Transarterial ONYX Embolization of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas in Adults
|
|
|
- Debra Lamb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI: / JTN Received: / Accepted: Published Online: Original Investigation Transarterial ONYX Embolization of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas in Adults Jihui LIU, Xinguo LI, Shengxue SUN, Yunjie WANG, Peizhuo ZANG The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Department of Neurosurgery, Shenyang, China ABSTRACT AIm: To present our experience on transarterial treatment of dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) with ONYX in adult patients. MaterIal and Methods: Between March 2008 and November 2012, 27 adult patients with DAVFs treated by transarterial ONYX embolization were included. Clinical data, including hospital records, operative reports, and angiograms, were reviewed and analyzed. Results: Complete obliteration of the fistula was achieved in 16/27 (59.3%) patients after 32 intra-arterial embolizations. One complication (3.7%) was transient hemiparesis. Follow-up imaging, which was available for 16 fistulas with angiographic cures, showed no evidence of recurrence. At mean 14.5 months follow-up, 26 patients (96.3%) had GOS score of 5 and 1 patient (3.7%) had GOS score of 3. ConclusIon: Transarterial ONYX embolization has become the main treatment for adult intracranial DAVFs and is associated with high safety and efficacy. Keywords: Dural arteriovenous fistula, Embolization, ONYX, Radiosurgery ABBREVIATIONS: AVF: Arteriovenous fistula, CT: Computed tomography, CVR: Cortical venous reflux, DAVF: Dural arteriovenous fistula, DCF: Dural cavernous fistula, ECA: External carotid artery, ICA: Internal carotid artery, IPS: Inferior petrosal sinus, MMA: Middle meningeal artery, VA: Vertebral artery, DAVF: Dural arteriovenous fistula, GOS: Glasgow Outcome Scale. INTRODUCTION In adults, it has been shown that dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are an acquired disease. The term dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) should therefore be used in adults, rather than in children (34). The arterial supply of the DAVFs is from the dural arteries and the dural branches of cerebral arteries. This is directly shunted into a venous sinus and/or arterialized leptomeningeal veins. The nidus of the DAVF is usually located within the dura mater (3,19). The venous drainage of DVAF is the most important predictor of the clinical behavior. DAVFs with cortical venous reflux (CVR) exhibit a much higher incidence of hemorrhage or venous infarction (29). The annual mortality rate for DAVFs with CVR may be as high as 10.4%, whereas the annual risk for hemorrhage or non-hemorrhagic neurological deficits during follow-up period are 8.1% and 6.9%, respectively, resulting in an annual event rate of 15% (29,42). In addition, re-bleeding rates are as high as 35% during the first 2 weeks after the first hemorrhage (10). Therefore, DVAFs need careful evaluation for the best therapeutic option (29). The current endovascular treatment of DAVFs is sometimes a complex strategy, including not only transarterial injection of any liquid embolic agent but also transvenous approaches and also surgical elements (16). Corresponding author: Peizhuo ZANG pzzang@mail.cmu.edu.cn 518 Turk Neurosurg 26(4): , 2016
2 With the advent of ONYX (Covidien, Irvine, CA), most intracranial DAVFs can be successfully managed with transarterial ONYX embolization via their supply from the external carotid artery (ECA) branches, which can be safely embolized (29). In this study, we report our experience with a series of 27 adult patients who underwent intra-arterial embolization for intracranial DAVFs. MATERIAL and METHODS Between March 2008 and November 2012, 27 (20 males, 7 females) consecutive adult patients with DAVFs treated using transarterial Onyx embolization (Tables I, II). The mean age was 46.3 years (range, years). Clinical presentations included hemorrhage in 11 patients (40.7%), chemosis in 4 patients (14.8%), bruit in 9 patients (33.3%), headaches in 5 patients (18.5%), blurred vision in 1 Table I: Demographic Characteristics of the 27 Patients Patient No. Age (years) Sex Presentation Location Suppliers Borden Type Approach 1 44 M Bruits BL, TS Torcula R, ECA/VA, L, OA II R, MMA; L, OA 2 40 F Chemosis, bruits, blurred vision R, CS R, ICA/ECA II R, MMA 3 42 F Headaches R, TS R, VA; BL, ECA II R, MMA 4 70 M Headaches, bruits, chemosis L, TS L, ICA/MMA/VA II L, MMA 5 50 F Bruits L, TS L, OA/MHT/MMA II L, MMA; L, OA 6 36 F Headaches, blurred vison R, TS BL, ECA II BL, MMA; R, OA 7 31 M Chemosis, bruits R, TS R, ICA/ECA II R, MMA 8 46 M Chemosis L, CS L, ICA/ECA II L, MMA 9 44 M ICH R, Fronto-parietal R, MMA III R, MMA M Chemosis R, TS BL, ECA III R, MMA M ICH R, TS R, ECA/VA; L, OA III R, MMA M Trigeminal neuralgia Meckel Cave R, ECA/ICA III R, MMA M ICH Ethmoidal BL, ICA; L, ECA III R, Opha M Headaches R, tentorial L, MMA; R, ECA/ICA III L, MMA M ICH R, tentorial BL, ECA/ICA III BL, MMA M ICH R, tentorial R, ICA/ECA/AICA III R, MMA M ICH R, tentorial R, ICA/ECA III R, MMA F ICH R, tentorial R, ECA/ICA III R, MMA M ICH R, tentorial R, SCA/MMA/MHT III R, MMA M Hypoesthesia R, tentorial R, MHT/SCA III R, SCA F ICH Craniocervical junction L, VA III L, PMA M Bruits Middle cranial fossa L, ECA III L, MMA F Bruits L, TS SSS R, fronto-parietal BL, ECA L, MCA II III III BL, MMA M Bruits L, TS L, ECA/ICA; R, OA III R, OA M Bruits L, fronto-parietal BL, MMA III L, MMA M ICH, headaches, bruits L, tentorial L, ECA/ICA III L, MMA M ICH L, clival L, MHT III L, MHT M: Male; F: Female, ICH: Intracranial hemorrhage, CN: Cranial nerve, TS: Transverse sigmoid, ECA: External carotid artery, ICA: Internal carotid artery, OA: Occipital artery, VA: Vertebral artery, CS: Cavernous sinus, Opha: Ophthalmic artery, SSS: Superior sagittal sinus, MMA: Middle meningeal artery, SCA: Superior cerebellar artery, MHT: Meningohypophyseal trunk, PMA: Posterior meningeal artery. Turk Neurosurg 26(4): ,
3 patient (3.7%), hypoesthesia in 1 patient (3.7%), and trigeminal neuralgia in 1 patient (3.7%). Multiple dural fistulas occurred in 2 patients (7.4%). The locations of the lesions were transverse-sigmoid sinus in 10 patients (37.0%), cavernous sinus in 1 patients (3.7%), tentorium in 8 patients (29.6%), ethmoidal in 1 patients (3.7%), frontoparietal in 3 patients (11.1%), saggital sinus in 1 patients (3.7%), Meckel cave in 1 patient (3.7%), middle fossa dura in 1 patients (3.7%), clivus in 1 patient (3.7%), craniocervical junction in 1 patient (3.7%) and torcula in 1 patient (3.7%). According to Borden classification (4), 8 fistulas (29.6%) were type II, and 19 (70.4%) were type III. All endovascular approaches were performed under general anesthesia. Diagnostic angiography was performed including six vessels. Cervical branches of the subclavian artery were Table II: Treatment and Follow-Up of the 27 Patients Patient No. Injection time (minutes) Material Adjunct treatment Angiographic result Complications Follow-up (months) Clinical outcome (GOS) score ONYX NO Incomplete no ONYX Radiosurgery Incomplete no ONYX NO Incomplete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Incomplete no ONYX NO Incomplete no ONYX NO Incomplete no ONYX NO Incomplete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX Radiosurgery Incomplete no ONYX NO Incomplete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Complete R, ICA stenosis, hemiparesis ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Incomplete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX NO Complete no ONYX Radiosurgery Incomplete no ONYX Balloon assistance Complete no 1 5 GOS: Glasgow outcome scale. 520 Turk Neurosurg 26(4): , 2016
4 included in selected cases. The decision of embolization, the route, and the embolizing material were chosen based on the angiographic findings (29). After transfemoral access and sheath placement, the patient was heparinized, with 3000 units intravenously and 1000 units per hour of intravenous heparin, to maintain an activated coagulation time of between 250 and 300 seconds (29). Standard coaxial techniques were used for embolization. Guide catheters were navigated into the appropriate parent vessel (external carotid artery, internal carotid artery, or vertebral artery) (38). A DMSO compatible microcatheter (Marathon or Echelon; Covidien) with a microwire (Mirage or Silverspeed; Covidien) was then advanced into the selective branches as close to the nidus as possible and allowing for an adequate distance for reflux of the embolic agent, and superselective angiography was performed on the target branch or branches for embolization (29,38). When there were multiple feeders, the feeder with maximum reflux distance from the skull base was chosen to decrease the chances of cranial nerve palsies (29). Embolization of the DAVF was then performed with ONYX-18 in the manner previously described (26-28). If the meningohypophyseal trunk was catheterized, ONYX embolization was performed with balloon assistance. The end point of the embolization was the angiographic obliteration of the fistula, with some filling of the draining veins (Figure 1A, B). Clinical follow-up (mean 13.2 months, range 1 29 months) data were supplemented by telephonic interviews and graded according to the Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) (18). An excellent outcome was defined as the resumption of normal life despite minor deficits (GOS Score 5). A good outcome was a moderate disability, but the patient was independent (GOS Score 4). A fair outcome was a severe disability, and the patient was dependent on the care of others (GOS Score 3). A poor outcome was a persistent vegetative state (GOS Score 2) or death (GOS Score 1). Most patients had follow-up angiograms approximately 6-11 months after the embolization procedure. The angiographic results of treatment were classified as incomplete or complete, based on the evidence of remnant fistula on the post-treatment angiogram. RESULTS Thirty-two intra-arterial ONYX embolization procedures were performed to treat dural fistulas in 27 patients (Table I). There were 32 transarterial approaches, 1 of which was performed with balloon assistance. Thirty-two ONYX injections were performed in 32 vessel branches, including 28 ECA branches, posterior meningeal artery (n=1), ophthalmic artery (n=1), meningohypophyseal artery (n=1), superior cerebellar artery (n=1). Twenty-three branches of the middle meningeal artery (MMA) were embolized along with 5 branches of the occipital artery. Thirteen lesions were cured with transarterial treatment via the MMA alone (Figure 1). Three fistulas were cured with transarterial treatment via the superior cerebellar artery, meningohypophyseal artery and posterior meningeal artery. Three patients underwent Gamma Knife radiosurgery, which was performed after incomplete embolization. Only one technical complication was associated with the transarterial ONYX embolization, resulting in a complication rate of 3.1%. A 35-year-old man presented with subarachnoid hemorrhage caused by a tentorial DAVF with supply from the right meningohypophyseal trunk, the right superior cerebellar artery and the right middle meningeal artery. The patient underwent transarterial ONYX embolization via the MMA. At the final stage, a small amount of ONYX appeared to reflux into the right internal carotid artery (ICA) via the meningophypophyseal trunk. Therefore, ONYX embolization was aborted, and the catheter was removed. Then, immediate angiography revealed complete occlusion of the fistula. The patient experienced left hemiparesis just after the procedure and discharged home on postoperative day 5. The hemiparesis had almost resolved completely at the fifteenth day after the embolization. A b Figure 1: A) left carotid artery angiogram (lateral view) demonstrating a left tentorial DAVF with supply from the left MMA and occipital artery and venous drainage into a cortical vein with a dilated venous varix that drains into the lateral mesencephalic veins. B) post-embolization left ICA angiogram (lateral view) showing residual fistula supplied by the meningeal hypophyseal trunk. Turk Neurosurg 26(4): ,
5 Of the 27 patients who had endovascular treatment, 16 (59.3 %) had complete obliteration of the fistula after embolization. Of the 11 fistulas, in which endovascular treatment was incomplete, 3 underwent radiosurgery. In the remaining 8 fistulas, the fistula was treated nearly complete obliteration or the post-embolization fistula was Borden type I, and the residual fistula remained stable on the follow-up angiogram, and no further treatment was performed. Of the 3 fistulas that underwent Gamma Knife radiosurgery, complete fistula obliteration was confirmed by 2-year followup angiogram in 2 and 1 will have follow-up angiography 2 years post-treatment. Twenty-six of 27 patients (96.3%) had a favorable outcome (GOS score 5) during the follow-up period. One patient with GOS score 3, the cause for the poor outcome was the initial insult of the hemorrhage. In our series, there was no procedure-related mortality. DISCUSSION The pathogenesis of DAVFs is still unclear, with a congenital and an acquired etiology having been proposed (19, 29). Lasjaunias et al. (19) proposed that a primary structural weakness of the dura coincides with a trigger factor and results in the formation of a DAVF (29). The common predisposing factor appears to be venous sinus thrombosis, with the body compensating for this by attempts at recanalization (12,13,17,29). In our series, sinus occlusion was observed in 8 patients. There were 2 patients with multifocal complex DAVFs in adults; and in 26 patients, no specific cause could be identified. We have a male predominance (76.9%) in our patients and this may suggest that it tends to have a more aggressive course in men (16, 34, 41). The incidence of DAVF by location, as reported in the literature, is as follows: transverse sigmoid sinus, 50%; cavernous sinus, 16%; tentorium, 12%; superior sagittal sinus, 8%, and anterior fossa, 2% (2, 4, 8, 25, 29). A patient s first hemorrhage from a DAVF is associated with 20% to 30% mortality, emphasizing the importance of early recognition and treatment of patients at highest risk (5,29). The natural history of DAVFs has been poorly documented until recently and has been based on retrospective reviews (2,8,29). Van Dijk et al. (42) had a 4.3 years follow-up on their 14 non-treated patients and 6 partially-treated patients. They found that persistence of the CVR in cranial DAVFs yielded an annual mortality rate of 10.4%. Recent studies demonstrate evidence that the risk of bleeding for a DAVF with CVR is less when the patient does not present with a hemorrhage or a nonhemorrhagic neurologic deficit (29,37,39). Strom et al. (39) report that asymptomatic versus symptomatic DAVFs (in patients presenting with hemorrhage or neurologic deficit) have annual hemorrhage rates of 1.4% versus 19%, respectively. Although small in size, these studies make the important point that the natural history may depend on the type of presentation (29,39). Nevertheless, lower annual hemorrhage rates of asymptomatic type II and III DAVFs (up to 1.5% per year) (29,37) still pose significant long-term risk to patients, thereby justifying treatment in appropriately selected patients (29). Our patients belonged to the high-risk category (Borden types II or III) and required active intervention to prevent risk of hemorrhage. At our institution, we perform aggressive treatment for symptomatic type II/III DAVFs. We also recommend treatment in asymptomatic type II/III DAVFs if the patient is a good candidate for embolization on the basis of their age, lifetime hemorrhage risk profile, and willingness or unwillingness to accept the natural history. Currently, several series have established a high degree of safety and efficacy of ONYX used intra-arterially and intra-venously in the treatment of intracranial DAVFs (1,6,9,29,31,32,40). The complete obliteration rate in arterial ONYX embolization was 61.3%-91.6% (22,31-33,40) and that in venous ONYX embolization was 100% (21,23). The efficiency of access through the MMA, even when the diameter was very small, than through other more dilated feeders (eg, occipital and posterior auricular arteries) due to the superior flow control and reliability of target vessel embolization has been described well in literatures (15,20,29,38). ONYX offers the possibility of venous sinus packing/occlusion from an arterial side approach, which may be quite helpful in cases with previous occlusion of the draining venous structures (14,29). Post-embolization complication rates of approximately 2% to 10% have been reported in most series (11,22,24,29,30). Complications associated with arterial embolization include cranial nerve deficits, draining vein occlusion or venous ONYX migration, brain infarction, reflexive bradycardia, brain infraction and microcatheter gluing (22,24). On our experience, complications associated with venous embolization were reflexive bradycardia and transient cranial nerve deficits. Our success rate of 63.9% seems comparable with previously reported results of 50% to 90% (6,7,9,31) and our complication rate was as low as 2.8%. The petrous branch of the middle meningeal trunk supplies the cranial nerves at the skull base (29). We avoid this branch and select another distal tentorial branch to embolize the fistula, even if that is not a direct feeder. The arterial or venous balloon assistance technique provides an adjunctive method in the transarterial and transvenous ONYX embolization of complex DAVFs (36). The balloon can be inflated in the ICA or vertebral arteries at the site of the meningeal feeding arteries, which have anastomotic connections with the target vessel being embolized (36). This technique prevented the untoward passage of ONYX into the ICA via the meningophypophyseal branch and vertebral artery via the posterior meningeal artery. It can thus prevent the embolic material from occluding the intracranial artery and/or causing distal embolism via those anastomotic channels (36). This technique is especially useful in DAVFs because of the rapid tapering, small-diameter feeding arteries resulting in early reflux during ONYX injection (36). Shi et al. have used the venous balloon assistance technique to prevent ONYX from inadvertently occluding the lumen of a functioning venous sinus and migrating into adjacent key 522 Turk Neurosurg 26(4): , 2016
6 cortical or deep veins when the balloon occludes the recipient venous structure (36). Radiosurgery is inefficient for DAVFs and it may be tried where embolization has failed and surgery appears to carry a high risk (25, 29, 44). Wu et al. reported a 75% angiographic obliteration rate at 24 months (43). In our series Gamma Knife radiosurgery was used in 3 patients. Complete obliteration has been achieved in 2 with 1 awaited for 2-year follow-up angiogram. Surgery is indicated for high-risk DAVFs with leptomeningeal retrograde venous drainage when embolization is technically difficult or has resulted in incomplete occlusion (29, 35). CONCLUSION Transarterial ONYX embolization has become the main treatment for adult intracranial DAVFs and is associated with high safety and efficacy. REFERENCES 1. Arat A, Inci S: Treatment of a superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula with Onyx: Technical case report. Neurosurgery 59:ONSE , Awad IA, Little JR, Akarawi WP, Ahl J: Intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations: Factors predisposing to an aggressive neurological course. J Neurosurg 72: , Barnwell SL, Halbach VV, Dowd CF, Higashida RT, Hieshima GB, Wilson CB: A variant of arteriovenous fistulas within the wall of dural sinuses. Results of combined surgical and endovascular therapy. J Neurosurg 74: , Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA: A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg 82: , Brown RD Jr, Wiebers DO, Nichols DA: Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: Angiographic predictors of intracranial hemorrhage and clinical outcome in nonsurgical patients. J Neurosurg 81: , Chew J, Weill A, Guilbert F, Raymond J, Audet ME, Roy D: Arterial Onyx embolisation of intracranial DAVFs with cortical venous drainage. Can J Neurol Sci 36: , Chong WKW, Holt M: Endovascular therapy for intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neuroradiol J 19: , Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, Bailly AL, Houdart E, Casasco A, Chiras J, Merland JJ: Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: Clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology 194: , Cognard C, Januel AC, Silva NA Jr, Tall P: Endovascular treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with cortical venous drainage: New management using Onyx. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29: , Duffau H, Lopes M, Janosevic V, Sichez JP, Faillot T, Capelle L, Isma M, Bitar A, Arthuis F, Fohanno D: Early rebleeding from intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: Report of 20 cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 90:78-84, Higashida RT, Halbach VV, Dowd CF, Hieshima GB: Endovascular surgical approach to intracranial vascular diseases. J Endovasc Surg 3: , Jiang C, Lv X, Li Y, Liu A, Lv M, Jiang P, Wu Z: Transvenous embolization of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula with Onyx-18 and plentinum coils: Technical Note. Neuroradiol J 20: 47-52, Jiang C, Lv X, Li Y, Liu A, Wu Z: Transvenous embolization with Onyx for dural arteriovenous fistula of cavernous sinus: A report of two case reports. Neuroradiol J 20: , Jiang C, Lv X, Li Y, Wu Z: Transarterial Onyx packing of the transverse sigmoid sinus for dural arteriovenous fistulas. Eur J Radiol 80: , Jiang C, Lv X, Li Y, Zhang J, Wu Z: Endovascular treatment of high-risk tentorial dural arteriovenous fistulas: Clinical outcomes. Neuroradiology 51: , Kuwayama N, Kubo M, Tsumura K, Yamamoto H, Endo S: Hemodynamic status and treatment of aggressive dural arteriovenous fistulas. Acta Neurochir Suppl 94: , Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A, Raybaud C: Surgical Neuroangiography. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, Lasjaunias P, Chiu M, ter Brugge K, Tolia A, Hurth M, Bernstein M: Neurological manifestations of intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 64: , Lasjaunias P, Magufis A, Goulao R, Suthipongchai S, Rodesch R, Alvarez H: Anatomoclinical aspects of dural arteriovenous shunts in children. Intervent Neuroradiol 2: , Lucas Cde P, Mounayer C, Spelle L, Piotin M, Rezende MT, Moret J: Endoarterial management of dural arteriovenous malformations with isolated sinus using Onyx-18: Technical case report. Neurosurgery 61(5 Suppl 2):E , Lv X, Jiang C, Li Y, Wu Z: Percutaneous transvenous packing of cavernous sinus with Onyx for cavernous dural arteriovenous fistula. Eur J Radiol 71: , Lv X, Jiang C, Li Y, Wu Z: Results and complications of transarterial embolization of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas using Onyx-18. J Neurosurg 109: , Lv X, Jiang C, Li Y, Yang X, Wu Z: Recovery of opthalmoplegia associated with cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas after transvenous cavernous sinus packing. Eur J Radiol 75: , Lv X, Jiang C, Zhang J, Li Y, Wu Z: Complications related to percutaneous transarterial embolization of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas in 40 patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30: , Lv X, Jiang C, Li Y, Liu L, Liu J, Wu Z: Transverse-sigmoid sinus dural arteriovenous fistulae. World Neurosurg 74: , Lv X, Jiang C, Li Y, Yang X, Wu Z: Transarterial embolization of tentorial dural arteriovenous fistulas with Onyx-18. Neuroradiol J 21: , Lv X, Li Y, Liu A, Jiang C, Wu Z: Transarterial embolization of dural arteriovenous fistulas of the anterior cranial fossa Onyx- 18: Case report. Neuroradiol J 20:53-59, 2007 Turk Neurosurg 26(4): ,
7 28. Natarajan SK, Ghodke B, Britz GW, Born DE, Sekhar LN: Multimodality treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations with microsurgery after embolization with onyx: Single-center experience and technical nuances. Neurosurgery 62: , Natarajan SK, Ghodke B, Kim LJ, Hallam DK, Britz GW, Sekhar LN: Multimodality treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas in the Onyx era: A single center experience. World Neurosurg 73(4): , Ng PP, Higashida RT, Cullen S, Malek R, Halbach VV, Dowd CF: Endovascular strategies for carotid cavernous and intracerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurg Focus 15:ECP1, Nogueira RG, Dabus G, Rabinov JD, Eskey CJ, Ogilvy CS, Hirsch JA, Pryor JC: Preliminary experience with onyx embolization for the treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:91-97, Panagiotopoulos V, Moller-Hartmann W, Asgari S, Sandalcioglu IE, Forsting M, Wanke IL: Onyx embolization as a first line treatment for intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with cortical venous reflux. Rofo 181: , Rezende MT, Piotin M, Mounayer C, Spelle L, Abud DG, Moret J: Dural arteriovenous fistula of the lesser sphenoid wing region treated with Onyx: Technical note. Neuroradiology 48: , Sarma D, ter Brugge K: Management of intracranial dural arteriovenous shunts in adults. Eur J Radiol 46: , Schuette AJ, Cawley CM, Barrow DL: Indocyanine green videoangiography in the management of dural arteriovenous fistulae. Neurosurgery 67: , Shi ZS, Loh Y, Duckwiler GR, Jahan R, Vinuela F: Balloonassisted transarterial embolization of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg 110: , Soderman M, Pavic L, Edner G, Holmin S, Andersson T: Natural history of dural arteriovenous shunts. Stroke 39: , Stiefel MF, Albuquerque FC, Park MS, Dashti SR: McDougall CG: Endovascular treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae using Onyx: A case series. Neurosurgery 65 ONS Suppl 1:ons132 ons140, Strom RG, Botros JA, Refai D, Moran CJ, Cross DT 3rd, Chicoine MR, Grubb RL Jr, Rich KM, Dacey RG Jr, Derdeyn CP, Zipfel GJ: Cranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: Asymptomatic cortical venous drainage portends less aggressive clinical course. Neurosurgery 64: , Toulgoat F, Mounayer C, Tulio Salles Rezende M, Piotin M, Spelle L, Lazzarotti G, Desal H, Moret J: Transarterial embolisation of intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations with ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer (Onyx18). J Neuroradiol 33: , Toya S, Shiobara R, Izumi J, Shinomiya Y, Shiga H, Kimura C: Spontaneous carotid cavernous fistula during pregnancy or in the postpartum stage. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 54: , van Dijk JM, terbrugge KG, Willinsky RA, Wallace MC: Clinical course of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with long-term persistent cortical venous reflux. Stroke 33: , Wu HM, Pan DH, Chung WY, Guo WY, Liu KD, Shiau CY, Wang LW, Chen SJ: Gamma Knife surgery for the management of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg 105 Suppl:43-51, Yang H, Kano H, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Horowitz MB, Lunsford LD: Stereotactic radiosurgery with or without embolization for intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurgery 67: , Turk Neurosurg 26(4): , 2016
Dural arteriovenous shunts (DAVSs), also called dural
 Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are abnormal. Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
 clinical article J Neurosurg 124:1123 1127, 2016 Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas Sudheer Ambekar, MD, Brandon G. Gaynor, MD, Eric C. Peterson,
clinical article J Neurosurg 124:1123 1127, 2016 Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas Sudheer Ambekar, MD, Brandon G. Gaynor, MD, Eric C. Peterson,
A.J. Hauer Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae
 A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
 J Neurosurg 101:31 35, 2004 Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas J. MARC C. VAN DIJK, M.D., PH.D., KAREL G. TERBRUGGE, M.D., ROBERT A.
J Neurosurg 101:31 35, 2004 Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas J. MARC C. VAN DIJK, M.D., PH.D., KAREL G. TERBRUGGE, M.D., ROBERT A.
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations and Fistulae (DAVM S DAVF S)
 Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center Cohort of 12 Patients
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.4.284 Original Article Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.4.284 Original Article Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) with retrograde
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
PEER-REVIEW REPORTS. various signs and symptoms such as headaches, tinnitus, bruit, neurologic deficits, venous hypertensive encephalopathy with
 Multimodality Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas in the Onyx Era: a Single Center Experience Sabareesh K. Natarajan 1, Basavaraj Ghodke 1,2, Louis J. Kim 1,2, Danial K. Hallam 1,2,
Multimodality Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas in the Onyx Era: a Single Center Experience Sabareesh K. Natarajan 1, Basavaraj Ghodke 1,2, Louis J. Kim 1,2, Danial K. Hallam 1,2,
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are acquired abnormal
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.G. Nogueira G. Dabus J.D. Rabinov C.J. Eskey C.S. Ogilvy J.A. Hirsch J.C. Pryor Preliminary Experience with Onyx Embolization for the Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.G. Nogueira G. Dabus J.D. Rabinov C.J. Eskey C.S. Ogilvy J.A. Hirsch J.C. Pryor Preliminary Experience with Onyx Embolization for the Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh September 2017 davfs Definition Clinical Presentation Natural History
Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh September 2017 davfs Definition Clinical Presentation Natural History
Cranial dural arteriovenous fistula: transarterial Onyx embolization experience and technical nuances
 Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona, USA Correspondence to Dr C G McDougall, Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow
Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona, USA Correspondence to Dr C G McDougall, Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow
An Onyx tunnel: reconstructive transvenous balloon-assisted Onyx embolization for dural arteriovenous fistula of the transverse-sigmoid sinus
 TECHNICAL NOTE J Neurosurg 129:922 927, 2018 An Onyx tunnel: reconstructive transvenous balloon-assisted Onyx embolization for dural arteriovenous fistula of the transverse-sigmoid sinus *Mena G. Kerolus,
TECHNICAL NOTE J Neurosurg 129:922 927, 2018 An Onyx tunnel: reconstructive transvenous balloon-assisted Onyx embolization for dural arteriovenous fistula of the transverse-sigmoid sinus *Mena G. Kerolus,
Andrew Carlson MD, Ali Alaraj MD, Sepideh Amin Hanjani MD, Fady Charbel MD, Victor Aletich MD.
 Endovascular Approach and Technique for Treatment of Transverse Sigmoid Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Cortical Reflux: The Importance of Venous Sinus Sacrifice Andrew Carlson MD, Ali Alaraj MD, Sepideh
Endovascular Approach and Technique for Treatment of Transverse Sigmoid Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Cortical Reflux: The Importance of Venous Sinus Sacrifice Andrew Carlson MD, Ali Alaraj MD, Sepideh
Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.2.106 Case Report Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.2.106 Case Report Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils
 High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas. Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients
 J Neurosurg 71:352-358,1989 Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients STANLEY L. BARNWELL, M.D., PH.D., VAN V. HALBACH, M.D., RANDALL
J Neurosurg 71:352-358,1989 Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients STANLEY L. BARNWELL, M.D., PH.D., VAN V. HALBACH, M.D., RANDALL
Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Clinical Characteristics and Management Based on Location and Hemodynamics
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery ISSN -8565, EISSN 87-9, http://dx.doi.org/0.76/jcen.0...9 Original Article Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Clinical Characteristics and
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery ISSN -8565, EISSN 87-9, http://dx.doi.org/0.76/jcen.0...9 Original Article Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Clinical Characteristics and
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are
 TOPIC DURAL FISTULAS DURAL FISTULAS Advances in Surgical Approaches to Dural Fistulas Patrick P. Youssef, MD Albert Jess Schuette, MD C. Michael Cawley, MD Daniel L. Barrow, MD Department of Neurosurgery,
TOPIC DURAL FISTULAS DURAL FISTULAS Advances in Surgical Approaches to Dural Fistulas Patrick P. Youssef, MD Albert Jess Schuette, MD C. Michael Cawley, MD Daniel L. Barrow, MD Department of Neurosurgery,
I-iodoamphetamine single photon emission computed tomography
 clinical article J Neurosurg 123:110 117, 2015 Cerebral hemodynamic disturbance in dural arteriovenous fistula with retrograde leptomeningeal venous drainage: a prospective study using 123 I-iodoamphetamine
clinical article J Neurosurg 123:110 117, 2015 Cerebral hemodynamic disturbance in dural arteriovenous fistula with retrograde leptomeningeal venous drainage: a prospective study using 123 I-iodoamphetamine
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations
 Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Kenan I. Amautovic, M.D., and Ali F. Krisht, M.D. '-...--- Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should: 1. Have an
Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Kenan I. Amautovic, M.D., and Ali F. Krisht, M.D. '-...--- Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should: 1. Have an
Treatment of Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula by Transarterial Multiple Balloon-assisted Onyx Embolization: A Case Report
 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0136 Treatment of Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula by Transarterial Multiple Balloon-assisted Onyx Embolization: A Case Report Shunsuke Yamashita, 1 Atsushi
DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0136 Treatment of Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula by Transarterial Multiple Balloon-assisted Onyx Embolization: A Case Report Shunsuke Yamashita, 1 Atsushi
Transarterial Occlusion of Solitary Intracerebral Arteriovenous Fistulas
 747 Transarterial Occlusion of Solitary Intracerebral Arteriovenous Fistulas Van V. Halbach 1 2 Randall T. Higashida 1 2 Grant B. Hieshima 1 2 Carl W. Hardin 1 Christopher F. Dowd 1 Stanley L. Barnwell
747 Transarterial Occlusion of Solitary Intracerebral Arteriovenous Fistulas Van V. Halbach 1 2 Randall T. Higashida 1 2 Grant B. Hieshima 1 2 Carl W. Hardin 1 Christopher F. Dowd 1 Stanley L. Barnwell
Fatal progression of posttraumatic dural arteriovenous fistulas refractory to multimodal therapy
 See the Letter to the Editor and the Response in this issue in Neurosurgical Forum, pp 858 861. J Neurosurg 94:831 835, 2001 Fatal progression of posttraumatic dural arteriovenous fistulas refractory to
See the Letter to the Editor and the Response in this issue in Neurosurgical Forum, pp 858 861. J Neurosurg 94:831 835, 2001 Fatal progression of posttraumatic dural arteriovenous fistulas refractory to
EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein
 J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are rare arteriovenous
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Progressive versus Nonprogressive Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Characteristics and Outcomes S.W. Hetts, T. Tsai, D.L. Cooke, M.R. Amans, F. Settecase, P.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Progressive versus Nonprogressive Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Characteristics and Outcomes S.W. Hetts, T. Tsai, D.L. Cooke, M.R. Amans, F. Settecase, P.
DAVFs are defined as abnormal communications between
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Lekkhong S. Pongpech K. ter Brugge P. Jiarakongmun R. Willinsky S. Geibprasert T. Krings Transvenous Embolization of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Shunts through Occluded Venous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Lekkhong S. Pongpech K. ter Brugge P. Jiarakongmun R. Willinsky S. Geibprasert T. Krings Transvenous Embolization of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Shunts through Occluded Venous
Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
 Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (dural AVFs) constitute 10%
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are direct. Gamma Knife surgery for clival epidural-osseous dural arteriovenous fistulas
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 128:1364 1371, 2018 Gamma Knife surgery for clival epidural-osseous dural arteriovenous fistulas Cheng-Chia Lee, MD, 1,4 Ching-Jen Chen, MD, 6 Shao-Ching Chen, MD, 1 Huai-Che
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 128:1364 1371, 2018 Gamma Knife surgery for clival epidural-osseous dural arteriovenous fistulas Cheng-Chia Lee, MD, 1,4 Ching-Jen Chen, MD, 6 Shao-Ching Chen, MD, 1 Huai-Che
Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving the Laterocavernous Sinus
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
Multiple Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Multiple Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Satoshi USHIKOSHI, Yoichi KIKUCHI*, Kiyohiro HOUKIN**, Hisatoshi SAITO, and Hiroshi ABE** Sapporo Azabu Neurosurgical Hospital, Sapporo; Departments of *Radiology
Multiple Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Satoshi USHIKOSHI, Yoichi KIKUCHI*, Kiyohiro HOUKIN**, Hisatoshi SAITO, and Hiroshi ABE** Sapporo Azabu Neurosurgical Hospital, Sapporo; Departments of *Radiology
Cranial dural arteriovenous fistulae (davf)
 Russell G. Strom, A.B. James A. Botros, B.A. Daniel Refai, M.D. Christopher J. Moran, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, DeWitte T. Cross III, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Michael R.
Russell G. Strom, A.B. James A. Botros, B.A. Daniel Refai, M.D. Christopher J. Moran, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, DeWitte T. Cross III, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Michael R.
Methods. Treatment options for intracranial arteriovenous malformations
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1139 1143, August 2004 Complete Obliteration of Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation with Endovascular Cyanoacrylate Embolization: Initial Success and Rate of Permanent Cure
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1139 1143, August 2004 Complete Obliteration of Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation with Endovascular Cyanoacrylate Embolization: Initial Success and Rate of Permanent Cure
Interlocking Detachable Coil Occlusion in the Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms: Preliminary Results
 Interlocking Detachable Coil Occlusion in the Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms: Preliminary Results H. Saruhan Cekirge, Isil Saatci, Murat M. Firat, Ferhun Balkanci, and Aytekin Besim PURPOSE:
Interlocking Detachable Coil Occlusion in the Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms: Preliminary Results H. Saruhan Cekirge, Isil Saatci, Murat M. Firat, Ferhun Balkanci, and Aytekin Besim PURPOSE:
Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment.
 Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment. Poster No.: C-1939 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Dotsu 1, H.
Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment. Poster No.: C-1939 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Dotsu 1, H.
A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Accompanying a Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2018; 12: 38 42 Online September 11, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2017-0056 A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Accompanying a Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2018; 12: 38 42 Online September 11, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2017-0056 A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Accompanying a Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous
The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience
 230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1715 1722, August 2005 Dural Sinus Compartment in Dural Arteriovenous Shunts: A New Angioarchitectural Feature Allowing Superselective Transvenous Dural Sinus Occlusion Treatment
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1715 1722, August 2005 Dural Sinus Compartment in Dural Arteriovenous Shunts: A New Angioarchitectural Feature Allowing Superselective Transvenous Dural Sinus Occlusion Treatment
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment
 Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVF) have long
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Noguchi M. Kubo N. Kuwayama Y. Kamisaki G. Tomizawa K. Kameda H. Kawabe S. Ogawa N. Watanabe S. Endo H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Retrograde Cortical Venous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Noguchi M. Kubo N. Kuwayama Y. Kamisaki G. Tomizawa K. Kameda H. Kawabe S. Ogawa N. Watanabe S. Endo H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Retrograde Cortical Venous
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula in Children: Endovascular Treatment and Outcomes in Seven Cases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1217 1225, June/July 2001 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula in Children: Endovascular Treatment and Outcomes in Seven Cases Patricia K. Kincaid, Gary R. Duckwiler, Y. Pierre Gobin, and
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1217 1225, June/July 2001 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula in Children: Endovascular Treatment and Outcomes in Seven Cases Patricia K. Kincaid, Gary R. Duckwiler, Y. Pierre Gobin, and
Modern treatment of brain arteriovenous malformation
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Brain AVM Embolization with Onyx BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: To report the initial experience by using a new liquid embolic agent (Onyx) for embolization
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Brain AVM Embolization with Onyx BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: To report the initial experience by using a new liquid embolic agent (Onyx) for embolization
New Concept in Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Correlation With Presenting Symptom and Venous Drainage Patterns
 New Concept in Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Correlation With Presenting Symptom and Venous Drainage s Dae Chul Suh, MD; Jeong Hyun Lee, MD; Sang Joon Kim, MD; Sun Ju Chung, MD; Choong Gon
New Concept in Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Correlation With Presenting Symptom and Venous Drainage s Dae Chul Suh, MD; Jeong Hyun Lee, MD; Sang Joon Kim, MD; Sun Ju Chung, MD; Choong Gon
Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1267 1273, August 1998 Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy Robert W. Hurst, Linda J. Bagley, Steven
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1267 1273, August 1998 Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy Robert W. Hurst, Linda J. Bagley, Steven
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Posterior Fossa Draining into Subarachnoid Veins
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Posterior Fossa Draining into Subarachnoid Veins Laurent Pierot, 1 Jacques Chiras, 1 Jean-Frans:ois Meder, 2 Michele Rose, 1 Maurice Rivierez, 3 and Claude Marsault
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Posterior Fossa Draining into Subarachnoid Veins Laurent Pierot, 1 Jacques Chiras, 1 Jean-Frans:ois Meder, 2 Michele Rose, 1 Maurice Rivierez, 3 and Claude Marsault
Transvenous Embolization of Dural Fistulas Involving the Transverse and Sigmoid Sinuses
 385 Transvenous Embolization of Dural Fistulas Involving the Transverse and Sigmoid Sinuses Van V. Halbach 1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 C. Mark Mehringer 2 Carl W. Hardin 1 Received February
385 Transvenous Embolization of Dural Fistulas Involving the Transverse and Sigmoid Sinuses Van V. Halbach 1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 C. Mark Mehringer 2 Carl W. Hardin 1 Received February
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
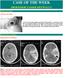 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma
 ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are abnormal arteriovenous
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.J. Kim D.I. Kim S.H. Suh J. Kim S.K. Lee E.Y. Kim T.S. Chung Results of Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Single-Center Experience with Emphasis on
ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.J. Kim D.I. Kim S.H. Suh J. Kim S.K. Lee E.Y. Kim T.S. Chung Results of Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Single-Center Experience with Emphasis on
point of dural arteriovenous fistul
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Efficacy of DynaCT digital angiogra point of dural arteriovenous fistul Hiu, Takeshi; Kitagawa, Naoki; Mori Horie, Nobutaka; Morofuji, Yoichi;
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Efficacy of DynaCT digital angiogra point of dural arteriovenous fistul Hiu, Takeshi; Kitagawa, Naoki; Mori Horie, Nobutaka; Morofuji, Yoichi;
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment
 166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
Cerebral DAVF is an acquired abnormal arterialto-venous
 Neurosurg Focus 32 (5):E10, 2012 Dural arteriovenous fistulas presenting with brainstem dysfunction: diagnosis and surgical treatment Charles Kulwin, M.D., Bradley N. Bohnstedt, M.D., John A. Scott, M.D.,
Neurosurg Focus 32 (5):E10, 2012 Dural arteriovenous fistulas presenting with brainstem dysfunction: diagnosis and surgical treatment Charles Kulwin, M.D., Bradley N. Bohnstedt, M.D., John A. Scott, M.D.,
Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona
 clinical article J Neurosurg 122:876 882, 2015 The role of microscope-integrated near-infrared indocyanine green videoangiography in the surgical treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
clinical article J Neurosurg 122:876 882, 2015 The role of microscope-integrated near-infrared indocyanine green videoangiography in the surgical treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
Cerebral haemorrhage from a remote varix in the venous outflow of an arteriovenous malformation treated successfully by embolisation
 The British Journal of Radiology, 83 (2010), e129 e134 CASE REPORT Cerebral haemorrhage from a remote varix in the venous outflow of an arteriovenous malformation treated successfully by embolisation 1
The British Journal of Radiology, 83 (2010), e129 e134 CASE REPORT Cerebral haemorrhage from a remote varix in the venous outflow of an arteriovenous malformation treated successfully by embolisation 1
7 TI - Radiosurgery of angiographically occult vascular malformations. AU - Kida Y, et al.
 1 TI - Cerebral arteriovenous malformation in pregnancy: presentation and neurologic, obstetric, and ethical significance. AU - Finnerty JJ, et al. SO - Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Aug;181(2):296-303. Review.
1 TI - Cerebral arteriovenous malformation in pregnancy: presentation and neurologic, obstetric, and ethical significance. AU - Finnerty JJ, et al. SO - Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Aug;181(2):296-303. Review.
Superior cerebellar artery aneurysms: incidence, clinical presentation and midterm outcome of endovascular treatment
 Neuroradiology (2007) 49:747 751 DOI 10.1007/s00234-007-0251-z INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY Superior cerebellar artery aneurysms: incidence, clinical presentation and midterm outcome of endovascular treatment
Neuroradiology (2007) 49:747 751 DOI 10.1007/s00234-007-0251-z INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY Superior cerebellar artery aneurysms: incidence, clinical presentation and midterm outcome of endovascular treatment
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Presenting with Status Epilepticus Treated Successfully with Endovascular Intervention
 52 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Presenting with Status Epilepticus Treated Successfully with Endovascular Intervention Chun-Yu Lee, Shin-Joe Yeh, Li-Kai Tsai, Sung-Chun Tang, Jiann-Shing Jeng Abstract-
52 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Presenting with Status Epilepticus Treated Successfully with Endovascular Intervention Chun-Yu Lee, Shin-Joe Yeh, Li-Kai Tsai, Sung-Chun Tang, Jiann-Shing Jeng Abstract-
Vein of Galen Aneurysms
 Interventional Neuroradiology 7 (Suppll): 99103, 2001 Vein of Galen Aneurysms Experience with Eleven Cases. KOIYAA, H. NAKAJIA,. NISHIKAWA, K. YAANAKA, Y. IWAI, T. YASUI, T. ORIKAWA*, S. KITANO*, H. SAKAOTO*,A.
Interventional Neuroradiology 7 (Suppll): 99103, 2001 Vein of Galen Aneurysms Experience with Eleven Cases. KOIYAA, H. NAKAJIA,. NISHIKAWA, K. YAANAKA, Y. IWAI, T. YASUI, T. ORIKAWA*, S. KITANO*, H. SAKAOTO*,A.
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are relatively
 case report J Neurosurg 122:1208 1213, 2015 Torcular dural arteriovenous fistula treated via stent placement and angioplasty in the affected straight and transverse sinuses: case report Shigeki Takada,
case report J Neurosurg 122:1208 1213, 2015 Torcular dural arteriovenous fistula treated via stent placement and angioplasty in the affected straight and transverse sinuses: case report Shigeki Takada,
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) constitute 10% to
 Color Doppler Flow Imaging of the Superior Ophthalmic Vein in Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Shoichiro Kawaguchi, MD; Toshisuke Sakaki, MD; Ryunosuke Uranishi, MD Background and Purpose This article evaluates
Color Doppler Flow Imaging of the Superior Ophthalmic Vein in Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Shoichiro Kawaguchi, MD; Toshisuke Sakaki, MD; Ryunosuke Uranishi, MD Background and Purpose This article evaluates
Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses
 Neurosurg Focus 5 (4):Article 10, 1998 Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses Katsuya Goto,
Neurosurg Focus 5 (4):Article 10, 1998 Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses Katsuya Goto,
Course of apparent diffusion coefficient values in cerebral edema of dural arteriovenous
 Title Page Title: Course of apparent diffusion coefficient values in cerebral edema of dural arteriovenous fistula before and after treatment Authors: Shigeyuki Sakamoto, Shinji Ohba, Masaaki Shibukawa,
Title Page Title: Course of apparent diffusion coefficient values in cerebral edema of dural arteriovenous fistula before and after treatment Authors: Shigeyuki Sakamoto, Shinji Ohba, Masaaki Shibukawa,
Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos
 Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Vascular Malformations
 Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Transfemoral Venous Embolization of Vein of Galen Malformations
 643 Transfemoral Venous Embolization of Vein of Galen Malformations Christopher F. Dowd 1 Van V. Halbach 1 2 Stanley L. Barnwell 1 2 Randall T. Higashida 1 2 MichaelS. B. Edwards 2 3 Grant B. Hieshima
643 Transfemoral Venous Embolization of Vein of Galen Malformations Christopher F. Dowd 1 Van V. Halbach 1 2 Stanley L. Barnwell 1 2 Randall T. Higashida 1 2 MichaelS. B. Edwards 2 3 Grant B. Hieshima
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography.
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography. Poster No.: C-2199 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Filipe, T. Parreira, C. Andrade, R. Santos, E. Azevedo;
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography. Poster No.: C-2199 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Filipe, T. Parreira, C. Andrade, R. Santos, E. Azevedo;
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Therapeutic Embolization of the Dural Arteriovenous Malformation Involving the Jugular Bulb
 J Korean Med Sci 2001; 16: 527-31 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Therapeutic Embolization of the Dural Arteriovenous Malformation Involving the Jugular Bulb Pulsatile tinnitus
J Korean Med Sci 2001; 16: 527-31 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Therapeutic Embolization of the Dural Arteriovenous Malformation Involving the Jugular Bulb Pulsatile tinnitus
Endovascular Treatment of Bilateral Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Therapeutic Strategy and Follow-Up Outcomes
 Original Article Neurointervention https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.334 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(2):334-341 Endovascular Treatment of Bilateral Cavernous Sinus Dural
Original Article Neurointervention https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.334 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(2):334-341 Endovascular Treatment of Bilateral Cavernous Sinus Dural
Evolutionary History of Multiple Dural Fistula
 683722HICXXX10.1177/2324709616683722Journal of Investigative Medicine High Impact Case ReportsMartinez-Burbano et al case-report2016 Case Report Evolutionary History of Multiple Dural Fistula Journal of
683722HICXXX10.1177/2324709616683722Journal of Investigative Medicine High Impact Case ReportsMartinez-Burbano et al case-report2016 Case Report Evolutionary History of Multiple Dural Fistula Journal of
Onyx Embolization of Intracranial Pial Arteriovenous Fistula
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2016.18.3.291 Case Report Onyx Embolization of Intracranial Pial Arteriovenous
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2016.18.3.291 Case Report Onyx Embolization of Intracranial Pial Arteriovenous
Selective Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms with a Liquid Embolic: A Single-Center Experience in 39 Patients with 41 Aneurysms
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:885 893, April 2005 Selective Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms with a Liquid Embolic: A Single-Center Experience in 39 Patients with 41 Aneurysms Boris Lubicz,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:885 893, April 2005 Selective Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms with a Liquid Embolic: A Single-Center Experience in 39 Patients with 41 Aneurysms Boris Lubicz,
Original Article Pial arteriovenous fistulas: two pediatric cases and a literature review
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(5):7855-7862 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0019732 Original Article Pial arteriovenous fistulas: two pediatric cases and a literature review Lei Feng *, Yunzhen Liu *, Jun
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(5):7855-7862 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0019732 Original Article Pial arteriovenous fistulas: two pediatric cases and a literature review Lei Feng *, Yunzhen Liu *, Jun
Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Brief Review on Classification and General Features
 Review rticle Intracranial ural rteriovenous istulas: rief Review on lassification and General eatures ltay SNR Talat KIRIfi epartment of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Istanbul University, stanbul,
Review rticle Intracranial ural rteriovenous istulas: rief Review on lassification and General eatures ltay SNR Talat KIRIfi epartment of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Istanbul University, stanbul,
Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:781 786, April 2000 Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Robert W. Hurst and Robert I. Grossman
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:781 786, April 2000 Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Robert W. Hurst and Robert I. Grossman
DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY
 Neuroradiology (2008) 50:1013 1023 DOI 10.1007/s00234-008-0433-3 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The anterior medullary anterior pontomesencephalic venous system and its bridging veins communicating to the dural
Neuroradiology (2008) 50:1013 1023 DOI 10.1007/s00234-008-0433-3 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The anterior medullary anterior pontomesencephalic venous system and its bridging veins communicating to the dural
7/5/2016. Neonatal high-output cardiac failure. Case 1 POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic dural arteriovenous fistula with perimedullary hypertension: case report
 Foreman et al. Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2013, 21:23 http://www.chiromt.com/content/21/1/23 CHIROPRACTIC & MANUAL THERAPIES CASE REPORT Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic
Foreman et al. Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2013, 21:23 http://www.chiromt.com/content/21/1/23 CHIROPRACTIC & MANUAL THERAPIES CASE REPORT Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic
Endovascular treatment with transvenous approach for embolization of carotid cavernous fistula
 169 Case Report Endovascular treatment with transvenous approach for embolization of carotid cavernous fistula Benny Young, Agusmanan Bojeng Department of Radiology, University Malaysia Sarawak, Faculty
169 Case Report Endovascular treatment with transvenous approach for embolization of carotid cavernous fistula Benny Young, Agusmanan Bojeng Department of Radiology, University Malaysia Sarawak, Faculty
Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus
 337 Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus Van V. Halbach1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 Mark Rosenblum 2 Les Cahan 3 We report the diagnosis
337 Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus Van V. Halbach1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 Mark Rosenblum 2 Les Cahan 3 We report the diagnosis
MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION!
 CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
Endovascular Embolization of Intracranial Dural AV Fistula- Benign?
 Endovascular Embolization of Intracranial Dural AV Fistula- Benign? Suneeta Gollapudy, M.D. Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology Director, Division of Neuroanesthesia Director, Division of PACU Rotation(
Endovascular Embolization of Intracranial Dural AV Fistula- Benign? Suneeta Gollapudy, M.D. Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology Director, Division of Neuroanesthesia Director, Division of PACU Rotation(
The treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurologic Complications of Arteriovenous Malformation Embolization Using Liquid Embolic Agents
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.V. Jayaraman M.L. Marcellus S. Hamilton H.M. Do D. Campbell S.D. Chang G.K. Steinberg M.P. Marks Neurologic Complications of Arteriovenous Malformation Embolization Using Liquid Embolic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.V. Jayaraman M.L. Marcellus S. Hamilton H.M. Do D. Campbell S.D. Chang G.K. Steinberg M.P. Marks Neurologic Complications of Arteriovenous Malformation Embolization Using Liquid Embolic
Brain Edema after Repeat Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for a Large Arteriovenous Malformation: A Case Report
 Posted online 2016 Jul. 19 Exp Neurobiol. 2016 Aug;25(4) pissn 1226-2560 eissn 2093-8144 Case Report Brain Edema after Repeat Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for a Large Arteriovenous Malformation: A Case Report
Posted online 2016 Jul. 19 Exp Neurobiol. 2016 Aug;25(4) pissn 1226-2560 eissn 2093-8144 Case Report Brain Edema after Repeat Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for a Large Arteriovenous Malformation: A Case Report
Department of Interventional Neuroradiology, Hôpital Dupuytren, Centre Regional Hospitalier Universitaire de Limoges, Limoges, France
 technical note J Neurosurg 123:1120 1124, 2015 Balloon-assisted microcatheter navigation for AVM embolization: technical note George A. C. Mendes, MD, Eduardo Pedrolo Silveira, MD, Suzana Saleme, MD, Christina
technical note J Neurosurg 123:1120 1124, 2015 Balloon-assisted microcatheter navigation for AVM embolization: technical note George A. C. Mendes, MD, Eduardo Pedrolo Silveira, MD, Suzana Saleme, MD, Christina
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh
 Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Recurrence of the Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula at Adjacent Sinuses
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Recurrence of the cavernous sinus d sinuses following repeated transven literature review. Hiu, Takeshi; Horie, Nobutaka; Haya Morikawa, Minoru;
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Recurrence of the cavernous sinus d sinuses following repeated transven literature review. Hiu, Takeshi; Horie, Nobutaka; Haya Morikawa, Minoru;
Disclosures. Take Home Points 9/6/2014. Endovascular Treatment of Aneurysms and Pseudoaneurysms
 Endovascular Treatment of Aneurysms and Pseudoaneurysms UCSF Stroke and Aneurysm Update CME Saturday September 6, 2014 Steven W. Hetts, MD Associate Professor of Radiology Interventional Neuroradiology
Endovascular Treatment of Aneurysms and Pseudoaneurysms UCSF Stroke and Aneurysm Update CME Saturday September 6, 2014 Steven W. Hetts, MD Associate Professor of Radiology Interventional Neuroradiology
Post-traumatic persistent trigeminal artery-cavernous fistula: a case report and review of literature
 . 252. Post-traumatic persistent trigeminal artery-cavernous fistula: a case report and review of literature HU Wei-peng 胡伟鹏 *, HUANG Tian-zao 黄天造, GAO Hong-zhi 高宏志, YU Mao-qing 余茂清 and XU Chao-yang 徐朝阳
. 252. Post-traumatic persistent trigeminal artery-cavernous fistula: a case report and review of literature HU Wei-peng 胡伟鹏 *, HUANG Tian-zao 黄天造, GAO Hong-zhi 高宏志, YU Mao-qing 余茂清 and XU Chao-yang 徐朝阳
Selective transvenous liquid embolization of a Type 1 dural arteriovenous fistula at the junction of the transverse and sigmoid sinuses
 J Neurosurg 92:1045 1049, 2000 Selective transvenous liquid embolization of a Type 1 dural arteriovenous fistula at the junction of the transverse and sigmoid sinuses Case report KAZUHIRO OHTAKARA, M.D.,
J Neurosurg 92:1045 1049, 2000 Selective transvenous liquid embolization of a Type 1 dural arteriovenous fistula at the junction of the transverse and sigmoid sinuses Case report KAZUHIRO OHTAKARA, M.D.,
Treatment of brain AVMs includes different modalities
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij S. Jacobs M. Sluzewski B. van der Pol G.N. Beute M.E. Sprengers Curative Embolization of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations with Onyx: Patient Selection, Embolization Technique,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij S. Jacobs M. Sluzewski B. van der Pol G.N. Beute M.E. Sprengers Curative Embolization of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations with Onyx: Patient Selection, Embolization Technique,
KEY WORDS: Carotid-cavernous fistula, Endovascular, Ethanol embolization. an artery and a vein. Carotidcavernous
 TECHNIQUE APPLICATIONS ALCOHOL EMBOLIZATION OF CAROTID-CAVERNOUS INDIRECT FISTULAE Christopher J. Koebbe, M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
TECHNIQUE APPLICATIONS ALCOHOL EMBOLIZATION OF CAROTID-CAVERNOUS INDIRECT FISTULAE Christopher J. Koebbe, M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
