High Fractional Anisotropy in Brain Abscesses versus Other Cystic Intracranial Lesions
|
|
|
- Felix Harvey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26: , May 2005 High Fractional Anisotropy in Brain Abscesses versus Other Cystic Intracranial Lesions Rakesh K. Gupta, Khader M. Hasan, Asht M. Mishra, Deepak Jha, Mazhar Husain, Kashi N. Prasad, and Ponnada A. Narayana BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: It is known that intracranial mass lesions are relatively isotropic on diffusion-weighted imaging. The purpose of this study is to report an unusually high fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (D av ) in the cavity of the brain abscess compared with other cystic lesions. METHODS: We performed diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) in 12 patients with cystic intracranial lesions (pyogenic abscess, n 5; cysticercus cysts, n 2; and low-grade astrocytoma, n 5). Mean FA, D av from the lesion core, perifocal edema, and corresponding contralateral normal-appearing regions were measured and compared for relative changes in these parameters. In the abscess cases, we placed regions of interest on areas with FA >0.2 and FA <0.2 to get FA and D av values. RESULTS: There were two patterns of FA values in the abscess cavity in all five patients. Part of the abscess showed mean FA , with D av ( ) 10 3 mm 2 /s, whereas other parts had FA with D av ( ) 10 3 mm 2 /s. The cystic tumors and neurocysticercosis showed very high D av ( , ) 10 3 mm 2 /s, with low FA ( , ), respectively. CONCLUSION: Brain abscess cavity shows regions of increased FA values with restricted mean diffusivity compared with other cystic intracranial lesions. This information may prevent misinterpretation of the DTI information as white matter fiber bundle abnormalities associated with mass lesions. Received July 26, 2004; accepted after revision October 6. From the Departments of Radiodiagnosis (R.K.G., A.M.M.) and Microbiology (K.N.P.), Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, and the Department of Neurosurgery (D.J., M.H.), King George s Medical University, Lucknow, India; and the Department of Radiology (K.M.H., P.A.N.), University of Texas Medical School at Houston, Houston, Texas. Supported by a grant from Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, India. Address correspondence to Rakesh K. Gupta, MD, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow , India. American Society of Neuroradiology Diffusion is anisotropic in white matter fiber tracts, as axonal membranes and myelin sheaths present barriers to the motion of water molecules, in directions not parallel to their own orientation (1). The direction of maximal diffusivity has been shown to coincide with the white matter tract information. This information is contained in the diffusion tensor, a mathematical construct of diffusion in 3D space (1, 2). Currently, information about fiber tracts obtained from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is being used by neurosurgeons in the planning of tumor resection (2). A brain abscess is characteristically defined as a focal suppurative process within the brain parenchyma (3). It forms important differential diagnosis with other tumor and nontumor ring-enhancing brain lesions (3). MR imaging techniques such as proton MR spectroscopy and diffusion-weighted (DW) imaging have been used in the differentiation of abscesses from nonabscess lesions with considerable success (4 6). Although most abscesses show restricted diffusion, there are reports showing high diffusivity in the treated abscesses and restricted diffusion in cystic metastases (4, 7, 8). It is proposed that combining DW imaging with in vivo proton MR spectroscopy may help in better characterization of these lesions (6). In this work, we report remarkably high fractional anisotropy (FA) from the cavity of brain abscess in five patients with restricted mean diffusivity in comparison to nonabscess cases. An attempt is made to explain this unusual observation, which, to the best of our knowledge, is described here for the first time in the literature. Subjects and Methods We performed MR imaging, including DTI, on 12 consecutive subjects with various intracranial mass lesions. There were seven male and five female subjects ranging in age from 4 to
2 1108 GUPTA AJNR: 26, May 2005 years. Five patients had brain abscess, five had low-grade astrocytoma, and two had neurocysticercosis (NCC). In the two patients with NCC, there were a total of five cysts of 2 cmin diameter. The diagnosis in the abscess and tumor patients was based on aspiration and culture of the pus and histopathologic reports in cystic neoplasm, respectively. The source of primary infection was otitis media (n 2), orbital infection (n 1), and tooth infection (n 2). The pus was evaluated for the number of viable leukocytes and microbial culture. The final diagnosis in patients with NCC was based on the demonstration of scolex on conventional imaging and CSF serology (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) positive for the parasitic antigen (9). Repeat imaging, including DTI, was also performed in three patients with abscess to look for the changes in FA following aspiration of the pus. We have also obtained DTI data from 10 healthy age- and sex-matched control subjects for the purpose of comparison with these subjects. MR Imaging Protocol Whole-brain conventional MR imaging and DTI were acquired on a 1.5-T MR imaging scanner (General Electric Medical System, Milwaukee, WI) using a standard quadrature birdcage receive and transmit radio-frequency head coil. The conventional MR imaging protocol included T2-weighted fast spin-echo (SE) images with repetition time TR/TE/NEX) 6000/200/16/2 and SE images with TR/TE/NEX 1000/14/1. Both T1- and T2-weighted images were acquired from axial sections of 5-mm section thickness with 0.5-mm intersection gap and 240-mm FOV. Postcontrast T1-weighted magnetization transfer (MT) MR imaging was done after injecting gadolinium diethylenetriaminepenta-acetic acid in the dose of 0.1 mmol/kg body weight (Schering, Berlin, Germany), using the same parameters as T1 except for the off-resonance pulse (1.2 khz) with pulse duration of 16 milliseconds and 670 flip angle to improve the sensitivity of the enhancement. DTI data were acquired using a single-shot echo-planar dual SE sequence with ramp sampling (10, 11). The dual SE sequence reduces image distortions in the diffusion-weighted images by compensating for the effect of eddy currents as shown elsewhere (12). The sequence used spectral-selective pulses for fat suppression. The diffusion-weighted sequence incorporated symmetric trapezoidal gradient pulses with pulse duration ( 25) and separation ( 28 ms). The diffusion weighting b-factor was set to 1,000 s/mm 2,TR 8 seconds, and TE 100 ms. A total of axial sections were acquired with a section thickness of 3 mm, no gap, FOV 240 mm x 240 mm, and an image matrix of (following zero-filling). The diffusion tensor encoding used was the balanced (13), rotationally invariant (14, 15) icosahderal scheme with 21 uniformly distributed directions over the unit hemisphere. To enhance the signal intensity-to-noise ratio (SNR) and reduce phase fluctuations, the magnitude constructed images were repeated (NEX 4) and temporally averaged by the scanner software (10). The SNR 0 in the (b 0) image was about 50 (parenchyma), which reduces the SNR-related biases in the DTI estimated metrics (15, 16). Data from a spherical water phantom were also acquired at 19 C by using the same DTI scheme for the purpose of b-factor calibration. DT-MR Imaging Data Analysis The magnitude-averaged data were transferred via file transfer protocol to a workstation for further analysis. In general, the DTI data analysis involves three major steps: preprocessing, processing, and postprocessing. Data Preprocessing The collected raw images were cropped and stripped using a semiautomated procedure to remove the scalp for isolating the brain. The DW imaging data were spatially filtered with a 3 3 median window. The data were then distortion-corrected for shear, scale, rotation, and translation by using the DT-MR imaging toolbox, which calls the 2D perspective models in the automated image and registration package (17, 18). Data Processing The distortion-corrected data were then interpolated to attain isotropic voxels and decoded to obtain the tensor field for each voxel. The tensor-filed data were then diagonalized using the analytical diagonalization method (19) to obtain the eigenvalues ( 1, 2, and 3 ) and the three orthonormal eigevectors (e 1,e 2, and e 3 ). The tensor field data and eigenvalues were then used to compute the DTI metrics such as the mean diffusivity (D av ; equation 1) and fractional anisotropy (20) (FA; equation 2) for each voxel. 1) D av Data Postprocessing and Quantification To facilitate region-of-interest placement for quantitative analysis, the DTI-derived maps were displayed and overlaid on images with different contrasts in the three orthogonal planes for a visual inspection. FA regional values were obtained by placing the regions of interest on the abscess cavity and other cystic lesions on all sections that contained the lesions. The region-of-interest placement on the lesions was based on the FA maps overlayed on the D av with a cut-off value of 0.20 so that voxels could be separated between the ones with FA values 0.20 and 0.20 for all the cystic lesions. This threshold was chosen because white matter was found to have this as minimal of 0.2 FA value in hundreds of brain images that we had analyzed. In addition, the same regions of interest were placed on the perifocal edema and the corresponding contralateral normal-appearing parenchyma as depicted by T2-weighted images. Size of the regions of interest was guided by the lesion size, and it was always more than 3 3 pixels in all the cases and typically 8 8 pixels, with shape varying from elliptical to rectangular. Data processing and analysis were performed using the analysis and design DTI-toolbox implemented under interactive data language (IDL) (Research Systems, Boulder, CO). FA and D av from the whole brain from three healthy subjects were also quantified for the purpose of comparison. Results Water Phantom Data For the purpose of quality control and b-factor calibration of the scanner gradient system, quantitative FA and diffusivities data were obtained from 25,000 voxels at the center of the water phantom gave 1 ( ) 10 3 mm 2 /s, 2 ( ) 10 3 mm 2 /s, 3 ( ) 10 3 mm 2 /s, D av ( ) 10 3 mm 2 /s, and FA Our water phantom calibration results are consistent with published literature at comparable room temperature (21). Clinical Data The abscesses were located in the right caudate nucleus (n 2), right temporal lobe (n 1), right temporoparietal region (n 1), and right frontal region (n 1). These appeared hyperintense on T2-
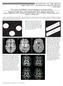
3 AJNR: 26, May 2005 HIGH FRACTIONAL ANISOTROPY IN BRAIN ABSCESSES 1109 FIG 1. A 4-year-old child presented with right ear discharge and brain abscess with intraventricular rupture and meningitis. T2-weighted axial image (A) through the lateral ventricles shows hyperintensity in the right periventricular region with mass effect. Note the layering in the left lateral ventricle. Corresponding T1-weighted image (B) shows the periventricular lesion as hypointense that displays rim enhancement on post contrast T1-weighted MT image (C). Note the enhancement of the ventricular lining that is more prominent on the right side, which suggests ependymitis (C). DW image (D) and D av map (E) at the same level show restricted diffusion in the cavity. Note the area of restricted diffusivity in the layered portion of the left lateral ventricle. FA map (F) shows areas of high FA values in the cavity mixed with intervening low FA values. Note the high FA values in the lower part of the left lateral ventricle medial to the optic radiation. Color modulated FA maps fused with D av map shows (G) orientation in the abscess cavity as well in the left lateral ventricle similar to what is observed in the oriented white matter. Three sections caudally, postcontrast T1-weighted MT image (H) shows the epicenter of the abscess cavity that appears highly oriented on the color-modulated FA maps fused with D av images. The measured FA values were higher than corpus callusm in some of the regions of the abscess cavity. The color coding is shown (G and I, lower left corner): red (right left), green (anteroposterior), blue (superior inferior).
4 1110 GUPTA AJNR: 26, May 2005 normal values reported in the literature (10). This is probably due to voxel contamination with CSF and the effect of pressure on the contralateral lobe by the pathology causing the increased water content in these regions. In three patients with brain abscess, a repeat study following surgical intervention showed a marked decrease in the residual cavity with no restriction of diffusion (Fig 3). FIG 2. Scatter plot of the FA values versus D av from the abscess cavities, tumor cavities cysts, corresponding contralateral normal-appearing parenchyma and whole brain of a healthy adult subject. The plot shows FA and D av values for the tumor cavity and cyst are separate from the abscess cavity. Note the marked variability of FA values in the abscess cavity. weighted images with peripheral hypointense rim, and iso- to hypointense on T1-weighted images. Postcontrast study showed rim enhancement. In one patient, the abscess ruptured into the right lateral ventricle with layering on T2, T1, and DW images and showed low D av and high FA values in the layer (Fig 1). The culture from the pus grew S. aureus (n 2), anaerobic streptococci (n 2), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (n 1). The viable leukocyte count varied from 7,000 to 16,000 in all the abscess cases. The tumors were located in the cerebellum (n 2), brain stem (n 1), right parietal (n 1), and left frontotemporal region (n 1). These appeared hyperintense on T2 and hypointense on T1 and showed rim enhancement on postcontrast study. There was no viable cell visible on microscopy in the fluid obtained from the tumor cavity. The axonal fibers around the cystic lesions showed displacement with marked decrease in FA values in the regions of edema when present focally. The changes in FA at different locations of the abscess, cystic tumors, NCC, and corresponding contralateral normal-appearing white matter and from the normal healthy individuals are plotted against D av (Fig 2). Part of the abscess with FA 0.2 and 0.2 showed mean FA with D av ( ) 10 3 mm 2 /s, and FA with D av ( ) 10 3 mm 2 /s, respectively (Figs 1 3). The cystic tumors (Fig 4) and NCC (Fig 5) showed very high D av ( ) 10 3 mm 2 /s, ( ) 10 3 mm 2 /s with low FA values ( and ), respectively. The mean FA and D av values from the perifocal edema normal-appearing corresponding contralateral parenchyma were , , and ( , ) 10 3 mm 2 /s, respectively. The D av values were toward the higher side compared with the normal healthy subjects and the Discussion The effect of cerebral neoplasm on the white matter tracts has been described using DTI as compressive, discontinued in the region of edema or tumor, or disrupted due to tumor infiltration (2, 22 24). This information was found to be useful for the purpose of tumor resection. We also observed displacement of the axons surrounding the lesions irrespective of the nature of the lesion along with low FA values in the region of the perifocal edema. In addition, in this study we observed markedly increased FA in the cavity of the abscess with different orientations that was not observed in the cavity of the cystic astrocytomas and neurocysticercosis (Figs 1 5). The MR features of a brain abscess vary with the lesion stage. During the initial cerebritis stage, an ill-defined subcortical hyperintense zone on T2- weighted images is associated with poorly delineated enhancing areas within the iso- to mildly hypointense edematous region on enhanced T1-weighted images. During the early and late capsule stages, the collagenous abscess capsule is visible on precontrast study as a comparatively thin-walled, well-delineated iso- to slightly hyperintense rim that becomes hypointense on T2-weighted sequences (3). These abscesses usually show restricted diffusion on DW imaging with low mean diffusivity (3, 5, 6). The purulent material obtained from the abscess cavity at the time of surgery shows inflammatory cells, necrotic cellular debris, proteins, and amino acids as well as low molecular weight metabolites (3, 25). In the present study, in addition to low diffusivity, we observed high FA in some part of the abscess cavity with orientation on the principal eigenvector maps in all of these cases. The FA values are as high as the normal white matter with orientation apparently suggesting an oriented structure within the cavity. Histologically, there was no structure other than the inflammatory cells, necrotic debris, proteins, and amino acids (3, 25). The high FA with low mean diffusivity has been described by several authors in cerebral ischemia and infarction. The previously reported FA values, however, were not as elevated as those observed in the current study (26 29). Recently, it has been shown that FA has a significant inverse correlation with T2 signal intensity in hyperacute stroke and there was no relation with D av measures (29). It was proposed that the initial decrease in extracellular water resulted in high FA and low D av (29). Increased FA has also been found in the first 24 hours after trauma with increased T2 and no change in D av (30). This has been explained by an increase in the largest ( 1 ) eigenvalue coupled with a
5 AJNR: 26, May 2005 HIGH FRACTIONAL ANISOTROPY IN BRAIN ABSCESSES 1111 FIG 3. An 8-year-old girl presented with fever, tooth infection, and signs of raised intracranial tension. T2-weighted axial image (A) through the lateral ventricles shows hyperintense lesion with hypointense peripheral rim in the right periventriclular region and is associated with mass effect. Corresponding T1 (B) and postcontrast T1-weighted MT (C) images show central hypointensity with peripheral rim extending to the body of the corpus callosum. DW image (D) and D av map (E) show areas of restricted diffusivity. FA map (F) show very high values in the medial part of the abscess cavity, and variable FA in the lateral part of the cavity ( ). Color-modulated FA map fused on D av map shows (G) the same with orientation. Following drill aspiration of the abscess cavity, a repeat DTI was done after 5 days. Follow-up T2-weighted image (H) shows residual cavity with mild ventricular dilatation. Postcontrast T1-weighted MT image (I) shows rim enhancement of the residual cavity with ependymal enhancement, which suggests ependimitis. D av map (J) shows high diffusivity and FA map (K) shows marked decrease in values compared with panel F. Color-modulated FA maps (L) fused with D av shows the loss of orientation compared with panel G. proportionately smaller decrease in the smallest ( 3 ) eigenvalue (30). The present clinical situation, however, is not similar to hyperacute stroke or acute traumatic brain injury and therefore cannot be explained on this basis. We propose that the inflammatory cells in the abscess cavity become oriented and organized, resulting in high diffusion anisotropy. The current observation, however, challenges the traditional view that brain anisotropy usually represents myelination and axonal packing (1, 2, 10, 11, 23, 24) and calls for some caution in the interpretation of DTI data. A number of studies have reported DTI results in brain tumors. The tumors have been shown to displace white matter tracts due to mass effect. In all published studies, there is an isotropic diffusion at the center of the cystic tumor cavity (3, 22, 24). We have observed 0 5 intact cells/mm 3 in the fluid obtained from 45 cystic brain neoplasms and three cysticercus cysts (authors unpublished data). On the other hand,
6 1112 GUPTA AJNR: 26, May 2005 FIG 4. A 55-year-old woman with left frontoparietal low-grade astrocytoma. T2-weighted axial image (A) through the lateral ventricle shows hyperintense mass on the left side with perifocal edema and mass effect. The lesion appears hypointense on T1WI image (B) and shows rim enhancement on postcontrast T1-weighted MT image (C). D av map (D) shows high diffusivity and FA map (E) shows little anisotropy. Color-modulated FA map shows no orientation in the cavity. a large number of intact inflammatory cells were seen in these patients with brain abscess. One possibility could be that these cells are tightly packed, thus reducing the extracellular space and therefore are responsible for a large anisotropy in the abscess cavity; however, this explanation is less likely. This is because we observed regions in the abscess cavity with high FA and restricted diffusion and another with low FA and restricted diffusion (Figs 1 3). Larger variation in FA values without a great difference in D av of the abscess cavity suggests that FA does not have a strong relationship with D av in the abscess model (Fig 2). The host response to the microorganisms consists of three pathologic mechanisms: tissue inflammation, granuloma, and abscess formation (31). The presence of bacteria challenges the expression of leukocytes that are activated by its presence. This results in a release of large amounts of chemotactic peptides and an up-regulation of intracellular adhesion molecules (ICAM-1) that are recruited to the cell surface to mediate their aggregation via lymphocyte functionassociated molecule 1 (LFA-1) (31 33). A large cellular aggregation has been shown by incubating the bacteria with the leukocytes after 5 hours that firm up after 24 hours (32). The capsular stage of the brain abscess occurs from the 10th day onward and is associated with the formation of a well-vascularized wall that sequesters the lesion. The cavity of the lesion contains inflammatory cells, bacteria, and debris (3). In the present study, viable leukocytes were found in the cavity and have grown microorganisms responsible for the abscess formation on pus culture. We postulate that the regions with high FA values in the cavity of the abscess contain aggregated (clumped) leukocytes due to the presence of adhesive molecules that are known to be up-regulated in the presence of bacteria. Low FA in some regions of the abscess cavity probably reflects areas devoid of leukocytes with adhesive properties due to the relative lack of up-regulation of the adhesive molecules on the sur-
7 AJNR: 26, May 2005 HIGH FRACTIONAL ANISOTROPY IN BRAIN ABSCESSES 1113 FIG 5. A 40-year-old man with neurocysticercosis. T2-weighted image (A) through the supraventricular region shows a hyperintense cyst on the left side with eccentrically placed hypointense scolex. The lesion appears hypointense with isointense scolex on T1-weighted image (B), and shows minimal rim enhancement on postcontrast T1-weighted MT image (C). D av map (D) shows high diffusivity, and FA map (E) shows little anisotropy. Color-modulated FA map shows no orientation in the cavity. face of the remaining leukocytes. This hypothesis, however, needs confirmation by performing further studies to demonstrate the adhesive molecules on the surface of the leukocytes with cell clumping. Conclusion The present study demonstrates that brain abscess cavity shows regions of increased FA values with restricted mean diffusivity compared with other cystic intracranial lesions. With an increasing use of DTI in surgical planning of brain-tumor resection, one may become more careful in interpreting these changes as oriented axonal fibers. References 1. Le Bihan D. Looking into the functional architecture of the brain with diffusion MRI. Nat Rev Neurosci 2003;4: Jellison BA, Field AS, Medow J, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of cerebral white matter: a pictorial review of physics, fiber tract anatomy, and tumor imaging patterns. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25: Venkatesh SK, Gupta RK. Pyogenic infections. In: Gupta RK, Lufkin RB, eds. MR imaging and spectroscopy of central nervous system infection. New York: Kluwer/Plenum;2001: Shukla-Dave A, Gupta RK, Roy R, et al. Prospective evaluation of in vivo proton MR spectroscopy in differentiation of similar appearing intracranial cystic lesions. Magn Reson Imaging 2001;19: Desprechins B, Stadnik T, Koerts G, et al. Use of diffusion weighted MR imaging in differential diagnosis between intracerebral necrotic tumors and cerebral abscesses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1999;20: Mishra AM, Gupta RK, Jaggi RS, et al. Role of diffusion-weighted imaging and in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the differential diagnosis of ring-enhancing intracranial cystic mass lesions. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2004;28: Holtas S, Geijer B, Stromblad LG, et al. A ring-enhancing metastasis with central high signal on diffusion-weighted imaging and low apparent diffusion coefficients. Neuroradiology 2000;42: Mikami T, Saito K, Kato T, et al. Detection and characterization of the evolution of cerebral abscesses with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging-two case reports. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2002;42: Del Brutto OH, Rajshekhar V, White AC, et al. Proposed diagnostic criteria for neurocysticercosis. Neurology 2001;57:
8 1114 GUPTA AJNR: 26, May Le Bihan D. Diffusion and perfusion magnetic resonance imaging: applications to functional MRI. New York: Raven Press;1995: Basser PJ. Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images. NMR Biomed 1995;8: Reese TG, Heid O, Weisskoff RM, Wedeen VJ. Reduction of eddy-current-induced distortion in diffusion MRI using a twicerefocused spin echo. Magn Reson Med 2003;49: Hasan KM, Parker DL, Alexander AL. Comparison of gradient encoding schemes for diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2001;13: Batchelor PG, Atkinson D, Hill DL, et al. Anisotropic noise propagation in diffusion tensor MRI sampling schemes. Magn Reson Med 2003;49: Hasan KM, Narayana PA. Computation of the fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity maps without tensor decoding and diagonalization: theoretical analysis and validation. Magn Reson Med 2003;50: Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ. Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med 1996;36: Woods RP, Grafton ST, Holmes CJ, et al. Automated image registration. I. General methods and intrasubject, intramodality validation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1998;22: Hasan KM, Alexander AL, Narayana PA. Does fractional anisotropy have better noise immunity characteristics than relative anisotropy in diffusion tensor MRI? An analytical approach. Magn Reson Med 2004;51: Hasan KM, Basser PJ, Parker DL, Alexander AL. Analytical computation of the eigenvalues and eigenvectors in DT-MRI. J Magn Reson 2001;152: Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C. Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 1996;111: Mills R. Self-diffusion in normal and heavy water in the range J Phys Chem 1973;77: Witwer BP, Moftakhar R, Hasan KM, et al. Diffusion-tensor imaging of white matter tracts in patients with cerebral neoplasm. J Neurosurg 2002;97: Clark CC, Barrick TR, Murphy MM, Bell BA. White matter fiber tracking in patients with space-occupying lesions of the brain: a new technique for neurosurgical planning? Neuroimage 2003;20: Mori S, Frederiksen K, van Zijl PCM, et al. Brain white matter anatomy of tumor patients evaluated with diffusion tensor imaging. Ann Neurol 2002;51: Garg M, Gupta RK, Husain M, et al. Brain abscesses: etiologic categorization with in vivo proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 2004;230: van der Toon A, Sykova E, Dijkhuizen RM, et al. Dynamic changes in water ADC, energy metabolism, extracellular space volume, and tortuosity in neonatal rat brain during global ischemia. Magn Reson Med 1996;36: Sorensen AG, Wu O, Copen WA, et al. Human acute cerebral ischemia: detection of changes in water diffusion anisotropy by using MR imaging. Radiology 1999;212: Green HA, Pena A, Price CJ, et al. Increased anisotropy in acute stroke: a possible explanation. Stroke 2002;33: Ozsunar Y, Grant PE, Huisman TAG, et al. Evolution of water diffusion and anisotropy in hyperacute stroke: significant correlation between fractional anisotropy and T2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25: Field AS, Hasan K, Jellison BJ, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging in an infant with traumatic brain swelling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003;24: Gibson FC 3rd, Onderdonk AB, Kasper DL, Tzianabos AO. Cellular mechanism of intraabdominal abscess formation by Bacteroides fragilis. J Immunol 1998;160: Moese S, Selbach M, Meyer TF, Backert S. cag Helicobacter pylori induces homotypic aggregation of macrophage-like cells by up-regulation and recruitment of intracellular adhesion molecule 1 to the cell surface. Infect Immun 2002;70: Kielian T, Hickey WF. Proinflammatory cytokine, chemokine, and cellular adhesion molecule expression during the acute phase of experimental brain abscess development. Am J Pathol 2000;157:
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology
 Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection. Page inserted by evaluation version
 PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:555 562 (2004) Original Research Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:555 562 (2004) Original Research Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor
 107 Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor Ping-Hong Lai 1,4, Shu-Shong Hsu 2,4, Yuk-Keung Lo 3,4, and Shang-Wu
107 Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor Ping-Hong Lai 1,4, Shu-Shong Hsu 2,4, Yuk-Keung Lo 3,4, and Shang-Wu
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 August 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
Brain abscess is a focal intracerebral infection, which begins
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D. Pal A. Bhattacharyya M. Husain K.N. Prasad C.M. Pandey R.K. Gupta In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy Evaluation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses: A Report of 194 Cases BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH D. Pal A. Bhattacharyya M. Husain K.N. Prasad C.M. Pandey R.K. Gupta In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy Evaluation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses: A Report of 194 Cases BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging features of intracranial lesions
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Diffusion MRI explores new indications
 DECEMBER 2001 Diffusion MRI finds new indications Neuroimaging expands with functional MRI 3-tesla MRI bests 1.5-tesla in body and brain Diffusion MRI explores new indications Diffusion tensor imaging
DECEMBER 2001 Diffusion MRI finds new indications Neuroimaging expands with functional MRI 3-tesla MRI bests 1.5-tesla in body and brain Diffusion MRI explores new indications Diffusion tensor imaging
The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 1, p. 11 17, 2004 MAJOR PAPER The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 1, p. 11 17, 2004 MAJOR PAPER The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!!
 Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Brain abscess is a focal suppurative process within the brain
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH V. Tomar A. Yadav R.K.S. Rathore S. Verma R. Awasthi V. Bharadwaj B.K. Ojha K.N. Prasad R.K. Gupta Apparent Diffusion Coefficient with Higher b-value Correlates Better with Viable Cell
ORIGINAL RESEARCH V. Tomar A. Yadav R.K.S. Rathore S. Verma R. Awasthi V. Bharadwaj B.K. Ojha K.N. Prasad R.K. Gupta Apparent Diffusion Coefficient with Higher b-value Correlates Better with Viable Cell
Meningiomas account for between 16% and 20% of primary
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.-H. Toh M. Castillo A.M.-C. Wong K.-C. Wei H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng Y.-L. Wan Differentiation Between and s with Use of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The differentiation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.-H. Toh M. Castillo A.M.-C. Wong K.-C. Wei H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng Y.-L. Wan Differentiation Between and s with Use of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The differentiation
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) results from a
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R. Trivedi R.K. Gupta A. Agarawal K.M. Hasan A. Gupta K.N. Prasad G. Bayu D. Rathore R.K.S. Rathore P.A. Narayana Assessment of White Matter Damage in Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R. Trivedi R.K. Gupta A. Agarawal K.M. Hasan A. Gupta K.N. Prasad G. Bayu D. Rathore R.K.S. Rathore P.A. Narayana Assessment of White Matter Damage in Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis
Case Report. Case Report
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
Differentiation of Tuberculous from Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy and Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1503 1509, September 2001 Differentiation of Tuberculous from Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy and Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging Rakesh K. Gupta,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1503 1509, September 2001 Differentiation of Tuberculous from Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy and Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging Rakesh K. Gupta,
Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
Pyogenic abscesses of hematogenous origin are solitary in
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Luthra A. Parihar K. Nath S. Jaiswal K.N. Prasad N. Husain M. Husain S. Singh S. Behari R.K. Gupta Comparative Evaluation of Fungal, Tubercular, and Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with Conventional
ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Luthra A. Parihar K. Nath S. Jaiswal K.N. Prasad N. Husain M. Husain S. Singh S. Behari R.K. Gupta Comparative Evaluation of Fungal, Tubercular, and Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with Conventional
Demonstration of Scolex within Calcified Cysticercus Cyst: Its Possible Role in the Pathogenesis of Perilesional Edema
 Epilepsia, 43(12):1502 1508, 2002 Blackwell Publishing, Inc. 2002 International League Against Epilepsy Demonstration of Scolex within Calcified Cysticercus Cyst: Its Possible Role in the Pathogenesis
Epilepsia, 43(12):1502 1508, 2002 Blackwell Publishing, Inc. 2002 International League Against Epilepsy Demonstration of Scolex within Calcified Cysticercus Cyst: Its Possible Role in the Pathogenesis
Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging
 Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging Yoshiyuki Nomura, Hajime Sakuma, Kan Takeda, Tomoyasu Tagami, Yasuyuki Okuda,
Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging Yoshiyuki Nomura, Hajime Sakuma, Kan Takeda, Tomoyasu Tagami, Yasuyuki Okuda,
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis. Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis by Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis by Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT
Overview. Fundamentals of functional MRI. Task related versus resting state functional imaging for sensorimotor mapping
 Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation
 MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS
 Anvita Bieza FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS Summary of Doctoral Thesis to obtain PhD degree in medicine Specialty Diagnostic Radiology Riga, 2013 Doctoral thesis
Anvita Bieza FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS Summary of Doctoral Thesis to obtain PhD degree in medicine Specialty Diagnostic Radiology Riga, 2013 Doctoral thesis
Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients
 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries
 1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
Study of the CNS. Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David Norman Thomas H. Newton
 271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
DWI that measures overall diffusivity in terms of directionally
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Toh K.-C. Wei C.-N. Chang P.-W. Hsu H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng M. Castillo C.-P. Lin Differentiation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses from Necrotic Glioblastomas with Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Toh K.-C. Wei C.-N. Chang P.-W. Hsu H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng M. Castillo C.-P. Lin Differentiation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses from Necrotic Glioblastomas with Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491 1499, September 1999 Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Andrew L. Tievsky, Thomas
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491 1499, September 1999 Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Andrew L. Tievsky, Thomas
The estimated annual incidence of central nervous system
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 32-channel coil boosts 3.0T neuro imaging at Kennedy Krieger Kennedy Krieger Institute sees significantly better fmri, DTI,
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 32-channel coil boosts 3.0T neuro imaging at Kennedy Krieger Kennedy Krieger Institute sees significantly better fmri, DTI,
T2, T2*, ute. Yeo Ju Kim. Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
 SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis
 In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
Diffusion Tensor Imaging 12/06/2013
 12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging in CNS Tuberculosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:867 875, May 1999 Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging in CNS Tuberculosis Rakesh K. Gupta, Manoj K. Kathuria, and Sunil Pradhan BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: CNS tuberculosis may simulate
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:867 875, May 1999 Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging in CNS Tuberculosis Rakesh K. Gupta, Manoj K. Kathuria, and Sunil Pradhan BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: CNS tuberculosis may simulate
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy of Untreated and Treated Brain Abscesses
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1049 1053, June/July 1999 Case Report In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy of Untreated and Treated Brain Abscesses Isabella M. Burtscher and Stig Holtås Summary: MR spectroscopy was
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1049 1053, June/July 1999 Case Report In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy of Untreated and Treated Brain Abscesses Isabella M. Burtscher and Stig Holtås Summary: MR spectroscopy was
Phase-Sensitive T1 Inversion Recovery Imaging: A Time-Efficient Interleaved Technique for Improved Tissue Contrast in Neuroimaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1432 1438, June/July 2005 Phase-Sensitive T1 Inversion Recovery Imaging: A Time-Efficient Interleaved Technique for Improved Tissue Contrast in Neuroimaging Ping Hou, Khader M.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1432 1438, June/July 2005 Phase-Sensitive T1 Inversion Recovery Imaging: A Time-Efficient Interleaved Technique for Improved Tissue Contrast in Neuroimaging Ping Hou, Khader M.
Diffusion tensor anisotropy magnetic resonance imaging: a new tool to assess synovial inflammation
 Rheumatology 2009;48:378 382 Advance Access publication 27 January 2009 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken499 Diffusion tensor anisotropy magnetic resonance imaging: a new tool to assess synovial inflammation
Rheumatology 2009;48:378 382 Advance Access publication 27 January 2009 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken499 Diffusion tensor anisotropy magnetic resonance imaging: a new tool to assess synovial inflammation
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography
 Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences
 Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH
 RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
Professional boxing is a controversial sport, and research
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
Kurtosis is a descriptor of the peakedness of a variable relative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:231-236 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.231 Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report Dan B. Karki 1, Ghanashyam Gurung 2,
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:231-236 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.231 Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report Dan B. Karki 1, Ghanashyam Gurung 2,
During human aging, the brain exhibits both macro- and
 Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Tracking the language pathways in edema patients: Preliminary results.
 Tracking the language pathways in edema patients: Preliminary results. Sarah M. E. Gierhan 1,2, Peter Rhone 3,4, Alfred Anwander 1, Isabel Jost 3, Clara Frydrychowicz 3, Karl-Titus Hoffmann 4, Jürgen Meixensberger
Tracking the language pathways in edema patients: Preliminary results. Sarah M. E. Gierhan 1,2, Peter Rhone 3,4, Alfred Anwander 1, Isabel Jost 3, Clara Frydrychowicz 3, Karl-Titus Hoffmann 4, Jürgen Meixensberger
FLAIR Diffusion-Tensor MR Tractography: Comparison of Fiber Tracking with Conventional Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:591 597, March 2005 FLAIR Diffusion-Tensor MR Tractography: Comparison of Fiber Tracking with Conventional Imaging Ming-Chung Chou, Yi-Ru Lin, Teng-Yi Huang, Chao-Ying Wang, Hsiao-Wen
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:591 597, March 2005 FLAIR Diffusion-Tensor MR Tractography: Comparison of Fiber Tracking with Conventional Imaging Ming-Chung Chou, Yi-Ru Lin, Teng-Yi Huang, Chao-Ying Wang, Hsiao-Wen
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Diffusion-tensor imaging in brain tumors
 REVIEW Diffusion-tensor imaging in brain tumors Diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) is the only novel imaging technique that is able to demonstrate white matter tracts and their structural changes related to
REVIEW Diffusion-tensor imaging in brain tumors Diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) is the only novel imaging technique that is able to demonstrate white matter tracts and their structural changes related to
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions
 110 Rizea et al 3D diffuse tensor imaging for preoperative planning 3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions R.E. Rizea, A.V. Ciurea,
110 Rizea et al 3D diffuse tensor imaging for preoperative planning 3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions R.E. Rizea, A.V. Ciurea,
Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
High-field MR imaging systems such as 3T strength aid in
 TECHNICAL NOTE H.-S. Liu H.-W. Chung C.-J. Juan S.-Y. Tsai C.-Y. Wang C.-C. Chan G.-S. Huang M.-C. Chou C.-S. Lee C.-W. Ko N.-Y. Cho C.-Y. Chen Anomalous J-Modulation Effects on Amino Acids in Clinical
TECHNICAL NOTE H.-S. Liu H.-W. Chung C.-J. Juan S.-Y. Tsai C.-Y. Wang C.-C. Chan G.-S. Huang M.-C. Chou C.-S. Lee C.-W. Ko N.-Y. Cho C.-Y. Chen Anomalous J-Modulation Effects on Amino Acids in Clinical
Diffusion Tensor Imaging Assessment of Brain White Matter Maturation During the First Postnatal Year
 DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
Role of MR Spectroscopy and Diffusion Weighted Techniques in Discrimination between Capsular Stage Brain Abscesses, Necrotic and Cystic Brain Lesions
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 80, No. 1, December: 699-710, 2012 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Role of MR Spectroscopy and Diffusion Weighted Techniques in Discrimination between Capsular Stage Brain
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 80, No. 1, December: 699-710, 2012 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Role of MR Spectroscopy and Diffusion Weighted Techniques in Discrimination between Capsular Stage Brain
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Intraoperative Diffusion Imaging on a 0.5 Tesla Interventional Scanner
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 13:115 119 (2001) Original Research Intraoperative Diffusion Imaging on a 0.5 Tesla Interventional Scanner Yoshiaki Mamata, MD, PhD, Hatsuho Mamata, MD, Arya Nabavi,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 13:115 119 (2001) Original Research Intraoperative Diffusion Imaging on a 0.5 Tesla Interventional Scanner Yoshiaki Mamata, MD, PhD, Hatsuho Mamata, MD, Arya Nabavi,
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Role of in Correlation with Mr Spectroscopy R. Archana 1, P. Sunil Kumar 2, Anurudh Kishore 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Post Graduate, Department of Radiodiagnosis:
Original Research Article Role of in Correlation with Mr Spectroscopy R. Archana 1, P. Sunil Kumar 2, Anurudh Kishore 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Post Graduate, Department of Radiodiagnosis:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry
 WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR Imaging
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
SHORTLY AFTER ITS FIRST DEpiction
 OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis
 Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Diffusion tensor imaging: serial quantitation of white matter tract maturity in premature newborns $
 Diffusion tensor imaging: serial quantitation of white matter tract maturity in premature newborns $ Savannah C. Partridge, a Pratik Mukherjee, a Roland G. Henry, a Steven P. Miller, b,c Jeffrey I. Berman,
Diffusion tensor imaging: serial quantitation of white matter tract maturity in premature newborns $ Savannah C. Partridge, a Pratik Mukherjee, a Roland G. Henry, a Steven P. Miller, b,c Jeffrey I. Berman,
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a motor neuron disease
 ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
Stereotactic Diffusion Tensor Tractography For Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
Extremely preterm infants are at high risk of brain injury
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.L.Y. Cheong D.K. Thompson H.X. Wang R.W. Hunt P.J. Anderson T.E. Inder L.W. Doyle Abnormal White Matter Signal on MR Imaging Is Related to Abnormal Tissue Microstructure BACKGROUND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.L.Y. Cheong D.K. Thompson H.X. Wang R.W. Hunt P.J. Anderson T.E. Inder L.W. Doyle Abnormal White Matter Signal on MR Imaging Is Related to Abnormal Tissue Microstructure BACKGROUND
General Identification. Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27
 General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:797 803, April 2005 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy Toshiaki Taoka, Masahiko Sakamoto, Satoru Iwasaki, Hiroyuki Nakagawa,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:797 803, April 2005 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy Toshiaki Taoka, Masahiko Sakamoto, Satoru Iwasaki, Hiroyuki Nakagawa,
Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls.
 Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls. Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. R. Udare, A. Mahajan, S. Juvekar, P. Shetty,
Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls. Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. R. Udare, A. Mahajan, S. Juvekar, P. Shetty,
A quality control program for MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 3, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2002 A quality control program for MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy Tao Wu* and Joel P. Felmlee Department of Radiology,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 3, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2002 A quality control program for MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy Tao Wu* and Joel P. Felmlee Department of Radiology,
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) comprise
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
Abdominal applications of DWI
 Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Enlarged Virchow-Robin spaces in a young man: a constrained spherical deconvolution tractography study
 Acta Biomed 2017; Vol. 88, N. 3: 319-324 DOI: 10.23750/abm.v%vi%i.5181 Mattioli 1885 Case report Enlarged Virchow-Robin spaces in a young man: a constrained spherical deconvolution tractography study Alberto
Acta Biomed 2017; Vol. 88, N. 3: 319-324 DOI: 10.23750/abm.v%vi%i.5181 Mattioli 1885 Case report Enlarged Virchow-Robin spaces in a young man: a constrained spherical deconvolution tractography study Alberto
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Brain
 Neurotherapeutics: The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Brain Andrew L. Alexander,* Jee Eun Lee,* Mariana Lazar, and Aaron S. Field *Departments
Neurotherapeutics: The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Brain Andrew L. Alexander,* Jee Eun Lee,* Mariana Lazar, and Aaron S. Field *Departments
NCC, the central nervous system form of cysticercosis, caused
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Reduced Diffusion in Neurocysticercosis: Circumstances of Appearance and Possible Natural History Implications G.T. Santos, C.C. Leite, L.R. Machado, A.M. McKinney, and L.T. Lucato
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Reduced Diffusion in Neurocysticercosis: Circumstances of Appearance and Possible Natural History Implications G.T. Santos, C.C. Leite, L.R. Machado, A.M. McKinney, and L.T. Lucato
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners
 Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners
 Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
