Axons in the desert II
|
|
|
- Logan Conrad Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Research Workshop of the Israel Science Foundation Ben-Gurion University of the Negev & Kibbutz Ein Gedi, Israel 1-4 November, 2015 Sponsored by:
2 1-4 November, 2015 Beer Sheva & Ein Gedi There has been a growing interest in various aspects of electrogenesis of central axons in both health and neurological disease. We therefore see this workshop as an opportunity to not only exchange our latest findings, but also to frankly confront controversies and try to resolve and understand some of the conflicting evidence that has arisen from studies entailing different techniques, experimental preparations and disciplines. Among the subjects we would like to address: What is the distribution of sodium channels of different subtype in soma-dendritic and axon initial segment membrane How should action potential generation be modeled and what parameters are lacking to make definitive models? What aspects of the axon initial segment are generalized to all cell types and what are specific to specific types? How do the protein-protein interactions that must occur in the complex axonal structure translate into function? What is the evidence for normal or pathogenic plasticity of the axon initial segment, what are the conditions under which this plasticity is seen, and what might be its functional consequence? How do myelination and demyelination affect action potential propagation? What is the role of the cytoskeletal elements that define the axon initial segment in establishing and maintaining functional polarity? 2
3 Mechanisms and consequences of axon initial segment innervation and modulation by GABAergic interneurons Energetics of action potential generation in the axon Relationships between action potentials and local Ca 2+ signaling in the axons How do axonal dynamic properties affect the firing properties of neurons and networks? Organizing Committee: Ilya Fleidervish, Mike Gutnick, Idan Segev, Alex Binshtok Program Committee: Ilya Fleidervish, Maarten Kole, Matthew Grubb Special thanks to Yana Khrapunsky for administrative assistance. 3
4 List of Speakers Yael Amitai Bernard Attali Alex Binshtok Romain Brette Juan Burrone Andreas Draguhn Alexei Egorov Ilya Fleidervish Dani Gitler David Golomb Matthew Grubb Mike Gutnick Stefan Hallermann John Huguenard Hanoch Kaphzan Maarten Kole Alon Korngreen Hiroshi Kuba Israel Melamed Alon Monsenego Andreas Neef Elior Peles John Rash Moran Rubinshtein Menahem Segal Idan Segev Mala Shah Maoz Shamir Yousheng Shu Maxim Volgushev Fred Wolf Yoel Yaari Tel-Aviv University, Israel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel CNRS and Université Paris Descartes, France King's College London, UK University of Heidelberg, Germany University of Heidelberg, Germany King's College London, UK The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel University Leipzig, Germany Stanford University, USA University of Haifa, Israel The Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, Netherlands Bar-Ilan University, Israel Nagoya University, Japan MPI for Dynamics and Self-Organization, Germany Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel Colorado State University, USA Tel Aviv University Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel University College London, UK Beijing Normal University, China University of Connecticut, USA MPI for Dynamics and Self-Organization, Germany The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel
5 Conference Programme Axons in the desert II Sunday, November 1 - Beer Sheva Venue: Ilse Katz Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology building (51, Ctrl+Click the interactive map below), room :30 Get together, light refreshments 14:45 Welcome, Introduction and Logistics Session 1: Myelinated axons: structure and function Chair: John Huguenard 15:00 Elior Peles, Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel The organization of myelinated axons - lessons from the PNS 15:45 John Rash, Colorado State University, USA Axonal KV1.1/KV1.2 delayed-rectifier channels are coupled to connexin 29 hemichannels in juxtaparanodal myelin of rodent sciatic nerve: Basis for a new K + kindling hypothesis of saltatory conduction 16:30 Maarten Kole, The Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, Netherlands Multiple roles of oligodendroglial cells in the initiation and conduction of action potentials 17:30 Transportation to Shevadron Farm Restaurant, link (in Hebrew), map (in Hebrew) 5
6 18:00 Dinner 20:00 Transportation to Kibbutz Ein Gedi 6
7 Monday, November 2, Ein Gedi 07:00 08:45 Breakfast Session 2: Axon initial segment plasticity Chair: Yoel Yaari 9:00 9:30 Matthew Grubb, King's College London, UK Structural change at the axon initial segment and its interaction with coincident mechanisms of activity-dependent plasticity 9:30 10:00 Hiroshi Kuba, Nagoya University, Japan Switching of Kv channels enhances neuronal excitability during structural plasticity at the axon initial segment 10:00 10:30 Juan Burrone, King's College London, UK Activity-dependent plasticity of the axon initial segment and its synapses 10:30 11:00 Coffee break Session 3: Axonal action potential initiation - I Chair: Juan Burrone 11:00 11:30 Andreas Neef, MPI for Dynamics and Self-Organization, Germany The biophysics of the action potential generator 11:30 12:00 Mike Gutnick, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel TBA 12:00 12:30 Romain Brette, CNRS and Université Paris Descartes, France The compartmentalization of spike initiation 12:30 14:00 Lunch Session 4: Axonal action potential initiation - II Chair: Hiroshi Kuba 14:00 14:30 Maxim Volgushev, University of Connecticut, USA Action potential generation and encoding in cortical neurons: What theory predicts and what experiments are showing 14:30 15:00 Yousheng Shu, Beijing Normal University, China Action potential initiation in neocortical inhibitory interneurons 15:00 15:30 Ilya Fleidervish, Ben-Gurion University, Israel Inactivation properties of the axonal sodium channels 7
8 15:30 16:00 Coffee break Session 5: Axonal action potential initiation - III Chair: Fred Wolf 16:00 16:30 Stefan Hallermann, University Leipzig, Germany Axonal hyperpolarization activated currents enable high-frequency firing 16:30 17:00 Moran Rubinstein, Tel-Aviv University, Israel Dissecting the phenotypes of Dravet syndrome by gene deletion 17:00 17:30 Alexei Egorov, University of Heidelberg, Germany Diversity of axonal origin in hippocampal pyramidal neurons 17:30 19:00 Poster session I 19:00 20:30 Dinner 20:30 -- Posters, Wine & Fruits 8
9 Tuesday, November 3, Ein Gedi 07:00 08:45 Breakfast Session 6: Action potential properties and information encoding in neuronal circuits Chair: Andreas Draguhn 9:00 9:30 Fred Wolf, MPI for Dynamics and Self-Organization, Germany TBA 9:30 10:00 Idan Segev, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel TBA 10:00 10:30 Alon Korngreen, Bar-Ilan University, Israel Realistic neuronal modeling: is it realistic? 10:30 11:00 Coffee break Session 7: Axons and circuits Chair: Yousheng Shu 11:00 11:30 Andreas Draguhn, University of Heidelberg, Germany Ectopic spike generation in hippocampal networks 11:30 12:00 John Huguenard, Stanford University, USA Cell type specific Na channel gating in barrel cortex 12:00 12:30 David Golomb, Response of layer-4 circuits to somatosensory thalamic inputs 12:30 14:00 Lunch Session 8: Potassium channels and modulation of axonal excitability Chair: Menachem Segal 14:00 14:30 Bernard Attali, Tel-Aviv University, Israel Imbalance of M-channel activity leads to fast homeostatic plasticity at the axon initial segment of hippocampal neurons 14:30 15:00 Mala Shah, University College London, UK Cholinergic fibre activity-induced axonal ion channel plasticity in adult hippocampal granule cells 9
10 15:00 15:30 Yoel Yaari, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel Axon initial segment KV7 channels as targets for inflammatory processes 15:30 16:00 Coffee break Session 9: Axonal properties - general Chair: John Rash 16:00 16:30 Alex Binshtok, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel Neuronal GPS: Mapping axonal projections using multispectral labeling technique 16:30 17:00 Menahem Segal, Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel Modulation of ankyrin in the axon initial segment 17:00 17:30 Hanoch Kaphzan, University of Haifa, Israel tdcs: axonal perspective 17:30 19:00 Poster session II 19:00 20:30 Dinner 20:30 -- Posters, Wine & Fruits 10
11 Wednesday, November 4, Ein Gedi 07:00 08:00 Breakfast 8:00 12:00 Trip to Masada National Park (control + click) 12:30 13:30 Lunch 13:30 15:00 General Discussion. Moderator: TBA 16:00 Transportation to Beer Sheva 11
12 Poster Session 1 - Monday, November 2-17:00-19:00, 20:30-1. Adna Dumitrescu, King's College London, UK Live imaging of the axon initial segment development and plasticity 2. Christopher Makinson, Stanford University, USA Contribution of the voltage gated sodium channel Nav1.6 to forward and back propagation within a thalamocortical circuit 3. Maria Teleńczuk, CNRS and Université Paris Descartes, France Origin of the kink of somatic action potentials 4. Elisa Galliano, King's College London, UK Development and plasticity of axon initial segments in bulbar dopaminergic neurons 5. Jonathan Lezmy, Tel-Aviv University, Israel Imbalance of M-channel activity produces fast homeostatic plasticity at the axon initial segment of cultured hippocampal neurons 6. Ohad Stoler, Ben-Gurion University, Israel Subthreshold calcium flux in axons of L5 pyramidal neurons 7. Guy Eyal, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel Human L2/3 pyramidal cells possess unique membrane and dendritic properties with augmented computational capabilities 12
13 Poster Session 2 - Tuesday, November 3-17:30-19:00, 20:30-1. Arne Battefeld, The Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience Neuron-oligodendrocyte calcium signaling in the grey matter 2. Mustafa S. Hamada, The Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience Functional impact of axon coupling to basal dendrites in pyramidal neurons 3. Marko Popovic, The Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience Spatio-temporal dynamics of calcium flux in the axonal initial segment 4. Niklas Byczkowicz, University Leipzig, Germany Hyperpolarization-activated currents in cerebellar mossy fibers 5. Robert Goldstein, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel Signal transduction and propagation at the nociceptive peripheral terminals 6. Omer Barkai, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel A new mechanism of opioid-induced tolerance and hyperaglesia 7. Winnie Wefelmeyer, King's College London, UK Activity-dependent mismatch between axo-axonic synapses and the axon initial segment controls neuronal output 13
The 3rd Joint Inter-Academy Symposium. Stability and Plasticity: Advances in Understanding Neuronal Representations
 The 3rd Joint Inter-Academy Symposium of the Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities and the German National Academy of Sciences, Leopoldina Stability and Plasticity: Advances in Understanding Neuronal
The 3rd Joint Inter-Academy Symposium of the Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities and the German National Academy of Sciences, Leopoldina Stability and Plasticity: Advances in Understanding Neuronal
Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability
 Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability Cristina Nigro and Jason Pipkin UCSD Neurosciences Graduate Program Abstract The axon initial segment (AIS) is the portion of the
Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability Cristina Nigro and Jason Pipkin UCSD Neurosciences Graduate Program Abstract The axon initial segment (AIS) is the portion of the
CYTOARCHITECTURE OF CEREBRAL CORTEX
 BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY CYTOARCHITECTURE OF CEREBRAL CORTEX ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 CELLULAR COMPOSITION OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX THE CEREBRAL CORTEX CONSISTS OF THE ARCHICORTEX (HIPPOCAMPAL FORMA- TION), PALEOCORTEX
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY CYTOARCHITECTURE OF CEREBRAL CORTEX ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 CELLULAR COMPOSITION OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX THE CEREBRAL CORTEX CONSISTS OF THE ARCHICORTEX (HIPPOCAMPAL FORMA- TION), PALEOCORTEX
Basics of Computational Neuroscience: Neurons and Synapses to Networks
 Basics of Computational Neuroscience: Neurons and Synapses to Networks Bruce Graham Mathematics School of Natural Sciences University of Stirling Scotland, U.K. Useful Book Authors: David Sterratt, Bruce
Basics of Computational Neuroscience: Neurons and Synapses to Networks Bruce Graham Mathematics School of Natural Sciences University of Stirling Scotland, U.K. Useful Book Authors: David Sterratt, Bruce
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Electrical Properties of Neurons. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Electrical Properties of Neurons Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Neuronal Communication Neurons communicate with other cells, often over long distances. The electrical
Electrical Properties of Neurons Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Neuronal Communication Neurons communicate with other cells, often over long distances. The electrical
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed.,
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
The Challenge of Chronic Pain 4-6 March Wellcome Genome Campus, Hinxton, Cambridge, UK
 The Challenge of Chronic Pain 4-6 March 2019 Wellcome Genome Campus, Hinxton, Cambridge, UK Lectures to be held in the Francis Crick Auditorium Lunch and dinner to be held in the Hall Restaurant Poster
The Challenge of Chronic Pain 4-6 March 2019 Wellcome Genome Campus, Hinxton, Cambridge, UK Lectures to be held in the Francis Crick Auditorium Lunch and dinner to be held in the Hall Restaurant Poster
Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning
 Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015
 EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex
 Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex Jeffrey E. Dahlen jdahlen@ucsd.edu and Kerin K. Higa khiga@ucsd.edu Department of Neuroscience
Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex Jeffrey E. Dahlen jdahlen@ucsd.edu and Kerin K. Higa khiga@ucsd.edu Department of Neuroscience
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
Summarized by B.-W. Ku, E. S. Lee, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence Laboratory, Seoul National University.
 Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Action potential. Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon
 Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
8:40 pm Miguel Nicolelis, Duke University Medical Center Neural ensemble dynamics in the mammalian somatosensory system: From rodents to man
 Sunday, November 15 3:00 pm Check-in 6:15 pm Reception (Lobby) 7:00 pm Dinner 8:00 pm Welcome and opening remarks (David Ginty) 8:10 pm Session 1 Chair: David Ginty 8:10 pm Maria Fitzgerald, University
Sunday, November 15 3:00 pm Check-in 6:15 pm Reception (Lobby) 7:00 pm Dinner 8:00 pm Welcome and opening remarks (David Ginty) 8:10 pm Session 1 Chair: David Ginty 8:10 pm Maria Fitzgerald, University
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e. Chapter 4: The action potential
 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e Chapter 4: The action potential Introduction Action Potential in the Nervous System Conveys information over long distances Action potential Initiated in the axon
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e Chapter 4: The action potential Introduction Action Potential in the Nervous System Conveys information over long distances Action potential Initiated in the axon
Outline. Animals: Nervous system. Neuron and connection of neurons. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Period: Date: Module 28: Nervous System, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: Module 28: Nervous System, Student Learning Guide Instructions: Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. Go to www.sciencemusicvideos.com.
Name: Period: Date: Module 28: Nervous System, Student Learning Guide Instructions: Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. Go to www.sciencemusicvideos.com.
TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki
 TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki Rich Turner (turner@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk) Gatsby Unit, 22/04/2005 Rich T. Introduction Interneuron def = GABAergic non-principal cell Usually
TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki Rich Turner (turner@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk) Gatsby Unit, 22/04/2005 Rich T. Introduction Interneuron def = GABAergic non-principal cell Usually
When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded.
 When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded. Stein, V et al., (2003) J Neurosci, 23:5503-6606. Also found in Rat Barrel Cortex Ehrlich & Malinow (2004) J. Neurosci. 24:916-927 Over-expression
When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded. Stein, V et al., (2003) J Neurosci, 23:5503-6606. Also found in Rat Barrel Cortex Ehrlich & Malinow (2004) J. Neurosci. 24:916-927 Over-expression
Simulation of myelinated neuron with focus on conduction speed and changeable excitability
 Simulation of myelinated neuron with focus on conduction speed and changeable excitability Pengfei Chen Sung Min Kim Abstract In this paper we focus on the two particular properties of myelinated neuron,
Simulation of myelinated neuron with focus on conduction speed and changeable excitability Pengfei Chen Sung Min Kim Abstract In this paper we focus on the two particular properties of myelinated neuron,
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 2 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 2 Alphabetical absolute refractory period absolute refractory period Time when neuron will not re-fire no matter how much stimulus it gets. action
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 2 Alphabetical absolute refractory period absolute refractory period Time when neuron will not re-fire no matter how much stimulus it gets. action
Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling
 Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling 7.1. Overview of the Nervous System (Figure 7.1) 7.2. Cells of the Nervous System o Neurons are excitable cells which can generate action potentials o 90%
Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling 7.1. Overview of the Nervous System (Figure 7.1) 7.2. Cells of the Nervous System o Neurons are excitable cells which can generate action potentials o 90%
Multi compartment model of synaptic plasticity
 Multi compartment model of synaptic plasticity E. Paxon Frady We introduce a biophysical model of a neuronal network that can accurately replicate many classical plasticity experiments. The model uses
Multi compartment model of synaptic plasticity E. Paxon Frady We introduce a biophysical model of a neuronal network that can accurately replicate many classical plasticity experiments. The model uses
LESSON 3.3 WORKBOOK. Why does applying pressure relieve pain?
 Postsynaptic potentials small changes in voltage (membrane potential) due to the binding of neurotransmitter. Receptor-gated ion channels ion channels that open or close in response to the binding of a
Postsynaptic potentials small changes in voltage (membrane potential) due to the binding of neurotransmitter. Receptor-gated ion channels ion channels that open or close in response to the binding of a
Neurophysiology scripts. Slide 2
 Neurophysiology scripts Slide 2 Nervous system and Endocrine system both maintain homeostasis in the body. Nervous system by nerve impulse and Endocrine system by hormones. Since the nerve impulse is an
Neurophysiology scripts Slide 2 Nervous system and Endocrine system both maintain homeostasis in the body. Nervous system by nerve impulse and Endocrine system by hormones. Since the nerve impulse is an
THE HISTORY OF NEUROSCIENCE
 THE HISTORY OF NEUROSCIENCE BIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF BEHAVIOR: THE NEURON & NEURAL COMMUNICATION NERVOUS SYSTEM Combined activity of the brain, spinal cord & other nerve fibers Acts as an information processing
THE HISTORY OF NEUROSCIENCE BIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF BEHAVIOR: THE NEURON & NEURAL COMMUNICATION NERVOUS SYSTEM Combined activity of the brain, spinal cord & other nerve fibers Acts as an information processing
Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology
 Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology V edit. Pg. 99-131 VI edit. Pg. 85-113 VII edit. Pg. 87-113 Input Zone Dendrites and Cell body Nucleus Trigger Zone Axon hillock Conducting Zone Axon (may be from 1mm to more
Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology V edit. Pg. 99-131 VI edit. Pg. 85-113 VII edit. Pg. 87-113 Input Zone Dendrites and Cell body Nucleus Trigger Zone Axon hillock Conducting Zone Axon (may be from 1mm to more
What is Anatomy and Physiology?
 Introduction BI 212 BI 213 BI 211 Ecosystems Organs / organ systems Cells Organelles Communities Tissues Molecules Populations Organisms Campbell et al. Figure 1.4 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology?
Introduction BI 212 BI 213 BI 211 Ecosystems Organs / organ systems Cells Organelles Communities Tissues Molecules Populations Organisms Campbell et al. Figure 1.4 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology?
Omar Sami. Muhammad Abid. Muhammad khatatbeh
 10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
Endocrine System Nervous System
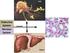 Cells Endocrine System Nervous System Tissues Controls Organs Nervous System vs Endocrine System Electrical signals (graded potentials and action potentials) and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) Fast
Cells Endocrine System Nervous System Tissues Controls Organs Nervous System vs Endocrine System Electrical signals (graded potentials and action potentials) and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) Fast
The Active Zone Meeting Preliminary Scientific Programme. Day 1 19 March Session 2 Chairs: Lu-Yang Wang (Toronto), Daniel Gitler (Beer-Sheva)
 Day 1 19 March 2014 09:00-09:15 Tobias Langenhan & Manfred Heckmann, Würzburg Greetings / Introduction Session 1 Chairs: Tobias Langenhan, Manfred Heckmann (Würzburg) 09:15-09:45 Christian Stigloher, Würzburg
Day 1 19 March 2014 09:00-09:15 Tobias Langenhan & Manfred Heckmann, Würzburg Greetings / Introduction Session 1 Chairs: Tobias Langenhan, Manfred Heckmann (Würzburg) 09:15-09:45 Christian Stigloher, Würzburg
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
9/28/2016. Neuron. Multipolar Neuron. Astrocytes Exchange Materials With Neurons. Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system)
 Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Neuroscience 201A Reading. Module 3 Integration
 Neuroscience 201A Reading Module 3 Integration Books/Book Chapters: Required (PDF): Appendix to The Synaptic Organization of the Brain 3 rd ed. Dendritic electrotonus and synaptic integration. Shepherd
Neuroscience 201A Reading Module 3 Integration Books/Book Chapters: Required (PDF): Appendix to The Synaptic Organization of the Brain 3 rd ed. Dendritic electrotonus and synaptic integration. Shepherd
A Biophysical Model of Cortical Up and Down States: Excitatory-Inhibitory Balance and H-Current
 A Biophysical Model of Cortical Up and Down States: Excitatory-Inhibitory Balance and H-Current Zaneta Navratilova and Jean-Marc Fellous ARL Division of Neural Systems, Memory and Aging University of Arizona,
A Biophysical Model of Cortical Up and Down States: Excitatory-Inhibitory Balance and H-Current Zaneta Navratilova and Jean-Marc Fellous ARL Division of Neural Systems, Memory and Aging University of Arizona,
Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue I. Functions and divisions of the nervous system A. Sensory input: monitor changes in internal and external environment B. Integrations: make decisions about
Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue I. Functions and divisions of the nervous system A. Sensory input: monitor changes in internal and external environment B. Integrations: make decisions about
Спайковые и бионические нейронные сети, нейроморфные системы. Dmitry Nowicki
 Спайковые и бионические нейронные сети, нейроморфные системы Dmitry Nowicki 1 Биологический нейрон 2 Нейрон МакКаллока-Питтса (не похож!?) 3 Сеть прямого распространения 4 Сеть Хопфилда: простейшая ассоциативная
Спайковые и бионические нейронные сети, нейроморфные системы Dmitry Nowicki 1 Биологический нейрон 2 Нейрон МакКаллока-Питтса (не похож!?) 3 Сеть прямого распространения 4 Сеть Хопфилда: простейшая ассоциативная
Endocrine System Nervous System
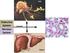 Cells Endocrine System Nervous System Tissues Controls Organs Nervous System vs Endocrine System Electrical signals (graded potentials and action potentials) and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) Fast
Cells Endocrine System Nervous System Tissues Controls Organs Nervous System vs Endocrine System Electrical signals (graded potentials and action potentials) and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) Fast
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Nervous System. Master controlling and communicating system of the body. Secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
 Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Neurons. Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons.
 Neurons Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons. MBL, Woods Hole R Cheung MSc Bioelectronics: PGEE11106 1 Neuron
Neurons Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons. MBL, Woods Hole R Cheung MSc Bioelectronics: PGEE11106 1 Neuron
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
Sunday, April 6 th. How to Read a Map: Understanding Structure-Function Relationships in the Brain. 3:00 pm Check-in. 6:00 pm Reception (Lobby)
 Sunday, April 6 th 3:00 pm Check-in 6:00 pm Reception (Lobby) 6:30 pm Dinner 7:30 pm Welcome and Introduction 7:45 pm Science Speed Dating! (Lobby) 9:15 pm Refreshments available at Bob s Pub NOTE: Meals
Sunday, April 6 th 3:00 pm Check-in 6:00 pm Reception (Lobby) 6:30 pm Dinner 7:30 pm Welcome and Introduction 7:45 pm Science Speed Dating! (Lobby) 9:15 pm Refreshments available at Bob s Pub NOTE: Meals
Models of Neocortical Layer 5b Pyramidal Cells Capturing a Wide Range of Dendritic and Perisomatic Active Properties
 Models of Neocortical Layer 5b Pyramidal Cells Capturing a Wide Range of Dendritic and Perisomatic Active Properties Etay Hay *, Sean Hill 2, Felix Schürmann 2, Henry Markram 2, Idan Segev,3 Interdisciplinary
Models of Neocortical Layer 5b Pyramidal Cells Capturing a Wide Range of Dendritic and Perisomatic Active Properties Etay Hay *, Sean Hill 2, Felix Schürmann 2, Henry Markram 2, Idan Segev,3 Interdisciplinary
Cellular Bioelectricity
 ELEC ENG 3BB3: Cellular Bioelectricity Notes for Lecture 24 Thursday, March 6, 2014 8. NEURAL ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY We will look at: Structure of the nervous system Sensory transducers and neurons Neural coding
ELEC ENG 3BB3: Cellular Bioelectricity Notes for Lecture 24 Thursday, March 6, 2014 8. NEURAL ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY We will look at: Structure of the nervous system Sensory transducers and neurons Neural coding
Bursting dynamics in the brain. Jaeseung Jeong, Department of Biosystems, KAIST
 Bursting dynamics in the brain Jaeseung Jeong, Department of Biosystems, KAIST Tonic and phasic activity A neuron is said to exhibit a tonic activity when it fires a series of single action potentials
Bursting dynamics in the brain Jaeseung Jeong, Department of Biosystems, KAIST Tonic and phasic activity A neuron is said to exhibit a tonic activity when it fires a series of single action potentials
Functions of Nervous System Neuron Structure
 Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
You submitted this quiz on Sun 7 Apr :08 PM IST (UTC +0530). You got a score of out of Your Answer Score Explanation
 Feedback Ex You submitted this quiz on Sun 7 Apr 0 :08 PM IST (UTC +00). You got a score of 0.00 out of 0.00. Question AIS Axon Initial Segment 0. Question https://class.coursera.org/bluebrain-00/quiz/feedback?submission_id=
Feedback Ex You submitted this quiz on Sun 7 Apr 0 :08 PM IST (UTC +00). You got a score of 0.00 out of 0.00. Question AIS Axon Initial Segment 0. Question https://class.coursera.org/bluebrain-00/quiz/feedback?submission_id=
Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology
 Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology Objectives Describe the two major divisions of the nervous system and their characteristics. Identify the structures/functions of a typical neuron. Describe the location
Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology Objectives Describe the two major divisions of the nervous system and their characteristics. Identify the structures/functions of a typical neuron. Describe the location
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
The Role of Mitral Cells in State Dependent Olfactory Responses. Trygve Bakken & Gunnar Poplawski
 The Role of Mitral Cells in State Dependent Olfactory Responses Trygve akken & Gunnar Poplawski GGN 260 Neurodynamics Winter 2008 bstract Many behavioral studies have shown a reduced responsiveness to
The Role of Mitral Cells in State Dependent Olfactory Responses Trygve akken & Gunnar Poplawski GGN 260 Neurodynamics Winter 2008 bstract Many behavioral studies have shown a reduced responsiveness to
SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION
 BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NERVE ENDINGS II. Interneuronal communication 2 INTERNEURONAL COMMUNICATION I. ELECTRONIC SYNAPSE GAP JUNCTION II. CHEMICAL SYNAPSE SYNAPSES
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NERVE ENDINGS II. Interneuronal communication 2 INTERNEURONAL COMMUNICATION I. ELECTRONIC SYNAPSE GAP JUNCTION II. CHEMICAL SYNAPSE SYNAPSES
CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems
 CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems 1. What are the three different types of neurons and what are their functions? a. b. c. 2. Label and list the function of each part of the neuron. 3. How does the
CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems 1. What are the three different types of neurons and what are their functions? a. b. c. 2. Label and list the function of each part of the neuron. 3. How does the
Thursday, January 22, Nerve impulse
 Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Neuromorphic computing
 Neuromorphic computing Robotics M.Sc. programme in Computer Science lorenzo.vannucci@santannapisa.it April 19th, 2018 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Fundamentals of neuroscience 3. Simulating the brain 4.
Neuromorphic computing Robotics M.Sc. programme in Computer Science lorenzo.vannucci@santannapisa.it April 19th, 2018 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Fundamentals of neuroscience 3. Simulating the brain 4.
BIOLOGY 2050 LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I (A. IMHOLTZ) FUNDAMENTALS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM AND NERVOUS TISSUE P1 OF 5
 P1 OF 5 The nervous system controls/coordinates the activities of cells, tissues, & organs. The endocrine system also plays a role in control/coordination. The nervous system is more dominant. Its mechanisms
P1 OF 5 The nervous system controls/coordinates the activities of cells, tissues, & organs. The endocrine system also plays a role in control/coordination. The nervous system is more dominant. Its mechanisms
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS. AP Biology Chapter 48
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
Evaluating the Effect of Spiking Network Parameters on Polychronization
 Evaluating the Effect of Spiking Network Parameters on Polychronization Panagiotis Ioannou, Matthew Casey and André Grüning Department of Computing, University of Surrey, Guildford, Surrey, GU2 7XH, UK
Evaluating the Effect of Spiking Network Parameters on Polychronization Panagiotis Ioannou, Matthew Casey and André Grüning Department of Computing, University of Surrey, Guildford, Surrey, GU2 7XH, UK
FEBS 2019 Advanced Lecture Course. Biological Surfaces and Interfaces: The Mechanistic View.
 FEBS 2019 Advanced Lecture Course Biological Surfaces and Interfaces: The Mechanistic View. June 30 July 5, 2019 Hotel Eden Roc Sant Feliu de Guixols, Spain Preliminary Program Chair Marta Bally Umeå University
FEBS 2019 Advanced Lecture Course Biological Surfaces and Interfaces: The Mechanistic View. June 30 July 5, 2019 Hotel Eden Roc Sant Feliu de Guixols, Spain Preliminary Program Chair Marta Bally Umeå University
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
Neurobiology. Cells of the nervous system
 Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2010 1 The nervous system Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) 2 Enteric nervous system (digestive tract, gall bladder and
Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2010 1 The nervous system Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) 2 Enteric nervous system (digestive tract, gall bladder and
Human Brain and Senses
 Human Brain and Senses Outline for today Levels of analysis Basic structure of neurons How neurons communicate Basic structure of the nervous system Levels of analysis Organism Brain Cell Synapses Membrane
Human Brain and Senses Outline for today Levels of analysis Basic structure of neurons How neurons communicate Basic structure of the nervous system Levels of analysis Organism Brain Cell Synapses Membrane
COGS 107B Week 1. Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm
 COGS 107B Week 1 Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm Before We Begin... Hyun Ji 4th year Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience Email: hji@ucsd.edu In subject, always add [COGS107B] Office hours: Wednesdays, 3-4pm in
COGS 107B Week 1 Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm Before We Begin... Hyun Ji 4th year Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience Email: hji@ucsd.edu In subject, always add [COGS107B] Office hours: Wednesdays, 3-4pm in
NEURONS Chapter Neurons: specialized cells of the nervous system 2. Nerves: bundles of neuron axons 3. Nervous systems
 NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
Outline. Neuron Structure. Week 4 - Nervous System. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses
 Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Neurophysiology. Corresponding textbook pages: ,
 Neurophysiology Corresponding textbook pages: 436-440, 442-455 Organization Helps maintain homeostasis in the body Nervous system and endocrine system Nervous system is faster due to nerve impulses 1 Fig.
Neurophysiology Corresponding textbook pages: 436-440, 442-455 Organization Helps maintain homeostasis in the body Nervous system and endocrine system Nervous system is faster due to nerve impulses 1 Fig.
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Branches of the Nervous System
 The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading to rest of body Anatomy
The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading to rest of body Anatomy
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons
 5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
Na + K + pump. The beauty of the Na + K + pump. Cotransport. The setup Cotransport the result. Found along the plasma membrane of all cells.
 The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
Correlated network activity in the developing hippocampus: role in synaptogenesis
 Enrico Cherubini Correlated network activity in the developing hippocampus: role in synaptogenesis SPACE PHYSICS and BIOLOGY Dubna, December 19-23, 2010 The construction of the brain relies on genetic
Enrico Cherubini Correlated network activity in the developing hippocampus: role in synaptogenesis SPACE PHYSICS and BIOLOGY Dubna, December 19-23, 2010 The construction of the brain relies on genetic
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Chapter 10
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters
 Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
CALLOSAL RESPONSES OF FAST-RHYTHMIC-BURSTING NEURONS DURING SLOW OSCILLATION IN CATS
 Neuroscience 147 (2007) 272 276 RAPID REPORT CALLOSAL RESPONSES OF FAST-RHYTHMIC-BURSTING NEURONS DURING SLOW OSCILLATION IN CATS Y. CISSÉ, 1,2 D. A. NITA, 2 M. STERIADE AND I. TIMOFEEV* Department of
Neuroscience 147 (2007) 272 276 RAPID REPORT CALLOSAL RESPONSES OF FAST-RHYTHMIC-BURSTING NEURONS DURING SLOW OSCILLATION IN CATS Y. CISSÉ, 1,2 D. A. NITA, 2 M. STERIADE AND I. TIMOFEEV* Department of
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
Exploring the Functional Significance of Dendritic Inhibition In Cortical Pyramidal Cells
 Neurocomputing, 5-5:389 95, 003. Exploring the Functional Significance of Dendritic Inhibition In Cortical Pyramidal Cells M. W. Spratling and M. H. Johnson Centre for Brain and Cognitive Development,
Neurocomputing, 5-5:389 95, 003. Exploring the Functional Significance of Dendritic Inhibition In Cortical Pyramidal Cells M. W. Spratling and M. H. Johnson Centre for Brain and Cognitive Development,
Dendritic Signal Integration
 Dendritic Signal Integration 445 Dendritic Signal Integration N Spruston, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA ã 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Overview: Questions Most neurons have elaborately
Dendritic Signal Integration 445 Dendritic Signal Integration N Spruston, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA ã 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Overview: Questions Most neurons have elaborately
LESSON 3.3 WORKBOOK. Why does applying pressure relieve pain? Workbook. Postsynaptic potentials
 Depolarize to decrease the resting membrane potential. Decreasing membrane potential means that the membrane potential is becoming more positive. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP) graded postsynaptic
Depolarize to decrease the resting membrane potential. Decreasing membrane potential means that the membrane potential is becoming more positive. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP) graded postsynaptic
Implantable Microelectronic Devices
 ECE 8803/4803 Implantable Microelectronic Devices Fall - 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo (mgh@gatech.edu) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo 1 Outline
ECE 8803/4803 Implantable Microelectronic Devices Fall - 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo (mgh@gatech.edu) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo 1 Outline
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 12 Nervous Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the nervous system helps to keep controlled conditions within
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 12 Nervous Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the nervous system helps to keep controlled conditions within
BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE
 1 Name: BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE Date: 1) Identify structures X, Y and Z and give one function of each. 2) Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z?
1 Name: BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE Date: 1) Identify structures X, Y and Z and give one function of each. 2) Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z?
D) around, bypassing B) toward
 Nervous System Practice Questions 1. Which of the following are the parts of neurons? A) brain, spinal cord, and vertebral column B) dendrite, axon, and cell body C) sensory and motor D) cortex, medulla
Nervous System Practice Questions 1. Which of the following are the parts of neurons? A) brain, spinal cord, and vertebral column B) dendrite, axon, and cell body C) sensory and motor D) cortex, medulla
Physiology of the nerve
 Physiology of the nerve Objectives Transmembrane potential Action potential Relative and absolute refractory period The all-or-none law Hoorweg Weiss curve Du Bois Reymond principle Types of nerve fibres
Physiology of the nerve Objectives Transmembrane potential Action potential Relative and absolute refractory period The all-or-none law Hoorweg Weiss curve Du Bois Reymond principle Types of nerve fibres
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition
 Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73
 DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73 1. Name 1 neurotransmitter that we have learned about. 2. Draw a basic graph of a neuron action potential. Label resting potential, threshold, depolarization, and repolarization
DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73 1. Name 1 neurotransmitter that we have learned about. 2. Draw a basic graph of a neuron action potential. Label resting potential, threshold, depolarization, and repolarization
Abstract. Introduction. Keywords: AHP, odour-learning, piriform cortex, pyramidal cells
 European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 10, pp. 1518 1523, 1998 European Neuroscience Association SHORT COMMUNICATION Reduced after-hyperpolarization in rat piriform cortex pyramidal neurons is associated
European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 10, pp. 1518 1523, 1998 European Neuroscience Association SHORT COMMUNICATION Reduced after-hyperpolarization in rat piriform cortex pyramidal neurons is associated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Modeling Depolarization Induced Suppression of Inhibition in Pyramidal Neurons
 Modeling Depolarization Induced Suppression of Inhibition in Pyramidal Neurons Peter Osseward, Uri Magaram Department of Neuroscience University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92092 possewar@ucsd.edu
Modeling Depolarization Induced Suppression of Inhibition in Pyramidal Neurons Peter Osseward, Uri Magaram Department of Neuroscience University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92092 possewar@ucsd.edu
Chapter Nervous Systems
 The Nervous System Chapter Nervous Systems Which animals have nervous systems? (Which do not) What are the basic components of a NS? What kind of fish performs brain operations? What differentiates one
The Nervous System Chapter Nervous Systems Which animals have nervous systems? (Which do not) What are the basic components of a NS? What kind of fish performs brain operations? What differentiates one
Neocortex. Cortical Structures in the Brain. Neocortex Facts. Laminar Organization. Bark-like (cortical) structures: Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12
 Neocortex Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12 Rodney Douglas, Henry Markram, and Kevan Martin Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Cortical Structures in the Brain Bark-like (cortical) structures:
Neocortex Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12 Rodney Douglas, Henry Markram, and Kevan Martin Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Cortical Structures in the Brain Bark-like (cortical) structures:
Physiology of synapses and receptors
 Physiology of synapses and receptors Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University REMEMBER These handouts will
Physiology of synapses and receptors Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University REMEMBER These handouts will
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Sunday, October 26 th
 Sunday, October 26 th 3:00 pm Check-in 6:00 pm Reception (Lobby) 7:00 pm Dinner 8:00 pm Welcome & Opening Remarks 8:05 pm Keynote Lecture Sean Eddy, Janelia Research Campus/HHMI Computational analysis
Sunday, October 26 th 3:00 pm Check-in 6:00 pm Reception (Lobby) 7:00 pm Dinner 8:00 pm Welcome & Opening Remarks 8:05 pm Keynote Lecture Sean Eddy, Janelia Research Campus/HHMI Computational analysis
