ORIGINAL ARTICLE TEMPORALIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF SKULL BASE DEFECTS
|
|
|
- Evangeline Owen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TEMPORALIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF SKULL BASE DEFECTS Jesse E. Smith, MD, 1,2 Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS(C), 1,2,3 Robert T. Adelson, MD 4 1 Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas. yducic@sbcglobal.net 2 Otolaryngology and Facial Plastic Surgery Associates, Fort Worth, Texas 3 Baylor Neuroscience Center for Skullbase Surgery, Dallas-Fort Worth, Texas 4 Division of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Otolaryngology, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida Accepted 3 April 2009 Published online 25 June 2009 in Wiley InterScience ( DOI: /hed Abstract: Background. The temporalis muscle flap (TMF) is a valuable reconstructive technique utilized in a variety of challenging defects. However, its use for repair of skull base defects is less commonly reported. Methods. A retrospective chart review was conducted for 35 patients who underwent reconstruction of skull base defects between March 1999 and July 2006 at a tertiary referral hospital. Patients with skull base defects after trauma or extirpative surgery underwent reconstruction with a TMF. The measured outcomes were as follows: defect size/location, need for additional flaps, bone necrosis, hardware exposure, dehiscence, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak, and meningitis. Results. Forty-two patients underwent reconstruction with a TMF, and 35/42 patient records were available for review. No flap failures, 1 transient CSF leak, 3 hardware exposures distant from the temporalis recipient site, and 3 hydroxyapatite cement infections or foreign body reaction were observed. Conclusion. The TMF represents a versatile reconstructive technique employed with minimal morbidity and a low complication rate to repair defects of the skull base. VC 2009 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Head Neck 32: , 2010 Keywords: temporalis muscle flap; regional flap; skull base surgery; skull base trauma; cerebrospinal fluid leak Correspondence to: Y. Ducic VC 2009 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Anterior and lateral skull base surgery for both benign and malignant lesions often results in significant defects of the craniofacial skeleton and surrounding soft tissues, allowing potential free communication between the extracranial and intracranial compartments. Tumor resection and trauma can result in osseous defects, violated dura, and contamination of the intracranial compartment with bacterial flora from the upper aerodigestive tract. It is necessary to separate these compartments to prevent the potential complications of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak, meningitis, bone flap necrosis, hemorrhage, and exposure of hardware. Successful early outcomes in skull base surgery are dependent on adequate healing at the surgical site. Therefore, reconstruction of the skull base is most appropriately accomplished with vascularized tissue. The temporalis muscle flap (TMF) is a reliable, nonbulky, myofascial flap, which has had a role in a wide variety of maxillofacial reconstructive problems over the last 100 years. 199 Temporalis Muscle Flap for Skull Base Defects HEAD & NECK DOI /hed February 2010
2 Although many authors credit Golovine (1898) with the TMF s original description, recent articles have demonstrated that his method of reconstructing orbital exenteration defects was a forehead skin flap and not a myofascial flap. 1 3 Probably, the first use of any part of a TMF has its origin in the surgical treatment of temporomandibular joint ankylosis, as portions of a TMF were used by Lentz (1895) and possibly by Verneuil (1872) during an interposition arthroplasty following resection of the conydylar neck of the mandible. 3,4 The first use of the entire TMF as a true transposition flap for maxillofacial reconstruction can be traced to Gillies (1917), who utilized the TMF in rehabilitating a cheek deformity resulting from traumatic loss of the zygomatic arch. 1,5 Modifications of the surgical technique and creative applications have extended the TMF for use in every location to which the pedicle s length and arc of rotation will allow. Sheehan (1935) augmented TMF mobilization by introducing temporary removal and replacement of the zygomatic arch. Rambo (1958) used this reliable flap to obliterate the middle ear and mastoid cavities in cases of chronic ear disease. 3,6 This study reviews our experience with the application of TMF for the repair of ablative and traumatic defects of the skull base. PATIENTS AND METHODS A retrospective chart review was conducted identifying patients who underwent a temporalis flap for reconstruction of a skull base defect. Forty-two patients were identified from March 1999 to July 2006 treated at a tertiary referral medical system by the senior author (Y.D.). Data were collected on the age of patient, size of defect, area of defect, cause of defect, follow-up, and complications. Thirty-five patient records were complete and available for review. The Institutional Review Board s approval was obtained for this study. Surgical Technique. A standard hemicoronal or bicoronal incision is used to harvest the TMF and to furnish access in most skull base approaches in this study. When required, transfacial approaches were combined with coronal incisions to allow appropriate access. The coronal incision is placed 1.5 cm posterior to the anterior hairline, although a more posterior orientation can accommodate patients with receding hair lines. Care should be observed laterally in the preauricular area to preserve the superficial temporal vessels. The supraorbital and supratrochlear vessels are freed from their foramen, if necessary, by using a 3-mm osteotome. This maneuver allows for an extended inferior reflection of the bicoronal flap without placing excessive traction on the vessels and nerves within the operative field. The surgical anatomy of the TMF has been reviewed in detail in previous publications, 7 and only the vascular supply and available dimensions as it relates to surgical harvest will be reviewed briefly herein. The main vascular supply to the flap is provided by the anterior and posterior branches of the deep temporal artery, which originates from the second (pterygoid) portion of the internal maxillary artery and enter the deep surface of the muscle, most commonly at the inferior third of the muscle and usually in the posterior half of the muscle. 8 The deep temporal artery courses between the skull and temporalis muscle, anastomozing with the middle temporal artery within the temporalis muscle. The middle temporal artery is a branch of the superficial temporal artery (STA), which usually originates 0 to 2 cm below the zygomatic arch and runs slightly posterior to the STA. The middle temporal artery then enters the deep temporal fascia immediately superior to the zygomatic arch. 9 It continues its course superiorly and sends some perforators deep into the temporalis muscle. Careful subperiosteal dissection will preserve the vascular supply as it enters the temporalis muscle on the deep surface. Once harvested, the TMF typically spans a length of 12 to 16 cm, with a thickness of 0.5 to 1.0 cm, provides an available surface of 4 cm 5 cm, and tolerates an arc of rotation up to ,10 The pericranium is then incised and elevated from the skull as a separate flap based on either its anterior or lateral vascular supply, should the pericranial flap be required for use during the procedure. To preserve the temporal branches of the facial nerve, the superficial layer of the deep temporal fascia should be incised over the superficial temporal fat pad. Dissection should proceed at a level just superficial to the deep temporalis fascia proceeding inferiorly to the zygomatic arch. Following tumor removal and/or neurosurgical intervention, the temporalis flap may be 200 Temporalis Muscle Flap for Skull Base Defects HEAD & NECK DOI /hed February 2010
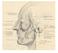
3 used to cover defects of the anterior, middle, or posterior cranial fossa, cribiform plate, ethmoid sinus, sphenoid sinus, orbital walls, and to provide cover and protection for calvarial bone grafts that might be incorporated within the skull base repair. The zygomatic arch is often osteotomized as part of the skull base approach to maximize the mobility of this pedicled flap and prevent uncomfortable geometries of the flap s vascular supply. The TMF is incorporated into the repair of any remaining dural defects and is suspended to the osseous margins of a craniotomy window to prevent prolapse of the flap into the postsurgical defect, thereby minimizing the risk of CSF leakage. Such water-tight closures are assured with proper peripheral flap suspension to prevent flap herniation as well as orientation of the fascial surface of the TMF toward the upper aerodigestive tract. The TMF may be exposed safely to the pharyngeal or nasal airway and allowed to mucosalize. Skin grafts are not required and were not utilized in this series of patients. Fibrin glue and other tissue sealants are helpful adjuncts in securing the skull base repair. Bone flaps are then rigidly fixated with miniplates. The coronal flap is closed over a suction drain, which is gently removed on either the first or second postoperative day. FIGURE 2. Temporalis muscle flap raised and prepared for the reconstruction of the anterior cranial fossa. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue of this article, which is available at as flap loss, meningitis, brain abscess, or permanent injury to the temporal branch of the facial nerve were considered. Minor complications included localized infection, seroma, hematoma, temporary nerve palsy, hair loss, trismus, and esthetic donor site complications. Each patient had either an extensive deficit created by the removal of a lesion in the skull base or an active CSF leak following skull base trauma (Figures 1 3). Eleven of the lesions were malignant, 21 were aggressive benign processes, and the remaining 3 represented persistent CSF leak following skull base trauma. Of the malignant RESULTS Thirty-five patient charts met criteria for the retrospective analysis. Major complications such FIGURE 1. Defect resulting from the resection of a massive midfacial basal cell carcinoma. Resection extends to include anterior cranial fossa and dura. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue of this article, which is available at FIGURE 3. Postoperative result following reconstruction. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue of this article, which is available at Temporalis Muscle Flap for Skull Base Defects HEAD & NECK DOI /hed February
4 processes, all lesions were classified as either T 3 or T 4. The most common pathologic diagnosis was meningioma (n ¼ 9). The average age of the patient was 50.9 years (range, 18 72), and there were 12 men and 23 women. The mean followup period for this study was 16.0 months (range, 3 62 months). For the purpose of this study, width was measured in a medial to lateral dimension, and the length was measured in an anterior to posterior dimension. Average defect width was 4.8 cm, and average defect length was 4.9 cm. Of the 35 TMFs, 15 were left-based and 20 were pedicled from the right side. Six patients received preoperative radiation therapy, and 15 patients received postoperative radiation therapy. One patient had received preoperative chemotherapy, and 6 patients received postoperative chemotherapy. Twenty patients received an average of 30.2 g of hydroxyapatite cement for a cranioplasty as part of a primary reconstruction of the TMF donor site. Defect locations included the base of middle cranial fossa in 21 cases, base of anterior cranial fossa in 8 cases, and combined defect in the remaining patients studied. Defect location did not appear to be correlated to the development of complications. We can easily and reliably utilize the temporalis to reach the cribriform in the midline superiorly and the superior aspect of the hypopharynx inferiorly. The key to such reach is tapering the temporalis pedicle to the central third of the zygomatic arch region with or without adjunctive use of coronoidectomy if needed for further mobilization. All exposures of hydroxyapatite cement occurred in patients who received postoperative radiation therapy (p <.01). The senior author routinely uses suction drains on all skull base operations, in which a bicoronal flap is utilized, irrespective of whether dural reconstruction is performed or not. He feels that water-tight closure of the dura is the most important factor in the development of CSF leaks and that suction drains (directed to posterior scalp) have no causative role in the development of such leaks but do play a role in preventing unwanted tissue swelling and postoperative seromas and hematomas. Throughout the follow-up period, only minor complications were noted, and all were temporary in nature. No patients suffered partial or total flap loss requiring debridement. Two patients experienced a temporary neuropraxic injury to the temporal branch of the facial nerve, and each resolved completely within 4 months after surgery. Two patients developed a seroma over the hydroxyapatite cement reconstruction, and this area was treated conservatively with serial sterile needle drainage and compressive dressings. Total resolution of the seroma without infectious sequela was achieved. One patient had exposure of the zygomatic hardware during the follow-up period. Three patients were eventually found to have an infection or foreign body reaction to the hydroxyapatite cement material, and this cranioplasty material was subsequently removed. One patient currently experiences trismus as a result of scarring around the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) area, which worsened after radiation therapy. One further patient underwent partial cement removal for delayed foreign body reaction. There were 2 cases of minor hardware exposure (superficial) treated with local wound care and local rotation flap coverage. One patient had extensive hardware exposure 3 years after radiation therapy, necessitating reconstruction with a free tissue flap in the temporal and orbital area. Notably, the patient s TMF flap covering the intracranial defect survived, but the thin skin at the TMF donor site underwent necrosis after radiation therapy. Seventy percent of patients underwent zygomatic arch osteotomy to improve the arc of rotation of the TMF. Seventeen percent of patients required coronoidectomy to further lengthen arc of rotation. There were no major complications and no deaths as a result of the procedures performed. Twenty-six percent of our patients underwent secondary lipotransfer to further refine the aesthetic result at the donor site. DISCUSSION Rehabilitation of the donor site defect remains as 1 of the longstanding controversies in the use of the TMF. Multiple methods have been used to fill the temporalis muscle defect, including lyophilized bovine cartilage, silastic, polyethylene, dermal fat grafts, methylmethacrylate, and hydroxyapatite. 3 Recently, hydroxyapatite cements have become readily available. We used hydroxyapatite to reconstruct most of our temporal defects. The hydroxyapatite bone cement allows the surgeon to replace the volume defect that results from TMF harvest without either the contour irregularity or the potential donor site 202 Temporalis Muscle Flap for Skull Base Defects HEAD & NECK DOI /hed February 2010
5 morbidity that other autologous reconstruction materials carry. Three of the TMF donor sites became infected and these hydroxyapatite reconstructions were subsequently removed without further reconstruction in 2 patients, whereas free tissue transfer was required by the resultant defect after complete removal of the material in another patient. One patient did have a large area of skin breakdown in the temporal area 3 years after initial treatment and postoperative radiation. We have observed clinically that TMF donor site skin and subcutaneous tissue thins significantly after postoperative radiation therapy. We offer many of our patients secondary lipotransfer to the temporal fossa to soften the ultimate appearance of the TMF donor site and achieve symmetry with the nonoperated side and have found this to be a useful technique associated with favorable aesthetic outcomes in our patient population. 11 Skin grafting of the TMF has not been found to be necessary in flaps that are exposed to the upper aerodigestive tract. Although free tissue transfer is occasionally required for skull base defect closure, the vast majority of such defects may be safely closed with temporalis and/or pericranial flaps. The added operative time, donor site morbidity, and comparable surgical alternatives in the majority of patients obviates the need for microvascular free tissue transfer in all but selective patients, such as those cases with massive through and through defects of the facial skin, orbit, and maxilla with wide dural/brain exposure. CONCLUSIONS The TMF is a thin, pliable, well-vascularized flap that is locally available and well suited to reconstruct a variety of skull base defects. No major complications were encountered, and the incidence of minor complications is consistent with that reported for other pedicled flaps used in the reconstruction of the skull base. Temporal fossa donor site abnormalities can be corrected with a variety of techniques, although we have found primary hydroxyapatite cement with occasional secondary lipotransfer to be safe, dependable, and aesthetically pleasing. 11 The TMF represents 1 of the workhorses of skull base reconstruction in our practice. REFERENCES 1. Speculand B. The origin of the temporalis muscle flap. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1992;30: Hoyo JAD, Sanroman JF, Gil-Diez JL, et al. The temporalis muscle flap: an evaluation and review of 38 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1994;52: Clauser L, Curioni C, Spanio S. The use of the temporalis muscle flap in facial and craniofacial reconstructive surgery. A review of 182 cases. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 1995;23: Hanasono MM, Utley DS, Goode RL. The temporalis muscle flap for reconstruction after head and neck oncologic surgery. Laryngoscope 2001;111: Cordeiro PG, Wolfe SA. The temporalis muscle flap revisited on its centennial: advantages, newer uses, and disadvantages. Plast Reconstr Surg 1996;98: Thomson CJR, Allison RS. The temporalis muscle flap in intraoral reconstruction. Aust NZ J Surg 1997;67: Smith JE, Ducic Y, Adelson R. The utility of the temporalis muscle flap for oropharyngeal, base of tongue, and nasopharyngeal reconstruction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2005;132: Bradley P, Brockbank J. The temporalis muscle flap in oral reconstruction. J Maxillofac Surg 1981;9: Abul-Hassan HS, Ascher GVD, Acland RD. Surgical anatomy and blood supply of the fascial layers of the temporal region. Plast Reconstr Surg 1986;77: Huttenbrink K-B. Temporalis muscle flap: an alternative in oropharyngeal reconstruction. Laryngoscope 1986;96: Ducic Y, Pontius AT, Smith JE. Lipotransfer as an adjunct in head and neck reconstruction. Laryngoscope 2003;113: Temporalis Muscle Flap for Skull Base Defects HEAD & NECK DOI /hed February
Interesting Case Series. Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
 Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Nasolabial Flap Reconstruction of Oral Cavity Defects: A Report of 18 Cases
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:1104-1108, 2000 Nasolabial Flap Reconstruction of Oral Cavity Defects: A Report of 18 Cases Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS (C),* and Mark Burye, DDS Purpose: This article describes
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:1104-1108, 2000 Nasolabial Flap Reconstruction of Oral Cavity Defects: A Report of 18 Cases Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS (C),* and Mark Burye, DDS Purpose: This article describes
cally, a distinct superior crease of the forehead marks this spot. The hairline and
 4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience
 80 Original Article THIEME Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience V. Velho 1 Hrushikesh U. Kharosekar 1 Jasmeet S. Thukral 1 Shonali Valsangkar
80 Original Article THIEME Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience V. Velho 1 Hrushikesh U. Kharosekar 1 Jasmeet S. Thukral 1 Shonali Valsangkar
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2
 RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. most commonly result. involving the paranasal sinuses, the overlying facial skin, or both. Such defects may result in substantial
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Use of Precontoured Positioning Plates and Pericranial Flaps in Midfacial Reconstruction to Optimize Aesthetic and Functional Outcomes Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCSC; Lance E. Oxford, MD Objectives:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Use of Precontoured Positioning Plates and Pericranial Flaps in Midfacial Reconstruction to Optimize Aesthetic and Functional Outcomes Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCSC; Lance E. Oxford, MD Objectives:
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
Temporalis Muscle Flap In Midfacial Region Defects
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 7 Number 1 S Yadav, V Dhupar, A Dhupar, F Akkara Citation S Yadav, V Dhupar, A Dhupar, F Akkara.. The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery. 2009
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 7 Number 1 S Yadav, V Dhupar, A Dhupar, F Akkara Citation S Yadav, V Dhupar, A Dhupar, F Akkara.. The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery. 2009
Disclosures. The Expanding Role of Microvascular Reconstruction. Overview. Things they are a Changing. Surgical Advisory Board, Genentech Corp
 Disclosures Surgical Advisory Board, Genentech Corp The Expanding Role of Microvascular Reconstruction P. Daniel Knott, MD FACS Associate Professor Director, Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery UCSF
Disclosures Surgical Advisory Board, Genentech Corp The Expanding Role of Microvascular Reconstruction P. Daniel Knott, MD FACS Associate Professor Director, Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery UCSF
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery
 Objectives Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery Identify important functional anatomy and aesthetic units of the face. Describe techniques used in facial reconstruction. Discuss postoperative
Objectives Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery Identify important functional anatomy and aesthetic units of the face. Describe techniques used in facial reconstruction. Discuss postoperative
Traumatic Hemi Facial Soft Tissue Amputation. Immediate Surgical Flap Reconstruction
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 3 Number 1 Traumatic Hemi Facial Soft Tissue Amputation. Immediate Surgical Flap Reconstruction J Mohammad Citation J Mohammad. Traumatic Hemi Facial
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 3 Number 1 Traumatic Hemi Facial Soft Tissue Amputation. Immediate Surgical Flap Reconstruction J Mohammad Citation J Mohammad. Traumatic Hemi Facial
Despite the apparent recent evolution and modification
 Extended orbitozygomatic approach to the skull base to improve access to the cavernous sinus and optic chiasm ALLISON TERESA PONTIUS, MD, and YADRANKO DUCIC, MD, FRCS(C), FACS, Dallas and Fort Worth, Texas
Extended orbitozygomatic approach to the skull base to improve access to the cavernous sinus and optic chiasm ALLISON TERESA PONTIUS, MD, and YADRANKO DUCIC, MD, FRCS(C), FACS, Dallas and Fort Worth, Texas
Extending the traditional resection limits of squamous cell carcinoma of the anterior skull base
 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2007) 137, 899-905 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SKULL BASE SURGERY Extending the traditional resection limits of squamous cell carcinoma of the anterior skull base Yadranko Ducic,
Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2007) 137, 899-905 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SKULL BASE SURGERY Extending the traditional resection limits of squamous cell carcinoma of the anterior skull base Yadranko Ducic,
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery FACIAL FRACTURES
 Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD
 Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD Axial Based upon a named artery. Survival length depends upon the artery not the width of the flap. Random Has random unnamed vessels supplying it. Survival length is directly proportional
Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD Axial Based upon a named artery. Survival length depends upon the artery not the width of the flap. Random Has random unnamed vessels supplying it. Survival length is directly proportional
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction
 THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts
 Aesth. Plast. Surg. 24:90 96, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002660010017 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts Ozan Sozer, M.D., and Thomas M. Biggs, M.D. İstanbul, Turkey and
Aesth. Plast. Surg. 24:90 96, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002660010017 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts Ozan Sozer, M.D., and Thomas M. Biggs, M.D. İstanbul, Turkey and
SCOPE OF PRACTICE PGY-6 PGY-7 PGY-8
 PGY-6 Round on all plastic surgery inpatients every day. Assess progress of patients and identify real or potential problems. Review patients progress with attending physicians daily and participate in
PGY-6 Round on all plastic surgery inpatients every day. Assess progress of patients and identify real or potential problems. Review patients progress with attending physicians daily and participate in
ALTHOUGH FIRST described
 The Cervicodeltopectoral Flap for Single-Stage Resurfacing of Anterolateral Defects of the Face and Neck Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCSC; Jesse E. Smith, MD SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Objective: To evaluate prospectively
The Cervicodeltopectoral Flap for Single-Stage Resurfacing of Anterolateral Defects of the Face and Neck Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCSC; Jesse E. Smith, MD SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Objective: To evaluate prospectively
Extended Bilaminar Forehead Flap With Cantilevered Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Full-Thickness Nasal Defects
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:566 570, 2005 Extended Bilaminar Forehead Flap With Cantilevered Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Full-Thickness Nasal Defects Jason K. Potter, DDS, MD,* Yadranko Ducic, MD,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:566 570, 2005 Extended Bilaminar Forehead Flap With Cantilevered Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Full-Thickness Nasal Defects Jason K. Potter, DDS, MD,* Yadranko Ducic, MD,
The nose, forming a prominent aesthetic highlight
 Nasal reconstruction in surgery of the anterior skull base YADRANKO DUCIC, MD, FACS, AND ALLISON T. PONTIUS, MD, Dallas and Fort Worth, Texas From the Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery,
Nasal reconstruction in surgery of the anterior skull base YADRANKO DUCIC, MD, FACS, AND ALLISON T. PONTIUS, MD, Dallas and Fort Worth, Texas From the Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery,
Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting
 Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting Received: 4/3/2013 Accepted: 14/5/2013 Introduction Reliable and simultaneous reconstruction of head-and-neck defects has been
Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting Received: 4/3/2013 Accepted: 14/5/2013 Introduction Reliable and simultaneous reconstruction of head-and-neck defects has been
Fracture frontal bone and its management
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 1, 2013 Fracture frontal bone and its management Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/14/ ISSN: 2250-0359
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 1, 2013 Fracture frontal bone and its management Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/14/ ISSN: 2250-0359
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide
 Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
be very thin and variable. Facial nerve branches that exit the parotid gland are deep to the SMAS.
 The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
Departmental Segregated Total Form for Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
 Departmental Segregated Total Form for Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Surgeons Revised, COPT 11/2001 Revised, BOT 2/2006, Effective,
Departmental Segregated Total Form for Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Surgeons Revised, COPT 11/2001 Revised, BOT 2/2006, Effective,
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Progressive Tension Sutures to Prevent Seroma Formation after Latissimus Dorsi Harvest
 Progressive Tension Sutures to Prevent Seroma Formation after Latissimus Dorsi Harvest Jose L. Rios, M.D., Todd Pollock, M.D., and William P. Adams, Jr., M.D. Dallas, Texas The latissimus dorsi muscle
Progressive Tension Sutures to Prevent Seroma Formation after Latissimus Dorsi Harvest Jose L. Rios, M.D., Todd Pollock, M.D., and William P. Adams, Jr., M.D. Dallas, Texas The latissimus dorsi muscle
Versatility of Reverse Sural Artery Flap for Heel Reconstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
Fascia Lata Free Flap Reconstruction of Limited Hard Palate Defects
 Open Access Original Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2356 Fascia Lata Free Flap Reconstruction of Limited Hard Palate Defects Rhorie P. Kerr 1, Andrea Hanick 1, Michael A. Fritz 1 1. Head and Neck Institute,
Open Access Original Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2356 Fascia Lata Free Flap Reconstruction of Limited Hard Palate Defects Rhorie P. Kerr 1, Andrea Hanick 1, Michael A. Fritz 1 1. Head and Neck Institute,
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
Prophylactic Midface Lift in Midfacial Trauma
 Rapid Communication 347 Ryan Brown, MD 1 Kirk Lozada, MD 2 Sameep Kadakia, MD 2 Eli Gordin, MD 3 Yadranko Ducic, MD 4 1 Department of Otolaryngology, Kaiser Permanente, Denver, Colorado 2 Department of
Rapid Communication 347 Ryan Brown, MD 1 Kirk Lozada, MD 2 Sameep Kadakia, MD 2 Eli Gordin, MD 3 Yadranko Ducic, MD 4 1 Department of Otolaryngology, Kaiser Permanente, Denver, Colorado 2 Department of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Reconstruction of the Frontal Sinus and Frontofacial Skeleton With Hydroxyapatite Cement
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstruction of the Frontal Sinus and Frontofacial Skeleton With Hydroxyapatite Cement Craig D. Friedman, MD; Peter D. Costantino, MD; C. H. Snyderman, MD; Lawrence C. Chow, PhD; Shozo
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstruction of the Frontal Sinus and Frontofacial Skeleton With Hydroxyapatite Cement Craig D. Friedman, MD; Peter D. Costantino, MD; C. H. Snyderman, MD; Lawrence C. Chow, PhD; Shozo
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Clinical teaching/experi ence. Lectures/semina rs/conferences Self-directed. learning. Clinical teaching/experi ence
 Regional Medical Center (The MED) Plastic Surgery PGY-3 By the end of the Plastic Surgery at the MED, the PGY-3 residents are expected to expand and cultivate knowledge and skills developed during previous
Regional Medical Center (The MED) Plastic Surgery PGY-3 By the end of the Plastic Surgery at the MED, the PGY-3 residents are expected to expand and cultivate knowledge and skills developed during previous
An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects V. Bhattacharya, Ganji Raveendra Reddy, Sheikh Adil Bashir,
Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects V. Bhattacharya, Ganji Raveendra Reddy, Sheikh Adil Bashir,
Esophageal Perforation
 Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Repair of scalp defect using a superficial temporal fascia pedicle VY advancement scalp flap *
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 676 680 Repair of scalp defect using a superficial temporal fascia pedicle VY advancement scalp flap * Kiyoshi Onishi a, *, Yu Maruyama b, Akiteru Hayashi
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 676 680 Repair of scalp defect using a superficial temporal fascia pedicle VY advancement scalp flap * Kiyoshi Onishi a, *, Yu Maruyama b, Akiteru Hayashi
There has been a resurgence in the description CME. Vascularized Calvarial Bone Flaps and Midface Reconstruction
 CME Vascularized Calvarial Bone Flaps and Midface Reconstruction Steven P. Davison, M.D., D.D.S. Ali N. Mesbahi, M.D. Mark W. Clemens, M.D. Catherine A. Picken, M.D. Washington, D.C. Learning Objectives:
CME Vascularized Calvarial Bone Flaps and Midface Reconstruction Steven P. Davison, M.D., D.D.S. Ali N. Mesbahi, M.D. Mark W. Clemens, M.D. Catherine A. Picken, M.D. Washington, D.C. Learning Objectives:
Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. some of the most difficult challenges in
 Temporoparietal Fascial Flap in Orbital Reconstruction Amy Lai, MD; Mack L. Cheney, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objective: To evaluate the success of the temporoparietal fascial flap (TPFF) in the primary or secondary
Temporoparietal Fascial Flap in Orbital Reconstruction Amy Lai, MD; Mack L. Cheney, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objective: To evaluate the success of the temporoparietal fascial flap (TPFF) in the primary or secondary
Three-Dimensional Alloplastic Orbital Reconstruction in Skull Base Surgery
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. HowIDoIt A Targeted Problem and Its Solution Three-Dimensional
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. HowIDoIt A Targeted Problem and Its Solution Three-Dimensional
Report of Ankylosis of the Temporomandibular Joint: Treatment with a Temporalis Muscle Flap and Augmentation Genioplasty
 Report of Ankylosis of the Temporomandibular Joint: Treatment with a Temporalis Muscle Flap and Augmentation Genioplasty Abstract A case of true bilateral ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
Report of Ankylosis of the Temporomandibular Joint: Treatment with a Temporalis Muscle Flap and Augmentation Genioplasty Abstract A case of true bilateral ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
Titanium Mesh and Hydroxyapatite Cement Cranioplasty: A Report of 20 Cases
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:272-276, 2002 Titanium Mesh and Hydroxyapatite Cement Cranioplasty: A Report of 20 Cases Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS(C)* Purpose: This article describes the use of titanium mesh
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:272-276, 2002 Titanium Mesh and Hydroxyapatite Cement Cranioplasty: A Report of 20 Cases Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS(C)* Purpose: This article describes the use of titanium mesh
Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects. O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery
 Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery Nasal defects and deformities Cleft palate and Velopharyngeal incompetence Pharyngeal and oesophageal defects Pinnal
Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery Nasal defects and deformities Cleft palate and Velopharyngeal incompetence Pharyngeal and oesophageal defects Pinnal
Management of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks After Vestibular Schwannoma Surgery
 Otology & Neurotology 32:1525Y1529 Ó 2011, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Management of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks After Vestibular Schwannoma Surgery *Brannon D. Mangus, *Alejandro Rivas, Mi Jin Yoo, JoAnn
Otology & Neurotology 32:1525Y1529 Ó 2011, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Management of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks After Vestibular Schwannoma Surgery *Brannon D. Mangus, *Alejandro Rivas, Mi Jin Yoo, JoAnn
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 + Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
+ Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
SYLLABUS OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY
 MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY AND SID SYLLABUS OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY (State examination) ACADEMIC YEAR 2015 2016 1. Asepsis
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY AND SID SYLLABUS OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY (State examination) ACADEMIC YEAR 2015 2016 1. Asepsis
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Large full-thickness nasal tip defects after Mohs
 RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury
 Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury 9 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2016 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Fireworks Topics to Cover Struts
Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury 9 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2016 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Fireworks Topics to Cover Struts
Occipital flattening in the infant skull
 Occipital flattening in the infant skull Kant Y. Lin, M.D., Richard S. Polin, M.D., Thomas Gampper, M.D., and John A. Jane, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of Plastic Surgery and Neurological Surgery, University
Occipital flattening in the infant skull Kant Y. Lin, M.D., Richard S. Polin, M.D., Thomas Gampper, M.D., and John A. Jane, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of Plastic Surgery and Neurological Surgery, University
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 01 Page January 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.36 Original Article A Study on the
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.36 Original Article A Study on the
Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H. Citation Journal of Clinical Urology, 7(5),
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Gluteal-fold adipofascial perforato fistula reconstruction Fujioka, Masaki; Hayashida, Kenji; Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H Citation Journal of Clinical
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Gluteal-fold adipofascial perforato fistula reconstruction Fujioka, Masaki; Hayashida, Kenji; Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H Citation Journal of Clinical
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PARAMEDIAN FOREHEAD FLAP NASAL RECONSTRUCTION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Brian Cervenka, Travis Tollefson, Patrik Pipkorn The paramedian forehead
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PARAMEDIAN FOREHEAD FLAP NASAL RECONSTRUCTION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Brian Cervenka, Travis Tollefson, Patrik Pipkorn The paramedian forehead
AN ELEVEN YEAR FOLLOW-UP CASE OF FACIAL HEMIATROPHY TREATED BY COMBINED APPROACHES OF CRANIOFACIAL AND
 Keio Journal of Medicine 34: 123-128, 1985 CASE REPORT AN ELEVEN YEAR FOLLOW-UP CASE OF FACIAL HEMIATROPHY TREATED BY COMBINED APPROACHES OF CRANIOFACIAL AND MICROVASCULAR SURGERIES TOYOMI FUJINO,*1 RYUZABURO
Keio Journal of Medicine 34: 123-128, 1985 CASE REPORT AN ELEVEN YEAR FOLLOW-UP CASE OF FACIAL HEMIATROPHY TREATED BY COMBINED APPROACHES OF CRANIOFACIAL AND MICROVASCULAR SURGERIES TOYOMI FUJINO,*1 RYUZABURO
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
ENDOSCOPIC-ASSISTED CRANIONASAL RESECTION OF OLFACTORY NEUROBLASTOMA
 ENDOSCOPIC-ASSISTED CRANIONASAL RESECTION OF OLFACTORY NEUROBLASTOMA Anthony Po-Wing Yuen, FRCS, 1 Yiu Wah Fan, FRCS, 2 Ching Fai Fung, FRCS, 2 Kwan Ngai Hung, FRCS 2 1 Division of Otorhinolaryngology,
ENDOSCOPIC-ASSISTED CRANIONASAL RESECTION OF OLFACTORY NEUROBLASTOMA Anthony Po-Wing Yuen, FRCS, 1 Yiu Wah Fan, FRCS, 2 Ching Fai Fung, FRCS, 2 Kwan Ngai Hung, FRCS 2 1 Division of Otorhinolaryngology,
Facelift approach for mandibular resection and reconstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Facelift approach for mandibular resection and reconstruction Bernardo Bianchi, MD, Andrea Ferri, MD, * Silvano Ferrari, MD, Chiara Copelli, MD, Enrico Sesenna, MD Maxillo-Facial Surgery
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Facelift approach for mandibular resection and reconstruction Bernardo Bianchi, MD, Andrea Ferri, MD, * Silvano Ferrari, MD, Chiara Copelli, MD, Enrico Sesenna, MD Maxillo-Facial Surgery
Single-Stage Full-Thickness Scalp Reconstruction Using Acellular Dermal Matrix and Skin Graft
 Single-Stage Full-Thickness Scalp Reconstruction Using Acellular Dermal Matrix and Skin Graft Yoon S. Chun, MD, a and Kapil Verma, BA b a Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery,
Single-Stage Full-Thickness Scalp Reconstruction Using Acellular Dermal Matrix and Skin Graft Yoon S. Chun, MD, a and Kapil Verma, BA b a Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery,
Skullbase Lesions. Skullbase Surgery Open vs endoscopic. Choice Of Surgical Approaches 12/28/2015. Skullbase Surgery: Evolution
 Skullbase Lesions Skullbase Surgery Open vs endoscopic Prof Asim Mahmood,FRCS,FACS,FICS,FAANS, Professor of Neurosurgery Henry Ford Hospital Detroit, MI, USA Anterior Cranial Fossa Subfrontal meningioma
Skullbase Lesions Skullbase Surgery Open vs endoscopic Prof Asim Mahmood,FRCS,FACS,FICS,FAANS, Professor of Neurosurgery Henry Ford Hospital Detroit, MI, USA Anterior Cranial Fossa Subfrontal meningioma
Technique Guide. Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. Surgical Technique Guide for Canthal Tendon Prodecures.
 Technique Guide Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. Surgical Technique Guide for Canthal Tendon Prodecures. Indications/Features Indications The Synthes Titanium Wire with Barb and straight Needle is
Technique Guide Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. Surgical Technique Guide for Canthal Tendon Prodecures. Indications/Features Indications The Synthes Titanium Wire with Barb and straight Needle is
The SCALP. Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The SCALP By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The SCALP includes FIVE layers external to the Calvaria. These are: S: Skin & Superficial Fascia C: Connective Tissue A: Aponeurosis (Epicranial) L: Loose
The SCALP By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The SCALP includes FIVE layers external to the Calvaria. These are: S: Skin & Superficial Fascia C: Connective Tissue A: Aponeurosis (Epicranial) L: Loose
Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect of Upper and Middle Third Leg
 Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts
 Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Ain Shams University,
Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Ain Shams University,
Transcranial resection of tumors of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity
 J Neurosurg 71:10-15, 1989 Transcranial resection of tumors of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity J. BoB BLACKLOCK, M.D., RANDAL S. WEBER, M.D., YA-YEN LEE, M.D., AND HELMUTH GOEPFERT~ M.D. Section
J Neurosurg 71:10-15, 1989 Transcranial resection of tumors of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity J. BoB BLACKLOCK, M.D., RANDAL S. WEBER, M.D., YA-YEN LEE, M.D., AND HELMUTH GOEPFERT~ M.D. Section
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
Reconstruction of Scalp Defects: An Algorithmic Approach Author: DR.M.Sundararaj, M.ch, Corresponding Author: DR.A.KavithaPriya, M.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. IX (Aug. 2017), PP 40-44 www.iosrjournals.org Reconstruction of Scalp Defects: An Algorithmic
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. IX (Aug. 2017), PP 40-44 www.iosrjournals.org Reconstruction of Scalp Defects: An Algorithmic
BUILDING A. Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation. 70 OCTOBER 2016 // dentaltown.com
 BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
T HERE is an unusual and interesting variety of craniosynostosis in
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps
 CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps Austin M. Badeau, BA, a and Frederic W.-B. Deleyiannis, MD, MPhil, MPH b
CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps Austin M. Badeau, BA, a and Frederic W.-B. Deleyiannis, MD, MPhil, MPH b
Wei-Liang Chen, DDS, MD, MBA, Jian-Tao Ye, DDS, MD, Zhao-Hui Yang, DDS, MD, Zhi-Quan Huang, DDS, MD, Da-Ming Zhang, DDS, MS, Ke Wang, DDS, MS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE REVERSE FACIAL ARTERY SUBMENTAL ARTERY MANDIBULAR OSTEOMUSCULAR FLAP FOR THE RECONSTRUCTION OF MAXILLARY DEFECTS FOLLOWING THE REMOVAL OF BENIGN TUMORS Wei-Liang Chen, DDS, MD, MBA, Jian-Tao
ORIGINAL ARTICLE REVERSE FACIAL ARTERY SUBMENTAL ARTERY MANDIBULAR OSTEOMUSCULAR FLAP FOR THE RECONSTRUCTION OF MAXILLARY DEFECTS FOLLOWING THE REMOVAL OF BENIGN TUMORS Wei-Liang Chen, DDS, MD, MBA, Jian-Tao
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Subciliary versus Subtarsal Approaches to Orbitozygomatic Fractures
 CME Subciliary versus Subtarsal Approaches to Orbitozygomatic Fractures Rod J. Rohrich, M.D., Jeffrey E. Janis, M.D., and William P. Adams, Jr., M.D. Dallas, Texas Learning Objectives: After studying this
CME Subciliary versus Subtarsal Approaches to Orbitozygomatic Fractures Rod J. Rohrich, M.D., Jeffrey E. Janis, M.D., and William P. Adams, Jr., M.D. Dallas, Texas Learning Objectives: After studying this
Salvage skull base reconstruction in the endoscopic era: Vastus lateralis free tissue transfer
 Received: 7 May 2017 Revised: 2 October 2017 Accepted: 10 January 2018 DOI: 10.1002/hed.25094 CASE REPORT Salvage skull base reconstruction in the endoscopic era: Vastus lateralis free tissue transfer
Received: 7 May 2017 Revised: 2 October 2017 Accepted: 10 January 2018 DOI: 10.1002/hed.25094 CASE REPORT Salvage skull base reconstruction in the endoscopic era: Vastus lateralis free tissue transfer
SOFT TISSUE SUPPORT IS AN
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstructive Application of the Endotine Suspension Devices James H. Boehmler IV, MD; Benjamin L. Judson, MD; Steven P. Davison, MD, DDS Objective: To illustrate the potential reconstructive
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstructive Application of the Endotine Suspension Devices James H. Boehmler IV, MD; Benjamin L. Judson, MD; Steven P. Davison, MD, DDS Objective: To illustrate the potential reconstructive
ISPUB.COM. Cutting Burr Otoplasty. D Wynne, N Balaji INTRODUCTION ANATOMY CUTTING BURR TECHNIQUE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 1 D Wynne, N Balaji Citation D Wynne, N Balaji.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 7 Number 1. Abstract Prominent
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 1 D Wynne, N Balaji Citation D Wynne, N Balaji.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 7 Number 1. Abstract Prominent
Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current
 INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Oculoplastic Surgery Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current Min-Hee Ryu, MD; David Kahng, MD; and Yongho Shin, MD, PhD Aesthetic Surgery Journal
INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Oculoplastic Surgery Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current Min-Hee Ryu, MD; David Kahng, MD; and Yongho Shin, MD, PhD Aesthetic Surgery Journal
Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Arezzo - Italy
 Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: info@urethralcenter.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it SHANGHAI February 6 8, 2009 Prof. Qiang FU Professor FU day Professor FU and night Anterior urethroplasty using
Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: info@urethralcenter.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it SHANGHAI February 6 8, 2009 Prof. Qiang FU Professor FU day Professor FU and night Anterior urethroplasty using
Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer
 Singh et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:227 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer Seema Singh, Rajesh Kumar Singh and Manoj
Singh et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:227 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer Seema Singh, Rajesh Kumar Singh and Manoj
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. The Palatal Island Flap for Reconstruction of Palatal and Retromolar Trigone Defects Revisited. decades, the range of reconstructive
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Palatal Island Flap for Reconstruction of Palatal and Retromolar Trigone Defects Revisited Eric M. Genden, MD; Bryant B. Lee, MD; Mark L. Urken, MD Background: Although a host of local
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Palatal Island Flap for Reconstruction of Palatal and Retromolar Trigone Defects Revisited Eric M. Genden, MD; Bryant B. Lee, MD; Mark L. Urken, MD Background: Although a host of local
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
Bundeswehrkrankenhaus Ulm Abteilung HNO Kopf-Halschirurgie
 Kai Johannes Lorenz and Klaus Effinger Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery Department of Radiology and interventional Radiology German Armed Forces Hospital Incidence of hemorrhage
Kai Johannes Lorenz and Klaus Effinger Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery Department of Radiology and interventional Radiology German Armed Forces Hospital Incidence of hemorrhage
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Reconstruction of the Nasal Columella. David A. Sherris, MD; Jon Fuerstenberg, MD; Daniel Danahey, MD, PhD; Peter A.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstruction of the Nasal Columella David A. Sherris, MD; Jon Fuerstenberg, MD; Daniel Danahey, MD, PhD; Peter A. Hilger, MD Objective: To report techniques successful for nasal columella
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstruction of the Nasal Columella David A. Sherris, MD; Jon Fuerstenberg, MD; Daniel Danahey, MD, PhD; Peter A. Hilger, MD Objective: To report techniques successful for nasal columella
