 The mrna Nuclear Export Machinery is Targeted by Influenza Virus and Antivirals Neal Gilpin
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Critical Review. Viral Interactions with the Nuclear Transport Machinery: Discovering and Disrupting Pathways
 IUBMB Life, 57(2): 65 72, February 2005 Critical Review Viral Interactions with the Nuclear Transport Machinery: Discovering and Disrupting Pathways Beatriz M. A. Fontoura 1,3, Paula A. Faria 1 and Daniel
IUBMB Life, 57(2): 65 72, February 2005 Critical Review Viral Interactions with the Nuclear Transport Machinery: Discovering and Disrupting Pathways Beatriz M. A. Fontoura 1,3, Paula A. Faria 1 and Daniel
RNA Processing in Eukaryotes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Nuclear Pore Tutorial
 Michael Brenner, Harvard January 7, 2010 Nuclear Pore Tutorial Outline (1) What is the nuclear pore/what does it look like? What are the proteins that make it up? (2) How does the nuclear pore work? The
Michael Brenner, Harvard January 7, 2010 Nuclear Pore Tutorial Outline (1) What is the nuclear pore/what does it look like? What are the proteins that make it up? (2) How does the nuclear pore work? The
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression q
 Review TRENDS in Biochemical Sciences Vol.28 No.4 April 2003 215 How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression q Hervé Le Hir 1,2, Ajit Nott 1 and Melissa J. Moore 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical
Review TRENDS in Biochemical Sciences Vol.28 No.4 April 2003 215 How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression q Hervé Le Hir 1,2, Ajit Nott 1 and Melissa J. Moore 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSPORT OF A MESSENGER RNP PARTICLE: NOVEL REGULATORY MECHANISMS
 From the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Medical Nobel Institute, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSPORT OF A MESSENGER RNP PARTICLE: NOVEL REGULATORY MECHANISMS
From the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Medical Nobel Institute, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSPORT OF A MESSENGER RNP PARTICLE: NOVEL REGULATORY MECHANISMS
Lecture 4. Protein Translocation & Nucleocytoplasmic Transport
 Lecture 4 Protein Translocation & Nucleocytoplasmic Transport Chapter 12 MBoC (5th Edition) Alberts et al. Reference paper: Tran and Wente, Cell 125, 1041-1053, 2006 2/6/2013 1 A Model for How a Soluble
Lecture 4 Protein Translocation & Nucleocytoplasmic Transport Chapter 12 MBoC (5th Edition) Alberts et al. Reference paper: Tran and Wente, Cell 125, 1041-1053, 2006 2/6/2013 1 A Model for How a Soluble
Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus:
 RNA Processing Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus: Transcripts are capped at their 5 end with a methylated guanosine nucleotide. Introns are removed
RNA Processing Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus: Transcripts are capped at their 5 end with a methylated guanosine nucleotide. Introns are removed
Mechanism of splicing
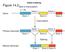 Outline of Splicing Mechanism of splicing Em visualization of precursor-spliced mrna in an R loop Kinetics of in vitro splicing Analysis of the splice lariat Lariat Branch Site Splice site sequence requirements
Outline of Splicing Mechanism of splicing Em visualization of precursor-spliced mrna in an R loop Kinetics of in vitro splicing Analysis of the splice lariat Lariat Branch Site Splice site sequence requirements
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
Protein Synthesis
 Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences
 Adding a 5 cap Lecture 4 mrna splicing and protein synthesis Another day in the life of a gene. Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences Introns are removed by a process
Adding a 5 cap Lecture 4 mrna splicing and protein synthesis Another day in the life of a gene. Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences Introns are removed by a process
Telomerase RNA TLC1 Shuttling to the Cytoplasm Requires mrna Export Factors and Is Important for Telomere Maintenance
 Report Telomerase RNA TLC1 Shuttling to the Cytoplasm Requires mrna Export Factors and Is Important for Telomere Maintenance Graphical Abstract Authors Haijia Wu, Daniel Becker, Heike Krebber Correspondence
Report Telomerase RNA TLC1 Shuttling to the Cytoplasm Requires mrna Export Factors and Is Important for Telomere Maintenance Graphical Abstract Authors Haijia Wu, Daniel Becker, Heike Krebber Correspondence
AN ANALYSIS OF MER1 FUNCTION DURING MEIOTIC SPLICING REGULATION IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE
 University of Missouri, St. Louis IRL @ UMSL Dissertations UMSL Graduate Works 5-8-2008 AN ANALYSIS OF MER1 FUNCTION DURING MEIOTIC SPLICING REGULATION IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE Frederick William Scherrer
University of Missouri, St. Louis IRL @ UMSL Dissertations UMSL Graduate Works 5-8-2008 AN ANALYSIS OF MER1 FUNCTION DURING MEIOTIC SPLICING REGULATION IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE Frederick William Scherrer
Bio 401 Sp2014. Multiple Choice (Circle the letter corresponding to the correct answer)
 MIDTERM EXAM KEY (60 pts) You should have 5 pages. Please put your name on every page. You will have 70 minutes to complete the exam. You may begin working as soon as you receive the exam. NOTE: the RED
MIDTERM EXAM KEY (60 pts) You should have 5 pages. Please put your name on every page. You will have 70 minutes to complete the exam. You may begin working as soon as you receive the exam. NOTE: the RED
Splicing and mrnp (Ribonucleoprotein Complex) Movement
 Volume-6, Issue-1, January-February-2016 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 518-522 Splicing and mrnp (Ribonucleoprotein Complex) Movement Punjab Singh Malik Department
Volume-6, Issue-1, January-February-2016 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 518-522 Splicing and mrnp (Ribonucleoprotein Complex) Movement Punjab Singh Malik Department
Section 6. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Section 6 Junaid Malek, M.D. The Golgi and gp160 gp160 transported from ER to the Golgi in coated vesicles These coated vesicles fuse to the cis portion of the Golgi and deposit their cargo in the cisternae
Section 6 Junaid Malek, M.D. The Golgi and gp160 gp160 transported from ER to the Golgi in coated vesicles These coated vesicles fuse to the cis portion of the Golgi and deposit their cargo in the cisternae
RNA-quality control by the exosome
 RNA-quality control by the exosome Jonathan Houseley, John LaCava and David Tollervey Abstract The exosome complex of 3 5 exonucleases is an important component of the RNA-processing machinery in eukaryotes.
RNA-quality control by the exosome Jonathan Houseley, John LaCava and David Tollervey Abstract The exosome complex of 3 5 exonucleases is an important component of the RNA-processing machinery in eukaryotes.
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2. November 13, 2006
 Name: TF: Section Time Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2 November 13, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use
Name: TF: Section Time Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2 November 13, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use
HIV/AIDS: Molecular Biology and pathogenesis. George N. Pavlakis National Cancer Institute, USA
 HIV/AIDS: Molecular Biology and pathogenesis George N. Pavlakis National Cancer Institute, USA Infection RNA Export, packaging Virion formation RNA Reverse transcription DNA RNA Integration Transcription
HIV/AIDS: Molecular Biology and pathogenesis George N. Pavlakis National Cancer Institute, USA Infection RNA Export, packaging Virion formation RNA Reverse transcription DNA RNA Integration Transcription
UNDERSTANDING THE ROLE OF ATP HYDROLYSIS IN THE SPLICEOSOME
 UNDERSTANDING THE ROLE OF ATP HYDROLYSIS IN THE SPLICEOSOME RNA Splicing Lecture 2, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Eight essential ATPases
UNDERSTANDING THE ROLE OF ATP HYDROLYSIS IN THE SPLICEOSOME RNA Splicing Lecture 2, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Eight essential ATPases
REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING
 REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING RNA Processing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, Hiten Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice site consensus sequences do have
REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING RNA Processing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, Hiten Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice site consensus sequences do have
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being A Eukaryote. Eukaryotic Cells. Basic eukaryotes have:
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Human Genome: Mapping, Sequencing Techniques, Diseases
 Human Genome: Mapping, Sequencing Techniques, Diseases Lecture 4 BINF 7580 Fall 2005 1 Let us review what we talked about at the previous lecture. Please,... 2 The central dogma states that the transfer
Human Genome: Mapping, Sequencing Techniques, Diseases Lecture 4 BINF 7580 Fall 2005 1 Let us review what we talked about at the previous lecture. Please,... 2 The central dogma states that the transfer
Biology. Lectures winter term st year of Pharmacy study
 Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 April 22, 2002
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 April 22, 2002 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 April 22, 2002 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
TRANSCRIPTION. DNA à mrna
 TRANSCRIPTION DNA à mrna Central Dogma Animation DNA: The Secret of Life (from PBS) http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=41_ne5ms2ls&list=pl2b2bd56e908da696&index=3 Transcription http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/
TRANSCRIPTION DNA à mrna Central Dogma Animation DNA: The Secret of Life (from PBS) http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=41_ne5ms2ls&list=pl2b2bd56e908da696&index=3 Transcription http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 13, 2006
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 13, 2006 Precursor mrna: introns and exons Intron: Transcribed RNA sequence removed from precursor RNA during the process of maturation (for class II genes:
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 13, 2006 Precursor mrna: introns and exons Intron: Transcribed RNA sequence removed from precursor RNA during the process of maturation (for class II genes:
RECAP (1)! In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas.! What was first evidence for this precursorproduct
 RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
The Human Nuclear Poly(A)-Binding Protein Promotes RNA Hyperadenylation and Decay
 The Human Nuclear Poly(A)-Binding Protein Promotes RNA Hyperadenylation and Decay Stefan M. Bresson, Nicholas K. Conrad* Department of Microbiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas,
The Human Nuclear Poly(A)-Binding Protein Promotes RNA Hyperadenylation and Decay Stefan M. Bresson, Nicholas K. Conrad* Department of Microbiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas,
Figure mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic).
 Splicing Figure 14.3 mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mrna Splicing rrna and trna are also sometimes spliced;
Splicing Figure 14.3 mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mrna Splicing rrna and trna are also sometimes spliced;
Nonsense-mediated decay does not occur within the yeast nucleus
 Nonsense-mediated decay does not occur within the yeast nucleus NICOLAS KUPERWASSER, SAVERIO BROGNA, KEN DOWER, and MICHAEL ROSBASH Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department of Biology, Brandeis University,
Nonsense-mediated decay does not occur within the yeast nucleus NICOLAS KUPERWASSER, SAVERIO BROGNA, KEN DOWER, and MICHAEL ROSBASH Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department of Biology, Brandeis University,
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation Discovered by P. Sharp and R. Roberts in late 1970s
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation Discovered by P. Sharp and R. Roberts in late 1970s
Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I
 01.25.10 Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I Intracellular transport and compartments 1. Protein sorting: How proteins get to their appropriate destinations within the cell 2. Vesicular
01.25.10 Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I Intracellular transport and compartments 1. Protein sorting: How proteins get to their appropriate destinations within the cell 2. Vesicular
Interaktionen von RNAs und Proteinen
 Sonja Prohaska Computational EvoDevo Universitaet Leipzig May 5, 2017 RNA-protein binding vs. DNA-protein binding Is binding of proteins to RNA the same as binding of proteins to DNA? Will the same rules
Sonja Prohaska Computational EvoDevo Universitaet Leipzig May 5, 2017 RNA-protein binding vs. DNA-protein binding Is binding of proteins to RNA the same as binding of proteins to DNA? Will the same rules
Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design
 Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes RNA makes protein Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes
Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes RNA makes protein Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes
Role of hnrnp A1 in the Regulation of HDM2 Gene Expression
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Dissertations, Theses, and Capstone Projects Graduate Center 9-30-2016 Role of hnrnp A1 in the Regulation of HDM2 Gene Expression Heriberto Moran
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Dissertations, Theses, and Capstone Projects Graduate Center 9-30-2016 Role of hnrnp A1 in the Regulation of HDM2 Gene Expression Heriberto Moran
REGULATORY MECHANISMS OF TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR FUNCTION
 Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Cycle G2 (lecture 13709) RG Clerc 04.04.2012 REGULATORY MECHANISMS OF TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR FUNCTION Protein synthesized Protein phosphorylated
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Cycle G2 (lecture 13709) RG Clerc 04.04.2012 REGULATORY MECHANISMS OF TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR FUNCTION Protein synthesized Protein phosphorylated
Two Closely Related Human Nuclear Export Factors Utilize Entirely Distinct Export Pathways
 Molecular Cell, Vol. 8, 397 406, August, 2001, Copyright 2001 by Cell Press Two Closely Related Human Nuclear Export Factors Utilize Entirely Distinct Export Pathways Jin Yang, 1 Hal P. Bogerd, 1 P. Jeremy
Molecular Cell, Vol. 8, 397 406, August, 2001, Copyright 2001 by Cell Press Two Closely Related Human Nuclear Export Factors Utilize Entirely Distinct Export Pathways Jin Yang, 1 Hal P. Bogerd, 1 P. Jeremy
Lisa A. Johnson, Ling Li, and Rozanne M. Sandri-Goldin*
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 2009, p. 6335 6346 Vol. 83, No. 13 0022-538X/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00375-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Cellular RNA Export
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 2009, p. 6335 6346 Vol. 83, No. 13 0022-538X/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00375-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Cellular RNA Export
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Central Dogma. Central Dogma. Translation (mrna -> protein)
 Central Dogma Central Dogma Translation (mrna -> protein) mrna code for amino acids 1. Codons as Triplet code 2. Redundancy 3. Open reading frames 4. Start and stop codons 5. Mistakes in translation 6.
Central Dogma Central Dogma Translation (mrna -> protein) mrna code for amino acids 1. Codons as Triplet code 2. Redundancy 3. Open reading frames 4. Start and stop codons 5. Mistakes in translation 6.
mrnp fiber undergoes several conformapore proteins present in a highly enriched NPC fraction, tional changes during translocation across the central
 1716 Brief Communication The DExH/D box protein HEL/UAP56 is essential for mrna nuclear export in Drosophila David Gatfield*, Hervé Le Hir, Christel Schmitt*, Isabelle C. Braun*, Thomas Köcher*, Matthias
1716 Brief Communication The DExH/D box protein HEL/UAP56 is essential for mrna nuclear export in Drosophila David Gatfield*, Hervé Le Hir, Christel Schmitt*, Isabelle C. Braun*, Thomas Köcher*, Matthias
Pol II - mrna synthesis
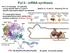 Pol II - mrna synthesis Pol II, S. cerevisiae (12 subunits) - core by specific Rpb1-3, 9 and 11 - Rpb5-6, 8, 10 and 12 - shared by Pol I-III - specific subcomplex Rpb4/7 not essential - TF: transcription
Pol II - mrna synthesis Pol II, S. cerevisiae (12 subunits) - core by specific Rpb1-3, 9 and 11 - Rpb5-6, 8, 10 and 12 - shared by Pol I-III - specific subcomplex Rpb4/7 not essential - TF: transcription
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins.
 Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles
 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Review the Concepts 1. In eukaryotes, protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane is most commonly cotranslational; it can also
13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Review the Concepts 1. In eukaryotes, protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane is most commonly cotranslational; it can also
The Other Lives of Ribosomal Proteins
 PSU McNair Scholars Online Journal Volume 10 Issue 1 Wings Outstretched: New Contributions in Undergraduate Research Article 9 2016 The Other Lives of Ribosomal Proteins Metrah M. Nader Portland State
PSU McNair Scholars Online Journal Volume 10 Issue 1 Wings Outstretched: New Contributions in Undergraduate Research Article 9 2016 The Other Lives of Ribosomal Proteins Metrah M. Nader Portland State
Translation Activity Guide
 Translation Activity Guide Student Handout β-globin Translation Translation occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is defined as the synthesis of a protein (polypeptide) using information encoded in an
Translation Activity Guide Student Handout β-globin Translation Translation occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is defined as the synthesis of a protein (polypeptide) using information encoded in an
Minor point: In Table S1 there seems to be a typo - multiplicity of the data for the Sm3+ structure 134.8?
 PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Finogenova and colleagues investigated aspects of the structural organization of the Nuclear Exosome Targeting (NEXT) complex,
PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Finogenova and colleagues investigated aspects of the structural organization of the Nuclear Exosome Targeting (NEXT) complex,
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation (non proteincoding sequence) Discovered by P. Sharp
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation (non proteincoding sequence) Discovered by P. Sharp
DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis.
 Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
MECHANISMS OF ALTERNATIVE PRE-MESSENGER RNA SPLICING
 Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003. 72:291 336 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720 Copyright 2003 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on February 27, 2003
Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003. 72:291 336 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720 Copyright 2003 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on February 27, 2003
Gammaretroviral pol sequences act in cis to direct polysome loading and NXF1/NXT-dependent protein production by gag-encoded RNA
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 9-12-2014 Gammaretroviral pol sequences act in cis to direct polysome loading
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 9-12-2014 Gammaretroviral pol sequences act in cis to direct polysome loading
Translation. Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation of eukaryotic translation involves many initiation factors
 Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Recruitment of the Complete htrex Complex Is Required for Kaposi s Sarcoma Associated Herpesvirus Intronless mrna Nuclear Export and Virus Replication
 Recruitment of the Complete htrex Complex Is Required for Kaposi s Sarcoma Associated Herpesvirus Intronless mrna Nuclear Export and Virus Replication James R. Boyne 1, Kevin J. Colgan 1, Adrian Whitehouse
Recruitment of the Complete htrex Complex Is Required for Kaposi s Sarcoma Associated Herpesvirus Intronless mrna Nuclear Export and Virus Replication James R. Boyne 1, Kevin J. Colgan 1, Adrian Whitehouse
Studying Alternative Splicing
 Studying Alternative Splicing Meelis Kull PhD student in the University of Tartu supervisor: Jaak Vilo CS Theory Days Rõuge 27 Overview Alternative splicing Its biological function Studying splicing Technology
Studying Alternative Splicing Meelis Kull PhD student in the University of Tartu supervisor: Jaak Vilo CS Theory Days Rõuge 27 Overview Alternative splicing Its biological function Studying splicing Technology
Multiple Export Mechanisms for mrnas
 Cells 2015, 4, 452-473; doi:10.3390/cells4030452 Review OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Multiple Export Mechanisms for mrnas Mildred Delaleau and Katherine L. B. Borden * Department
Cells 2015, 4, 452-473; doi:10.3390/cells4030452 Review OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Multiple Export Mechanisms for mrnas Mildred Delaleau and Katherine L. B. Borden * Department
Alternative splicing. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6
 Alternative splicing Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6 Function(s) of RNA splicing Splicing of introns must be completed before nuclear RNAs can be exported to the cytoplasm. This led to early
Alternative splicing Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6 Function(s) of RNA splicing Splicing of introns must be completed before nuclear RNAs can be exported to the cytoplasm. This led to early
Types of cells. Cell size comparison. The Jobs of Cells 10/5/2015. Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Introduction retroposon
 17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth 2 points.
 MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY).
 Problem Set 11 (Due Nov 25 th ) 1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY). a. Why don t trna molecules contain a 5 triphosphate like other RNA molecules
Problem Set 11 (Due Nov 25 th ) 1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY). a. Why don t trna molecules contain a 5 triphosphate like other RNA molecules
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
TRANSLATION: 3 Stages to translation, can you guess what they are?
 TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
Cells and Tissues 3PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART C Protein Synthesis Gene DNA segment that carries a blueprint for building
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART C Protein Synthesis Gene DNA segment that carries a blueprint for building
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Chapter 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles
 Chapter 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Chapter 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles 13.1 Targeting Proteins To and Across the ER Membrane 13.2 Insertion of Membrane Proteins
Chapter 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Chapter 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles 13.1 Targeting Proteins To and Across the ER Membrane 13.2 Insertion of Membrane Proteins
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Ashraf
 number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
1. Identify and characterize interesting phenomena! 2. Characterization should stimulate some questions/models! 3. Combine biochemistry and genetics
 1. Identify and characterize interesting phenomena! 2. Characterization should stimulate some questions/models! 3. Combine biochemistry and genetics to gain mechanistic insight! 4. Return to step 2, as
1. Identify and characterize interesting phenomena! 2. Characterization should stimulate some questions/models! 3. Combine biochemistry and genetics to gain mechanistic insight! 4. Return to step 2, as
Cbl ubiquitin ligase: Lord of the RINGs
 Cbl ubiquitin ligase: Lord of the RINGs Not just quite interesting - really interesting! A cell must be able to degrade proteins when their activity is no longer required. Many eukaryotic proteins are
Cbl ubiquitin ligase: Lord of the RINGs Not just quite interesting - really interesting! A cell must be able to degrade proteins when their activity is no longer required. Many eukaryotic proteins are
Explain that each trna molecule is recognised by a trna-activating enzyme that binds a specific amino acid to the trna, using ATP for energy
 7.4 - Translation 7.4.1 - Explain that each trna molecule is recognised by a trna-activating enzyme that binds a specific amino acid to the trna, using ATP for energy Each amino acid has a specific trna-activating
7.4 - Translation 7.4.1 - Explain that each trna molecule is recognised by a trna-activating enzyme that binds a specific amino acid to the trna, using ATP for energy Each amino acid has a specific trna-activating
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Cytopathogenesis and Inhibition of Host Gene Expression by RNA Viruses
 MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Dec. 2000, p. 709 724 Vol. 64, No. 4 1092-2172/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cytopathogenesis and Inhibition
MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Dec. 2000, p. 709 724 Vol. 64, No. 4 1092-2172/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cytopathogenesis and Inhibition
