Clinicopathological Study of Mass-forming Gallbladder Cancer Focusing on the Grade of Cellular Dysplasia
|
|
|
- Gerard Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Showa Univ J Med Sci 30 1, 35 42, March 2018 Original Clinicopathological Study of Mass-forming Gallbladder Cancer Focusing on the Grade of Cellular Dysplasia Nobukazu SHIMA 1, Nobuyuki OHIKE 2), Reika SUZUKI 2, Tomoko NOROSE 2, Tomohide ISOBE 2, Akira SHIOKAWA 2, Nobuyuki TAKEYAMA 3, Junichi TANAKA 4, Masahiko MURAKAMI 5 and Masafumi TAKIMOTO 1 Abstract : The relationship between the clinicopathological features and the grade of cellular dysplasia of the neoplastic glands in mass-forming gallbladder cancer was investigated. In this retrospective study, 41 mass-forming 1 cm gallbladder cancer specimens from 83 resected cases were examined. Tumors were classified into three groups : Group A had intraluminal masses consisting of neoplastic glands with only low-grade dysplasia ; Group B had mixed low- and high-grade dysplasia, and Group C had only high-grade dysplasia. Of the 41 tumors, 13 were classified as Group A, 11 as Group B, and 17 as Group C. For Group A, B, and C, respectively, the mean tumor diameter was 1.6, 3.7 and 3.4 cm ; macroscopic type pedunculated / semi-pedunculated / sessile was 7 / 5 / 1, 4 / 6 / 1 and 0 / 10 / 7 ; frequency of an invasive component inside the mass was 0, 9 and 82 ; and cell lineage biliary / metaplastic / mixed was 2 / 1 / 10, 8 / 1 / 2 and 14 / 1 / 2. In addition, invasion depth Tis T1 / T2 / T3 was 13 / 0 / 0, 7 / 4 / 0 and 3 / 10 / 4 ; lymph node metastases were present in 0, 9 and 24 of patients ; 3-year survival rate was 100, 100 and 82 ; and 5-year survival rate was 100, 100 and 69, for A, B and C, respectively. Significant intergroup differences were seen for positive lymph node metastasis rate and 5-year survival rate. The present study indicates that the clinicopathological features of mass-forming gallbladder cancer are different depending on the grade of cellular dysplasia of the mass lesion. The tumors in Groups A and B were of lower malignancy than those in Group C and the prognosis of patients in the former groups was excellent. Group A and B tumors may be intracholecystic papillary-tubular neoplasms, a recently proposed new disease concept. Key words : mass-forming gallbladder cancer, cellular dysplasia, clinicopathological study, intracholecystic papillary-tubular neoplasm ICPN 1 Department of Pathology, Showa University School of Medicine, 1-5-8, Hatanodai, Shinagawa-Ku, , Tokyo, Japan. 2 Department of Pathology, Showa University Fujigaoka Hospital. 3 Department of Radiology, Showa University Fujigaoka Hospital. 4 Department of Gastroenterological and General Surgery, Showa University Fujigaoka Hospital. 5 Department of Surgery, Division of General and Gastroenterological Surgery, Showa University School of Medicine. To whom corresponding should be addressed.
2 36 Nobukazu SHIMA, et al Introduction Opportunities for the detection of elevated lesions in the lumen of the gallbladder are increasing with the widespread use of, and advances in, clinical imaging. These elevated lesions form a diverse group that includes not only cholesterol polyps, hyperplastic polyps, and adenomyomatosis, but also adenomas and adenocarcinomas. Adenocarcinomas are further subdivided into low-grade tumors, which may be confused with adenomas and hyperplastic polyps, and obviously high-grade tumors 1-3. The present study focused on the characteristics of the neoplastic cells in intraluminal elevated lesions in patients diagnosed with massforming gallbladder cancer, as well as the influence of the cellular dysplastic grade on the clinicopathological features, including staging and prognosis. Subjects and methods From 83 patients who underwent surgical resection at our institutions Showa University Hospital and Showa University Fujigaoka Hospital and were histologically diagnosed with primary adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder between 1998 and 2015, 46 patients with macrosized approximately 1 cm polypoid or papillary mass lesions in the gallbladder lumen were initially selected. This retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board and was conducted in accordance with the Health Insurance Portability Accountability Act. The institutional review board waived the requirement for informed patient consent. Clinicopathological study Tumors were classified into the following three groups, based on the dysplastic grade of the tumor cells that composed the elevated lesions protruding into the lumen of the gallbladder, and their clinicopathological features were compared. Group A tumors were intraluminal masses consisting solely of low-grade dysplastic glands Fig. 1a, Group B were intraluminal masses with a mixture of low-grade and high-grade dysplastic glands arbitrarily with each component accounting for at least 25 of the whole tumor, and Group C were intraluminal masses consisting extensively of high-grade dysplastic glands usually showing complex papillo-tubular structures and cribriform structures ; Fig. 1b. Low-grade dysplastic glands were characterized by the regular arrangement of uniform and relatively simple glands with mild nuclear enlargement, while high-grade dysplastic glands were characterized by the irregular arrangement of complex glands with prominent nuclear enlargement and more significant hyperchromasia. The mean age, sex ratio, macroscopic type, mean tumor diameter, presence of an invasive carcinoma component inside the mass lesion, presence of tumors exhibiting p53-overexpression, invasion depth, rate of lymph node metastasis, rate of distant metastasis, and postoperative prognosis were investigated to make comparisons among these three groups. The duration of postoperative follow-up ranged from 45 to 4,137 days, and 5 patients who died of other causes such as myocardial infarction and pneumonia were excluded from the analysis of prognosis. Statistical analysis was carried out using the Kruskal- Wallis test, with the log-rank test for Kaplan-Meier curves ; P 0.05 was regarded as significant.
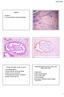
3 Clinicopathological Study of Gallbladder Cancer 37 Fig. 1. Microscopic features of mass-forming gallbladder cancer. a-1 Intraluminal mass consists extensively of low-grade dysplastic glands. Hematoxylin and eosin H E stain, 50 magnification. a-2 Intraluminal mass consists extensively of low-grade dysplastic glands. H E stain, 200 magnification. b-1 Intraluminal mass consists extensively of high-grade dysplastic glands. H E stain, 50 magnification. b-2 Intraluminal mass consists extensively of high-grade dysplastic glands. H E stain, 200 magnification. Investigation of cell lineage The cell lineage of the neoplastic glands composing the mass lesion was investigated histomorphologically and immunohistochemically for all cases. a Histomorphological observation : Tumor cells were categorized as biliary type, intestinal INT type, or gastric GAS type through observation of hematoxylin and eosin-stained specimens under light microscopy, and each tumor was classified as either biliary, metaplastic GAS or INT, or mixed biliary GAS and / or INT Briefly, the histological characteristics of these different cell lineages were as follows : biliary type was characterized by cuboidal or low-columnar epithelial cells with oval nuclei and scant mucinous cytoplasm resembling proper biliary tract epithelium. INT type consisted of tall columnar epithelium with spindle-shaped, pseudostratified nuclei and stronglystained cytoplasm resembling colorectal adenoma. The presence of goblet cells and Paneth cells was also considered indicative of INT lineage. GAS type consisted of tall columnar epithelium with mucinous cytoplasm resembling gastric foveolar epithelium or small tubular units similar to gastric pyloric glands. If more than one of these characteristics were present simultaneously, the
4 38 Nobukazu SHIMA, et al most prominent cell type was used, taking into account the predominant features and degree of cellular dysplasia. b Immunohistochemical analysis : For each patient, thin sections 3 µm were prepared for immunostaining using one or two formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections including the maximum area of the tumor. Staining was performed using the avidin-biotin complex detection method with a BenchMark automated immunostainer Ventana Medical Systems, Inc., Tucson, AZ, USA. The primary antibodies used were MUC1 Ma695, Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd, Newcastle, UK ; 100- fold dilution, MUC2 Ccp58, Leica ; 200-fold dilution, MUC5AC CLH2, Leica ; 200-fold dilution, MUC6 CLH5, Leica ; 50-fold dilution, and CDX-2 AMT28, Leica ; 50-fold dilution. MUC1 was used as a marker for biliary type, MUC2 and CDX-2 for INT type, and MUC5AC and MUC6 for GAS type The proportion of cells staining positive for each marker as a percentage of the total number of neoplastic cells was calculated. Immunostaining for p53 DO-7, Leica ; 800-fold dilution was also carried out following the same staining procedure 1-3. Results Of the 41 patients, 13 were classified with tumors belonging to Group A, 11 to Group B, and 17 to Group C. Clinicopathological study Table 1 The mean age was 65 years in Group A, 71 years in Group B, and 77 years in Group C, and the male female ratio was 10 3 in Group A, 4 7 in Group B, and 7 10 in Group C. Groups B and C tended to be older and to include more women than Group A, but these differences were not significant. The mean tumor diameter was 1.6 cm in Group A, but 3.7 cm in Group B and 3.4 cm in Group C, with the latter groups being significantly larger than Group A. When the tumors were classified as pedunculated, semipedunculated, or sessile on the basis of their macroscopic morphology, Group A included 7 pedunculated, 5 semipedunculated, and 1 sessile tumor, Group B included 4 pedunculated, 6 semipedunculated, and 1 sessile tumor, and Group C included only 10 semipedunculated, and 7 sessile tumors, with Group C containing significantly more sessile tumors than the other groups. The frequency of the presence of invasive carcinoma inside the mass was 0 in Group A and 9 in Group B, while it was significantly higher, at 82, in Group C. Invasion depth was classified as no invasion Tis, invasion into the mucosa T1, invasion into the muscularis propria T2, or invasion into the subserosa T3, and expressed as Tis T1 / T2 / T3. The number of tumors of each invasion depth was 13 / 0 / 0 in Group A, 7 / 4 / 0 in Group B, and 3 / 10 / 4 in Group C, and these differences were significant. The rate of lymph node metastasis was 0 in Group A, 9.1 in Group B, and 23.5 in Group C, and these differences were also significant. The 3-year survival rate was 100 in Groups A and B, but only 82.4 in Group C. The 5-year survival was 100 in Groups A and B, but significantly lower in Group C at The significance of this difference was also confirmed by the log-rank test P 0.02.
5 Clinicopathological Study of Gallbladder Cancer 39 Table 1. Clinicopathological features of mass-forming gallbladder cancer Number Grp A n 13 Grp B n 11 Grp C n 17 P-value Mean age years Sex n Male Female Mean tumor diameter cm Morphology n Pedunculated Semipedunculated Sessile Frequency of invasive carcinoma inside the mass lesion Cell lineage n Biliary Mixed Metaplastic p53-overexpression rate Invasion depth n Tis T T T Lymph node metastasis rate Distant metastasis rate year survival rate year survival rate Grp, Group ; Tis T1, no invasion or invasion into mucosa ; T2, invasion into muscularis propria ; T3, invasion into subserosa. Investigation of cell lineage and immunohistochemical studies When cell lineages were histomorphologically classified as biliary, metaplastic, or mixed, 2 of the tumors in Group A were classified as biliary, 1 as metaplastic, and 10 as mixed ; in Group B, 8 were classified as biliary, 1 as metaplastic, and 2 as mixed ; and in Group C, 14 were classified as biliary, 1 as metaplastic, and 2 as mixed. Group A contained significantly more mixed-type tumors, while Groups B and C contained significantly more biliary-type tumors. In Group A, 33.6 of tumors were immunohistochemically positive for MUC1, 0.8 for MUC2, 26 for MUC5AC, 73.8 for MUC6, and 32.5 for CDX2. Similarly, the percentages in Group B were 20, 7, 23, 48, and 36, and those in Group C were 37, 2.6, 15.7, 27, and 29.8, respectively. Group A contained a conspicuously high proportion of
6 40 Nobukazu SHIMA, et al MUC6-positive tumor cells. The frequency of tumors exhibiting p53-overexpression was 7.7 in Group A, but significantly higher at 36.3 in Group B and 41.2 in Group C. Discussion This study showed that the clinicopathological features of mass-forming gallbladder cancer were different depending on the grade of cellular dysplasia of the neoplastic glands within the intraluminal elevated lesions. In Group A, with mass lesions consisting of low-grade dysplastic glands, there was a high proportion of men, more lesions were pedunculated masses of mean diameter 2 cm, they did not contain an invasive carcinoma component, the rate of p53- overexpression was low, tumors invaded no deeper than the mucosa, there were no lymph node metastases, and the 5-year survival rate was 100. The cell type was most commonly mixed, consisting of biliary GAS, and a high proportion stained positive for MUC6. In contrast, in Group C with mass lesions consisting of high-grade dysplastic glands, there was a high proportion of women, more tumors were semipedunculated or sessile masses with mean diameters greater than 3 cm, most elevated lesions already contained an invasive carcinoma component, the p53-overexpression rate exceeded 40, many of the lesions had invaded the muscularis or deeper, lymph node metastases were present in almost a quarter of patients, and the 5-year survival rate was 68. The cell type was most commonly biliary. Group B was intermediate between Groups A and C in most respects, but the 5-year survival rate was 100, the same positive outcome as in Group A. Group C had tumors with a deeper invasion and poorer prognosis than Group A or B. The difference between these groups may be due to the difference in stage. In the future, legitimate evaluation of these tumors should be performed to accumulate a larger number of cases for analysis. Histological classification focusing on the grade of cellular dysplasia has not been well established for gallbladder carcinoma. Recently, however, a new disease concept of intracholecystic papillary-tubular neoplasm ICPN has been proposed ICPNs are defined as intraluminal mass-forming preinvasive neoplasms occurring within the gallbladder which are highly analogous to pancreatic or biliary intraductal papillary and tubular neoplasms, as evidenced by their papillary and / or tubular growth, variable cell lineage, and spectrum of dysplastic change adenoma-carcinoma sequence ICPNs are biologically indolent ; noninvasive examples show an excellent prognosis, whereas those with invasion exhibit a malignant, but nevertheless significantly better prognosis, compared to ordinary invasive carcinomas unaccompanied by ICPN. The majority of tumors in Groups A and B in the present study would appear to be classified as ICPNs, while the majority of tumors in Group C would be excluded from ICPN and should be classified as ordinary high-grade invasive papillary adenocarcinoma or tubular adenocarcinoma because many of them contained an invasive carcinoma component within the intraluminal mass lesion. The present results may be useful for several issues in the diagnosis and treatment of massforming gallbladder cancer. For instance, low-grade adenocarcinoma, as shown in tumors in Group A, might be regarded as hyperplasia or adenoma depending on the pathologist 13.
7 Clinicopathological Study of Gallbladder Cancer 41 However, the present study shows that a different diagnosis would not be a crucial problem because such tumors usually show an almost benign course. Mass-forming gallbladder cancer may be associated with intraepithelial spread along a Rokitansky-Aschoff sinus RAS, which often is confused with non-neoplastic RAS or invasive tubular adenocarcinoma. The present study indicates that in tumors of Group A which are rarely associated with an invasive component, it is appropriate to firstly consider non-neoplastic RAS or intraepithelial spread, even if glandular ducts are present in the deep gallbladder wall. Conversely, in tumors in Group C, the possibility of invasive tubular adenocarcinoma should be aggressively pursued. Finally, as for treatment strategies for mass-forming gallbladder cancer, particularly surgical procedures, simple cholecystectomy seems to be sufficient for tumors in Group A. In Groups B or C with lymph node metastasis, however, a surgical procedure including lymph node dissection must be considered. Therefore, if preoperative classification of the tumor into one of the Groups A-C is feasible, it would be a highly worthwhile process. Conclusion The present study indicated that the clinicopathological features of mass-forming gallbladder cancer were different depending on the cellular dysplastic grade of the mass lesion. Tumors with an intraluminal mass consisting of low-grade dysplastic glands were of lower malignancy and the prognosis of patients with such tumors was excellent. These results may support the significance of the disease concept of ICPN. Acknowledgments We would like to thank Ms. Tomoko Nagai for technical assistance with the immunohistochemical studies. Conflict of interest disclosure None of the authors have any conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose. References 1 Albores-Saavedra J, Chable-Montero F, Gonzalez-Romo MA, et al. Adenomas of the gallbladder. Morphologic features, expression of gastric and intestinal mucins, and incidence of high-grade dysplasia / carcinoma in situ and invasive carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2012;43: Adsay V, Jang KT, Roa JC, et al. Intracholecystic papillary-tubular neoplasms ICPN of the gallbladder neoplastic polyps, adenomas, and papillary neoplasms that are 1.0cm : clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 123 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36: You Y, Bui K, Bui MM, et al. Histopathological and immunophenotypical features of intestinal-type adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder and its precursors. Cancer Control. 2014;21: Bennett S, Marginean EC, Paquin-Gobeil M, et al. Clinical and pathological features of intraductal papillary neoplasm of the biliary tract and gallbladder. HPB Oxford. 2015;17: Sasaki M, Yamato T, Nakanuma Y, et al. Expression of MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6 apomucins in carcinoma, dysplasia and non-dysplastic epithelia of the gallbladder. Pathol Int. 1999;49:38-44.
8 42 Nobukazu SHIMA, et al 6 Sato R, Ando T, Tateno H, et al. Intracystic papillary neoplasm with an associated mucinous adenocarcinoma arising in Rokitansky-Aschoff sinus of the gallbladder. Surg Case Rep. 2016;2:62. accessed 2017 Sep 7 Available from: 7 Washington K, Gottfried MR. Expression of p53 in adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Liver. 1996;16: Sai JK, Suyama M, Nobukawa B, et al. Severe dysplasia of the gallbladder associated with occult pancreatobiliary reflux. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40: Hughes NR, Bhathal PS. Adenocarcinoma of gallbladder: an immunohistochemical profile and comparison with cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2013;66: Argon A, Barbet FY, Nart D. The relationship between intracholecystic papillary-tubular neoplasms and invasive carcinoma of the gallbladder. Int J Surg Pathol. 2016;24: Hashimoto S, Horaguchi J, Fujita N, et al. Intracholecystic papillary-tubular neoplasm of the gallbladder presenting with jaundice. Intern Med. 2014;53: Isozaki M, Ohike N, Tajiri T, et al. Clinicopathological study of intracholecystic papillary-tubular neoplasms ICPNs of the gallbladder. Showa Univ J Med Sci. 2014;26: Kai K. Organ-specific concept and controversy for premalignant lesions and carcinogenesis of gallbladder cancer. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2016;5: Received September 28, 2017 : Accepted October 26, 2017
Biliary tract tumors
 Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Papillary Carcinomas of the Gallbladder. Analysis of Noninvasive and Invasive Types
 Papillary Carcinomas of the Gallbladder Analysis of Noninvasive and Invasive Types Jorge Albores-Saavedra, MD; Matthew Tuck, BS; Bernadette K. McLaren, MD; Kelley S. Carrick, MD; Donald Earl Henson, MD
Papillary Carcinomas of the Gallbladder Analysis of Noninvasive and Invasive Types Jorge Albores-Saavedra, MD; Matthew Tuck, BS; Bernadette K. McLaren, MD; Kelley S. Carrick, MD; Donald Earl Henson, MD
Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms Lined by Abundant Mucinous Epithelium Frequently Involve KRAS Mutations and Malignant Progression
 doi:10.21873/anticanres.12178 Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms Lined by Abundant Mucinous Epithelium Frequently Involve KRAS Mutations and Malignant Progression HIDEKI SHIBATA 1,2,3, NOBUYUKI OHIKE 2, TOMOKO
doi:10.21873/anticanres.12178 Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms Lined by Abundant Mucinous Epithelium Frequently Involve KRAS Mutations and Malignant Progression HIDEKI SHIBATA 1,2,3, NOBUYUKI OHIKE 2, TOMOKO
p53 expression in invasive pancreatic adenocarcinoma and precursor lesions
 Malaysian J Pathol 2011; 33(2) : 89 94 ORIGINAL ARTICLE p53 expression in invasive pancreatic adenocarcinoma and precursor lesions NORFADZILAH MY MBBCH,* Jayalakshmi PAILOOR MPath, FRCPath,* RETNESWARI
Malaysian J Pathol 2011; 33(2) : 89 94 ORIGINAL ARTICLE p53 expression in invasive pancreatic adenocarcinoma and precursor lesions NORFADZILAH MY MBBCH,* Jayalakshmi PAILOOR MPath, FRCPath,* RETNESWARI
Resident Short Reviews. Updates on Precancerous Lesions of the Biliary Tract. Biliary Precancerous Lesion. Sanaz Ainechi, MD; Hwajeong Lee, MD
 Resident Short Reviews Updates on Precancerous Lesions of the Biliary Tract Precursor lesions of invasive adenocarcinoma of the bile duct (cholangiocarcinoma) have been increasingly recognized during the
Resident Short Reviews Updates on Precancerous Lesions of the Biliary Tract Precursor lesions of invasive adenocarcinoma of the bile duct (cholangiocarcinoma) have been increasingly recognized during the
Surgical Significance of Superficial Cancer Spread in Early Gallbladder Cancer
 Surgical Significance of Superficial Cancer Spread in Early Gallbladder Cancer Hidetoshi Eguchi 1, Osamu Ishikawa 1, Hiroaki Ohigashi 1, Tsutomu Kasugai 2, Shigekazu Yokoyama 3, Terumasa Yamada 1, Yuichiro
Surgical Significance of Superficial Cancer Spread in Early Gallbladder Cancer Hidetoshi Eguchi 1, Osamu Ishikawa 1, Hiroaki Ohigashi 1, Tsutomu Kasugai 2, Shigekazu Yokoyama 3, Terumasa Yamada 1, Yuichiro
Appendix 4: WHO Classification of Tumours of the pancreas 17
 S3.01 The WHO histological tumour type must be recorded. CS3.01a The histological type of the tumour should be recorded based on the current WHO classification 17 (refer to Appendices 4-7). Appendix 4:
S3.01 The WHO histological tumour type must be recorded. CS3.01a The histological type of the tumour should be recorded based on the current WHO classification 17 (refer to Appendices 4-7). Appendix 4:
Pyloric gland adenoma of gallbladder reports of two cases and a brief review of literature
 Case Report Pyloric gland adenoma of gallbladder reports of two cases and a brief review of literature Guang Yang 1, Haixia Qin 2, Anwar Raza 1, George W. Saukel 1, Naveenraj Solomon 3, Marcos Michelotti
Case Report Pyloric gland adenoma of gallbladder reports of two cases and a brief review of literature Guang Yang 1, Haixia Qin 2, Anwar Raza 1, George W. Saukel 1, Naveenraj Solomon 3, Marcos Michelotti
Intracystic papillary neoplasm with an associated mucinous adenocarcinoma arising in Rokitansky Aschoff sinus of the gallbladder
 Sato et al. Surgical Case Reports (2016) 2:62 DOI 10.1186/s40792-016-0189-7 CASE REPORT Intracystic papillary neoplasm with an associated mucinous adenocarcinoma arising in Rokitansky Aschoff sinus of
Sato et al. Surgical Case Reports (2016) 2:62 DOI 10.1186/s40792-016-0189-7 CASE REPORT Intracystic papillary neoplasm with an associated mucinous adenocarcinoma arising in Rokitansky Aschoff sinus of
Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares
 Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares Aatur D. Singhi, MD PhD Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Department of Pathology singhiad@upmc.edu Objectives Briefly give an overview
Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares Aatur D. Singhi, MD PhD Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Department of Pathology singhiad@upmc.edu Objectives Briefly give an overview
Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions
 Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer. Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu Hishima Author for correspondence: T. Hashimoto
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu Hishima Author for correspondence: T. Hashimoto
Overview. Disclosure. PRE INVASIVE NEOPLASIA OF BILIARY TREE New Perspectives on Old Themes. N. Volkan Adsay, MD
 PRE INVASIVE NEOPLASIA OF BILIARY TREE New Perspectives on Old Themes N. Volkan Adsay, MD Professor and Vice-Chair Director of Anatomic Pathology Emory University and Emory Winship Cancer Institute Atlanta,
PRE INVASIVE NEOPLASIA OF BILIARY TREE New Perspectives on Old Themes N. Volkan Adsay, MD Professor and Vice-Chair Director of Anatomic Pathology Emory University and Emory Winship Cancer Institute Atlanta,
Tubulopapillary adenoma of the gallbladder accompanied by bile duct tumor thrombus
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8736 World J Gastroenterol 2014 July 14; 20(26): 8736-8739 ISSN 1007-9327 (print)
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8736 World J Gastroenterol 2014 July 14; 20(26): 8736-8739 ISSN 1007-9327 (print)
Case in discussion. Common diagnostic problems in gallbladder pathology 62, F
 Common diagnostic problems in gallbladder pathology N. Volkan Adsay, M.D. 62, F Case in discussion Underwent cholecystectomy with the diagnosis of chronic cholecystititis and cholelithiasis Professor and
Common diagnostic problems in gallbladder pathology N. Volkan Adsay, M.D. 62, F Case in discussion Underwent cholecystectomy with the diagnosis of chronic cholecystititis and cholelithiasis Professor and
Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation
 Anatomic Pathology / LARGE COLORECTAL ADENOMAS AND PATHOLOGIC EVALUATION Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation Elizabeth D. Euscher, MD, 1 Theodore H. Niemann, MD, 1 Joel G. Lucas,
Anatomic Pathology / LARGE COLORECTAL ADENOMAS AND PATHOLOGIC EVALUATION Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation Elizabeth D. Euscher, MD, 1 Theodore H. Niemann, MD, 1 Joel G. Lucas,
Biliary Tract Neoplasia: A Cyto-histologic Review. Michelle Reid, MD, MSc Professor of Pathology Director of Cytopathology Emory University Hospital
 Biliary Tract Neoplasia: A Cyto-histologic Review Michelle Reid, MD, MSc Professor of Pathology Director of Cytopathology Emory University Hospital Bile Duct Brushings (BDB) BDBs are the initial diagnostic
Biliary Tract Neoplasia: A Cyto-histologic Review Michelle Reid, MD, MSc Professor of Pathology Director of Cytopathology Emory University Hospital Bile Duct Brushings (BDB) BDBs are the initial diagnostic
Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute
 J Clin Pathol 1987;40:13-18 Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute lesions of intestinal metaplasia in ulcerated stomachs K MUKAWA, T NAKAMURA, G NAKANO, Y NAGAMACHI From the First Department
J Clin Pathol 1987;40:13-18 Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute lesions of intestinal metaplasia in ulcerated stomachs K MUKAWA, T NAKAMURA, G NAKANO, Y NAGAMACHI From the First Department
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID. Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
malignant polyp Daily Challenges in Digestive Endoscopy for Endoscopists and Endoscopy Nurses BSGIE Annual Meeting 18/09/2014 Mechelen
 Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Clinicopathological Characteristics of Superficial Type
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, 1995, Vol. 2, pp. 99-105 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1995 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, 1995, Vol. 2, pp. 99-105 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1995 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma
 Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Case Report Intrabiliary Hepatic Metastasis of Colorectal Carcinoma Mimicking Primary Cholangiocarcinoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 4704781, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4704781 Case Report Intrabiliary Hepatic Metastasis of Colorectal Carcinoma Mimicking Primary Cholangiocarcinoma:
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 4704781, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4704781 Case Report Intrabiliary Hepatic Metastasis of Colorectal Carcinoma Mimicking Primary Cholangiocarcinoma:
ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE. (Plates I-V)
 [GANN, 57, 1-7; February, 1966] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.24]:547.831.6-31:616.24-006-031.6 ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE (Plates I-V) Kazuo MORI, Jo HIRATSUKA, Shuhei
[GANN, 57, 1-7; February, 1966] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.24]:547.831.6-31:616.24-006-031.6 ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE (Plates I-V) Kazuo MORI, Jo HIRATSUKA, Shuhei
Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance
 & 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
& 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
ACCME/Disclosures. Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate. Case
 Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
Neoplasias Quisticas del Páncreas
 SEAP -Aproximación Práctica a la Patología Gastrointestinal- Madrid, 26 de mayo, 2006 Neoplasias Quisticas del Páncreas Gregory Y. Lauwers, M.D. Director, Service Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard
SEAP -Aproximación Práctica a la Patología Gastrointestinal- Madrid, 26 de mayo, 2006 Neoplasias Quisticas del Páncreas Gregory Y. Lauwers, M.D. Director, Service Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard
Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus
 Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
what is the alternative mechanism of histogenesis? Aspects of the morphology of the adenomacarcinoma Morphology of the
 Refer to: Morson B: Polyps and cancer of the large bowel. West J Med 125:93-99, Aug 1976 THE WESTERN Journal of Miedicine Polyps and Cancer of the Large Bowel BASIL MORSON, MD, London MORTALITY STATISTICS
Refer to: Morson B: Polyps and cancer of the large bowel. West J Med 125:93-99, Aug 1976 THE WESTERN Journal of Miedicine Polyps and Cancer of the Large Bowel BASIL MORSON, MD, London MORTALITY STATISTICS
The esophageal submucosal glands are considered to be a continuation
 248 Significance of Involvement by Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Ducts of Esophageal Submucosal Glands Analysis of 201 Surgically Resected Superficial Squamous Cell Carcinomas Yusuke Tajima, M.D. 1,2
248 Significance of Involvement by Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Ducts of Esophageal Submucosal Glands Analysis of 201 Surgically Resected Superficial Squamous Cell Carcinomas Yusuke Tajima, M.D. 1,2
Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach Clinicopathological
 THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL Vo1. 43, p. 289-294, 1996 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach Clinicopathological Studies KIKUO KOUFUJI, JINRYO TAKEDA, ATSUSHI TOYONAGA, ISSEI KODAMA, KEISHIRO
THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL Vo1. 43, p. 289-294, 1996 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach Clinicopathological Studies KIKUO KOUFUJI, JINRYO TAKEDA, ATSUSHI TOYONAGA, ISSEI KODAMA, KEISHIRO
Serrated Lesions in the Bowel Cancer Screening Programme
 Serrated Lesions in the Bowel Cancer Screening Programme Mark Arends Cambridge & Edinburgh Serrated Lesions of Large Bowel 1. Hyperplastic polyp 2. Serrated adenoma 3. Mixed polyp 4. Sessile serrated lesion
Serrated Lesions in the Bowel Cancer Screening Programme Mark Arends Cambridge & Edinburgh Serrated Lesions of Large Bowel 1. Hyperplastic polyp 2. Serrated adenoma 3. Mixed polyp 4. Sessile serrated lesion
CASE 4 21/07/2017. Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix. Female 31. LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities
 Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Title:COX-2 overexpression in resected pancreatic head adenocarcinomas correlates with favourable prognosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:COX-2 overexpression in resected pancreatic head adenocarcinomas correlates with favourable prognosis Authors: Ewa Pomianowska (ewa.pomianowska@medisin.uio.no) Aasa R
Author's response to reviews Title:COX-2 overexpression in resected pancreatic head adenocarcinomas correlates with favourable prognosis Authors: Ewa Pomianowska (ewa.pomianowska@medisin.uio.no) Aasa R
Case Report Cystic and Papillary Neoplasm at the Hepatic Hilum Possibly Originating in the Peribiliary Glands
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 9130754, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9130754 Case Report Cystic and Papillary Neoplasm at the Hepatic Hilum Possibly Originating in the Peribiliary
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 9130754, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9130754 Case Report Cystic and Papillary Neoplasm at the Hepatic Hilum Possibly Originating in the Peribiliary
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma
 Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Mucin-producing urothelial-type adenocarcinoma of prostate: report of two cases of a rare and diagnostically challenging entity
 & 2005 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/05 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Mucin-producing urothelial-type adenocarcinoma of prostate: report of two cases of a rare and diagnostically challenging
& 2005 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/05 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Mucin-producing urothelial-type adenocarcinoma of prostate: report of two cases of a rare and diagnostically challenging
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Small Intestine. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition
 Small Intestine Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the small intestine, including those with focal endocrine differentiation. Excludes carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, and stromal tumors (sarcomas).
Small Intestine Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the small intestine, including those with focal endocrine differentiation. Excludes carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, and stromal tumors (sarcomas).
Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland
 Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland TAKAO OBARA,* YOSHIHIDE FUJIMOTO* AND MOTOHIKO AIBA** *Department of Endocrine Surgery and **Department of Surgical Pathology, Tokyo Women's Medical College,
Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland TAKAO OBARA,* YOSHIHIDE FUJIMOTO* AND MOTOHIKO AIBA** *Department of Endocrine Surgery and **Department of Surgical Pathology, Tokyo Women's Medical College,
Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. and invasive lobular carcinoma
 Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
colorectal cancer Colorectal cancer hereditary sporadic Familial 1/12/2018
 colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
Wendy L Frankel. Chair and Distinguished Professor
 1 Wendy L Frankel Chair and Distinguished Professor Case 1 59 y/o woman Abdominal pain No personal or family history of cancer History of colon polyps Colonoscopy Polypoid rectosigmoid mass Biopsy 3 4
1 Wendy L Frankel Chair and Distinguished Professor Case 1 59 y/o woman Abdominal pain No personal or family history of cancer History of colon polyps Colonoscopy Polypoid rectosigmoid mass Biopsy 3 4
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE. Jonathan I. Epstein
 INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare
 Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Update of mixed tumours of the GI tract, the pancreas and the liver Introduction to the concept of mixed tumours and clinical implication Jean-Yves SCOAZEC Surgical
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Update of mixed tumours of the GI tract, the pancreas and the liver Introduction to the concept of mixed tumours and clinical implication Jean-Yves SCOAZEC Surgical
Formula One Study. Assessment criteria of pathological parameters. Ver.2. UK Japan Joint Study for Risk Factors of Lymph Node
 APPENDIX 01: Assessment criteria Formula One Study UK Japan Joint Study for Risk Factors of Lymph Node Metastasis in Submucosal Invasive (pt1) Colorectal Cancer Assessment criteria of pathological parameters
APPENDIX 01: Assessment criteria Formula One Study UK Japan Joint Study for Risk Factors of Lymph Node Metastasis in Submucosal Invasive (pt1) Colorectal Cancer Assessment criteria of pathological parameters
Distant and Lymph Node Metastases of Thyroid Nodules with No Pathological Evidence of Malignancy: A Limitation of Pathological Examination
 Endocrine Journal 2008, 55 (5), 889 894 Distant and Lymph Node Metastases of Thyroid Nodules with No Pathological Evidence of Malignancy: A Limitation of Pathological Examination YASUHIRO ITO, TOMONORI
Endocrine Journal 2008, 55 (5), 889 894 Distant and Lymph Node Metastases of Thyroid Nodules with No Pathological Evidence of Malignancy: A Limitation of Pathological Examination YASUHIRO ITO, TOMONORI
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy
 Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
PSA. HMCK, p63, Racemase. HMCK, p63, Racemase
 Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Expression of the GLUT1 and p53 Protein in Atypical Mucosal Lesions Obtained from Gastric Biopsy Specimens
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2006; 40: 32-8 Expression of the GLUT1 and p53 Protein in Atypical Mucosal Lesions Obtained from Gastric Biopsy Specimens In Gu Do Youn Wha Kim Yong-Koo Park Department
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2006; 40: 32-8 Expression of the GLUT1 and p53 Protein in Atypical Mucosal Lesions Obtained from Gastric Biopsy Specimens In Gu Do Youn Wha Kim Yong-Koo Park Department
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER. Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D.
 NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Morphological Classification of Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of the Bile Duct with Survival Correlation
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.1.207 RESEARCH ARTICLE Morphological Classification of Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of the Bile Duct with Survival Correlation Vor Luvira 1 *, Kulyada Somsap 2, Ake Pugkhem
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.1.207 RESEARCH ARTICLE Morphological Classification of Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of the Bile Duct with Survival Correlation Vor Luvira 1 *, Kulyada Somsap 2, Ake Pugkhem
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
The Incidence and Significance of Villous Change in Adenomatous Polyps
 The Incidence and Significance Villous Change in Adenomatous Polyps CHRISTOPHER H. K. FUNC, M.D., AND HARVEY GOLDMAN, M.D. Department Pathology, Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Hospital, Boston,
The Incidence and Significance Villous Change in Adenomatous Polyps CHRISTOPHER H. K. FUNC, M.D., AND HARVEY GOLDMAN, M.D. Department Pathology, Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Hospital, Boston,
3/28/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference. Differential Diagnosis:
 GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
Anatomy of the biliary tract
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Oesophagus and Stomach update dysplasia and early cancer
 Oesophagus and Stomach update dysplasia and early cancer Dr Tim Bracey STR teaching 13/4/16 Please check pathkids.com for previous talks One of the biggest units in the country (100 major resections per
Oesophagus and Stomach update dysplasia and early cancer Dr Tim Bracey STR teaching 13/4/16 Please check pathkids.com for previous talks One of the biggest units in the country (100 major resections per
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate
 Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate (with emphasis on cancer mimics) Rodolfo Montironi, MD (IT), FRCPath (UK), IFCAP (USA) Polytechnic University of Marche Region (Ancona) School of Medicine,
Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate (with emphasis on cancer mimics) Rodolfo Montironi, MD (IT), FRCPath (UK), IFCAP (USA) Polytechnic University of Marche Region (Ancona) School of Medicine,
Introduction of GB polyp
 Management of Gallbladder Polyp as Physician's View Sang Hyub Lee, MD, PhD Seoul National University College of Medicine Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Department of Internal Medicine Division
Management of Gallbladder Polyp as Physician's View Sang Hyub Lee, MD, PhD Seoul National University College of Medicine Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Department of Internal Medicine Division
MVST BOD & NST PART IB Thurs. 2 nd & Fri. 3 rd March 2017 Pathology Practical Class 23
 MVST BOD & NST PART IB Thurs. 2 nd & Fri. 3 rd March 2017 Pathology Practical Class 23 Neoplasia I Neoplasia I: Benign and malignant neoplasms in glandular epithelium and mesenchyme 1.0. Aims 1. To understand
MVST BOD & NST PART IB Thurs. 2 nd & Fri. 3 rd March 2017 Pathology Practical Class 23 Neoplasia I Neoplasia I: Benign and malignant neoplasms in glandular epithelium and mesenchyme 1.0. Aims 1. To understand
Imaging Evaluation of Polyps. CT Colonography: Sessile Adenoma. Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon Objectives
 Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon: Pathology and Imaging of the Colon and Rectum Angela D. Levy and Leslie H. Sobin Washington, DC Drs. Levy and Sobin have indicated that they have no relationships which, in the
Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon: Pathology and Imaging of the Colon and Rectum Angela D. Levy and Leslie H. Sobin Washington, DC Drs. Levy and Sobin have indicated that they have no relationships which, in the
Case history: Figure 1. H&E, 5x. Figure 2. H&E, 20x.
 1 Case history: A 49 year-old female presented with a 5 year history of chronic anal fissure. The patient s past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. On digital rectal examination there was a very
1 Case history: A 49 year-old female presented with a 5 year history of chronic anal fissure. The patient s past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. On digital rectal examination there was a very
DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY)
 Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
5/2/2018. Low Grade Dysplasia of GI Tract. High Grade Dysplasia of GI Tract. Dysplasia in Gastrointestinal Tract: Practical Pearls and Issues
 Dysplasia in Gastrointestinal Tract: Practical Pearls and Issues Arief Suriawinata, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Department of Pathology and
Dysplasia in Gastrointestinal Tract: Practical Pearls and Issues Arief Suriawinata, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Department of Pathology and
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum
 2012 66 4 351 356 Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum a b* c c c a a b d a c b d 352 Ohara et al. received remedies at another hospital. Hematemesis then recurred
2012 66 4 351 356 Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum a b* c c c a a b d a c b d 352 Ohara et al. received remedies at another hospital. Hematemesis then recurred
Pancreatic Cystic Lesions 원자력병원
 Pancreatic Cystic Lesions 원자력병원 박선 후 Lines of cellular differentiation Ductal Acinar Undetermined Ductal adenocarcinoma Serous/ mucinous tumor Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm Acinar cell carcinoma
Pancreatic Cystic Lesions 원자력병원 박선 후 Lines of cellular differentiation Ductal Acinar Undetermined Ductal adenocarcinoma Serous/ mucinous tumor Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm Acinar cell carcinoma
polyps of the colon and rectum
 J. clin. Path., 1973, 26, 25-31 Pseudo-carcinomatous invasion in adenomatous polyps of the colon and rectum T. MUTO, H. J. R. BUSSEY, AND B. C. MORSON From St Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The histology
J. clin. Path., 1973, 26, 25-31 Pseudo-carcinomatous invasion in adenomatous polyps of the colon and rectum T. MUTO, H. J. R. BUSSEY, AND B. C. MORSON From St Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The histology
Case Report A Case Report of Intraductal Papillary-Mucinous Neoplasm of the Pancreas Showing Morphologic Transformation during Followup Periods
 Oncology Volume 2009, Article ID 373465, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2009/373465 Case Report A Case Report of Intraductal Papillary-Mucinous Neoplasm of the Pancreas Showing Morphologic Transformation during Followup
Oncology Volume 2009, Article ID 373465, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2009/373465 Case Report A Case Report of Intraductal Papillary-Mucinous Neoplasm of the Pancreas Showing Morphologic Transformation during Followup
SAMs Guidelines DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST QUESTIONS. Ver. #
 SAMs Guidelines DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST Ver. #5-02.12.17 GUIDELINES FOR DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST The USCAP is accredited by the American Board of Pathology (ABP) to offer
SAMs Guidelines DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST Ver. #5-02.12.17 GUIDELINES FOR DEVELOPING SELF-ASSESSMENT MODULES TEST The USCAP is accredited by the American Board of Pathology (ABP) to offer
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma
 http://dx.doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.1.66 KMJ Case Report Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma Jeong Hyun Oh 1, Taek Sang Kim 1, Hyun Yul Rhew 1, Bong Kwon Chun
http://dx.doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.1.66 KMJ Case Report Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma Jeong Hyun Oh 1, Taek Sang Kim 1, Hyun Yul Rhew 1, Bong Kwon Chun
Analysis of gallbladder polypoid lesion size as an indication of the risk of gallbladder cancer
 Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 24;8:9-3 http://dx.doi.org/.47/kjhbps.24.8..9 Original Article Analysis of gallbladder polypoid lesion size as an indication of the risk of gallbladder cancer Ji Eun
Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 24;8:9-3 http://dx.doi.org/.47/kjhbps.24.8..9 Original Article Analysis of gallbladder polypoid lesion size as an indication of the risk of gallbladder cancer Ji Eun
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN
 EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci. Colon polyps. Colorectal cancer
 Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Colon polyps Colorectal cancer Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18 Ed. 2012 Colorectal cancer 70% Colorectal cancer CRC and colon
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Colon polyps Colorectal cancer Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18 Ed. 2012 Colorectal cancer 70% Colorectal cancer CRC and colon
Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma
 Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male Female Intersex/indeterminate
Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male Female Intersex/indeterminate
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma. in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis. of Lymph Node Metastasis
 Kitakanto Med J 2002 ; 52 : 189-193 189 A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis of Lymph Node Metastasis Susumu Kawate,' Susumu Ohwada,'
Kitakanto Med J 2002 ; 52 : 189-193 189 A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis of Lymph Node Metastasis Susumu Kawate,' Susumu Ohwada,'
Sonic hedgehog expression in gastric cancer and gastric adenoma
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 17: 1051-1055, 2007 Sonic hedgehog expression in gastric cancer and gastric adenoma SUN-YOUNG LEE 1, HYE SEUNG HAN 2, KYUNG YUNG LEE 3, TAE SOOK HWANG 2, JEONG HWAN KIM 1, IN-KYUNG SUNG
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 17: 1051-1055, 2007 Sonic hedgehog expression in gastric cancer and gastric adenoma SUN-YOUNG LEE 1, HYE SEUNG HAN 2, KYUNG YUNG LEE 3, TAE SOOK HWANG 2, JEONG HWAN KIM 1, IN-KYUNG SUNG
Frequency of gall bladder diseases in 200 cholecystectomies lesions.
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 12-2017 Frequency of gall
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 12-2017 Frequency of gall
Greater Manchester and Cheshire HPB Unit Guidelines for the Assessment & Management of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Chapter 14
 Greater Manchester and Cheshire HPB Unit Guidelines for the Assessment & Management of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Chapter 14 Contents 14. Neuroendocrine Tumours 161 14.1. Diagnostic algorithm
Greater Manchester and Cheshire HPB Unit Guidelines for the Assessment & Management of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Chapter 14 Contents 14. Neuroendocrine Tumours 161 14.1. Diagnostic algorithm
Colorectal adenocarcinoma leading cancer in developed countries In US, annual deaths due to colorectal adenocarcinoma 57,000.
 Colonic Neoplasia Remotti Colorectal adenocarcinoma leading cancer in developed countries In US, annual incidence of colorectal adenocarcinoma 150,000. In US, annual deaths due to colorectal adenocarcinoma
Colonic Neoplasia Remotti Colorectal adenocarcinoma leading cancer in developed countries In US, annual incidence of colorectal adenocarcinoma 150,000. In US, annual deaths due to colorectal adenocarcinoma
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Case Report Synchronous Bilateral Solid Papillary Carcinomas of the Breast
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 812129, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/812129 Case Report Synchronous Bilateral Solid Papillary Carcinomas of the Breast Noriko Yoshimura, 1 Shigeru
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 812129, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/812129 Case Report Synchronous Bilateral Solid Papillary Carcinomas of the Breast Noriko Yoshimura, 1 Shigeru
Adenocarcinoma Arising in Segmental Adenomyomatosis of the Gallbladder: A Case Report 1
 Adenocarcinoma Arising in Segmental Adenomyomatosis of the Gallbladder: A Case Report 1 Jin-Sun Yeon, M.D., June-Sik Cho, M.D., Kyung-Sook Shin, M.D., Byung-Seok Lee, M.D. 2, Heon-Young Lee, M.D. 2, In-Sang
Adenocarcinoma Arising in Segmental Adenomyomatosis of the Gallbladder: A Case Report 1 Jin-Sun Yeon, M.D., June-Sik Cho, M.D., Kyung-Sook Shin, M.D., Byung-Seok Lee, M.D. 2, Heon-Young Lee, M.D. 2, In-Sang
Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland
 Pathology International 2008; 58: 322 326 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02231.x Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland Hidetaka Yamamoto, 1 Hideoki Uryu,
Pathology International 2008; 58: 322 326 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02231.x Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland Hidetaka Yamamoto, 1 Hideoki Uryu,
The impact of routine histopathological examination on cholecystectomy specimens from an Asian demographic
 GENERAL SURGERY doi 10.1308/003588412X13171221501708 The impact of routine histopathological examination on cholecystectomy specimens from an Asian demographic KF Chin 1, AA Mohammad 2, YY Khoo 1, T Krishnasamy
GENERAL SURGERY doi 10.1308/003588412X13171221501708 The impact of routine histopathological examination on cholecystectomy specimens from an Asian demographic KF Chin 1, AA Mohammad 2, YY Khoo 1, T Krishnasamy
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017
 Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Importance of Histopathology in Routine Cholecystectomies
 Original Research Article DOI: 10.18231/2394-6792.2017.0064 Ashwini B.R. 1,*, Hafsa Saif 2, Siddiq M. Ahmed 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 P.G. Student, 3 Professor, Dept. of Pathology, Bangalore Medical College
Original Research Article DOI: 10.18231/2394-6792.2017.0064 Ashwini B.R. 1,*, Hafsa Saif 2, Siddiq M. Ahmed 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 P.G. Student, 3 Professor, Dept. of Pathology, Bangalore Medical College
Citation American Journal of Surgery, 196(5)
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Multifocal branch-duct pancreatic i neoplasms Tajima, Yoshitsugu; Kuroki, Tamotsu Amane; Adachi, Tomohiko; Mishima, T Kanematsu, Takashi Citation American
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Multifocal branch-duct pancreatic i neoplasms Tajima, Yoshitsugu; Kuroki, Tamotsu Amane; Adachi, Tomohiko; Mishima, T Kanematsu, Takashi Citation American
Tumours of the Oesophagus & Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Histopathology Reporting Proforma
 Tumours of the Oesophagus & Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given
Tumours of the Oesophagus & Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given
