Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma: a series of seven cases including genetically confirmed aggressive cases and a literature review
|
|
|
- Leo Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Saito et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:31 DOI /s y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma: a series of seven cases including genetically confirmed aggressive cases and a literature review Kenichi Saito 1,3, Eisuke Kobayashi 1*, Akihiko Yoshida 2, Yoshihiro Araki 1, Daisuke Kubota 1, Yoshikazu Tanzawa 1, Akira Kawai 1, Takashi Yanagawa 3, Kenji Takagishi 3 and Hirokazu Chuman 1 Abstract Background: Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma (AFH) is a rare soft tissue tumor of intermediate biologic potential. Because of its rarity and nonspecific radiological and diverse pathological findings, AFH is often clinically misdiagnosed. However, few clinical reports have described this tumor. As reported herein, we analyzed the clinical and radiological features and clinical outcomes of AFH. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of seven cases histopathologically diagnosed as AFH. We examined clinical features, MRI findings, histopathological diagnoses, treatments, and outcomes. Results: These seven cases comprised five male and two female patients with ages ranging from 8 to 50 years old. The primary locations included upper extremities in 2, lower extremities in 4, and the inguinal region in one patient. Of the tumors, 4 occurred in subcutaneous tissues and 3 occurred in deep tissues. No cases were diagnosed as AFH from MRI and needle biopsy results. All cases were diagnosed histopathologically after excision. After treatment, 2 patients (29%) had tumor recurrence and metastasis, one of whom died from disease progression. These 2 aggressive cases involved both EWSR1 and CREB1 gene rearrangements as determined by FISH. The other patients were alive and well without recurrence or metastasis. Conclusion: AFH is a rare tumor that is difficult to diagnose. Therefore, it tends to be misdiagnosed and to be treated inadequately by referring physicians. Surgeons must therefore be mindful of the presence of AFH, learn about appropriate treatment necessary for this tumor, and conduct careful follow-up because AFH can engender poor outcomes. Keywords: Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma, Diagnosis, Prognosis Background Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma (AFH), a rare soft tissue neoplasm, was described initially as angiomatoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma by Enzinger in 1979 [1]. Today, the precise line of differentiation remains unknown, but this entity is no longer regarded as malignant because of its benign microscopic appearance and favorable prognosis. In the 2013 World Health Organization (WHO) * Correspondence: ekobayas@ncc.go.jp 1 Division of Muscloskeletal Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tsukiji, Chuo-ku, Tokyo , Japan Full list of author information is available at the end of the article classification, this tumor was placed under the category of intermediate tumors of uncertain differentiation as AFH [2]. AFH often presents as a soft tissue mass in the subcutis or deep dermis in the extremities of children and young adults, with a median age of 13 years [1, 3, 4]. Clinically and radiologically, it is often difficult to differentiate this tumor from vascular tumors, such as hemangioendothelioma and angiosarcoma, or simply organized hematoma. Although the prognosis of patients with AFH is not poor, it recurs in up to 15% of cases and metastasizes in fewer than 1% of cases [5, 6]. Because of its rarity, few reports have described its related clinical and The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
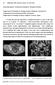
2 Saito et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:31 Page 2 of 8 Fig. 1 Histopathological studies of AFH. The photomicrographic images show: (a) peritumoral lymphoplasmacytic cuffing mimicking a lymph node; (b) the growth of spindle cells with storiform distributions; (c) pseudoangiomatous spaces filled with blood, fibrous pseudocapsules, and hemosiderin deposition; and (d) desmin immunoreactivity. (a) Case 3 and (b)-(d) case 6 radiological findings or treatment outcomes. This report presents the (i) clinical features, (ii) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings, (iii) histopathological diagnoses, and (iv) treatments and outcomes of seven cases of AFH. Methods We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of seven cases histopathologically diagnosed as AFH at two institutions. All histopathological specimens were examined by a soft tissue pathologist to confirm the diagnosis (Figs. 1 and 2). All diagnoses were classified according to Fig. 2 A FISH analysis of AFH. The presence of split red and green signals indicates the presence of EWSR1 rearrangement (case 6) current WHO criteria [2]. All of the patients provided informed consent to the publication of case information. In the case of children, who could not give consent, their parents provided consent on their behalf. Clinical features related to gender, age, tumor size and site, and symptoms were obtained (Table 1). Furthermore, we examined the MRI findings (Table 2), histopathological diagnoses, treatments, and outcomes (Table 3). Results Clinical features These seven cases were composed of five male and two female patients with an age range of 8 to 50 years (mean, 26.4 years). The primary locations were upper extremity in two patients, lower extremity in four patients, and the inguinal region in one patient. Regarding the tumor sites, four patients had subcutaneous lesions and three had deep lesions. Five patients presented with a painless mass, whereas one presented with a painful mass. Only one patient (case 5) had no symptoms. However, the mass had been occasionally noted as an abnormal finding after medical examinations. The average and median sizes of the tumors were 69 mm and 45 mm (range, mm), respectively (Table 1). Magnetic resonance imaging Some groups have reported the MRI features of AFH, including cystic areas, pseudocapsules, peritumoral edema, enhancement, and fluid fluid level [7 13]. On the basis of these findings, we evaluated the imaging characteristics of each case (Table 2, Figs. 3, 4 and 5).
3 Saito et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:31 Page 3 of 8 Table 1 Clinical features of patients with AFH Case No. Sex Age (years) Size (mm) Site Symptom 1 F thigh, subcutaneous mass 2 M finger, subcutaneous mass 3 F 8 10 crus, subcutaneous mass, pain 4 M upper arm, subcutaneous mass 5 M popliteus, intermuscular no 6 M thigh, intramuscular mass 7 M 8 62 groin, intramuscular mass Almost all of the lesions were homogeneously or heterogeneously isointense to muscle on T1 WI and heterogeneously hyperintense on T2 WI. All cases, excluding case 7, presented variegated gadolinium-enhanced imaging. Additionally, pseudocapsule and multilocular findings were obtained in five cases and peritumoral edema was noted in six cases. We confirmed the cystic area and fluid fluid level in two cases each. Based on MRI images, the initial diagnoses were hemangioma/arteriovenous malformation in two cases and hematoma, synovial sarcoma, and myxofibrosarcoma in one case each. No case was initially diagnosed as AFH. Histopathological diagnosis No needle biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of AFH. Four of the seven cases were initially misdiagnosed as other soft tissue tumors (cases 2, 3, 5, and 6): these diagnoses included myxoid liposarcoma, Ewing s sarcoma, myxofibrosarcoma, and synovial sarcoma. Case 4 was initially diagnosed as a spindle cell tumor. The diagnoses of these five cases (cases 2 6) were amended to AFH after pathological review or additional wide resection. Only two cases were correctly diagnosed as AFH by initial excisions (Table 3). Treatments and outcomes The treatments and outcomes of AFH are presented in Table 3. Cases 2, 4, and 5 underwent wide excision in the first treatment. Case 1 was diagnosed as AFH after an excisional biopsy. Thereafter, we performed additional wide excision at our institution. Because cases 3 and 6 were diagnosed as Ewing s sarcoma and synovial sarcoma, respectively, at their former institutions, these patients were administered chemotherapy (case 3, vincristine, doxorubicin, ifosfamide, and actinomycin-d; case 6, doxorubicin and ifosfamide) and wide excision. In case 7, only a marginal resection was performed. For five patients (cases 1, 2, 4, 5, and 7), no further local recurrence or distant metastasis was observed on the last day of follow-up. Case 3 had local recurrence and lymph node metastases at six months after the operation. Therefore, we performed wide re-excision and lymph node dissection. This patient has had no local recurrence or metastasis during the two years following the operation. The case 6 patient developed local recurrence twice and multiple lung metastases after wide resection. The patient was administered chemotherapy (gemcitabine and docetaxel); unfortunately, this patient died four years after initial treatment despite the induction of systemic chemotherapy. Table 2 Magnetic resonance imaging findings Case No. T1 T2 Cystic area Multilocular area Pseudocapsule Fluid fluid level Peritumoral edema Enhancement Initial diagnosis 1 homo, iso to muscle hetero hemangioma, AVM 2 hetero, iso/hyper to muscle hetero NA 3 homo, iso to muscle hetero NA 4 homo, iso to muscle hetero synovial sarcoma 5 homo, iso to muscle hetero myxofibrosarcoma 6 hetero, iso/hyper to muscle 7 hetero, iso/hyper to muscle NA not applicable, AVM arteriovenous malformation hetero hemangioma, AVM hetero NA hematoma
4 Saito et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:31 Page 4 of 8 Table 3 Histopathological diagnosis, treatments, and outcomes Case No Diagnosis of NB Diagnosis of EB Additional treatment EWSR1 rearrangement Recurrence / Metastasis Outcome Follow-up (mo.) 1 NA AFH WE NA / CDF 10 2 NA myxoid ray amputation + / CDF 5 liposarcoma 3 Ewing sarcoma NA Chemo + WE +# + / + NED 18 4 spindle cell tumor NA WE + / CDF 57 5 myxofibrosarcoma NA WE + / CDF 61 6 NA synovial sarcoma Chemo + WE +# + / + DOD 55 7 NA AFH observation NA / CDF 40 NB needle biopsy, EB excisional biopsy, ME marginal excision, WE wide excision, CDF continuous disease free, NED no evidence of disease, DOD died of disease, NA not applicable. #. CREB1 rearrangement was also demonstrated by FISH, using custom CREB1 break-apart probe set (GSP laboratory, Kobe, Japan) Discussion Classified as an intermediate tumor using the WHO classification, AFH rarely metastasizes [2]. It generally follows an excellent clinical course overall. It frequently occurs in children and young adults in soft tissues, forming a well-circumscribed subcutaneous nodule on the extremities, head, neck, and trunk. No well-organized clinical reports exist for AFH because it is a very rare soft tissue tumor. Although patients with AFH typically present with a subcutaneous soft tissue lump, Costa and Weiss et al. reported that 18% of tumors invaded deep structures such as skeletal muscle [3]. In our series, three cases (43%) were in deep lesions. According to previous reports, pain and tenderness were rarely encountered in AFH patients [1, 6, 14]. In our series, only one case (case 3) had a painful mass. In addition, AFH often occurs in children and young adults [1, 2]. However, three of seven patients examined in the present study were older than 30 years. On MRI examination, AFH shows homogeneously hypointense lesions on the T1 WI and heterogeneously hyperintense lesions on the T2 WI [12]. The pattern of a b c Fig. 3 A 28-year-old woman diagnosed with angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma (case 1): (a) T1-weighted spin echo, (b) T2-weighted spin echo, and (c) STIR images. A mm well-circumscribed, round mass is present in the subcutaneous fat of the posterior right thigh. The lesion is homogeneously hypointense on T1 WI and presents fluid fluid level (green arrow) and pseudocapsule (yellow arrow) on T2 WI. STIR shows peritumoral edema (red arrows)
5 Saito et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:31 Page 5 of 8 a b c d e Fig. 4 A 36-year-old man diagnosed with angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma (case 5): (a) T1-weighted spin echo, (b) T2-weighted spin echo, and (c) contrast-enhanced MR images. (d) Non-enhanced and (e) enhanced CT images. A mm asymptomatic mass is present in the popliteal lesion of right knee. The lesion is homogeneously isointense on T1 WI and presents with a multilocular area (pink arrow) and pseudocapsule (yellow arrow) on T2 WI. A contrast-enhanced MR image shows intratumoral and peritumoral (white arrow) enhancement. In addition, an enhanced CT image shows variegated enhancement gadolinium enhancement is a variegated internal and nodular peripheral appearance. In addition, some groups reported that AFH shows cystic areas, pseudocapsules, hemosiderin, and fluid fluid levels on MRI [7 13]. Martinez et al. reported the double rim sign and invasive pattern as novel MRI findings for AFH [15]. The double rim sign refers to the presence of a rim of high signal intensity (RHS) and an adjacent rim of low signal intensity (RLS), which can be observed on both T2-weighted and post-contrast images. The invasive pattern presents as irregular infiltrating peritumoral strings of high signal intensity on T2-weighted and post-contrast images. We believe that these signs were present in the pseudocapsule, peritumoral edema, and enhancement of our series. However, these two typical views were observed only in two cases (cases 3 and 5). Consequently, the MRI findings of AFH are nonspecific. Because of its radiological features and indolent clinical behavior [14], it is often mistaken for a benign condition such as a hematoma or hemangioma, potentially leading to inappropriate treatments. Indeed, in our series, three cases were misdiagnosed from initial MRI findings as a hematoma or hemangioma. Consequently, histopathological examination is extremely important to reach a definitive diagnosis. The characteristic histological features of AFH have been well described [2]. These features include the following: (i) multinodular growth of myoid spindled or histiocytoid cells with a distinctive syncytial appearance,
6 Saito et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:31 Page 6 of 8 a b c d Fig. 5 A 34-year-old man diagnosed with angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma (case 6): (a) T1-weighted spin echo, (b, c) T2-weighted spin echo, and (d) contrast-enhanced images. A mm painless mass is present in the vastus intermedius of the right thigh. The lesion is heterogeneously iso-hyperintense on T1 WI and presents with a multilocular area, cystic area (blue arrows), fluid fluid level (green arrows), pseudocapsule, and peritumoral edema (red arrows) on T2 WI. A contrast-enhanced image shows partial gadolinium enhancement (white arrows) (ii) pseudoangiomatous spaces filled with blood and surrounded by tumor cells, (iii) a thick fibrous pseudocapsule with prominent hemosiderin deposition, and (iv) peritumoral lymphoplasmacytic cuffing with occasional germinal center formation. However, AFH can display a wide morphological spectrum. One or more of the above-described histological findings might be lacking. Nevertheless, multinodular growth of myoid spindle cells is consistent. Devoting attention to this pattern and cytology is crucial for accurate diagnosis. Unusual morphological features that have been reported in a small number of AFHs include clear cells, small cells with scanty cytoplasm resembling Ewing s sarcoma, and rhabdomyoblast-like cells [2, 16, 17]. In addition, a myxoid variant has been established recently in which the tumors exhibit reticular growth in a prominent myxoid background. The diagnosis of myxoid AFH can be particularly challenging. Differential diagnosis includes other myxoid tumors such as low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma, extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma, and myxoid liposarcoma [18]. Although there are no entirely specific immunohistochemical markers for AFH, approximately half of the tumors express desmin. Epithelial membrane antigen expression is also characteristic of AFHs. In addition, AFHs can be uncommonly positive for other myoid markers such as smooth muscle actin, calponin, or, rarely, h-caldesmon, but skeletal muscle markers such as myogenin or MyoD1 are consistently negative [19]. In our series, aside from two cases (cases 1 and 7), none were diagnosed correctly as AFH from the initial biopsies. Cases 2 and 6 were misdiagnosed even after excision. Recent reports have noted that molecular analyses are useful ancillary diagnostic techniques for AFH. These analyses include fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to detect the rearrangement of EWSR1 or FUS and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to elucidate EWSR1-CREB1, EWSR1-ATF1, or FUS-ATF1 fusion transcripts [16, 17, 20]. Tanas et al. reported that 76% of assessed AFH were shown by FISH to harbor EWSR1 rearrangement [20]. Thway et al. showed that both FISH and RT-PCR are equally reliable for facilitating an AFH diagnosis because one technique can identify the cases that the other method misses [21]. The detection of EWSR1 rearrangement by FISH was indeed helpful for reaching the correct diagnosis in our
7 Saito et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:31 Page 7 of 8 series, including five cases (cases 2 6) to which incorrect labeling was assigned initially. In addition, CREB1 gene rearrangement further supported the diagnoses in 2 cases (cases 3 and 6) that showed unexpected aggressive courses. We believe that molecular methods are sometimes necessary for the diagnosis of AFH. A summary and comparison of the clinical outcomes of AFH cases described in earlier reports are presented in Table 4. Although some groups reported a favorable prognosis of AFH after treatment [3, 22, 23], Enzinger et al. reported that 63% and 21% of patients had local recurrence and metastasis, respectively, and that 12% of patients had died of the disease. In a study by Pettinato et al. [22], the prognoses were not good: recurrence occurred in 25% of cases, metastasis occurred in 5% of cases, and death occurred in 5% of cases. However, some reports published before the establishment of molecular analyses might have included malignant neoplasms other than AFH. In our series, five patients remained alive and well without recurrence or metastasis after resection. However, two patients (29%) had tumor recurrence and metastasis, one of whom died from disease progression. Notably, the diagnosis of AFH in both of these aggressive cases was confirmed by FISH on a molecular level for the presence of rearrangements of both EWSR1 and CREB1. Tamas et al. reported that the influence of the EWSR1-CREB1 fusion gene on prognosis was not clear [24]. In the AFH cases in which the EWSR1-CREB1 fusion gene was detected, only one recurrence case was reported [16]; there were no reported deaths. Case 6 may be the first fatal case in which EWSR1-CREB1 was detected. Therefore, the clinical outcome of our cases was unexpectedly worse than that of others described in the literature. Additionally, we administered systemic chemotherapy in case 6, but it was ineffective. Our results suggest that AFH patients may follow an unfortunate course that can rarely be predicted. Costa et al. reported that an irregular tumor border as well as a head and neck location were associated with local recurrence, and the depth of the tumor was correlated with subsequent local and distant metastasis [3]. Furthermore, they showed that the mitotic activity, extreme pleomorphism, inflammatory response, tumor size, patient age, and adjuvant therapy were not correlated with the clinical behavior. In other studies, the degree of mitotic activity and atypia showed no correlation with the risk of recurrence. There have been no reports showing that genetic factors or immunohistochemical profiles are related to clinical behavior. In our small number of cases, we detected no definite correlation between clinical characteristics and prognosis. Nevertheless, we did note several features that might be relevant in the two cases that showed an aggressive course (cases 3 and 6). Specifically, the primary tumor in case 3 was the only one in our series that presented as a painful mass, and it exhibited an unusual small round cell morphology with marked mitotic activity, although its recurrence showed the classic spindle cell histology of AFH. Case 6 manifested as a large mass in a deep location, and its recurrence demonstrated focally increased nuclear atypia and pleomorphism compared to the classic morphology of primary tumors. Interestingly, these pleomorphic tumor cells harbored an increased (up to 12 copies) number of rearranged EWSR1 genes in contrast to a signal copy in non-pleomorphic areas. We suspect that it may be worthwhile to investigate these features to see if they predict local recurrence and distant metastasis. Conclusions Not only is AFH a rare soft tissue neoplasm, but its diagnosis is often difficult because of the lack of specific clinical symptoms and radiological and histopathological features. In our series, AFH occurred in older patients and was found in deep lesions. Although it appears that patients with AFH have excellent prognoses, the rates of Table 4 Literature review Author No. of cases Average age (yr range)) Recurrence cases (%) Metastasis cases (%) Death cases (%) Follow-up (mo. (range)) Enzinger [1] (5 25) 15 (63) 5 (21) 3 (12) 36 (12 240) Costa and Weiss et al. [3] (2 70) 11 (12) 4 (4) 1 (1) 63 (5 189) Pettinato et al. [22] (3 42) 5 (25) 1 (5) 1 (5) NA Fanburg et al. [19] (2 71) 2 (2) 1 (1) 0 6 (12 276) Hasegawa et al. [23] (0.5 54) 1 (25) (84 204) Chen et al. [16] 8 48 (22 65) 1 (12.5) (3 78) Shi et al. [25] (8 83) 2 (9.5) (4 148) Wilk et al. [26] 9 24 (3 67) 0 NA NA 75 (30 132) Our series (8 50) 2 (29) 2 (29) 1 (14.3) 35.1 (5 61) NA not applicable
8 Saito et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:31 Page 8 of 8 local recurrence and metastasis might be higher than initially expected. Surgeons must therefore be aware of AFH and include it in clinical, radiological, and histological differential diagnoses. Abbreviations AFH: Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma; FISH: Fluorescence in situ hybridization; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; RT-PCR: Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction Acknowledgments Not applicable. Funding No funding was obtained for this study. Availability of data and materials Please find all summarized datasets reported in the results section and the tables. Authors contributions KS and EK performed the design and conception of the research, collected and analyzed the data, and drafted and finalized the manuscript. AY performed the pathological examination and revised the manuscript. KS, EK, AK, TY, and HC were the operating surgeons and managed the patients. YA, DK, and YT collected and analyzed the data. AK, TY, KT, and HC provided advice and guidance regarding the surgical procedure and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Consent for publication Consent to publish the data was obtained from the patients or their parents/ guardians. Ethics approval and consent to participate The participants provided their consent to participate as well as consent to publish (or their parents/guardians if under 18 years of age). This study has been approved by the National Cancer Center Institutional Review Board (approval number ). Author details 1 Division of Muscloskeletal Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tsukiji, Chuo-ku, Tokyo , Japan. 2 Division of Pathology and Clinical Laboratories, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tsukiji, Chuo-ku, Tokyo , Japan. 3 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gunma University Graduate School of Medicine, Showa-machi, Maebashi, Gunma , Japan. Received: 8 July 2016 Accepted: 11 January 2017 References 1. Enzinger FM. Angiomatoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma: a distinct fibrohistiocytic tumor of children and young adults simulating a vascular neoplasm. Cancer. 1979;44: Antonescu CR, Rossi S. Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma. In: Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F, editors. WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC; p Costa MJ, Weiss SW. Angiomatoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma. A followup study of 108 cases with evaluation of possible histologic predictors of outcome. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990;14: Thway K. Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma: a review with recent genetic findings. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008;132: Weiss SW, Goldblum JR. Fibrohistiocytic tumors of intermediate malignancy. In: Weiss SW, Goldblum JR, editors. Enzinger and Weiss s soft tissue tumors. Philadelphia: Elsevier Ltd; p Fletcher CD. The evolving classification of soft tissue tumours: An update based on the new WHO classification. Histopathology. 2006;48: Murphey MD, Gross TM, Rosenthal HG. From the archives of the AFIP. Musculoskeletal malignant fibrous histiocytoma: radiologic pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 1994;14: Li CS, Chan WP, Chen WT, et al. MRI of angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma. Skeletal Radiol. 2004;33: Ajlan AM, Sayegh K, Powell T, et al. Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma: magnetic resonance imaging appearance in 2 cases. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2010;34: Mansfield A, Larson B, Stafford SL, Shives TC, Haddock MG, Dingli D. Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma in a 25-year-old male. Rare Tumors. 2010; 2:e Petrey WB, LeGallo RD, Fox MG, Gaskin CM. Imaging characteristics of angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma of bone. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40: Bauer A, Jackson B, Marner E, Gilbertson-Dahdal D. Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma: a case report and review of the literature. J Radiol Case Rep. 2012;6: Yikilmaz A, Ngan BY, Navarro OM. Imaging of childhood angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma with pathological correlation. Pediatr Radiol. 2015;45: Grossman LD, White 4th RR, Arber DA. Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma. Ann Plast Surg. 1996;36(6): Martinez SJ, Moreno CC, Vinson EN, Dodd LG, Brigman BE. Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma: novel MR imaging findings. Skeletal Radiol. 2016;45: Chen G, Folpe AL, Colby TV, et al. Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma: unusual sites and unusual morphology. Mod Pathol. 2011;24: Antonescu CR, Dal Cin P, Nafa K, et al. EWSR1-CREB1 is the predominant gene fusion in angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2007;46: Schaefer IM, Fletcher CD. Myxoid variant of so-called angiomatoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma : clinicopathologic characterization in a series of 21 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014;38: Fanburg-Smith JC, Miettinen M. Angiomatoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma: a clinicopathologic study of 158 cases and further exploration of the myoid phenotype. Hum Pathol. 1999;30: Tanas MR, Rubin BP, Montgomery EA, et al. Utility of FISH in the diagnosis of angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma: a series of 18 cases. Mod Pathol. 2010;23: Thway K, Gonzalez D, Wren D, Dainton M, Swansbury J, Fisher C. Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma: comparison of fluorescence in situ hybridization and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction as adjunct diagnostic modalities. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2015;19: Pettinato G, Manivel JC, De Rosa G, Petrella G, Jaszcz W. Angiomatoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma: cytologic, immunohistochemical, ultrastructural, and flow cytometric study of 20 cases. Mod Pathol. 1990;3: Hasegawa T, Seki K, Ono K, Hirohashi D. Angiomatoid (malignant) fibrous histiocytoma: a peculiar low-grade tumor showing immunophenotype heterogeneity and ultrastructure. Pathol Int. 2000;50: Tornóczky T, Bogner B, Krausz T, Ottóffy G, Szuhai K. Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma: Pleomorphic Variant Associated with Multiplication of EWSR1- CREB1 Fusion Gene. Pathol Oncol Res. 2012;18: Shi H, Li H, Zhen T, et al. Clinicopathological features of angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma: a series of 21 cases with variant morphology. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8: Wilk M, Zelger BG, Debiec-Rychter M, Sciot R, Zelger B. Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma case series with emphasis on a late fibrotic variant. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13:441 8.
Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma : A Case Report
 영남의대학술지제24권제2호 Yeungnam Univ. J. of Med. Vol.24 No.2 p315-321, Dec. 2007 증례 Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma : A Case Report Joon Hyuk Choi, Woo Jung Sung, Nam Hyuk Lee* Department of Pathology, and *Department
영남의대학술지제24권제2호 Yeungnam Univ. J. of Med. Vol.24 No.2 p315-321, Dec. 2007 증례 Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma : A Case Report Joon Hyuk Choi, Woo Jung Sung, Nam Hyuk Lee* Department of Pathology, and *Department
Treatment of angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma after unplanned excision: a case report
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-018-3736-4 BMC Research Notes CASE REPORT Open Access Treatment of angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma after unplanned excision: a case report Kazuhiko Hashimoto *, Shunji Nishimura,
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-018-3736-4 BMC Research Notes CASE REPORT Open Access Treatment of angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma after unplanned excision: a case report Kazuhiko Hashimoto *, Shunji Nishimura,
A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen
 May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
Research Article A Clinicopathological Analysis of Soft Tissue Sarcoma with Telangiectatic Changes
 Sarcoma Volume 2015, Article ID 740571, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/740571 Research Article A Clinicopathological Analysis of Soft Tissue Sarcoma with Telangiectatic Changes Hiroshi Kobayashi,
Sarcoma Volume 2015, Article ID 740571, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/740571 Research Article A Clinicopathological Analysis of Soft Tissue Sarcoma with Telangiectatic Changes Hiroshi Kobayashi,
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis
 Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Prognostic Significance of Grading and Staging Systems using MIB-1 Score in Adult Patients with Soft Tissue Sarcoma of the Extremities and Trunk
 843 Prognostic Significance of Grading and Staging Systems using MIB-1 Score in Adult Patients with Soft Tissue Sarcoma of the Extremities and Trunk Tadashi Hasegawa, M.D. 1 Seiichiro Yamamoto, Ph.D. 2
843 Prognostic Significance of Grading and Staging Systems using MIB-1 Score in Adult Patients with Soft Tissue Sarcoma of the Extremities and Trunk Tadashi Hasegawa, M.D. 1 Seiichiro Yamamoto, Ph.D. 2
Fi r s t described by Enzinger5 in 1979, AFH is a rare
 J Neurosurg 112:978 982, 2010 Intracranial angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma presenting as recurrent multifocal intraparenchymal hemorrhage Case report Paw e l G. Oc h a l s k i, M.D., 1 Ja m e s T. Ed
J Neurosurg 112:978 982, 2010 Intracranial angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma presenting as recurrent multifocal intraparenchymal hemorrhage Case report Paw e l G. Oc h a l s k i, M.D., 1 Ja m e s T. Ed
Pathology of Sarcoma ELEANOR CHEN, MD, PHD, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON
 Pathology of Sarcoma ELEANOR CHEN, MD, PHD, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON Presentation outline Background and epidemiology of sarcomas Sarcoma classification Sarcoma
Pathology of Sarcoma ELEANOR CHEN, MD, PHD, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON Presentation outline Background and epidemiology of sarcomas Sarcoma classification Sarcoma
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Slide Seminar Spanish Society of Pathology
 Slide Seminar Spanish Society of Pathology John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine 1921 Original
Slide Seminar Spanish Society of Pathology John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine 1921 Original
Surgical Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2015
 Surgical Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2015 John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Pathology, Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Surgical Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2015 John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Pathology, Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Takayuki Ohguri 1 Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masanori Hisaoka 2 Hideyuki Watanabe 1 Katsumi Nakamura 1 Hiroshi Hashimoto 2 Toshitaka Nakamura 3 Hajime Nakata 1
 Takayuki Ohguri 1 Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masanori Hisaoka 2 Hideyuki Watanabe 1 Katsumi Nakamura 1 Hiroshi Hashimoto 2 Toshitaka Nakamura 3 Hajime Nakata 1 Received July 1, 2002; accepted after revision November
Takayuki Ohguri 1 Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masanori Hisaoka 2 Hideyuki Watanabe 1 Katsumi Nakamura 1 Hiroshi Hashimoto 2 Toshitaka Nakamura 3 Hajime Nakata 1 Received July 1, 2002; accepted after revision November
Evaluating and Reporting Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors after Imatinib Mesylate Treatment
 The Open Pathology Journal, 2009, 3, 53-57 53 Open Access Evaluating and Reporting Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors after Imatinib Mesylate Treatment Katie L. Dennis * and Ivan Damjanov Department of Pathology
The Open Pathology Journal, 2009, 3, 53-57 53 Open Access Evaluating and Reporting Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors after Imatinib Mesylate Treatment Katie L. Dennis * and Ivan Damjanov Department of Pathology
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare
 Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Diagnoses one would not like to miss in soft tissue pathology early in your career Marta Sbaraglia, MD Department of Pathology Hospital of Treviso University of Padua
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Diagnoses one would not like to miss in soft tissue pathology early in your career Marta Sbaraglia, MD Department of Pathology Hospital of Treviso University of Padua
Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
USCAP 2011: ASDP companion meeting. Steven D. Billings 1
 USCAP 2011: ASDP companion meeting. Steven D. Billings (billins@ccf.org) 1 Spindle cell tumors that make you say, Oh $*&%! This lecture will focus on examples of cutaneous tumors that present particular
USCAP 2011: ASDP companion meeting. Steven D. Billings (billins@ccf.org) 1 Spindle cell tumors that make you say, Oh $*&%! This lecture will focus on examples of cutaneous tumors that present particular
Newer soft tissue entities
 Newer soft tissue entities Examples among fibroblastic tumors Turku, May 6, 2010 Markku Miettinen, M.D. AFIP, Washington, DC Fibroblastic neoplasms Solitary fibrous tumor /Hemangiopericytoma Low-grade
Newer soft tissue entities Examples among fibroblastic tumors Turku, May 6, 2010 Markku Miettinen, M.D. AFIP, Washington, DC Fibroblastic neoplasms Solitary fibrous tumor /Hemangiopericytoma Low-grade
Molecular Diagnosis of Soft Tissue Tumors: Avoid Pitfalls
 Molecular Diagnosis of Soft Tissue Tumors: Avoid Pitfalls Cristina Antonescu, MD Department of Pathology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York Overview I. When should we rely on the help of
Molecular Diagnosis of Soft Tissue Tumors: Avoid Pitfalls Cristina Antonescu, MD Department of Pathology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York Overview I. When should we rely on the help of
CASE REPORT PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE.
 PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
Surgery for Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma, Presenting Two Radiologically and Pathologically Distinctive Patterns
 Surgery for Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma, Presenting Two Radiologically and Pathologically Distinctive Patterns Manabu Hoshi 1, Seiichi Matsumoto 1, Jun Manabe 1, Taisuke Tanizawa 1, Toshio Shigemitsu
Surgery for Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma, Presenting Two Radiologically and Pathologically Distinctive Patterns Manabu Hoshi 1, Seiichi Matsumoto 1, Jun Manabe 1, Taisuke Tanizawa 1, Toshio Shigemitsu
57th Annual HSCP Spring Symposium 4/16/2016
 An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling
 Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
Klinisch belang van chromosomale translocatie detectie in sarcomen
 Translocations in sarcomas Klinisch belang van chromosomale translocatie detectie in sarcomen Judith V.M.G. Bovée, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology Leiden University Medical Center RNA binding DNA binding
Translocations in sarcomas Klinisch belang van chromosomale translocatie detectie in sarcomen Judith V.M.G. Bovée, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology Leiden University Medical Center RNA binding DNA binding
Update On Lipomatous Tumors: Old Standbys and New Concepts
 Update On Lipomatous Tumors: Old Standbys and New Concepts John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Update On Lipomatous Tumors: Old Standbys and New Concepts John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Ultrasound screening of soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity - a BSG guide for ultrasonographers and primary care
 Ultrasound screening of soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity - a BSG guide for ultrasonographers and primary care Introduction Soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity are common and most
Ultrasound screening of soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity - a BSG guide for ultrasonographers and primary care Introduction Soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity are common and most
Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement
 Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
Financial disclosures
 Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchc Geisel School of
Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchc Geisel School of
SOFT TISSUE TUMOR PATHOLOGY: AN UPDATE
 SOFT TISSUE TUMOR PATHOLOGY: AN UPDATE Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD July 18, 2013 Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA I have no disclosures. New Soft
SOFT TISSUE TUMOR PATHOLOGY: AN UPDATE Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD July 18, 2013 Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA I have no disclosures. New Soft
The Impact of Advances in Molecular Genetic Pathology on the. Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment of Selected Soft Tissue
 The Impact of Advances in Molecular Genetic Pathology on the Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment of Selected Soft Tissue Tumors of the Head and Neck Joaquín J. García MD and Andrew L. Folpe MD Department
The Impact of Advances in Molecular Genetic Pathology on the Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment of Selected Soft Tissue Tumors of the Head and Neck Joaquín J. García MD and Andrew L. Folpe MD Department
5/10. Pathology Soft tissue tumors. Farah Bhani. Mohammed Alorjani
 5/10 Pathology Soft tissue tumors Mohammed Alorjani Farah Bhani Slides are included in this sheet. Objectives: Soft tissue tumors 1. Describe soft tissue tumors. 2. Understand the classification of soft
5/10 Pathology Soft tissue tumors Mohammed Alorjani Farah Bhani Slides are included in this sheet. Objectives: Soft tissue tumors 1. Describe soft tissue tumors. 2. Understand the classification of soft
No financial or other disclosures
 Case 2014-5 Esther N. Bit-Ivan, DO Northwestern University Jason Wang, MD Jason Park, MD Korgun Koral, MD Children s Medical Center Charles Timmons, MD Veena Rajaram, MD No financial or other disclosures
Case 2014-5 Esther N. Bit-Ivan, DO Northwestern University Jason Wang, MD Jason Park, MD Korgun Koral, MD Children s Medical Center Charles Timmons, MD Veena Rajaram, MD No financial or other disclosures
Tumores de células pequeñas, redondas y azules: diagnóstico diferencial cuando el tiempo apremia
 Tumores de células pequeñas, redondas y azules: diagnóstico diferencial cuando el tiempo apremia Sílvia Bagué Servei de Patologia Hospital de Sant Pau Barcelona Soft tissue sarcomas Heterogeneous group
Tumores de células pequeñas, redondas y azules: diagnóstico diferencial cuando el tiempo apremia Sílvia Bagué Servei de Patologia Hospital de Sant Pau Barcelona Soft tissue sarcomas Heterogeneous group
Invasive Papillary Breast Carcinoma
 410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
Extraosseous Ewing s Sarcoma Presented as a Rectal Subepithelial Tumor: Radiological and Pathological Features
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:51-55 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.1.51 Extraosseous Ewing s Sarcoma Presented as a Rectal Subepithelial Tumor: Radiological and Pathological Features
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:51-55 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.1.51 Extraosseous Ewing s Sarcoma Presented as a Rectal Subepithelial Tumor: Radiological and Pathological Features
Desmoplastic Melanoma R/O BCC. Clinical Information. 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o BCC
 R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
Pleomorphic Liposarcoma: A Clinicopathologic Analysis Of 19 Cases
 Pleomorphic Liposarcoma: A Clinicopathologic Analysis Of 19 Cases Katharine A. Downes, M.D., John R. Goldblum, M.D., Elizabeth A. Montgomery, M.D., Cyril Fisher, M.D., F.R.C.Path. Departments of Anatomic
Pleomorphic Liposarcoma: A Clinicopathologic Analysis Of 19 Cases Katharine A. Downes, M.D., John R. Goldblum, M.D., Elizabeth A. Montgomery, M.D., Cyril Fisher, M.D., F.R.C.Path. Departments of Anatomic
Taku Naiki, 1 Shuzo Hamamoto, 1 Noriyasu Kawai, 1 Aya Naiki-Ito, 2 Yoshiyuki Kojima, 1 Takahiro Yasui, 1 Keiichi Tozawa, 1 and Kenjiro Kohri 1
 International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2011, Article ID 261735, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/261735 Case Report Giant Retroperitoneal Mucinous Tumor Supportively Diagnosed as a Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma
International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2011, Article ID 261735, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/261735 Case Report Giant Retroperitoneal Mucinous Tumor Supportively Diagnosed as a Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma
Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT
 Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT during follow- up. ALT, AST, Alk Phos and bilirubin were
Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT during follow- up. ALT, AST, Alk Phos and bilirubin were
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 EXTRA SKELETAL MESENCHYMAL CHONDROSARCOMA :A CASE REPORT Rajaraman R Subbiah S Navin Naushad Kilpaulk Medical College Abstract:
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 EXTRA SKELETAL MESENCHYMAL CHONDROSARCOMA :A CASE REPORT Rajaraman R Subbiah S Navin Naushad Kilpaulk Medical College Abstract:
ACCME/Disclosures ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS. Tumor types with ALK rearrangements. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase. Jason L.
 Companion Meeting of the International Society of Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology The Evolving Concept of Mesenchymal Tumors ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD March 13, 2016
Companion Meeting of the International Society of Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology The Evolving Concept of Mesenchymal Tumors ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD March 13, 2016
Case 2. Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset
 Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
Protocol for the Examination of Biopsy Specimens From Pediatric Patients With Ewing Sarcoma
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Pediatric Patients With Ewing Sarcoma Version: EwingSarcoma 4.0.0.0 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use of this protocol
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Pediatric Patients With Ewing Sarcoma Version: EwingSarcoma 4.0.0.0 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use of this protocol
From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology. Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport
 From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport I have no Conflict of Interest. FNA on Lymphoproliferative
From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport I have no Conflict of Interest. FNA on Lymphoproliferative
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
Case 27 Male 42. Painless, static, well-circumscribed, subcutaneous nodule right lower leg,?lipoma. The best diagnosis is:
 Case 27 Male 42. Painless, static, well-circumscribed, subcutaneous nodule right lower leg,?lipoma. The best diagnosis is: A. Angiosarcoma B. Haemangiopericytoma C.Myopericytoma D.Myofibroma E. Angioleiomyoma
Case 27 Male 42. Painless, static, well-circumscribed, subcutaneous nodule right lower leg,?lipoma. The best diagnosis is: A. Angiosarcoma B. Haemangiopericytoma C.Myopericytoma D.Myofibroma E. Angioleiomyoma
Primary Hepatic Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma: CT and angiographic findings in two cases
 J Radiol Sci 2013; 38: 15-19 Primary Hepatic Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma: CT and angiographic findings in two cases Jan-Wen Ku Ying-Chi Tseng Kuo-Luon Kung Hsien-Chang Shen Yen-Lin Huang Chi-Jen
J Radiol Sci 2013; 38: 15-19 Primary Hepatic Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma: CT and angiographic findings in two cases Jan-Wen Ku Ying-Chi Tseng Kuo-Luon Kung Hsien-Chang Shen Yen-Lin Huang Chi-Jen
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Risk factors for distant metastasis of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2016) 17:261 266 DOI 10.1007/s10195-016-0415-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk factors for distant metastasis of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans Keiko Hayakawa 1 Seiichi Matsumoto 1 Keisuke
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2016) 17:261 266 DOI 10.1007/s10195-016-0415-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk factors for distant metastasis of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans Keiko Hayakawa 1 Seiichi Matsumoto 1 Keisuke
Case Report Spindle cell lipoma of the wrist, occurring in a distinctly rare location: a case report with review of literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(3):3299-3303 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0004992 Case Report Spindle cell lipoma of the wrist, occurring in a distinctly rare location: a case report with review of
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(3):3299-3303 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0004992 Case Report Spindle cell lipoma of the wrist, occurring in a distinctly rare location: a case report with review of
3/27/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma
 AKA Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma Acral Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomaam.j.surg.path1998; 22; 911-924 Inflammatory myxoid tumour of soft parts with bizarre giant cells [Pathol.Res.Pract.
AKA Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma Acral Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomaam.j.surg.path1998; 22; 911-924 Inflammatory myxoid tumour of soft parts with bizarre giant cells [Pathol.Res.Pract.
Multicentric localized giant cell tumor of the tendon. sheath
 Multicentric localized giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath Toshihiro Akisue, Tetsuji Yamamoto ( ), Teruya Kawamoto, Toshiaki Hitora, Takashi Marui, Tetsuya Nakatani, Takafumi Onga, and Masahiro Kurosaka.
Multicentric localized giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath Toshihiro Akisue, Tetsuji Yamamoto ( ), Teruya Kawamoto, Toshiaki Hitora, Takashi Marui, Tetsuya Nakatani, Takafumi Onga, and Masahiro Kurosaka.
CASE REPORT Benign epithelioid peripheral nerve sheath tumour resembling schwannoma
 Malaysian J Pathol 2014; 36(3) : 217 221 CASE REPORT Benign epithelioid peripheral nerve sheath tumour resembling schwannoma Thejasvi KRISHNAMURTHY MD and SR NIVEDITHA MD, DNB Department of Pathology,
Malaysian J Pathol 2014; 36(3) : 217 221 CASE REPORT Benign epithelioid peripheral nerve sheath tumour resembling schwannoma Thejasvi KRISHNAMURTHY MD and SR NIVEDITHA MD, DNB Department of Pathology,
Journal of Solid Tumors, April 2012, Vol. 2, No. 2
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Utility of fluorescence in situ hybridization in subclassifying unclassified high-grade sarcomas: A study of 40 cases using break-apart probes of EWSR1, FOXO1A, SS18 and DDIT3 genes Alfredo
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Utility of fluorescence in situ hybridization in subclassifying unclassified high-grade sarcomas: A study of 40 cases using break-apart probes of EWSR1, FOXO1A, SS18 and DDIT3 genes Alfredo
Slide seminar: Soft tissue and bone pathology
 Slide seminar: Soft tissue and bone pathology Unusual tumors of bone and soft tissue or unusual presentations of common ones Gunhild Mechtersheimer Institute of Pathology, Heidelberg/DE (Sylvia Höller,
Slide seminar: Soft tissue and bone pathology Unusual tumors of bone and soft tissue or unusual presentations of common ones Gunhild Mechtersheimer Institute of Pathology, Heidelberg/DE (Sylvia Höller,
Division of Pathology
 Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
Financial disclosures
 Mesenchymal Neoplasms with Melanocytic Differentiation By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel
Mesenchymal Neoplasms with Melanocytic Differentiation By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel
Mojca Velikonja Jože Pižem
 Mojca Velikonja Jože Pižem An 81-year old woman presented with an exophytic, wart-like skin lesion on her neck that she had observed for one year. Cryotherapy had been applied twice, but proved unsuccessful.
Mojca Velikonja Jože Pižem An 81-year old woman presented with an exophytic, wart-like skin lesion on her neck that she had observed for one year. Cryotherapy had been applied twice, but proved unsuccessful.
Distant and Lymph Node Metastases of Thyroid Nodules with No Pathological Evidence of Malignancy: A Limitation of Pathological Examination
 Endocrine Journal 2008, 55 (5), 889 894 Distant and Lymph Node Metastases of Thyroid Nodules with No Pathological Evidence of Malignancy: A Limitation of Pathological Examination YASUHIRO ITO, TOMONORI
Endocrine Journal 2008, 55 (5), 889 894 Distant and Lymph Node Metastases of Thyroid Nodules with No Pathological Evidence of Malignancy: A Limitation of Pathological Examination YASUHIRO ITO, TOMONORI
Disclosures. An update on ancillary techniques in the diagnosis of soft tissue tumors. Ancillary techniques. Introduction
 Disclosures An update on ancillary techniques in the diagnosis of soft tissue tumors. I have nothing to disclose. Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Clinical Professor, Pathology Introduction Ancillary techniques
Disclosures An update on ancillary techniques in the diagnosis of soft tissue tumors. I have nothing to disclose. Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Clinical Professor, Pathology Introduction Ancillary techniques
Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report
 Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report Rosanna Nenna 1 Cosimo Damiano Inchingolo 1 Domenico Palmieri 2 Annalisa De Lucia 1 Giusy Elicio 1 Pina Miscioscia 1 ( 1 ) U.O.C. di Anatomia Patologica,
Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report Rosanna Nenna 1 Cosimo Damiano Inchingolo 1 Domenico Palmieri 2 Annalisa De Lucia 1 Giusy Elicio 1 Pina Miscioscia 1 ( 1 ) U.O.C. di Anatomia Patologica,
LAC + USC.
 Jeff McDavit,, M.D. LAC + USC mcdavit@usc.edu Clinical History 55 year old male with large, deep, non- tender left thigh mass. Seen at LAC+USC Med Ctr FNA clinic No h/o trauma or radiation Vimentin
Jeff McDavit,, M.D. LAC + USC mcdavit@usc.edu Clinical History 55 year old male with large, deep, non- tender left thigh mass. Seen at LAC+USC Med Ctr FNA clinic No h/o trauma or radiation Vimentin
Pleomorphic Rhabdomyosarcoma Of The Urinary Bladder?mitating A Pelvic Mass: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 11 Number 2 Pleomorphic Rhabdomyosarcoma Of The Urinary Bladder?mitating A Pelvic Mass: A Case Report C Ceylan, T A Serel, A Albayrak, O G Doluoglu Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Urology Volume 11 Number 2 Pleomorphic Rhabdomyosarcoma Of The Urinary Bladder?mitating A Pelvic Mass: A Case Report C Ceylan, T A Serel, A Albayrak, O G Doluoglu Citation
Part 1. Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013
 Part 1 Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013 Pediatric Pathology Soft Tissue Tumors AN UPDATE Rita Alaggio Azienda Ospedaliera Università di Padova Soft Tissue Tumors More
Part 1 Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013 Pediatric Pathology Soft Tissue Tumors AN UPDATE Rita Alaggio Azienda Ospedaliera Università di Padova Soft Tissue Tumors More
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh
 Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
Keywords solitary fibrous tumor, dedifferentiation, dedifferentiated solitary fibrous tumor, STAT6, GRIA2, cytokeratin, rhabdomyosarcomatous
 758452IJSXXX10.1177/1066896918758452International Journal of Surgical PathologyCreytens et al research-article2018 Pitfalls in Pathology Multifocal Cytokeratin Expression in a Dedifferentiated Solitary
758452IJSXXX10.1177/1066896918758452International Journal of Surgical PathologyCreytens et al research-article2018 Pitfalls in Pathology Multifocal Cytokeratin Expression in a Dedifferentiated Solitary
Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 384238, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/384238 Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma Kunihiko Tokashiki, Kiyoaki
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 384238, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/384238 Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma Kunihiko Tokashiki, Kiyoaki
Hemangioendothelioma with a Prominent Lymphoid Infiltrate Mimicking Follicular Dendritic Cell Tumor: Report of a Case
 Journal of Cancer Research Updates, 2013, 2, 135-139 135 Hemangioendothelioma with a Prominent Lymphoid Infiltrate Mimicking Follicular Dendritic Cell Tumor: Report of a Case Justin Kerstetter 1, Mia Perez
Journal of Cancer Research Updates, 2013, 2, 135-139 135 Hemangioendothelioma with a Prominent Lymphoid Infiltrate Mimicking Follicular Dendritic Cell Tumor: Report of a Case Justin Kerstetter 1, Mia Perez
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis
 Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
PROBLEMS OF PROGNOSTICATION IN SOFT TISSUE TUMOURS. Christopher D.M. Fletcher Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 PROBLEMS OF PROGNOSTICATION IN SOFT TISSUE TUMOURS Christopher D.M. Fletcher Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Dr. Fletcher has no conflict of interest or disclosures to
PROBLEMS OF PROGNOSTICATION IN SOFT TISSUE TUMOURS Christopher D.M. Fletcher Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Dr. Fletcher has no conflict of interest or disclosures to
21/07/2017. Hobnail endothelial cells are not the same as epithelioid endothelial cells
 UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
Chondroid lipoma: A rare recently described benign lipomatous tumor
 Al-Malki et al. 7 case report peer Reviewed open OPEN ACCESS Chondroid lipoma: A rare recently described benign lipomatous tumor Salman T. Al-Malki, Abdullah S. Al-Khamiss Abstract Introduction: lipomatous
Al-Malki et al. 7 case report peer Reviewed open OPEN ACCESS Chondroid lipoma: A rare recently described benign lipomatous tumor Salman T. Al-Malki, Abdullah S. Al-Khamiss Abstract Introduction: lipomatous
Brief History. Identification : Past History : HTN without regular treatment.
 Brief History Identification : Name : 陳 x - Admission : 94/10/06 Gender : male Age : 75 y/o Chief Complaint : Urinary difficulty for months. Past History : HTN without regular treatment. Brief History
Brief History Identification : Name : 陳 x - Admission : 94/10/06 Gender : male Age : 75 y/o Chief Complaint : Urinary difficulty for months. Past History : HTN without regular treatment. Brief History
Dermatopathology. Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia
 Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia DERMATOPATHOLOGY CASE CHALLENGE: RECOGNIZING MIMIS AND MASQUERADERS Rosalie Elenitsas. University of Pennsylvania Spectrum Lupus
Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia DERMATOPATHOLOGY CASE CHALLENGE: RECOGNIZING MIMIS AND MASQUERADERS Rosalie Elenitsas. University of Pennsylvania Spectrum Lupus
أملس عضلي غرن = Leiomyosarcoma. Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5
 Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules
 Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules YASUHIRO ITO, TAKUYA HIGASHIYAMA, YUUKI TAKAMURA, AKIHIRO MIYA, KAORU KOBAYASHI, FUMIO MATSUZUKA, KANJI KUMA
Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules YASUHIRO ITO, TAKUYA HIGASHIYAMA, YUUKI TAKAMURA, AKIHIRO MIYA, KAORU KOBAYASHI, FUMIO MATSUZUKA, KANJI KUMA
1/10/2018. Soft Tissue Tumors Showing Melanocytic Differentiation. Overview. Desmoplastic/ Spindle Cell Melanoma
 2016 MFMER slide-1 2016 MFMER slide-2 2016 MFMER slide-3 Soft Tissue Tumors Showing Melanocytic Differentiation Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
2016 MFMER slide-1 2016 MFMER slide-2 2016 MFMER slide-3 Soft Tissue Tumors Showing Melanocytic Differentiation Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Case Report Extremely Rare Case of Vulvar Myxoid Epithelioid Sarcoma
 Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2015, Article ID 971217, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/971217 Case Report Extremely Rare Case of Vulvar Myxoid Epithelioid Sarcoma Joana Lima Rego,
Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2015, Article ID 971217, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/971217 Case Report Extremely Rare Case of Vulvar Myxoid Epithelioid Sarcoma Joana Lima Rego,
A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1
 A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1 1 Animal Health Trust, Newmarket, UK 2 608 Equine and Farm Vets, Rowington, UK Signalment: Horse,
A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1 1 Animal Health Trust, Newmarket, UK 2 608 Equine and Farm Vets, Rowington, UK Signalment: Horse,
Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck. Kevin Harrington
 Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck Kevin Harrington Overview Classification and incidence of sarcomas Clinical presentation Challenges to treatment Management approaches Prognostic factors Radiation-induced
Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck Kevin Harrington Overview Classification and incidence of sarcomas Clinical presentation Challenges to treatment Management approaches Prognostic factors Radiation-induced
Case Report Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Nasal Septum
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 670105, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/670105 Case Report Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Nasal Septum Yuri Okumura, 1 Kazuhiro
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 670105, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/670105 Case Report Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Nasal Septum Yuri Okumura, 1 Kazuhiro
Update on Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumors. Thomas Brenn
 Update on Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumors Thomas Brenn Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumours Wide morphological and biological spectrum Myofibroblastic, smooth muscle, neural, vascular, apidocytic, undifferentiated;
Update on Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumors Thomas Brenn Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumours Wide morphological and biological spectrum Myofibroblastic, smooth muscle, neural, vascular, apidocytic, undifferentiated;
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
The Genetics of Myoepithelial Tumors: salivary glands, soft tissue and bone
 The Genetics of Myoepithelial Tumors: salivary glands, soft tissue and bone Cristina Antonescu, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York Nothing to declare Disclosure Spectrum of Myoepithelial
The Genetics of Myoepithelial Tumors: salivary glands, soft tissue and bone Cristina Antonescu, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York Nothing to declare Disclosure Spectrum of Myoepithelial
Disclosures. An update on ancillary techniques in the diagnosis of soft tissue tumors. Ancillary techniques. Introduction
 Disclosures An update on ancillary techniques in the diagnosis of soft tissue tumors. I have nothing to disclose. Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Clinical Professor, Pathology Introduction Ancillary techniques
Disclosures An update on ancillary techniques in the diagnosis of soft tissue tumors. I have nothing to disclose. Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Clinical Professor, Pathology Introduction Ancillary techniques
Myxoid soft tissue tumor in the loin
 J1 Myxoid soft tissue tumor in the loin Atsuji Matsuyama 1, Masamichi Nakayama 2, Masanori Hisaoka 1 1 Department of Pathology & Oncology, School of Medicine, University of Occupational & Environmental
J1 Myxoid soft tissue tumor in the loin Atsuji Matsuyama 1, Masamichi Nakayama 2, Masanori Hisaoka 1 1 Department of Pathology & Oncology, School of Medicine, University of Occupational & Environmental
Soft tissue lipomas, lipoma variants and liposarcomas: MRI evaluation and review of literature
 Soft tissue lipomas, lipoma variants and liposarcomas: MRI evaluation and review of literature Poster No.: R-0122 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit A. A. Tandon,
Soft tissue lipomas, lipoma variants and liposarcomas: MRI evaluation and review of literature Poster No.: R-0122 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit A. A. Tandon,
Disclosures. Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone. Outline. The osteoclast. Giant cell rich tumors 5/21/11
 Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
K-1 (Kyung Hee University, S )
 Case History K-1 (Kyung Hee University, S12-00829) A 17-year-old male presented with posterior neck pain and numbness in both upper extremities after a diving injury. He had no relevant medical history.
Case History K-1 (Kyung Hee University, S12-00829) A 17-year-old male presented with posterior neck pain and numbness in both upper extremities after a diving injury. He had no relevant medical history.
Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors. James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon
 Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon www.tumorsurgery.org Definitions Primary Bone / Soft tissue tumors Mesenchymally derived tumors (Mesodermal)
Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon www.tumorsurgery.org Definitions Primary Bone / Soft tissue tumors Mesenchymally derived tumors (Mesodermal)
A 60-year old Man with Left Jaw Mass. Simon Chiosea, MD University of Pittsburgh medical Center 3/15/2016
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
Disclosure. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None. Off Label Usage None MFMER slide-1
 Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO ATYPICAL MELANOCYTIC LESIONS BIJAN HAGHIGHI M.D, DIRECTOR OF DERMATOPATHOLOGY, ST. JOSEPH HOSPITAL
 A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO ATYPICAL MELANOCYTIC LESIONS BIJAN HAGHIGHI M.D, DIRECTOR OF DERMATOPATHOLOGY, ST. JOSEPH HOSPITAL OBJECTIVES Discuss current trends and changing concepts in our understanding of
A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO ATYPICAL MELANOCYTIC LESIONS BIJAN HAGHIGHI M.D, DIRECTOR OF DERMATOPATHOLOGY, ST. JOSEPH HOSPITAL OBJECTIVES Discuss current trends and changing concepts in our understanding of
Recurrent Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma in Psoas Muscle: A Case Report
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 3, pp 211~215, 2012 Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma in Psoas Muscle / 211 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.3.211 Recurrent Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma in Psoas Muscle:
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 3, pp 211~215, 2012 Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma in Psoas Muscle / 211 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.3.211 Recurrent Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma in Psoas Muscle:
MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 5 Number 2 MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System C Costelloe, A Yasko, W Murphy, R Kumar, V Lewis, P Lin, R Stafford,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 5 Number 2 MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System C Costelloe, A Yasko, W Murphy, R Kumar, V Lewis, P Lin, R Stafford,
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Ewing and Ewing like sarcomas Using Genetic Signatures in Refining Small Blue Round Cell Tumor Classification Cristina Antonescu, MD Department of Pathology Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
Ewing and Ewing like sarcomas Using Genetic Signatures in Refining Small Blue Round Cell Tumor Classification Cristina Antonescu, MD Department of Pathology Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee joint- A Case Report and Review of Literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.5 March. (2018), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.5 March. (2018), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors
 The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
Multidisciplinary management of retroperitoneal sarcomas
 Multidisciplinary management of retroperitoneal sarcomas Eric K. Nakakura, MD UCSF Department of Surgery UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center San Francisco, CA 7 th Annual Clinical Cancer Update North Lake
Multidisciplinary management of retroperitoneal sarcomas Eric K. Nakakura, MD UCSF Department of Surgery UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center San Francisco, CA 7 th Annual Clinical Cancer Update North Lake
