5) Which of he following is not one of the main clinical symptoms of Schizophrenia? a) Delusions b) Hallucinations c) Apathy d) Narcolepsy (A)
|
|
|
- Cameron Barrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 7.teachers 1 In Schizophrenia, the phenomenon known as downward drift means? a) Falling to the bottom of the social ladder b) Become homeless c) Inability to hold down a job 2) Which of the following is not a symptom of Schizophrenia? a) Dysfunctions of perception b) Dysfunctions of inferential thinking c) Dysfunctions of language and communication d) Dysfunctions of memory (A) 3) Which of the following are lifetime prevalence rates for Schizophrenia? a) 0.5-2% b) 24 million sufferers worldwide c) No difference in prevalence rates between men and women 4) Which of the following are some of the symptoms of Schizophrenia? a) Disorganized speech b) Flat affect c) Poverty of speech 5) Which of he following is not one of the main clinical symptoms of Schizophrenia? a) Delusions b) Hallucinations c) Apathy d) Narcolepsy (A) 6) Dementia praecox was a disease first identified by? a) Freud b) Kraepelin (A) c) Beck d) Watson 7) According to Kraepelin, which of the following was not a symptom of Dementai praecox? a) Paranoia, b) Catatonia c) Hebephrenia d) Quadraphenia (A) 8) The first psychiatrist to utilise the term Schizophrenia was? a) Bleuler (A) b) Kraepelin c) Salkovskis
2 d) Rogers 9) In Schizophrenia symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, disorganised speech (e.g. incoherence), and grossly disorganised or catatonic behaviour are referred to as: a) Negative symptoms b) Positive symptoms (A) c) Mediating symptoms d) Catastrophic symptoms 10) In Schizophrenia which if the following is not a positive symptom? a) Hallucinations b) Delusions c) Alogia (A) d) Disorganised speech 11) In Schizophrenia which if the following is not a positive symptom? a) Alogia b) Avolition c) Flattened affect d) Disorganised speech (A) 12) In Schizophrenia misinterpretation of perceptions or experiences are known as: a) Delusions (A) b) Hallucinations c) Misperceptions d) Avolition 13) In Schizophrenia the when an individual believes they are in danger, this is referred to as: a) Delusions of persecution (A) b) Delusions of grandeur c) Delusions of control d) Nihilistic delusions 14) In Schizophrenia the when an individual believes they are someone with fame or power, this is referred to as: a) Delusions of grandeur (A) b) Delusions of control c) Delusions of reference d) Nihilistic delusions 15) In Schizophrenia the when an individual believes that messages are being sent directly to their brain, this is referred to as: a) Delusions of control (A) b) Delusions of persecution c) Delusions of reference d) Delusions of grandeur 16) In Schizophrenia the when an individual believes that messages are being sent directly to him or her, this is referred to as: a) Delusions of persecution
3 b) Delusions of reference (A) c) Nihilistic delusions d) Delusions of persecution 17) In Schizophrenia, when an individual believes that some aspect of either the world or themselves has ceased to exist, this is known as: a) Nihilistic delusions (A) b) Delusions of persecution c) Delusions of control d) Delusions of grandeur 18) In Schizophrenia, which of the following ways might hallucinations be experienced? a) Auditory b) Olfactory c) Gustatory 19) In Schizophrenia which is the most commonly experienced type of hallucination? a) Auditory hallucinations b) Gustatory hallucinations c) Olfactory hallucinations d) Tactile hallucinations 20) In Schizophrenia, what percent of sufferers experience auditory hallucinations? a) 40% b) 70% (A) c) 10% d) 80% 21) In Schizophrenia gustatory hallucinations refer to: a) Foods that taste unusual (A) b) Smells that are not present c) Tingling skin d) Shapes that are not present 22) In Schizophrenia olfactory hallucinations refer to: a) Smells that are not present (A) b) Tingling skin c) Shapes that are not present d) Foods that taste unusal 23) In Schizophrenia reality-monitoring deficit refers to: a) Problems distinguishing between what actually occurred and what did not (A) b) Problems distinguishing between thoughts and ideas they generated themselves c) Problems with memory loss d) Problems with spatial ability
4 24) In Schizophrenia self-monitoring deficit refers to: a) Problems distinguishing between thoughts and ideas they generated themselves (A) b) Problems distinguishing between what actually occurred and what did not c) Problems with spatial ability d) Problems with memory loss 25) In Schizophrenia which of the following come under the term of disorganised speech? a) Derailment b) Loose associations c) Word salads 26) In disorganised speech derailment refers to: a) Where the individual may drift quickly from one topic to another during a conversation (A) b) Answers to questions may not be relevant c) Speech may be neither structured nor comprehensible d) Individuals only communicate with words that rhyme 27) In disorganised speech tangentiality refers to: a) Individuals only communicate with words that rhyme b) Answers to questions may not be relevant c) Speech may be neither structured nor comprehensible (A) d) Individuals only communicate with words that rhyme 28) In disorganised speech the term clanging refers to: a) Individuals only communicate with words that rhyme (A) b) Answers to questions may not be relevant c) Individuals only communicate with words that rhyme d) Speech may be neither structured nor comprehensible 29) In disorganised speech neologisms refers to: a) Individuals often make up words and use them to communicate (A) b) Individuals only communicate with words that rhyme c) Speech may be neither structured nor comprehensible d) Answers to questions may not be relevant 30) In disorganised speech word salads refers to: a) Individuals are able to link one word to the next (A) b) Individuals only communicate with words that rhyme c) Answers to questions may not be relevant d) Speech may be neither structured nor comprehensible 31) In Schizophrenia poverty of content refers to: a) Speech appears to be detailed in terms of numbers of words, but is grammatically incorrect (A) b) A tendency to jump from one topic to another within a sentence c) Poor use of vocabulary d) Poor use of grammar
5 32) Which of the following are example of Catatonic Behaviour in Schizophrenia: a) Resisting attempts to be moved b) Maintaining rigid, immobile postures c) Decrease in reactivity to the environment 33) Which of the following are examples of Grossly Disorganised Behaviour in Schizophrenia? a) Behaviour may be childlike and silly and inappropriate for the person s chronological age b) Behaviour may be inappropriate to the context c) Behaviour may be unpredictable and agitated 34) Which of the following are examples of Affective flattening in Schizophrenia? a) Expressionless and unresponsive facial appearance b) Lack of eye contact c) Monotonous voice tone 35) In Schizophrenia, the term anhedonia refers to? a) An inability to react to enjoyable or pleasurable events (A) b) An inability to enjoy food c) An inability express empathy d) An inability to react appropriately to social cues 36) Paranoid schizophrenia is a sub-type of Schizophrenia which is characterised by: a) The presence of delusions or auditory hallucinations (A) b) The presence of disorganised behaviour and flat or inappropriate affect c) The severe disturbances of motor behaviour d) A lack of prominent positive symptoms with evidence of on-going negative symptoms 37) Disorganized schizophrenia is a sub-type of Schizophrenia which is characterised by: a) A lack of prominent positive symptoms with evidence of on-going negative symptoms b) The presence of delusions or auditory hallucinations c) The presence of disorganised behaviour and flat or inappropriate affect (A) d) The severe disturbances of motor behaviour 38) Catatonic schizophrenia is a sub-type of Schizophrenia which is characterised by: a) The severe disturbances of motor behaviour (A) b) The presence of disorganised behaviour and flat or inappropriate affect c) The presence of delusions or auditory hallucinations d) A lack of prominent positive symptoms with evidence of on-going negative symptoms 39) Residual Type schizophrenia is a sub-type of Schizophrenia which is characterised by: a) The presence of delusions or auditory hallucinations b) A lack of prominent positive symptoms with evidence of on-going negative symptoms (A) c) The presence of disorganised behaviour and flat or inappropriate affect
6 d) The severe disturbances of motor behaviour 40) Immigrants from developing countries are at higher risk of developing Schizophrenia. Which of the following are potential risk factors? a) Language difficulties b) Unemployment c) Poor housing 41) Studies suggest that between: a) 5-15% (A) b) 19-20% c) 25-30% d) 30-40% of those diagnosed with schizophrenia successfully commit suicide. 42) A study of nine countries by the World Health Organization found that: a) 51% (A) b) 63% c)12% d)5% of individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia were aged between 15 and 25 years of age 43) A study of nine countries by the World Health Organization found that: a) 80%(A) b) 30% c) 12% d) 60%
7 are between 15 and 35 years of age 44) Which of the following symptoms is known as the Prodromal stage in Schizophrenia? a) Slow withdrawal from normal life and social interaction b) Shallow and inappropriate emotions c) Deterioration in personal care 45) Which of the following symptoms is known as the Active Stage in Schizophrenia? a) Delusions b) Disordered speech and communication c) Halluciantions 46) Which of the following symptoms is known of the Residual Stage in Schizophrenia? a) When the individual ceases to show prominent signs of positive symptoms (A) b) May exhibit negative symptoms c) May find it difficult to cope to normal day to day activities 47) Long term studies of Schizophrenia have suggested that around: a) 28% (A) b) 50% c) 10% d) 5% will remit after one or more active stage 48) Long term studies of Schizophrenia have suggested that around: a) 22%(A)
8 b) 45% c) 10% d) 15% will continue to show positive symptoms over the long-term 49) Long term studies of Schizophrenia have suggested that around: a) 50%(A) b) 70% c) 30% d) 15% will alternate between active and residual stages 50) In Schizophrenia` relapse is relatively common, which of the following can explain this? a) Stressful life events or return to a stressful family environment after a period of hospitalisation or care b) Nonadherence to medication c) Inadequate discharge or aftercare planning 51) In Schizophrenia the diathesis-stress perspective refers to which combination? a) Genetically-inherited biological factors and environmental stress (A) b) Low self esteem and environmental stress c) Gender and environmental stress d) Intelligence and life stress 52) In Schizophrenia they may be an inherited genetic disposition. Concordance rates with spouse are: a) 1% (A)
9 b) 2% c)3% 4% 53) In Schizophrenia they may be an inherited genetic disposition. Concordance rates with grandchildren are: a) 2.84% (A) b) 5% c) 7.83% d) 3% 54) In Schizophrenia they may be an inherited genetic disposition. Concordance rates with nieces/nephews are: a) 2.65% (A) b) 5.84% c)7.35% d) 1% 55) In Schizophrenia they may be an inherited genetic disposition. Concordance rates with children are: a) 9.35% (A) b) 5.69% c) 15.43% d) 3% 56) In Schizophrenia they may be an inherited genetic disposition. Concordance rates with siblings are: a) 7.30% (A) b) 5.8%
10 c) 2.5% d) 15.8% 57) In Schizophrenia they may be an inherited genetic disposition. Concordance rates with Dizygotic (Fraternal) Twins are: a) 12.08% (A) b) 7.30% c) 20.67% d) 3.5% 58) In Schizophrenia they may be an inherited genetic disposition. Concordance rates with Monozygotic (Identical) Twins are: a) 44.30% (A) b) 12.08% c) 60.57% d) 15.45% 59) In adoption studies of Schizophrenia (Heston 1966) which of the following concordance rates were found between children and biological Schizophrenic mother? a) 16.6% (A) b) 24.3% c) 82% d)6% 60) According to Kety et al.(1994) which of the following concordance rates were found between adopted children and biological relatives with Schizophrenia? a) 21.4% (A) b) 66.2% c)51.4%
11 d) 3.6% 61) In Schizophrenia blood samples are collected in order to study the inheritance patterns within families that have members diagnosed with schizophrenia. This is known as: a) Genetic linkage analyses (A) b) Hemo-predisposition analysis c) Genetic blood work d) Psychoz-biological analysis 62) The biochemical theory of schizophrenia know an the Dopamine hypothesis refers to: a) Excess Dopamine activity (A) b) Insufficient Dopamine activity c) Contaminated Dopamine d) Allergic sensitivity to Dopamine 63) In Schizophrenia, antipsychotic drugs such as the phenothiazines work by: a) Blocking the brain s dopamine receptor sites and so reducing dopamine activity (A) b) Increasing brain Dopamine activity c) Replacing Dopamine with Norepinepeherine d) Preventing re-uptake of Seretonin 64) Amphetamine psychosis results in disturbed behaviour patterns by: a) `Increasing brain dopamine activity (A) b) Blocking the brain s dopamine receptor sites and so reducing dopamine activity c) Increasing production of Norepinepherine d) Increasing levels of Cortisol
12 65) In brain imaging studies, which of the following areas have been implicated in Schizophrenia? a) The frontal lobes b) The temporal lobe-limbic structures c) The basal ganglia 66) In Schizophrenia, PET scans have shown abnormalities in brain functioning in which of the following? a) Decreased frontal lobe activity (A) b) Increased frontal lobe activity c) Deformed frontal lobes d) Inactive frontal lobes 67) In Schizophrenia under activity in the frontal lobes is associated with which of the following? a) Poor performance on cognitive tasks b) Abstraction/categorization c) Memory and sustained attention 68) According to psychodynamic theories of Schizophrenia psychosis is caused by regression to a previous ego state. This is known as: a) Primary narcissism(a) b) Ego Defence c) Discounting d) Primary reformulation 69) According to Fromm-Reichmann, which of the following attributes does a Schizophrenogenic mother posess?
13 a) Rejecting b) Distant c) Dominating 70) In cognitive theories of Schizophrenia which of the following reactions are part of the normal attentional process? a) Changes in skin conductance b) Changes in brain activity c) Changes in heart rate and blood pressure 71) In Schizophrenia according to some research, paranoid delusions may also be the result of abnormal attributional processes. This refers to? a) A bias towards attributing negative life events to external causes (A) b) A bias towards attributing negative life events to internal causes c) A bias towards attributing all life events to God d) A bias towards attributing others behaviour to themselves 72) Research suggests that information processing biases may be involved in the development of persecutory delusions. Which of the following factors are important in contributing to the development of cognitive biases involved in persecutory ideation? a) Anomalous experiences b) Anxiety, depression and worry, that would normally cause a bias towards negative thinking and threatening interpretations of events c) Reasoning biases on the part of the individual which lead them to seek confirmatory evidence for their persecutory interpretations rather than question them 73) In Schizophrenia individuals who cannot infer the beliefs, attitudes and intentions of others are said to lack: a) Theory of Mind (A)
14 b) Intelligence c) Self esteem d) Sense of self 74) Which of the following are factors in the sociogenic hypothesis of Schizophrenia? a) Stressors are associated with unemployment, poor educational levels, crime and poverty generally (A) b) Jealousy of people in a higher socioeconomic class c) Childhood in a low socioeconomic class d) Lack of education 75) Which of the following are examples of social-selection theory of Schizophrenia? a) Individuals displaying psychotic symptoms will drift into lifestyles where there is less social pressure to achieve (A) b) Individuals displaying psychotic symptoms will choose to social only with others sharing similar symptoms c) Individuals displaying psychotic symptoms will automatically be excluded by their social circle d) Individuals displaying psychotic symptoms will automatically be hospitalised 76) Which of the following are features of social labelling in Schizophrenia? a) Others will begin to behave differently towards sufferers, and define any deviant behaviour as a symptom of schizophrenia b) The person who is diagnosed may themselves assume a role as someone who has a disorder, and play that role to the detriment of other - perhaps more adaptive roles c) The individual generates a self-fulfilling prophecy, in which a diagnosis leads to the individual, their family and friends behaving in ways which are likely to maintain pathological symptom 77) Which of the flowing statements describes the double-bind hypothesis in Schizophrenia? a) A mother may both request displays of affection, such as a hug, and then reject them as being a sign of weakness (A) b) A mother may repell all displays of affection c) A mother may demand over excessive public displays of affection
15 d) Both parents actively encourage the individual to remain childlike and dependant 78) In Schizophrenia the construct called communication deviance in families is related to the development of psychotic symptoms. Which of the following are examples of these types of communications? a) Abandoned or abruptly ceased remarks or sentences b) Inconsistent references to events or situations c) Using words or phrases oddly or wrongly 79) In Schizophrenia a term which is closely linked to the appearance and reappearance of psychotic symptoms is called: a) Expressed Emotion (A) b) Repressed Emotions c) Regressed Emotions d) Unexpressed Emotions 80) Which of the following are constructs of Expressed Emotion in Schizophrenia? a) High levels of criticism b) Hostility c) Emotional involvement between key family members 81) In Schizophrenia Social Breakdown syndrome due to hospitalisation may involve which of the following? a) Confrontational and challenging behaviour b) Physical aggressiveness c) A lack of interest in personal welfare and hygiene
16 82) In treatment of Schizophrenia attempts to create a therapeutic community on the ward was known as milieu therapies. Which of the following are features of this therapeutic community? a) Mutual respect between staff and patients b) The opportunity for patients to become involved in vocational activities c) The opportunity for patients to become involved in recreational activities 83) In Schizophrenia Token Economy programmes are used to reinforce desired behaviours. Which of the following are examples of these desired behaviours? a) Communicating coherently b) Washing c) Combing hair 84) In Schizophrenia, an example of a reward used in Token Economy programs could be: a) Chocolate, b) Cigarettes c) Hospital privileges 85) Electroconvulsive Therapy for Schizophrenia involves passing an electric current through the head of the patient for around: a) Half a second (A) b) One minute c) Three minutes d) Five minutes
17 86) One of the forms of Psychosurgery commonly used in the 1930s is know as a prefrontal lobotomy. This procedure involves: a) Severing the pathways between the frontal lobes and lower brain areas (A) b) Removing the frontal lobes c) Removing one of the frontal lobes d) Removing a section of the right frontal lobe 87) In Schizophrenia which of the following are categories of antipsychotic drugs? a) Typical or conventional antipsychotics b) Less typical antipsychotics c) Atypical antipsychotics All of the above (A) 88) Which of the following are typical symptoms of tardive dyskinesia in Schizophrenia? a) Limb tremors b) Lip-smacking and chin-wagging c) Involuntary tics 89) In Schizophrenia Personal therapy is a broad-based cognitive-behaviour programme that is designed to help such individuals with the skills needed to adapt to day-to-day living after discharge. Which of the following are examples of this type of therapy? a) Learning to identify signs of relapse b) Acquiring relaxation techniques designed to help the client deal with the anxiety and stress caused by challenging events c) ) Identifying inappropriate emotional and behavioural responses to events, and learning new and adaptive responses
18 90) In Schizophrenia a recent intervention is known as cognitive enhancement therapy. Which of the following 2 deficits does this theary address? a) Defectits in Social cognition (A) b) Deficits in Neuro cognition (A) c) Deficits in Retro cognition d) Deficits in Soma cognition 91) In Schizophrenia cognitive rehabilitation or cognitive remediation therapy is a type of training method used to improve: a) Basic cognitive processes (A) b) Social skills c) Physical ability d) Intelligence 92) Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for schizophrenia attempts to challenging the client s interpretation of: a) Their hallucinations (A) b) Their personal hygiene c) Dreams d) Dysfunctional attributions 93) In Schizophrenia reattribution therapy attempts to challenge: a) Dysfunctional attributions (A) b) Hallucinations c) Dreams d) Their personal hygiene 94) In Schizophrenia supportive family management can be used to: a) Provide reassurance and a network of social support (A)
19 b) Elect a notional headn of the family c) Enrol family members in further education d) Provide sex education 95) In Schizophrenia applied family management goes beyond education and support to include: a) Active behavioural training elements (A) b) Finacial support c) A live in counsellor d) Housing benefit 96) One of the main aims of Assertive community treatment is to: a) Decrease the number of people being treated in hospital for mental health problems (A) b) Educate communities about mental health issues c) Create specifc community centres d) Encourage care in the community 97) One of the main aims of assertive outreach treatment is to: a) Allow staff to meet clients in the client s own environment (A) b) Meet the needs of rural communities c) Serve the needs of impoverished communities d) Facilitate education third world countries 98) In Schizophrenia the community care approach has also given rise to concerns for the physical safety of individuals with mental health problems who are exposed to the stresses and rigours of everyday life, and for the safety of others in the communities in which they live. Which percent of people with mental health problems living in the community suffer physical and verbal harassment? a) 41% (A)
20 b) 2% c) 15% d) 60% 99) Australian statistics between 1975 and 1995 showed that individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia living in the community were likely to have committed a criminal offence over this period. Which of the following is the correct statistic? a) 21.6% (A) b) 40% c) 5% d) 40% 100) In Schizophrenia research suggests that the development of psychotic symptoms is related to the use of: a) Cannabis (A) b) Tobacco c) Alcohol d) Caffeine
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS
 CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
Chapter 12. Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders. PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Age Distribution of Onset 2/24/2009. Schizophrenia. Hallmark trait is psychosis
 Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis
 Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception
 Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
The psychological disorders
 The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
9/3/2014. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com
 Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications
 Reality Non-reality VS. Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications Disorganized thinking, hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behaviors What is Psychosis? Psychosis is mental disorganization to such a degree
Reality Non-reality VS. Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications Disorganized thinking, hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behaviors What is Psychosis? Psychosis is mental disorganization to such a degree
Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes
 Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes Psychotic Disorders- Week 7- Chapter 4 Narrow definitions of psychosis only require the presence of hallucinations and delusions, whereas broad definitions of psychosis incorporate
Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes Psychotic Disorders- Week 7- Chapter 4 Narrow definitions of psychosis only require the presence of hallucinations and delusions, whereas broad definitions of psychosis incorporate
Schizophrenia. Nikita Verma 2017 Page 1
 Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Schizophrenia. Positive Symptoms. Course of Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Schizophrenia. Introduction. Overview and Facts
 Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Chapter 13
 Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
8/22/2016. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited
 SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 II. A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited agitation), hebephrenia (i.e., silly and immature
SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 II. A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited agitation), hebephrenia (i.e., silly and immature
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia - continued
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS 5. Schizophrenia Schizophrenia- a group of severe psychotic disorders characterized by distortions in thinking, perception, emotion, & behavior Schizophrenia cont. Paranoid Schizophrenia
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS 5. Schizophrenia Schizophrenia- a group of severe psychotic disorders characterized by distortions in thinking, perception, emotion, & behavior Schizophrenia cont. Paranoid Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia. Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior.
 Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders The Misunderstood Disorder Speak the word schizophrenia and you ll likely receive reactions ranging from misunderstanding to fear. The disorder is largely shrouded in
Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders The Misunderstood Disorder Speak the word schizophrenia and you ll likely receive reactions ranging from misunderstanding to fear. The disorder is largely shrouded in
Schizophrenia as a mental disorder: symptoms, features, two explanations and two treatments
 D 3.5 Schizophrenia Schizophrenia as a mental disorder: symptoms, features, two explanations and two treatments Your course requires that you study two mental disorders: one being schizophrenia, and the
D 3.5 Schizophrenia Schizophrenia as a mental disorder: symptoms, features, two explanations and two treatments Your course requires that you study two mental disorders: one being schizophrenia, and the
Dr. Fred Rose. Schizophrenia. Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview. Prevalence of Schizophrenia 10/20/10. Schizophrenia vs.
 Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Autism. Childhood Autism and Schizophrenia. Autism, Part 1 Diagnostic Criteria (DSM-IV-TR) Behavioral Characteristics of Autism
 Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses
 Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
D. Exclusion of schizoaffective disorder and mood disorder with psychotic features.
 65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
Schizophrenia. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Overview. Characterized by. Disorganized Thoughts Hallucinations Delusions Bizarre behaviors
 Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Chapter 12 1/29/2018. Schizophrenia and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders. Epidemiology. Comorbidity. Lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia is 1%
 Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Epidemiology Lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia is 1% No difference related to 2 Comorbidity Substance abuse disorders Anxiety, depression,
Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Epidemiology Lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia is 1% No difference related to 2 Comorbidity Substance abuse disorders Anxiety, depression,
CHAPTER 3. Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment
 CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
Active listening. drugs used to control anxiety and agitation. Antianxiety drugs
 Active listening empathic listening in which the listener echoes, restates, and clarifies. A feature of Rogers' client-centered therapy. Antianxiety drugs drugs used to control anxiety and agitation. Antidepressant
Active listening empathic listening in which the listener echoes, restates, and clarifies. A feature of Rogers' client-centered therapy. Antianxiety drugs drugs used to control anxiety and agitation. Antidepressant
Psychotic Disorders. There is a loss of contact with and difficulty in recognizing reality.
 Psychotic Disorders A psychosis or psychotic disorder, involves a major disorganization of thought processes, confused and extreme emotional responses, and distorted perceptions of the world. There is
Psychotic Disorders A psychosis or psychotic disorder, involves a major disorganization of thought processes, confused and extreme emotional responses, and distorted perceptions of the world. There is
SCHIZOPHRENIA AND DELUSIONAL DISORDERS
 SCHIZOPHRENIA AND DELUSIONAL DISORDERS Introduction Schizophrenia and delusional disorder are distinct disorders that may share certain features, such as paranoia, suspiciousness, and unrealistic thinking.
SCHIZOPHRENIA AND DELUSIONAL DISORDERS Introduction Schizophrenia and delusional disorder are distinct disorders that may share certain features, such as paranoia, suspiciousness, and unrealistic thinking.
Schizophrenia. This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available.
 This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available. What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a severe mental health condition. However,
This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available. What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a severe mental health condition. However,
AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders
 AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders 1. If a criminal claimed that voices in their head told them to commit a murder, should they be found guilty or innocent? Why? 2. Describe interactions
AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders 1. If a criminal claimed that voices in their head told them to commit a murder, should they be found guilty or innocent? Why? 2. Describe interactions
Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness
 Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness A Psychosis refers to a state where a person loses contact with reality. The word is derived from the Latin words "psyche" meaning mind and "osis" meaning illness.
Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness A Psychosis refers to a state where a person loses contact with reality. The word is derived from the Latin words "psyche" meaning mind and "osis" meaning illness.
SCHIZOPHRENIA. The Training and Education Center Network Mental Health Association of Southeastern Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
 1 SCHIZOPHRENIA The Training and Education Center Network Mental Health Association of Southeastern Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Appendix II Handout (1/96) 2 SCHIZOPHRENIA I. WHAT IS SCHIZOPHRENIA?
1 SCHIZOPHRENIA The Training and Education Center Network Mental Health Association of Southeastern Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Appendix II Handout (1/96) 2 SCHIZOPHRENIA I. WHAT IS SCHIZOPHRENIA?
PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives
 Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders?
 Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Psychosis. Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah
 Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Announcements. Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class)
 Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
Announcements. Abnormal Psychology. I. Introduction. Deviant Distressful Dysfunctional. Deviant Distressful Dysfunctional 4/30/2014
 Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
Schizophrenia 1. Symptoms What are the symptoms? 2. Causes What is the mechanism? 3. Treatment How is it treated?
 Schizophrenia 1. Symptoms What are the symptoms? 2. Causes What is the mechanism? 3. Treatment How is it treated? 1 Video Examples of Delusional Type Schizophrenia 1) Subjective symptoms Somebody threatens
Schizophrenia 1. Symptoms What are the symptoms? 2. Causes What is the mechanism? 3. Treatment How is it treated? 1 Video Examples of Delusional Type Schizophrenia 1) Subjective symptoms Somebody threatens
PSYCHIATRIC MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION. Jerry L. Dennis, M.D. Medical Director, ADHS/DBHS
 PSYCHIATRIC MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION Jerry L. Dennis, M.D. Medical Director, ADHS/DBHS Mental Status Examination General Considerations Based on Observations During the Assessment Process Spontaneity
PSYCHIATRIC MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION Jerry L. Dennis, M.D. Medical Director, ADHS/DBHS Mental Status Examination General Considerations Based on Observations During the Assessment Process Spontaneity
Department of Public Welfare PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPAIRMENT REPORT
 Department of Public Welfare PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPAIRMENT REPORT The purpose of this report is to outline the information needed to make a disability determination. This is not a required format; however,
Department of Public Welfare PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPAIRMENT REPORT The purpose of this report is to outline the information needed to make a disability determination. This is not a required format; however,
CHAPTER 6: ANXIETY AND STRESSOR-RELATED PROBLEMS KEY TERMS
 CHAPTER 6: ANXIETY AND STRESSOR-RELATED PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Affectionless Control A type of parenting characterized by high levels of overprotection combined with a lack of warmth and care. Amygdala The
CHAPTER 6: ANXIETY AND STRESSOR-RELATED PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Affectionless Control A type of parenting characterized by high levels of overprotection combined with a lack of warmth and care. Amygdala The
Orientation to Mental Health - Student Assignment
 Orientation to Mental Health - Student Assignment This is an example structure of a case study assignment given by the Practice Educator whilst on placement. ABOUT THIS SERVICE 1. Describe the role of
Orientation to Mental Health - Student Assignment This is an example structure of a case study assignment given by the Practice Educator whilst on placement. ABOUT THIS SERVICE 1. Describe the role of
What is Schizophrenia?
 What is Schizophrenia? What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a mental illness which affects one person in every hundred. Schizophrenia interferes with the mental functioning of a person and, in the long
What is Schizophrenia? What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a mental illness which affects one person in every hundred. Schizophrenia interferes with the mental functioning of a person and, in the long
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA
 Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
Mental Status Exam 101. A Concurrent Disorders Lunch & Learn
 Mental Status Exam 101 A Concurrent Disorders Lunch & Learn 2 HELLO! Bradley Labuguen RN BScN MHM CPMHN(c) blabugue@stjosham.on.ca Nurse Educator St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton 3 Objectives Time: 50
Mental Status Exam 101 A Concurrent Disorders Lunch & Learn 2 HELLO! Bradley Labuguen RN BScN MHM CPMHN(c) blabugue@stjosham.on.ca Nurse Educator St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton 3 Objectives Time: 50
Biological Psych Schizophrenia
 Biological Psych Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Slightly more common in men Earlier onset, more severe Originally: dementia
Biological Psych Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Slightly more common in men Earlier onset, more severe Originally: dementia
Schizoaffective Disorder
 Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Psych 120. General Psychology. Today s class. Anxiety Disorders 7/26/2010
 Psych 120 General Psychology Christopher Gade Office: 1030A Office hours: MW 4:30-5:30 Email: gadecj@gmail.com Class MW 1:30-4:30 Room 2240 In the final three lecture sections of the course, we ll be discussing
Psych 120 General Psychology Christopher Gade Office: 1030A Office hours: MW 4:30-5:30 Email: gadecj@gmail.com Class MW 1:30-4:30 Room 2240 In the final three lecture sections of the course, we ll be discussing
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Chapter 15 Class Objectives What are Mood Disorders? Depression, Mania and Bipolar What are Psychotic Disorders? Schizophrenia Moods THINK on your own What are some everyday moods
Psychological Disorders Chapter 15 Class Objectives What are Mood Disorders? Depression, Mania and Bipolar What are Psychotic Disorders? Schizophrenia Moods THINK on your own What are some everyday moods
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY. Descriptions of Symptoms & Signs. Dr. Janaka Pushpakumara Department of Psychiatry FMAS/RUSL
 PSYCHOPATHOLOGY Descriptions of Symptoms & Signs Dr. Janaka Pushpakumara Department of Psychiatry FMAS/RUSL Symptoms & Signs In General Medicine, there is a clear definition of, and separation between,
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY Descriptions of Symptoms & Signs Dr. Janaka Pushpakumara Department of Psychiatry FMAS/RUSL Symptoms & Signs In General Medicine, there is a clear definition of, and separation between,
WEEK 1 - Application of the stress-vulnerability model in the context of schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder:
 WEEK 1 - Application of the stress-vulnerability model in the context of schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder: Aetiological models Theories relating to the aetiology of the mental illness can be
WEEK 1 - Application of the stress-vulnerability model in the context of schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder: Aetiological models Theories relating to the aetiology of the mental illness can be
Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health
 Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW
 SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your physician,
SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your physician,
A-Z of Mental Health Problems
 Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Unit 6: Psychopathology and Psychotherapy (chapters 11-12)
 Unit 6: Psychopathology and Psychotherapy (chapters 11-12) Learning Objective 1 (pp. 381-382): Conceptions of Mental Illness Biological Dysfunction 1. What is psychopathology? 2. What criteria are used
Unit 6: Psychopathology and Psychotherapy (chapters 11-12) Learning Objective 1 (pp. 381-382): Conceptions of Mental Illness Biological Dysfunction 1. What is psychopathology? 2. What criteria are used
Ultimate in psychological breakdown The Mad Characterized by:
 Schizophrenia Ultimate in psychological breakdown The Mad Characterized by: Gross distortions in reality Withdrawal from relationships Disorganization and fragmentation of perception, thought, emotion
Schizophrenia Ultimate in psychological breakdown The Mad Characterized by: Gross distortions in reality Withdrawal from relationships Disorganization and fragmentation of perception, thought, emotion
Bipolar Disorder. Bipolar Disorder. Theory of Depression. Explaining Mood Disorders. Theory of Depression. Suicide
 Bipolar Disorder Formerly called manic-depressive disorder. An alternation between depression and mania signals bipolar disorder. Depressive Symptoms Manic Symptoms Bipolar Disorder Many great writers,
Bipolar Disorder Formerly called manic-depressive disorder. An alternation between depression and mania signals bipolar disorder. Depressive Symptoms Manic Symptoms Bipolar Disorder Many great writers,
3/9/2017. A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course. Our purpose
 A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course Our purpose 1 What is mental Illness Definition of Mental Illness A syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual
A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course Our purpose 1 What is mental Illness Definition of Mental Illness A syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual
SCHIZOPHRENIA. What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US
 SCHIZOPHRENIA What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are there different types of Schizophrenia Yes there are Paranoid Schizophrenia: In this version of the disease, hallucinations
SCHIZOPHRENIA What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are there different types of Schizophrenia Yes there are Paranoid Schizophrenia: In this version of the disease, hallucinations
Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects
 Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects a person s thoughts, feelings and behaviours. Whilst it is serious, schizophrenia is both treatable and manageable, and we
Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects a person s thoughts, feelings and behaviours. Whilst it is serious, schizophrenia is both treatable and manageable, and we
Abnormal Passenger Behaviour. An awareness for air crew on mental illness
 Abnormal Passenger Behaviour An awareness for air crew on mental illness Why? > To build awareness for aircrew around dealing with passengers suffering from mental illness. > Develop an understanding of
Abnormal Passenger Behaviour An awareness for air crew on mental illness Why? > To build awareness for aircrew around dealing with passengers suffering from mental illness. > Develop an understanding of
Abnormal Psychology Notes
 Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
Mary Schepler
 Mary Schepler Mary.Schepler@thresholds.org WHAT WORDS OR PHRASES HAVE YOU HEARD ASSOCIATED WITH MENTAL ILLNESS? People with mental illness frighten and embarrass us and so we marginalize people who most
Mary Schepler Mary.Schepler@thresholds.org WHAT WORDS OR PHRASES HAVE YOU HEARD ASSOCIATED WITH MENTAL ILLNESS? People with mental illness frighten and embarrass us and so we marginalize people who most
General Psychology. Chapter Outline. Psychological Disorders 4/28/2013. Psychological Disorders: Maladaptive patterns of behavior that cause distress
 General Psychology Jeffrey D. Leitzel, Ph.D. Chapter 1: Behavioral (Psychological) Disorders 1 Chapter Outline Defining abnormality Historical perspectives on abnormality Classifying/identifying disorders
General Psychology Jeffrey D. Leitzel, Ph.D. Chapter 1: Behavioral (Psychological) Disorders 1 Chapter Outline Defining abnormality Historical perspectives on abnormality Classifying/identifying disorders
CHAPTER 1: CONCEPTS, PARADIGMS AND STIGMA KEY TERMS
 CHAPTER 1: CONCEPTS, PARADIGMS AND STIGMA KEY TERMS American Psychiatric Association (APA) A scientific and professional organization that represents psychiatry in the United States Amygdala The region
CHAPTER 1: CONCEPTS, PARADIGMS AND STIGMA KEY TERMS American Psychiatric Association (APA) A scientific and professional organization that represents psychiatry in the United States Amygdala The region
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents
 Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
25 Things To Know. disorders
 Biological Psych 25 Things To Know Schizo phrenia disorders Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Schizophrenia Demographic Data Slightly
Biological Psych 25 Things To Know Schizo phrenia disorders Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Schizophrenia Demographic Data Slightly
Schizophrenia. Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia? 11/30/2008. Name that Psychotic Disorder! Other psychotic disorders and causes
 Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Name that Psychotic Disorder! Chris has started spending large amounts of time guarding his home. They have bugged his phone and are sending cars past
Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Name that Psychotic Disorder! Chris has started spending large amounts of time guarding his home. They have bugged his phone and are sending cars past
Severe Mental Disorders. Etheldreda Nakimuli-Mpungu, MMed (Psych), MBChB Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Bi-polar MDD. Repeated episodes of mania and depression
 MDD Long-lasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life. Bi-polar Repeated episodes of mania and depression Biology of Depression: The
MDD Long-lasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life. Bi-polar Repeated episodes of mania and depression Biology of Depression: The
4. General overview Definition
 4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI
 Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenia. Class Objectives. Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia? 12/7/2011. Other psychotic disorders and causes
 Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Class Objectives What are Delusional Disorders? What causes Schizophrenia? How can Schizophrenia be treated? Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Class Objectives What are Delusional Disorders? What causes Schizophrenia? How can Schizophrenia be treated? Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia?
7/3/2013 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER FOURTEEN CHAPTER OUTLINE. Dementia, Delirium, and Amnestic Disorders. Oltmanns and Emery
 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION Oltmanns and Emery PowerPoint Presentations Prepared by: Ashlea R. Smith, Ph.D. This multimedia and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are
ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION Oltmanns and Emery PowerPoint Presentations Prepared by: Ashlea R. Smith, Ph.D. This multimedia and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment of Delusions and Paranoia. Dennis Combs, Ph.D. University of Tulsa
 Cognitive Behavioral Treatment of Delusions and Paranoia Dennis Combs, Ph.D. University of Tulsa Brief Background Many persons consider that the only effective treatments for schizophrenia are antipsychotic
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment of Delusions and Paranoia Dennis Combs, Ph.D. University of Tulsa Brief Background Many persons consider that the only effective treatments for schizophrenia are antipsychotic
Chapter 14 & 15: Psychological Disorders and Treatments
 Chapter 14 & 15: Psychological Disorders and Treatments 1. A person may have a strong fear of spiders, but it is not considered a disorder unless it is: A) not based in reality. B) the result of a traumatic
Chapter 14 & 15: Psychological Disorders and Treatments 1. A person may have a strong fear of spiders, but it is not considered a disorder unless it is: A) not based in reality. B) the result of a traumatic
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia
 and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
Three Minute Review. Test Yourself. and Dissociative Identity Disorder
 and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
 Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Psychosis, schizophrenia What does psychosis mean? What does schizophrenia mean? Is there any difference between them? Psychosis, schizophrenia Psychosis: -
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Psychosis, schizophrenia What does psychosis mean? What does schizophrenia mean? Is there any difference between them? Psychosis, schizophrenia Psychosis: -
Psychological Disorders: More Than Everyday Problems 14 /
 Psychological Disorders: More Than Everyday Problems 14 / Psychological Disorder(p.630) The presence of a constellation of symptoms that create significant distress; impair work, school, family, relationships,
Psychological Disorders: More Than Everyday Problems 14 / Psychological Disorder(p.630) The presence of a constellation of symptoms that create significant distress; impair work, school, family, relationships,
Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders
 Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders Dr: Weibo Liu E-mail:liuweibo1020@163.com The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University College of Medicine Category of psychotic disorders Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders Dr: Weibo Liu E-mail:liuweibo1020@163.com The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University College of Medicine Category of psychotic disorders Schizophrenia
MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS
 MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS DIAGNOSIS OF MENTAL DISORDERS DSM-IV-TR Published by APA ( 2000 ) Multiaxial system 5 categories called axes Facilitate holistic assessment for care Is a great resource
MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS DIAGNOSIS OF MENTAL DISORDERS DSM-IV-TR Published by APA ( 2000 ) Multiaxial system 5 categories called axes Facilitate holistic assessment for care Is a great resource
DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help
 DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help Introduction: The DSM5 is a foreign language! Three Questions: I. The first was, What the key assumptions made to determine the organization of the DSM5? A. Mental
DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help Introduction: The DSM5 is a foreign language! Three Questions: I. The first was, What the key assumptions made to determine the organization of the DSM5? A. Mental
Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3. By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin
 Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3 By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin ADHD: DSM-IV DSM-IV Codes are the classification found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders This is primary
Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3 By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin ADHD: DSM-IV DSM-IV Codes are the classification found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders This is primary
Index 1. The Author(s) 2018 L. Bortolotti (ed.), Delusions in Context,
 Index 1 A Abductive inferences, 42 Abuse, 3, 14, 15, 101, 105 Action, 2, 3, 10, 20, 39, 48, 50, 54, 75, 79, 87, 100, 108, 112, 113 Adaptiveness, 48, 53, 76, 83, 98,,, n8, 110 Adjustment heuristic, 45,
Index 1 A Abductive inferences, 42 Abuse, 3, 14, 15, 101, 105 Action, 2, 3, 10, 20, 39, 48, 50, 54, 75, 79, 87, 100, 108, 112, 113 Adaptiveness, 48, 53, 76, 83, 98,,, n8, 110 Adjustment heuristic, 45,
Who has Schizophrenia? What is Schizophrenia? 11/20/2013. Module 33. It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders!
 What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man walks the streets of New York with aluminum foil under
What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man walks the streets of New York with aluminum foil under
Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 2
 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 2 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 3 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 4 Phobic Disorders A phobia is an intense and irrational fear of a particular object or situation;
Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 2 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 3 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 4 Phobic Disorders A phobia is an intense and irrational fear of a particular object or situation;
Psychology Chapter 15 Study Guide
 Psychology Chapter 15 Study Guide Psychological disorders patterns of thoughts feelings or actions that are deviant distressful of dysfunctional Disorder refers state of mental/behavioral ill health Patterns
Psychology Chapter 15 Study Guide Psychological disorders patterns of thoughts feelings or actions that are deviant distressful of dysfunctional Disorder refers state of mental/behavioral ill health Patterns
Cognitive Disorders, Anxiety Disorders and Mood Disorders
 Cognitive Disorders, Anxiety Disorders and Mood Disorders Schizophrenia Severe psychological disorder characterized by disturbances in thought and language perception and attention motor activity mood
Cognitive Disorders, Anxiety Disorders and Mood Disorders Schizophrenia Severe psychological disorder characterized by disturbances in thought and language perception and attention motor activity mood
Schizophrenia. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Psychological Disorders. Module 51. Schizophrenia
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Schizophrenia Module 51 2 Psychological Disorders Schizophrenia Symptoms
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Schizophrenia Module 51 2 Psychological Disorders Schizophrenia Symptoms
ASAM Criteria, Third Edition Matrix for Matching Adult Severity and Level of Function with Type and Intensity of Service
 1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 0 1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 1 1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 2 The patient
1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 0 1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 1 1: Acute Intoxication and/or Withdrawal Potential Risk Rating: 2 The patient
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
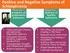 Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
CHAPTER 13 SCHIZOPHRENIA
 1 Psychotic Disorders Bio Treatment Last Prev 2 CHAPTER 13 SCHIZOPHRENIA AND OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS (PP. 476-511) History Kraepelin Positive Delusions Hallucinations Avolition Perspectives Bleuler Symptoms
1 Psychotic Disorders Bio Treatment Last Prev 2 CHAPTER 13 SCHIZOPHRENIA AND OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS (PP. 476-511) History Kraepelin Positive Delusions Hallucinations Avolition Perspectives Bleuler Symptoms
Schizophrenia and Related Psychotic Disorders
 and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
