Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions
|
|
|
- Laurence McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song, Keon Ha Kim, Bae Ju Kwon, Hyo-Cheol Kim, Jae Hyoung Kim, and Moon Hee Han BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Carbon monoxide intoxication has delayed effects on the cerebral white matter characterized by bilateral, confluent lesions that reflect diffuse demyelination. To increase our understanding of this process, we assessed the diffusion characteristics of these lesions. METHODS: Five consecutive patients with delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication were examined with diffusion MR imaging. Diffusion-weighted images (DWIs) were obtained days after their exposure to CO and during a relapse of neuropsychiatric symptoms, which occurred after an initial recovery. Imaging was performed at 1.5 T by using a spin-echo echo-planar sequence with diffusion gradients of 0, 500, and 1000 s/mm 2. DWIs and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps were visually evaluated, and mean ADCs were calculated from the periventricular white matter and the centrum semiovale, where confluent hyperintensity was seen on T2-weighted images. Findings were compared with those of normal-looking white matter. RESULTS: In all five patients, both T2-weighted images and DWIs showed the white matter lesions as bilateral, diffuse, confluent areas of hyperintensity in the periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale. On ADC maps, these lesions were isointense, with focal areas of hypointensity (n 4) or diffuse hypointensity (n 1). Mean ADC values of the white matter lesions were significantly lower than those of normal-looking white matter, regardless of their isointensity or hypointensity on ADC maps (P <.05). CONCLUSION: Bilateral, confluent, white matter lesions in patients with delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication show decreased diffusivity. Delayed encephalopathy of carbon monoxide intoxication is clinically characterized by a recurrence of neurologic or psychiatric symptoms. This recurrence is preceded by a temporary asymptomatic period (lucid interval) of variable duration (usually 2 3 weeks) after a recovery from the acute stage of CO intoxication (1, 2). Similar postanoxic delayed encephalopathies may also be seen in cases of respiratory arrest (3), strangling (4), drug overuse, exposure to toxins, Received January 20, 2003; accepted after revision March 28. From the Department of Radiology (J.K., K.-H.C., I.C.S., K.H.K., B.J.K., H.-C.K., J.H.K., M.H.H.), the Institute of Radiation Medicine (K.-H.C., I.C.S., M.H.H.), and the Neuroscience Research Institute (K.-H.C., M.H.H.), Seoul National University College of Medicine, Korea. This study was supported in part by the 2002 BK21 Project for Medicine, Dentistry, and Pharmacy. Address reprint requests to Kee-Hyun Chang, Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, 28 Yongon-dong, Chongno-gu, Seoul, , Korea. American Society of Neuroradiology anaphylaxis, seizures, or anesthesia (2). The course of the delayed encephalopathy varies with the severity of CO intoxication, ranging from full recovery to a progressive deterioration ending in coma or death. Clinical symptoms and signs include the characteristic symptom triad of mental deterioration, urinary incontinence, and gait disturbance, as well as other neuropsychiatric manifestations (1, 2, 5). The underlying pathologic lesion is thought to be diffuse demyelination of the cerebral white matter (5, 6); however, the pathogenic mechanism remains unexplained. Conventional MR imaging findings of delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication have been well described (7, 8). T2-weighted images typically show bilateral, symmetric, confluent areas of high signal intensity in the periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale. Two case reports (9, 10) suggest reduced diffusion in the cerebral white matter in patients with delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication. The purpose of this study was to investigate these findings on diffu- 1592
2 AJNR: 24, September 2003 CARBON MONOXIDE INTOXICATION 1593 TABLE 1: Summary of clinical features in five patients with delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication Patient/Age, y/sex* Initial Manifestations of Acute CO Intoxication Lucid Interval, wk Major Clinical Findings of Delayed Encephalopathy 1/54/F Coma with multiple burn injury 3 Short-term memory loss, confabulation; much improved at 7-mo follow-up 2/71/M Sudden decrease of verbal output, free voiding 1 Aphasia, gait disturbance; much improved at 5-mo follow-up 3/63/M Abnormal repetitive behavior, progressive abulia 3 Abulia, akinetic mutism; much improved at 8-mo follow-up 4/65/F Coma, decrease of verbal output and cognitive dysfunction 4 Urinary/fecal incontinence, short-stepped gait; persistent clinical symptoms at 6-mo follow-up 5/63/F Coma, free voiding, and defecation 4 Abulia, bradykinesia, free voiding; much improved at 5-mo follow-up * In all patients except patient 4, the cause of their exposure to CO gas was a gas leakage from an under-the-floor home heating system. Patient 4 was exposed to exhaust gas from a car. sion-weighted images (DWIs) and on apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps and to assess ADC values in the bilateral, confluent lesions in the cerebral white matter in patients with delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication. Methods We retrospectively reviewed six DWIs and ADC maps in five patients (two men, three women; mean age, 63.2 years; age range, years) with delayed encephalopathy of acute CO intoxication. In our patients, CO intoxication was diagnosed on the basis of clear evidence of their exposure and a consistent clinical course. Four of the five patients were exposed to CO gas, which leaked from an under-the-floor home heating system, and one patient was exposed exhaust gas in a car. Three patients were found unconscious. They underwent hyperbaric oxygen therapy and then awakened within 24 hours. Two patients had neuropsychiatric symptoms of acute onset, without coma. All patients completely or partially recovered from the initial symptoms within several days to weeks. After apparent lucid intervals of 1 4 weeks, sudden or progressive neuropsychiatric impairments developed again. The patients clinical features are summarized in Table 1. MR images were obtained days after CO exposure. In one patient (case 4), images were acquired two times, on days 55 and 82. MR imaging was performed by using a 1.5-T unit (Magnetom Vision Plus; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). Conventional MR images were obtained with axial T2-weighted fast spin-echo (TR/TE, 4000/98), axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) (TR/TE/TI, 9000/110/2200), and sagittal T1-weighted spin-echo (500/20) sequences. DWIs and ADC maps were obtained in the axial plane by using a single-shot spin-echo echo-planar imaging sequence with the following parameters: TR/TE/NEX of 6500/98.9/1, a matrix, a cm field of view, and a 5-mm section thickness with a 1 3-mm gap. Diffusion gradients were applied along three orthogonal directions (x, y, and z axes) with three b values (0, 500, and 1000 s/mm 2 ). Iterative nonlinear least-squares fit of a monoexponential decay was used to produce a trace ADC map, which was written on an IDL platform. Conventional MR images, DWIs, and ADC maps were visually evaluated with the focus on the signal intensity of the white matter lesions. The mean and range of ADC values in the white matter lesions were calculated and compared with those of normal-looking white matter. To obtain the mean values of ADCs in each patient, the ADC value of the white matter lesion was measured in eight regions of interest (ROIs) placed in the lesions in the periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale, as depicted on T2-weighted and FLAIR images. Four ROIs were placed in the areas of low signal intensity, and the other four ROIs were positioned in the areas of isointensity on the ADC map. ADC values of the white matter that appeared normal on T2- weighted and FLAIR images were measured in three ROIs located in the periventricular or subcortical white matter or in the centrum semiovale. The size of each ROI was 2.25 cm 2, or cm 3, containing 64 voxels. The statistical significance of differences in the mean ADC values of the white matter lesions and the values of normallooking white matters was calculated with the Mann-Whitney test. A P value of.05 was considered to indicate a significant difference. Results In all five patients, DWIs showed bilateral areas of confluent high signal intensity in the periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale. These areas were similar to those seen on T2-weighted and FLAIR images (Figs 1 3). The hyperintensity varied from slight to severe. In three patients, the finding was more intense and prominent in the frontal lobes than in other regions (Fig 1). In four patients, images showed diffuse, symmetric distribution of the lesions throughout the cerebral white matter. In the remaining patient (case 2), the white matter lesions appeared asymmetric (Fig 2). The abnormality had slight hypointensity or isointensity. In four patients, most of the white matter lesions appeared isointense relative to the normal-looking white matter on ADC maps, as seen on T2-weighted and FLAIR images. Focal areas of low signal intensity were located mainly in the frontal lobes (Figs 1, 2). In the remaining patient (case 4), who had persistent neuropsychiatric impairment at 6-month clinical follow-up, the white matter lesions had diffuse low signal intensity on the ADC maps (Fig 3). The 1-month follow-up MR image of these lesions showed no substantial interval changes in the ADC. In all five patients, mean ADC values of the white matter lesions were significantly lower than those of normal-looking white matter, regardless of their isointensity or hypointensity on ADC maps (P.05). Mean ADC values of the hypointense or isointense white matter lesions, as seen on ADC maps, were mm 2 /s or
3 1594 KIM AJNR: 24, September 2003 FIG 1. Case 1. MR images obtained in a 54-year-old woman on day 25 after CO exposure. A and B, T2-weighted images (TR/TE/ NEX, 4000/98/1) show bilateral, symmetric, confluent areas of high signal intensity in both the centrum semiovale (A) and periventricular white matter (B). The high intensity appears more prominent in the frontal lobes than elsewhere. C and D, ADC maps (calculated from DWIs [6500/98/1, b 0 and 1000 s/mm 2 ]) obtained at the same levels as in A and B, respectively, show focal areas of low signal intensity (decreased diffusion) in the bilateral frontal lobes. Most of the remaining centrum semiovale and periventricular white matter appears isointense. DWIs at the same levels showed confluent high signal intensity in the centrum semiovale and periventricular white matter. The appearance was similar to that on the T2- weighted images (not shown) and mainly resulted from a T2 shine-through effect. FIG 2. Case 2. MR images obtained in a 71- year-old man on day 41 after CO exposure. A, FLAIR image (TR/TE/TI/NEX, 9000/110/2200/1) shows asymmetric distribution of the high-intensity lesions in the periventricular white matter and corpus callosum. B, DWI (TR/TE/NEX, 6500/98/1; b 1000 s/mm 2 ) shows similar high signal intensity in the periventricular white matter and corpus callosum. The high intensity is more prominent in the right frontal lobe and on the right side of the genu of the corpus callosum than elsewhere. C, ADC map shows a focal area of subtle low signal intensity in the right frontal lobe (arrow). Other white matter lesions appear isointense.
4 AJNR: 24, September 2003 CARBON MONOXIDE INTOXICATION 1595 Case 4. MR images obtained in a 65-year-old woman on day 55 after CO exposure. A, FLAIR image (TR/TE/TI/NEX, 9000/110/2200/1) shows diffuse high-intensity lesions in the periventricular white matter. B, DWI (TR/TE/NEX, 6500/98/1; b 1000 s/mm 2 ) shows confluent high signal intensity in the same periventricular white matter. C, ADC map shows diffuse low signal intensity in the periventricular white matter. FIG 3. TABLE 2: Summary of findings on conventional MR images, DWIs, and ADC maps, with ADC values in five patients with delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication Patient Interval to Imaging, d* Findings on T2-Weighted and FLAIR Images 1 25 Diffuse high intensity in the, more prominent in both frontal lobes; high intensity in both globi pallidus 2 41 Asymmetric high intensity in the PVWM, centrum semiovale, and corpus callosum; more prominent on R side 3 56 Diffuse high intensity in the Findings on DWIs Diffuse high intensity in the, more prominent in both frontal lobes Asymmetric high intensity in the PVWM, centrum semiovale, and corpus callosum; more prominent on the R side Diffuse high intensity in the Findings on ADC Maps Focal areas of low intensity in both frontal lobes Focal areas of low intensity in R frontal lobe Focal areas of low intensity in both frontal lobes Diffuse low intensity in the PVWM Mean ADC Values, 10 3 mn 0.61 ( )/ ( )/ ( )/ Diffuse high intensity in the Diffuse high intensity in the 0.56 ( )/ No change No change No change 0.53 ( )/ Diffuse high intensity in the Diffuse high intensity in the Focal areas of low 0.75 ( )/0.94, intensity in both more prominent in both frontal frontal lobes lobes; high intensity in both globi pallidus Note. PVWM indicates periventricular white matter. * Interval between CO Exposure and MR Imaging. Data are the value in the WM lesions (range)/value in normal-looking WM on T2-weighted images. Follow-up MR examination mm 2 /s, respectively, whereas the mean ADC value of normal-looking white matter was mm 2 /s, P.05). The mean ADC value was the lowest in the patient with persistent neuropsychiatric impairment on follow-up (case 4), whereas it was the highest in the patient with relatively mild neuropsychiatric symptoms (case 5). The findings on conventional MR images, DWIs, and ADC maps and the ADC values in the white matter lesions are summarized in Table 2. Discussion The principal neuropathologic feature of delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication is diffuse white matter abnormalities. Three types of white matter abnormalities have been described (5, 6): multifocal necrotic lesions predominantly within the centrum semiovale and commissures, extensive necrotic zones in the periventricular white matter with extension across the corpus callosum and commissures, and
5 1596 KIM AJNR: 24, September 2003 patchy or extensive demyelination of the periventricular and deep central white matter. Selective white matter demyelination is thought to be more closely associated with delayed postanoxic encephalopathy, whereas white matter necrosis is more closely associated with a monophasic, nonrelapsing illness. However, the clinical and pathologic findings may overlap. The pathogenesis of the delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication remains uncertain. The results of the present study indicate that the white matter lesions have decreased diffusivity, although in four patients, most white matter lesions appeared isointense on the ADC map. In those patients, the high signal intensity on DWI is thought to be mainly due to a T2 shine-through effect. Our results suggest that, in delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication, the restricted diffusion of the white matter lesion develops late after the patient s exposure to CO and persists longer than usual 2 3 weeks after an acute ischemic infarct. In acute stroke, the ADC value is most reduced at 8 32 hours, it remains markedly reduced for 3 5 days, and it returns to baseline at 1 4 weeks (11). Acute cell necrosis with cytotoxic edema, as seen in acute ischemic infarction, does not seem to occur. However, tissue injury caused by slowly progressive cytotoxic edema related to the direct toxic effect of CO gas or some other unknown mechanism results in reduced diffusion in the delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication. The latency of the clinical symptoms, the delayed appearance of MR imaging findings (including decreased diffusivity), and the pathologic findings might reflect late-developing biochemical changes that becomes evident when some metabolites are accumulated. Murata et al (9) described serial diffusion imaging findings in a case of delayed encephalopathy of CO poisoning. ADC values in the frontal white matter appeared to be within the normal range on day 23 after CO exposure, but they progressively decreased until day 38 after exposure, then slowly increased. The values were higher values at day 118 after exposure than they were immediately after the appearance of sequelae. In one of two patients with CO intoxication reported by Teksam et al (10), follow-up MR imaging was performed 2 months after their initial admission, when the neurologic symptoms of delayed encephalopathy developed. The images showed additional aggravation of the lesions in bilateral periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale, with new development of subtle restriction of water diffusion in the cerebral white matter. This last finding completely resolved on another follow-up image obtained 10 months after the initial admission. The MR imaging findings in our cases were similar to those of the previous reports (10, 11). One patient (case 4) (Fig 3) of the present series did not have clinical improvement at 6-month follow-up, and the mean ADC values of the white matter lesions remained decreased on days 55 and 82. Singhal et al (12) reported diffusion MR imaging findings in three patients of anoxic encephalopathy. One had acute CO intoxication, and diffusion MR imaging performed 3 days after the patient s exposure to CO gas showed decreased ADC values in the bilateral globi pallidus, the hippocampus, and temporal and occipital cortices. No abnormality was observed in the periventricular white matter or centrum semiovale, unlike the white matter lesions noted in delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication. However, Chalela et al (13) described symmetric areas of restricted diffusion in the periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale, which were observed in seven patients with anoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. These patients included one with acute CO intoxication who underwent brain MR imaging within 7 days of the insult. The authors speculated that, in their patients, the low ADC values related to acute myelinopathy likely represented early cytotoxic edema secondary to cellular energy failure. Unfortunately, further follow-up imaging was not performed in their study. The duration and degree of the decreased diffusivity in the white matter may vary, and it may be correlated with the clinical outcome, depending on the severity of the CO intoxication. In the present study, patient 4 (Fig 3) had the lowest ADC value and an area of low signal intensity on the ADC map that was wider than that of the other patients. This patient also had a poorer clinical course and a smaller area of focal low signal intensity on the ADC map. This observation suggests that the extent and degree of low ADC values in the white matter are correlated with the clinical course, and such findings may possibly enable us to predict the prognosis. Further systematic studies of diffusion imaging, including diffusion tensor imaging, with larger number of patients are needed to assess the prognosis and to clarify the pathogenesis of delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication. Conclusion In all five patients with delayed encephalopathy of CO intoxication, DWIs showed diffuse, confluent areas of high signal intensity in the periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale. These areas were similar to those seen on T2-weighted and FLAIR images. On ADC maps, the white matter lesions appeared as either diffuse isointensity with focal hypointensity (n 4) or diffuse hypointensity (n 1). Mean ADC values of the white matter lesions were significantly lower than those of normal-looking white matter in all five patients, regardless of the isointensity or hypointensity on ADC maps. We speculate that latedeveloping cytotoxic edema or some other mechanism related to the accumulation of unknown toxic biochemical products results in reduced diffusion. Further studies of diffusion imaging with larger numbers of patients are needed to correlate the extent and degree of low ADC values in the white matter with the clinical outcomes and prognosis. References 1. Choi IS. Delayed neurologic sequelae in carbon monoxide intoxication. Arch Neurol 1983;40:
6 AJNR: 24, September 2003 CARBON MONOXIDE INTOXICATION Ginsberg MD. Delayed neurological deterioration following hypoxia. Adv Neurol 1979;26: Roychowdhury S, Maljian JA, Galetta SL, Grossman RI. Postanoxic encephalopathy: diffusion MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1998;22: Dooling EC, Richardson P Jr. Delayed encephalopathy after strangling. Arch Neurol 1976;33: Ginsberg MD, Myers RE, McDonagh BF. Experimental carbon monoxide encephalopathy in the primate, II: clinical aspects, neuropathology, and physiologic correlation. Arch Neurol 1974;30: Lapresle J, Fardeau M. The central nervous system and carbon monoxide poisoning, II: anatomical study of brain lesions following intoxication with carbon monoxide. Prog Brain Res 1967;24: Chang KH, Han MH, Kim HS, Wie BA, Han MC. Delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide intoxication: MR imaging features and distribution of cerebral white matter lesions. Radiology 1992;184: Horowitz AL, Kaplan R, Sarpel G. Carbon monoxide toxicity: MR imaging in the brain. Radiology 1987;162: Murata T, Kimura H, Kado H, et al. Neuronal damage in the interval form of CO poisoning determined by serial diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging plus 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;71: Teksam M, Casey SO, Michel E, Liu H, Truwit CL. Diffusionweighted MR imaging findings in carbon monoxide poisoning. Neuroradiology 2002;44: Schaefer PW, Grant E, Gonzalez RG. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 2000;217: Singhal A, Topcuoglu MA, Koroshetz WJ. Diffusion MRI in three types of anoxic encephalopathy. J Neurol Sciences 2002; 196: Chalela JA, Wolf RL, Maldjian JA, Kasner SE. MRI identification of early white matter injury in anoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Neurology 2001;56:
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Biopsy-Proven Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in iopsy-proven reutzfeldt-jakob Disease Hyo-heol Kim, MD 1 Kee-Hyun hang, MD 1 In han Song, PhD 1 Sang Hyun Lee, MD 1 ae Ju Kwon, MD 1 Moon Hee Han, MD 1 Sang-Yun Kim, MD
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in iopsy-proven reutzfeldt-jakob Disease Hyo-heol Kim, MD 1 Kee-Hyun hang, MD 1 In han Song, PhD 1 Sang Hyun Lee, MD 1 ae Ju Kwon, MD 1 Moon Hee Han, MD 1 Sang-Yun Kim, MD
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Brain Injury After Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Early and Late Complications
 T and MRI of arbon Monoxide Poisoning Neuroradiology Pictorial Essay ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.199.82 on 02/28/18 from IP address 46.3.199.82. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights
T and MRI of arbon Monoxide Poisoning Neuroradiology Pictorial Essay ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.199.82 on 02/28/18 from IP address 46.3.199.82. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
CO poisoning causes serious damage to the brain and cardiac
 REVIEW ARTICLE The Role of MR Imaging in Assessment of Brain Damage from Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Review of the Literature T. Beppu ABSTRACT SUMMARY: The aim of this article is to review how MR imaging
REVIEW ARTICLE The Role of MR Imaging in Assessment of Brain Damage from Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Review of the Literature T. Beppu ABSTRACT SUMMARY: The aim of this article is to review how MR imaging
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Brain MRI Findings of Carbon Disulfide Poisoning
 Brain MRI Findings of Carbon Disulfide Poisoning Joo Hee Cha, MD 1, 2 Sam Soo Kim, MD 2 Heon Han, MD 2 Rok Ho Kim, MD 3 Sang Hyuk Yim, MD 4 Mi Jung Kim, MD 5 Objective: To evaluate the findings of brain
Brain MRI Findings of Carbon Disulfide Poisoning Joo Hee Cha, MD 1, 2 Sam Soo Kim, MD 2 Heon Han, MD 2 Rok Ho Kim, MD 3 Sang Hyuk Yim, MD 4 Mi Jung Kim, MD 5 Objective: To evaluate the findings of brain
Masayuki Maeda, Tatsuya Yamamoto, Shouichiro Daimon, Hajime Sakuma, and Kan Takeda
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :6 66, April 001 Arterial Hyperintensity on Fast Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Images: A Subtle Finding for Hyperacute Stroke Undetected by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Masayuki
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :6 66, April 001 Arterial Hyperintensity on Fast Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Images: A Subtle Finding for Hyperacute Stroke Undetected by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Masayuki
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a sensitive technique
 Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0842 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.S. Seo K.-H. Chang D.G. Na B.J. Kwon D.H. Lee High b-value Diffusion (b 3000 s/mm 2 )MR Imaging in Cerebral Gliomas at 3T: Visual and
Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0842 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.S. Seo K.-H. Chang D.G. Na B.J. Kwon D.H. Lee High b-value Diffusion (b 3000 s/mm 2 )MR Imaging in Cerebral Gliomas at 3T: Visual and
Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
1 Maiser. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy. Samuel Maiser, MD. Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota
 1 Maiser 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Samuel Maiser, MD Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota Case This is a 57-year-old right-handed male with a history of
1 Maiser 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Samuel Maiser, MD Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota Case This is a 57-year-old right-handed male with a history of
Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department
 298 / = Abstract = Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department Sung Pil Chung, M.D, Suk Woo Lee, M.D., Young Mo Yang, M.D., Young Rock Ha, M.D., Seung Whan Kim, M.D., and
298 / = Abstract = Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department Sung Pil Chung, M.D, Suk Woo Lee, M.D., Young Mo Yang, M.D., Young Rock Ha, M.D., Seung Whan Kim, M.D., and
Original Article Brainstem auditory evoked potentials in patients with delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):14000-14005 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0025428 Original Article Brainstem auditory evoked potentials in patients with delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):14000-14005 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0025428 Original Article Brainstem auditory evoked potentials in patients with delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide
Toxins in Brain! Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging of Toxic Leukoencephalopathy A Pictorial Essay
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 311-319 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.901791 REVIEW ARTICLE Received: 2016.10.02 Accepted: 2016.10.11 Published: 2017.06.13 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 311-319 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.901791 REVIEW ARTICLE Received: 2016.10.02 Accepted: 2016.10.11 Published: 2017.06.13 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging features of intracranial lesions
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
Marchiafava Bignami Disease (MBD) and Diffusion Tensor Image (DTI) Tractography. Priscilla Chukwueke, MD, MPH
 Marchiafava Bignami Disease (MBD) and Diffusion Tensor Image (DTI) Tractography Priscilla Chukwueke, MD, MPH INTRODUCTION Definition: A rare CNS disease characterized by demyelination of the Corpus Callosum.
Marchiafava Bignami Disease (MBD) and Diffusion Tensor Image (DTI) Tractography Priscilla Chukwueke, MD, MPH INTRODUCTION Definition: A rare CNS disease characterized by demyelination of the Corpus Callosum.
CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype S E V E N
 CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype S E V E N CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype R. van den Boom S.A.J. Lesnik Oberstein A.A. van den
CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype S E V E N CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype R. van den Boom S.A.J. Lesnik Oberstein A.A. van den
Hypoglycemia is the sudden decrease in serum glucose level
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E.G. Kang S.J. Jeon S.S. Choi C.J. Song I.K. Yu Diffusion MR Imaging of Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: MR imaging features of HE have not been fully established.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E.G. Kang S.J. Jeon S.S. Choi C.J. Song I.K. Yu Diffusion MR Imaging of Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: MR imaging features of HE have not been fully established.
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme
 Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Sawada J, Orimoto R, Misu T, Katayama T, Aizawa H, Asanome A, Takahashi K, Saito T, Anei R, Kamada K, Miyokawa N, Takahashi T, Fujihara K, Hasebe N.
 Mult Scler (2014.9) 20(10):1413-1416. A case of pathology-proven neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with Sjögren syndrome manifesting aphasia and apraxia due to a localized cerebral white matter lesion.
Mult Scler (2014.9) 20(10):1413-1416. A case of pathology-proven neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with Sjögren syndrome manifesting aphasia and apraxia due to a localized cerebral white matter lesion.
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum
 Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
 Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
SHORTLY AFTER ITS FIRST DEpiction
 OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
False-negative and False-positive Diffusion-weighted MR Findings in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Stroke-like Episodes
 JRural Med 2005 ; 1 : 27 32 Original Article False-negative and False-positive Diffusion-weighted MR Findings in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Stroke-like Episodes Shuzo Shintani 1,HiroakiYokote 1,KaoruHanabusa
JRural Med 2005 ; 1 : 27 32 Original Article False-negative and False-positive Diffusion-weighted MR Findings in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Stroke-like Episodes Shuzo Shintani 1,HiroakiYokote 1,KaoruHanabusa
POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES
 Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Marchiafava-Bignami Disease
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
Rapid Regression of White Matter Changes in Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy
 www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 18(4) : 357-361, 2014 pissn 1226-9751 / eissn 2288-3800 Case Report Rapid Regression of White Matter Changes in Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy Sang-wook Son, Kye-ho Lee, Dong-soo Yoo
www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 18(4) : 357-361, 2014 pissn 1226-9751 / eissn 2288-3800 Case Report Rapid Regression of White Matter Changes in Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy Sang-wook Son, Kye-ho Lee, Dong-soo Yoo
Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies the Clinically Relevant Small-Penetrator Infarcts
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies the Clinically Relevant Small-Penetrator Infarcts Jamary Oliveira-Filho, MD; Hakan Ay, MD; Pamela W. Schaefer, MD; Ferdinando
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies the Clinically Relevant Small-Penetrator Infarcts Jamary Oliveira-Filho, MD; Hakan Ay, MD; Pamela W. Schaefer, MD; Ferdinando
The estimated annual incidence of central nervous system
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) WCPCG 2014
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE
 TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
Neuroradiology of AIDS
 Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature.
 Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature. Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Chaves, M. S. TORONCHIK, P. M.
Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature. Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Chaves, M. S. TORONCHIK, P. M.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance imaging: a case report
 Chuang et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-019-0310-z CASE REPORT Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance
Chuang et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-019-0310-z CASE REPORT Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance
Hypoxic Ischemic Injury in adult patients post cardiac arrest: A Pictoral essay
 Hypoxic Ischemic Injury in adult patients post cardiac arrest: A Pictoral essay Poster No.: C-0558 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Bhatia; New Delhi/IN Ischemia
Hypoxic Ischemic Injury in adult patients post cardiac arrest: A Pictoral essay Poster No.: C-0558 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Bhatia; New Delhi/IN Ischemia
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in the Acute Phase of Transient Ischemic Attacks
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:77 83, January 2002 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in the Acute Phase of Transient Ischemic Attacks Alex Rovira, Antoni Rovira-Gols, Salvador Pedraza, Elisenda Grivé, Carlos Molina,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:77 83, January 2002 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in the Acute Phase of Transient Ischemic Attacks Alex Rovira, Antoni Rovira-Gols, Salvador Pedraza, Elisenda Grivé, Carlos Molina,
Dong Gyu Na, Vincent N. Thijs, Gregory W. Albers, Michael E. Moseley, and Michael P. Marks. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25: , September 2004
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari
 Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
CSM is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction
 Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
MR Assessment of Myelination in Infants and Children: Usefulness of Marker Sites
 731 MR ssessment of Myelination in Infants and Children: Usefulness of Marker Sites C. Roger ird 1 Mary Hedberg urton P. Drayer Paul J. Keller Richard. Flom John. Hodak retrospective study was made of
731 MR ssessment of Myelination in Infants and Children: Usefulness of Marker Sites C. Roger ird 1 Mary Hedberg urton P. Drayer Paul J. Keller Richard. Flom John. Hodak retrospective study was made of
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies
 Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:186-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.186 Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation Joonseok
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:186-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.186 Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation Joonseok
Delayed Encephalopathy and Cognitive Sequelae after Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Report of a Case and Review of the Literature
 Case Report Delayed Encephalopathy and Cognitive Sequelae after Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Report of a Case and Review of the Literature Toungrat Tapeantong MD*, Niphon Poungvarin MD, FRCP, FRCP(E)*
Case Report Delayed Encephalopathy and Cognitive Sequelae after Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Report of a Case and Review of the Literature Toungrat Tapeantong MD*, Niphon Poungvarin MD, FRCP, FRCP(E)*
The Asymmetric Mamillary Body: Association with Medial Temporal Lobe Disease Demonstrated with MR
 The Mamillary Body: Association with Medial Temporal Lobe Disease Demonstrated with MR Alexander C. Mamourian, Lawrence Rodichok, and Javad Towfighi PURPOSE: To determine whether mamillary body atrophy
The Mamillary Body: Association with Medial Temporal Lobe Disease Demonstrated with MR Alexander C. Mamourian, Lawrence Rodichok, and Javad Towfighi PURPOSE: To determine whether mamillary body atrophy
Case Report. Case Report
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
Introduction. Cytokine and Chemokine Profiles in Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Marked Elevation of Interleukin-6 in Cerebrospinal Fluid
 Cytokine and Chemokine Profiles in Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Marked levation of Interleukin-6 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Toshimitsu Ide, Y Kamijo, A Ide, K Yoshimura, T ishikawa, K Soma, H Mochizuki
Cytokine and Chemokine Profiles in Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Marked levation of Interleukin-6 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Toshimitsu Ide, Y Kamijo, A Ide, K Yoshimura, T ishikawa, K Soma, H Mochizuki
Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease
 Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease Giuseppe Fariello, Carlo Dionisi-Vici, Cinzia Orazi, Saverio Malena, Andrea Bartuli, Paolo Schingo, Enza Carnevale, Isora Saponara, and Gaetano Sabetta
Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease Giuseppe Fariello, Carlo Dionisi-Vici, Cinzia Orazi, Saverio Malena, Andrea Bartuli, Paolo Schingo, Enza Carnevale, Isora Saponara, and Gaetano Sabetta
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics. Disclosures. Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor 4/14/2017
 Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases
 White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
Marchiafava-Bignami Disease: Longitudinal MR Imaging and MR Spectroscopy Study
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:249 253, February 2003 Case Report Marchiafava-Bignami Disease: Longitudinal MR Imaging and MR Spectroscopy Study Anna Gambini, Andrea Falini, Lucia Moiola, Giancarlo Comi, and
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:249 253, February 2003 Case Report Marchiafava-Bignami Disease: Longitudinal MR Imaging and MR Spectroscopy Study Anna Gambini, Andrea Falini, Lucia Moiola, Giancarlo Comi, and
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain John R. Hesselink, M.D. T1-Weighted Images Normal White Matter Contents Axons with envelope of myelin Neuroglia
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain John R. Hesselink, M.D. T1-Weighted Images Normal White Matter Contents Axons with envelope of myelin Neuroglia
B. Understanding radiation- and chemotherapy-induced changes after treatment of brain tumours
 B. Understanding radiation- and chemotherapy-induced changes after treatment of brain tumours Poster No.: A-083 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Invited Speaker Authors: Y. Özsunar; Aydin/TR Keywords: Neuroradiology
B. Understanding radiation- and chemotherapy-induced changes after treatment of brain tumours Poster No.: A-083 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Invited Speaker Authors: Y. Özsunar; Aydin/TR Keywords: Neuroradiology
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction
 Original Article ISSN (o):2321 7251 Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction Kalidindi Ravi Kumar Varma 1, Chaparla Lakshmana Rao 2 1 - Associate Professor,Maharajah
Original Article ISSN (o):2321 7251 Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction Kalidindi Ravi Kumar Varma 1, Chaparla Lakshmana Rao 2 1 - Associate Professor,Maharajah
A Case of Anterograde Amnesia with Bilateral Hippocampus Involvement After Acute Glufosinate Ammonium Intoxication
 www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 18(4) : 352-356, 2014 pissn 1226-9751 / eissn 2288-3800 Case Report A Case of Anterograde Amnesia with Bilateral Hippocampus Involvement After Acute Glufosinate Ammonium Intoxication
www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 18(4) : 352-356, 2014 pissn 1226-9751 / eissn 2288-3800 Case Report A Case of Anterograde Amnesia with Bilateral Hippocampus Involvement After Acute Glufosinate Ammonium Intoxication
Magnetic resonance imaging (MR!) provides
 0 Wallerian Degeneration of the Pyramidal Tract in Capsular Infarction Studied by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jesiis Pujol, MD, Josep L. Marti-Vilalta, MD, Carme Junqu6, PhD, Pere Vendrell, PhD, Juan Fernandez,
0 Wallerian Degeneration of the Pyramidal Tract in Capsular Infarction Studied by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jesiis Pujol, MD, Josep L. Marti-Vilalta, MD, Carme Junqu6, PhD, Pere Vendrell, PhD, Juan Fernandez,
Cerebrovascular Disorders. Blood, Brain, and Energy. Blood Supply to the Brain 2/14/11
 Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
Yi-Te Lin 1, Shao-Yuan Chen 1,2,6, Chung-Ping Lo 3, Jiunn-Tay Lee 4, Chung-Fen Tsai 1,6, Ping-Keung Yip 1,6, Vinchi Wang 1,6, Yu-Ming Fan 5,6
 57 Utilizing Cerebral Perfusion Scan and Diffusion-tensor MR Imaging to Evaluate the Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Carbon Monoxide-induced Delayed Neuropsychiatric Seqeulae- A Case Report and
57 Utilizing Cerebral Perfusion Scan and Diffusion-tensor MR Imaging to Evaluate the Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Carbon Monoxide-induced Delayed Neuropsychiatric Seqeulae- A Case Report and
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
MRI of Pathological Aging Brain
 MRI of Pathological Aging Brain Yukio Miki Department of Radiology, Osaka City University A variety of pathological changes occur in the brain with aging, and many of these changes can be identified by
MRI of Pathological Aging Brain Yukio Miki Department of Radiology, Osaka City University A variety of pathological changes occur in the brain with aging, and many of these changes can be identified by
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans
 PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
Takaaki Beppu Shunrou Fujiwara Hideaki Nishimoto Atsuhiko Koeda Shinsuke Narumi Kiyoshi Mori Kuniaki Ogasawara Makoto Sasaki
 J Neurol (2012) 259:1698 1705 DOI 10.1007/s00415-011-6402-5 ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Fractional anisotropy in the centrum semiovale as a quantitative indicator of cerebral white matter damage in the subacute
J Neurol (2012) 259:1698 1705 DOI 10.1007/s00415-011-6402-5 ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Fractional anisotropy in the centrum semiovale as a quantitative indicator of cerebral white matter damage in the subacute
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Arch Neurol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2008 November 5.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Arch Neurol. 2008 June ; 65(6): 812 816. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.6.812. 7T MRI: New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Arch Neurol. 2008 June ; 65(6): 812 816. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.6.812. 7T MRI: New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple
Original Article INTRODUCTION. Abstract
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/19 Patterns of Restricted Diffusion within Corpus Callosum in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy and its Significance
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/19 Patterns of Restricted Diffusion within Corpus Callosum in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy and its Significance
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI
 Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences
 Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
Magnetic Resonance Study of White Matter Lesions: A Cross-sectional Study
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/559 Magnetic Resonance Study of White Matter Lesions: A Cross-sectional Study Mallikarjun M Devareddy 1, Shilpa Devakar
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/559 Magnetic Resonance Study of White Matter Lesions: A Cross-sectional Study Mallikarjun M Devareddy 1, Shilpa Devakar
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists.
 Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
MRI of the Brain: A Primer on What, How, Why, and When. September Amit Malhotra, Harvard Medical School, Year- IV. Gillian Lieberman, MD
 September 2000 MRI of the Brain: A Primer on What, How, Why, and When Hornak, J.P. The Basics of MRI. 1996-2000 Amit Malhotra, Harvard Medical School, Year- IV Magnetic Resonance Imaging A Brief History
September 2000 MRI of the Brain: A Primer on What, How, Why, and When Hornak, J.P. The Basics of MRI. 1996-2000 Amit Malhotra, Harvard Medical School, Year- IV Magnetic Resonance Imaging A Brief History
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI)
 Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging
 Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy
 Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy Schepers S, Barthels C Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2011, Nov. 3 Patient: 67 year(s), male Authors' Institution Department of Radiology, Jessa ziekenhuis campus
Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy Schepers S, Barthels C Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2011, Nov. 3 Patient: 67 year(s), male Authors' Institution Department of Radiology, Jessa ziekenhuis campus
First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body
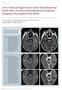 Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to
 125 A B C Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to obtain entire dimension of the hippocampal body.
125 A B C Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to obtain entire dimension of the hippocampal body.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy (MIE) is a rare
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Kim D.G. Na E.Y. Kim J.H. Kim K.R. Son K.H. Chang MR Imaging of Metronidazole-Induced Encephalopathy: Lesion Distribution and Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Findings BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Kim D.G. Na E.Y. Kim J.H. Kim K.R. Son K.H. Chang MR Imaging of Metronidazole-Induced Encephalopathy: Lesion Distribution and Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Findings BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
