Cronicon OPHTHALMOLOGY. Research Article Optic Nerve Regeneration after Traumatic Crush. Nataliya Moyseyenko* Abstract
|
|
|
- Beatrice Baldwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS OPHTHALMOLOGY Research Article Optic Nerve Regeneration after Traumatic Crush Nataliya Moyseyenko* Assistant professor, Ivano-Frankivsk national medical university, Ukraine *Corresponding Author: Nataliya Moyseyenko, Assistant professor, Ivano-Frankivsk national medical university, Ukraine. Received: May 19, 2015; Published: June 30, 2015 Abstract The aim was to activate regenerative processes in the optic nerve traumatic crush at high doses of corticosteroids. It has been used 6 mature rabbits (Group injured), which made damage the optic nerve. 6 rabbits (treated group) on the second day after the injury were treated with the use administration of methyl prednisolone. At 14 days after treatment of intracranial optic nerve improves microcirculation observed, accompanied by a decrease in swelling. There was detected remielinisation regeneration of these fibers. There are young mitochondria in the axoplasma. There were formed microtubules and structured neuro filaments, which is an early sign of regenerative processes of the optic nerve. Conclusion: Consequently found that for traumatic optic nerve damage high doses of corticosteroids for 14 days results in improvement of microcirculation reduce swelling, remielinisation and activation of regeneration. Keywords: optic nerve traumatic crush; regeneration; remyelinisation; high doses of corticosteroids. Introduction The research on the possibilities of regeneration of the optic nerve turns attention by scientist for many decades. It is known that the regenerative processes in the eye occur in three stages: alterations, changes of microcirculation and cell proliferation [1]. However regenerative mechanisms of optic nerve s different parts are still not clear. The most popular meaning is that in normal retinal ganglion cells are not able to regenerate after damage to the optic nerve. For example Marcus Ohlsson [2] in 2003 explains that an imbalance between inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors damaged optic nerve reveals and reduces the capacity of its recovery. But nowadays the most progressive scientists are looking for possibility to make optic nerve to regenerate. According to experimental studies it is known that reducing the death of retinal ganglion cells after optic nerve injury in mammals can achieve by applying inhibitory of apoptosis and growth factors that distinguish peripheral nerves [3,4]. Stimulation of regenerative processes can occur because of macrophages intraocular system activation [2]. Guy J Ben Simon. [5] showed that secondary indirect damage to the optic nerve arises as a result of exposure neurotoxins secreted by retinal ganglion cells. The brain neurotrophic factor s concentration increases in the ganglion cells on the affected side and decreases on the opposite after brain damage. While ganglion cells produce their own protective factor that ensures their survival. This neuroprotective effect is inhibited by high doses of glucocorticoids and provides opportunities for treatment traumatic optic neuropathy. In these cases proved the efficacy of high-dose corticosteroids (30 mg/kg) [6]. Thus the study regenerative processes that occur in the optic nerve under the influence of corticosteroids require detailed studies that will optimize how they use and, if possible, to reduce their negative impact. Aim: was to activate regenerative processes in the optic nerve traumatic crush at high doses of corticosteroids.
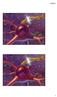
2 20 Material and Methods 6 mature rabbits (group injured) males, weighing 3.54 kg Soviet Chinchilla breeds were used as an experimental model. Additionally, 6 rabbits (treated group) on the second day after the injury were treated using a/m administration of methylprednisolone 30 mg/kg for 3 days, then the dose is gradually reduced. The control group consisted of 15 intact rabbits. The modulation of right traumatic optic nerve damages was made [7] in the operating conditions Department of Human Anatomy Ivano-Frankovsk National Medical University of the rules of asepsis. Pets and removing them from the experiment was carried out in accordance with the Requirements bioethics Helsinki Declaration on ethical regulation of medical research. Both groups of animals injured were removed from the experiment using the guillotine after 2 weeks. Cranial part of both eyes the optic nerve was morphological examined. As a control, use the appropriate structure of the control group. The material pieces were fixed in 2% osmium tetroxide solution, performed and contrasted by generally accepted method for electron microscopic examination. The study was performed on material electron microscope REM 125 K, the accelerating voltage of 75 kv, followed by photographing at magnifications of 1,200 to 25,000 times. Hemi thin sections, 1 mm thick, stained with 1% methylene blue solution. Hemi thin sections were examined under a light microscope MS 300 (THR) and photographed using Digital camera for microscope DCM 900 extension 1200h1600. We conducted a morphometric study of electron for an objective assessment of the nerve fibers of the optic nerve of the rabbit. Negatives were scanned electron, translating into positive, and stored in the same format. Morphometry was performed on these specimens using software NIH USA Image J manually taking into account increases. The measurements myelin membranes of axons and fibers in general were conducted. Index g determined by the formula: g = a/d, where A - area of the axon, d - area of a myelin fibers. The thickness of the myelin sheath was determined by the formula: l = D - d, where l - thickness of myelin, D - the average diameter of the fibers, d - average diameter of the axon. Computer data processing was performed using Statistical Package Stat. Soft. Inc; Tulsa, OK, USA. Statistica 6. Results There were founded reduce swelling endoneural connective tissue at 14th day compared the group without treatment with treated group after experimental traumatic crush orbital modeling of the right optic nerve in rabbits. There swelling has stayed in the subperyneural area and around of micro vessels (Figure 1). The myelin nerve fiber (MNF) became round, oval, irregular satellite and polygonal shapes. Some MNF outer and inner contours of the myelin sheath (MS) were concentric, while others - the inner layers of myelin shaped protrusions of different shapes and heights that show evidence preservation degenerative changes of MNF [8]. The reactive changes observed on the opposite side of the lesion. Figure 1: The right sided in rabbits traumatic crush s intracranial part of right (a) and the left optic nerve (b) morph structure manifestations at14 th day after use of high doses of corticosteroids. Hemi thin sections were stained with polychrome dye. Inc.: x1000. Notes: 1 - newly of MNF, 2 - newly formed collagen fibers, 3 - destructively altered MNF, 4 - core fibroblast, 5 - reactive changes.
3 The area of intracranial part of MNF of the right optic nerve decreased according to group without treatment s parameters (p = ). The index of g was statistically significant increased (p = ). This was indicated of fibers remyelinisation. There were manifested MNF, which MS consisted only of a few blades of myelin, that was expressly ordered (Figure 2) in the study of ultrathin cross sections of the right optic nerve with an electron microscope in animals treated group. Young elongated mitochondria with dense matrix and ordered christes were founded in axoplasma of MNF. The moderate amount of microtubule clearly structured and neyrofilamenty were indicated the recovery of backbone and conductivity of the neural fibers [9]. The large nucleus with dispersed chromatin and multiple clear nucleolemas shallow invagination of young mitochondria and clearly arranged tank granular endoplasmic reticulum were detected in the cytoplasm of neurolemocytes. Many ribosomes were situated on its surface. These morphological features are evidence of active electric utility and biosynthetic processes that occur in neyrolemocytes [10]. 21 Figure 2: The rabbit right optic nerve intracranial part with traumatic crush s restorative processes at 14 th day after treatment. Inc.: Notes: 1 - MS, 2 - microtubules and neyrofilamenty of axoplasme in MNF, 3 - neurolemocites cytoplasm. But it were present MNF with widespread MS else. There lamellar structure of myelin was disorder. Different size vacuoles were found between the individual lamellas. MS had incorrect form (Figure 3). Such fibers observed shrinkage and increased axial cylinder in there peryaxonal space where electoral compact cells, myelin remains and multibubble structure were often detected. Single fibrous layers situated in the epi-, peri- and endonevral spaces. But there was much less as in untreated animals. Endoneural tissue was still swollen surrounds the vessel. Figure 3: The right intracranial optic nerve with traumatic crush of the rabbit destructive changes at 14 th day after high doses cortecosteroides. Inc.: Notes: 1 - swelling of the axolema of nerve fiber, 2 - Strips bundle myelin, 3 - swelling of the myelin sheath, 4 - MNF of preserved ultra structure, 5 - core of neurolemocytes.
4 Such changes morphological structure of the right optic nerve recovery occurred against the backdrop of blood. The endoneural tissue s capillaries were round shape with a rounded or oval lumen. The nuclei of the endothelial cells became elongated with marginally located chromatin (Figure 4). Cytoplasm was increased electron optical density (Figure 4a) and contained young mitochondria, single micropinocytal bubbles in some endothelial. There were young endothelial cells [11]. Other endothelial cytoplasm were moderate and low density of large and small vacuoles and plenty of micropinocytal bubbles, indicating the presence of edema processes in these cells [11]. Luminal plasmolema of endothelial surface had a different shape and depth of the protrusion. They were often segregated into the lumen of the capillary forming microclasmatos (Figure 4b) [12]. 22 Figure 4: The right intracranial optic nerve traumatic crush s hemodynamic restorations at the 14 th day high doses cortecosteroides used. Inc.: Notes: 1 - endothelial nuclei elongated with marginally located chromatin, 2 - capillary lumen, 3 - vacuoles in the cytoplasm of endothelial cells, 4 - microklasmatos. Thus there were found microcirculation observed, a swelling decrease and remyelinisation of traumatic damaged intracranial part optic nerve s fibers at 14 th day after the use of high doses of corticosteroids. MS is clearly ordered. There are young elongated mitochondria in its axoplasme, microtubules are formed and structured neurofilaments. All this indicates the recovery of backbone and conductivity. There are early manifestations of optic nerve regenerative [13]. However, disregarding the direct neuroprotective effect of high-dose corticosteroids, this method of treatment has a strong negative effect, due to its high toxicity and high mortality in animals up to 1 month of experimental animals in both groups. This cases it difficult to use high doses of corticosteroids in clinical settings and necessitates an alternative method for the treatment of traumatic optic neuropathy [14]. Conclusion Consequently results showed reduce of microcirculation swelling and remiyelinisation of MNF that improves of activation of optic nerve crush regeneration by corticosteroids high doses at the 14 th day. High toxicity necessitates an alternative method for the treatment of traumatic optic neuropathy.
5 23 Bibliography 1. Ivanova NV Pathogenetic role of steroid hormones and polovыh fibronectin at posttravmatycheskom reparative processes in eye correction and Efficiency s violations [Pathogenetic role of steroid hormones and polovыh fibronectin at posttravmatycheskom reparative processes in eye correction and Efficiency s violations] [dissertation] Sevastopol (Ukraine); Ohlsson M., et al. Complement Activation following Optic Nerve Crush in the Adult Rat. Journal of Neurotrauma 20.9 (2003): Schmidt A., et al. Guanosine Prevents Thermal Hyperalgesia in a Rat Model of Peripheral Mononeuropathy. The Journal of Pain 11.2 (2010): Sarikcioglu L., et al. Detrimental Effects of Immobilization on Functional Recovery After Sciatic Nerve Crush. Journal of Reconstructive Microsurgery 21.5 (2005): Simon G., et al. Traumatic Brain Injury Induced Neuroprotection of Retinal Ganglion Cells to Optic Nerve Crush. Journal of Neurotrauma 23.7(2006): Li Y., et al. Axon regeneration in goldfish and rat retinal ganglion cells: differential responsiveness to carbohydrates and camp. Journal of Neuroscience (2003): Moiseenko NM., et al. Structural changes of the cranial part of t he optic nerve in traumatic injury of its orbital part in experiment Journal of ophthalmology (Ukraine) 6 (2014): Abdulaev MS. Nerves in the history of anatomy, their mieloarhitektonika. Rising dereneratsiya nerves. The vegetative nature of the neuron. Baku: Nurlan, (2002): Azerbaijan. 9. VA Levitsky., et al. Degeneration and reparative regeneration of nerve volokonsidnychoho nerve in terms of laser irradiation. Galician drug Gazette 1 (2009): Shin R. Treatment of a Segmental Nerve Defect in the Rat with Use of Bioabsorbable Synthetic Nerve Conduits: A Comparison of Commercially Available Conduits. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 91.9 (2009): Helwig B. Aging alters regulation of visceral sympathetic nerve responses to acute hypothermia. AJP: Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology (2006): R573-R Pace A., et al. Vitamin E neuroprotection for cisplatin neuropathy: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 74.9 (2010): Weibel D., et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) prevents lesion-induced axonal die-back in young rat optic nerve. Brain Research (1995): Meyer-Franke A., et al. Characterization of the signaling interactions that promote the survival and growth of developing retinal ganglion cells in culture. Neuron 15.4 (1995): Volume 1 Issue 1 June 2015 All rights are reserved by Nataliya Moyseyenko.
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey*
 Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei
 Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei General description: nerve tissue nerve cells (neurons): show numerous long processes receive the stimulation make contact with each other, conduct the nerve impulse
Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei General description: nerve tissue nerve cells (neurons): show numerous long processes receive the stimulation make contact with each other, conduct the nerve impulse
Development of the myelin sheath of the hypogastric nerves in a human foetus aged 23 weeks
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 289 301 Copyright 2004 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Development of the myelin sheath of the hypogastric nerves in a human
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 289 301 Copyright 2004 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Development of the myelin sheath of the hypogastric nerves in a human
The Neuron. Consists Of: - cell body. - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin. dendrites Axon terminal. Cell body. nucleus. axon.
 The Neuron Consists Of: - cell body - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin dendrites Axon terminal Cell body nucleus myelin axon THE SYNAPSE Definition: It is a point of contact between the axon of
The Neuron Consists Of: - cell body - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin dendrites Axon terminal Cell body nucleus myelin axon THE SYNAPSE Definition: It is a point of contact between the axon of
(3) Chemical synapse ---structure
 (3) Chemical synapse ---structure LM: in silver preparation dark brown color button-liked on the surface of cell body and dendrites called synaptic button LM: synaptic button (3) Chemical synapse ---structure
(3) Chemical synapse ---structure LM: in silver preparation dark brown color button-liked on the surface of cell body and dendrites called synaptic button LM: synaptic button (3) Chemical synapse ---structure
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System
 Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Nervous system. 1. Neurons :
 Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
Muscle tissues. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Collin County Community College BIOL Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
THE PHARMA INNOVATION - JOURNAL Electron microscopic changes of sciatic nerves in rats with experimental peripheral neuropathy caused by paclitaxel.
 Received: 16-01-2014 Accepted: 18-02-2014 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 3 No. 1. 2014 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
Received: 16-01-2014 Accepted: 18-02-2014 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 3 No. 1. 2014 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more
 Nervous system Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Devoid from connective
Nervous system Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Devoid from connective
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
8.2. Types of Neurons
 Chapter 8 Nervous Tissue The neuron is the functional and the structural unit of the nervous system. It displays two highly developed physiological traits: 1. Irritability - the capacity to generate a
Chapter 8 Nervous Tissue The neuron is the functional and the structural unit of the nervous system. It displays two highly developed physiological traits: 1. Irritability - the capacity to generate a
Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich)
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Unit Six The Nervous System
 Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
The 7 th lecture. Anatomy and Physiology For the. 1 st Class. By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza
 The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
OCT in the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Glaucoma
 OCT in the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Glaucoma Karim A Raafat MD. Professor Of Ophthalmology Cairo University Hmmmm! Do I have Glaucoma or not?! 1 Visual Function 100% - N Gl Structure : - 5000 axon /
OCT in the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Glaucoma Karim A Raafat MD. Professor Of Ophthalmology Cairo University Hmmmm! Do I have Glaucoma or not?! 1 Visual Function 100% - N Gl Structure : - 5000 axon /
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue
 Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Cells of the nervous system
 Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2011 1 Cells of the nervous system Neuroglia : part 2 The non excitable cells of the nervous system that provide support to neuronal survival and
Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2011 1 Cells of the nervous system Neuroglia : part 2 The non excitable cells of the nervous system that provide support to neuronal survival and
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp 1- Coronal pulp
 Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder
 Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder 3 Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder 5 6 Atlas of the Shoulders
Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder 3 Neuromuscular Control and Proprioception of the Shoulder 5 6 Atlas of the Shoulders
Skeletal muscle. General features :
 Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
Integrated Muscle. Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File
 Integrated Muscle Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES Identify and describe the histological structure of the three types of muscle cells and list the
Integrated Muscle Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES Identify and describe the histological structure of the three types of muscle cells and list the
XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University
 SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
! BIOL 2401! Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
NERVOUS TISSUE. 1. Functional units of the nervous system; receive, process, store and transmit information to other neurons, muscle cells or glands.
 NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
Nervous Tissue. The unit of nervous tissue is called neuron. It is the longest cell & it doesn t undergo cell division in matured state.
 Nervous Tissue The unit of nervous tissue is called It is the longest cell & it doesn t undergo cell division in matured state. It is a special modified tissuess or cells for getting following two basic
Nervous Tissue The unit of nervous tissue is called It is the longest cell & it doesn t undergo cell division in matured state. It is a special modified tissuess or cells for getting following two basic
Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology
 Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology Nancy J. Newman, MD Emory University Atlanta, GA Consultant for Gensight Biologics, Santhera Data Safety Monitoring Board for Quark AION Study Medical-legal
Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology Nancy J. Newman, MD Emory University Atlanta, GA Consultant for Gensight Biologics, Santhera Data Safety Monitoring Board for Quark AION Study Medical-legal
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
EM: myelin sheath shows a series of concentrically arranged lamellae
 EM: myelin sheath shows a series of concentrically arranged lamellae ---- how to form myelin sheath? Schwann cell invagination and envelop the axon form mesaxon mesaxon become longer and longer winding
EM: myelin sheath shows a series of concentrically arranged lamellae ---- how to form myelin sheath? Schwann cell invagination and envelop the axon form mesaxon mesaxon become longer and longer winding
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS
 THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS W. C. MA AND CHIEN-LIANG HSU (From the Departmt-nts of Anatomy and Radiology, Peiping Union M~dical College, Peiping, China) From the extensive
THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS W. C. MA AND CHIEN-LIANG HSU (From the Departmt-nts of Anatomy and Radiology, Peiping Union M~dical College, Peiping, China) From the extensive
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
IT has been shown (Chou, 1957 a, b) that there are three kinds of lipid
 279 The Ultra-fine Structure of Lipid Globules in the Neurones of Helix aspersa By J. T. Y. CHOU and G. A. MEEK (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology; and Department of Human Anatomy,
279 The Ultra-fine Structure of Lipid Globules in the Neurones of Helix aspersa By J. T. Y. CHOU and G. A. MEEK (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology; and Department of Human Anatomy,
Introduction to Nervous Tissue
 Introduction to Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Nerve Autografts, Allografts, Conduits, Wraps, and Glue. What Should I Do?
 Nerve Autografts, Allografts, Conduits, Wraps, and Glue. What Should I Do? David Kahan, MD Fellow, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery Rothman Institute at Thomas Jefferson University Outline Wallerian Degeneration
Nerve Autografts, Allografts, Conduits, Wraps, and Glue. What Should I Do? David Kahan, MD Fellow, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery Rothman Institute at Thomas Jefferson University Outline Wallerian Degeneration
Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis)
 Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Major Structures of the Nervous System. Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors
 Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat
 Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat Lecture Objectives Classify the types of neurons. Describe the structure of the different parts of neurons. Describe the
Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat Lecture Objectives Classify the types of neurons. Describe the structure of the different parts of neurons. Describe the
HISTOLOGY OF NERVOUS SYSTEM. DR. Nabil Khouri
 HISTOLOGY OF NERVOUS SYSTEM DR. Nabil Khouri 2 NERVOUS SYSTEM 25/01/2017 The most complex system in the human body Formed by network more than 100 million neuron Each neuron has a thousand interconnection
HISTOLOGY OF NERVOUS SYSTEM DR. Nabil Khouri 2 NERVOUS SYSTEM 25/01/2017 The most complex system in the human body Formed by network more than 100 million neuron Each neuron has a thousand interconnection
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Chapter 4. Cartilage and Bone. Li Shu-Lei instructor. Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University
 Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system)
 Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
THE EYE: RETINA AND GLOBE
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
Nervous System. Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI
 Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei Department of Histology & Embryology
 The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
CHANGES OF THE HEMOMICROCIRCULATORY FLOW AT THE MOUTH CORNER AND LIPS AT THE LATE STAGES OF EXPERIMENTAL STREPTOZOTOCIN-INDUCED DIABETES
 DDC-UDC 611.728.36 Anzeige Info@dwherold.de Deutscher Wissenschaftsherold German Science Herald, N 1/2017 DOI:10.19221/201715 Hnidyk J.V. Department of normal anatomy. Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical
DDC-UDC 611.728.36 Anzeige Info@dwherold.de Deutscher Wissenschaftsherold German Science Herald, N 1/2017 DOI:10.19221/201715 Hnidyk J.V. Department of normal anatomy. Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical
BME NEUROSCIENCE PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL SCIENCE 1 ST SEMESTER GRADUATE COURSE HYOUNG F. KIM
 BME NEUROSCIENCE PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL SCIENCE 1 ST SEMESTER GRADUATE COURSE HYOUNG F. KIM BASIC CONCEPT OF CELL BIOLOGY CELL & NEURON What are the differences? BASIC CONCEPT OF CELL 1. What are the cells
BME NEUROSCIENCE PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL SCIENCE 1 ST SEMESTER GRADUATE COURSE HYOUNG F. KIM BASIC CONCEPT OF CELL BIOLOGY CELL & NEURON What are the differences? BASIC CONCEPT OF CELL 1. What are the cells
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II. Ventral Lobe Epithelium
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
ABSTRACT. 2. METhODS 3. RESULTS
 Laser induced retinal nerve fiber layer (NFL) damage H. Zwick, D.A. Gagliano, J.A. Zuclich, B.E. Stuck, M. Belkin USArmy Medical Research Detachment Walter Reed Army Institute of Research San Antonio,
Laser induced retinal nerve fiber layer (NFL) damage H. Zwick, D.A. Gagliano, J.A. Zuclich, B.E. Stuck, M. Belkin USArmy Medical Research Detachment Walter Reed Army Institute of Research San Antonio,
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy MUSCLE Skeletal (striated) Cardiac (striated) Smooth Identification based on Fiber size, shape and presence/absence of branching Number, shape and position of nuclei
PRACTICAL ROADMAP MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy MUSCLE Skeletal (striated) Cardiac (striated) Smooth Identification based on Fiber size, shape and presence/absence of branching Number, shape and position of nuclei
NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA
 NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA MAJOR LESTER S. KING, M.C., A.U.S. From the Laboratory Service of the William Beaumont General Hospital, El Paso, Texas Until relatively recently, the immediate
NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA MAJOR LESTER S. KING, M.C., A.U.S. From the Laboratory Service of the William Beaumont General Hospital, El Paso, Texas Until relatively recently, the immediate
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
CNB12 Plus. by ChiroNutraceutical. Recommended for:
 CNB12 Plus by ChiroNutraceutical Recommended for: Increased Metabolism Nervous System Repair & Support Anti-Brain Aging Anemia Parkinson s, Alzheimer s and Multiple Sclerosis What is Methylcobalamin? Methylcobalamin
CNB12 Plus by ChiroNutraceutical Recommended for: Increased Metabolism Nervous System Repair & Support Anti-Brain Aging Anemia Parkinson s, Alzheimer s and Multiple Sclerosis What is Methylcobalamin? Methylcobalamin
n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Composed of stratified squamous epith. n 5% of total corneal thickness (50-90micro m thick)
 Cornea overview Dr. Sarita Tuladhar MD, Ophthalmology Gandaki Medical College Embryology CORNEA: n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Corneal stroma, descement memb, bowman s layer,
Cornea overview Dr. Sarita Tuladhar MD, Ophthalmology Gandaki Medical College Embryology CORNEA: n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Corneal stroma, descement memb, bowman s layer,
The Neuron by Richard H. Hall, 1998
 The Neuron by Richard H. Hall, 1998 External Structure A neuron can be defined as a nerve cell. The neuron is often thought of as the "building block" of the nervous system, and for good reason. The neuron
The Neuron by Richard H. Hall, 1998 External Structure A neuron can be defined as a nerve cell. The neuron is often thought of as the "building block" of the nervous system, and for good reason. The neuron
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
Nervous system. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
The Nervous System. Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes =
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA
 THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA DEFINITION OF A NEURON Neuron is the name given to the nerve cell and all its processes. Neurons are excitable cells that are specialized for the reception
THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA DEFINITION OF A NEURON Neuron is the name given to the nerve cell and all its processes. Neurons are excitable cells that are specialized for the reception
Nervous Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Nervous Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with
Nervous Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with
Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance?
 1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih
 Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 246 PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE, CHIASM, AND TRACT*t BY J. REIMER WOL-TER AND ROMAN R. KNOBLICH From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Pathology
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 246 PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE, CHIASM, AND TRACT*t BY J. REIMER WOL-TER AND ROMAN R. KNOBLICH From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Pathology
HISTOLOGY د.عبد الجبار فالح الربيعي
 Nervous System The human Nervous system is the most complex system in the human body, is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Anatomically
Nervous System The human Nervous system is the most complex system in the human body, is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Anatomically
BIOL241 - Lecture 12a
 Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
ervous system: central nervous system (CNS) and eripheral nervous system (PNS) NS includes the brain and spinal cord NS consists of the cranial
 Physiology of the peripheral nervous system ervous system: central nervous system (CNS) and eripheral nervous system (PNS) NS includes the brain and spinal cord NS consists of the cranial nerves from brain
Physiology of the peripheral nervous system ervous system: central nervous system (CNS) and eripheral nervous system (PNS) NS includes the brain and spinal cord NS consists of the cranial nerves from brain
Histology of the Eye
 Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Acute Glaucoma in Dogs. Richard R Dubielzig
 The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Acute Glaucoma in Dogs Richard R Dubielzig Overview of Glaucoma Intraocular Pressure too High to Support a Healthy Optic Nerve Terminology used in the classification of
The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Acute Glaucoma in Dogs Richard R Dubielzig Overview of Glaucoma Intraocular Pressure too High to Support a Healthy Optic Nerve Terminology used in the classification of
Skeletal Muscle : Structure
 1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
Chapter 2 Cell. Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s)
 Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology)
 Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook
 Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook For the 1 st year Medical Student s In Histology and cell Biology Mansoura university Faculty
Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook For the 1 st year Medical Student s In Histology and cell Biology Mansoura university Faculty
The Egyptian journal of hospital medicine (2009)vol.,36:
 The Egyptian journal of hospital medicine (2009)vol.,36: 468-482 QUANTITATIVE AND HISTOCHEMICAL STUDY ON THE ADRENAL MEDULLA IN POST NATAL PERIOD OF ALBINO RAT Wagieh k.baiomy; Abdel-mawgood Anas; Mamdooh
The Egyptian journal of hospital medicine (2009)vol.,36: 468-482 QUANTITATIVE AND HISTOCHEMICAL STUDY ON THE ADRENAL MEDULLA IN POST NATAL PERIOD OF ALBINO RAT Wagieh k.baiomy; Abdel-mawgood Anas; Mamdooh
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided into: CNS (central nervous system) = brain + spinal cord
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided into: CNS (central nervous system) = brain + spinal cord
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
Basophilic. Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue
 Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Florida Gainsville, FL
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0145 TITLE: Nerve Degeneration and Regeneration Associated with NF1 Tumors PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: David F. Muir CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Florida Gainsville,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0145 TITLE: Nerve Degeneration and Regeneration Associated with NF1 Tumors PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: David F. Muir CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Florida Gainsville,
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Nervous tissue. Lab. 7
 Nervous tissue Lab. 7 Nervous tissue :- is responsible for transport nervous impulse (motor and sensory impulse), and it is formed by network more than 100 million nerve cell (neurons), nerve fiber and
Nervous tissue Lab. 7 Nervous tissue :- is responsible for transport nervous impulse (motor and sensory impulse), and it is formed by network more than 100 million nerve cell (neurons), nerve fiber and
Nervous Tissue. Prof. Zhou Li Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Nervous Tissue Prof. Zhou Li Dept. of Histology and Embryology Organization: neurons (nerve cells) neuroglial cells Function: Ⅰ Neurons 1. structure of neuron soma neurite a. dendrite b. axon 1.1 soma
Nervous Tissue Prof. Zhou Li Dept. of Histology and Embryology Organization: neurons (nerve cells) neuroglial cells Function: Ⅰ Neurons 1. structure of neuron soma neurite a. dendrite b. axon 1.1 soma
Neuronal plasma membrane
 ORGANELLES ORGANELLES Neuronal plasma membrane The neuronal plasma membrane contains several local domains with unique properties Presynaptic terminal Endoplasmic Reticulum In neurons the Nissl bodies
ORGANELLES ORGANELLES Neuronal plasma membrane The neuronal plasma membrane contains several local domains with unique properties Presynaptic terminal Endoplasmic Reticulum In neurons the Nissl bodies
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
