Histologic Characteristics of Normal Perivascular Spaces along the Optic Tract: New Pathogenetic Mechanism for Edema in Tumors in the Pituitary Region
|
|
|
- Leonard Ward
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25: , August 2004 Histologic Characteristics of Normal Perivascular Spaces along the Optic Tract: New Pathogenetic Mechanism for Edema in Tumors in the Pituitary Region Naokatsu Saeki, Yuichiro Nagai, Iichiro Matsuura, Yoshio Uchino, Motoo Kubota, Hisayuki Murai, Hiroshi Ishikura, Hiroo Ikehira, and Akira Yamaura BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Perivascular (PV) spaces are known to distend and cause edema along the optic tract (OT) in pituitary-region tumors. Interstitial fluid may be retained in PV spaces when tumors block their drainage outlets to subarachnoid spaces. However, these spaces and their outlets have not been anatomically elucidated. Our purpose was to evaluate how often large PV spaces are present along the OT and demonstrate their superficial communication points to adjacent subarachnoid spaces. METHODS: We examined serial histologic sections of 10 hemispheric blocks obtained from cadavers without cerebral abnormality. RESULTS: Large PV spaces, mm in maximum height, were always present along the middle portion of the OT. Perforation points of the largest spaces were noted at the medial sulcus of the OT in seven hemispheres and through the OT in three. CONCLUSION: Large PV spaces are present along the middle portion of the OT. Their communication point to adjacent subarachnoid spaces was histologically demonstrated. The locations and variations of the outlet of large PV spaces explain the clinical features of edemas; these findings anatomically support the hypothesis that blockage of the outlets to subarachnoid spaces may play a role in distending the PV spaces and in causing edema in pituitary-region tumors. Only MR imaging has revealed this change; further pathologic investigations are awaited. The advent of MR imaging has enabled detailed visualization of the perivascular (PV) spaces (called Virchow-Robin spaces) in the brain (1 6). Among the various MR images, heavily T2-weighted imaging can depict fine structures in and around the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) space and are considered sufficiently sensitive for depicting the PV spaces, which are of CSF signal intensity (7). Using the heavily T2-weighted pulse sequence, Saeki et al (8) highlighted the PV spaces along the OT in cases of pituitary region tumors from a new Received August 19, 2003; accepted after revision January 10, From the Departments of Neurologic Surgery (N.S., I.M., Y.U., M.K., H.M., A.Y.) and Pathology (Y.N., H. Ishikura), Chiba University Graduate School of Medicine, and the Department of Medical Imaging (H. Ikehira), National Institute of Radiologic Sciences, Japan. Address reprint requests to Naokatsu Saeki, Department of Neurologic Surgery, Chiba University School of Medicine, Inohana 1 8-1, Chuo-ku, Chiba City, Chiba , Japan. American Society of Neuroradiology clinical viewpoint. Regarding tumors touching or compressing the optic pathway, the edema was visible in four of 25 pituitary adenomas, eight of 11 craniopharyngiomas (Fig 1), one germ cell tumor, and one malignant lymphoma. This observation showed that edema along the OT, which was previously thought to be specific for craniopharyngioma, is in fact seen in a range of pituitary region tumors. The change disappears or decreases after successful treatment. Comparison of the pretreatment and post-treatment MR images revealed that the change had been located at the normally present large PV spaces along the OT (Fig 1B and C) (8). This finding led the authors to propose that the edema is related to distension of normal PV spaces rather than regional inflammation from microscopic leakage of cyst contents. Previous animal experiments have revealed that extracellular or interstitial fluid leaves along the PV spaces, moving toward the subarachnoid space (9, 10). On the basis of such experiments, Saeki et al (8) hypothesized that the edema is due to the retention of interstitial fluid in PV spaces after tumors block their 1218
2 AJNR: 25, August 2004 OPTIC TRACT PERIVASCULAR SPACE 1219 FIG 1. Representative MR images show an edema along the OT in a 33-year-old woman with craniopharyngioma (reproduced from reference 8 with the permission of the American Society of Neuroradiology). A, T1-weighted contrast-enhanced coronal MR image before treatment. High- and low-signal-intensity mass (arrowhead) is visible at the suprasellar cistern. Low-signal-intensity edema (arrow) is noted along the left OT. B, Heavily T2-weighted coronal MR image before treatment shows bilateral edemas (thick arrows) along the OT. The left side is more prominent. The OTs are difficult to differentiate from the edemas. On the right side, a curvilinear area of high signal intensity (thin arrow) originates from the edema. C, On this heavily T2-weighted coronal MR image obtained 3 months after surgery (similar level as in B), the edema disappears on the right side. A large PV space (left thick arrow), present in normal conditions, is visible along the right OT (thin arrow). Edema (right thick arrow) remains on the left side. drainage outlets to the subarachnoid space. However, PV spaces along the OT and their outlets to the adjacent subarachnoid space have not been anatomically elucidated. This study was designed to provide background data about the formation mechanism of the edema along the OTs. Our purpose was to define the large PV spaces along the OT and to demonstrate the superficial perforation points of the vessels in these spaces (ie, communication routes between the subarachnoid space and the PV spaces along the OT). Methods Ten hemispheres were obtained from five cadaveric brains from year-old men and women who died from nonneurologic causes. The specimens were fixed in 60% ethanol solution for 4 6 months. In this study, the OT was anatomically defined as the optic pathway located between coronal sections, including the pituitary stalk and the anterior border of the lateral geniculate body (11, 12) After the whole length of the OT was exposed, the OT was divided and cut into three equal portions: anterior, middle, and posterior (Fig 2). Each portion was coronally cut into a mm-long tissue block, which was embedded in paraffin. Sections 4 m thick were stained by using hematoxylin-eosin and myelin staining. The sections were viewed by using low-power light microscopy at up to 50 magnification. On the basis of previous reports, the PV spaces were pathologically defined as spaces lined by a pial layer, including vessels, and surrounded by the brain parenchyma without ischemic or necrotic components (1 5). In addition, histologic similarities were compared between large PV spaces along the OT and around the anterior commissure where they had pathologically proved PV spaces. Results FIG 2. Schematic representation of the anatomy in an 85-yearold man shows the basal view of the OT and surrounding brain tissue in the left hemisphere. The whole length of the OT is exposed by removing the left temporal lobe. The tract is divided into three equal-sized portions: anterior, middle, and posterior. Numerous perforation points are present medial to (thick arrows) and through (thin arrows) the OT. These are mainly located in the middle and posterior portions of the OT. In all 10 hemispheres, several large and small PV spaces were always visible along the middle and posterior portions of the OT (Figs 3A, 4B D, and 5B F). Only a few were seen along the anterior portion of the OT. The largest space in each specimen was always present along the middle portion of the OT on the section including the mammillary body and the anterior portion of the cerebral peduncle (Figs 2, 4D, and 5F). It was horizontally long and narrow (Fig 4C) or oval (Fig 5F). The space was mm in maximum height (Figs 3A, 4A and D, and 5A and F) and adjacent to or within the upper part of the OT (Figs 4C and 5F). Large spaces along the OT included vessels and were lined with a pial layer (Fig 3A). The spaces
3 1220 SAEKI AJNR: 25, August 2004 FIG 3. Histologic samples obtained in a 79-year-old woman. A, Coronal section of the middle portion of the OT shows the cerebral peduncle (CP) (hematoxylin-eosin stain, original magnification 20) Along the OT, a large 1.5-mm-high space has a pial layer (thin arrow) that lines its inner surface. Vessels (thick arrows) are present in the space, and no necrotic or ischemic changes are visible in the surrounding brain tissue. The histologic features are compatible with those of PV spaces around the anterior commissure shown in B. Small spaces (arrowheads) are present adjacent to the OT. B, Coronal section at the anterior commissure (AC) and the lower basal ganglia shows multiple PV spaces (hematoxylin-eosin stain, original magnification 40). Adjacent to the anterior commissure are multiple PV spaces with vessels lined by a pial layer (arrows). No necrotic or ischemic changes are visible in the surrounding brain tissue. FIG 4. Histologic samples obtained in an 86-year-old woman. A, Section shows lines corresponding to sections in B D. B D, Continuous thin sections show a penetrating vessel (arrow) from the perforation point at the subarachnoid space (B) tothe largest PV space adjacent to the OT (C and D). Its maximum height is 0.5 mm. Sections show the perforation point medial to the OT, which corresponds to the large arrows in Figure 2. Small PV spaces (arrowheads) are present (myelin staining, original magnification 25). CP indicates cerebral peduncle. along the OT and those around the anterior commissure had the same histologic features, as described in the previous reports (1 5) (Fig 3B). Therefore, the spaces along the OT were considered PV spaces (Figs 4 and 5). The vessel passed the perforation point medial to the OT (the sulcus between the OT and tuber cinereum) in seven of 10 hemispheric blocks (Figs 2 and 4) and through the OT in the remaining three (Figs 2 and 5) before reaching the large PV space on the OT. Therefore, there were two variations in the communication point between the PV space along the OT and the adjacent subarachnoid space.
4 AJNR: 25, August 2004 OPTIC TRACT PERIVASCULAR SPACE 1221 FIG 5. Histologic samples obtained in an 81-year-old man. CP indicates cerebral peduncle. A, Section shows lines corresponding to sections in B F. B F, Continuous thin sections show a penetrating vessel from the perforation point in the subarachnoid space (B) to the largest PV space within the upper part of the OT (F). Its maximum height is 0.7 mm. Sections show the perforation point through the OT, which corresponds to the small arrows in Figure 2. A few small PV spaces (arrowheads) are visible along the OT (myelin staining, original magnification 25). Bracket in E 1 mm. Discussion Although our sample size was small, our histologic studies of 10 specimens showed the consistent presence of large PV spaces along the middle and posterior portions of the OT. The largest space in each specimen was present along the middle portion on the coronal section including mammillary body and anterior midbrain. The spaces possess histologic features compatible with those of spaces previously reported. Photographs from human anatomic atlases demonstrate similarly thin and small spaces in the same location on coronal brain sections but without correlation to their anatomic or clinical importance (13, 14). We believe that these large PV spaces along the OT are always present. The present histologic studies also revealed that the outlets of the PV spaces along the OT to the adjacent subarachnoid space are present at two sites: medial to and through the OT. The present anatomic findings of possible drainage outlets of interstitial fluid from PV spaces along the OT may explain clinical features of the edema along the OT in pituitary region tumors (Fig 6). First, the location of the outlets to the subarachnoid space in the middle portion of the OT may explain why the edema is common in tumors in which the main mass is located behind the optic chiasm; examples of these include craniopharyngiomas, lymphomas, and germinomas (8). Tumors in the pituitary region commonly extend behind the optic chiasm and involve the posterior lobe system and the floor of the third ventricle FIG 6. Schematic representation shows a possible new mechanism for edema along the OT in pituitary-region tumors. Right, In the normal anatomy, the PV space along the OT communicates with the adjacent subarachnoid space through a thin channel medial to the OT. Left, Tumor can block this channel with mechanical, inflammatory, or adhesive processes. The PV space retains interstitial fluid and distends along the OT (dotted area). (6, 8, 15). Second, the change is occasionally and remarkably unilateral and deviated to the side of tumoral extension (8) (Fig 1). This explanation is feasible because the outlets to the subarachnoid space are not on the midline; they are present bilaterally and off the midline. Third, the presence of at least two outlet points may explain why the change does not always occur in a larger tumor. To produce the
5 1222 SAEKI AJNR: 25, August 2004 edema, a tumor must be larger in a patient with an outlet point through the OT, rather than in a patient with the point medial to the OT. Likewise, even a small tumor may have accompanied edema when the points are located medially (8, 15). The distance between tumors and outlet points may play a role in how readily tumor causes PV spaces to be distended. Therefore, this present study has provided supportive anatomic evidence for dilated PV spaces along the OT as a formation mechanism of the edema along the OT in pituitary-region tumors (Fig 6). In addition to such anatomic considerations, other factors, such as the extent and degree of peritumoral edema, the growth speed, the invasiveness of malignant tumors, and tumor adhesion to the surrounding tissue, influence the edema formation (8, 15). Clinicoanatomic correlation between patients with tumors in the pituitary region and healthy subjects is important, because this pattern of edema has not been pathologically proved in humans. This change may be associated with a new pattern of brain edema in addition to vasogenic, cytotoxic, osmotic, hydrostatic, and interstitial edemas (16), or it may be an unrecognized variation of one of these mechanisms. Accordingly, the clinical application of this knowledge has great potential. Because this new type of brain edema has been revealed by using MR imaging, pathologic investigations are required. An MR imaging system of higher field strength may succeed in demonstrating the detailed pathologic anatomy of this edema. Acknowledgments We express sincere gratitude to Dr. Umeo Ito, one of the worldwide pioneering researchers on brain edema, for his indispensable advice in preparing this manuscript; to our colleagues in our department; and to Dr. Kenro Sunami and the other medical staff at Kawatetsu Chiba Hospital for their cooperation in collecting the clinical data. References 1. Braffman BH, Zimmerman RA, Trojanowski JQ, Gonatas NK, Hickey WF, Schlaepfer W. Brain MR: Pathologic correlation with gross and histopathology, I: lacunar infarction and Virchow-Robin spaces. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1988;9: Elster AD, Richardson DN. Focal high signal on MR scans of the midbrain caused by enlarged perivascular spaces: MR-pathologic correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1991;11: Heier LA, Bauer CJ, Schwartz L, Zimmerman RD, Morgello S, Deck MD. Large Virchow-Robin spaces: MR-clinical correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1989;10: Jungreis CA, Kanal E, Hirsch WL, Martinez AJ, Moossy J. Normal perivascular spaces mimicking lacunar infarction: MR imaging. Radiology 1988;169: Song CJ, Kim JH, Kier EL, Bronen RA. MR imaging and histologic features of subinsular bright spots on T2-weighted MR images: Virchow-Robin spaces of the extreme capsule and insular cortex. Radiology 2000;214: Seeger JF. Normal variations of the skull and its contents. In: Zimmerman RA, Gibby WA, Carmody RF, eds. Neuroimaging. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2000: Mamata Y, Muro I, Matsumae M, et al. Magnetic resonance cisternography for visualization of intracisternal fine structures. J Neurosurg 1998;88: Saeki N, Uchino Y, Murai H, et al. MR study on edema-like change along the optic tract in patients with pituitary region tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003;24: Rennels M, Gregory TF, Blaumanis O, Fujimoto K, Grady PA. Evidence of a paravascular fluid circulation in the mammalian central nervous system, provided by the rapid distribution of tracer protein throughout the brain to the subarachnoid space. Brain Res 1985;326: Weller RO, Kida S, Zhang E. Pathways of fluid drainage from the brain-morphological aspects and immunological significance in rat and man. Brain Pathol 1992;2: Tamraz JC, Outin-Tamraz C, Saban R. MR imaging anatomy of the optic pathways. Radiol Clin North Am 1999;37: Horton JC, Landau K, Maeder P, Hoyt WF. Magnetic resonance imaging of the human lateral geniculate body. Arch Neurol 1990;47: DeArmond S, Fusco MM, Dewey MM. Structure of the Human Brain. New York: Oxford Press; 1976: Mai JK, Assheuer J, Paxinos G. Atlas of the Human Brain. San Diego: Academic Press; 1997: Nagahata M, Hosoya T, Kayama T, Yamaguchi K. Edema along the optic tract: useful MR finding for the diagnosis of craniopharyngiomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1998;19: Miller JD, Ironside JW. Raised intracranial pressure, edema and hydrocephalus. In: Graham DI, Lantos PL, eds. Greenfield s Neuropathology. Vol 1. 6th ed. London: Arnold; 1997:
MR Imaging of Normal Perivascular Space Expansion at Midbrain
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:566 571, March 2005 MR Imaging of Normal Perivascular Space Expansion at Midbrain Naokatsu Saeki, Motoki Sato, Motoo Kubota, Yoshio Uchino, Hisayuki Murai, Yuichiro Nagai, Hiroshi
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:566 571, March 2005 MR Imaging of Normal Perivascular Space Expansion at Midbrain Naokatsu Saeki, Motoki Sato, Motoo Kubota, Yoshio Uchino, Hisayuki Murai, Yuichiro Nagai, Hiroshi
In some patients with pituitary macroadenoma, visual acuity
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation
 MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Criteria for early CLINICAL STUDY. N Fujimoto 1, N Saeki 2, O Miyauchi 1
 (2002) 16, 731 738 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye N Fujimoto 1, N Saeki 2, O Miyauchi 1 Criteria for early and E Adachi-Usami 1 detection of temporal
(2002) 16, 731 738 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye N Fujimoto 1, N Saeki 2, O Miyauchi 1 Criteria for early and E Adachi-Usami 1 detection of temporal
Cystic lesions of the brain parenchyma pose an important diagnostic
 CLINICAL REPORT BRAIN Subcortical Cystic Lesions within the Anterior Superior Temporal Gyrus: A Newly Recognized Characteristic Location for Dilated Perivascular Spaces S. Rawal, S.E. Croul, R.A. Willinsky,
CLINICAL REPORT BRAIN Subcortical Cystic Lesions within the Anterior Superior Temporal Gyrus: A Newly Recognized Characteristic Location for Dilated Perivascular Spaces S. Rawal, S.E. Croul, R.A. Willinsky,
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
Characteristic features of CNS pathology. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans
 PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP:
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
T HE visual field changes that accompany
 J. Neurosurg. / Volume 31 / September, 1969 The Arterial Supply of the Human Optic Chiasm RICHARD BERGLAND, M.D.,* AND BRONSON S. RAY, M.D. Department of Surgery (Neurosurgery), New York Hospital-Cornell
J. Neurosurg. / Volume 31 / September, 1969 The Arterial Supply of the Human Optic Chiasm RICHARD BERGLAND, M.D.,* AND BRONSON S. RAY, M.D. Department of Surgery (Neurosurgery), New York Hospital-Cornell
MR Evaluation of Hydrocephalus
 591 MR Evaluation of Hydrocephalus Taher EI Gammal 1 Marshall B. Allen, Jr. 2 Betty Sue Brooks 1 Edward K. Mark2 An analysis of sagittal T1-weighted MR studies was performed in 23 patients with hydrocephalus,
591 MR Evaluation of Hydrocephalus Taher EI Gammal 1 Marshall B. Allen, Jr. 2 Betty Sue Brooks 1 Edward K. Mark2 An analysis of sagittal T1-weighted MR studies was performed in 23 patients with hydrocephalus,
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography
 Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
DIRECT SURGERY FOR INTRA-AXIAL
 Kitakanto Med. J. (S1) : 23 `28, 1998 23 DIRECT SURGERY FOR INTRA-AXIAL BRAINSTEM LESIONS Kazuhiko Kyoshima, Susumu Oikawa, Shigeaki Kobayashi Department of Neurosurgery, Shinshu University School of Medicine,
Kitakanto Med. J. (S1) : 23 `28, 1998 23 DIRECT SURGERY FOR INTRA-AXIAL BRAINSTEM LESIONS Kazuhiko Kyoshima, Susumu Oikawa, Shigeaki Kobayashi Department of Neurosurgery, Shinshu University School of Medicine,
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA
 RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA O.BAKKACHA, H.MALAJATI, M.RHISSASSI, H. BENCHAABOUNE, N.CHAKIR, My R. EL HASSANI,M.JIDDANE Department of Neuroradiology specialties Hospital. Rabat Objective: New imaging
RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA O.BAKKACHA, H.MALAJATI, M.RHISSASSI, H. BENCHAABOUNE, N.CHAKIR, My R. EL HASSANI,M.JIDDANE Department of Neuroradiology specialties Hospital. Rabat Objective: New imaging
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Sandlike Appearance of Virchow-Robin Spaces in Early Multiple Sclerosis: A Novel Neuroradiologic Marker
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:376 380, March 2002 Sandlike Appearance of Virchow-Robin Spaces in Early Multiple Sclerosis: A Novel Neuroradiologic Marker Anat Achiron and Meir Faibel BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:376 380, March 2002 Sandlike Appearance of Virchow-Robin Spaces in Early Multiple Sclerosis: A Novel Neuroradiologic Marker Anat Achiron and Meir Faibel BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1570 1574, September 2003 The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease Andrew Slater, Niall R. Moore, and Susan M. Huson BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1570 1574, September 2003 The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease Andrew Slater, Niall R. Moore, and Susan M. Huson BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Tumor-related edema of the optic tract (EOT) was
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Pediatr 21:516 522, 2018 of the optic tract in patients with tumors of the sellar region: clinical and visual implications in the pediatric population Aurore Bussat, MD, 1
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Pediatr 21:516 522, 2018 of the optic tract in patients with tumors of the sellar region: clinical and visual implications in the pediatric population Aurore Bussat, MD, 1
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries.
 DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
Hypothalamus. To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine secretions NTA Ch 14, pgs Key Figs: 14-3; 14-4,
 Hypothalamus Objectives To learn the general organization of the hypothalamus and the functions of the major nuclei NTA Ch 14, pgs. 419-422 Key Figs: 14-2, 14-3 To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine
Hypothalamus Objectives To learn the general organization of the hypothalamus and the functions of the major nuclei NTA Ch 14, pgs. 419-422 Key Figs: 14-2, 14-3 To learn how the brain regulates neuroendocrine
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization
 Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization Poster No.: C-1574 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Cucos, A. Puiu, S. Manole ; Cluj-Napoca/RO, Cluj napoca/ RO Keywords: Cerebrospinal
Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization Poster No.: C-1574 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Cucos, A. Puiu, S. Manole ; Cluj-Napoca/RO, Cluj napoca/ RO Keywords: Cerebrospinal
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Fig.1: A, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a
 Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Histology of the CNS
 Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
Meningeal carcinomatosis presenting with leukoencephalopathylike imaging findings
 Accepted Manuscript Meningeal carcinomatosis presenting with leukoencephalopathylike imaging findings Hiroshi Tsuji, Shioya Ayako, Norio Takayashiki, Toshiyuki Irie, Satoshi Itoi, Taisuke Kodama, Yuki
Accepted Manuscript Meningeal carcinomatosis presenting with leukoencephalopathylike imaging findings Hiroshi Tsuji, Shioya Ayako, Norio Takayashiki, Toshiyuki Irie, Satoshi Itoi, Taisuke Kodama, Yuki
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
ALLEN Human Brain Atlas
 TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER: CASE QUALIFICATION AND DONOR PROFILES The case review process described here was employed for three components of the ALLEN Human Brain Atlas: (1) the Survey; (2) the Neurotransmitter
TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER: CASE QUALIFICATION AND DONOR PROFILES The case review process described here was employed for three components of the ALLEN Human Brain Atlas: (1) the Survey; (2) the Neurotransmitter
CSF. Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System
 Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
I T IS well known that aneurysms occur at
 The Lateral Perforating Branches of the Anterior and Middle Cerebral Arteries* HARRY A. KAPLAN, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Seton Hall College of Medicine, and Jersey City Medical Center, Jersey City,
The Lateral Perforating Branches of the Anterior and Middle Cerebral Arteries* HARRY A. KAPLAN, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Seton Hall College of Medicine, and Jersey City Medical Center, Jersey City,
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
Outline of the next three lectures
 Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
MR Imaging of Acute Coccidioidal Meningitis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2:59 514, March 1999 MR Imaging of Acute Coccidioidal Meningitis William K. Erly, Richard J. Bellon, Joachim F. Seeger, and Raymond F. Carmody BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2:59 514, March 1999 MR Imaging of Acute Coccidioidal Meningitis William K. Erly, Richard J. Bellon, Joachim F. Seeger, and Raymond F. Carmody BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
TABLES. Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging. Conclusions. Author (Year) Classification Process/Evid ence Class
 TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
Study of the CNS. Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David Norman Thomas H. Newton
 271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
Residence of Discipline of Neurosurgery of Hospital da Santa Casa de Misericórdia of Sao Paulo Sao Paulo, Brazil
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS NEUROLOGY Research Article Efficacy of the Lamina Terminalis Fenestration Associated With the Liliequist Membrane Fenestration in Reducing Shunt-Dependent Hydrocephalus Following Aneurysm
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS NEUROLOGY Research Article Efficacy of the Lamina Terminalis Fenestration Associated With the Liliequist Membrane Fenestration in Reducing Shunt-Dependent Hydrocephalus Following Aneurysm
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas
 External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline.
 The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex
 Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex Optic radiation: anatomy Pathologies of the postchiamsatic visual pathways and visual cortex Characterized by homonymous hemianopsia. This
Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex Optic radiation: anatomy Pathologies of the postchiamsatic visual pathways and visual cortex Characterized by homonymous hemianopsia. This
From a suspicious cystic pineal gland to pineoblastoma in a patient with familial unilateral retinoblastoma
 From a suspicious cystic pineal gland to pineoblastoma in a patient with familial unilateral retinoblastoma Marcus C de Jong, Annette C Moll, Sophia Göricke, Paul van der Valk, Wijnanda A Kors, Jonas A
From a suspicious cystic pineal gland to pineoblastoma in a patient with familial unilateral retinoblastoma Marcus C de Jong, Annette C Moll, Sophia Göricke, Paul van der Valk, Wijnanda A Kors, Jonas A
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann
 Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. Meninges 2. Cerebral cortex-cytoarchitecture 3. Diencephalon (thalamus/hypothalamus) (this replaces
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. Meninges 2. Cerebral cortex-cytoarchitecture 3. Diencephalon (thalamus/hypothalamus) (this replaces
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Cerebral Cortex 1. Sarah Heilbronner
 Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
LIMBIC SYSTEM. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
Mass Histology Service
 Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
Longitudinal anterior-to-posterior shift of collateral channels in patients with moyamoya disease: an implication for its hemorrhagic onset
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Longitudinal anterior-to-posterior shift of collateral channels in patients with moyamoya disease: an implication for its hemorrhagic onset Shusuke Yamamoto, MD, Satoshi Hori, MD, PhD,
CLINICAL ARTICLE Longitudinal anterior-to-posterior shift of collateral channels in patients with moyamoya disease: an implication for its hemorrhagic onset Shusuke Yamamoto, MD, Satoshi Hori, MD, PhD,
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
MR CASE STUDY: Autopsy-proven CMV fetopathy.
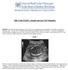 MR CASE STUDY: Autopsy-proven CMV fetopathy. HISTORY: Elderly primigravida patient with normal first trimester screen presents at 21-weeks for detailed anatomy scan. At that time, ultrasound demonstrates
MR CASE STUDY: Autopsy-proven CMV fetopathy. HISTORY: Elderly primigravida patient with normal first trimester screen presents at 21-weeks for detailed anatomy scan. At that time, ultrasound demonstrates
Menigitidis. Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline
 Menigitidis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Review Normal Microanatomy Image Ref: www.histology-world.com
Menigitidis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Review Normal Microanatomy Image Ref: www.histology-world.com
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
MR Volume Estimation of Subcortical Brain Lesions and Ventricular Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Simple and Accurate Stereologic Method
 MR Volume Estimation of Subcortical Brain Lesions and Ventricular Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Simple and Accurate Stereologic Method O. J. M. Vogels, J. C. M. Zijlmans, M. A. van t Hof, H. O. M. Thijssen, and
MR Volume Estimation of Subcortical Brain Lesions and Ventricular Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Simple and Accurate Stereologic Method O. J. M. Vogels, J. C. M. Zijlmans, M. A. van t Hof, H. O. M. Thijssen, and
Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study
 Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study Mark C. DeLano, F. Y. Fun, and S. James Zinreich PURPOSE: To delineate the relationship between the optic nerves
Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study Mark C. DeLano, F. Y. Fun, and S. James Zinreich PURPOSE: To delineate the relationship between the optic nerves
Imaging The Turkish Saddle. Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman
 Imaging The Turkish Saddle Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Review the anatomy of the sellar region Discuss the differential diagnosis of sellar masses Discuss typical
Imaging The Turkish Saddle Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Review the anatomy of the sellar region Discuss the differential diagnosis of sellar masses Discuss typical
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Brain, Cranial Nerves, and Spinal Cord
 Bio101 Laboratory 13 Neuron/Spinal Cord Histology Brain Anatomy Ear & Eye Anatomy 1 Brain, Cranial Nerves, and Spinal Cord Objectives for today s lab Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the brain
Bio101 Laboratory 13 Neuron/Spinal Cord Histology Brain Anatomy Ear & Eye Anatomy 1 Brain, Cranial Nerves, and Spinal Cord Objectives for today s lab Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the brain
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A
 Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
Coincidental aneurysms with tumours of pituitary origin
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 972-979 Coincidental aneurysms with tumours of pituitary origin JAN JAKUBOWSKI AND BRIAN KENDALL From the Gough Cooper Department of Neurological
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 972-979 Coincidental aneurysms with tumours of pituitary origin JAN JAKUBOWSKI AND BRIAN KENDALL From the Gough Cooper Department of Neurological
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
KEY WORDS gamma knife surgery metastatic brain tumor radiation injury tumor recurrence thallium-201 single-photon emission computerized tomography
 J Neurosurg (Suppl) 102:266 271, 2005 Diagnostic value of thallium-201 chloride single-photon emission computerized tomography in differentiating tumor recurrence from radiation injury after gamma knife
J Neurosurg (Suppl) 102:266 271, 2005 Diagnostic value of thallium-201 chloride single-photon emission computerized tomography in differentiating tumor recurrence from radiation injury after gamma knife
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1991, 36
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Large Periureteral Lipoma Associa Hydronephrosis. Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Imamura, Atushi Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Large Periureteral Lipoma Associa Hydronephrosis. Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Imamura, Atushi Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
NACC Vascular Consortium. NACC Vascular Consortium. NACC Vascular Consortium
 NACC Vascular Consortium NACC Vascular Consortium Participating centers: Oregon Health and Science University ADC Rush University ADC Mount Sinai School of Medicine ADC Boston University ADC In consultation
NACC Vascular Consortium NACC Vascular Consortium Participating centers: Oregon Health and Science University ADC Rush University ADC Mount Sinai School of Medicine ADC Boston University ADC In consultation
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1
 Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging
 Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Magnetic resonance imaging (MR!) provides
 0 Wallerian Degeneration of the Pyramidal Tract in Capsular Infarction Studied by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jesiis Pujol, MD, Josep L. Marti-Vilalta, MD, Carme Junqu6, PhD, Pere Vendrell, PhD, Juan Fernandez,
0 Wallerian Degeneration of the Pyramidal Tract in Capsular Infarction Studied by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jesiis Pujol, MD, Josep L. Marti-Vilalta, MD, Carme Junqu6, PhD, Pere Vendrell, PhD, Juan Fernandez,
PARA210 SUMMARY Hyperglycaemia (DKA & HHS) Brain & Nervous System Anatomy & Physiology Degenerative Neurological Disorders
 PARA210 SUMMARY Page Topic 01-03 Diabetes Mellitus 04-05 Hyperglycaemia (DKA & HHS) 06-13 Toxicology 14-18 12 Lead ECG 19-21 Brain & Nervous System Anatomy & Physiology 22-24 Degenerative Neurological
PARA210 SUMMARY Page Topic 01-03 Diabetes Mellitus 04-05 Hyperglycaemia (DKA & HHS) 06-13 Toxicology 14-18 12 Lead ECG 19-21 Brain & Nervous System Anatomy & Physiology 22-24 Degenerative Neurological
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
Cerebral vasculitis in Wegener's granulomatosis
 Cerebral vasculitis in Wegener's granulomatosis Case report Fred V. Lucas, M.D. Sanford P. Benjamin, M.D. Marta C. Steinberg, M.D. Department of Pathology Wegener's granulomatosis is a necrotizing granulomatous
Cerebral vasculitis in Wegener's granulomatosis Case report Fred V. Lucas, M.D. Sanford P. Benjamin, M.D. Marta C. Steinberg, M.D. Department of Pathology Wegener's granulomatosis is a necrotizing granulomatous
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
BIOL Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain
 BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
Long-term Observation of Lateral Medullary Infarction due to Vertebral Artery Dissection Assessed with Multimodal Neuroimaging
 Case Reports Long-term Observation of Lateral Medullary Infarction due to Vertebral Artery Dissection Assessed with Multimodal Neuroimaging Koichi Nomura 1, Masahiro Mishina 1,SeijiOkubo 1, Satoshi Suda
Case Reports Long-term Observation of Lateral Medullary Infarction due to Vertebral Artery Dissection Assessed with Multimodal Neuroimaging Koichi Nomura 1, Masahiro Mishina 1,SeijiOkubo 1, Satoshi Suda
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Imaging of Moya Moya Disease
 Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Methods. E. Leon Kier, Lawrence H. Staib, Lawrence M. Davis, and Richard A. Bronen. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25: , May 2004
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:677 691, May 2004 MR Imaging of the Temporal Stem: Anatomic Dissection Tractography of the Uncinate Fasciculus, Inferior Occipitofrontal Fasciculus, and Meyer s Loop of the Optic
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:677 691, May 2004 MR Imaging of the Temporal Stem: Anatomic Dissection Tractography of the Uncinate Fasciculus, Inferior Occipitofrontal Fasciculus, and Meyer s Loop of the Optic
The distribution of plaques in the cerebrum in
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1962, 25, 315 The distribution of plaques in the cerebrum in multiple sclerosis BETTY BROWNELL AND J. TREVOR HUGHES From the Departments of Neurology and Pathology, Radcliffe
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1962, 25, 315 The distribution of plaques in the cerebrum in multiple sclerosis BETTY BROWNELL AND J. TREVOR HUGHES From the Departments of Neurology and Pathology, Radcliffe
