Body Fluid Examination
|
|
|
- Angelica Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Specimen Handling Body Fluid Examination CSF: Treated as STATS because of cell lysis Studies have shown approximately 40% of CSF WBCs will have lysed after 2 hours at RT. Only 15% had lysed if the fluid was held at 4 degrees C Amniotic Fluid and Synovial Fluid also requires one hour rule because of cell lysis Pleural, Peritoneal and Pericardial Fluids may be examined ASAP. Smears may be made up to 24 hours later on refrigerated specimens. Body Fluid Examination QUALITY CONTROL: To QC Cell Counts Cell-Chex Chex from Streck LI and LII completed each shift To QC Cell Identification CAP Surveys Challenge Slides 2
2 April Challenge This is a cytospin prep of pleural fluid from an 80 year old male with CHF (Congestive Heart Failure). Identify the cells pictured. a. Monocyte/macrophages b. Reactive mesothelial cells c. Malignant cell d. Normal mesothelial cells Correct ANSWER: Normal Mesothelial cells Manual Cell Count Examine the fluid in the tube macroscopically and microscopically~ if there are cellular clumps or clots, MANUAL cell counts are performed. Body Fluid Examination 3
3 Body Fluid Examination Electronic Cell Count Blank is run prior to specimen WBC limit < 0.09 RBC limit < Results considered in the reportable range WBC: > 0.20 = 200 RBC: > = 10,000 Limitations: Cellular interference High WBC counts make a significant impact on the RBC count Never run BAL or Amniotic Fluid Differential Protocol: When to prepare a Cytospin Prep All CSF with over 5 Nucleated Cells/mm3 All body fluids, unless M.D. requests only a cell count. It is important to scan body fluids for the presence of Malignant Cells. All orders for CSF Cytology. 4
4 Optimum Cytospin Slide Quality Agitate fibrinous clots Saline wash technique for fibrinous, mucoid or highly viscous fluids specimens Pour 0.5 to 1 ml of fluid into a tube and add 10 ml of Isoton. Mix. Spin down gently in conventional centrifuge (1800 RPMs for 7 min) and make push smears from sediment. Remove supernatant fluid and prepare a cytospin prep from the sediment. Be sure to add 1 drop of albumin to the final dilution. Optimum Cytospin Slide Quality Tips for bloody: 1 drop fluid + Isoton until faint blood tinge Mucoid fluids: Mucolytic product like Mucolexx Highly viscous fluids (Synovial Fluids): Weigh 5 mg. aliquots (a pinch) of hyaluronidase and store in the freezer. Add a small volume of fluid (~0.5-1 ml) to the hyaluronidase and mix well or vortex for several seconds. Typically, the specimen will liquefy quickly (within 5 minutes). Longer incubation and/or placing the fluid in the 37 o dri-bath warmer may be needed for more resistant specimens. There is no dilution factor when hyaluronidase is used. Cytospin preps can be made from the liquefied specimen. 5
5 Optimum Cytospin Slide Quality Dilution of cellular specimens Develop a dilution scheme to avoid introducing too many cells to the cytospin chamber. Overcrowding the preparation distorts cellular morphology. Both the WBC and RBC count must be considered in developing a scheme. Suggested scheme: Maximum cell count/suspension: WBC 500/uL RBC 5,000/uL Amount cell suspension/chamber: 5 drops Optimum Cytospin Slide Quality Improper Dilution: Individual Cells can not be identified Proper Dilution of cellular specimens Proper Dilution: Same patient- Reactive Neutrophilia 6
6 Optimum Cytospin Slide Quality Cellularity Cytospin prep must show ample cellularity Cells are concentrated 20-fold by cytocentrifugation Even hypocellular samples with chamber counts of zero can yield ~35 cells per smear THE KEY: Use the maximum (0.5 ml) Optimal Cellularity WBC = 7 PREP MUST BE CELLULAR TO INSURE THAT ABNORMAL CELLS/or CONDITIONS ARE DETECTED. The Negative Gram Stain Use established guidelines when making fluid dilutions. These are not absolute criteria and should be modified as necessary to produce a cellular prep. IMPORTANT: Always use the maximum volume (0.5 ml) for preps when the WBC count is less than 50. 7
7 Optimum Cytospin Slide Quality Cytospin chamber technical tips Insure that the clip, funnel, and filter card are in place to deposit a thin layer of cells in a clearly defined area of a microscope slide. The filter card absorbs any excess fluid. For sample volumes of up to 0.5 ml, use the White Filter Card It provides a cell deposition area of 6 mm (28 mm squared). For samples volumes of up to 0.4 ml, such as Spinal Fluids for example, use the Brown Filter Card and Cap. It allows for a slower absorption of fluids. Use both brown and white card for bloody specimens. Add drop of 22% Albumin to the cytospin funnel before the addition of CSF. The albumin enhances the adherence of cells to the glass slide and reduces cell smudging or disintegration, particularly for low protein specimens such as CSF. Optimum Cytospin Slide Quality The use of albumin is not recommended for fluids other than CSF as body fluids typically contain abundant protein. Adding albumin to other body fluids may make it more difficult to produce a good prep as the excess protein clogs the filter card and reduces fluid absorption. 8
8 Optimum Cytospin Slide Quality When the fluid has a high protein content: Better slide preparation will be obtained if albumin is NOT added. All amniotic and many body fluids fall in this category. CSF specimens with a high h protein value also should not have albumin added. MOST CSF preps benefit from the addition of albumin. Optimum Cytospin Slide Quality When using Albumin, watch for INTRAcellular vs EXTRAcellular BACTERIA 9
9 DO NOT let unspun fluid run onto slide Tilt the cytospin funnel forward when removing it from the cytospin head. Artifactual changes will occur if residual fluid remaining in the cell chamber is allowed to flow back onto the slide. When this occurs, the stained cells may appear shrunken or rounded-up. Optimum Cytospin Slide Quality Cytospin Artifact Cells in Interior may be smaller with a denser nucleus than cells at the periphery 10
10 Cytospin Artifact: Nucleus Prominent Nucleolus Distorted Shape to nuclear membrane Fragments or Budding Nuclear Holes Cytospin Artifact: Nucleus Hypersegmentation g Peripheral p nucleus 11
11 Cytospin Artifact: Cytoplasm Fragmentation Cytoplasmic Shredding Localization of granules Cytospin Smear Quality Control Scan the entire cytospin prep under 10x BEFORE performing the differential If 10x scan is not done, it is possible that low volume malignant cells may be missed! Maximum volume (0.5 ml) must be used for low counts. Remake all slides that do not show good cellular distribution. If possible, review the patient diagnosis and previous reports to be alerted to the type of malignant cell that may be present. 12
12 Cerebrospinal Fluid Normal Reference Values Macroscopic Findings Microscopic Findings Cellular Morphology = Clinical Significance Malignant Cells Formed in the choroid plexus by filtration and active transport. The normal rate of CSF production is approximately 20 ml per hour. 20% of the CSF is contained in the ventricles, the rest contained in the subarachnoid space in the cranium and spinal cord. In normal adults, the CSF volume is 125 to 150 ml CSF Production The choroid plexus consists of projections of vessels and pia mater that protrude into the ventricular cavities as frond-like villi. The villi contain capillaries in a loose connective stroma. A specialized layer of ependymal cells called the choroidal epithelium overlies these villi Science Photo - Choroid plexus secretory cells, SEM 13
13 Normal Reference Values For Cerebrospinal Fluid Leukocyte count Leukocyte differential 0-5mononuclearcells cells Adults Lymphocytes 60% + 20 Monocytes 30% + 15 Neutrophils 2% + 4 Neonates Lymphocytes 20% + 15 Monocytes 70% + 20 Neutrophils 4% + 4 Macroscopic Findings: Color Appearance Normal= Clear Abnormal Xanthochromic= = RBC breakdown, increased bilirubin Bloody= = Intracranial hemorrhage, traumatic tap Cloudy= = Meningitis, CNS leukemia Turbidity: Graded 0-4+ based on the ability to read print through the CSF. Semi-quantitated: slightly hazy, hazy, slightly cloudy, cloudy, turbid 14
14 Tramatic Tap vs Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Indications of a traumatic tap: Clearing of the fluid as it is aspirated, with > blood in tube #1, < blood in tube #3 Colorless supernatant Clot in the sample Indications of pathologic bleeding: Xanthrochromia Erythrophagocytosis Positive D-dimer for cross-linked fibrin DEPOCYTE Macroscopic Appearance Cloudy = Bacterial Infection Things are not always as they seem Beware the Depocyte Used for the intrathecal treatment of neoplastic meningitis due to breast cancer Gross appearance- Milky to Cloudy Cytospin prep does not yield WBCs WBC 15
15 Microscopic Findings: Normal CSF Cells Mature Lymphocytes Reactive Lymphocytes: Reported as Few, Mod, or Many PLASMA CELL Eccentric nucleus Perinuclear halo Deep blue cytoplasm Monocytes Normal CSF Cells Intracranial Hemorrhage In body fluids, monocytes will become MACROPHAGES/HISTIOCYTES 16
16 Normal CSF Cells Erythrophage : Macrophage with variable number of phagocytosed erythrocytes Siderophage : Hemosiderin granules are golden-brown when unstained, but a deep Blue-purple stained with Wright stain. Macrophage with Hematin Crystal: Orange, rhomboid-shaped Crystals of hematoidin from the breakdown of hemoglobin Normal CSF Cells Lipophage : Macrophage with multiple small clear vacuoles. 17
17 Normal CSF Cells Immature neutrophils Mature Neutrophils Hypersegmentation maybe present Immature neutrophils are not seen normally Normal CSF Cells NRBCs/Nucleated Red Blood Cells Associated disease states and conditions: Peripheral blood contamination due to traumatic tap or hemorrhage 18
18 NRBCs/ Nucleated Red Blood Cells Normal CSF Cells With a Neutrophilia, beware the pyknotic BONE nucleus MARROW which resembles CONTAMINATION a NRBC Associated disease states and conditions: Peripheral blood contamination due to traumatic tap or hemorrhage Bone marrow contamination Case #1: This CSF Slide from a Neonate male is being evaluated. Identify the cells seen in cluster. 1. Malignant clump 2. Monocytes 3. Chondrocytes 4. CSF Lining cells 19
19 Benign Cells Uncommonly Found: Chondrocyte: Cartilage Cell Capillary Associated disease states and conditions: Cartilage Cells and/or capillaries may be present in postoperative states or after a traumatic tap Benign Cells Uncommonly Found: Ventricular Lining Cells 20
20 Benign Cells Uncommonly Found: Choroid plexus Lining cells Benign Cells Uncommonly Found: Ependymal Cells Lining cells 21
21 Case #2: CSF Slide from one-month old female with hydrocephalus. Identify the cells seen in cluster. 1. Lymphocytes 2. Malignant clump 3. Monocytes 4. CSF Lining Cells Benign Cells Uncommonly Found: Mitotic Cells Mitotic Figure Bone Marrow Contamination Rare in benign CSF Associated with Lymphocytosis, Usually Reactive 22
22 Case #3: CSF Slide from 4-month old female with hydrocephalus. What significant findings are demonstrated and should be included in the comments on this CSF exam? 1. Lymphocytes 2. Basophils 3. Capillaries and Brain tissue RED FLAG Use caution when examining a CSF that has been collected from a intra-ventricular shunt. Low Power BRAIN TISSUE CAPILLARY 23
23 Benign Cells Uncommonly Found: Endothelial cells which line the capillary RBCs captured traveling through the capillary Benign Cells Uncommonly Found: CSF collection from an intra-ventricular shunt Brain tissue Nucleus Nissle bodies Note: Individual neurons may be present Dendrites 24
24 Cellular Morphology= Clinical Significance Pleocytosis= when there are normal cells present in abnormal numbers Cells present which may be diagnostic of a disease process Microorganisms Malignant cells from metastatic tumors Predominance of Neutrophils ACUTE PHASE: Intracellular & Extracellular Bacteria PROLIFERATIVE: Neutrophage Mixed Cellular Reaction REPAIR PHASE: Reactive Lymphocytes 25
25 Predominance of Lymphocytes MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Note Plasmacytoid Lymphocytes Viral Degenerative Neurological Disorders Inflammatory Conditions Case #4: CSF from 23 year old male admitted to the ER with a headache, neck stiffness and altered mental status. The cell identified by the arrow is? 1. Malignant cell 2. Benign cell 26
26 Mixed Cellular Reaction Monocytes, Macrophages, Lymphocytes, y Neutrophage Variable # of neutrophils Erythrophage Associated disease states and conditions: Lipophage Proliferative phase of bacterial meningitis Generally seen in chronic inflammatory conditions involving the meninges caused by tuberculous, leptospiral or fungal meningitis Eosinophils and Basophils EOSINOPHILS: > 5% Parasitic infection Foreign body reaction BASOPHILS: Inflammatory diseases Parasitic infections Foreign body reactions 27
27 Immediate: >6000 RBC/ul 12 hours-1 Week: Erythrophages Cellular Reaction to CNS Hemorrhage 2 days-20 weeks: Siderophages/Hematin Crystals Lipophage: Tissue necrosis Bone Marrow Contamination Immature granulocytes Nucleated RBCs Mitotic figures 28
28 Hemocytometer Microorganisms India Ink Wright Stain Cryptococcus neoformans Immunodeficient patient Microorganisms AIDS patient Candida species Burn patient Note intra- and extracellular forms 29
29 What should you report? 1. Fiber contaminant 2. Yeast with Pseudohyphae Case History: 12 year old male complaining of neck pain and fever for 24 hours, arrives in the E.R. disoriented and unresponsive. History of recent swimming party at a friend s lake home. Cytospin displayed many segmented neutrophils and necrotic debris um in diameter, with sky blue cytoplasm and a distinct, finely granular, violet nucleus? Is this a degenerating macrophage? 30
30 NOT Normal CSF Cells Primary amebic meningoencephalitis due to Naegleria fowleri Malignant Cells: Carcinoma Breast Most common sites to metastasize BREAST LUNG GASTRIC Lung Lung 31
31 Malignant Cells: Carcinoma Colon Cancer Metastatic Malignant Melanoma Malignant Cells: Clump of malignant cells are individually much larger than the RBC. The cytoplasm contains numerous dark, variable sized pigment granules. Compare the melanoma cell to the large, mono/macrophage which has phagocytized degenerate material. 32
32 Malignant Cells: Carcinoma Metastatic Malignant Melanoma What should you report? 1. Monocyte/Macrophage 2. Ventricular Lining Cell 3. Malignant Cell 33
33 Malignant Cells: Primary Brain Tumors Less than 15%h have positive CSF Cytology Choroid Plexus Carcinoma Malignant Cells: Primary Brain Tumors Glioblastoma Cells Medulloblastoma Cells Difficult to distinguish from leukemia or lymphoma cells 34
34 Case #5: CSF Slide from a 5 year old oncology patient previously diagnosed with Germinoma. Diagnosis? Malignant Cells: Primary Brain Tumors Germinoma Tumor Cells 35
35 Malignant Cells: ALL L1 L2 RED FLAG: Increased Smudges may suggest malignant or fragile cells Lymphoblasts: Note convoluted nucleus Prominent nucleoli Burkitt s Leukemia/ Lymphoma or ALL-L3 L3 Malignant Cells: ALL The malignant cell has prominent punched-out vacuoles. Normal cells do not have vacuoles overlying the chromatin in the nucleus. 36
36 Malignant Cells: Lymphoma HALLMARK: Convoluted nucleus Malignant Cells: Lymphoma Lymphoma: Displays clumping under low power Compare large Lymphoma cell to normal lymphocyte 37
37 Malignant Cells: AML 3 Year Old with AML Pleural, Peritoneal, & Pericardial Fluid cells 1. Cells listed under Cerebrospinal Fluid 2. Mesothelial cells Normal Reactive or atypical Malignant 3. Metastatic tumor cells Transudate vs. Exudate TRANSUDATE: Disease outside cavity Clear, pale, yellow EXUDATE: Disease inside cavity Cloudy, turbid, may clot due to presence of fibrinogen = Exudate 38
38 Macroscopic Appearance Case Study Neonatal patient with turbid pleural fluid Immature Lymphocytes Increased Lymphocytes Increase Lipophages Chylomicrons present Macroscopic Appearance Case Study Adult patient with turbid pleural fluid Increased Triglycerides Increase Chylomicrons History of surgery on the esphagus 39
39 Microscopic Evaluation Diagnosis: Damage or Obstruction to Thoracic Duct Eccentric nucleous Basophilic cytoplasm Perinuclear clear zone Cells Counts Increased WBC Pleural > 1,000 Peritoneal > 300 Effusion is exudate, primary disease in the body cavity 40
40 O v a r i a n Cell Counts A d e n o c a r c i n Increased RBC Traumatic tap Organ hemorrhage Malignancy Hemothorax Pancreatitis TB Serous Fluid Cells Cellular Morphology= Clinical Significance Neutrophils Associated disease states and conditions: Bacterial infection, blood contamination, crystal-induced arthropathies 41
41 Neutrophils at Work Fungal Organisms Peritoneal Fluid Broncho-pneumonia Pleural Fluid Serous Fluid Cells L.E. Cell Lupus Erythematosis Cell in Pleural Fluid Associated disease states and conditions: Lupus erythematosus Rheumatoid arthritis Oh Other autoimmune disordersd 42
42 How would you classify this cell? 1. NRBC 2. Segmented Neutrophil 3. Degenerating Cell Serous Fluid Cells Lymphocytes Associated disease states and conditions: Viral infections, especially acute EBV and CMV infection Chronic inflammatory conditions Chylous effusions Chronic: Congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, Nephrotic syndrome 43
43 How would you classify this cell? 1. Lymphocyte 2. Plasma cell 3. Reactive Lymphocyte How should you classify this cell? 1. Mesothelial Cell 2. Lymphocyte 3. Mitotic figure 44
44 Eosinophils Seen in Pneumothorax Serous Fluid Cells Associated disease states and conditions: Parasitic infections Allergy, hypersensitivity or foreign body reactions or asthma Collagen vascular disease Ventriculo-peritoneal shunts Chest tubes Pneumothorax or other trauma Fluids from patients with myeloproliferative disorders Serous Fluid Cells Basophils Peritoneal Associated disease states and conditions: Peritoneal dialysis Fluids from patients with myeloproliferative disorders MeningitisM i i i Inflammatory conditions Foreign body reactions Parasitic infections 45
45 Macrophages/ Mesothelial Neutrophage Mesothelial Cells/ Macrophages present in variable numbers in chronic effusions. Lipophage : Serous Fluid Cells Macrophage with multiple small clear vacuoles. In pleural and pericardial fluids, derived from cell injury. Lipophages lipids are from the products of cell membrane destruction ti and breakdown, so they are found in fluids with increased necrosis. 46
46 Azurophilic cellular material = Intracellular microorganism? Histoplasma capsulatum Pleural Undetermined cellular debris Pleural- Smoker Mesothelial/ Macrophages Signet Ring Descriptive term seen equally as often in benign and malignant cells 47
BODY FLUID ANALYSIS. Synovial Fluid. Synovial Fluid Classification. CLS 426 Urinalysis and Body Fluid Analysis Body Fluid Lecture Session 1
 BODY FLUID ANALYSIS Synovial Fluid Serous fluids the 3 P s Peritoneal Pleural Pericardial Cerebrospinal Fluid Karen Keller, MT(ASCP), SH Synovial Fluid Lubricant and sole nutrient source of joint. Normal
BODY FLUID ANALYSIS Synovial Fluid Serous fluids the 3 P s Peritoneal Pleural Pericardial Cerebrospinal Fluid Karen Keller, MT(ASCP), SH Synovial Fluid Lubricant and sole nutrient source of joint. Normal
FEARLESS FLUIDS WHAT WE LL COVER. DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST CSF, SEROUS, SYNOVIAL MANUAL CELL COUNTS A LITTLE, VERY LITTLE
 FEARLESS FLUIDS DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST YUCKY CELL COUNTS SCARY CELLS WHAT WE LL COVER. CSF, SEROUS, SYNOVIAL MANUAL CELL COUNTS A LITTLE, VERY LITTLE AUTOMATED CELL COUNTS WHAT S IMPORTANT
FEARLESS FLUIDS DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST YUCKY CELL COUNTS SCARY CELLS WHAT WE LL COVER. CSF, SEROUS, SYNOVIAL MANUAL CELL COUNTS A LITTLE, VERY LITTLE AUTOMATED CELL COUNTS WHAT S IMPORTANT
Cerebrospinal fluid - role
 Cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrospinal fluid CSF is a mixture of fluid generated locally in the brain and filtered serum Total volume 150 ml (the fluid that fills the cerebral ventricles, subarachnoid space
Cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrospinal fluid CSF is a mixture of fluid generated locally in the brain and filtered serum Total volume 150 ml (the fluid that fills the cerebral ventricles, subarachnoid space
MLAB 1211 Body Fluids BF Differentials - pretest
 MLAB 1211 BF Differentials - pretest Instructor: Carolyn Ragland MLAB 1211 pre-test #2 Spring No Extra Materials Needed Name Date Instructions: Neatly write your answer in the space provided. Unless otherwise
MLAB 1211 BF Differentials - pretest Instructor: Carolyn Ragland MLAB 1211 pre-test #2 Spring No Extra Materials Needed Name Date Instructions: Neatly write your answer in the space provided. Unless otherwise
SCBM343- Body fluid examination
 SCBM343- Body fluid examination Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
SCBM343- Body fluid examination Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
Introduction. 23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology. FLUIDS, Part 1. Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT
 23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT FLUIDS, Part 1 "Blue walls", Claudia Hansen, 2009 Introduction o Challenging to everyone o Almost any benign or malignant process
23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT FLUIDS, Part 1 "Blue walls", Claudia Hansen, 2009 Introduction o Challenging to everyone o Almost any benign or malignant process
FEAR. DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST
 FEARLESS FLUIDS FEAR. DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST YUCKY CELL COUNTS SCARY CELLS WHAT WE LL COVER. CSF, SEROUS, SYNOVIAL MANUAL CELL COUNTS A LITTLE, VERY LITTLE AUTOMATED CELL COUNTS AMR, CRR, METHOD
FEARLESS FLUIDS FEAR. DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST YUCKY CELL COUNTS SCARY CELLS WHAT WE LL COVER. CSF, SEROUS, SYNOVIAL MANUAL CELL COUNTS A LITTLE, VERY LITTLE AUTOMATED CELL COUNTS AMR, CRR, METHOD
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
CASE STUDIES PERIPHERAL BLOOD AND BODY FLUIDS
 CASE STUDIES PERIPHERAL BLOOD AND BODY FLUIDS WHERE TO START anemias hemoglobinopathies new and old parameters uncommon things fluids.benign and malignant.yuk! really annoying stuff and maybe some entertainment
CASE STUDIES PERIPHERAL BLOOD AND BODY FLUIDS WHERE TO START anemias hemoglobinopathies new and old parameters uncommon things fluids.benign and malignant.yuk! really annoying stuff and maybe some entertainment
Detail PRINCIPLE: Body fluids other than blood and urine will be analyzed according to their site of origin, and the providers specific orders.
 Subject Body Fluid Analysis - Affiliate Index Number Lab-8760 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional/Affiliates Category Departmental Contact Munson, Karen Last Revised 6/28/2017 References Required document
Subject Body Fluid Analysis - Affiliate Index Number Lab-8760 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional/Affiliates Category Departmental Contact Munson, Karen Last Revised 6/28/2017 References Required document
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DIFFERENTIATING IMMATURE PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs
 Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a 48-year-old male with a 30-year history of diabetes mellitus and new onset renal failure. Laboratory data include:
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a 48-year-old male with a 30-year history of diabetes mellitus and new onset renal failure. Laboratory data include:
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology
 Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Successful flow cytometric immunophenotyping of body fluid specimens
 Successful flow cytometric immunophenotyping of body fluid specimens Fiona E. Craig, MD Division of Hematopathology Mayo Clinic Arizona 2017 MFMER slide-1 Financial disclosure No conflicts 2017 MFMER slide-2
Successful flow cytometric immunophenotyping of body fluid specimens Fiona E. Craig, MD Division of Hematopathology Mayo Clinic Arizona 2017 MFMER slide-1 Financial disclosure No conflicts 2017 MFMER slide-2
Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR. Dr. Tamara Alqudah
 Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR Dr. Tamara Alqudah Differential Leukocyte Count (DLC) There are 5 main types of WBCs: 1. Neutrophils: 40-80% 2. Eosinophils: 1-6 % 3. Basophils: < 1-2% 4. Lymphocytes:
Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR Dr. Tamara Alqudah Differential Leukocyte Count (DLC) There are 5 main types of WBCs: 1. Neutrophils: 40-80% 2. Eosinophils: 1-6 % 3. Basophils: < 1-2% 4. Lymphocytes:
Almost any suspected tumor can be aspirated easily and safely. Some masses are more risky to aspirate including:
 DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
Agenda. Components of blood. Blood is Fluid Connective Tissue. Blood: General functions
 Agenda Chapter 19: Blood Major functions Major Components Structure of RBCs and WBCs ABO Blood Types, and Rh Factor Lab 34.1 and Blood Typing Blood: General functions Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients,
Agenda Chapter 19: Blood Major functions Major Components Structure of RBCs and WBCs ABO Blood Types, and Rh Factor Lab 34.1 and Blood Typing Blood: General functions Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients,
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF]
![CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF]](/thumbs/89/100552494.jpg) CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] All question is compulsory Minimum passing mark is 15. 1. Full form of a) CSF = b) LDH = c) ADA = 2. If patient serum glucose level is 300 mg%,than expected csf glucose level
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] All question is compulsory Minimum passing mark is 15. 1. Full form of a) CSF = b) LDH = c) ADA = 2. If patient serum glucose level is 300 mg%,than expected csf glucose level
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal 1 0.
 Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Microscopic Examination of Urine
 Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
The differential cytology of cerebrospinal fluids prepared by cytocentrifugation
 The differential cytology of cerebrospinal fluids prepared by cytocentrifugation Gerald A. Hoeltge, M.D. Anthony Furlan, M.D. George C. Hoffman, M.B., B. Chir., F.R.C. Path. Department of Laboratory Hematology
The differential cytology of cerebrospinal fluids prepared by cytocentrifugation Gerald A. Hoeltge, M.D. Anthony Furlan, M.D. George C. Hoffman, M.B., B. Chir., F.R.C. Path. Department of Laboratory Hematology
Formation of Blood Cells
 Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
Urine Sediment Photographs
 Urine Sediment Photographs Case History CMP-04 This urine sample is from a 35-year-old female as part of a routine exam. Laboratory data include: Specific Gravity = 1.015; ph = 7.0; ketones, glucose, protein,
Urine Sediment Photographs Case History CMP-04 This urine sample is from a 35-year-old female as part of a routine exam. Laboratory data include: Specific Gravity = 1.015; ph = 7.0; ketones, glucose, protein,
Blood: Functions. Liquid connective tissue 3 general functions 1. Transportation. 2. Regulation. 3. Protection
 Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
LGM International, Inc.
 Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Synovial Fluid CHAPTER. Key Terms. Learning Objectives
 Synovial Fluid CHAPTER 11 Key Terms ANTINUCLEAR ANTIBODY ARTHROCENTESIS BULGE TEST CRYSTAL-INDUCED ARTHRITIS GROUND PEPPER HYALURONATE MUCIN OCHRONOTIC SHARDS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RHEUMATOID FACTOR
Synovial Fluid CHAPTER 11 Key Terms ANTINUCLEAR ANTIBODY ARTHROCENTESIS BULGE TEST CRYSTAL-INDUCED ARTHRITIS GROUND PEPPER HYALURONATE MUCIN OCHRONOTIC SHARDS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RHEUMATOID FACTOR
Chapter 14. Blood. Blood Volume. Blood Composition. Blood
 Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
Requirements: Glass slides Leishman stain Microscopes Disposable needles Vials containing anticoagulants Methylated-spirit Staining rack
 Aim: To make a blood smear and to count the different types of leucocytes present in a stained blood smear and express their relative counts in percentage Principle - The blood contains various types of
Aim: To make a blood smear and to count the different types of leucocytes present in a stained blood smear and express their relative counts in percentage Principle - The blood contains various types of
Hemopoiesis and Blood
 Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS)
 GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
Hematopathology Lab. Third year medical students
 Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Pulmonary Morning Report. Ashley Schmehl D.O. PGY-3 January,
 Pulmonary Morning Report Ashley Schmehl D.O. PGY-3 January, 8 2015 Pleural Effusion Unilateral versus Bilateral Associated symptoms Transudate versus Exudate Light s Criteria: Pleural protein: Serum protein
Pulmonary Morning Report Ashley Schmehl D.O. PGY-3 January, 8 2015 Pleural Effusion Unilateral versus Bilateral Associated symptoms Transudate versus Exudate Light s Criteria: Pleural protein: Serum protein
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs
 Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-04 This urine sample is from a 56-year-old male with kidney and liver failure. Laboratory data include: Specific gravity 1.012, ph = 5, blood,
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-04 This urine sample is from a 56-year-old male with kidney and liver failure. Laboratory data include: Specific gravity 1.012, ph = 5, blood,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Utility of Modified Cell Block Technique in Cases of Pleural Effusion Suspected of Malignancy
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Utility of Modified Cell Block Technique in Cases of Pleural Effusion Suspected of Malignancy
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD. MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
BLOOD. Dr. Vedat Evren
 BLOOD Dr. Vedat Evren Blood Liquid suspension of formed elements Blood = Blood cells + plasma Plasma = Coagulation factors + serum Cells = Erythrocytes + Leukocytes + Thrombocytes 8 % of the total body
BLOOD Dr. Vedat Evren Blood Liquid suspension of formed elements Blood = Blood cells + plasma Plasma = Coagulation factors + serum Cells = Erythrocytes + Leukocytes + Thrombocytes 8 % of the total body
Serous fluids. Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 Serous fluids 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition 2 The closed cavities of the body namely, the pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal
Serous fluids 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition 2 The closed cavities of the body namely, the pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99
 What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99 Presenting Complaint: Acute onset of lethargy Vomited twice (partially digested food)
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99 Presenting Complaint: Acute onset of lethargy Vomited twice (partially digested food)
Management of Pleural Effusion
 Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih
 Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture.
 Name: Period: 10 Blood Study Guide I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture. 1. Composition and Function of Blood: 2. Hematopoiesis: 1 Miss School, Miss Out
Name: Period: 10 Blood Study Guide I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture. 1. Composition and Function of Blood: 2. Hematopoiesis: 1 Miss School, Miss Out
Chapter 21 Outline. General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements
 Chapter 21 Outline General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements Introduction Blood serves many functions. Some examples
Chapter 21 Outline General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements Introduction Blood serves many functions. Some examples
Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (2016)
 Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (216) Performance Evaluation of the XN-55 Automated Hematology Analyzer Body Fluid Mode Considerations for Operational Conditions for Cell Counting with Cerebrospinal
Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (216) Performance Evaluation of the XN-55 Automated Hematology Analyzer Body Fluid Mode Considerations for Operational Conditions for Cell Counting with Cerebrospinal
Case 3: what grew? BA Gram stain morphology Mucoid colonies on BA
 Case 3: what grew? BA Gram stain morphology Mucoid colonies on BA 43 Case 3: probability split! Gram variable, grows on BA, MAC, barely on CHOC Oxidase positive Vitek: probability split, Acinetobacter
Case 3: what grew? BA Gram stain morphology Mucoid colonies on BA 43 Case 3: probability split! Gram variable, grows on BA, MAC, barely on CHOC Oxidase positive Vitek: probability split, Acinetobacter
CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Blood Clotting Functions of Blood Transportation
 1 CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Functions of Blood Transportation Protection Regulation ph Temperature Composition of Blood Plasma: liquid
1 CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Functions of Blood Transportation Protection Regulation ph Temperature Composition of Blood Plasma: liquid
What is the composition of blood, including blood cells? What organs and structures control the flow of blood throughout the body?
 3 Chapter 10: Circulatory System and Lymphatic System In this chapter, you will learn about the structure and function of the circulatory system and lymphatic system. What is the composition of blood,
3 Chapter 10: Circulatory System and Lymphatic System In this chapter, you will learn about the structure and function of the circulatory system and lymphatic system. What is the composition of blood,
Cytology of Inflammatory Cutaneous lesions in the Dog and Cat
 Cytology of Inflammatory Cutaneous lesions in the Dog and Cat Rick L. Cowell, DVM, MS, MRCVS, Diplomate ACVP Clinical Pathologist IDEXX Laboratories Inc A. Cytologic Patterns of Inflammation: 1. Neutrophilic
Cytology of Inflammatory Cutaneous lesions in the Dog and Cat Rick L. Cowell, DVM, MS, MRCVS, Diplomate ACVP Clinical Pathologist IDEXX Laboratories Inc A. Cytologic Patterns of Inflammation: 1. Neutrophilic
Leukocytes and Platelets
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The leukocyte, commonly known as a white blood cell (or WBC), is a major component of the body s defenses against disease. Leukocytes protect the body against invading microorganisms
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The leukocyte, commonly known as a white blood cell (or WBC), is a major component of the body s defenses against disease. Leukocytes protect the body against invading microorganisms
Branch of medicine that deals with blood, its formation and disorders is called. Three main functions of cardiovascular system are,, and.
 Chapter 19 The Blood Human body must maintain a balance called. Body fluid inside the cells is called fluid; that outside is called or fluid. Two major fluid networks that help in connecting cells are
Chapter 19 The Blood Human body must maintain a balance called. Body fluid inside the cells is called fluid; that outside is called or fluid. Two major fluid networks that help in connecting cells are
Collect and label sample according to standard protocols. Gently invert tube 8-10 times immediately after draw. DO NOT SHAKE. Do not centrifuge.
 Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/
 Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
Case Log Number(s) Veterinarian or VTS Accurately report test results, using appropriate units of measurement Quality Control/Assurance Date Mastered
 AVCPT Skills List Candidate: Understanding of test methodology, techniques and ability to perform testing must be applied to each skill. The overall goal is to provide accurate and valid results to assist
AVCPT Skills List Candidate: Understanding of test methodology, techniques and ability to perform testing must be applied to each skill. The overall goal is to provide accurate and valid results to assist
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY
 BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
Blood. Kris*ne Kra.s, M.D.
 Blood Kris*ne Kra.s, M.D. The most beau*ful thing we can experience is the mysterious. It is the source of all true art and science. - Albert Einstein Blood Lecture Objec*ves Be able to iden*fy and
Blood Kris*ne Kra.s, M.D. The most beau*ful thing we can experience is the mysterious. It is the source of all true art and science. - Albert Einstein Blood Lecture Objec*ves Be able to iden*fy and
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1
 Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1 LINDA S. LUCAS,2 JACQUELINE J. K..WHANG,3 J. H. TJIO,4 ROBERT A. MANAKER,2
Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1 LINDA S. LUCAS,2 JACQUELINE J. K..WHANG,3 J. H. TJIO,4 ROBERT A. MANAKER,2
XN-SERIES. XN Technology and Case Studies
 XN Technology and Case Studies Karen Hoffman MT(ASCP) Clinical Applications Specialist OBJECTIVES Explain how scattergrams and histogram pictures can provide great insight into abnormal hematology samples
XN Technology and Case Studies Karen Hoffman MT(ASCP) Clinical Applications Specialist OBJECTIVES Explain how scattergrams and histogram pictures can provide great insight into abnormal hematology samples
BLOOD. EEI n: t.ee# Required Name : Due : April 12,2018 COMPOSITION AND FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD. Beginningof Class
 t.ee# Required Name : Due : April 12,2018 Beginningof Class BLOOD Blood, the "life fluid" that courses through the body's blood vessels, provides the means by which the body's cells receive vital nutrients
t.ee# Required Name : Due : April 12,2018 Beginningof Class BLOOD Blood, the "life fluid" that courses through the body's blood vessels, provides the means by which the body's cells receive vital nutrients
Blood. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 11 Blood Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu Community
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 11 Blood Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu Community
Blood Cells. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood & Blood Formation
 Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Host Response to Disease Resistance- ability
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Host Response to Disease Resistance- ability
temperature 38 o C (100.4 o F) The temperature of blood is slightly higher than the normal body temperature of 37 o C (98.6 o F).
 1 Chapter 1 Blood Definition -Blood is a type of connective tissue that consists of cells surrounded by a fluid extracellular matrix. -Blood, blood vessels, and the heart collectively form the cardiovascular
1 Chapter 1 Blood Definition -Blood is a type of connective tissue that consists of cells surrounded by a fluid extracellular matrix. -Blood, blood vessels, and the heart collectively form the cardiovascular
CM-B 2009: Clinical and Laboratory Aspects of Pleural, Peritoneal, and Pericardial Effusions
 INTRODUCTION Accumulation of body fluids (effusions) is an abnormal clinical finding. can occur in multiple sites within the body including the pleural, peritoneal, and pericardial cavities. Patients may
INTRODUCTION Accumulation of body fluids (effusions) is an abnormal clinical finding. can occur in multiple sites within the body including the pleural, peritoneal, and pericardial cavities. Patients may
Urine Sediment Photographs
 CMP-17 Urine Sediment Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a patient whose chief complaint is vaginal itching. Laboratory data include: specific gravity = 1.015; ph = 6.0; blood, leukocyte
CMP-17 Urine Sediment Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a patient whose chief complaint is vaginal itching. Laboratory data include: specific gravity = 1.015; ph = 6.0; blood, leukocyte
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
Practical Histology. Lab 3: Connective tissue
 Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs
 Urine Sediment Photomicrographs Case History CM-03 and CM-04 This urine sample is from a 63-year-old male with lower back pain, believed to be musculoskeletal in origin. Urinalysis showed ph = 5.0, nitrite
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs Case History CM-03 and CM-04 This urine sample is from a 63-year-old male with lower back pain, believed to be musculoskeletal in origin. Urinalysis showed ph = 5.0, nitrite
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood
 Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood vessels hematology = the
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood vessels hematology = the
Serous Effusions. Spasenija Savic Prince, MD Pathology, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland
 Serous Effusions Spasenija Savic Prince, MD Pathology, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland Serous membrane Body cavities: Pleural Pericardial Peritoneal Effusion = Excess of fluid 80% Benign 20% Malignant
Serous Effusions Spasenija Savic Prince, MD Pathology, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland Serous membrane Body cavities: Pleural Pericardial Peritoneal Effusion = Excess of fluid 80% Benign 20% Malignant
Individual cells Extracellular matrix
 Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Elements Individual cells Extracellular matrix»fibers» Collagen» Elastic» Reticular»Ground Substance» PG (proteoglycans)» GAG (glycosaminoglycan)» GP (glycoprotein)
Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Elements Individual cells Extracellular matrix»fibers» Collagen» Elastic» Reticular»Ground Substance» PG (proteoglycans)» GAG (glycosaminoglycan)» GP (glycoprotein)
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
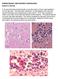 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 12 year-old male presented with a one-day history of fever and headache on the right side. Two days after admission, he developed a stiff neck
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 12 year-old male presented with a one-day history of fever and headache on the right side. Two days after admission, he developed a stiff neck
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood
 Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System VS Cardiovascular System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System VS Cardiovascular System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood
Notes for the 2 nd histology lab
 Notes for the 2 nd histology lab Note : Please refer to the slides and see the morphological characteristics of each cell, as the practical exam will be in the form of figures. SLIDE #2 Erythropoiesis
Notes for the 2 nd histology lab Note : Please refer to the slides and see the morphological characteristics of each cell, as the practical exam will be in the form of figures. SLIDE #2 Erythropoiesis
CSF. Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System
 Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
ADVL0411 study. (temozolomide in patients with leukemia)
 ADVL0411 study (temozolomide in patients with leukemia) I. Overview of study: We are interested in determining the level of MGMT activity and MRS mutations in leukemic samples (plasma and lymphoblasts)
ADVL0411 study (temozolomide in patients with leukemia) I. Overview of study: We are interested in determining the level of MGMT activity and MRS mutations in leukemic samples (plasma and lymphoblasts)
Blood. Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11
 Blood Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Outline I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood
Blood Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Outline I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood
five lineages of stem cells producing all of the various formed elements.
 Chapter 6 Blood Tissue 6.1. Basic Composition of Blood Blood is a connective tissue composed of free cells in a fluid matrix. Unlike other types of connective tissues, blood lacks fibers except during
Chapter 6 Blood Tissue 6.1. Basic Composition of Blood Blood is a connective tissue composed of free cells in a fluid matrix. Unlike other types of connective tissues, blood lacks fibers except during
Autopsy findings in 51 year-old man with mantle cell lymphoma
 Autopsy findings in 51 year-old man with mantle cell lymphoma Bobbi S. Pritt, MD, MSc Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires
Autopsy findings in 51 year-old man with mantle cell lymphoma Bobbi S. Pritt, MD, MSc Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires
Leukocytes (White Blood Cells)
 Leukocytes (White Blood Cells) As we, leukocytes ( white blood cells ) are of two types : 1- Granulocytes :have granules in the cytoplasm and include neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. 2- Agranulocytes:
Leukocytes (White Blood Cells) As we, leukocytes ( white blood cells ) are of two types : 1- Granulocytes :have granules in the cytoplasm and include neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. 2- Agranulocytes:
Blood. The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue. Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma
 Blood Blood The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma Blood Physical Characteristics of Blood Color range Oxygen-rich
Blood Blood The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma Blood Physical Characteristics of Blood Color range Oxygen-rich
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa
 Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
BIOCHEMISTRY OF BLOOD
 BCH 471 BIOCHEMISTRY OF BLOOD Amal Alamri Experiment 1 Separation of Plasma and Serum from Whole Blood Whole Blood It is living tissue that circulates through the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries
BCH 471 BIOCHEMISTRY OF BLOOD Amal Alamri Experiment 1 Separation of Plasma and Serum from Whole Blood Whole Blood It is living tissue that circulates through the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries
Case 1. Slide 1 History: 65 year old male presents with bilateral pleural effusions, a 40 pack year smoking history and peripheral and hilar lung
 Case 1. Slide 1 History: 65 year old male presents with bilateral pleural effusions, a 40 pack year smoking history and peripheral and hilar lung masses. Specimen shown is from a tap of the pleural effusion.
Case 1. Slide 1 History: 65 year old male presents with bilateral pleural effusions, a 40 pack year smoking history and peripheral and hilar lung masses. Specimen shown is from a tap of the pleural effusion.
4/5/17. Blood. Blood. Outline. Blood: An Overview. Functions of Blood
 Outline Blood Biol 105 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood cells
Outline Blood Biol 105 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood cells
Microscopic Sediment Epithelial Cells
 Epithelial Cells Cells sloughed from the kidney, urethra, bladder and genital track. Unless increased in number or abnormal forms, they are normal part of sediment. Three major types classified according
Epithelial Cells Cells sloughed from the kidney, urethra, bladder and genital track. Unless increased in number or abnormal forms, they are normal part of sediment. Three major types classified according
Chapter 19. Openstax: Chapter 18. Blood
 Chapter 19 Blood Openstax: Chapter 18 Chapter 19 Learning Outcomes After completing Chapter 19, you will be able to: 1. Describe the components and major functions of blood and list the physical characteristics
Chapter 19 Blood Openstax: Chapter 18 Chapter 19 Learning Outcomes After completing Chapter 19, you will be able to: 1. Describe the components and major functions of blood and list the physical characteristics
Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz
 Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz Question Prompt: 1 Mononuclear white blood cells (agranulocyte) formed in lymph tissue, also a phagocyte and a precursor of macrophages are leukocytes. True False Question Prompt:
Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz Question Prompt: 1 Mononuclear white blood cells (agranulocyte) formed in lymph tissue, also a phagocyte and a precursor of macrophages are leukocytes. True False Question Prompt:
Brain Tumors. Medulloblastoma. Pilocytic astrocytoma: Ahmed Koriesh, MD. Pathological finding
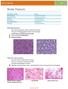 NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
