CHAPTER 13 SCHIZOPHRENIA
|
|
|
- Dora Lynch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Psychotic Disorders Bio Treatment Last Prev 2 CHAPTER 13 SCHIZOPHRENIA AND OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS (PP ) History Kraepelin Positive Delusions Hallucinations Avolition Perspectives Bleuler Symptoms Diverse Symptoms Negative Alogia Disorganized Speech Clinical Description Anhedonia Types Emotion & Behav Aff-Flat Stats Paranoid Catatonic Causes Genes Undiff Dev Disorganized Residual Asociality PsySoc Neuro Dop Cult Brain Other PsyDis Culture Psy/Soc Stress Schizophreniform Schizoaffective Delusional Brief Psy Dis Families & Relapse Shared Psy Dis SCHIZOPHRENIA & PSYCHOSIS: PERSPECTIVES (PP ) Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis: broad term refers to hallucinations and/or delusions Schizophrenia: type of psychosis with disturbed thought, language, and behaviour Psychoses and Schizophrenia heterogeneous (mixed) Canadian National Outcomes Measurement Study: most people with schizophrenia unemployed and poor (Smith et al., 2006) Historical Background Benedict Morel: Demence (loss of mind) precoce (early, premature) Emil Kraepelin: Dementia Praecox, focus on onset and outcomes (+1) Eugen Bleuler: introduced Schizophrenia or Splitting of Mind (+2) 3 KRAEPELIN S SYMPTOMS (1919) 1. Hallucinations A. Auditory Unpleasant voices Voices that comment on thoughts and doings of patient Commanding voices Patient's own thoughts spoken aloud B. Tactile Somatic Sexual C. Smell and Taste 2. Delusions Delusions of influence Delusions of persecution Grandiose delusions Sexual delusions Ideas of reference 3. Incoherence of thought and speech Stereotypy of speech Poverty of speech Mutism Neologisms 4. Catatonic symptoms Automatic obedience Echolalia and echopraxia Stereotypy of movement Catatonic excitement Mannerisms Negativism 5. Disordered Attention 6. Disordered Judgement 7. Emotional dullness 8. Avolition 9. Autism 4 BLEULER S FUNDAMENTAL SYMPTOMS (1911) 1. Association Lack of purpose or goal in speech; poverty of ideas Thought condensations Stereotypy; echolalia Thought blocking Pressure of thoughts; clang associations 2. Affectivity Lack of depth to affect; restricted affect Lack of consistency of affective manifestation Inappropriate or blunted affect 3. Attention Lack of selectivity of attention; impaired active attention 4. Ambivalence Affective ambivalence: same concept accompanied simultaneously by pleasant and unpleasant feelings Ambivalence of will: patient wishes and does not wish same thing at same time Intellectual ambivalence: patient expresses contradictory thoughts in same sentence 5. Autism 5 SCHIZOPHRENIA AND PSYCHOSIS: PERSPECTIVES 6 Impact of Early Ideas on Current Thinking About Schizophrenia Many of Kraepelin and Bleuler s ideas still with us Understanding onset and course still considered important Identifying symptoms No shared set of characteristics Number of distinct symptoms not shared by all diagnosed with Schizophrenia Serious disorder and quite prevalent (+1) Associated with much stigma (+2) 1
2 RELATIVE PREVALENCE 7 STIGMA AND SCHIZOPHRENIA 8 8 SCHIZOPHRENIA: CLINICAL DESCRIPTION Clinical Description DSM criteria (+1) Symptoms (+2): 3 Clusters Positive Negative Disorganized Types of Schizophrenia Other Psychotic Disorders Statistics Development Culture SCHIZOPHRENIA: POSITIVE SYMPTOM CLUSTER (PP ) 12 Positive Symptoms Active displays of abnormal behaviour, distortions of normal behaviour e.g., delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech Delusions: The Basic Feature of Madness Gross misrepresentations of reality e.g., delusions of grandeur or persecution (+1) Hallucinations: Auditory and/or Visual Experience of sensory events without environmental input Can involve all senses, primarily auditory (+2) Nature of auditory and visual hallucinations: SPECT studies (+3) and verbal reports (+4) 2
3 Delusion of control 13 False belief that people or external forces control one's thoughts, feelings, impulses, or behavior. May describe experience that aliens actually make him or her move in certain ways and that person affected has no control over bodily movements. Thought broadcasting (false belief that affected person's thoughts are heard aloud), thought insertion, and thought withdrawal (belief that outside force, person, or group of people is removing or extracting person's thoughts). Delusion of reference Falsely believes insignificant remarks, events, or objects in environment have personal meaning or significance. May believe that he or she is receiving special messages from news anchor person on television. Usually meaning assigned to these events is negative, but "messages" can also have grandiose quality. Persecutory delusions Most common type. Involve theme of being followed, harassed, cheated, poisoned or drugged, conspired against, spied on, attacked, or obstructed in pursuit of goals. Sometimes delusion is isolated and fragmented (such as false belief that co-workers are harassing), but sometimes well-organized complex set of delusions ("systematized delusions"). Person with persecutory delusions may believe, for example, that he or she is followed by government organizations because "persecuted" person has been falsely identified as a spy. Systems can be so broad and complex that they explain everything that happens to person. Religious delusion Delusion with religious or spiritual content. May be combined with other delusions, such as grandiose delusions (belief that affected person chosen by God, for example), delusions of control, or delusions of guilt. Beliefs normal for religious or cultural background not delusions. Hallucinations 14 Perceive something that is not really there Affect about 70% of Schizophrenia patients Auditory hallucinations, or hearing things Most common type of hallucination in Schizophrenia Person may hear voice calling his or her name or hear many voices talking, sometimes saying things that are frightening May hear voices telling them to do things (command hallucinations), such as harm themselves or someone else Visual hallucinations, or seeing things Person may see another person, animal, or object that other people do not see Sometimes pleasant, and sometimes frightening Other types of hallucinations Include tasting (gustatory hallucination), smelling (olfactory hallucination), or feeling (tactile hallucination) something that is not there Not all hallucinations are symptoms of mental illness May occur when person is about to fall asleep (hypnagogic hallucinations) or when person is just waking up (hypnopompic hallucinations) People may wrongly hear someone call their name Widows and Widowers imagine sounds associated with dead partner Auditory hallucinations associated with Broca s area (speech production) 15 How people with Schizophrenia describe their hallucinations (Nayani et al, 1995) Commanding, Critical, Abusive, Frightening, Third person or neutral, Arguing, Pleasant, Questioning, Laughing, Sad 16 SCHIZOPHRENIA: NEGATIVE SYMPTOM CLUSTER (PP ) Negative Symptoms Absence or insufficiency of normal behaviour e.g., emotional / social withdrawal, apathy, poverty of thought / speech Spectrum of Negative Symptoms Avolition (or apathy): inability to initiate and persist in activities Alogia: relative absence of speech Anhedonia: lack of pleasure, or indifference to pleasurable activities Affective flattening: show little expressed emotion, but may still feel emotion Asociality: Poor social skills, little interest in socializing 17 SCHIZOPHRENIA: DISORGANIZED SYMPTOM CLUSTER (P. 484) Disorganized Symptoms Include severe and excess disruptions in speech, behaviour, emotion e.g., rambling speech, erratic behaviour, inappropriate affect Disorganized Speech ( ) Cognitive slippage: illogical and incoherent speech Tangentiality: Going off on a tangent and not answering a question directly Loose associations or derailment: taking conversation in unrelated directions 18 3
4 Tangentiality 19 Replying to questions in tangential or irrelevant manner. e.g: Q: "What city are you from? A: "Well, that's a hard question. I'm from Iowa. I really don't know where my relatives came from, so I don't know if I'm Irish or French". Derailment Ideas slip off track on to another which is obliquely related or unrelated. e.g. "The next day when I'd be going out you know, I took control, like uh, I put bleach on my hair in California". Circumstantiality Speech that is delayed at reaching goal. Excessive long windedness. e.g. "What is your name?" "Well, sometimes when people ask me that I have to think about whether or not I will answer because some people think its an odd name even though I don t really because my mom gave it to me but its as good a name as any in my opinion but yeah it's Tom. Loss of goal Failure to show chain of thought to natural conclusion. Distractible speech During mid speech, subject is changed in response to a stimulus. e.g. "Then I left San Francisco and moved to... where did you get that tie?" Blocking Interruption of train of speech before completed. 20 Pressure of Speech Increase in amount of spontaneous speech compared to what is considered customary. Incoherence (word salad) Speech that is unintelligible: real words strung together in incoherent gibberish, e.g. question "Why do people believe in God?" elicits response like "Because he makes a twirl in life, my box is broken help me blue elephant. Isn't lettuce brave? I like electrons. Hello, beautiful." Illogicality Conclusions are reached that do not follow logically (non sequiturs or faulty inductive inferences). e.g. "Do you think this will fit in that box?" draws a reply like "well duh, its brown, isn t it?" Clanging Sounds rather than meaningful relationships appear to govern words. e.g. "I'm not trying to make noise. I'm trying to make sense. If you can't make sense out of nonsense, well, have fun". Echolalia Echoing other people's speech e.g. "Can we talk for a few minutes?", "Talk for a few minutes". Neologisms: 21 New word formations: e.g. "I got so angry I picked up a dish and threw it at the geshinker". Word approximations Old words used in new and unconventional way. e.g. "His boss was a seeover". Perseveration Persistent repetition of words or ideas. e.g. "I'll think I'll put on my hat, my hat, my hat, my hat, my hat..." Stilted speech Speech excessively stilted and formal: e.g. "The attorney comported himself indecorously". Self-reference Patient repeatedly and inappropriately refers back to self: e.g. "What's the time?", "It's 7 o'clock. That's my problem". Phonemic paraphasia Mispronunciation; syllables out of sequence: e.g. "I slipped on the lice broke my arm". Semantic paraphasia Substitution of inappropriate word. e.g. "I slipped on the coat, on the ice I mean, and broke my book". SCHIZOPHRENIA: DISORGANIZED SYMPTOM CLUSTER (PP ) Nature of Disorganized Affect Inappropriate emotional behaviour: e.g., crying when should be laughing Nature of Disorganized Behaviour Variety of unusual behaviours Catatonia: spectrum from wild agitation, waxy flexibility, to complete immobility 22 SUBTYPES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA (PP ) Subtypes (+1) Paranoid Type (DSM +2) Intact cognitive skills and affect Do NOT show disorganized behaviour Hallucinations and delusions thematic (grandeur or persecution) Best prognosis of all types Disorganized Type (DSM +2) Marked disruptions in speech and behaviour, flat or inappropriate affect Hallucinations and delusions have theme, but fragmented Develops early, tends to be chronic, lacks periods of remissions 4
5 25 SUBTYPES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA (P. 486) Catatonic Type (DSM +1) Unusual motor responses and odd mannerisms: e.g., echolalia, echopraxia Tends to be severe and quite rare Undifferentiated Type Wastebasket category Major symptoms of schizophrenia, but fail to meet criteria for another type Residual Type (DSM +2) One past episode of schizophrenia Continue to display less extreme residual symptoms (e.g., odd beliefs) OTHER DISORDERS WITH PSYCHOTIC FEATURES 29 (PP ) Schizophreniform Disorder Schizophrenic symptoms for few months Good premorbid functioning; most resume normal lives Schizoaffective Disorder Independent symptoms of schizophrenia and mood disorder Prognosis similar to people with schizophrenia Do not tend to get better on their own Delusional Disorder Delusions contrary to reality without other major symptoms Many show other negative symptoms of schizophrenia Type of delusions include erotomanic, grandiose, jealous, persecutory, and somatic Extremely rare, better prognosis than schizophrenia OTHER DISORDERS WITH PSYCHOTIC FEATURES (PP ) Brief Psychotic Disorder Experience one or more positive symptoms of schizophrenia Usually precipitated by extreme stress or trauma Tends to remit on its own Shared Psychotic Disorder Delusions from one person manifest in another person Little is known about this condition Schizotypal Personality Disorder May reflect less severe form of schizophrenia 30 5
6 SCHIZOPHRENIA: SOME FACTS AND STATISTICS (PP ) Onset and Prevalence of Schizophrenia worldwide About 0.2% to 1.5% (or about 1% population) : implies about 300,000 in Canada; 10,000 in Manitoba Usually develops in early adulthood, but can emerge at any time Generally Chronic Most moderate-to-severe impairment throughout lives Life expectancy in persons with schizophrenia slightly less than average : Suicide, Lifestyle (Smoking, Overweight) Affects Males and Females About Equally Females tend to have better long-term prognosis Schizophrenia Appears to Have Strong Genetic Component (see Causes) STATISTICS Development (Natural History) Some signs of disorder in children prior to full manifestation Early onset, earlier for males than females (+1) Positive symptoms tend to diminish in older adults and Negative symptoms increase Relapse Rates (F ) Repeated episodes common Relapse rates high; see also Expressed Emotion Gender differences in onset of schizophrenia in a sample of 470 patients STATISTICS Cultural Factors Disorder observed in many diverse cultures: some debate about whether prevalence varies Universally causes distress Course and outcome varies somewhat (see later discussion of relapse and Emotional Expression) Incidence higher in Immigrants to developed countries Blacks and other minorities more likely to be diagnosed with Psychotic disorder (+1) Bias and stereotyping during diagnosis Stress of racism and discrimination EDELSOHN (2005) 36 Reviewed psychiatric emergency visits from 1997 to visits for 1362 patients 13 to 17 years old Measured age, sex, ethnicity, voluntary or involuntary arrival status, involvement of child protection services, and violent behavior (used weapon, fought with or without implement, inflicted property damage, or made threats) African Americans 3.3 times as likely as Whites to be diagnosed with schizophrenia or psychosis Latinos 2.9 times more likely than Whites to have these diagnoses Results present controlling for gender, age, substance abuse, involvement of protective services, arrival status 6
7 CAUSES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA 37 CAUSES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA: GENETIC RESEARCH (PP ) Family Studies Inherit tendency for schizophrenia, not specific form Other family members at increased risk, but genes alone not enough Twin Studies (+1 +2) Risk in monozygotic twins is 48% Risk drops to 17% for fraternal (dizygotic) twins Genetic Relatedness Risk increases as function of genetic relatedness (+3) One need not show symptoms to pass on genes (+4) Adoption Studies Risk high in adopted children of biological parent with schizophrenia 38 Genain quadruplets All identical twins All affected with Schizophrenia, two more seriously CAUSES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA: GENETIC RESEARCH (P. 492) 42 CAUSES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA: GENETIC RESEARCH (P. 491) 7
8 GENETIC & BEHAVIOURAL MARKERS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA (P. 493) Search for Genetic Markers: Linkage and Association Studies Identify sites on chromosomes with relevant genes Search for genetic markers is still inconclusive Promising effects often fail to replicate Schizophrenia likely to involve multiple genes (polygenic) Search for Behavioural Markers: Smooth-Pursuit Eye Movement Method: track moving object visually with head kept still Tracking deficit in persons with schizophrenia, and relatives 43 CAUSES : NEUROTRANSMITTER INFLUENCES (PP ) Neurobiology and Neurochemistry: Dopamine Hypothesis Drugs that increase dopamine (agonists), result in schizophreniclike behaviour(+1) Drugs that decrease dopamine (antagonists), reduce schizophrenic-like behaviour(+1) e.g., neuroleptics and L-Dopa for Parkinson s disease Dopamine hypothesis problematic and overly simplistic Current theories emphasize several neurotransmitters and their interaction 44 CAUSES: NEUROTRANSMITTERS (P. 494) 45 CAUSES: OTHER NEUROBIOLOGICAL 46 INFLUENCES (PP ) Structural and Functional Abnormalities in Brain Enlarged ventricles and reduced tissue volume (+1 +2) Hypofrontality: less active frontal lobes (major dopamine pathway) Viral Infections During Early Prenatal Development Relation between early viral exposure and schizophrenia inconclusive Conclusions About Neurobiology and Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is associated with diffuse Neurobiological Dysregulation Structural and functional abnormalities in brain not unique to Schizophrenia CAUSES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA: NEUROTRANSMITTER INFLUENCES (P. 495) 8
9 CAUSES: PSYCHOLOGICAL & SOCIAL (PP ) Stress and other environmental factors May activate underlying vulnerability or increase risk of relapse Obstetric factors: maternal exposure to viruses while pregnant, other prenatal stressors, birth complications (+1) e.g., increase in incidence during WW II famine in Netherlands (+2) Incidence higher in cities, especially core, and in immigrants: social disadvantage? (Chicago data +3) Family Interactions Families show ineffective communication patterns High Expressed Emotion in family associated with relapse (+4 +5 and slide 72 in treatment) Role of Psychological Factors Psychological factors likely minimal effect as cause Diathesis-Stress Models (+6 +7) SCHIZOPHRENIA AND WAR-TIME FAMINE DISTRIBUTION OF SCHIZOPHRENIA IN CHICAGO: SOCIAL CLASS? EXPRESSED EMOTION Definition Criticism: Statements of dislike, annoyance, resentment with negative tone Over-involvement: Extreme over-protectiveness, overconcern, self-sacrifice, exaggerated emotional responses regarding patient High Expressed Emotion "I always say, 'Why don't you pick up a book, do a crossword or something like that to keep your mind off it.' That's even too much trouble." "I've tried to jolly him out of it and pestered him into doing things." "He went round the garden 90 times, in the door, back out the door. I said 'Have a chair, sit out in the sun.' Well he nearly bit my head off." Low Expressed Emotion "I know it's better for her to be on her own, to get away from me and try to do things on her own." "Whatever she does suits me." "I just tend to let it go because I know that when she wants to speak she will speak." 53 CAUSES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA: PSYCHOLOGICAL AND SOCIAL INFLUENCES (P. 498) 54 9
10 Schizophrenia results from elevated Susceptibility plus exposure to stress Example of Cannabis use (+1 +2) DIATHESIS-STRESS MODEL 55 Genetic Predisposition interacts with Cannabis Abuse Risk & Cannabis Use (+1) COMT gene influences neurotransmitter functioning, especially in frontal lobes Inherit Val or Met variant of COMT gene from Mother and Father: 4 possibilities: M+M, M+V, V+M, and V+V V+V group increased risk IF they regularly consume cannabis during adolescence (Caspi et al, 2005) Hypothetical outcome (right) DIATHESIS-STRESS AND CANNABIS USE 56 SCHIZOPHRENIA AND CANNABIS USE 57 TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA TREATMENT: BIOLOGICAL (PP ) Historical Precursors 59 Antipsychotic (Neuroleptic) Medications Medication treatment often first line treatment (+1) Began in 1950s: reduced hospitalizations (+2) Most reduce or eliminate positive symptoms, and modify brain functioning (+3) Acute and permanent extrapyramidal and Parkinson-like side effects are common (+1 +4) Compliance often problem because of side effects Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Relatively untested procedure for treatment of hallucinations 60 10
11 Frequency of Side Effects in Schizophrenics 64 Muscle Spasms, Tremors, Inner Restlessness, Weight Gain, Loss Of Energy (sedation), Loss of Sex Drive, Effects on Eyes PSYCHOSOCIAL INTERVENTIONS (PP ) Historical Precursors Psychosocial Approaches: Overview and Goals Behavioural (i.e., token economies) on inpatient units (+1) Community care programs Social and living skills training Behavioural family therapy Vocational rehabilitation 1996 British Review of treatments (+2) Recent Review of Cognitive-Behavioral Approaches (+3) Psychosocial approaches provide benefits over medication therapy alone Relapse rates lower with psychosocial interventions added to medication (+4) Early Interventions (+5) include Family (& EE +6) 65 Dickerson et al (2005). The token economy for schizophrenia: Review of the literature and recommendations for future research. Schizophrenia Research, 75, principles of operant conditioning and social learning Developed in 1950s and 1960s for long-stay hospital patients 66 Fallen out of favor since 13 controlled studies of token economy reviewed Evidence of token economy's effectiveness in increasing adaptive behaviors of patients with schizophrenia Most studies limited by methodological shortcomings and historical context More research needed to determine specific benefits of token economy when used in combination with contemporary psychosocial and psychopharmacological treatments Wong (2006) Describes successful behavioral programs in 1960s and 1970s, including token economies Argues that behavioral approaches were undermined by perhaps questionable efforts of drug companies and psychiatrists to promote biological model for disorders, a perspective that Wong challenges 11
12 67 Gould et al (2004). Cognitive Therapy for Psychosis in 68 Schizophrenia: An Effect Size Analysis Meta-analysis used all available controlled treatment outcome studies of cognitive therapy (CT) for psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia Effect sizes calculated for 7 studies involving 340 subjects Mean effect size for reduction of psychotic symptoms was 0.65 Follow-up analyses in 4 studies indicated that CT patients continued to make gains over time (ES = 0.93) Findings suggest that CT effective treatment for schizophrenics with persistent psychotic symptoms Further research needed to: Determine replicability of standardized cognitive interventions Evaluate clinical significance of cognitive therapy for schizophrenia Determine which patients most likely to benefit PSYCHOSOCIAL TREATMENT (P. 504) Early Interventions for Schizophrenia FAMILY INTERVENTION AND EE 71 SUMMARY OF SCHIZOPHRENIA AND PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS (P. 508) 72 Schizophrenia includes spectrum of cognitive, emotional, and behavioural dysfunctions Positive, Negative, and Disorganized symptom clusters DSM-IV divides schizophrenia into five subtypes Other DSM-IV disorders include psychotic features Several causative factors implicated for schizophrenia Successful treatment rarely includes complete recovery 71 12
Chapter 12. Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders. PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Dr. Fred Rose. Schizophrenia. Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview. Prevalence of Schizophrenia 10/20/10. Schizophrenia vs.
 Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Age Distribution of Onset 2/24/2009. Schizophrenia. Hallmark trait is psychosis
 Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception
 Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis
 Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited
 SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 II. A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited agitation), hebephrenia (i.e., silly and immature
SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 II. A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited agitation), hebephrenia (i.e., silly and immature
The psychological disorders
 The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
9/3/2014. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia - continued
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
8/22/2016. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications
 Reality Non-reality VS. Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications Disorganized thinking, hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behaviors What is Psychosis? Psychosis is mental disorganization to such a degree
Reality Non-reality VS. Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications Disorganized thinking, hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behaviors What is Psychosis? Psychosis is mental disorganization to such a degree
Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness
 Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness A Psychosis refers to a state where a person loses contact with reality. The word is derived from the Latin words "psyche" meaning mind and "osis" meaning illness.
Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness A Psychosis refers to a state where a person loses contact with reality. The word is derived from the Latin words "psyche" meaning mind and "osis" meaning illness.
Schizophrenia. Nikita Verma 2017 Page 1
 Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Schizophrenia. Positive Symptoms. Course of Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
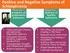 Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Schizophrenia. Introduction. Overview and Facts
 Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS
 CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network
 Positive and Negative Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart
Ultimate in psychological breakdown The Mad Characterized by:
 Schizophrenia Ultimate in psychological breakdown The Mad Characterized by: Gross distortions in reality Withdrawal from relationships Disorganization and fragmentation of perception, thought, emotion
Schizophrenia Ultimate in psychological breakdown The Mad Characterized by: Gross distortions in reality Withdrawal from relationships Disorganization and fragmentation of perception, thought, emotion
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com
 Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Psychotic Disorders. There is a loss of contact with and difficulty in recognizing reality.
 Psychotic Disorders A psychosis or psychotic disorder, involves a major disorganization of thought processes, confused and extreme emotional responses, and distorted perceptions of the world. There is
Psychotic Disorders A psychosis or psychotic disorder, involves a major disorganization of thought processes, confused and extreme emotional responses, and distorted perceptions of the world. There is
D. Exclusion of schizoaffective disorder and mood disorder with psychotic features.
 65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
Autism. Childhood Autism and Schizophrenia. Autism, Part 1 Diagnostic Criteria (DSM-IV-TR) Behavioral Characteristics of Autism
 Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW
 SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your physician,
SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your physician,
Schizophrenia. This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available.
 This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available. What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a severe mental health condition. However,
This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available. What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a severe mental health condition. However,
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses
 Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
Schizophrenia and Related Psychotic Disorders
 and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes
 Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes Psychotic Disorders- Week 7- Chapter 4 Narrow definitions of psychosis only require the presence of hallucinations and delusions, whereas broad definitions of psychosis incorporate
Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes Psychotic Disorders- Week 7- Chapter 4 Narrow definitions of psychosis only require the presence of hallucinations and delusions, whereas broad definitions of psychosis incorporate
Announcements. Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class)
 Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
Schizophrenia. This factsheet covers -
 Schizophrenia There are many misconceptions about schizophrenia. It is an illness that can be treated. One in a hundred people will experience schizophrenia during their lifetime 1 and the majority of
Schizophrenia There are many misconceptions about schizophrenia. It is an illness that can be treated. One in a hundred people will experience schizophrenia during their lifetime 1 and the majority of
Announcements. Abnormal Psychology. I. Introduction. Deviant Distressful Dysfunctional. Deviant Distressful Dysfunctional 4/30/2014
 Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
Schizophrenia. Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior.
 Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Psychosis. Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah
 Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Chapter 13
 Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives
 Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
SCHIZOPHRENIA. What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US
 SCHIZOPHRENIA What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are there different types of Schizophrenia Yes there are Paranoid Schizophrenia: In this version of the disease, hallucinations
SCHIZOPHRENIA What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are there different types of Schizophrenia Yes there are Paranoid Schizophrenia: In this version of the disease, hallucinations
Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders The Misunderstood Disorder Speak the word schizophrenia and you ll likely receive reactions ranging from misunderstanding to fear. The disorder is largely shrouded in
Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders The Misunderstood Disorder Speak the word schizophrenia and you ll likely receive reactions ranging from misunderstanding to fear. The disorder is largely shrouded in
Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects
 Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects a person s thoughts, feelings and behaviours. Whilst it is serious, schizophrenia is both treatable and manageable, and we
Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects a person s thoughts, feelings and behaviours. Whilst it is serious, schizophrenia is both treatable and manageable, and we
Disorganized Symptoms of Psychosis
 Disorganized Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart Technologies
Disorganized Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart Technologies
5) Which of he following is not one of the main clinical symptoms of Schizophrenia? a) Delusions b) Hallucinations c) Apathy d) Narcolepsy (A)
 Chapter 7.teachers 1 In Schizophrenia, the phenomenon known as downward drift means? a) Falling to the bottom of the social ladder b) Become homeless c) Inability to hold down a job 2) Which of the following
Chapter 7.teachers 1 In Schizophrenia, the phenomenon known as downward drift means? a) Falling to the bottom of the social ladder b) Become homeless c) Inability to hold down a job 2) Which of the following
Schizophrenia. Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia? 11/30/2008. Name that Psychotic Disorder! Other psychotic disorders and causes
 Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Name that Psychotic Disorder! Chris has started spending large amounts of time guarding his home. They have bugged his phone and are sending cars past
Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Name that Psychotic Disorder! Chris has started spending large amounts of time guarding his home. They have bugged his phone and are sending cars past
DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help
 DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help Introduction: The DSM5 is a foreign language! Three Questions: I. The first was, What the key assumptions made to determine the organization of the DSM5? A. Mental
DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help Introduction: The DSM5 is a foreign language! Three Questions: I. The first was, What the key assumptions made to determine the organization of the DSM5? A. Mental
SCHIZOPHRENIA AND DELUSIONAL DISORDERS
 SCHIZOPHRENIA AND DELUSIONAL DISORDERS Introduction Schizophrenia and delusional disorder are distinct disorders that may share certain features, such as paranoia, suspiciousness, and unrealistic thinking.
SCHIZOPHRENIA AND DELUSIONAL DISORDERS Introduction Schizophrenia and delusional disorder are distinct disorders that may share certain features, such as paranoia, suspiciousness, and unrealistic thinking.
Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health
 Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
 Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Psychosis, schizophrenia What does psychosis mean? What does schizophrenia mean? Is there any difference between them? Psychosis, schizophrenia Psychosis: -
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Psychosis, schizophrenia What does psychosis mean? What does schizophrenia mean? Is there any difference between them? Psychosis, schizophrenia Psychosis: -
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Chapter 12 PART II V. What Are Dissociative Disorders? Sudden but temporary alteration in consciousness, identity, sensorimotor behavior, or memory Relatively rare, but very dramatic
Psychological Disorders Chapter 12 PART II V. What Are Dissociative Disorders? Sudden but temporary alteration in consciousness, identity, sensorimotor behavior, or memory Relatively rare, but very dramatic
10. Psychological Disorders & Health
 10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA
 Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY. Descriptions of Symptoms & Signs. Dr. Janaka Pushpakumara Department of Psychiatry FMAS/RUSL
 PSYCHOPATHOLOGY Descriptions of Symptoms & Signs Dr. Janaka Pushpakumara Department of Psychiatry FMAS/RUSL Symptoms & Signs In General Medicine, there is a clear definition of, and separation between,
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY Descriptions of Symptoms & Signs Dr. Janaka Pushpakumara Department of Psychiatry FMAS/RUSL Symptoms & Signs In General Medicine, there is a clear definition of, and separation between,
Chapter 12 1/29/2018. Schizophrenia and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders. Epidemiology. Comorbidity. Lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia is 1%
 Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Epidemiology Lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia is 1% No difference related to 2 Comorbidity Substance abuse disorders Anxiety, depression,
Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Epidemiology Lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia is 1% No difference related to 2 Comorbidity Substance abuse disorders Anxiety, depression,
Bi-polar MDD. Repeated episodes of mania and depression
 MDD Long-lasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life. Bi-polar Repeated episodes of mania and depression Biology of Depression: The
MDD Long-lasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life. Bi-polar Repeated episodes of mania and depression Biology of Depression: The
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI
 Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Psychosis, Mood, and Personality: A Clinical Perspective
 Psychosis, Mood, and Personality: A Clinical Perspective John R. Chamberlain, M.D. Assistant Director, Psychiatry and the Law Program Assistant Clinical Professor University of California San Francisco
Psychosis, Mood, and Personality: A Clinical Perspective John R. Chamberlain, M.D. Assistant Director, Psychiatry and the Law Program Assistant Clinical Professor University of California San Francisco
Orientation to Mental Health - Student Assignment
 Orientation to Mental Health - Student Assignment This is an example structure of a case study assignment given by the Practice Educator whilst on placement. ABOUT THIS SERVICE 1. Describe the role of
Orientation to Mental Health - Student Assignment This is an example structure of a case study assignment given by the Practice Educator whilst on placement. ABOUT THIS SERVICE 1. Describe the role of
Schizophrenia. Class Objectives. Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia? 12/7/2011. Other psychotic disorders and causes
 Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Class Objectives What are Delusional Disorders? What causes Schizophrenia? How can Schizophrenia be treated? Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Class Objectives What are Delusional Disorders? What causes Schizophrenia? How can Schizophrenia be treated? Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia?
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents
 Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
4. General overview Definition
 4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
ACOEM Commercial Driver Medical Examiner Training Program
 ACOEM Commercial Driver Medical Examiner Training Program Module 7: Psychological Psychological 49 CFR 391.41(b)(9) "A person is physically qualified to drive a commercial motor vehicle if that person
ACOEM Commercial Driver Medical Examiner Training Program Module 7: Psychological Psychological 49 CFR 391.41(b)(9) "A person is physically qualified to drive a commercial motor vehicle if that person
Schizophrenia: an inside view. Nepean High School, November 2016 Introduction to Psychology class.
 Schizophrenia: an inside view Nepean High School, November 2016 Introduction to Psychology class. Schizophrenia: basic definition Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects how
Schizophrenia: an inside view Nepean High School, November 2016 Introduction to Psychology class. Schizophrenia: basic definition Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects how
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders?
 Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
PSYCHIATRIC MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION. Jerry L. Dennis, M.D. Medical Director, ADHS/DBHS
 PSYCHIATRIC MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION Jerry L. Dennis, M.D. Medical Director, ADHS/DBHS Mental Status Examination General Considerations Based on Observations During the Assessment Process Spontaneity
PSYCHIATRIC MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION Jerry L. Dennis, M.D. Medical Director, ADHS/DBHS Mental Status Examination General Considerations Based on Observations During the Assessment Process Spontaneity
- - PSYCHOSIS SUPPLEMENT. Page 1 of 15 of Psychotic Supplement. Subject ID: INTERVIEW #: INTERVIEW DATE: / / I. HALLUCINATIONS
 Subject ID: - - Page 1 of 15 of Psychotic Supplement INTERVIEW #: 1 2 3 4 5 (1 = Baseline visit, 2+ = followup visits) INTERVIEW DATE: / / PSYCHOSIS SUPPLEMENT I. HALLUCINATIONS Probes: In addition to
Subject ID: - - Page 1 of 15 of Psychotic Supplement INTERVIEW #: 1 2 3 4 5 (1 = Baseline visit, 2+ = followup visits) INTERVIEW DATE: / / PSYCHOSIS SUPPLEMENT I. HALLUCINATIONS Probes: In addition to
Schizophrenia 1. Symptoms What are the symptoms? 2. Causes What is the mechanism? 3. Treatment How is it treated?
 Schizophrenia 1. Symptoms What are the symptoms? 2. Causes What is the mechanism? 3. Treatment How is it treated? 1 Video Examples of Delusional Type Schizophrenia 1) Subjective symptoms Somebody threatens
Schizophrenia 1. Symptoms What are the symptoms? 2. Causes What is the mechanism? 3. Treatment How is it treated? 1 Video Examples of Delusional Type Schizophrenia 1) Subjective symptoms Somebody threatens
Abnormal Psychology Notes
 Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
What is Schizophrenia?
 What is Schizophrenia? What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a mental illness which affects one person in every hundred. Schizophrenia interferes with the mental functioning of a person and, in the long
What is Schizophrenia? What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a mental illness which affects one person in every hundred. Schizophrenia interferes with the mental functioning of a person and, in the long
Schizophrenia. Delusional disorders are characterized by a persistent belief that is contrary to reality. Why do people stalk?
 Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Delusional disorders are characterized by a persistent belief that is contrary to reality. There are several subtypes recognized by the DSM IV: - - Grandiose
Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Delusional disorders are characterized by a persistent belief that is contrary to reality. There are several subtypes recognized by the DSM IV: - - Grandiose
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Chapter 15 Class Objectives What are Mood Disorders? Depression, Mania and Bipolar What are Psychotic Disorders? Schizophrenia Moods THINK on your own What are some everyday moods
Psychological Disorders Chapter 15 Class Objectives What are Mood Disorders? Depression, Mania and Bipolar What are Psychotic Disorders? Schizophrenia Moods THINK on your own What are some everyday moods
Schizophrenia. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Overview. Characterized by. Disorganized Thoughts Hallucinations Delusions Bizarre behaviors
 Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
The National Institute of Mental Health:
 The National Institute of Mental Health: http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/schizophrenia/index.shtml Schizophrenia What Is Schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe, and disabling brain disorder
The National Institute of Mental Health: http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/schizophrenia/index.shtml Schizophrenia What Is Schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe, and disabling brain disorder
Mental Status Exam 101. A Concurrent Disorders Lunch & Learn
 Mental Status Exam 101 A Concurrent Disorders Lunch & Learn 2 HELLO! Bradley Labuguen RN BScN MHM CPMHN(c) blabugue@stjosham.on.ca Nurse Educator St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton 3 Objectives Time: 50
Mental Status Exam 101 A Concurrent Disorders Lunch & Learn 2 HELLO! Bradley Labuguen RN BScN MHM CPMHN(c) blabugue@stjosham.on.ca Nurse Educator St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton 3 Objectives Time: 50
 Psychopathology Psychopathy (con t) Psychopathy Characteristics High impulsivity Thrill seeking Low empathy Low anxiety What is the common factor? Callous Self-Centeredness N M P Dr. Robert Hare
Psychopathology Psychopathy (con t) Psychopathy Characteristics High impulsivity Thrill seeking Low empathy Low anxiety What is the common factor? Callous Self-Centeredness N M P Dr. Robert Hare
Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia
 Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia I. Key Points a. Schizophrenia is a chronic illness affecting all aspects of person s life i. Treatment Planning Goals 1.
Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia I. Key Points a. Schizophrenia is a chronic illness affecting all aspects of person s life i. Treatment Planning Goals 1.
Disorders. Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality.
 Disorders Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be:
Disorders Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be:
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS 5. Schizophrenia Schizophrenia- a group of severe psychotic disorders characterized by distortions in thinking, perception, emotion, & behavior Schizophrenia cont. Paranoid Schizophrenia
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS 5. Schizophrenia Schizophrenia- a group of severe psychotic disorders characterized by distortions in thinking, perception, emotion, & behavior Schizophrenia cont. Paranoid Schizophrenia
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia
 and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
Three Minute Review. Test Yourself. and Dissociative Identity Disorder
 and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
Abnormal Psychology. Defining Abnormality
 Abnormal Psychology Defining Abnormality Statistical Approach abnormality = infrequency but this is not sufficient on its own Valuative Approach abnormality = social deviance unacceptable or doesn t conform
Abnormal Psychology Defining Abnormality Statistical Approach abnormality = infrequency but this is not sufficient on its own Valuative Approach abnormality = social deviance unacceptable or doesn t conform
Schizoaffective Disorder
 Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
3/9/2017. A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course. Our purpose
 A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course Our purpose 1 What is mental Illness Definition of Mental Illness A syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual
A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course Our purpose 1 What is mental Illness Definition of Mental Illness A syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual
25 Things To Know. disorders
 Biological Psych 25 Things To Know Schizo phrenia disorders Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Schizophrenia Demographic Data Slightly
Biological Psych 25 Things To Know Schizo phrenia disorders Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Schizophrenia Demographic Data Slightly
Biological Psych Schizophrenia
 Biological Psych Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Slightly more common in men Earlier onset, more severe Originally: dementia
Biological Psych Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Slightly more common in men Earlier onset, more severe Originally: dementia
A-Z of Mental Health Problems
 Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Outline. Definition. Distress* Deviance 10/31/2012. What is abnormal? Statistical infrequency. Personal suffering. Culturally-based.
 Outline Definition Defining Abnormality Categorization and Assessment of Psychological Disorders Cultural Differences in Psychological Disorders Culture Bound Disorders Mental Health of Specific Groups
Outline Definition Defining Abnormality Categorization and Assessment of Psychological Disorders Cultural Differences in Psychological Disorders Culture Bound Disorders Mental Health of Specific Groups
Schizophrenia. Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia? 12/2/2007. Name that Psychotic Disorder! Other psychotic disorders and causes
 Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Name that Psychotic Disorder! Chris has started spending large amounts of time guarding his home. They have bugged his phone and are sending cars past
Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Name that Psychotic Disorder! Chris has started spending large amounts of time guarding his home. They have bugged his phone and are sending cars past
Psychiatry an Overview Dr. Alok Bajpai Humanities and social science Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Psychiatry an Overview Dr. Alok Bajpai Humanities and social science Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module-03 Psychiatric Disorders and their treatment-1 Lecture-10 Schizophrenia Welcome again
Psychiatry an Overview Dr. Alok Bajpai Humanities and social science Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module-03 Psychiatric Disorders and their treatment-1 Lecture-10 Schizophrenia Welcome again
SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS Psychiatry 2 Practical # 2
 Psychiatrická klinika LFUK a UNB, Bratislava SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS Psychiatry 2 Practical # 2 Author: MUDr. Ľubomíra Izáková, PhD. Supervisor: doc. MUDr. Ján Pečeňák, CSc. Podporené grantom
Psychiatrická klinika LFUK a UNB, Bratislava SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS Psychiatry 2 Practical # 2 Author: MUDr. Ľubomíra Izáková, PhD. Supervisor: doc. MUDr. Ján Pečeňák, CSc. Podporené grantom
Psychosis is a difficult term to define and is frequently misused, not only in the. Psychosis and Schizophrenia
 CHAPTER 1 Psychosis and Schizophrenia Symptom dimensions in schizophrenia Clinical description of psychosis Schizophrenia is more than a psychosis Beyond positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
CHAPTER 1 Psychosis and Schizophrenia Symptom dimensions in schizophrenia Clinical description of psychosis Schizophrenia is more than a psychosis Beyond positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Early Stages of Psychosis. Learning Objectives
 Early Stages of Psychosis Stephan Heckers, MD MSc Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Vanderbilt University Learning Objectives Summarize the five domains of psychosis Describe how psychotic
Early Stages of Psychosis Stephan Heckers, MD MSc Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Vanderbilt University Learning Objectives Summarize the five domains of psychosis Describe how psychotic
Aging and Mental Health Current Challenges in Long Term Care
 Aging and Mental Health Current Challenges in Long Term Care Stephanie Saur & Christina Pacheco Acute Care Behavioural Consultants Alzheimer Society Peel What is Mental Health? Mental health includes our
Aging and Mental Health Current Challenges in Long Term Care Stephanie Saur & Christina Pacheco Acute Care Behavioural Consultants Alzheimer Society Peel What is Mental Health? Mental health includes our
Who has Schizophrenia? What is Schizophrenia? 11/20/2013. Module 33. It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders!
 What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man walks the streets of New York with aluminum foil under
What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man walks the streets of New York with aluminum foil under
Schizophrenia. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Psychological Disorders. Module 51. Schizophrenia
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Schizophrenia Module 51 2 Psychological Disorders Schizophrenia Symptoms
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Schizophrenia Module 51 2 Psychological Disorders Schizophrenia Symptoms
Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders
 Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders Dr: Weibo Liu E-mail:liuweibo1020@163.com The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University College of Medicine Category of psychotic disorders Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders Dr: Weibo Liu E-mail:liuweibo1020@163.com The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University College of Medicine Category of psychotic disorders Schizophrenia
PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders
 PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders Chapter 10 Schizophrenia and Psychotic Disorders Outline/Overview Schizophrenia Statistics/Impact/History Criteria Prognostic indicators/ suicide Epidemiology/correlates
PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders Chapter 10 Schizophrenia and Psychotic Disorders Outline/Overview Schizophrenia Statistics/Impact/History Criteria Prognostic indicators/ suicide Epidemiology/correlates
LO S I N G TO U C H W I T H R E A L I T Y SEARCHING FOR THE SEEDS OF PSYCHOSIS
 LO S I N G TO U C H W I T H R E A L I T Y SEARCHING FOR THE SEEDS OF PSYCHOSIS Dolores Malaspina, MD, MS, MSPH Anita & Joseph Steckler Professor of Psychiatry & Child Psychiatry - NYU Langone Medical Center
LO S I N G TO U C H W I T H R E A L I T Y SEARCHING FOR THE SEEDS OF PSYCHOSIS Dolores Malaspina, MD, MS, MSPH Anita & Joseph Steckler Professor of Psychiatry & Child Psychiatry - NYU Langone Medical Center
AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders
 AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders 1. If a criminal claimed that voices in their head told them to commit a murder, should they be found guilty or innocent? Why? 2. Describe interactions
AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders 1. If a criminal claimed that voices in their head told them to commit a murder, should they be found guilty or innocent? Why? 2. Describe interactions
Results of a Survey of Expert Clinicians on Psychosis Symptoms in Deaf Individuals
 Results of a Survey of Expert Clinicians on Psychosis Symptoms in Deaf Individuals Robert Pollard, Ph.D. Deaf Wellness Center URMC Department of Psychiatry Deaf Wellness Center Staff Bob Pollard Amanda
Results of a Survey of Expert Clinicians on Psychosis Symptoms in Deaf Individuals Robert Pollard, Ph.D. Deaf Wellness Center URMC Department of Psychiatry Deaf Wellness Center Staff Bob Pollard Amanda
Accurate Diagnosis of Primary Psychotic Disorders
 Accurate Diagnosis of Primary Psychotic Disorders The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart
Accurate Diagnosis of Primary Psychotic Disorders The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart
Have you ever known someone diagnosed with a psychological disorder or on psychiatric medication?
 What is Abnormal anyway? Chapter 13-Psychological Disorders CLASS OBJECTIVES: How do we define abnormal behavior? What are Anxiety Disorders? What are Mood Disorders? What is Schizophrenia? Have you ever
What is Abnormal anyway? Chapter 13-Psychological Disorders CLASS OBJECTIVES: How do we define abnormal behavior? What are Anxiety Disorders? What are Mood Disorders? What is Schizophrenia? Have you ever
