Pol II - mrna synthesis
|
|
|
- Kathlyn Morris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pol II - mrna synthesis Pol II, S. cerevisiae (12 subunits) - core by specific Rpb1-3, 9 and 11 - Rpb5-6, 8, 10 and 12 - shared by Pol I-III - specific subcomplex Rpb4/7 not essential - TF: transcription factors - associated factors RAP74, RAP30 (TFIIF) - auxiliary complexes: Mediator, SAGA Gnatt et al, Science, 2001 (Kornberg s lab) CTD: Tyr 1 Ser 2 Pro 3 Thr 4 Ser 5 Pro 6 Ser 7 26 (yeast) - 52 (human) repeats
2 Co-transcriptional mrna processing CTD posphorylation status Phospho-CTD Associated Proteins - transcription - chromatin structure - RNA processing (splicing, 3 end formation) - RNA export - RNA degradation - snrna modification - snornp biogenesis - DNA metabolism - protein synthesis and degradation Phatnani and Greenleaf, 2006
3 CAPPING H 2 N N N OH O N N + OH O O O O P O - O P O γ β α O - P O - O OH O N N OH O N NH NH 2 O - CH 3 7-methylguanosine 5-5 -triphosphate bridge (m 7 G) Co-transcriptional capping - occurs after the synthesis of nt of RNA - CE recruitment to CTD requires high Ser5-P GT/Ceg1-guanylyltransferase MT/Abd1-methyltransferase (promote early elongation) Cet1-RNA triphopshatase (inhibits re-initiation) CBC-cap binding complex Guo and Lima, Cur. Op.Str.Biol., 2005
4 Co-transcriptional mrna processing: SPLICING Exon1 Intron Exon2 Spliceosome Munoz et al., TiBS, 2009 pre-mrna: - m7g cap synthesis (Ser5-P) - spliceosome assembly - splicing, at least partially
5 Pre-mRNA SPLICING Cryo EM native spliceosome active center Alberts B, Bray D, Lewis J, et al., Molecular Biology of the Cell. 3rd edition;
6 de Almeida and Carmo-Fonseca, FEBS Lett, 2008
7 Pre-mRNA SPLICING: CIS ELEMENTS yeast human The consensus splicing sequences are not so conserved after all 5 Splice Site Branch Point A 3 Splice Site 5 Exon A 3 Exon 5 Splice Site 3 Splice Site Zbigniew Dominski, lectures 2008 Warf and Berglund, 2010, TiBS; Reddy, Ann.Rev.PlantBiol., 2007
8 Pre-mRNA SPLICING: TRANS ELEMENTS 5 snrnas U1, U2, U4, U5, U6 active center E G D3 F B D1 D2 Sm/Lsm snrnas pre-mrna::snrna base-pairing Warf and Berglund, 2010, TiBS; Reddy, Ann.Rev.PlantBiol., 2007
9 Chemistry of pre-mrna splicing and U2/U6 model
10 TRANSCRIPTION AND SPLICING CTD Ser-P and splicing Elongation rate and splicing Lenasi and Barboric, WIREsRNA, 2013
11 ALERNATIVE SPLICING (AS) communication between the 3 and 5 splice sites Reddy, Ann.Rev.PlantBiol., 2007; Chen and Manley, Nat.Rev.Mol.CellBiol., 2009
12 ALERNATIVE SPLICING (AS) Reddy, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2007 Exons and introns often contain sequences that facilitate or inhibit splice site usage. These elements bind splicing activators or repressors. ESR exonic splicing regulatory elements ISR intronic splicing regulatory elements ESS/ISS exonic/intronic splicing silencers ESE/ISE - exonic/intronic splicing enhancers SR Ser/Arg rich proteins PTB polypyrimidine tract-binding proteins hnrnp heterogenous nuclear RNP AS occurs at the level of recognition of splice sites and other regulatory elements by RNA-binding proteins
13 Luco and Misteli, Curr Op Gene Dev, 2011 AS splicing CODE: chromatin, ncrnas, SF
14 CLEAVAGE AND POLYADENYLATION mrna ncrna Cleavage and polyadenylation complex (CP) (recruited at Ser2-P CTD) Jacquier, Nat. Rev. Genet, 2009 yeast metazoan the the Millevoi and Vagner, NAR, 2008
15 TRANSCRIPTION TERMINATION: hybrid allosteric- torpedo model CP Luo and Bentley, Gene Dev, 2006 Pap1 3 -end processing factors are recruited to Ser2-P CTD at 3 end of genes via CID (CTD-interacting domain) of Pcf11 for CP and Rtt103 for Rat1 5-3 exonuclease and its activator Rai1. Pcf11 and Rat1 coordinately contribute to the recruitment of 3 - end processing factors
16 Nrd1/Nab3/Sen1-dependent TERMINATION CTD Pol II Nrd1/Nab3/Sen1 complex sn/snornas CUTs (Ser5-P) short mrnas (< 600 nt) ncrna mrna Jacquier, Nat. Rev. Genet 2009
17 HISTONE mrna 3 end FORMATION (nonpolyadenylated, metazoa, unique) SL structure endonuclease unique Sm/Lsm10/11 Dominski and Marzluff, Gene, 2007 U7 snrnp Histone pre-mrna contains conserved stem-loop (SL) structure, recognized by the SLBP (SL-binding protein) SLBP, ZFP100 and HDE (histone downstream element) stabilize the binding of U7 U7 snrnp, specificaly Lsm11, recruits cleavage factors and the cleavage by endonuclease CPSF-73 generates mature 3 end of histone mrna
18 POLYMERASE BACKTRACKING Polymerase backtracking in genome stability Double-strand break (DSB) formation as a result of codirectional collisions between the replisome and backtracked RNA polymerase in bacteria. Transcript cleavage factor (Gre) prevents polymerase backtracking and R loop formation, preserving genome integrity. Nudlerr, Cell, 2013
19 sn/snorna processing (small nuclear and nucleolar RNAs) 3 and 5 processing Fatica et al., EMBO, 2000 Rat1/Xrn1 Rnt1 RNP proteins Rnt1 RNA precursor RNP proteins RNA precursor termination
20 sn/snorna processing AAAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAAAA Exosome: 3-5 exo/endo-nuclease complex; 10 core components (RNA BP) catalytically active hydrolytic Dis3/Rrp44 (RNase II) nuclear cofactors- RNA BP Rrp47, nuclease Rrp6 (RNase D), RNA helicase Mtr4 cytoplasmic cofactors- Ski2-3-8 complex (RNA helicase Ski2), GTPase Ski7 subtrates- processing and/or degradation of almost all RNAs TRAMP: nuclear surveillance Trf4/5 + Air1/2 + Mtr4 poly(a) polymerase RNA binding proteins RNA DEVH helicase
21 RNA EXPORT Röther and Sträßer, Nuclear Transport,2009
22 Strambio-De-Castillia et al., Nat.Rev.Mol.Cel.Biol,2007 mrna EXPORT ALL FACTORS
23 Co-transcriptional mrna EXPORT: GENE GATING (yeast) nucleus cytoplasm NUCLEAR PORE COMPLEX Iglesias and Stutz, FEBS Lett, 2008 SAGA histone acetyltransferase complex (including Spt, Ada, Gcn5); trx activation THO mrnp biogenesis and export: Hpr1, Mft1, Tho2 and Thp2 (human THOC1-7) TREX transcription-export complex: THO/Sub2/Yra1, interacts with NPC via Mex67-Mtr2 TREX-2 transcription-export complex: Cdc31/Thp1/Sac3 and Sus1 from SAGA TREX-2 and TREX complexes link transcription (Pol II via THO, initiation complex SAGA via Sus1) to export receptors (Mex67, Yra1) and Nuclear Pore Complex
24 Köhler and Hurt, Nat.Rev.Mol.Cel.Biol,2007 EXPORT of other RNAs
25 Mature mrna: TRANSLATION eif3 EJC PABP1 m 7 GpppG eif4e eif4g 5 UTR AUG UAA 3 UTR AAAAAAAAAAAAA nts UTR- UNTRANSLATED REGION EJC- EXON JUNCTION COMPLEX eif4e eif3 m 7 Gppp 40S met 40S met met met met UAC AUG eif4g 60S A A Pab1p A A A A A UAA eif4e interacts with m7g cap to form translationally active mrna: cap dependent translation circular mrna protects agains degradation and stimulates translation eif4e/eif4g/pab recruits small ribosomal subunit trna-bound 40S scans mrna to locate START
26 THE RIBOSOME Three trna binding sites: A site = amino-acyl trna binding site P site = peptidyl-trna binding site E site = exit site
27 Schmeing and Ramakrishnan, Nature, 2009 THE RIBOSOME
Genetics. Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA
 Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA 1 3.4 A 2 Expression of Genetic information DNA Double stranded In the nucleus Transcription mrna Single stranded Translation In the cytoplasm
Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA 1 3.4 A 2 Expression of Genetic information DNA Double stranded In the nucleus Transcription mrna Single stranded Translation In the cytoplasm
Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus:
 RNA Processing Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus: Transcripts are capped at their 5 end with a methylated guanosine nucleotide. Introns are removed
RNA Processing Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus: Transcripts are capped at their 5 end with a methylated guanosine nucleotide. Introns are removed
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation Discovered by P. Sharp and R. Roberts in late 1970s
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation Discovered by P. Sharp and R. Roberts in late 1970s
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation (non proteincoding sequence) Discovered by P. Sharp
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation (non proteincoding sequence) Discovered by P. Sharp
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 13, 2006
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 13, 2006 Precursor mrna: introns and exons Intron: Transcribed RNA sequence removed from precursor RNA during the process of maturation (for class II genes:
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 13, 2006 Precursor mrna: introns and exons Intron: Transcribed RNA sequence removed from precursor RNA during the process of maturation (for class II genes:
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control
 Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation
 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription. 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra
 Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra Splicing process overview Splicing process overview Sequence context RNA secondary structure Tissue-specific Proteins Development
Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra Splicing process overview Splicing process overview Sequence context RNA secondary structure Tissue-specific Proteins Development
Mechanism of splicing
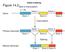 Outline of Splicing Mechanism of splicing Em visualization of precursor-spliced mrna in an R loop Kinetics of in vitro splicing Analysis of the splice lariat Lariat Branch Site Splice site sequence requirements
Outline of Splicing Mechanism of splicing Em visualization of precursor-spliced mrna in an R loop Kinetics of in vitro splicing Analysis of the splice lariat Lariat Branch Site Splice site sequence requirements
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression. (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs)
 Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 April 22, 2002
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 April 22, 2002 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 April 22, 2002 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about gene expression control in eukaryotes is correct? Question #1 (A)
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about gene expression control in eukaryotes is correct? Question #1 (A)
MCB Chapter 11. Topic E. Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes. Reading :
 MCB Chapter 11 Topic E Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes Reading : 419-449 Topic E Michal Linial 14 Jan 2004 1 Self-splicing group I introns were the first examples of catalytic
MCB Chapter 11 Topic E Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes Reading : 419-449 Topic E Michal Linial 14 Jan 2004 1 Self-splicing group I introns were the first examples of catalytic
RNA Processing in Eukaryotes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
1. Identify and characterize interesting phenomena! 2. Characterization should stimulate some questions/models! 3. Combine biochemistry and genetics
 1. Identify and characterize interesting phenomena! 2. Characterization should stimulate some questions/models! 3. Combine biochemistry and genetics to gain mechanistic insight! 4. Return to step 2, as
1. Identify and characterize interesting phenomena! 2. Characterization should stimulate some questions/models! 3. Combine biochemistry and genetics to gain mechanistic insight! 4. Return to step 2, as
Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences
 Adding a 5 cap Lecture 4 mrna splicing and protein synthesis Another day in the life of a gene. Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences Introns are removed by a process
Adding a 5 cap Lecture 4 mrna splicing and protein synthesis Another day in the life of a gene. Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences Introns are removed by a process
TRANSCRIPTION CAPPING
 Messenger RNA Eucaryotic gene expression transcription START site exons upstream elements promoter elements TRANSCRIPTION CAPPING introns gene m 7 G pre-mrna m 7 G SPLICING POLYADENYLATION AAAAAAAAAn
Messenger RNA Eucaryotic gene expression transcription START site exons upstream elements promoter elements TRANSCRIPTION CAPPING introns gene m 7 G pre-mrna m 7 G SPLICING POLYADENYLATION AAAAAAAAAn
RECAP (1)! In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas.! What was first evidence for this precursorproduct
 RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design
 Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes RNA makes protein Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes
Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes RNA makes protein Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes
1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY).
 Problem Set 11 (Due Nov 25 th ) 1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY). a. Why don t trna molecules contain a 5 triphosphate like other RNA molecules
Problem Set 11 (Due Nov 25 th ) 1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY). a. Why don t trna molecules contain a 5 triphosphate like other RNA molecules
RECAP FROM MONDAY AND TUESDAY LECTURES
 RECAP FROM MONDAY AND TUESDAY LECTURES Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport factors: interact with the target macromolecule (signal recognition) interact with the NPC (nucleoporin Phe - Gly repeats) NPC cytoplasmic
RECAP FROM MONDAY AND TUESDAY LECTURES Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport factors: interact with the target macromolecule (signal recognition) interact with the NPC (nucleoporin Phe - Gly repeats) NPC cytoplasmic
RECAP (1)! In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas.! What was first evidence for this precursorproduct
 RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
Messenger RNA maturation. Dr.ssa Mariangela Morlando
 Messenger RNA maturation Dr.ssa Mariangela Morlando Features of RNA molecule Synthe(sed from a DNA template (transcrip(on) Single strand molecule Contains ribose in place of deoxyribose Contains Uracil
Messenger RNA maturation Dr.ssa Mariangela Morlando Features of RNA molecule Synthe(sed from a DNA template (transcrip(on) Single strand molecule Contains ribose in place of deoxyribose Contains Uracil
Translation. Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation of eukaryotic translation involves many initiation factors
 Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Figure mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic).
 Splicing Figure 14.3 mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mrna Splicing rrna and trna are also sometimes spliced;
Splicing Figure 14.3 mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mrna Splicing rrna and trna are also sometimes spliced;
RNA-quality control by the exosome
 RNA-quality control by the exosome Jonathan Houseley, John LaCava and David Tollervey Abstract The exosome complex of 3 5 exonucleases is an important component of the RNA-processing machinery in eukaryotes.
RNA-quality control by the exosome Jonathan Houseley, John LaCava and David Tollervey Abstract The exosome complex of 3 5 exonucleases is an important component of the RNA-processing machinery in eukaryotes.
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER
 REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER RNA Splicing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice
REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER RNA Splicing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins.
 Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes
 Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes biologiemoleculara.usmf.md pass.: bmgu e.usmf.md 1 DNA in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria biologiemoleculara.usmf.md e.usmf.md pass.: bmgu
Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes biologiemoleculara.usmf.md pass.: bmgu e.usmf.md 1 DNA in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria biologiemoleculara.usmf.md e.usmf.md pass.: bmgu
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression q
 Review TRENDS in Biochemical Sciences Vol.28 No.4 April 2003 215 How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression q Hervé Le Hir 1,2, Ajit Nott 1 and Melissa J. Moore 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical
Review TRENDS in Biochemical Sciences Vol.28 No.4 April 2003 215 How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression q Hervé Le Hir 1,2, Ajit Nott 1 and Melissa J. Moore 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical
Protein Synthesis
 Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
TRANSCRIPTION. DNA à mrna
 TRANSCRIPTION DNA à mrna Central Dogma Animation DNA: The Secret of Life (from PBS) http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=41_ne5ms2ls&list=pl2b2bd56e908da696&index=3 Transcription http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/
TRANSCRIPTION DNA à mrna Central Dogma Animation DNA: The Secret of Life (from PBS) http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=41_ne5ms2ls&list=pl2b2bd56e908da696&index=3 Transcription http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/
Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN
 Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN Institute for Brain Disorders and Neural Regeneration F.M. Kirby Program in Neural
Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN Institute for Brain Disorders and Neural Regeneration F.M. Kirby Program in Neural
REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING
 REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING RNA Processing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, Hiten Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice site consensus sequences do have
REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING RNA Processing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, Hiten Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice site consensus sequences do have
Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone
 Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone mrna is coated and compacted by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), forming large messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mrnps). RBPs assemble on nascent and mature mrnas.
Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone mrna is coated and compacted by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), forming large messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mrnps). RBPs assemble on nascent and mature mrnas.
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Prediction and Statistical Analysis of Alternatively Spliced Exons
 Prediction and Statistical Analysis of Alternatively Spliced Exons T.A. Thanaraj 1 and S. Stamm 2 The completion of large genomic sequencing projects revealed that metazoan organisms abundantly use alternative
Prediction and Statistical Analysis of Alternatively Spliced Exons T.A. Thanaraj 1 and S. Stamm 2 The completion of large genomic sequencing projects revealed that metazoan organisms abundantly use alternative
RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
 RNA (Ribonucleic acid) Structure: Similar to that of DNA except: 1- it is single stranded polunucleotide chain. 2- Sugar is ribose 3- Uracil is instead of thymine There are 3 types of RNA: 1- Ribosomal
RNA (Ribonucleic acid) Structure: Similar to that of DNA except: 1- it is single stranded polunucleotide chain. 2- Sugar is ribose 3- Uracil is instead of thymine There are 3 types of RNA: 1- Ribosomal
RNA DECAY PART I - GENERAL MECHANISMS PART II - SPECIFIC PATHWAYS
 RNA DECAY PART I - GENERAL MECHANISMS PART II - SPECIFIC PATHWAYS REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 1) PolII assembly 2) transcription 3) mrna processing 4) mrna export 5) translation 6) protein stability
RNA DECAY PART I - GENERAL MECHANISMS PART II - SPECIFIC PATHWAYS REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 1) PolII assembly 2) transcription 3) mrna processing 4) mrna export 5) translation 6) protein stability
Interaktionen von RNAs und Proteinen
 Sonja Prohaska Computational EvoDevo Universitaet Leipzig May 5, 2017 RNA-protein binding vs. DNA-protein binding Is binding of proteins to RNA the same as binding of proteins to DNA? Will the same rules
Sonja Prohaska Computational EvoDevo Universitaet Leipzig May 5, 2017 RNA-protein binding vs. DNA-protein binding Is binding of proteins to RNA the same as binding of proteins to DNA? Will the same rules
DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis.
 Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Viral Control of SR Protein Activity
 Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1078 Viral Control of SR Protein Activity BY CAMILLA ESTMER NILSSON ACTA UNIVERSITATIS UPSALIENSIS UPPSALA 2001 Dissertation
Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1078 Viral Control of SR Protein Activity BY CAMILLA ESTMER NILSSON ACTA UNIVERSITATIS UPSALIENSIS UPPSALA 2001 Dissertation
MECHANISMS OF ALTERNATIVE PRE-MESSENGER RNA SPLICING
 Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003. 72:291 336 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720 Copyright 2003 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on February 27, 2003
Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003. 72:291 336 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720 Copyright 2003 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on February 27, 2003
Elongation and pre-mrna processing RNAPII
 Elongation and pre-mrna processing RNAPII Introduction Themes Stage 1 - first steps - RNA polymerase II is released Stage 2 - promoter proximal events - pausing, checkpoint control Stage 3 - productive
Elongation and pre-mrna processing RNAPII Introduction Themes Stage 1 - first steps - RNA polymerase II is released Stage 2 - promoter proximal events - pausing, checkpoint control Stage 3 - productive
V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs
 What are micrornas? V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs How can one identify micrornas? What is the function of micrornas? Elisa Izaurralde, MPI Tübingen Huntzinger, Izaurralde, Nat. Rev. Genet. 12,
What are micrornas? V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs How can one identify micrornas? What is the function of micrornas? Elisa Izaurralde, MPI Tübingen Huntzinger, Izaurralde, Nat. Rev. Genet. 12,
TRANSLATION. Translation is a process where proteins are made by the ribosomes on the mrna strand.
 TRANSLATION Dr. Mahesha H B, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Mysuru. Translation is a process where proteins are made by the ribosomes on the mrna strand. Or The process in the ribosomes of a
TRANSLATION Dr. Mahesha H B, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Mysuru. Translation is a process where proteins are made by the ribosomes on the mrna strand. Or The process in the ribosomes of a
TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSPORT OF A MESSENGER RNP PARTICLE: NOVEL REGULATORY MECHANISMS
 From the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Medical Nobel Institute, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSPORT OF A MESSENGER RNP PARTICLE: NOVEL REGULATORY MECHANISMS
From the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Medical Nobel Institute, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSPORT OF A MESSENGER RNP PARTICLE: NOVEL REGULATORY MECHANISMS
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
9/3/2009 DNA i DNA n euk euk yotes Organizatio Organ izatio n of o f gen ge e n tic Locati t on: In n ucleu e s material mater in e ial
 DNA in eukaryotes Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria DNA in eukaryotes Nuclear DNA: Long, linear molecules; Chromatin chromosomes; 10% of DNA in genes,
DNA in eukaryotes Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria DNA in eukaryotes Nuclear DNA: Long, linear molecules; Chromatin chromosomes; 10% of DNA in genes,
V23 Regular vs. alternative splicing
 Regular splicing V23 Regular vs. alternative splicing mechanistic steps recognition of splice sites Alternative splicing different mechanisms how frequent is alternative splicing? Effect of alternative
Regular splicing V23 Regular vs. alternative splicing mechanistic steps recognition of splice sites Alternative splicing different mechanisms how frequent is alternative splicing? Effect of alternative
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. It is known today that GENES direct the production of the proteins that determine the phonotypical characteristics of organisms.
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS It is known today that GENES direct the production of the proteins that determine the phonotypical characteristics of organisms.» GENES = a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that performs
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS It is known today that GENES direct the production of the proteins that determine the phonotypical characteristics of organisms.» GENES = a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that performs
This thesis is based on the following papers, referred to in the text by their roman numerals:
 List of papers This thesis is based on the following papers, referred to in the text by their roman numerals: I II Margaret Rush, Xiaomin Zhao, Stefan Schwartz. (2005) A splicing enhancer in the E4 coding
List of papers This thesis is based on the following papers, referred to in the text by their roman numerals: I II Margaret Rush, Xiaomin Zhao, Stefan Schwartz. (2005) A splicing enhancer in the E4 coding
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II
 MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
Alternative splicing control 2. The most significant 4 slides from last lecture:
 Alternative splicing control 2 The most significant 4 slides from last lecture: 1 2 Regulatory sequences are found primarily close to the 5 -ss and 3 -ss i.e. around exons. 3 Figure 1 Elementary alternative
Alternative splicing control 2 The most significant 4 slides from last lecture: 1 2 Regulatory sequences are found primarily close to the 5 -ss and 3 -ss i.e. around exons. 3 Figure 1 Elementary alternative
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
MCB 102 Third Exam Spring 2015
 MCB 102 Third Exam Spring 2015 Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Problem 8 Problem 9 Problem 10 (14 points) (9 points) (10 points) (9 points) (5 points) (6 points) (7
MCB 102 Third Exam Spring 2015 Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Problem 8 Problem 9 Problem 10 (14 points) (9 points) (10 points) (9 points) (5 points) (6 points) (7
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression II TRANSLATION RIBOSOMES: protein synthesizing machines Translation takes place on defined
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression II TRANSLATION RIBOSOMES: protein synthesizing machines Translation takes place on defined
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Objectives: Prof.Dr. H.D.El-Yassin
 Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
UNDERSTANDING THE ROLE OF ATP HYDROLYSIS IN THE SPLICEOSOME
 UNDERSTANDING THE ROLE OF ATP HYDROLYSIS IN THE SPLICEOSOME RNA Splicing Lecture 2, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Eight essential ATPases
UNDERSTANDING THE ROLE OF ATP HYDROLYSIS IN THE SPLICEOSOME RNA Splicing Lecture 2, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Eight essential ATPases
Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers.
 Page 1 of 13 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers. THE exam has an 'A' and 'B' section SECTION A (based on Dykyy's
Page 1 of 13 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers. THE exam has an 'A' and 'B' section SECTION A (based on Dykyy's
Amino acids. Side chain. -Carbon atom. Carboxyl group. Amino group
 PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
Pre-mRNA Processing Reaches Back to Transcription and Ahead to Translation
 Leading Edge Review Pre-mRNA Processing Reaches Back to Transcription and Ahead to Translation Melissa J. Moore 1,2, * and Nick J. Proudfoot 3, * 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute 2 Department of Biochemistry
Leading Edge Review Pre-mRNA Processing Reaches Back to Transcription and Ahead to Translation Melissa J. Moore 1,2, * and Nick J. Proudfoot 3, * 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute 2 Department of Biochemistry
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
V24 Regular vs. alternative splicing
 Regular splicing V24 Regular vs. alternative splicing mechanistic steps recognition of splice sites Alternative splicing different mechanisms how frequent is alternative splicing? Effect of alternative
Regular splicing V24 Regular vs. alternative splicing mechanistic steps recognition of splice sites Alternative splicing different mechanisms how frequent is alternative splicing? Effect of alternative
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being A Eukaryote. Eukaryotic Cells. Basic eukaryotes have:
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Biochemistry 2000 Sample Question Transcription, Translation and Lipids. (1) Give brief definitions or unique descriptions of the following terms:
 (1) Give brief definitions or unique descriptions of the following terms: (a) exon (b) holoenzyme (c) anticodon (d) trans fatty acid (e) poly A tail (f) open complex (g) Fluid Mosaic Model (h) embedded
(1) Give brief definitions or unique descriptions of the following terms: (a) exon (b) holoenzyme (c) anticodon (d) trans fatty acid (e) poly A tail (f) open complex (g) Fluid Mosaic Model (h) embedded
Chapter 32: Translation
 Chapter 32: Translation Voet & Voet: Pages 1343-1385 (Parts of sections 1-3) Slide 1 Genetic code Translates the genetic information into functional proteins mrna is read in 5 to 3 direction Codons are
Chapter 32: Translation Voet & Voet: Pages 1343-1385 (Parts of sections 1-3) Slide 1 Genetic code Translates the genetic information into functional proteins mrna is read in 5 to 3 direction Codons are
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 OCTOBER 31, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 OCTOBER 31, 2006
mrna cis Elements Located in Non-Protein-Coding Regions
 mrna cis Elements Located in Non-Protein-Coding Regions IRP Repressor mirnas Bcd/4EHP Repressor cap 5 Leader ORF 3 UTR (A) n eif4e/4e-bp 2 o structure uorf eif2α kinases Localization Transcript-independent
mrna cis Elements Located in Non-Protein-Coding Regions IRP Repressor mirnas Bcd/4EHP Repressor cap 5 Leader ORF 3 UTR (A) n eif4e/4e-bp 2 o structure uorf eif2α kinases Localization Transcript-independent
DSB. Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci
 DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
Alternative splicing. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6
 Alternative splicing Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6 Function(s) of RNA splicing Splicing of introns must be completed before nuclear RNAs can be exported to the cytoplasm. This led to early
Alternative splicing Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6 Function(s) of RNA splicing Splicing of introns must be completed before nuclear RNAs can be exported to the cytoplasm. This led to early
Gene Regulation Part 2
 Michael Cummings Chapter 9 Gene Regulation Part 2 David Reisman University of South Carolina Other topics in Chp 9 Part 2 Protein folding diseases Most diseases are caused by mutations in the DNA that
Michael Cummings Chapter 9 Gene Regulation Part 2 David Reisman University of South Carolina Other topics in Chp 9 Part 2 Protein folding diseases Most diseases are caused by mutations in the DNA that
Transcription and chromatin. General Transcription Factors + Promoter-specific factors + Co-activators
 Transcription and chromatin General Transcription Factors + Promoter-specific factors + Co-activators Cofactor or Coactivator 1. work with DNA specific transcription factors to make them more effective
Transcription and chromatin General Transcription Factors + Promoter-specific factors + Co-activators Cofactor or Coactivator 1. work with DNA specific transcription factors to make them more effective
Translation Activity Guide
 Translation Activity Guide Student Handout β-globin Translation Translation occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is defined as the synthesis of a protein (polypeptide) using information encoded in an
Translation Activity Guide Student Handout β-globin Translation Translation occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is defined as the synthesis of a protein (polypeptide) using information encoded in an
The Human Nuclear Poly(A)-Binding Protein Promotes RNA Hyperadenylation and Decay
 The Human Nuclear Poly(A)-Binding Protein Promotes RNA Hyperadenylation and Decay Stefan M. Bresson, Nicholas K. Conrad* Department of Microbiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas,
The Human Nuclear Poly(A)-Binding Protein Promotes RNA Hyperadenylation and Decay Stefan M. Bresson, Nicholas K. Conrad* Department of Microbiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas,
Islamic University Faculty of Medicine
 Islamic University Faculty of Medicine 2012 2013 2 RNA is a modular structure built from a combination of secondary and tertiary structural motifs. RNA chains fold into unique 3 D structures, which act
Islamic University Faculty of Medicine 2012 2013 2 RNA is a modular structure built from a combination of secondary and tertiary structural motifs. RNA chains fold into unique 3 D structures, which act
Biology. Lectures winter term st year of Pharmacy study
 Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Regulation of Core Splicing Factors by Alternative Splicing and Nonsense-mediated mrna Decay
 Regulation of Core Splicing Factors by Alternative Splicing and Nonsense-mediated mrna Decay by Arneet L. Saltzman A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Regulation of Core Splicing Factors by Alternative Splicing and Nonsense-mediated mrna Decay by Arneet L. Saltzman A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Central Dogma. Central Dogma. Translation (mrna -> protein)
 Central Dogma Central Dogma Translation (mrna -> protein) mrna code for amino acids 1. Codons as Triplet code 2. Redundancy 3. Open reading frames 4. Start and stop codons 5. Mistakes in translation 6.
Central Dogma Central Dogma Translation (mrna -> protein) mrna code for amino acids 1. Codons as Triplet code 2. Redundancy 3. Open reading frames 4. Start and stop codons 5. Mistakes in translation 6.
The Multifunctional Nature of the Adenovirus L4-22K Protein
 Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1185 The Multifunctional Nature of the Adenovirus L4-22K Protein SUSAN LAN ACTA UNIVERSITATIS UPSALIENSIS UPPSALA 2016
Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1185 The Multifunctional Nature of the Adenovirus L4-22K Protein SUSAN LAN ACTA UNIVERSITATIS UPSALIENSIS UPPSALA 2016
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Genética Molecular e Populacional. Course: Regulation of Gene Expression
 Genética Molecular e Populacional Course: Regulation of Gene Expression Date: 9-13 May 2016 Location: i3s, Room B Coordinator: Alexandra Moreira Faculty and invited speakers: Alexandra Moreira, Natalia
Genética Molecular e Populacional Course: Regulation of Gene Expression Date: 9-13 May 2016 Location: i3s, Room B Coordinator: Alexandra Moreira Faculty and invited speakers: Alexandra Moreira, Natalia
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit
 Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
AN ANALYSIS OF MER1 FUNCTION DURING MEIOTIC SPLICING REGULATION IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE
 University of Missouri, St. Louis IRL @ UMSL Dissertations UMSL Graduate Works 5-8-2008 AN ANALYSIS OF MER1 FUNCTION DURING MEIOTIC SPLICING REGULATION IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE Frederick William Scherrer
University of Missouri, St. Louis IRL @ UMSL Dissertations UMSL Graduate Works 5-8-2008 AN ANALYSIS OF MER1 FUNCTION DURING MEIOTIC SPLICING REGULATION IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE Frederick William Scherrer
