Intraoperative ultrasound assistance in resection of intracranial meningiomas
|
|
|
- Moris Bond
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Intraoperative ultrasound assistance in resection of intracranial meningiomas Hailiang Tang 1*, Huaping Sun 2*, Liqian Xie 1*, Qisheng Tang 1*, Ye Gong 1, Ying Mao 1, Qing Xie 1, Mingzhe Zheng 1, Daijun Wang 1, Hongda Zhu 1, Jianhong Zhu 1, Xiaoyuan Feng 2, Zhenwei Yao 2, Xiancheng Chen 1, Liangfu Zhou 1 1 eurosurgery Department of Huashan Hospital, Shanghai , China; 2 Radiology Department of Huashan Hospital, Shanghai , China *These authors contribute equally to the paper. Corresponding to: Ye Gong. eurosurgery Department of Huashan Hospital, Shanghai , China. drgongye@163.com; Xiaoyuan Feng. Radiology Department of Huashan Hospital, Shanghai , China. xyfeng@fudan.edu.cn. Objective: Intracranial meningiomas, especially those located at anterior and middle skull base, are difficult to be completely resected due to their complicated anatomy structures and adjacent vessels. It s essential to locate the tumor and its vessels precisely during operation to reduce the risk of neurological deficits. The purpose of this study was to evaluate intraoperative ultrasonography in displaying intracranial meningioma and its surrounding arteries, and evaluate its potential to improve surgical precision and minimize surgical trauma. Methods: Between December 2011 and January 2013, 20 patients with anterior and middle skull base meningioma underwent surgery with the assistance of intraoperative ultrasonography in the eurosurgery Department of Shanghai Huashan Hospital. There were 7 male and 13 female patients, aged from 31 to 66 years old. Their sonographic features were analyzed and the advantages of intraoperative ultrasonography were discussed. Results: The border of the meningioma and its adjacent vessels could be exhibited on intraoperative ultrasonography. The sonographic visualization allowed the neurosurgeon to choose an appropriate approach before the operation. In addition, intraoperative ultrasonography could inform neurosurgeons about the location of the tumor, its relation to the surrounding arteries during the operation, thus these essential arteries could be protected carefully. Conclusions: Intraoperative ultrasonography is a useful intraoperative technique. When appropriately applied to assist surgical procedures for intracranial meningioma, it could offer very important intraoperative information (such as the tumor supplying vessels) that helps to improve surgical resection and therefore might reduce the postoperative morbidity. Key Words: Intraoperative ultrasonography; intracranial meningioma Submitted May 03, Accepted for publication May 25, doi: /j.issn Scan to your mobile device or view this article at: Introduction Intracranial meningiomas are relatively common tumors derived from arachnoidal cells and most frequently occur in association with intracranial meninges. They account about 20% of primary brain tumors (1,2). Most intracranial meningiomas are benign tumors (WHO grade I) with well prognosis after standard treatment (3). Usually, the optimal therapy of intracranial meningioma is surgical removal of the lesion using microsurgical techniques. The precise resection of the tumor is essential. However, there are some problems the neurosurgeon may encounter during the operation. For instance, it ll be very difficult to remove the tumors completely if they are closely related to the vessels,
2 340 Tang et al. Intraoperative ultrasound assistance in resection of intracranial meningiomas especially those wrap up the arteries, which will result in tumor residual (4). owadays, many advanced image techniques are applied into intracranial meningioma removal, which greatly improve the tumor resection rate and minimize postoperative neurological deficits (5). Pre-operative CT and MRI scan could reveal the location and volume of the tumor. The magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) could exhibit the vessels surrounding the tumor. The relationship of tumor and its adjacent vessels could be further evaluated by three-dimensional (3D) graphics provided by Virtual Reality. Moreover, the neurosurgeon could even obtain more information about the tumor using intra-operative neuro-navigation system. Intraoperative ultrasound is also available in modern neurosurgery, which has been applied for brain tumor resection for many years. Though its poor image quality, intraoperative ultrasound is still a less invasive and more convenient approach, especially its ability of displaying blood flow. Researches proved that intraoperative ultrasound could assist in determine the brain tumor vessels in an intraoperative setting. It has been applied in intracranial lesion resection (6-8), such as glioma, meningioma, and intradural spinal tumors, which make the operation more precise. In the paper, we report our experience with intraoperative ultrasonography as assistance for locating and determining the tumor and its supplying arteries during intracranial meningioma resection, correlate the sonographic images to preoperative CT and MRI images, and analyze the advantages of this technique. It s proved that intraoperative ultrasonography is a useful technique in intracranial meningioma resection. Patients and methods Patient information 20 patients with anterior or middle skull base meningioma were operated under the guidance of intraoperative ultrasound at the eurosurgery Department of Shanghai Huashan Hospital from December 2011 to January There were 7 male and 13 female patients, aged from 31 to 66 years old. 10 patients suffered from headache and 6 patients suffered from dizziness; 4 patients presented with visual disorders (3 of vision blur; 1 of vision decrease); 2 patients showed loss of olfactory sensation; 2 patients had aphasia; and 1 patient found intracranial lesion by check up. The duration of initial symptoms prior to admission ranged from 2 weeks to (Table 1). Imaging examination Preoperative CT and MRI scanning (Figure 1A-C) with contrast enhancement were performed in all patients. Brain MRA was also performed by Siemens 3T MRI scanner (Figure 1D). The three dimensional time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (3D-TOF MRA) sequence was used and the scanning parameters were as follows: TR =21 ms, TE =3.6 ms, FOV =200 mm, averages =1, slice thickness = 0.9 mm. The images data were post-processed by maximum intensity projection (MIP) in the workstation to display the relationships of the tumor and intracranial arteries. Virtual reality planning All the patients imaging data of brain CT, MRI and MRA were transferred to a virtual reality (VR) workstation (Dextroscope, Volume Interactions, Singapore) (9). The images were processed within the RadioDexter software (Volume Interactions) in order to display the 3D stereoscopic images of tumor and its adjacent supplying arteries, including internal carotid artery (ICA) and its branches such as anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and middle cerebral artery (MCA), which makes the relationship of tumor and vessels more clear and vivid. euronavigation A Medtronic navigational system (Treon, Medtronic Stealth Station) was used in all surgical manipulations (10). The day before surgery, at least 8-10 fiducials were placed on the patients in a scattered pattern for reference prior to imaging and for viewing on the resulting images. Brain CT, MRI and MRA data of the patients were input into the workstation of the navigation system. Registration was performed in the operating room by touching the markers with the probe while indicating to the surgical workstation where marker was being touched. After registration, the lesion on the scalp projection was localized for surgical incision. Treatment and intraoperative ultrasound Prior to the dura was opened and tumor resection, the extent of tumor was detected intraoperatively by ultrasonography (ALOKA, Japan). The ultrasonic probe
3 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research, Vol 25, o 3 June Table 1 List of the 20 patients with intracranial meningioma Case o. Gender/age Symptom and duration Tumor location Surgical removal Complications (Y/) 1 Female/40 Intermittent headache for Anterior skull base, left Sympson II sphenoid ridge 2 Male/31 Headache for Anterior skull base, Sympson II olfactory groove 3 Male/59 Headache for 20 days Anterior skull base, Sympson I olfactory groove 4 Female/48 Dizziness and left vision blur Anterior skull base, left Sympson II for 6 months sphenoid ridge 5 Female/58 Dizziness for 2 months Right sphenoid ridge, Sympson I right middle skull base 6 Male/40 Bilateral vision decrease for Anterior skull base, sellar Sympson II 6 months region 7 Female/49 Headache and loss of Anterior skull base Sympson I olfactory sensation for 8 Male/39 Found intracranial lesion by Anterior skull base Sympson III Y check up 9 Male/36 Vision blur for 3 months Anterior skull base Sympson I 10 Female/46 Headache for 1 year Right middle skull base Sympson II 11 Female/51 Dizziness and vision blur for Anterior skull base Sympson I 1 month 12 Female/63 Insensitive reaction for Anterior skull base Sympson I 2 months, and aphasia for 1 month 13 Female/55 Intermittent headache for Left sphenoid ridge Sympson I 14 Female/66 Headache and dizziness for Anterior skull base, Sympson II 6 months olfactory groove 15 Female/49 Dizziness for 1 year Right sphenoid ridge, Sympson I right middle skull base 16 Male/62 Headache for 6 months Anterior skull base Sympson I 17 Male/59 Aphasia for 1 month Left sphenoid ridge, left Sympson II middle skull base 18 Female/53 Intermittent headache and Left sphenoid ridge Sympson I left facial numbness for 19 Female/37 Headache and dizziness for Right sphenoid ridge, Sympson II 2 weeks right middle skull base 20 Female/31 Loss of olfactory sensation for 5 months Bilateral anterior and middle skull base Sympson II
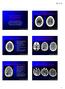
4 342 Tang et al. Intraoperative ultrasound assistance in resection of intracranial meningiomas A B C D E F G H I J K L Figure 1 Preoperation, intraoperation and postoperation situation of patient 17 with left sphenoid ridge and middle cranial fossa giant meningioma. A-C. Pre-operative MRI images showed a giant meningioma with homogenously enhancement located on the left sphenoid ridge and middle cranial fossa; D. Brain MRA indicated that the left ICA and MCA were compressed away by the tumor, and the left MCA was pushed inferiorly and upward; E-F. VR further revealed the relationships of the tumor and the adjacent vessels. After cut the partial tumor, the engulfed arteries were exposed clearly; G. The intra-operative neuronavigation could also detect the vessels surrounding the tumor from different points of view; H-J. Intraoperative ultrasonography could determine the tumor borders, the tumor supplying arteries and blood flow (the colorful dots in the images), and the relationships of the tumor and its supplying vessels; K. During the operation, the important arteries could be carefully protected (the upper white arrow) while the tumor (the left white arrow) was safely resected. The right white arrow showed the lateral cleft vessels; L. Post-operative contrast MRI scan showed the tumor was completely removed without tumor residual Chinese Journal of Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
5 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research, Vol 25, o 3 June with sterile package was put directly on the brain surface, using a small amount of sterile saline as the contact agent (11). The tumor appeared high echo, and the surface borderlines of the tumor were confirmed through coronal, sagittal and horizontal scanning. During the operation, the ultrasonography could be used to detect the tumor supplying arteries, which helps to protect these important vessels (Video 1). After the resection, the ultrasonography was also used to figure out the resection of the tumor and other intracranial situations. Results Ultrasound imaging Guided tumor resection with intraoperative ultrasonography was carried out in all operations. The image quality was good in all cases, enabling a clear visualization of tumor borders and its adjacent vessels (Figure 1H-J). The meningiomas are hyperechoic compared to normal brain tissue. During the tumor resection, the intraoperative ultrasonography was used to detect the arteries that surrounding the meningioma, or supplying the meningioma, or wrapped by the meningioma (Figure 1H-J). Intraoperative ultrasonography is very useful and safety for intracranial meningioma resection, especially those closely related to adjacent vessels. After partial tumor resection, the intraoperative ultrasonography could also real-timely track the location of arteries and its shift. Intraoperative ultrasonography It s very important for neurosurgeons to know exactly the vessels that surrounding the tumor during the operation (Video 1). Intraoperative ultrasound angiography could be assessed for visualizing vessels engulfed by the tumor. Also major intracranial arteries and their branches feeding the tumor could be revealed within the tumor (Figure 1H-J). In patient o.17, the left ICA and MCA were partial engulfed in the tumor and the MCA was pushed inferiorly, which could be visualized from the preoperative MRA and VR images (Figure 1D-F). During the operation, the intraoperative neuronavigation also confirmed the situations (Figure 1G). Moreover, the neurosurgeon could easily figure out the tumor borders (Figure 1H), its adjacent vessels and blood flow by using the intraoperative ultrasound angiography before tumor resection, which was indicated by the colorful dots and oscillogram in Figure 1I-J. This intraoperative technique is essential for avoiding those vital arteries and protecting them while safely removing the tumor (Figure 1K). Overall outcomes Among the 20 patients, total tumor resection (Simpson grade I) was performed in 10 patients and postoperative MRI showed no sign of residual tumor tissue (Figure 1L); tumor resection (Simpson grade II) was achieved in 9 patients, and subtotal tumor resection (Simpson grade III) was performed in 1 patient whose tumor had extensive extent and invaded to scalp and skull (Table 1). Compared to the preoperative MRI, no new significant diffusion changes that could indicate circulatory changes because of traction or trauma to the adjacent parenchyma were seen after surgery. one of the patients died, and all patient experienced postoperative improvement of their symptoms except the patient of case o.8. The patient had tumor residual because of extensive tumor invading. There were no reoperations due to complications. Discussion Meningiomas arise from meningeal arachnoidal cells, and they account for about 20% of all primary brain lesions (1,2). Meningiomas may occur in any location throughout the neuraxis. The optimal therapeutic option of intracranial meningiomas is surgical removal. Except for malignant meningiomas (WHO grade II and III) that may relapse postoperatively, most benign meningiomas (WHO grade I) have good prognoses after surgical resection (3,4,12). However, neurosurgical procedures of anterior and middle skull base meningiomas are extremely difficult due to their complicated anatomy structures and the close relationships of the tumor with its adjacent arteries. How to radically resect the meningioma while safely preserving the arteries well is becoming the key, which is also the goal that neurosurgeon pursues all the time. With the availability of CT, MRI, vessel-related imaging technique (CTA and MRA), and modern image processing workstation (Virtual Reality), it now becomes possible for neurosurgeons to get detail information about the tumor, its supply arteries and its relationships with adjacent brain tissues (5,9). Over the past decades, intraoperative imaging techniques such as neuronavigation have been applied for neurological surgery (10,13). In spite of higher resolution, these technologies require complicated procedures, are rigid and
6 344 Tang et al. Intraoperative ultrasound assistance in resection of intracranial meningiomas difficult to adopt for real-time imaging during surgery. In comparison, intraoperative ultrasonography is of low cost and flexible, different ultrasound probes can be applied relatively easily to adapt to various sizes and shapes to address various applications in brain tumor surgery (14). Intraoperative ultrasonography could help with surgical planning during the operation. Its capability of continuous visualization of intracranial meningioma provides a valuable tool to define the exact tumor location and size, the shift of tumor supplying vessels, and the relationships of the two parts (Figure 1H-J). Bearing in mind with the knowledge about the tumor and its surrounding important arteries, neurosurgeons could carefully plan and adapt an image-guided optimal removal of the tumor with less injury (Figure 1K). Intraoperative ultrasonography could help to confirm the tumor location beneath the dura and optimize the dimension of the dura incision. Intraoperative ultrasonography made it possible to identify the entire expansion of the tumor. Meningiomas usually are hard, and should be removed little by little so as to not cause brain tissue trauma, and complete resection of the adherent part are also essential to prevent tumor recurrence (15) (Figure 1L). The displaying of tumor vessels is essential to preserve the normal brain tissue functions, and might prevent brain damage and minimize bleeding (Video 1) (16). High image quality and resolution are crucial for successful image-guided surgery. Higher frequency in intraoperative ultrasonography produced improved resolution but reduced tissue penetration. Early studies employed ultrasound probes with a frequency of 5 and 7.5 MHz. ow the 10 MHz probes are frequently used (17), which is suited for spinal cord tumor resection (11). In our experience, we employed multi-frequency probes according to the tumor volume for an increased resolution for tumor vessels. The advantages of intraoperative ultrasonography application in intracranial meningioma resection should be assessed in larger series studies in the future (18). Furthermore, ultrasound image quality may decrease during the operation because of blood and air bubbles in the surgical area. It s true that current imaging techniques may not fully reflect the biological extent of the tumor. However, the aim of intraoperative ultrasonography guidance would be to achieve the optimal extent of intracranial meningioma resection without vessels injury (19,20). Conclusions Our experiences in this series of intracranial meningiomas indicated that intraoperative ultrasonography is really a sensitive tool in intracranial meningioma resection. The application of intraoperative ultrasonography in detecting tumor border and its supplying arteries during tumor resection helps to plan the operation and decrease severe post-operative neurological deficits. Intraoperative ultrasonography guidance in anterior and middle skull base meningioma resection could establish clear anatomical landmarks to guide the tumor resection, protect the vital structures, especially the important surrounding arteries, and eventually reduce the surgical complications. Acknowledgments The study was supported by ational atural Science Foundation of China ( , , ), Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (12JC ), and 2011 Shanghai Medical College Young Scientist Fund of Fudan University (11L-24). Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest. References 1. Riemenschneider MJ, Perry A, Reifenberger G. Histological classification and molecular genetics of meningiomas. Lancet eurol 2006;5: Mawrin C, Perry A. Pathological classification and molecular genetics of meningiomas. J eurooncol 2010;99: Perry A, Louis D, Scheithauer BW, et al. Meningiomas. In: Louis D, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, et al. eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of the ervous System. Lyon: IARC, 2007: Alexiou GA, Gogou P, Markoula S, et al. Management of meningiomas. Clin eurol eurosurg 2010;112: Saloner D, Uzelac A, Hetts S, et al. Modern meningioma imaging techniques. J eurooncol 2010;99: Miller D, Heinze S, Tirakotai W, et al. Is the image guidance of ultrasonography beneficial for neurosurgical routine? Surg eurol 2007;67:579-87; discussion Sure U, Benes L, Bozinov O, et al. Intraoperative landmarking of vascular anatomy by integration of duplex and Doppler ultrasonography in image-guided surgery. Technical note. Surg eurol 2005;63:133-41; discussion Tirakotai W, Miller D, Heinze S, et al. A novel platform for image-guided ultrasound. eurosurgery 2006;58:710-8; discussion
7 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research, Vol 25, o 3 June Tang HL, Sun HP, Gong Y, et al. Preoperative surgical planning for intracranial meningioma resection by virtual reality. Chin Med J (Engl) 2012;125: Mao Y, Zhou L, Du G, et al. Image-guided resection of cerebral cavernous malformations. Chin Med J (Engl) 2003;116: Zhou H, Miller D, Schulte DM, et al. Intraoperative ultrasound assistance in treatment of intradural spinal tumours. Clin eurol eurosurg 2011;113: Tang H, Sun H, Chen H, et al. Clinicopathological analysis of metaplastic meningioma: report of 15 cases in Huashan Hospital. Chin J Cancer Res 2013;25: Bernays RL. Intraoperative imaging in neurosurgery. MRI, CT, ultrasound. Introduction. Acta eurochir Suppl 2003;85: Unsgaard G, Ommedal S, Muller T, et al. euronavigation by intraoperative three-dimensional ultrasound: initial experience during brain tumor resection. eurosurgery 2002;50:804-12; discussion Li F, Lin J, Zhu G, et al. euroimaging and functional navigation as potential tools to reduce the incidence of surgical complications of lateral ventricular meningiomas. Clin eurol eurosurg 2011;113: Solheim O, Selbekk T, Lindseth F, et al. avigated resection of giant intracranial meningiomas based on intraoperative 3D ultrasound. Acta eurochir (Wien) 2009;151: Reinacher PC, van Velthoven V. Intraoperative ultrasound imaging: practical applicability as a real-time navigation system. Acta eurochir Suppl 2003;85: Bozinov O, Burkhardt JK. Intra-operative computedtomography-like real-time three-dimensional ultrasound in neurosurgery. World eurosurg 2012;78: Chacko AG, Kumar K, Chacko G, et al. Intraoperative ultrasound in determining the extent of resection of parenchymal brain tumours--a comparative study with computed tomography and histopathology. Acta eurochir (Wien) 2003;145:743-8; discussion Bai HM, Wang WM, Li TD, et al. Three core techniques in surgery of neuroepithelial tumors in eloquent areas: awake anaesthesia, intraoperative direct electrical stimulation and ultrasonography. Chin Med J (Engl) 2011;124: Cite this article as: Tang H, Sun H, Xie L, Tang Q, Gong Y, Mao Y, Xie Q, Zheng M, Wang D, Zhu H, Zhu J, Feng X, Yao Z, Chen X, Zhou L. Intraoperative ultrasound assistance in resection of intracranial meningiomas. Chin J Cancer Res 2013;25(3): doi: /j.issn
Clinicopathological analysis of metaplastic meningioma: report of 15 cases in Huashan Hospital
 Original rticle Clinicopathological analysis of metaplastic meningioma: report of 15 cases in Huashan Hospital Hailiang Tang 1*, Huaping Sun 2*, Hong Chen 3*, Ye Gong 1, Ying Mao 1, Qing Xie 1, Liqian
Original rticle Clinicopathological analysis of metaplastic meningioma: report of 15 cases in Huashan Hospital Hailiang Tang 1*, Huaping Sun 2*, Hong Chen 3*, Ye Gong 1, Ying Mao 1, Qing Xie 1, Liqian
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma
 Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
Meningioma tumor. Meningiomas are named according to their location (Fig. 1) and cause various symptoms: > 1
 Meningioma tumor Overview A meningioma is a type of tumor that grows from the protective membranes, called meninges, which surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign (not cancer) and
Meningioma tumor Overview A meningioma is a type of tumor that grows from the protective membranes, called meninges, which surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign (not cancer) and
Rapid recurrence of a malignant meningioma: case report
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 2 2017 April-June Article Rapid recurrence of a malignant meningioma: case report Oguz Baran, Sima Sayyahmeli, Taner Tanriverdi, Pamir Erdincler TURKEY DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2017-0027
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 2 2017 April-June Article Rapid recurrence of a malignant meningioma: case report Oguz Baran, Sima Sayyahmeli, Taner Tanriverdi, Pamir Erdincler TURKEY DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2017-0027
Application of Intraoperative Ultrasonography for Guiding Microneurosurgical Resection of Small Subcortical Lesions
 Original rticle http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.5.541 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(5):541-546 pplication of Intraoperative Ultrasonography for Guiding Microneurosurgical
Original rticle http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.5.541 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(5):541-546 pplication of Intraoperative Ultrasonography for Guiding Microneurosurgical
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS LIGIA TATARANU, MD, Ph D NEUROSURGICAL CLINIC, BAGDASAR ARSENI CLINICAL HOSPITAL BUCHAREST, ROMANIA SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONFIRMING HISTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS REDUCING TUMOR
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS LIGIA TATARANU, MD, Ph D NEUROSURGICAL CLINIC, BAGDASAR ARSENI CLINICAL HOSPITAL BUCHAREST, ROMANIA SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONFIRMING HISTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS REDUCING TUMOR
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator. Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol
 NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol Neurosurgery What will be covered? Meningioma Vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma)
NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol Neurosurgery What will be covered? Meningioma Vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma)
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Application of neuronavigation in Neurosurgery at King Hussein Medical Center, Jordan
 Keeping up with technology Application of neuronavigation in Neurosurgery at King Hussein Medical Center, Jordan Abdullah al-akayleh Department of Neuosurgery, King Hussean Medical Center, Jordan. ABSTRACT
Keeping up with technology Application of neuronavigation in Neurosurgery at King Hussein Medical Center, Jordan Abdullah al-akayleh Department of Neuosurgery, King Hussean Medical Center, Jordan. ABSTRACT
Error analysis in neuronavigation
 Fakultät für Informatik - Humanoids and Intelligence Systems Lab Institut für Anthropomatik Mittwochs von 12:15-13:45 Error analysis in neuronavigation Uwe Spetzger Neurochirurgische Klinik, Klinikum Karlsruhe
Fakultät für Informatik - Humanoids and Intelligence Systems Lab Institut für Anthropomatik Mittwochs von 12:15-13:45 Error analysis in neuronavigation Uwe Spetzger Neurochirurgische Klinik, Klinikum Karlsruhe
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MENINGIOMA CNS Site Group Meningioma Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MENINGIOMA CNS Site Group Meningioma Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION
Radiological Appearance of Extra-axial CNS Hemangioma
 Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 183-190 183 Radiological Appearance of Extra-axial CNS Hemangioma MING-SHIANG YANG CLAYTON CHI-CHANG CHEN WEN-HSIEN CHEN HAO-CHUN HUNG SAN-KAN LEE Department of Radiology, Taichung
Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 183-190 183 Radiological Appearance of Extra-axial CNS Hemangioma MING-SHIANG YANG CLAYTON CHI-CHANG CHEN WEN-HSIEN CHEN HAO-CHUN HUNG SAN-KAN LEE Department of Radiology, Taichung
Dosimetry, see MAGIC; Polymer gel dosimetry. Fiducial tracking, see CyberKnife radiosurgery
 Subject Index Acoustic neuroma, neurofibromatosis type 2 complications 103, 105 hearing outcomes 103, 105 outcome measures 101 patient selection 105 study design 101 tumor control 101 105 treatment options
Subject Index Acoustic neuroma, neurofibromatosis type 2 complications 103, 105 hearing outcomes 103, 105 outcome measures 101 patient selection 105 study design 101 tumor control 101 105 treatment options
The View through the Nose: ENT considerations for Pituitary/Skull Base Surgery
 The View through the Nose: ENT considerations for Pituitary/Skull Base Surgery Edsel Kim, M.D. Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery The Oregon Clinic Providence Brain and Spine Institute Pituitary, Thyroid
The View through the Nose: ENT considerations for Pituitary/Skull Base Surgery Edsel Kim, M.D. Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery The Oregon Clinic Providence Brain and Spine Institute Pituitary, Thyroid
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego. MR Angiography. Techniques & Applications. John R. Hesselink, M.D.
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MR Angiography Techniques & Applications John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vascular Imaging Arterial flow void Flow enhancement Gadolinium enhancement Vascular
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MR Angiography Techniques & Applications John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vascular Imaging Arterial flow void Flow enhancement Gadolinium enhancement Vascular
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
The role of the intraoperative ultrasonography in low-grade gliomas. Case report
 354 V. Pasca et al Intraoperative ultrasonography in low-grade gliomas The role of the intraoperative ultrasonography in low-grade gliomas. Case report V. Pasca 1, Şt.I. Florian 1,2, Andreea Magyoros 1
354 V. Pasca et al Intraoperative ultrasonography in low-grade gliomas The role of the intraoperative ultrasonography in low-grade gliomas. Case report V. Pasca 1, Şt.I. Florian 1,2, Andreea Magyoros 1
Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations S.-F. GONG 1,2, X.-B. WANG 1,3, Y.-Q. LIAO 1,2, T.-P. JIANG 1,2, J.-B. HE 1,2,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations S.-F. GONG 1,2, X.-B. WANG 1,3, Y.-Q. LIAO 1,2, T.-P. JIANG 1,2, J.-B. HE 1,2,
Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Virtual Navigator study: Subset of preliminary data about cerebral venous circulation
 Perspectives in Medicine (2012) 1, 385 389 Bartels E, Bartels S, Poppert H (Editors): New Trends in Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics an Update. Perspectives in Medicine (2012) 1, 385 389 journal
Perspectives in Medicine (2012) 1, 385 389 Bartels E, Bartels S, Poppert H (Editors): New Trends in Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics an Update. Perspectives in Medicine (2012) 1, 385 389 journal
Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization
 Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization Poster No.: C-1574 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Cucos, A. Puiu, S. Manole ; Cluj-Napoca/RO, Cluj napoca/ RO Keywords: Cerebrospinal
Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization Poster No.: C-1574 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Cucos, A. Puiu, S. Manole ; Cluj-Napoca/RO, Cluj napoca/ RO Keywords: Cerebrospinal
General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]
![General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ] General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]](/thumbs/76/74079340.jpg) General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression
 MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
Overview
 Overview Tutorial Script 1 Script for the Virtual Stroke Lab Tutorial Overview http://www.ilstu.edu Background and Vocabulary This podcast provides an overview of The Virtual Stroke Lab, a free virtual
Overview Tutorial Script 1 Script for the Virtual Stroke Lab Tutorial Overview http://www.ilstu.edu Background and Vocabulary This podcast provides an overview of The Virtual Stroke Lab, a free virtual
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas
 External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
Extracranial-to-Intracranial Bypass Using Radial Artery Grafting for Complex Skull Base Tumors: Technical Note
 Extracranial-to-Intracranial Bypass Using Radial Artery Grafting for Complex Skull Base Tumors: Technical Note Saleem I. Abdulrauf, M.D., F.A.C.S. 1 ABSTRACT The management of complex skull base tumors
Extracranial-to-Intracranial Bypass Using Radial Artery Grafting for Complex Skull Base Tumors: Technical Note Saleem I. Abdulrauf, M.D., F.A.C.S. 1 ABSTRACT The management of complex skull base tumors
Intraoperative case studies. Portable full body 32-slice CT scanner
 Intraoperative case studies Portable full body 32-slice CT scanner Point-of-care CT imaging Your multi-departmental imaging solution Orthopedic surgery Arthroplasty Musculoskeletal disorders Hip replacement
Intraoperative case studies Portable full body 32-slice CT scanner Point-of-care CT imaging Your multi-departmental imaging solution Orthopedic surgery Arthroplasty Musculoskeletal disorders Hip replacement
Open clipping surgery to treat cerebral aneurysms. Head-up display may facilitate safe keyhole surgery for cerebral aneurysm clipping
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 129:883 889, 2018 Head-up display may facilitate safe keyhole surgery for cerebral aneurysm clipping Terushige Toyooka, MD, PhD, Naoki Otani, MD, PhD, Kojiro Wada, MD, PhD,
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 129:883 889, 2018 Head-up display may facilitate safe keyhole surgery for cerebral aneurysm clipping Terushige Toyooka, MD, PhD, Naoki Otani, MD, PhD, Kojiro Wada, MD, PhD,
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
DIRECT SURGERY FOR INTRA-AXIAL
 Kitakanto Med. J. (S1) : 23 `28, 1998 23 DIRECT SURGERY FOR INTRA-AXIAL BRAINSTEM LESIONS Kazuhiko Kyoshima, Susumu Oikawa, Shigeaki Kobayashi Department of Neurosurgery, Shinshu University School of Medicine,
Kitakanto Med. J. (S1) : 23 `28, 1998 23 DIRECT SURGERY FOR INTRA-AXIAL BRAINSTEM LESIONS Kazuhiko Kyoshima, Susumu Oikawa, Shigeaki Kobayashi Department of Neurosurgery, Shinshu University School of Medicine,
Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Leksell Gamma Knife Icon. Treatment information
 Leksell Gamma Knife Icon Treatment information You may be feeling frightened or overwhelmed by your recent diagnosis. It can be confusing trying to process a diagnosis, understand a new and challenging
Leksell Gamma Knife Icon Treatment information You may be feeling frightened or overwhelmed by your recent diagnosis. It can be confusing trying to process a diagnosis, understand a new and challenging
Surgical Treatment of Olfactory Groove Meningioma
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., VoL 81, No. 1, March: 133-137, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Surgical Treatment of Olfactory Groove Meningioma AHMED ELSAWAF, M.D., Ph.D. The Department of Neurosurgery,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., VoL 81, No. 1, March: 133-137, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Surgical Treatment of Olfactory Groove Meningioma AHMED ELSAWAF, M.D., Ph.D. The Department of Neurosurgery,
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis
 Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Impact of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery on the neurosurgical management of skull-base lesions: The Combined Approach
 Radiosurgery as part of the neurosurgical armamentarium: Educational Symposium November 24 th 2011 Impact of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery on the neurosurgical management of skull-base lesions: The Combined
Radiosurgery as part of the neurosurgical armamentarium: Educational Symposium November 24 th 2011 Impact of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery on the neurosurgical management of skull-base lesions: The Combined
Skullbase Lesions. Skullbase Surgery Open vs endoscopic. Choice Of Surgical Approaches 12/28/2015. Skullbase Surgery: Evolution
 Skullbase Lesions Skullbase Surgery Open vs endoscopic Prof Asim Mahmood,FRCS,FACS,FICS,FAANS, Professor of Neurosurgery Henry Ford Hospital Detroit, MI, USA Anterior Cranial Fossa Subfrontal meningioma
Skullbase Lesions Skullbase Surgery Open vs endoscopic Prof Asim Mahmood,FRCS,FACS,FICS,FAANS, Professor of Neurosurgery Henry Ford Hospital Detroit, MI, USA Anterior Cranial Fossa Subfrontal meningioma
THE EFFECTIVE OF BRAIN CANCER AND XAY BETWEEN THEORY AND IMPLEMENTATION. Mustafa Rashid Issa
 THE EFFECTIVE OF BRAIN CANCER AND XAY BETWEEN THEORY AND IMPLEMENTATION Mustafa Rashid Issa ABSTRACT: Illustrate malignant tumors that form either in the brain or in the nerves originating in the brain.
THE EFFECTIVE OF BRAIN CANCER AND XAY BETWEEN THEORY AND IMPLEMENTATION Mustafa Rashid Issa ABSTRACT: Illustrate malignant tumors that form either in the brain or in the nerves originating in the brain.
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 7: Biomedical Applications
 Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 7: Biomedical Applications Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 7: Biomedical Applications Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease
 CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
Parathyroid Imaging: Current Concepts. Maria Gule-Monroe, M.D. Nancy Perrier, M.D.
 Parathyroid Imaging: Current Concepts Maria Gule-Monroe, M.D. Nancy Perrier, M.D. Disclosures None Objectives Ultrasound characteristics of parathyroid adenomas vs. lymph nodes 4D-CT evaluation of hyperparathyroidism
Parathyroid Imaging: Current Concepts Maria Gule-Monroe, M.D. Nancy Perrier, M.D. Disclosures None Objectives Ultrasound characteristics of parathyroid adenomas vs. lymph nodes 4D-CT evaluation of hyperparathyroidism
TABLES. Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging. Conclusions. Author (Year) Classification Process/Evid ence Class
 TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Hrushchak N.M. The Pharma Innovation Journal 2014; 3(9): 38-42
 2014; 3(9): 38-42 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2014; 3(9): 38-42 2013 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 10-10-2014 Accepted: 23-11-2014 Ivano-Frankivsk national medical university Kalush regional hospital.
2014; 3(9): 38-42 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2014; 3(9): 38-42 2013 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 10-10-2014 Accepted: 23-11-2014 Ivano-Frankivsk national medical university Kalush regional hospital.
Alessandro Della Puppa
 Intraoperative measurement of arterial blood flow in complex cerebral aneurysms surgery Studio flussimetrico intra-operatorio nel clipping degli aneurismi complessi Alessandro Della Puppa NEUROSURGERY
Intraoperative measurement of arterial blood flow in complex cerebral aneurysms surgery Studio flussimetrico intra-operatorio nel clipping degli aneurismi complessi Alessandro Della Puppa NEUROSURGERY
IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT
 IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT Ramneet Wadi 1, Anil Kumar Shukla 2, Seetha Pramila V. V 3, Sabyasachi Basu 4, Sonam Sanjay 5 1Postgraduate Student, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT Ramneet Wadi 1, Anil Kumar Shukla 2, Seetha Pramila V. V 3, Sabyasachi Basu 4, Sonam Sanjay 5 1Postgraduate Student, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Tips and Tricks in Ventral Skull Base Dissection Narayanan Janakiram, Dharambir S. Sethi, Onkar K. Deshmukh, and Arvindh K.
 05 Tips and Tricks in Ventral Skull Base Dissection Narayanan Janakiram, Dharambir S. Sethi, Onkar K. Deshmukh, and Arvindh K. Gananathan Introduction...75 General Principles...76 Tips and Tricks in Ventral
05 Tips and Tricks in Ventral Skull Base Dissection Narayanan Janakiram, Dharambir S. Sethi, Onkar K. Deshmukh, and Arvindh K. Gananathan Introduction...75 General Principles...76 Tips and Tricks in Ventral
Original Article The potential risk factors for atypical and anaplastic meningiomas: clinical series of 1,239 cases
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5696-5700 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002668 Original Article The potential risk factors for atypical and anaplastic meningiomas: clinical series of 1,239 cases Ruo-Fei
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5696-5700 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002668 Original Article The potential risk factors for atypical and anaplastic meningiomas: clinical series of 1,239 cases Ruo-Fei
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Daily inspiration. Ultrasound system HS70A SAMSUNG MEDISON CO., LTD. Scan code or visit to learn more
 CT-HS70A-V1.01-GI-FTW-160415-EN Ultrasound system HS70A Scan code or visit www.samsungmedison.com/ to learn more SAMSUNG MEDISON CO., LTD. 2015-2016 Samsung Medison All Rights Reserved. Samsung Medison
CT-HS70A-V1.01-GI-FTW-160415-EN Ultrasound system HS70A Scan code or visit www.samsungmedison.com/ to learn more SAMSUNG MEDISON CO., LTD. 2015-2016 Samsung Medison All Rights Reserved. Samsung Medison
Penetration of the Optic Nerve or Chiasm by Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms. - Three Case Reports-
 Penetration of the Optic Nerve or Chiasm by Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms. - Three Case Reports- Tetsuyoshi Horiuchi 1, Toshiya Uchiyama 1, Yoshikazu Kusano 1, Maki Okada 1, Kazuhiro Hongo 1,
Penetration of the Optic Nerve or Chiasm by Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms. - Three Case Reports- Tetsuyoshi Horiuchi 1, Toshiya Uchiyama 1, Yoshikazu Kusano 1, Maki Okada 1, Kazuhiro Hongo 1,
NEURO PROTOCOLS MRI NEURO PROTOCOLS (SIEMENS SCANNERS)
 Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
Certification Review. Module 28. Medical Coding. Radiology
 Module 28 is the study of x-rays, using radiant energy and other imaging techniques, such as resonance imaging or ultrasound, to diagnose illnesses and diseases. Vocabulary Barium enema (BE): lower gastrointestinal
Module 28 is the study of x-rays, using radiant energy and other imaging techniques, such as resonance imaging or ultrasound, to diagnose illnesses and diseases. Vocabulary Barium enema (BE): lower gastrointestinal
NEUROSURGERY DEPARTMENT OF NARAYANA MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL NELLORE, ANDHRA PRADESH
 DEPARTMENT OF NEUROSURGERY Honest Opinion State-of-the-Art Equipment World Class Surgical Skills Experienced and Dedicated Staff Compassionate Care Affordable Cost NARAYANA MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL NELLORE,
DEPARTMENT OF NEUROSURGERY Honest Opinion State-of-the-Art Equipment World Class Surgical Skills Experienced and Dedicated Staff Compassionate Care Affordable Cost NARAYANA MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL NELLORE,
Author(s) Gohji, Kazuo; Gotoh, Akinobu; Kamid. Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1990), 36(7):
 Title Giant renal angiomyolipoma with an pattern: a case report Author(s) Gohji, Kazuo; Gotoh, Akinobu; Kamid Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1990), 36(7): 837-840 Issue Date 1990-07 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/116942
Title Giant renal angiomyolipoma with an pattern: a case report Author(s) Gohji, Kazuo; Gotoh, Akinobu; Kamid Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1990), 36(7): 837-840 Issue Date 1990-07 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/116942
Role of 3D T2 weighted imaging at 3T in evaluation of cranial nerve pathologies - An overview
 Role of 3D T2 weighted imaging at 3T in evaluation of cranial nerve pathologies - An overview Poster No.: C-1153 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Kasi Arunachalam 1, R. Renganathan
Role of 3D T2 weighted imaging at 3T in evaluation of cranial nerve pathologies - An overview Poster No.: C-1153 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Kasi Arunachalam 1, R. Renganathan
Seamless pre-surgical fmri and DTI mapping
 Seamless pre-surgical fmri and DTI mapping Newest release Achieva 3.0T X-series and Eloquence enable efficient, real-time fmri for brain activity mapping in clinical practice at Nebraska Medical Center
Seamless pre-surgical fmri and DTI mapping Newest release Achieva 3.0T X-series and Eloquence enable efficient, real-time fmri for brain activity mapping in clinical practice at Nebraska Medical Center
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
W. CHRISTOPHER FOX, M.D., 1 SCOTT WAWRZYNIAK, 2 AND WILLIAM F. CHANDLER, M.D. 1. be very useful during transsphenoidal pituitary surgery as well.
 J Neurosurg 108:746 750, 2008 Intraoperative acquisition of three-dimensional imaging for frameless stereotactic guidance during transsphenoidal pituitary surgery using the Arcadis Orbic System W. CHRISTOPHER
J Neurosurg 108:746 750, 2008 Intraoperative acquisition of three-dimensional imaging for frameless stereotactic guidance during transsphenoidal pituitary surgery using the Arcadis Orbic System W. CHRISTOPHER
Flow Measurement Techniques from Medical Modalities for Computational Fluid Dynamics. Fukasaku K, Negoro M*
 Flow Measurement Techniques from Medical Modalities for Computational Fluid Dynamics # ## Fukasaku K, Negoro M* Riken, Department of Neurosurgery Motojima General Hospital Department of Neurosurgery Fujita
Flow Measurement Techniques from Medical Modalities for Computational Fluid Dynamics # ## Fukasaku K, Negoro M* Riken, Department of Neurosurgery Motojima General Hospital Department of Neurosurgery Fujita
ASJ. Myxopapillary Ependymoma of the Cauda Equina in a 5-Year-Old Boy. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 Asian Spine Journal 846 Masashi Case Uehara Report et al. Asian Spine J 2014;8(6):846-851 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.6.846 Asian Spine J 2014;8(6):846-851 Myxopapillary Ependymoma of the Cauda
Asian Spine Journal 846 Masashi Case Uehara Report et al. Asian Spine J 2014;8(6):846-851 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.6.846 Asian Spine J 2014;8(6):846-851 Myxopapillary Ependymoma of the Cauda
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
Vasculature and Aneurysm Design
 Vasculature and Aneurysm Design Amy Swartz November 18, 2016 Team 23: In-vitro Tube Model System ME450 Section 3 Dr. David Trevas and Dr. Sarah Oman Introduction The primary goal of this capstone project
Vasculature and Aneurysm Design Amy Swartz November 18, 2016 Team 23: In-vitro Tube Model System ME450 Section 3 Dr. David Trevas and Dr. Sarah Oman Introduction The primary goal of this capstone project
1Pulse sequences for non CE MRA
 MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Goals. Objectives
 Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Length: 1 month of PGY-1 (Orthopaedic Designated Residents) or 1 month of PGY-2, -3, or -4 year Location: The Queen's Medical Center Primary Supervisor: William Obana,
Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Length: 1 month of PGY-1 (Orthopaedic Designated Residents) or 1 month of PGY-2, -3, or -4 year Location: The Queen's Medical Center Primary Supervisor: William Obana,
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
X-Plain Brain Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Brain Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. About 20,000 Americans are diagnosed with brain cancer or related cancer of the nervous system. This reference summary will
X-Plain Brain Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. About 20,000 Americans are diagnosed with brain cancer or related cancer of the nervous system. This reference summary will
Original Article Surgical Management of Sphenoid Wing Meningiomas
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 29 / No. 3 / July - September 214 17-24 Original Article Surgical Management of Sphenoid Wing Meningiomas Mohamed Emara, Alaa Farag*, Walid Badawy, Hosam Maaty,
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 29 / No. 3 / July - September 214 17-24 Original Article Surgical Management of Sphenoid Wing Meningiomas Mohamed Emara, Alaa Farag*, Walid Badawy, Hosam Maaty,
Medtronic International Ltd
 This report will reflect on the Business Department of Student working for in terms of purpose, values and responsibilities to the company and the community in large. As well as, future standing of its
This report will reflect on the Business Department of Student working for in terms of purpose, values and responsibilities to the company and the community in large. As well as, future standing of its
B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with 64-MD-CT Angiography
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Full ultrasound breast volumes. Faster scans. Streamlined workflow. ACUSON S2000 Automated Breast Volume Scanner. Answers for life.
 Full ultrasound breast volumes. Faster scans. Streamlined workflow. ACUSON S2000 Automated Breast Volume Scanner Answers for life. 1 ACQUIRE An automated whole breast solution. Reduced acquisition time.
Full ultrasound breast volumes. Faster scans. Streamlined workflow. ACUSON S2000 Automated Breast Volume Scanner Answers for life. 1 ACQUIRE An automated whole breast solution. Reduced acquisition time.
Pre-and Post Procedure Non-Invasive Evaluation of the Patient with Carotid Disease
 Pre-and Post Procedure Non-Invasive Evaluation of the Patient with Carotid Disease Michael R. Jaff, D.O., F.A.C.P., F.A.C.C. Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Vascular Medicine
Pre-and Post Procedure Non-Invasive Evaluation of the Patient with Carotid Disease Michael R. Jaff, D.O., F.A.C.P., F.A.C.C. Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Vascular Medicine
Intraoperative Ultrasound Imaging in Neurosurgery
 Ludwig M.Auer Vera Van Velthoven Intraoperative Ultrasound Imaging in Neurosurgery Comparison with CT and MRI With 466 Figures in 547 Separate Illustrations Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London
Ludwig M.Auer Vera Van Velthoven Intraoperative Ultrasound Imaging in Neurosurgery Comparison with CT and MRI With 466 Figures in 547 Separate Illustrations Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm of the Anterior Circulation
 Original Articles * Division of Neurosurgery Department of Surgery Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm of the Anterior Circulation Management and Microsurgical Treatment Ossama Al-Mefty, MD* ABSTRACT Based on the
Original Articles * Division of Neurosurgery Department of Surgery Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm of the Anterior Circulation Management and Microsurgical Treatment Ossama Al-Mefty, MD* ABSTRACT Based on the
From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is a Stroke? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is a Stroke? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair
Case Conference: Neuroradiology. Case 1: Tumor Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures
 Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
S. Inagawa, N. Yoshimura, Y. Ito; Niigata/JP spinal sacral areteriovenous fistulae, CTA, MRA /ecr2010/C-2581
 Localization of sacral spinal arteriovenous fistulae in reference to the dural structure with CTA and MRA of high spatial resolution: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-2581 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
Localization of sacral spinal arteriovenous fistulae in reference to the dural structure with CTA and MRA of high spatial resolution: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-2581 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
NANOS Patient Brochure
 NANOS Patient Brochure Pituitary Tumor Copyright 2015. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for informational
NANOS Patient Brochure Pituitary Tumor Copyright 2015. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for informational
A NOVEL CAUSE FOR CAUDA- EQUINA SYNDROME WITH A NEW RADIOLOGICAL SIGN
 A NOVEL CAUSE FOR CAUDA- EQUINA SYNDROME WITH A NEW RADIOLOGICAL SIGN W Singleton, D Ramnarine, N Patel, C Wigfield Department of Neurological Surgery, Frenchay Hospital, Bristol, UK Introduction We present
A NOVEL CAUSE FOR CAUDA- EQUINA SYNDROME WITH A NEW RADIOLOGICAL SIGN W Singleton, D Ramnarine, N Patel, C Wigfield Department of Neurological Surgery, Frenchay Hospital, Bristol, UK Introduction We present
MANAGEMENT N OF PRIMARY BRAIN TUMOURS IN THE ELDERLY
 MANAGEMENT N OF PRIMARY BRAIN TUMOURS IN THE ELDERLY Meningioma, Glioma, Lymphoma Cornu Ph, Keime-Guibert F, Hoang-Xuan K, Pierga JY, Delattre JY Neuro-oncology Group of Pitie-Salpetriere hospital-paris-france
MANAGEMENT N OF PRIMARY BRAIN TUMOURS IN THE ELDERLY Meningioma, Glioma, Lymphoma Cornu Ph, Keime-Guibert F, Hoang-Xuan K, Pierga JY, Delattre JY Neuro-oncology Group of Pitie-Salpetriere hospital-paris-france
Neurosurgery Review. Mudit Sharma, MD May 16 th, 2008
 Neurosurgery Review Mudit Sharma, MD May 16 th, 2008 Dr. Mudit Sharma, Neurosurgeon Manassas, Fredericksburg, Virginia http://www.virginiaspinespecialists.com Phone: 1-855-SPINE FIX (774-6334) Fundamentals
Neurosurgery Review Mudit Sharma, MD May 16 th, 2008 Dr. Mudit Sharma, Neurosurgeon Manassas, Fredericksburg, Virginia http://www.virginiaspinespecialists.com Phone: 1-855-SPINE FIX (774-6334) Fundamentals
INTRAOPERATIVE ULTRASOUND IN NEUROSURGERY
 INTRAOPERATIVE ULTRASOUND IN NEUROSURGERY MYTHS Image Quality:?inferior to MR Minimally invasive surgery incompatible:?need for bigger craniotomies No use at end of surgery?, decline in image quality US
INTRAOPERATIVE ULTRASOUND IN NEUROSURGERY MYTHS Image Quality:?inferior to MR Minimally invasive surgery incompatible:?need for bigger craniotomies No use at end of surgery?, decline in image quality US
SPECIAL PAPER IN CELEBRATION OF PROF. YANG'S 50 YEARS CAREER IN MEDICINE
 JOURNAL OF OTOLOGY SPECIAL PAPER IN CELEBRATION OF PROF. YANG'S 50 YEARS CAREER IN MEDICINE ADVANCES IN SURGICAL TREATMENT OF ACOUSTIC NEUROMA HAN Dongyi,CAI Chaochan Acoustic Neuroma (AN) arises from
JOURNAL OF OTOLOGY SPECIAL PAPER IN CELEBRATION OF PROF. YANG'S 50 YEARS CAREER IN MEDICINE ADVANCES IN SURGICAL TREATMENT OF ACOUSTIC NEUROMA HAN Dongyi,CAI Chaochan Acoustic Neuroma (AN) arises from
Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke
 Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Cerebral angiography. Information for families. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust
 Cerebral angiography Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust This leaflet explains about the cerebral angiography procedure and what to expect when your
Cerebral angiography Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust This leaflet explains about the cerebral angiography procedure and what to expect when your
Evaluation and treatment of intracranial aneurysms using Dual Energy CT Angiography (DECTA) and rotational Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA).
 Evaluation and treatment of intracranial aneurysms using Dual Energy CT Angiography (DECTA) and rotational Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA). L. Testaverde, G. Pelle, A. Saltarelli, P. Rabuffi, M.
Evaluation and treatment of intracranial aneurysms using Dual Energy CT Angiography (DECTA) and rotational Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA). L. Testaverde, G. Pelle, A. Saltarelli, P. Rabuffi, M.
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Surgical techniques and procedures for cerebrovascular surgery. Surgery for the AVF at the cranio-cervical junction and high cervical spine
 VS-1 Surgery for the AVF at the cranio-cervical junction and high cervical spine Hiroyuki Kinouchi University of Yamanashi, Department of Neurosurgery Dural AVFs have been recognized as common type of
VS-1 Surgery for the AVF at the cranio-cervical junction and high cervical spine Hiroyuki Kinouchi University of Yamanashi, Department of Neurosurgery Dural AVFs have been recognized as common type of
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
