SCBM343- Body fluid examination
|
|
|
- Brett Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SCBM343- Body fluid examination Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: , 1
2 Objectives 1. Describe the definition and basic classification of body fluid. 2. Describe the macro- and microscopic appearance of body fluid. 3. Discuss the principles performance of body fluid analysis. 2
3 What is body fluid? 1. Cerebrospinal fluid 2. Serous fluid 3. Synovial fluid 4. Seminal fluid 5. Amniotic fluid 3
4 Clear fluid, circulates in the brain and spinal cord Normal adult ml and newborn ml Function: Buffer Regulates intracranial pressure Carries nutrients to the nervous system Excretory channel for metabolic wastes in the CNS 1. Cerebrospinal fluid 4
5 1. Cerebrospinal fluid Lumbar puncture was first introduced in 1891 by the German physician Heinrich Irenaeus Quincke ( ). 5
6 Lumbar Puncture Indications for lumbar puncture 1. Suspected involvement of the meninges by infection or malignancy 2. Documentation of subarachnoid hemorrhage 3. Diagnosis of infectious or inflammatory conditions involving brain or spinal cord 4. Treatment of intracranial hypertension in pseudotumor cerebri 6
7 Lumbar Puncture How the test is performed Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is the most common site of collecting CSF. The patient are positioned on the side with knees curled up to abdomen and chin tucked into chest. The skin is scrubbed, and a local anesthetic is injected over the lower spine. 7
8 Lumbar Puncture The spinal needle is inserted, usually between the 3 rd and 4 th lumbar vertebrae. 8
9 Doctor_injects_anaesthetic_before_lumbar_puncture-SPL.jpg 9
10 Tube 1: Cell count and differential Tube 2: Gram stain, bacterial and viral cultures Tube 3-4: Glucose, protein, Tube 3 or 4 can be used for special tests or additional cultures 10
11 CSF color Normal CSF is crystal clear and the consistency of water Turbidity : indicate WBC, bacteria, excess protein or fat Radiographic dye will give the CSF an oily look Clotting may be from a traumatic tap A, Normal B, Blood (trauma or subarachnoid hemorrhage?) C, Centrifuged CSF in a traumatic tap D, CSF from a patient with subarachnoid hemorrhage. There is blood at the bottom of the tube and the supernatant is yellow (xanthochromic) as a result of breakdown of blood cells in the CSF before the lumbar puncture. 11
12 Cells in CSF Normally very few cells are found in CSF No Rbc, 0-5 Wbc PMN = bacterial infection Lymphocytes = viral infection Usually counted manually, undiluted, when a cell count is over 30 white cells /ml a differential count is done Smear made from centrifuged sediment and stained Macrophage Lymphocytosis Monocyte 12
13 Protein in CSF Normal range is mg/dl (less than 1% of plasma conc.) Increased levels : Infections Decreased levels: Leakage of fluid from CNS 13
14 Glucose in CSF Usually about 60-80% of blood glucose, at the same time Decrease - bacterial meningitis Increase - diabetic coma India ink stains for cryptococcus Meningitis due to Streptococcus pneumoniae 14
15 Reference Pressure: mm H 2 O Appearance: clear, colorless CSF total protein: mg/dl Gamma globulin: 3-12% of the total protein CSF glucose: mg/dl (or approximately 2/3 of serum glucose level) CSF cell count: 0-5 WBC, no RBC Chloride: meq/l 15
16 2. SEROUS FLUIDS Pleural, pericardial and peritoneal : Fluids contained within closed cavities of the body Fluid fills space between layers of cells to lubricate the surfaces as they move against each other Fluids are formed and reabsorbed, volume is very small Increased volume is referred to as an effusion 16
17 EXAMINATION OF SEROUS FLUIDS: CELL COUNTS 17
18 EXAMINATION OF SEROUS FLUIDS: CELL COUNTS Differential white cell count Microbiological Gram stain Chemical analysis Protein to distinguish exudate from transudate Glucose - low levels could indicate bacterial infection 18
19 PLEURAL FLUID ANALYSIS A pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid between the layers of the membrane that lines the lungs and chest cavity. Thoracentesis is a procedure to remove fluid from the space between the lungs and the chest wall called the pleural space. 19
20 Pleural fluid 1. Transudative effusions - congestive heart failure 2. Exudative effusions - Cancer, pneumonia, tuberculosis and other lung infections, drug Pleural fluid with LE cells Pleural fluid with small cell carcinoma 20
21 21
22 22
23 Pleural fluid appearance 23
24 Pericardiocentesis Pericardiocentesis involves the use of a needle to withdraw fluid from the pericardial sac (membrane that surrounds the heart). 24
25 Abnormal results : Pericarditis Congestive heart failure Cancer Pericardial fluid analysis Cardiac trauma Rupture of a ventricular aneurysm Clumps of tumor cells in pericardial fluid (metastatic breast cancer) 25
26 Peritoneal fluid analysis The peritoneum is the membrane lining the abdominal cavity. Examine fluid in the peritoneal space The sample is obtained by an abdominal tap or ascitic tap or paracentesis. 26
27 Abnormal results : Peritoneal fluid analysis Milk-colored --- disease such as carcinoma, lymphoma, tuberculosis or infection Bloody fluid --- tumor or trauma Bile-stained fluid --- gallbladder problems High WBC --- peritonitis or cirrhosis Peritonitis 27
28 3. SYNOVIAL FLUID Fluid contained in joints Normal synovial fluid Ultrafiltrate of plasma with extra hyaluronate Lubricates the joints More viscous than CSF About 1 ml in each large joint Wbc count <200 /ul, most are mononuclear No Rbc or crystals 28
29 Synovial fluid analysis Collection and analysis Usually aspirated from joint Swelling Pain Analysis for cells and crystals Gram stain and culture Acute gout (uric acid crystals) 29
30 30
31 31
32 Synovial fluid analysis Non-inflammatory joint disease (Fluid is considered "noninflammatory" if it contains less than 2000 cells/mm 3.) Seen in osteoarthritis Traumatic arthritis Neurogenic joint disease Clear and viscous Low cell count Colorless, clear synovial fluid from a patient with osteoarthritis accompanied by a low synovial-fluid white cell count. Glucose and protein normal 32
33 Synovial fluid analysis Inflammatory joint disease (Fluid is considered "inflammatory" if it contains greater than 2000 cells/mm 3.) Rheumatoid arthritis Lupus arthritis Cloudy, yellow, low viscosity Moderately high cell count Glucose normal, protein high These fluid cloudy but translucent inflammatory synovial fluid were taken from rheumatoid arthritis (left) and gout (right). 33
34 Synovial fluid analysis Synovial infections Mostly bacterial infections Cloudy, may be yellow or green and milky Low viscosity Very high cell count Low glucose Protein high This fluid is a cloudy, pus-like fluid aspirated from a patient with acute bacterial infectious arthritis. 34
35 Synovial fluid analysis Crystal induced effusion Gout Pseudogout Yellow, cell count may be increased Crystals Monosodium urates seen in gout Calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate in pseudogout 35
36 4. SEMINAL FLUID Testing : Infertility Post vasectomy Forensic analysis Artificial insemination programs (การผสมเท ยม) 36
37 Seminal fluid collection Abstinence 3 days Sterile container Room temperature and delivered within one hour Record collection and receipt time Standard precautions 37
38 Seminal fluid analysis 1. Macroscopic: Appearance, volume, viscosity, ph 2. Microscopic: Count, motility, morphology 3. Additional testing: Sperm viability, seminal fluid fructose, anti-sperm antibodies, microbial testing, chemical testing, post vasectomy analysis and sperm function tests 38
39 39
40 Reference Color translucent gray white color Volume 2 5 ml Viscosity Pours in droplets ph Count million/ml Motility >50% within one hour Morphology >30% normal forms WBC <1.0 million/ml 40
41 5. AMNIOTIC FLUID This fluid is a clear, slightly yellowish liquid that surrounds the unborn baby (fetus) during pregnancy -- it is contained in the amniotic sac. Protects the fetus from injury and temperature changes. Allow for freedom of fetal movement and permits musculoskeletal development. 41
42 Amniotic fluid During pregnancy the amniotic fluid increases in volume as the fetus grows. It is greatest (800 ml) at approximately 34 weeks of gestation, This fluid is constantly circulated by the baby swallowing and "inhaling" existing fluid and replacing it through "exhalation" and urination. 42
43 Amniotic fluid An excessive amount of amniotic fluid is called polyhydramnios. This condition may accompany multiple pregnancy (twins or triplets), congenital anomalies, or gestational diabetes. 43
44 Amniotic fluid An abnormally small amount of amniotic fluid is known as oligohydramnios. This condition may accompany post dates pregnancies, ruptured membranes, placental dysfunction, or fetal abnormalities In amniocentesis a hollow needle is inserted into the mother's abdomen into the uterus, and amniotic fluid is drawn for analysis. 44
45 Amniotic fluid Testing : Suspected chromosomal abnormalities Metabolic disorders Neural tube defects HDN -Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn Gestational age Infection Fetal maturity 45
46 Amniotic fluid collection Amniocentesis needle aspiration 30 ml of fluid collected (maximum amount) Protect from light collect in amber colored tubes Must be delivered to laboratory promptly Procedures perform immediately Temperature critical Filtration or centrifugation important Standard precautions should be taken 46
47 References Textbook of Urinalysis and Body Fluids: A Clinical Approach. by Landy McBride 1998 Graff's Textbook of Urinalysis and Body Fluids. 2 nd ed. by Lillian Mundt Kristy Shanahan 2010 Urinalysis and Body Fluids by Susan King Strasinger, Marjorie Schaub Di Lorenzo
48 SCBM343 Body fluid examination 48
BODY FLUID ANALYSIS. Synovial Fluid. Synovial Fluid Classification. CLS 426 Urinalysis and Body Fluid Analysis Body Fluid Lecture Session 1
 BODY FLUID ANALYSIS Synovial Fluid Serous fluids the 3 P s Peritoneal Pleural Pericardial Cerebrospinal Fluid Karen Keller, MT(ASCP), SH Synovial Fluid Lubricant and sole nutrient source of joint. Normal
BODY FLUID ANALYSIS Synovial Fluid Serous fluids the 3 P s Peritoneal Pleural Pericardial Cerebrospinal Fluid Karen Keller, MT(ASCP), SH Synovial Fluid Lubricant and sole nutrient source of joint. Normal
Serous fluids. Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 Serous fluids 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition 2 The closed cavities of the body namely, the pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal
Serous fluids 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition 2 The closed cavities of the body namely, the pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal
Cerebrospinal fluid - role
 Cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrospinal fluid CSF is a mixture of fluid generated locally in the brain and filtered serum Total volume 150 ml (the fluid that fills the cerebral ventricles, subarachnoid space
Cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrospinal fluid CSF is a mixture of fluid generated locally in the brain and filtered serum Total volume 150 ml (the fluid that fills the cerebral ventricles, subarachnoid space
MLAB 1211 Body Fluids BF Differentials - pretest
 MLAB 1211 BF Differentials - pretest Instructor: Carolyn Ragland MLAB 1211 pre-test #2 Spring No Extra Materials Needed Name Date Instructions: Neatly write your answer in the space provided. Unless otherwise
MLAB 1211 BF Differentials - pretest Instructor: Carolyn Ragland MLAB 1211 pre-test #2 Spring No Extra Materials Needed Name Date Instructions: Neatly write your answer in the space provided. Unless otherwise
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF]
![CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF]](/thumbs/89/100552494.jpg) CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] All question is compulsory Minimum passing mark is 15. 1. Full form of a) CSF = b) LDH = c) ADA = 2. If patient serum glucose level is 300 mg%,than expected csf glucose level
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] All question is compulsory Minimum passing mark is 15. 1. Full form of a) CSF = b) LDH = c) ADA = 2. If patient serum glucose level is 300 mg%,than expected csf glucose level
Synovial Fluid CHAPTER. Key Terms. Learning Objectives
 Synovial Fluid CHAPTER 11 Key Terms ANTINUCLEAR ANTIBODY ARTHROCENTESIS BULGE TEST CRYSTAL-INDUCED ARTHRITIS GROUND PEPPER HYALURONATE MUCIN OCHRONOTIC SHARDS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RHEUMATOID FACTOR
Synovial Fluid CHAPTER 11 Key Terms ANTINUCLEAR ANTIBODY ARTHROCENTESIS BULGE TEST CRYSTAL-INDUCED ARTHRITIS GROUND PEPPER HYALURONATE MUCIN OCHRONOTIC SHARDS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) RHEUMATOID FACTOR
Semen. Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 Semen Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Diagram of the male genitalia Dr.
Semen Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Diagram of the male genitalia Dr.
Sysmex Educational Enhancement & Development
 Sysmex Educational Enhancement & Development SEED-Africa Newsletter No 10 2011 Introducing automated body fluid analysis into the haematology laboratory Automated Body Fluid Analysis The purpose of this
Sysmex Educational Enhancement & Development SEED-Africa Newsletter No 10 2011 Introducing automated body fluid analysis into the haematology laboratory Automated Body Fluid Analysis The purpose of this
Michelle Moy, MAd Ed, MT(ASCP)SC Program Director Clinical Laboratory Science Program Loyola University Chicago, Illinois
 Reviewers Lorraine Doucette, MS, MLS(ASCP)CM Associate Professor and Medical Laboratory Technician Program Coordinator Anne Arundel Community College Arnold, Maryland Pamela B. Lonergan, MS, MT(ASCP)SC
Reviewers Lorraine Doucette, MS, MLS(ASCP)CM Associate Professor and Medical Laboratory Technician Program Coordinator Anne Arundel Community College Arnold, Maryland Pamela B. Lonergan, MS, MT(ASCP)SC
LUMBAR PUNCTURE. Multimedia Health Education
 LUMBAR PUNCTURE Disclaimer This film is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All such decisions must be made in consultation with a physician or licensed healthcare
LUMBAR PUNCTURE Disclaimer This film is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All such decisions must be made in consultation with a physician or licensed healthcare
Pulmonary Morning Report. Ashley Schmehl D.O. PGY-3 January,
 Pulmonary Morning Report Ashley Schmehl D.O. PGY-3 January, 8 2015 Pleural Effusion Unilateral versus Bilateral Associated symptoms Transudate versus Exudate Light s Criteria: Pleural protein: Serum protein
Pulmonary Morning Report Ashley Schmehl D.O. PGY-3 January, 8 2015 Pleural Effusion Unilateral versus Bilateral Associated symptoms Transudate versus Exudate Light s Criteria: Pleural protein: Serum protein
FEARLESS FLUIDS WHAT WE LL COVER. DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST CSF, SEROUS, SYNOVIAL MANUAL CELL COUNTS A LITTLE, VERY LITTLE
 FEARLESS FLUIDS DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST YUCKY CELL COUNTS SCARY CELLS WHAT WE LL COVER. CSF, SEROUS, SYNOVIAL MANUAL CELL COUNTS A LITTLE, VERY LITTLE AUTOMATED CELL COUNTS WHAT S IMPORTANT
FEARLESS FLUIDS DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST YUCKY CELL COUNTS SCARY CELLS WHAT WE LL COVER. CSF, SEROUS, SYNOVIAL MANUAL CELL COUNTS A LITTLE, VERY LITTLE AUTOMATED CELL COUNTS WHAT S IMPORTANT
Detail PRINCIPLE: Body fluids other than blood and urine will be analyzed according to their site of origin, and the providers specific orders.
 Subject Body Fluid Analysis - Affiliate Index Number Lab-8760 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional/Affiliates Category Departmental Contact Munson, Karen Last Revised 6/28/2017 References Required document
Subject Body Fluid Analysis - Affiliate Index Number Lab-8760 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional/Affiliates Category Departmental Contact Munson, Karen Last Revised 6/28/2017 References Required document
Lumbar cistern is site of lumbar puncture for removal of CSF sample LC contains cauda equina. Anatomical Review
 Lumbar Puncture Lumbar cistern is site of lumbar puncture for removal of CSF sample LC contains cauda equina Anatomical Review Anatomical review Overview An LP (lumbar puncture) is an invasive diagnostic
Lumbar Puncture Lumbar cistern is site of lumbar puncture for removal of CSF sample LC contains cauda equina Anatomical Review Anatomical review Overview An LP (lumbar puncture) is an invasive diagnostic
SCBM343- Urinalysis. Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul. Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University
 SCBM343- Urinalysis Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 OBJECTIVES 1.
SCBM343- Urinalysis Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 OBJECTIVES 1.
February 1, 2016 Body Fluid order changes
 February 1, 2016 Body order changes Laboratory will be making the following changes to Body tests: 1. Changing orders in Power plans (see below list). 2. All folders will be updated accordingly: If the
February 1, 2016 Body order changes Laboratory will be making the following changes to Body tests: 1. Changing orders in Power plans (see below list). 2. All folders will be updated accordingly: If the
Abnormalities of Spermatogenesis
 Abnormalities of Spermatogenesis Male Factor 40% of the cause for infertility Sperm is constantly produced by the germinal epithelium of the testicle Sperm generation time 73 days Sperm production is thermoregulated
Abnormalities of Spermatogenesis Male Factor 40% of the cause for infertility Sperm is constantly produced by the germinal epithelium of the testicle Sperm generation time 73 days Sperm production is thermoregulated
Management of Pleural Effusion
 Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
FEAR. DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST
 FEARLESS FLUIDS FEAR. DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST YUCKY CELL COUNTS SCARY CELLS WHAT WE LL COVER. CSF, SEROUS, SYNOVIAL MANUAL CELL COUNTS A LITTLE, VERY LITTLE AUTOMATED CELL COUNTS AMR, CRR, METHOD
FEARLESS FLUIDS FEAR. DEPENDS ON WHAT YOU DREAD THE MOST YUCKY CELL COUNTS SCARY CELLS WHAT WE LL COVER. CSF, SEROUS, SYNOVIAL MANUAL CELL COUNTS A LITTLE, VERY LITTLE AUTOMATED CELL COUNTS AMR, CRR, METHOD
Pleural fluid. creatinine - urinothorax haematocrit -haemothorax bilirubin gut perforation. Fluid samples 1st Plain Universal ( cell count)
 Examination Purpose of test Sample 17725 Fluid Profile (appearance, culture, WBC differential, ph, total protein, glucose, amylase, triglyceride, albumin, HDL) Peritoneal/ascitic and pleural fluid are
Examination Purpose of test Sample 17725 Fluid Profile (appearance, culture, WBC differential, ph, total protein, glucose, amylase, triglyceride, albumin, HDL) Peritoneal/ascitic and pleural fluid are
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood
 Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System VS Cardiovascular System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System VS Cardiovascular System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood
Body Fluid Examination
 Specimen Handling Body Fluid Examination CSF: Treated as STATS because of cell lysis Studies have shown approximately 40% of CSF WBCs will have lysed after 2 hours at RT. Only 15% had lysed if the fluid
Specimen Handling Body Fluid Examination CSF: Treated as STATS because of cell lysis Studies have shown approximately 40% of CSF WBCs will have lysed after 2 hours at RT. Only 15% had lysed if the fluid
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion
 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
Fellowship in Cytopathology Department of Pathology. All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India
 Fellowship in Cytopathology Department of Pathology All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Syllabus for Fellowship in Cytopathology: FNAC Direct, Guided, EUS Exfoliative
Fellowship in Cytopathology Department of Pathology All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Syllabus for Fellowship in Cytopathology: FNAC Direct, Guided, EUS Exfoliative
Scottish Surveillance of Healthcare Associated Infection Programme (SSHAIP) Health Protection Scotland (HPS) SSI Surveillance Protocol 7th Edition
 1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
RADPrimer Curriculum Breast Topics Covered Basic Intermediate 225
 Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Pleural Effusions. Kyle J Henry, MD Pulmonary/ CCM Fellow PGY4 (210) (602)
 Pleural Effusions Kyle J Henry, MD Pulmonary/ CCM Fellow PGY4 (210) 275 8583 (602) 202 0351 None Disclosures Objectives Understand the presentation of a pleural effusion How to diagnose and treat Differentiate
Pleural Effusions Kyle J Henry, MD Pulmonary/ CCM Fellow PGY4 (210) 275 8583 (602) 202 0351 None Disclosures Objectives Understand the presentation of a pleural effusion How to diagnose and treat Differentiate
It s not just water! What is Urinalysis?
 It s not just water! An introduction to Urinalysis What is Urinalysis? Urinalysis or the analysis of urine is one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine. It is a good test for
It s not just water! An introduction to Urinalysis What is Urinalysis? Urinalysis or the analysis of urine is one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine. It is a good test for
Introduction. 23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology. FLUIDS, Part 1. Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT
 23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT FLUIDS, Part 1 "Blue walls", Claudia Hansen, 2009 Introduction o Challenging to everyone o Almost any benign or malignant process
23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT FLUIDS, Part 1 "Blue walls", Claudia Hansen, 2009 Introduction o Challenging to everyone o Almost any benign or malignant process
New Technique uses to Evaluate Cerebrospinal Fluid Lactic Acid as an Aid Differential Diagnosis of Bacterial and Viral Meningitis
 New Technique uses to Evaluate Cerebrospinal Fluid Lactic Acid as an Aid Differential Diagnosis of Bacterial and Viral Meningitis Mohammed Kadum Al-Araji College of Pharmacy, University of Al-Mustansiriyah
New Technique uses to Evaluate Cerebrospinal Fluid Lactic Acid as an Aid Differential Diagnosis of Bacterial and Viral Meningitis Mohammed Kadum Al-Araji College of Pharmacy, University of Al-Mustansiriyah
Marta Kalousová Institute of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Diagnostics, 1 st Faculty of Medicine and General University Hospital, Charles
 Examination of cerebrospinal fluid Marta Kalousová Institute of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Diagnostics, 1 st Faculty of Medicine and General University Hospital, Charles University, Prague Cerebrospinal
Examination of cerebrospinal fluid Marta Kalousová Institute of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Diagnostics, 1 st Faculty of Medicine and General University Hospital, Charles University, Prague Cerebrospinal
Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (2016)
 Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (216) Performance Evaluation of the XN-55 Automated Hematology Analyzer Body Fluid Mode Considerations for Operational Conditions for Cell Counting with Cerebrospinal
Sysmex Journal International Vol.26 No.1 (216) Performance Evaluation of the XN-55 Automated Hematology Analyzer Body Fluid Mode Considerations for Operational Conditions for Cell Counting with Cerebrospinal
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Aurora Health Care South Region EMS st Quarter CE Packet
 Name: Dept: Date: Aurora Health Care South Region EMS 2010 1 st Quarter CE Packet Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammatory disease of the leptomeninges. Leptomeninges refer to the pia matter and the arachnoid
Name: Dept: Date: Aurora Health Care South Region EMS 2010 1 st Quarter CE Packet Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammatory disease of the leptomeninges. Leptomeninges refer to the pia matter and the arachnoid
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood
 Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood vessels hematology = the
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood vessels hematology = the
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Urine Casts. Microscopic Sediment Casts. Unit 2; Session 6
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 6 Urine Casts Urine Casts Overview of Urinary Cast Formation Hyaline Casts Cellular Casts Granular Casts Waxy Casts Pseudo Casts Microscopic Sediment Casts
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 6 Urine Casts Urine Casts Overview of Urinary Cast Formation Hyaline Casts Cellular Casts Granular Casts Waxy Casts Pseudo Casts Microscopic Sediment Casts
Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural
 Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural San José, Costa Rica Junio 29, 2017 Rodrigo Cartín Ceba, MD, MSc Consultant, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic 2010 MFMER
Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural San José, Costa Rica Junio 29, 2017 Rodrigo Cartín Ceba, MD, MSc Consultant, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic 2010 MFMER
Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report
 Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report Endry Martinez, and Judith Berger SBH Health System, 4422 Third Ave, Bronx, NY 10457 Key words: brain abscess, rupture
Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report Endry Martinez, and Judith Berger SBH Health System, 4422 Third Ave, Bronx, NY 10457 Key words: brain abscess, rupture
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS)
 GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
2) An 87 year old female who is 2 weeks post TKR presents with a sore swollen knee. She has a history of atrial fibrillation. Her vital signs are:
 EMQ - Rheumatology For each clinical vignette match the correct diagnosis. Reiter s syndrome Pseudogout Septic arthritis Gout Haemarthrosis Traumatic effusion Ankylosing spondylitis Rheumatoid arthritis
EMQ - Rheumatology For each clinical vignette match the correct diagnosis. Reiter s syndrome Pseudogout Septic arthritis Gout Haemarthrosis Traumatic effusion Ankylosing spondylitis Rheumatoid arthritis
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Dr. Mohamed S. Daoud Biochemistry Department College of Science, KSU. Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 Dr. Mohamed S. Daoud Biochemistry Department College of Science, KSU 1 Course symbol: BCH 472 Course Title: Biochemistry of biological fluids Credit hours: 3(2+1) 2 Clinical Biochemistry is one of the
Dr. Mohamed S. Daoud Biochemistry Department College of Science, KSU 1 Course symbol: BCH 472 Course Title: Biochemistry of biological fluids Credit hours: 3(2+1) 2 Clinical Biochemistry is one of the
DISCUSSION BY: Dr M. R. Shakeebi, MD, Rheumatologist
 Case presentations Related to some Rheumatic Diseases Lab & Clinic i Programs, Tuesday, April 24, 2012 COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD, Immunologist COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD,
Case presentations Related to some Rheumatic Diseases Lab & Clinic i Programs, Tuesday, April 24, 2012 COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD, Immunologist COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD,
Bacterial pneumonia with associated pleural empyema pleural effusion
 EMPYEMA Synonyms : - Parapneumonic effusion - Empyema thoracis - Bacterial pneumonia - Pleural empyema, pleural effusion - Lung abscess - Complicated parapneumonic effusions (CPE) 1 Bacterial pneumonia
EMPYEMA Synonyms : - Parapneumonic effusion - Empyema thoracis - Bacterial pneumonia - Pleural empyema, pleural effusion - Lung abscess - Complicated parapneumonic effusions (CPE) 1 Bacterial pneumonia
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Objectives Upon completion of this laboratory exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Perform microscopic examinations on a minimum of five urine specimens, obtaining
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Objectives Upon completion of this laboratory exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Perform microscopic examinations on a minimum of five urine specimens, obtaining
STANDARDIZED PROCEDURE NEONATAL LUMBAR PUNCTURE (Neonatal)
 I. Definition The lumbar puncture is used to sample the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) to determine if an infection exists, to diagnose certain disease states, or (with order of Attending/Fellow) to drain
I. Definition The lumbar puncture is used to sample the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) to determine if an infection exists, to diagnose certain disease states, or (with order of Attending/Fellow) to drain
TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS AND
 TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS 1970-2000 AND 2004-2014 FLORIDA 1 UNITED STATES 1 YEAR WHITE2 BLACK2 HISPANIC3 WHITE2
TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS 1970-2000 AND 2004-2014 FLORIDA 1 UNITED STATES 1 YEAR WHITE2 BLACK2 HISPANIC3 WHITE2
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF BLOODY PLEURAL EFFUSION
 DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF BLOODY PLEURAL EFFUSION Mamatha S, Manish Kumar Singh, Pravati Dutta, Rekha Manjhi, Sudarsan Pothal,Amit Kumar Jha, Nilam Nigam, Sanjay Kumar Nigam 1. Senior Resident, Department
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF BLOODY PLEURAL EFFUSION Mamatha S, Manish Kumar Singh, Pravati Dutta, Rekha Manjhi, Sudarsan Pothal,Amit Kumar Jha, Nilam Nigam, Sanjay Kumar Nigam 1. Senior Resident, Department
Table S1. World Health Organization bleeding scale
 Table S1. World Health Organization bleeding scale Oral and nasal Skin, soft tissue, musculoskeletal Gastrointestinal Genitourinary Grade 1 Oropharyngeal bleeding total duration of all episodes in previous
Table S1. World Health Organization bleeding scale Oral and nasal Skin, soft tissue, musculoskeletal Gastrointestinal Genitourinary Grade 1 Oropharyngeal bleeding total duration of all episodes in previous
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg CAUTION. Abnormal Crystals of Metabolic Origin. Unit 2; Session 5. Abnormal crystals
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 5 Crystals Found in the Urine Microscopic Examination - Part D, Abnormal Crystals CAUTION Abnormal crystals should not be reported haphazardly are rarely
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 5 Crystals Found in the Urine Microscopic Examination - Part D, Abnormal Crystals CAUTION Abnormal crystals should not be reported haphazardly are rarely
LIVER CIRRHOSIS. The liver extracts nutrients from the blood and processes them for later use.
 LIVER CIRRHOSIS William Sanchez, M.D. & Jayant A. Talwalkar, M.D., M.P.H. Advanced Liver Disease Study Group Miles and Shirley Fiterman Center for Digestive Diseases Mayo College of Medicine Rochester,
LIVER CIRRHOSIS William Sanchez, M.D. & Jayant A. Talwalkar, M.D., M.P.H. Advanced Liver Disease Study Group Miles and Shirley Fiterman Center for Digestive Diseases Mayo College of Medicine Rochester,
Central Nervous System: Part 2
 Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II
 MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II Session 11 April 11, 2016 STUDENT COPY MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 2 CASE HISTORY 1 Chief complaint: Our baby
MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II Session 11 April 11, 2016 STUDENT COPY MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 2 CASE HISTORY 1 Chief complaint: Our baby
BELLWORK page 343. Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary Remember the structures of the respiratory system 1
 BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99
 What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99 Presenting Complaint: Acute onset of lethargy Vomited twice (partially digested food)
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99 Presenting Complaint: Acute onset of lethargy Vomited twice (partially digested food)
The Digestive System and Excretory System
 The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
SMALL ANIMAL SOFT TISSUE CASE-BASED EXAMINATION
 SMALL ANIMAL SOFT TISSUE CASE-BASED EXAMINATION CASE-BASED EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS The case-based examination measures surgical principles in case management prior to, during, and after surgery. Information
SMALL ANIMAL SOFT TISSUE CASE-BASED EXAMINATION CASE-BASED EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS The case-based examination measures surgical principles in case management prior to, during, and after surgery. Information
Case Report Pseudoseptic Arthritis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2011, Article ID 942023, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/942023 Case Report Pseudoseptic Arthritis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature Brian P. Oppermann, 1
Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2011, Article ID 942023, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/942023 Case Report Pseudoseptic Arthritis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature Brian P. Oppermann, 1
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Session Outline. Routine Urinalysis a historical perspective. Unit 2; Session 8
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 8 Session Outline Historical perspective Importance of testing Basic urine composition Types of collection Timing of collection Urine preservatives Urinalysis
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 8 Session Outline Historical perspective Importance of testing Basic urine composition Types of collection Timing of collection Urine preservatives Urinalysis
Case 3: what grew? BA Gram stain morphology Mucoid colonies on BA
 Case 3: what grew? BA Gram stain morphology Mucoid colonies on BA 43 Case 3: probability split! Gram variable, grows on BA, MAC, barely on CHOC Oxidase positive Vitek: probability split, Acinetobacter
Case 3: what grew? BA Gram stain morphology Mucoid colonies on BA 43 Case 3: probability split! Gram variable, grows on BA, MAC, barely on CHOC Oxidase positive Vitek: probability split, Acinetobacter
Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Pleural effusions Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases A pleural effusion is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space resulting from excess fluid production or decreased
Pleural effusions Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases A pleural effusion is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space resulting from excess fluid production or decreased
Date Lab Pd. Lecture Notes (57)
 Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs
 Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a 48-year-old male with a 30-year history of diabetes mellitus and new onset renal failure. Laboratory data include:
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a 48-year-old male with a 30-year history of diabetes mellitus and new onset renal failure. Laboratory data include:
ENROLLMENT : Line of Business Summary
 ENROLLMENT : Line of Business Summary Date Range : JAN 2017 through DEC 2017 COMPREHENSIVE MAJOR MEDICAL Print Date : 1/19/2018 9:43:49AM Page 1 of 1 Month Year Single 2 Person : Emp/Spouse 2 Person :
ENROLLMENT : Line of Business Summary Date Range : JAN 2017 through DEC 2017 COMPREHENSIVE MAJOR MEDICAL Print Date : 1/19/2018 9:43:49AM Page 1 of 1 Month Year Single 2 Person : Emp/Spouse 2 Person :
Pleural Effusion. Exudative pleural effusion - Involve an increase in capillary permeability and impaired pleural fluid resorption
 Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
1.) 3 yr old FS Siamese cat: 3 day history of lethargy, anorexia. Dyspneic, thin, febrile.
 1.) 3 yr old FS Siamese cat: 3 day history of lethargy, anorexia. Dyspneic, thin, febrile. NUCLEATED CELLS 19.5 High 4.0-14.0 x 10^3/ul METAMYELOCYTES 9 % 1.8 High 0.0-0.0 x 10^3/ul BAND NEUTROPHILS 61
1.) 3 yr old FS Siamese cat: 3 day history of lethargy, anorexia. Dyspneic, thin, febrile. NUCLEATED CELLS 19.5 High 4.0-14.0 x 10^3/ul METAMYELOCYTES 9 % 1.8 High 0.0-0.0 x 10^3/ul BAND NEUTROPHILS 61
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
Light yellow to dark golden yellow Clear ph range Specific gravity Sediments
 #11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
#11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
Supplemental Digital Content: Definitions Based on the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification
 Supplemental Digital Content: Definitions Based on the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) Diagnose and Procedures Codes 1. ICD-9-CM definition of
Supplemental Digital Content: Definitions Based on the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) Diagnose and Procedures Codes 1. ICD-9-CM definition of
REPRODUCIBILITY OF SYNOVIAL FLUID ANALYSES
 770 REPRODUCIBILITY OF SYNOVIAL FLUID ANALYSES A Study Among Four Laboratories H. RALPH SCHUMACHER, JR., MARIE S. SIECK, SUSAN ROTHFUSS, GILDA M. CLAYBURNE, DOROTHY F. BAUMGARTEN, BONNIE S. MOCHAN, and
770 REPRODUCIBILITY OF SYNOVIAL FLUID ANALYSES A Study Among Four Laboratories H. RALPH SCHUMACHER, JR., MARIE S. SIECK, SUSAN ROTHFUSS, GILDA M. CLAYBURNE, DOROTHY F. BAUMGARTEN, BONNIE S. MOCHAN, and
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells (lymphocytes) of the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system.
 Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
Cerebrospinal Fluid in CNS Infections
 Cerebrospinal Fluid in CNS Infections Osvaldo M. Takayanagui Departamento de Neurologia Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto Universidade de São Paulo Diagnosis of CNS Infections 1891- Heinrich Quincke
Cerebrospinal Fluid in CNS Infections Osvaldo M. Takayanagui Departamento de Neurologia Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto Universidade de São Paulo Diagnosis of CNS Infections 1891- Heinrich Quincke
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Feces. Feces. Unit 5. 5 Feces & miscellaneous handouts draft
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 5 5 & miscellaneous handouts draft Composition Bacteria, Cellulose & other undigested foodstuffs GI secretions, enzymes, bile pigments Cells Electrolytes and water Indications
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 5 5 & miscellaneous handouts draft Composition Bacteria, Cellulose & other undigested foodstuffs GI secretions, enzymes, bile pigments Cells Electrolytes and water Indications
Pleural fluid analysis
 Pleural fluid analysis Dr Akash Verma Senior Consultant- Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore 308433 Adj A/Professor- Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine
Pleural fluid analysis Dr Akash Verma Senior Consultant- Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore 308433 Adj A/Professor- Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Meg Carman DNP, ACNP-BC, ENP-BC, FAEN Melinda Johnson, MSN, FNP-BC, AGACNP-BC, ENP-C. performing lumbar puncture (LP) in the emergency care setting
 Lumbar Puncture Meg Carman DNP, ACNP-BC, ENP-BC, FAEN Melinda Johnson, MSN, FNP-BC, AGACNP-BC, ENP-C Objectives 1. Identify indications, contraindications, and considerations for performing lumbar puncture
Lumbar Puncture Meg Carman DNP, ACNP-BC, ENP-BC, FAEN Melinda Johnson, MSN, FNP-BC, AGACNP-BC, ENP-C Objectives 1. Identify indications, contraindications, and considerations for performing lumbar puncture
Ultrasound Table of contents
 Ultrasound Table of contents Ultrasound-Abdomen (Gallbladder, Liver, Pancreas, Spleen) Ultrasound-Amniocentesis Ultrasound-Aorta Ultrasound-Biophysical Profile Ultrasound-Breast Ultrasound-Breast Needle
Ultrasound Table of contents Ultrasound-Abdomen (Gallbladder, Liver, Pancreas, Spleen) Ultrasound-Amniocentesis Ultrasound-Aorta Ultrasound-Biophysical Profile Ultrasound-Breast Ultrasound-Breast Needle
Characteristic. Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils
 ACUTE INFLAMMATION Characteristic Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils TYPES Serous Inflammation Fibrinous Inflammation
ACUTE INFLAMMATION Characteristic Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils TYPES Serous Inflammation Fibrinous Inflammation
Hths 2231 Laboratory 7 Infection
 Watch Movie: Meningitis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-3. Activity #1: Go to the patho web page and click on activity 1. Click on Tutorials Click on Immunopathology
Watch Movie: Meningitis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-3. Activity #1: Go to the patho web page and click on activity 1. Click on Tutorials Click on Immunopathology
Medical Microbiology
 Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION pdp-pyrazinamide Pyrazinamide Tablets, USP 500 mg Antimycobacterial / Antituberculosis Agent PENDOPHARM, Division of Pharmascience Inc.. 6111, Royalmount Ave, Suite 100 Montréal,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION pdp-pyrazinamide Pyrazinamide Tablets, USP 500 mg Antimycobacterial / Antituberculosis Agent PENDOPHARM, Division of Pharmascience Inc.. 6111, Royalmount Ave, Suite 100 Montréal,
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion
 Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (IV) No (I) January-June 2015 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Rushi Patel*, Viral Shah*, Deepali Kamdar** Abstract : Aim : Normally the pleural cavities contain
Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (IV) No (I) January-June 2015 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Rushi Patel*, Viral Shah*, Deepali Kamdar** Abstract : Aim : Normally the pleural cavities contain
Seminal fluid analysis
 What is semen? Semen is the fluid formed at ejaculation. Made of secretions of all the accessory glands of the male genital tract and testicular sperm component Semen quality is maintained by all the accessory
What is semen? Semen is the fluid formed at ejaculation. Made of secretions of all the accessory glands of the male genital tract and testicular sperm component Semen quality is maintained by all the accessory
Chylothorax Basics OVERVIEW GENETICS SIGNALMENT/DESCRIPTION OF PET
 Chylothorax Basics OVERVIEW Chylo- refers to chyle; thorax refers to the chest Chyle is a milky to slightly yellow fluid composed of lymph and fats (rich in triglycerides) taken up from the intestines
Chylothorax Basics OVERVIEW Chylo- refers to chyle; thorax refers to the chest Chyle is a milky to slightly yellow fluid composed of lymph and fats (rich in triglycerides) taken up from the intestines
Karyotype = a test to identify and evaluate the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body cells.
 Karyotype = a test to identify and evaluate the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body cells. Homologous chromosomes are arranged by size, banding patterns, and centromere placement.
Karyotype = a test to identify and evaluate the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body cells. Homologous chromosomes are arranged by size, banding patterns, and centromere placement.
LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis Notes 1. This lab combines the objectives and activities of the macroscopic and microscopic lab activities. Students are expected to review those labs for reference.
LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis Notes 1. This lab combines the objectives and activities of the macroscopic and microscopic lab activities. Students are expected to review those labs for reference.
Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases
 Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases are caused by bacteria. Pneumococcal bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) are the
Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases are caused by bacteria. Pneumococcal bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) are the
Successful flow cytometric immunophenotyping of body fluid specimens
 Successful flow cytometric immunophenotyping of body fluid specimens Fiona E. Craig, MD Division of Hematopathology Mayo Clinic Arizona 2017 MFMER slide-1 Financial disclosure No conflicts 2017 MFMER slide-2
Successful flow cytometric immunophenotyping of body fluid specimens Fiona E. Craig, MD Division of Hematopathology Mayo Clinic Arizona 2017 MFMER slide-1 Financial disclosure No conflicts 2017 MFMER slide-2
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System
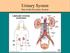 Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
My child is having a lumbar puncture
 My child is having a lumbar puncture Children s Ward Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for parents whose child needs to have a lumbar puncture. It explains about: the process of
My child is having a lumbar puncture Children s Ward Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for parents whose child needs to have a lumbar puncture. It explains about: the process of
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
LIVER BIOPSY. The liver
 LIVER BIOPSY The liver The liver is a big organ located in the right top part of the abdominal cavity. A healthy liver can metabolize proteins, carbohydrates and fats. It also produces digestive fluid
LIVER BIOPSY The liver The liver is a big organ located in the right top part of the abdominal cavity. A healthy liver can metabolize proteins, carbohydrates and fats. It also produces digestive fluid
Chapter 14. The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid
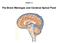 Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
4/19/2018. St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT
 St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT Review Fetal Circulation Provide Indications for Umbilical Artery, Middle Cerebral Artery, and Ductus Venosus Doppler studies. Demonstrate normal
St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT Review Fetal Circulation Provide Indications for Umbilical Artery, Middle Cerebral Artery, and Ductus Venosus Doppler studies. Demonstrate normal
Contents. 1. General Introduction 3
 Section 1 Medical Laboratory 1. General Introduction 3 Guidelines 3 Code of Ethics for Laboratory Technicians 3 Responsibilities of Medical Technician 3 Instructions for Laboratory Technicians 5 Arrangement
Section 1 Medical Laboratory 1. General Introduction 3 Guidelines 3 Code of Ethics for Laboratory Technicians 3 Responsibilities of Medical Technician 3 Instructions for Laboratory Technicians 5 Arrangement
