1. Identify and characterize interesting phenomena! 2. Characterization should stimulate some questions/models! 3. Combine biochemistry and genetics
|
|
|
- Prudence Wilkerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Identify and characterize interesting phenomena! 2. Characterization should stimulate some questions/models! 3. Combine biochemistry and genetics to gain mechanistic insight! 4. Return to step 2, as often as necessary!
2 Interesting phenomenon #1! Sharp and Roberts labs 1977! 1. Hybridized Adenovirus mrna (~ 3,000 nt) back to Adenovirus genomic DNA restriction enzyme fragments (15 kb).! 2. Analyzed structure of heteroduplexes in EM!
3 Sharp and Roberts labs 1977! mrna is non-contiguous with the DNA that encodes it! How can one mrna molecule that spans several widely separated parts of the template DNA be generated?!
4 DNA Observation:! Nuclear RNA pool consists of very high molecular weight species as well as lower molecular weight.! Darnell asked if there is a relationship between the high and low molecular weight RNAs!
5 Experiment:! Treat cells with UV for varying periods of time. Thymidine dimers will form, blocking transcription. To assess the effects on the two pools of RNA, pulse cells with 3 H- Uridine and measure counts in each pool! DNA Example UV dose that hits 1X/1000 bp! X! X! X! X! X! X! X! X! X! X! If long RNAs are precursors then both long and short pools should exhibit comparable UV sensitivity! If long and short RNAs are independently transcribed, then they should exhibit different UV sensitivity!
6 Experiment:! Treat cells with UV for varying periods of time. Thymidine dimers will form, blocking transcription. To assess the effects on the two pools of RNA, pulse cells with 3 H- Uridine and measure counts in each pool! DNA Example UV dose that hits 1X/1000 bp! X! X! X! X! X! X! X! X! X! X! If long RNAs are precursors then both long and short pools should exhibit comparable UV sensitivity! If long and short RNAs are independently transcribed, then they should exhibit different UV sensitivity!
7 In eukaryotes sequences are excised from the primary transcript!
8 Question/Model! How can one mrna molecule that spans several widely separated parts of the template DNA be generated?! Model 1: A change in DNA topology! RNA! DNA! Model 2: Processing of a long precursor RNA! How would you distinguish between these models?!
9 Interesting phenomenon #2! The same primary transcript can yield many different mrnas! > 50% of human genes undergo alternative splicing!
10 !! DSCAM is a fly gene encoding 38,016 splice isoforms Receptor diversity -> complex neural circuits in development.!
11 Human Dystrophin gene! 260 kb intron! 2.4 Mb! 79 exons, which make up < 1% of the total mrna sequence! (14 kb) estimated to require 16 hours to transcribe!
12 Questions! How are the exons identified?! How are the intervening sequences removed?!
13 How are the intervening sequences removed? (biochemistry)! incubate hot beta-globin! intron containing RNA with! HeLa cell nuclear! extracts, separate! products on denaturing! gel! unspliced! spliced!
14 How are the intervening sequences removed? (biochemistry)!
15 How are the intervening sequences removed? (genetics)! Mutational analysis of spliced reporters in transient transfection assays in mammalian cells or standard mutagenesis in yeast!
16 RNA! - single stranded, though base pairs to form complex secondary and tertiary structures! - contains ribose (hydroxyl group attached to the pentose ring in the 2 position)! - 2 hydroxyl, when not base paired or masked by protein, can chemically attack the adjacent phosphodiester bond and cleave the back bone!
17 group 1 self-splicing introns! Interesting phenomenon #3! RNAs can splice themselves!
18 Two classes of self-splicing introns!
19 Self-splicing introns have specific secondary structures!
20 Splicing proceeds through two isoenergetic transesterification reactions.!
21 RNA The excision of introns and the ligation of exons is catalyzed by! the spliceosome! Spliceosome
22 The spliceosome is made up of 5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein subunits + > 100 proteins. These snrnps are called: U1, U2, U4, U5, U6, and assemble in a stepwise pathway onto each intron. There are also many additional non-snrnp proteins in the spliceosome.!
23 snrnps.! named U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6! Each snrnp is a small particle composed of a small nuclear RNA molecule bound by a specific set of proteins!
24 Structures of the Spliceosomal snrnas U1, U2, U4, U5 RNA Pol II transcripts TriMethyl G Cap Bound by Sm Proteins U6 RNA Pol III transcript Unusual Cap Not bound by Sm proteins Each snrna has a specific sequence and secondary structure and is bound by additional specific proteins
25 The earliest snrnp to bind to the pre-mrna is U1, which uses its snrna to base-pair to the 5 splice site.!
26 The U2 snrnp binds to the branchpoint via RNA/RNA base-pairs to create a bulged A residue. This forms the pre-spliceosomal A complex, which requires ATP hydrolysis to assemble.!
27 The protein U2AF (U2 Auxiliary Factor) binds to the Polypyrimidine tract and the AG of the 3 splice site and helps U2 snrnp to bind to the branchpoint.! U2AF65! 35!
28 Remember that the splice sites do not always perfectly match the consensus sequences. Thus, the base-pairing interactions between the snrnas and the pre-mrna are not always the same.! U2AF Pre-spliceosome!
29 Pre-mRNA The interactions of U1 with the 5 splice site and U2 with the branchpoint were proven by creating mutant splice sites that bound the snrna so poorly that splicing was inhibited. Compensating mutations in the snrna that restored complementarity (base-pairing) with the splice site restored splicing.!
30 The full spliceosome is formed from the pre-spliceosome by the addition of the U4/U5/U6 Tri-snRNP. This step also requires ATP hydrolysis.!
31 In the U4/U6 Di-snRNP and the U4/U5/U6 Tri-snRNP, the U4 and U6 snrnas are base-paired to each other. This interaction is later disrupted in the formation of the active spliceosome.! U6 snrna Cap 5 U4 snrna
32 After the formation of the full spliceosome, the U1 and the U4 snrnps are detached and the remaining U2, U5 and U6 snrnas are rearranged. This conformational change creates the catalytic spliceosome and requires ATP.!
33 U6 snrna U2 snrna U5 snrna In the catalytically active spliceosome, the U2, U5 and U6 snrnas make very specific contacts with the splice sites.! intron
34 The two transesterification reactions of splicing take place in the mature spliceosome.!
35 After the second transesterification reaction, the spliceosome comes apart. The snrnps are recycled, and the spliced exons and the lariat intron are released.!
36 The lariat intron is debranched by Debranching Enzyme returning it to a typical linear state. This linear intron is quickly degraded by ribonucleases.!
37 Splicing is dynamic, with sequential regulated alterations! in RNA:RNA and RNA:protein interactions!
38 DEAD-box helicases found at every step!
39 Biochemistry 101! Biological Regulatory Mechanisms! February 9, 2015! mrna processing and its regulation, part 1! 1. In Eukaryotes, mrna is non-contiguous with the DNA that encodes it.! 2. To generate the mature mrna intervening sequences (introns) are removed and the expressed (exons) sequences are spliced together.! 3. Elaborate splicing patterns have evolved, with alternate exon usage and even splicing between transcripts.! 4. RNA by virtue of its 2 OH can attack itself.! 5. Secondary structures can direct this suicidal activity to produce selfsplicing RNAs.! 6. An RNA protein-machine, termed the spliceosome, catalyzes splicing by identifying splice sites and providing the correct secondary structures to promote catalysis.! 7. While the the trans-esterification reactions do not require energy, there are several ATP-dependent steps in splicing, allowing regulation.!
40 Splicing Reviews:!! Splicing of Messenger RNA Precursors! Annual Review of Biochemistry! Vol. 55: (Volume publication date July 1986)! R A Padgett, P J Grabowski, M M Konarska, S Seiler, and P A Sharp! Self-Splicing of Group I Introns! Annual Review of Biochemistry! Vol. 59: (Volume publication date July 1990)! T R Cech! Dynamic RNA-RNA Interactions in the Spliceosome! Annual Review of Genetics! Vol. 28: 1-26 (Volume publication date December 1994)! H D Madhani and C Guthrie! Group I and Group II Ribozymes as RNPs: Clues to the Past and Guides to the Future! Philip S. Perlman!
41
RECAP (1)! In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas.! What was first evidence for this precursorproduct
 RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1)! In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas.! What was first evidence for this precursorproduct
 RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 13, 2006
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 13, 2006 Precursor mrna: introns and exons Intron: Transcribed RNA sequence removed from precursor RNA during the process of maturation (for class II genes:
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 13, 2006 Precursor mrna: introns and exons Intron: Transcribed RNA sequence removed from precursor RNA during the process of maturation (for class II genes:
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation Discovered by P. Sharp and R. Roberts in late 1970s
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation Discovered by P. Sharp and R. Roberts in late 1970s
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation (non proteincoding sequence) Discovered by P. Sharp
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation (non proteincoding sequence) Discovered by P. Sharp
Figure mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic).
 Splicing Figure 14.3 mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mrna Splicing rrna and trna are also sometimes spliced;
Splicing Figure 14.3 mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mrna Splicing rrna and trna are also sometimes spliced;
Mechanism of splicing
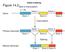 Outline of Splicing Mechanism of splicing Em visualization of precursor-spliced mrna in an R loop Kinetics of in vitro splicing Analysis of the splice lariat Lariat Branch Site Splice site sequence requirements
Outline of Splicing Mechanism of splicing Em visualization of precursor-spliced mrna in an R loop Kinetics of in vitro splicing Analysis of the splice lariat Lariat Branch Site Splice site sequence requirements
Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus:
 RNA Processing Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus: Transcripts are capped at their 5 end with a methylated guanosine nucleotide. Introns are removed
RNA Processing Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus: Transcripts are capped at their 5 end with a methylated guanosine nucleotide. Introns are removed
UNDERSTANDING THE ROLE OF ATP HYDROLYSIS IN THE SPLICEOSOME
 UNDERSTANDING THE ROLE OF ATP HYDROLYSIS IN THE SPLICEOSOME RNA Splicing Lecture 2, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Eight essential ATPases
UNDERSTANDING THE ROLE OF ATP HYDROLYSIS IN THE SPLICEOSOME RNA Splicing Lecture 2, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Eight essential ATPases
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING
 REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING RNA Processing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, Hiten Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice site consensus sequences do have
REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING RNA Processing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, Hiten Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice site consensus sequences do have
REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER
 REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER RNA Splicing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice
REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER RNA Splicing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control
 Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences
 Adding a 5 cap Lecture 4 mrna splicing and protein synthesis Another day in the life of a gene. Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences Introns are removed by a process
Adding a 5 cap Lecture 4 mrna splicing and protein synthesis Another day in the life of a gene. Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences Introns are removed by a process
MECHANISMS OF ALTERNATIVE PRE-MESSENGER RNA SPLICING
 Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003. 72:291 336 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720 Copyright 2003 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on February 27, 2003
Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003. 72:291 336 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720 Copyright 2003 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on February 27, 2003
RNA Processing in Eukaryotes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
MCB Chapter 11. Topic E. Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes. Reading :
 MCB Chapter 11 Topic E Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes Reading : 419-449 Topic E Michal Linial 14 Jan 2004 1 Self-splicing group I introns were the first examples of catalytic
MCB Chapter 11 Topic E Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes Reading : 419-449 Topic E Michal Linial 14 Jan 2004 1 Self-splicing group I introns were the first examples of catalytic
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation
 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
Role of small nuclear RNAs in eukaryotic gene expression
 The Authors Journal compilation 2013 Biochemical Society Essays Biochem. (2013) 54, 79 90: doi: 10.1042/BSE0540079 Role of small nuclear RNAs in eukaryotic gene expression 6 Saba Valadkhan 1 and Lalith
The Authors Journal compilation 2013 Biochemical Society Essays Biochem. (2013) 54, 79 90: doi: 10.1042/BSE0540079 Role of small nuclear RNAs in eukaryotic gene expression 6 Saba Valadkhan 1 and Lalith
the basis of the disease is diverse (see ref. 16 and references within). One class of thalassemic lesions is single-base substitutions
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 87, pp. 6253-6257, August 1990 Biochemistry Mechanism for cryptic splice site activation during pre-mrna splicing (thalassemia/ul small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle/5'
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 87, pp. 6253-6257, August 1990 Biochemistry Mechanism for cryptic splice site activation during pre-mrna splicing (thalassemia/ul small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle/5'
TRANSCRIPTION CAPPING
 Messenger RNA Eucaryotic gene expression transcription START site exons upstream elements promoter elements TRANSCRIPTION CAPPING introns gene m 7 G pre-mrna m 7 G SPLICING POLYADENYLATION AAAAAAAAAn
Messenger RNA Eucaryotic gene expression transcription START site exons upstream elements promoter elements TRANSCRIPTION CAPPING introns gene m 7 G pre-mrna m 7 G SPLICING POLYADENYLATION AAAAAAAAAn
LS1a Fall 2014 Problem Set #4 Due Monday 11/3 at 6 pm in the drop boxes on the Science Center 2 nd Floor
 LS1a Fall 2014 Problem Set #4 Due Monday 11/3 at 6 pm in the drop boxes on the Science Center 2 nd Floor Note: Adequate space is given for each answer. Questions that require a brief explanation should
LS1a Fall 2014 Problem Set #4 Due Monday 11/3 at 6 pm in the drop boxes on the Science Center 2 nd Floor Note: Adequate space is given for each answer. Questions that require a brief explanation should
The U1 snrnp Base Pairs with the 5 Splice Site within a Penta-snRNP Complex
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, May 2003, p. 3442 3455 Vol. 23, No. 10 0270-7306/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.10.3442 3455.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, May 2003, p. 3442 3455 Vol. 23, No. 10 0270-7306/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.10.3442 3455.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Islamic University Faculty of Medicine
 Islamic University Faculty of Medicine 2012 2013 2 RNA is a modular structure built from a combination of secondary and tertiary structural motifs. RNA chains fold into unique 3 D structures, which act
Islamic University Faculty of Medicine 2012 2013 2 RNA is a modular structure built from a combination of secondary and tertiary structural motifs. RNA chains fold into unique 3 D structures, which act
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Genetics. Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA
 Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA 1 3.4 A 2 Expression of Genetic information DNA Double stranded In the nucleus Transcription mrna Single stranded Translation In the cytoplasm
Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA 1 3.4 A 2 Expression of Genetic information DNA Double stranded In the nucleus Transcription mrna Single stranded Translation In the cytoplasm
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Spliceosome Pathway. is required for a stable interaction between U2 snrnp and
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Sept. 1988, p. 3755-3760 Vol. 8, No. 9 0270-7306/88/093755-06$02.00/0 Copyright 1988, American Society for Microbiology Early Commitment of Yeast Pre-mRNA to the Spliceosome
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Sept. 1988, p. 3755-3760 Vol. 8, No. 9 0270-7306/88/093755-06$02.00/0 Copyright 1988, American Society for Microbiology Early Commitment of Yeast Pre-mRNA to the Spliceosome
particles at the 3' splice site
 Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 89, pp. 1725-1729, March 1992 Biochemistry The 35-kDa mammalian splicing factor SC35 mediates specific interactions between Ul and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles
Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 89, pp. 1725-1729, March 1992 Biochemistry The 35-kDa mammalian splicing factor SC35 mediates specific interactions between Ul and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles
1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY).
 Problem Set 11 (Due Nov 25 th ) 1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY). a. Why don t trna molecules contain a 5 triphosphate like other RNA molecules
Problem Set 11 (Due Nov 25 th ) 1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY). a. Why don t trna molecules contain a 5 triphosphate like other RNA molecules
U2 toggles iteratively between the stem IIa and stem IIc conformations to promote pre-mrna splicing
 U2 toggles iteratively between the stem IIa and stem IIc conformations to promote pre-mrna splicing Angela K. Hilliker, 1 Melissa A. Mefford, 2 and Jonathan P. Staley 1,3 1 Department of Molecular Genetics
U2 toggles iteratively between the stem IIa and stem IIc conformations to promote pre-mrna splicing Angela K. Hilliker, 1 Melissa A. Mefford, 2 and Jonathan P. Staley 1,3 1 Department of Molecular Genetics
SPLICING SILENCING BY THE CUGBP2 SPLICING FACTOR: MECHANISM OF ACTION AND COMBINATORIAL CODE FOR SPLICING SILENCING WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR
 SPLICING SILENCING BY THE CUGBP2 SPLICING FACTOR: MECHANISM OF ACTION AND COMBINATORIAL CODE FOR SPLICING SILENCING WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR AUTOREGULATION by Jill A. Dembowski Bachelor of Science, Clarion
SPLICING SILENCING BY THE CUGBP2 SPLICING FACTOR: MECHANISM OF ACTION AND COMBINATORIAL CODE FOR SPLICING SILENCING WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR AUTOREGULATION by Jill A. Dembowski Bachelor of Science, Clarion
Alternative Splicing and Genomic Stability
 Alternative Splicing and Genomic Stability Kevin Cahill cahill@unm.edu http://dna.phys.unm.edu/ Abstract In a cell that uses alternative splicing, the total length of all the exons is far less than in
Alternative Splicing and Genomic Stability Kevin Cahill cahill@unm.edu http://dna.phys.unm.edu/ Abstract In a cell that uses alternative splicing, the total length of all the exons is far less than in
Post-Transcriptional Regulation: Splicing
 Post-Transcriptional Regulation: Splicing Pre-RNA terminal modifications Splicing Editing chemical modifications cutting capping polya base change X X pre-rrna 45S (poli) intron removal new chemical groups
Post-Transcriptional Regulation: Splicing Pre-RNA terminal modifications Splicing Editing chemical modifications cutting capping polya base change X X pre-rrna 45S (poli) intron removal new chemical groups
Association of U6 snrna with the 5'-splice site region of pre-mrna in the spliceosome
 Association of U6 snrna with the 5'-splice site region of pre-mrna in the spliceosome Hitoshi Sawa and Yoshiro Shimura^ Department of Biophysics, Faculty of Science, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606, Japan
Association of U6 snrna with the 5'-splice site region of pre-mrna in the spliceosome Hitoshi Sawa and Yoshiro Shimura^ Department of Biophysics, Faculty of Science, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606, Japan
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Translation. Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation of eukaryotic translation involves many initiation factors
 Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
The role of the mammalian branchpoint sequence in pre-mrna splicing
 The role of the mammalian branchpoint sequence in pre-mrna splicing Robin Reed and Tom Maniatis Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138 USA
The role of the mammalian branchpoint sequence in pre-mrna splicing Robin Reed and Tom Maniatis Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138 USA
Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design
 Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes RNA makes protein Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes
Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes RNA makes protein Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes
Prediction and Statistical Analysis of Alternatively Spliced Exons
 Prediction and Statistical Analysis of Alternatively Spliced Exons T.A. Thanaraj 1 and S. Stamm 2 The completion of large genomic sequencing projects revealed that metazoan organisms abundantly use alternative
Prediction and Statistical Analysis of Alternatively Spliced Exons T.A. Thanaraj 1 and S. Stamm 2 The completion of large genomic sequencing projects revealed that metazoan organisms abundantly use alternative
Evidence that U5 snrnp recognizes the 3 splice site for catalytic step II in mammals
 The EMBO Journal Vol.16 No.15 pp.4746 4759, 1997 Evidence that U5 snrnp recognizes the 3 splice site for catalytic step II in mammals Maria Dolores Chiara 1, Leon Palandjian, sites in pre-mrna very near
The EMBO Journal Vol.16 No.15 pp.4746 4759, 1997 Evidence that U5 snrnp recognizes the 3 splice site for catalytic step II in mammals Maria Dolores Chiara 1, Leon Palandjian, sites in pre-mrna very near
Splicing function of mammalian U6 small nuclear RNA: Conserved
 Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. SA Vol. 91, pp. 903-907, February 1994 Biochemistry Splicing function of mammalian 6 small nuclear RNA: Conserved positions in central domain and helix I are essential during the
Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. SA Vol. 91, pp. 903-907, February 1994 Biochemistry Splicing function of mammalian 6 small nuclear RNA: Conserved positions in central domain and helix I are essential during the
The nuclear pre-mrna introns of eukaryotes are removed by
 U4 small nuclear RNA can function in both the major and minor spliceosomes Girish C. Shukla and Richard A. Padgett* Department of Molecular Biology, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic Foundation,
U4 small nuclear RNA can function in both the major and minor spliceosomes Girish C. Shukla and Richard A. Padgett* Department of Molecular Biology, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic Foundation,
Alternative splicing control 2. The most significant 4 slides from last lecture:
 Alternative splicing control 2 The most significant 4 slides from last lecture: 1 2 Regulatory sequences are found primarily close to the 5 -ss and 3 -ss i.e. around exons. 3 Figure 1 Elementary alternative
Alternative splicing control 2 The most significant 4 slides from last lecture: 1 2 Regulatory sequences are found primarily close to the 5 -ss and 3 -ss i.e. around exons. 3 Figure 1 Elementary alternative
Received 26 January 1996/Returned for modification 28 February 1996/Accepted 15 March 1996
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, June 1996, p. 3012 3022 Vol. 16, No. 6 0270-7306/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Base Pairing at the 5 Splice Site with U1 Small Nuclear RNA
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, June 1996, p. 3012 3022 Vol. 16, No. 6 0270-7306/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Base Pairing at the 5 Splice Site with U1 Small Nuclear RNA
Determinants of Plant U12-Dependent Intron Splicing Efficiency
 This article is published in The Plant Cell Online, The Plant Cell Preview Section, which publishes manuscripts accepted for publication after they have been edited and the authors have corrected proofs,
This article is published in The Plant Cell Online, The Plant Cell Preview Section, which publishes manuscripts accepted for publication after they have been edited and the authors have corrected proofs,
GENOME-WIDE COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF SMALL NUCLEAR RNA GENES OF ORYZA SATIVA (INDICA AND JAPONICA)
 GENOME-WIDE COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF SMALL NUCLEAR RNA GENES OF ORYZA SATIVA (INDICA AND JAPONICA) M.SHASHIKANTH, A.SNEHALATHARANI, SK. MUBARAK AND K.ULAGANATHAN Center for Plant Molecular Biology, Osmania
GENOME-WIDE COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF SMALL NUCLEAR RNA GENES OF ORYZA SATIVA (INDICA AND JAPONICA) M.SHASHIKANTH, A.SNEHALATHARANI, SK. MUBARAK AND K.ULAGANATHAN Center for Plant Molecular Biology, Osmania
An ATP-independent complex commits pre-mrna to the mammaiian spliceosome assembly pathway
 An ATP-independent complex commits pre-mrna to the mammaiian spliceosome assembly pathway Susan Michaud and Robin Reed Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology and Program in Cellular and Developmental
An ATP-independent complex commits pre-mrna to the mammaiian spliceosome assembly pathway Susan Michaud and Robin Reed Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology and Program in Cellular and Developmental
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins.
 Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage:
 Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Role of the snrnas in spliceosomal active site
 RNA Biology ISSN: 1547-6286 (Print) 1555-8584 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/krnb20 Role of the snrnas in spliceosomal active site Saba Valadkhan To cite this article: Saba Valadkhan
RNA Biology ISSN: 1547-6286 (Print) 1555-8584 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/krnb20 Role of the snrnas in spliceosomal active site Saba Valadkhan To cite this article: Saba Valadkhan
DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis.
 Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Viral Control of SR Protein Activity
 Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1078 Viral Control of SR Protein Activity BY CAMILLA ESTMER NILSSON ACTA UNIVERSITATIS UPSALIENSIS UPPSALA 2001 Dissertation
Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1078 Viral Control of SR Protein Activity BY CAMILLA ESTMER NILSSON ACTA UNIVERSITATIS UPSALIENSIS UPPSALA 2001 Dissertation
Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription. 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra
 Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra Splicing process overview Splicing process overview Sequence context RNA secondary structure Tissue-specific Proteins Development
Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra Splicing process overview Splicing process overview Sequence context RNA secondary structure Tissue-specific Proteins Development
TRANSCRIPTION. DNA à mrna
 TRANSCRIPTION DNA à mrna Central Dogma Animation DNA: The Secret of Life (from PBS) http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=41_ne5ms2ls&list=pl2b2bd56e908da696&index=3 Transcription http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/
TRANSCRIPTION DNA à mrna Central Dogma Animation DNA: The Secret of Life (from PBS) http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=41_ne5ms2ls&list=pl2b2bd56e908da696&index=3 Transcription http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/
integral components of snrnps (26-30), whereas PRP19 is not tightly associated with any of the five snrnas required
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 90, pp. 10821-10825, November 1993 Biochemistry Yeast precursor mrna processing protein PRP19 associates with the spliceosome concomitant with or just after dissociation
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 90, pp. 10821-10825, November 1993 Biochemistry Yeast precursor mrna processing protein PRP19 associates with the spliceosome concomitant with or just after dissociation
The conserved central domain of yeast U6 snrna: Importance of U2-U6 helix I a in spliceosome assembly
 RNA (2002), 8:997 1010+ Cambridge University Press+ Printed in the USA+ Copyright 2002 RNA Society+ DOI: 10+1017+S1355838202025013 The conserved central domain of yeast U6 snrna: Importance of U2-U6 helix
RNA (2002), 8:997 1010+ Cambridge University Press+ Printed in the USA+ Copyright 2002 RNA Society+ DOI: 10+1017+S1355838202025013 The conserved central domain of yeast U6 snrna: Importance of U2-U6 helix
Analyzing mechanisms of alternative pre-mrna splicing using in vitro splicing assays
 Methods 37 (2005) 306 313 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymeth Analyzing mechanisms of alternative pre-mrna splicing using in vitro splicing assays Martin J. Hicks, Bianca J. Lam, Klemens J. Hertel * Department
Methods 37 (2005) 306 313 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymeth Analyzing mechanisms of alternative pre-mrna splicing using in vitro splicing assays Martin J. Hicks, Bianca J. Lam, Klemens J. Hertel * Department
Pyrimidine Tracts between the 5 Splice Site and Branch Point Facilitate Splicing and Recognition of a Small Drosophila Intron
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, May 1997, p. 2774 2780 Vol. 17, No. 5 0270-7306/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Pyrimidine Tracts between the 5 Splice Site and Branch Point
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, May 1997, p. 2774 2780 Vol. 17, No. 5 0270-7306/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Pyrimidine Tracts between the 5 Splice Site and Branch Point
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2. November 13, 2006
 Name: TF: Section Time Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2 November 13, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use
Name: TF: Section Time Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2 November 13, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use
Human Genome: Mapping, Sequencing Techniques, Diseases
 Human Genome: Mapping, Sequencing Techniques, Diseases Lecture 4 BINF 7580 Fall 2005 1 Let us review what we talked about at the previous lecture. Please,... 2 The central dogma states that the transfer
Human Genome: Mapping, Sequencing Techniques, Diseases Lecture 4 BINF 7580 Fall 2005 1 Let us review what we talked about at the previous lecture. Please,... 2 The central dogma states that the transfer
Review of Biochemistry
 Review of Biochemistry Chemical bond Functional Groups Amino Acid Protein Structure and Function Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Each amino acids in a protein contains a amino group, - NH 2,
Review of Biochemistry Chemical bond Functional Groups Amino Acid Protein Structure and Function Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Each amino acids in a protein contains a amino group, - NH 2,
Lecture 34. Carbohydrate Metabolism 2. Glycogen. Key Concepts. Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen degradation
 Lecture 34 Carbohydrate Metabolism 2 Glycogen Key Concepts Overview of Glycogen Metabolism Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen degradation Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen synthesis What mechanisms
Lecture 34 Carbohydrate Metabolism 2 Glycogen Key Concepts Overview of Glycogen Metabolism Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen degradation Biochemistry and regulation of glycogen synthesis What mechanisms
Objectives: Prof.Dr. H.D.El-Yassin
 Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
Generation of antibody diversity October 18, Ram Savan
 Generation of antibody diversity October 18, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #10 Slide 1 of 30 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 : Structural features of the BCR and TCR Janeway Chapter
Generation of antibody diversity October 18, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #10 Slide 1 of 30 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 : Structural features of the BCR and TCR Janeway Chapter
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression. (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs)
 Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Point total. Page # Exam Total (out of 90) The number next to each intermediate represents the total # of C-C and C-H bonds in that molecule.
 This exam is worth 90 points. Pages 2- have questions. Page 1 is for your reference only. Honor Code Agreement - Signature: Date: (You agree to not accept or provide assistance to anyone else during this
This exam is worth 90 points. Pages 2- have questions. Page 1 is for your reference only. Honor Code Agreement - Signature: Date: (You agree to not accept or provide assistance to anyone else during this
Achieving targeted and quantifiable alteration of mrna splicing with Morpholino oligos
 Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 358 (2007) 521 527 www.elsevier.com/locate/ybbrc Achieving targeted and quantifiable alteration of mrna splicing with Morpholino oligos Paul A. Morcos
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 358 (2007) 521 527 www.elsevier.com/locate/ybbrc Achieving targeted and quantifiable alteration of mrna splicing with Morpholino oligos Paul A. Morcos
Protein Synthesis
 Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
Regulation of Alternative Splicing: More than Just the ABCs *
 MINIREVIEW This paper is available online at www.jbc.org THE JOURNA OF BIOOGICA CHEMISTRY VO. 283, NO. 3, pp. 1217 1221, January 18, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,
MINIREVIEW This paper is available online at www.jbc.org THE JOURNA OF BIOOGICA CHEMISTRY VO. 283, NO. 3, pp. 1217 1221, January 18, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
The CUGBP2 Splicing Factor Regulates an Ensemble of Branchpoints from Perimeter Binding Sites with Implications for Autoregulation
 The CUGBP2 Splicing Factor Regulates an Ensemble of Branchpoints from Perimeter Binding Sites with Implications for Autoregulation Jill A. Dembowski, Paula J. Grabowski* Department of Biological Sciences,
The CUGBP2 Splicing Factor Regulates an Ensemble of Branchpoints from Perimeter Binding Sites with Implications for Autoregulation Jill A. Dembowski, Paula J. Grabowski* Department of Biological Sciences,
Investigating the mechanism of alternative splicing regulation of the RNA-binding proteins T-STAR and Sam68
 Investigating the mechanism of alternative splicing regulation of the RNA-binding proteins T-STAR and Sam68 Marina Danilenko Institute of Genetic Medicine A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of
Investigating the mechanism of alternative splicing regulation of the RNA-binding proteins T-STAR and Sam68 Marina Danilenko Institute of Genetic Medicine A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of
Introduction retroposon
 17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
AP Biology Summer Assignment Chapter 3 Quiz
 AP Biology Summer Assignment Chapter 3 Quiz 2016-17 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following are found in a DNA nucleotide
AP Biology Summer Assignment Chapter 3 Quiz 2016-17 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following are found in a DNA nucleotide
1) DNA unzips - hydrogen bonds between base pairs are broken by special enzymes.
 Biology 12 Cell Cycle To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: it must grow, during which it performs protein synthesis (G1 phase) replicate its genetic material /DNA (S phase), and physically
Biology 12 Cell Cycle To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: it must grow, during which it performs protein synthesis (G1 phase) replicate its genetic material /DNA (S phase), and physically
The 5 0 EndofU2snRNAIsinCloseProximity to U1 and Functional Sites of the Pre-mRNA in Early Spliceosomal Complexes
 Article The 5 0 EndofU2snRNAIsinCloseProximity to U1 and Functional Sites of the Pre-mRNA in Early Spliceosomal Complexes Gizem Dönmez, 1 Klaus Hartmuth, 1 Berthold Kastner, 1 Cindy L. Will, 1 and Reinhard
Article The 5 0 EndofU2snRNAIsinCloseProximity to U1 and Functional Sites of the Pre-mRNA in Early Spliceosomal Complexes Gizem Dönmez, 1 Klaus Hartmuth, 1 Berthold Kastner, 1 Cindy L. Will, 1 and Reinhard
The 59 and 39 domains of yeast U6 snrna: Lsm proteins facilitate binding of Prp24 protein to the U6 telestem region
 RNA (2002), 8:1011 1033+ Cambridge University Press+ Printed in the USA+ Copyright 2002 RNA Society+ DOI: 10+1017+S1355838202026092 The 59 and 39 domains of yeast U6 snrna: Lsm proteins facilitate binding
RNA (2002), 8:1011 1033+ Cambridge University Press+ Printed in the USA+ Copyright 2002 RNA Society+ DOI: 10+1017+S1355838202026092 The 59 and 39 domains of yeast U6 snrna: Lsm proteins facilitate binding
A Novel Type of Splicing Enhancer Regulating Adenovirus Pre-mRNA Splicing
 A Novel Type of Splicing Enhancer Regulating Adenovirus Pre-mRNA Splicing Oliver Mühlemann, Bai-Gong Yue, Svend Petersen-Mahrt and Göran Akusjärvi Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20(7):2317. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.7.2317-2325.2000.
A Novel Type of Splicing Enhancer Regulating Adenovirus Pre-mRNA Splicing Oliver Mühlemann, Bai-Gong Yue, Svend Petersen-Mahrt and Göran Akusjärvi Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20(7):2317. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.7.2317-2325.2000.
The organization of 3' splice-site sequences in mammalian introns
 The organization of 3' splice-site sequences in mammalian introns Robin Reed Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115 USA A model pre-mrna substrate
The organization of 3' splice-site sequences in mammalian introns Robin Reed Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115 USA A model pre-mrna substrate
Translation Activity Guide
 Translation Activity Guide Student Handout β-globin Translation Translation occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is defined as the synthesis of a protein (polypeptide) using information encoded in an
Translation Activity Guide Student Handout β-globin Translation Translation occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is defined as the synthesis of a protein (polypeptide) using information encoded in an
Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4)
 Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4) Vahagn Stepanyan Department of Biological Sciences, Fordham University Abstract: Alternative splicing is an
Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4) Vahagn Stepanyan Department of Biological Sciences, Fordham University Abstract: Alternative splicing is an
MCB 102 Third Exam Spring 2015
 MCB 102 Third Exam Spring 2015 Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Problem 8 Problem 9 Problem 10 (14 points) (9 points) (10 points) (9 points) (5 points) (6 points) (7
MCB 102 Third Exam Spring 2015 Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Problem 8 Problem 9 Problem 10 (14 points) (9 points) (10 points) (9 points) (5 points) (6 points) (7
Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone
 Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone mrna is coated and compacted by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), forming large messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mrnps). RBPs assemble on nascent and mature mrnas.
Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone mrna is coated and compacted by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), forming large messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mrnps). RBPs assemble on nascent and mature mrnas.
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about gene expression control in eukaryotes is correct? Question #1 (A)
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about gene expression control in eukaryotes is correct? Question #1 (A)
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Ashraf
 number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
Identification of cis-acting Intron and Exon Regions in Influenza
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Mar. 1992, p. 962-970 0270-7306/92/030962-09$02.00/0 Copyright ) 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 12, No. 3 Identification of cis-acting Intron and Exon Regions
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Mar. 1992, p. 962-970 0270-7306/92/030962-09$02.00/0 Copyright ) 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 12, No. 3 Identification of cis-acting Intron and Exon Regions
Effects of Second Messengers
 Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II
 MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
7.014 Problem Set 7 Solutions
 MIT Department of Biology 7.014 Introductory Biology, Spring 2005 7.014 Problem Set 7 Solutions Question 1 Part A Antigen binding site Antigen binding site Variable region Light chain Light chain Variable
MIT Department of Biology 7.014 Introductory Biology, Spring 2005 7.014 Problem Set 7 Solutions Question 1 Part A Antigen binding site Antigen binding site Variable region Light chain Light chain Variable
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Signal Transduction Cascades
 Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Isolation and Characterization of Human Precatalytic Spliceosomal B Complexes
 Aus dem Max-Planck-Institut für Biophysikalische Chemie in Göttingen Abteilung Zelluläre Biochemie Direktor: Prof. Dr. Reinhard Lührmann Isolation and Characterization of Human Precatalytic Spliceosomal
Aus dem Max-Planck-Institut für Biophysikalische Chemie in Göttingen Abteilung Zelluläre Biochemie Direktor: Prof. Dr. Reinhard Lührmann Isolation and Characterization of Human Precatalytic Spliceosomal
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
Office number.
 The University of Jordan Faculty: Pharmacy Department: Biopharmaceutics and Clinical Pharmacy Program: Pharmacy Academic Year/ Fall Semester: 2014/15 BIOCHEMISTRY 2 [1203253] Credit hours 3 Level 2 nd
The University of Jordan Faculty: Pharmacy Department: Biopharmaceutics and Clinical Pharmacy Program: Pharmacy Academic Year/ Fall Semester: 2014/15 BIOCHEMISTRY 2 [1203253] Credit hours 3 Level 2 nd
