Magnetic Resonance Study of White Matter Lesions: A Cross-sectional Study
|
|
|
- Mervyn Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Print ISSN: Online ISSN: X DOI: /ijss/2016/559 Magnetic Resonance Study of White Matter Lesions: A Cross-sectional Study Mallikarjun M Devareddy 1, Shilpa Devakar 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiology, Navodaya Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Raichur, Karnataka, India, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiology, Raichur Institute of Medical Sciences, Raichur, Karnataka, India Abstract Background: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an important noninvasive imaging modality with very high sensitivity for detecting white matter lesions. The objectives are to evaluate the role of MRI in white matter diseases, to establish an accurate diagnosis. To assess the severity and extent of the underlying lesion in various conditions and to demonstrate the different patterns of abnormal myelination in white matter diseases. Materials and Methods: A total of 50 patients who were clinically suspected of white matter diseases underwent MR imaging in using 1.5T PHILIPS Achieva machine. Various MR sequences were used in imaging. Results: Among the 50 patients, 26% had leukodystrophies, 16% had acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (16%) and 16% had vacuolating leukoencephalopathies, 12% had hypomyelination, 8% had multiple sclerosis and microvascular ischemic changes (SVIC), 4% each of Leigh s disease, human immunodeficiency virus encephalopathy, nonspecific demyelination, and 2% had progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Patients in the pediatric age group constituted 82% of the total study group with slight male predominance. Conclusion: MR imaging has become the primary imaging modality in patients with white matter diseases and plays an important role in the identification, localization, and characterization of underlying white matter abnormalities in affected patients. Its multiplanar imaging capability and excellent gray-white matter resolution make MRI very sensitive in detecting subtle white matter lesions. In our study, we observed that Fluid attenuated inversion recovery sequence has better sensitivity for white matter lesions especially those in periventricular locations. Specificity of MR imaging can be improved by MR Spectroscopy studies. Key words: Leukodystrophies, Leukoencephalopathy, Magnetic resonance imaging, White matter diseases INTRODUCTION Only recently with the advances in imaging technology have white matter diseases of central nervous system been extensively studied and understood. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are the imaging modalities which are currently available for the investigation of these diseases and it has been proven beyond doubt that MRI is far superior to CT and the imaging modality of the choice in these diseases. Access this article online Month of Submission : Month of Peer Review : Month of Acceptance : Month of Publishing : Functional MRI of brain was introduced by Oqawa et al., in 1992, and developed by Rosen et al. In 2003, Paul Lauterbur and Sir Peter Mansfield awarded jointly Nobel Prize for their discoveries concerning MRI. 1 MRI has a very high sensitivity for detecting white matter lesions due to its excellent gray-white matter resolution. Multiplanar imaging is possible only with MRI, which helps in the detection and localization of lesions. It is also found to be ideal in posterior fossa imaging and allows simultaneous imaging of extracerebral sites such as spinal cord and optic nerve. MRI thus is very helpful in defining the pathogenesis and in the early diagnosis of disease and in monitoring the treatment. Recent advances such as MR spectroscopy (MRS), diffusion imaging, and magnetization transfer imaging have revolutionized the role of MRI in increasing the specificity of diagnosis in many of these conditions. By correlating the clinical features and biochemical analysis with the MRI findings, we can come to a diagnosis in the majority of cases. Many of the diseases if detected early Corresponding Author: Dr. Mallikarjun M Devareddy, Navodaya Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Raichur, Karnataka, India. Phone: mallikarjunclarity@gmail.com 13 International Journal of Scientific Study November 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8
2 are reversible, and thus, play the major role of MRI in the early diagnosis so that the treatable conditions among them can be detected early and cured. Ashikaga et al. evaluated cases of HSE with conventional SE and fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequences and opined that the lesion conspicuity in the gray and white matter was found to be greatest with FLAIR sequence. 2 This study is selected because of the important role of MRI in investigating white matter diseases and also to evaluate the data obtained from cranial MRI in these diseases. The objectives of the study were to evaluate the role of MRI in white matter diseases, to assess the severity and extent of the underlying lesion in various conditions of white matter diseases and to demonstrate the different patterns of abnormal myelination in white matter diseases. MATERIALS AND METHODS The source of data for the study is patients from Navodaya Medical College Hospital and Research Centre. All patients referred to the Department of Radio Diagnosis with clinical history suspicious of white matter diseases and the patients with incidental finding of white matter diseases/ lesions in all age groups in a period of 1-year from October 2015 to September 2016 were included in the study. The patients with clinical suspicion of post-traumatic white matter injury, intracranial tumors and metastatic disease, history of claustrophobia and history of metallic implants insertion, cardiac pacemakers, and metallic foreign body in situ were excluded from the study. A total of 50 patients were included. Imaging was done with 1.5 Tesla PHILIPS Achieva machine using sense head coils. Sequences like localizer sequence conventional spin echo, sagittal FLAIR, short time inversion recovery, T1 FS, axial and sagittal T1-images, axial, sagittal and coronal T2-images, proton density images, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map and axial gray matter only and white matter only sequences were used for imaging purpose. Other optional sequences like diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tracking; IV contrast study; time of flight (TOF) angiography were included in the study as and when required. MRI findings were correlated with biochemical parameters (for metabolites) where feasible to increase the accuracy of diagnosis. A circulatory head coil was used for excitation and signal reception. Standard head coil was used for the acquisition of images. The MR imaging protocol is part of our routine protocol and comprises T2-weighted (T2W) (axial and coronal), T1-weighted (T1W) (axial), FLAIR (axial), DWI (axial), gradient recalled echo (axial), susceptibility weighted imaging (axial) and magnetic resonance angiography (TOF-circle of Willis and neck). The total imaging time with 1.5 T-whole body MR imager was approximately 20 min 53 s. After localizer images were obtained, the axial images were titled parallel to the corpus callosum. The sagittal images were planned on the axial sections. The coronal images were planned on the sagittal/axial sections. For PD + T2W axial imaging, we used a turbo spin echo sequence with a repetition time (TR) of 3380 ms; echo time (TE) of 14,86 ms; 5 mm section thickness; 30 mm intersection gap; 150 flip angle; 230 nm field of view; matrix and imaging time of 3 min 7 s. For T1W axial imaging, we used a turbo spin echo sequence with a repetition time (TR) of 500 ms, echo time (TE) of 8.1 ms, 5 mm section thickness, 30 mm intersection gap, 90 flip angle; 230 mm field of view, matrix and imaging time of 3 min 55 s. For FLAIR axial imaging, we used a turbo spin echo sequence with a repetition time (TR) of 9000 ms, echo time (TE) of 87 ms, 5 mm section thickness, 30 mm intersection gap, 150 flip angle, 230 mm field of view, matrix and imaging time of 4 min 32 s. For T2W coronal imaging, we used a turbo spin echo sequence with a repetition time (TR) of 3850 ms, echo time (TE) of 114 ms, 5 mm section thickness, 30 mm intersection gap, 150 flip angle, 210 mm field of view, matrix and imaging time of 2 min 39 s. Diffusion-weighted axial imaging was performed with a single shot echo planar sequence with three diffusion weighted b values of and 1000 s/mm 2. The imaging parameters were a repetition time (TR) of 4200 ms, echo time (TE) of 109 ms, 5 mm section thickness, 30 mm intersection gap, 90 flip angle, 230 mm field of view, matrix and imaging time of 52 s. ADC maps were produced from diffusion weighted images. For gradient axial imaging, we used a gradient echo sequence with a repetition time (TR) of 860 ms, echo time (TE) of 26 ms, 5 mm section thickness, 30 mm intersection gap, 20 flip angle, 230 mm field of view, matrix and imaging time of 2 min 58 s. About 3 ml of gadolinium based contrast was used for selected cases. SV PRESS 144, SV PRESS 31 Single voxel spectroscopy; 2D PRESS 144 multi voxel spectroscopy was performed at TE of 144 ms and 31 ms, TR was at 2000 ms. In single voxel studies, the voxel is placed on the lesion so that it covers the maximum area of the solid tumoral area. In multivoxel spectroscopy, the voxel was extended to cover perilesional area in selective cases of high-grade tumors, avoiding areas of cysts or necrosis and with minimal contamination from the surrounding non-tumoral tissue. Volume of interest size ranged between 1.5 cm 1.5 cm 1.5 cm (3.4 ml) and 2 cm 2 cm 2 cm (8 ml). We used PRESS and T1 FFE postcontrast sequence as localization sequence with International Journal of Scientific Study November 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8 14
3 5 mm thickness. Spectroscopy was avoided in small lesions close to the bone and sinuses. MultiHance (Gadobenate Dimeglumine) was used as contrast agents in dose of 0.1 mmol/kg body weight. Post-contrast coronal and axial T1W were taken and sagittal T1W were taken wherever necessary. Special sequence like FLAIR sequence was obtained in all cases. The images were analyzed for lesion number, size, location, signal intensity changes, mass effect, and contrast enhancement. Detailed clinical history was noted in patients admitted in our hospital and for referred cases from outside hospitals as per the pro forma. All patients were followed up to reach a therapeutic/ biopsy diagnosis. Findings of cerebrospinal fluid examination, muscle or nerve biopsy, electromyography, and electroencephalography were compared with the MRI features. The symptomatic response of the patient to medical therapy was noted which helped in the retrospective confirmation of the diagnosis, and thus the final outcome of the disease was recorded. Biochemical analysis could not be performed since the facility is not available in our institution. However, we could retrospectively confirm our diagnosis from patients who were referred to higher center and came back to our institute for follow-up treatment. Data were entered into Microsoft Excel data sheet and analyzed using Epi Info 7 version software. Categorical data were represented in the form of frequencies and proportions. Bar diagrams and Pie chart were plotted to represent graphically wherever necessary. RESULTS In the study, it was observed that most common white matter disease was leukodystrophy (26%). Leukodystrophies includes adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD), Alexander disease, Canavan disease, Krabbes disease, metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD), and nonspecific leukodystrophy. Second most common disease was acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) (16%) and cavitating leukoencephalopathies (16%) (periventricular leukomalacia [PVL], megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy and cavitating leukoencephalopathy and vanishing white matter disease (WMD). Followed by hypomyelination (12%), multiple sclerosis and microvascular ischemic changes (SVIC) (8%) and others (Table 1). The majority of the subjects were in the age group of <5 years, i.e., 70% and least no of subjects were observed in the age group >50 years 8%. Hence, the white matter diseases are common in children that in adults and elderly (Table 2). In this study, the majority (n = 47) of the patients were found with supratentorial lesions and 19 were found to be having infratentorial lesions. Degree of myelination was adequate in nearly two-thirds of the individuals (n = 35) (Table 3). According to the locations of the lesions, in nearly half of the cases, the lesions were in frontal region (n = 24), in 26 patients the lesions were seen in parietal area, 22 had lesions in temporal area, 19 in occipital region, deep gray matter lesions were seen in 17 cases, periventricular lesions in 36 cases and brainstem lesions were seen in 10 cases (Table 4). In all the cases, hypointensity was noticed in T1W images and hyperintensity in the case of T2W images. Hyperintensity was observed in diffusion weighted images in case of 15 study participants, and ADC matching was present in the case of only 10 cases. Contrast enhancement was seen in 8 cases out of 16 in whom the contrast study was done (Table 5). Table 1: MRI diagnosis in white matter diseases MRI diagnosis Frequency (%) Leukodystrophy 13 (26) ADEM 8 (16) Cavitating leukoencephalopathies 8 (16) Hypomyelination 6 (12) Multiple sclerosis 4 (8) SVIC 4 (8) Leigh s disease 2 (4) HIV encephalopathy 2 (4) Nonspecific 2 (4) PML 1 (2) Total 50 (100) MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging, ADEM: Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, SVIC: Microvascular ischemic changes, HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus, PML: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy Table 2: Age distribution of subjects Age (years) Frequency (%) <5 35 (70) (22) >50 4 (8) Total 50 (100) Table 3: Supratentorium and infratentorium lesions in white matter disease and degree of myelination Lesions Frequency (%) Supratentorium Absent 3 (6) Present 47 (94) Infratentorium Absent 31 (62) Present 19 (38) Degree of myelination Inadequate 15 (30) Adequate 35 (70) 15 International Journal of Scientific Study November 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8
4 Table 4: Location of lesions Lesions Frequency (%) Frontal Absent 26 (52) Present 24 (48) Parietal Absent 24 (48) Present 26 (52) Temporal Absent 28 (56) Present 22 (44) Occipital Absent 31 (62) Present 19 (38) Deep gray matter Absent 33 (66) Present 17 (34) Periventricular Absent 14 (28) Present 36 (72) Subcortical U-fibers Absent 34 (68) Present 16 (32) Cerebellum Absent 37 (74) Present 13 (26) Brainstem Absent 40 (80) Present 10 (20) Table 5: MRI findings MRI method and finding Frequency (%) T1W Hypointense 50 (100) T2W Hyperintense 50 (100) DWI Hypointense 35 (70) Hyperintense 15 (30) ADC Matching Absent 40 (80) Present 10 (20) Contrast enhancement Not performed 34 (68) Present 8 (16) Absent 8 (16) DWI: Diffusion-weighted imaging, ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient In the study, only 11 patients were taken for MRS peak and it was observed that in leukodystrophy MRS peak was observed in choline, N-acetyl aspartate, Myo inositol and lactate. In leukoencephalopathies, MRS peak was observed only in lactate. ADEM had peak for choline (Table 6). Among 13 leukodystrophy conditions various diagnosis in the study were MLD (38.4%), ALD (23.1%), Canavan disease (15.4%), 7.7% Krabbes disease, Alexander disease, and nonspecific leukodystrophy (Table 7). Among 8 leukoencephalopathies 50% was PVL, 25% was megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy and 12.5% was cavitating leukoencephalopathy, vanishing WMD, respectively (Table 8). In ADEM, the lesion was more common in Frontal region (75%), followed by parietal lesion in 62.5%. Lesion was observed in all the regions in varying proportions (Table 9). DISCUSSION This study was directed to evaluate the role of MRI in patients presenting with global developmental delay and clinically suspected of white matter disease. About 50 patients clinically suspected of white matter disorders were submitted for MRI scan of brain. In the study, it was observed that most common white matter disease was leukodystrophy (26%). The second most common disease was ADEM (16%) and cavitating leukoencephalopathies (16%) followed by hypomyelination (12%), multiple sclerosis and SVIC (8%) and others. In our study, five out of 13 cases of leukodystrophies suffered from MLD (38.4%), among which 4 were males (80%) and 1 was female (20%). Alves et al. 3 reported that late infantile constitutes 70% of all cases and this is the commonest variety. MR imaging of these patients revealed bilaterally symmetrical and confluent lesions in all cases among which 100% incidence of periventricular white matter involvement, 80% of patients showing frontal white matter involvement and 60% showing parietal, temporal and cerebellar white matter involvement. Kim et al. 4 studied 7 patients of MLD, of which all of them showed bilateral, symmetrical and confluent high signal intensities on T2W imaging. They reported 100% incidence of periventricular white matter and centrum semi ovale. One of our patients, aged 25 months, showed involvement of subcortical U-fibers. This is in correlation with the study by Kim et al. 4 who reported that a follow-up MRI of a 26-month-old patient showed demyelinating process progressed to the subcortical U-fibers. In a study of three patients of MLD by Humera et al., 5 all of which were male patients showed 100% involvement of periventricular white matter showing high signal intensities on T2W and FLAIR images (Figure 1). In our study, three out of 13 cases of leukodystrophies suffered from ALD (23.1%), among which two were males (66.67%) and one was female (33.33%). Age of patients ranged from 9 months to 6 years. Snyder et al. 6 reported that childhood onset ALD (4-8 years) is the most common type. White matter abnormalities usually appear in the occipital regions initially, with early involvement of the splenium of the corpus callosum and posterior limbs of internal capsules. 7 The progression pattern of the disease is centrifugal and posteroanterior. 8 This results International Journal of Scientific Study November 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8 16
5 Figure 1: Metachromatic leukodystrophy: Axial T2 and fluid attenuated inversion recovery hyperintensities are seen in bifrontal, temporal and parietal periventricular white matter with sparing of subcortical U-fibers. The hyperintensities is more marked in bifrontal lobes and cerebellum. Oval hyperintense foci with central cystic area are seen involving bilateral thalami Table 6: MRS peak among the white matter diseases White matter diseases MRS peak Total Not performed N-acetyl choline Choline Myo inositol Lactate Leukodystrophy ADEM Leukoencephalopathies Hypomyelination Multiple sclerosis SVIC Leigh s disease HIV encephalopathy Nonspecific PML Total ADEM: Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, MRS: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy, PML: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus, SVIC: Microvascular ischemic changes Table 7: Various types of leukodystrophy white matter diseases Leukodystrophies Table 8: Various types of leukoencephalopathies in white matter disease Leukoencephalopathies Frequency (%) (n=8) PVL 4 (50) Megaloencephalic leukoencephalopathy 2 (25) Cavitating leukoencephalopathy 1 (12.5) Vanishing WMD 1 (12.5) Total 8 PVL: Periventricular leukomalacia, WMD: White matter disease Frequency (%) (n=13) Leukodystrophy MLD 5 (38.4) ALD 3 (23.1) Canavan disease 2 (15.4) Krabbes disease 1 (7.7) Alexander disease 1 (7.7) Nonspecific leukodystrophy 1 (7.7) Total 13 MLD: Metachromatic leukodystrophy, ALD: Adrenoleukodystrophy in the most characteristic imaging feature of the disease. Our study shows no involvement of frontal white matter in all three patients. All patients showed temporal and occipital white matter abnormalities (100%) and 66.67% showing periventricular and brain stem involvement. All patients showed enhancement on contrast study (100%) and also choline peak in MRS. In a study of three patients of ALD by Ahsan et al., 5 it was reported 66.67% involvement of periventricular white matter specifically in trigonal area showing high signal intensities on T2W and FLAIR images. Melhem et al. 9 in a study of 43 patients of ALD reported 21 patients (49%) showing contrast enhancement. MR imaging findings of multiple sclerosis patients were bilateral periventricular hyperintensities on T2W and FLAIR images. Deep gray matter hyperintensities were also identified in all patients. One patient showed hyperintense lesions in bilateral frontal, parietal and occipital lobes, each lesion measuring approximately 5-10 mm in size. In a study by Tas et al. 10 showed that gadolinium-enhancement 17 International Journal of Scientific Study November 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8
6 Table 9: Location of lesion in ADEM (n=8) Location of lesions Present ADEM Percentage Frontal lesion 6 75 Parietal lesion Temporal lesion 4 50 Occipital lesion 2 25 Deep gray matter lesion Periventricular lesion Subcortical U-fibers lesion 4 50 Cerebellum lesion 4 50 Brainstem lesion 4 50 ADEM: Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis was more specific for diagnosing multiple sclerosis than abnormalities revealed on T2W imaging. In a study of 42 patients by Barkhof et al., 11 Gadolinium enhancement was identified as the most predictive MRI parameter. When compared these results with our study where we have found similar diagnostic criteria for MS on MRI such as 9 or more T2 hyperintense lesions, periventricular lesions and gadolinium enhancement in all the 4 patients of our study who were clinically suspected strongly for multiple sclerosis. Thus, our study results correlated with these studies (Figure 2). In our study, seven patients suffering from ADEM were obtained among which four were females and three were male patients ranging from 2 to 16 years of age. Mikaeloff et al. 12 reported in their study that 66% pf their patients suffering from ADEM showed juxtacortical hyperintensities on MR imaging. Marchioni et al., 13 in their study, reported that 42% of their patients with ADEM showed gadolinium enhancement whereas Lin et al. 14 reported that 40 % of their patients suffering from ADEM showed gadolinium enhancement. These findings are in correlation with our study (Figure 3). Our study revealed one male patient of 2 years of age found to be a case of alexander disease (Figure 4). MR imaging study of this patient showed hyperintensities on T2W images predominantly in the frontal white matter with extension into the parietal and temporal white matter, periventricular regions and subcortical U-fibers. The lesions show contrast enhancement. MRS revealed a rise in Lactate peak. In a study by van der Knaap et al., 15 five MR imaging criteria were defined: Extensive cerebral white matter changes with frontal predominance, a periventricular rim with high signal on T1W images and low signal on T2W images, abnormalities of basal ganglia and thalami, brain stem abnormalities, and contrast enhancement of particular gray and white matter structures. Four of the five criteria had to be met for an MR imaging-based diagnosis. Our study meets four criteria mentioned in their study, thus correlating with the study. Figure 2: Periventricular leukomalacia: Axial and coronal fluid attenuated inversion recovery images show bilateral symmetric periventricular cystic lesions measuring 8-12 mm are seen in adjacent to frontal/body of lateral ventricles and also anterior to temporal horns. In addition smaller size lesions are seen in bilateral posterior periventricular white matter. Mild volume loss is seen in bilateral periventricular brain parenchyma Figure 3: Acute disseminating encephalomyelitis: Diffuse ill-defined abnormal signal intensities are seen predominantly involving the cortices of both cerebellar hemispheres (R>L) and cerebellar vermis, appearing homogenously hyperintense on T2 and fluid attenuated inversion recovery, hypointense on T1-weighted. There is minimal mass effect seen in the form of effacement of the involved sulci In this study, two patients out of 13 cases of leukodystrophies were reported to have Canavan disease (Figure 5). One of our two patients showed diffuse bilateral symmetric cerebral and cerebellar white matter high signal intensities on T2 and FLAIR images and no lobar predominance. Another patient showed involvement of bilateral deep gray matter and subcortical U-fibers. Both the patients were subjected to MRS study which revealed and marked rise in the N-acetylaspartate (NAA) peak. Michel and Given 16 reported a case of Canavan disease in which there was diffuse, bilateral, and symmetric increased T2 signal intensity throughout the cerebral white matter. These findings were noted to a lesser degree in the cerebellar white matter, thalamus, globi pallidi, and dorsal brainstem. The white matter abnormality specifically involved the subcortical white matter. There was no lobar predominance of white matter abnormalities. Single-voxel point-resolved spatially localized MRS revealed a marked increase in both International Journal of Scientific Study November 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8 18
7 Figure 4: Alexander disease: Axial T2 and fluid attenuated inversion recovery cortical hyperintensities are seen in bilateral high frontal lobe and also in posterior periventricular white matter the NAA peak and the ratio of NAA to creatinine. The choline peak was not elevated. Our MR findings are in correlation with their study. Figure 5: Canavan disease: Axial T2-weighted image shows high signal in white matter typically a diffuse bilateral involvement of sub cortical U-fibers. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy - markedly elevated N-acetylaspartate (NAA) and NAA:creatine ratio One case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) was encountered in our study (Figure 6). The patient was 33-year-old male patient with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) seropositive status. MR imaging findings revealed multifocal bilateral parietal, occipital, periventricular, subcortical U-fibers, deep gray matter and bilateral cerebellar white matter hyperintensities on T2W and FLAIR images. Ahsan et al. 5 reported, in their study, that one male patient suffered from PML. He was 30-year-old and tested positive for HIV. MRI showed abnormal signal intensity in deep white matter of brain in right frontal regions, parietooccipital regions, putamen, and midbrain. The signals were isointense on T1 and hyperintense on T2W images. It is observed that these findings are in correlation with our study. CONCLUSION Figure 6: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: Axial T2-weighted images show multifocal bilateral parietal, occipital, periventricular, subcortical U-fibers, deep gray matter hyperintensities. Sagittal T1-weighted image shows posterior hypointensities. Coronal T2-weighted image shows occipital and bilateral cerebellar white matter involvement In general, patients in the pediatric age group constituted 82% of the total study group, and there was slight male predominance. Leukodystrophies constituted 26% of total cases, the commonest being MLD. All patients of acute disseminating encephalomyelitis had a prior history of viral fever. The most common symptom noted was altered sensorium and site of involvement was cerebral white matter, asymmetric multifocal pattern being the most common. The patient with PML was HIV positive and showed focal white matter lesions without mass effect or enhancement. In leukodystrophies, we had 13 cases of which five were MLD, three were ALD, two cases of Canavan disease and one each case of Krabbes disease, Alexander disease and nonspecific leukodystrophy. In leukoencephalopathies, we had 8 cases of which four were PVL, two were megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy and one each case of cavitating leukoencephalopathy and vanishing WMD. All patients were 19 International Journal of Scientific Study November 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8
8 from the pediatric age group, and male predominance was noted. All cases of hypomyelination showed periventricular white matter involvement. Elderly patients showed punctate and confluent hyperintensities involving supratentorial and infratentorial brain white matter lesions, attributing to degenerative changes of small vessels multiplanar imaging capability and excellent gray - white matter resolution makes MRI very sensitive in detecting subtle white matter lesions. FLAIR sequence has better sensitivity for white matter lesions especially those in periventricular locations. Post-contrast studies help in differentiating acute from chronic lesions and thus monitoring the progression of the disease. Allows simultaneous imaging of orbit especially in cases of multiple sclerosis. Helps in early diagnosis of mild and atypical cases so that treatment can be started early in curable disease. Ideal for posterior fossa and spinal cord imaging. Noninvasive imaging modality which can be done on outpatient basis and with no radiation hazards. Specificity of MR imaging can be improved by MRS studies. Only limitation is that though sensitive and not as specific in aiding in the specific diagnosis of diseases. However, the specificity can be improved by clinical correlation and laboratory tests. REFERENCES 1. Atlas SN. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain and Spine. 4 th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; p. 2-14, Ashikaga R, Araki Y, Ishida O. MR FLAIR imaging of herpes simplex encephalitis. Radiat Med 1996;14: Alves D, Pires MM, Guimarães A, Miranda MC. Four cases of late onset metachromatic leucodystrophy in a family: Clinical, biochemical and neuropathological studies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1986;49: Kim TS, Kim IO, Kim WS, Choi YS, Lee JY, Kim OW, et al. MR of childhood metachromatic leukodystrophy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1997;18: Ahsan H, Rafique MZ, Ajmal F, Wahid M, Azeemuddin M, Iqbal F. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings in white matter disease of brain. J Pak Med Assoc 2008;58: Snyder RD, King JN, Keck GM, Orrison WW. MR imaging of the spinal cord in 23 subjects with ALD-AMN complex. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1991;12: Barkovich AJ, Ferriero DM, Bass N, Boyer R. Involvement of the pontomedullary corticospinal tracts: A useful finding in the diagnosis of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1997;18: van der Knaap MS, Valk J. The MR spectrum of peroxisomal disorders. Neuroradiology 1991;33: Melhem ER, Loes DJ, Georgiades CS, Raymond GV, Moser HW. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: The role of contrast-enhanced MR imaging in predicting disease progression. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2000;21: Tas MW, Barkhol F, van Walderveen MA, Polman CH, Hommes OR, Valk J. The effect of gadolinium on the sensitivity and specificity of MR in the initial diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1995;16: Barkhof F, Filippi M, Miller DH, Scheltens P, Campi A, Polman CH, et al. Comparison of MRI criteria at first presentation to predict conversion to clinically definite multiple sclerosis. Brain 1997;120: Mikaeloff Y, Caridade G, Husson B, Suissa S, Tardieu M; Neuropediatric KIDSEP Study Group of the French Neuropediatric Society. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis cohort study: Prognostic factors for relapse. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2007;11: Marchioni E, Ravaglia S, Piccolo G, Furione M, Zardini E, Franciotta D, et al. Postinfectious inflammatory disorders: Subgroups based on prospective follow-up. Neurology 2005;65: Lin CH, Jeng JS, Hsieh ST, Yip PK, Wu RM. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: A follow-up study in Taiwan. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2007;78: van der Knaap MS, Naidu S, Breiter SN, Blaser S, Stroink H, Springer S, et al. Alexander disease: Diagnosis with MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22: Michel SJ, Given CA 2 nd. Case 99: Canavan disease. Radiology 2006;241: How to cite this article: Devareddy MM, Devakar S. Magnetic Resonance Study of White Matter Lesions: A Cross Sectional Study. Int J Sci Stud 2016;4(8): Source of Support: Nil, Conflict of Interest: None declared. International Journal of Scientific Study November 2016 Vol 4 Issue 8 20
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
 Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic resonance imaging: a case report
 Nishibayashi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:194 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic
Nishibayashi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:194 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases
 White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas
 Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari
 Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
MRI diagnosis of infantile Alexander disease in a 14 month old African boy
 MRI diagnosis of infantile Alexander disease in a 14 month old African boy Nondumiso Dlamini 1*, Vicci du Plessis 2 1. Department of Radiology, Greys' Hospital, Pietermaritzburg Metropolitan Complex, South
MRI diagnosis of infantile Alexander disease in a 14 month old African boy Nondumiso Dlamini 1*, Vicci du Plessis 2 1. Department of Radiology, Greys' Hospital, Pietermaritzburg Metropolitan Complex, South
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies
 Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI
 Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis
 APRIL 2002 103 Magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis Beside the ability to detect the Olga Ciccarelli and David H. Miller NMR Unit, Institute of Neurology, University College London, Queen Square,
APRIL 2002 103 Magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis Beside the ability to detect the Olga Ciccarelli and David H. Miller NMR Unit, Institute of Neurology, University College London, Queen Square,
Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter. Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
 Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter Bhagwan Moorjani American Society of Neuroimaging 37 th Annual Meeting Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter Bhagwan Moorjani American Society of Neuroimaging 37 th Annual Meeting Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS
 Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum
 Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Leukoencephalopathies constitute a large heterogeneous
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Rossi R. Biancheri F. Zara C. Bruno G. Uziel M.S. van der Knaap C. Minetti P. Tortori-Donati Hypomyelination and Congenital Cataract: Neuroimaging Features of a Novel Inherited White
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Rossi R. Biancheri F. Zara C. Bruno G. Uziel M.S. van der Knaap C. Minetti P. Tortori-Donati Hypomyelination and Congenital Cataract: Neuroimaging Features of a Novel Inherited White
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
Chronology of normal brain myelination in newborns with MR imaging
 Chronology of normal brain myelination in newborns with MR imaging Poster No.: C-0577 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit F. Fernandez Usagre; Sevilla/ES Neuroradiology
Chronology of normal brain myelination in newborns with MR imaging Poster No.: C-0577 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit F. Fernandez Usagre; Sevilla/ES Neuroradiology
Neuroradiology of AIDS
 Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports
 Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports "This work has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health,
Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports "This work has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health,
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CT and MR Imaging in Young Stroke Patients
 CT and MR Imaging in Young Stroke Patients Ashfaq A. Razzaq,Behram A. Khan,Shahid Baig ( Department of Neurology, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi. ) Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 66
CT and MR Imaging in Young Stroke Patients Ashfaq A. Razzaq,Behram A. Khan,Shahid Baig ( Department of Neurology, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi. ) Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 66
multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging
 Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
Toxins in Brain! Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging of Toxic Leukoencephalopathy A Pictorial Essay
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 311-319 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.901791 REVIEW ARTICLE Received: 2016.10.02 Accepted: 2016.10.11 Published: 2017.06.13 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 311-319 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.901791 REVIEW ARTICLE Received: 2016.10.02 Accepted: 2016.10.11 Published: 2017.06.13 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology
 General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18
 IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI
 Chapter 4 Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI Lishya Liauw Jeroen van der Grond Valerie Slooff Francisca Wiggers-de Bruïne Laura Laan Saskia
Chapter 4 Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI Lishya Liauw Jeroen van der Grond Valerie Slooff Francisca Wiggers-de Bruïne Laura Laan Saskia
Normal myelination: a practical pictorial review
 Normal myelination: a practical pictorial review Poster No.: C-1486 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Gaha, N. Mama, N. Arifa, H. Jemni, K. Tlili Graiess; Sousse/TN
Normal myelination: a practical pictorial review Poster No.: C-1486 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Gaha, N. Mama, N. Arifa, H. Jemni, K. Tlili Graiess; Sousse/TN
Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Neurological Conditions. Lawrance Yip Department of Radiology Queen Mary Hospital
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Neurological Conditions Lawrance Yip Department of Radiology Queen Mary Hospital Outline Strength and limitations of MRI for neurological conditions MR Imaging techniques
Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Neurological Conditions Lawrance Yip Department of Radiology Queen Mary Hospital Outline Strength and limitations of MRI for neurological conditions MR Imaging techniques
Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
COPYRIGHT 2012 THE TRANSVERSE MYELITIS ASSOCIATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
myelin in the CNS Multiple axons are oligodendrocyte
 Pathologic classification of white matter disorders d Demyelinating - loss of normal myelin autoimmune/inflammatory component Dysmyelinating - loss of chemically abnormal myelin Hypomyelinating - paucity
Pathologic classification of white matter disorders d Demyelinating - loss of normal myelin autoimmune/inflammatory component Dysmyelinating - loss of chemically abnormal myelin Hypomyelinating - paucity
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings
 Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Role of MRI in the evaluation of white matter diseases of Brain
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE ISSN: 2455-944X www.darshanpublishers.com DOI:10.22192/ijcrbm Volume 3, Issue 1-2018 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrbm.2018.03.01.005
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE ISSN: 2455-944X www.darshanpublishers.com DOI:10.22192/ijcrbm Volume 3, Issue 1-2018 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrbm.2018.03.01.005
Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging features of intracranial lesions
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review.
 Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review. Poster No.: C-0817 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. I. MICHELIN,
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review. Poster No.: C-0817 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. I. MICHELIN,
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
MLD is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Martin C. Sevin C. Lazarus C. Bellesme P. Aubourg C. Adamsbaum Toward a Better Understanding of Brain Lesions during Metachromatic Leukodystrophy Evolution BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Martin C. Sevin C. Lazarus C. Bellesme P. Aubourg C. Adamsbaum Toward a Better Understanding of Brain Lesions during Metachromatic Leukodystrophy Evolution BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy: The Role of Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging in Predicting Disease Progression
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :839 844, May 000 X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy: The Role of Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging in Predicting Disease Progression Elias R. Melhem, Daniel J. Loes, Christos S. Georgiades,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :839 844, May 000 X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy: The Role of Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging in Predicting Disease Progression Elias R. Melhem, Daniel J. Loes, Christos S. Georgiades,
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children
 Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
mr brain volume analysis using brain assist
 mr brain volume analysis using brain assist This Paper describes the tool named BrainAssist, which can be used for the study and analysis of brain abnormalities like Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD), Heterotopia
mr brain volume analysis using brain assist This Paper describes the tool named BrainAssist, which can be used for the study and analysis of brain abnormalities like Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD), Heterotopia
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans
 PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Role of imaging (images) in my practice. Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases
 Role of imaging (images) in my practice Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases Medical images: My thoughts Images are just images Subject to the intellect of the interpreter View it in conjuction
Role of imaging (images) in my practice Dr P Senthur Nambi Consultant Infectious Diseases Medical images: My thoughts Images are just images Subject to the intellect of the interpreter View it in conjuction
Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy
 Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy Schepers S, Barthels C Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2011, Nov. 3 Patient: 67 year(s), male Authors' Institution Department of Radiology, Jessa ziekenhuis campus
Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy Schepers S, Barthels C Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2011, Nov. 3 Patient: 67 year(s), male Authors' Institution Department of Radiology, Jessa ziekenhuis campus
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
MR Imaging and Proton Spectroscopy in 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Lyase Deficiency
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:78 82, February 1998 MR Imaging and Proton Spectroscopy in -Hydroxy--Methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Lyase Deficiency M. S. van der Knaap, H. D. Bakker, and J. Valk Summary: Three patients
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:78 82, February 1998 MR Imaging and Proton Spectroscopy in -Hydroxy--Methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Lyase Deficiency M. S. van der Knaap, H. D. Bakker, and J. Valk Summary: Three patients
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis Arjan Minneboo, MD; Frederick Barkhof, MD; Chris H. Polman,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis Arjan Minneboo, MD; Frederick Barkhof, MD; Chris H. Polman,
Encephalitis. HSV Encephalitis. Encephalitis. Viral CNS Infection. WNV Encephalitis GRAY MATTER. Zoran Rumboldt
 Encephalitis Viral CNS Infection Hematogenous dissemination ( along peripheral nerves ) Zoran Rumboldt University of Rijeka Medical University of South Carolina Telemedicine Clinic MarinMed Clinic Many
Encephalitis Viral CNS Infection Hematogenous dissemination ( along peripheral nerves ) Zoran Rumboldt University of Rijeka Medical University of South Carolina Telemedicine Clinic MarinMed Clinic Many
Disclosure. + Outline. Case-based approach to neurological emergencies that might present to the ED
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain
 An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
Role of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in diagnosis of pilocytic astrocytoma in children
 Alexandria Journal of Medicine (2012) 48, 131 137 Alexandria University Faculty of Medicine Alexandria Journal of Medicine www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Alexandria Journal of Medicine (2012) 48, 131 137 Alexandria University Faculty of Medicine Alexandria Journal of Medicine www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics. Disclosures. Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor 4/14/2017
 Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
MR Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Adult Krabbe Disease
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1478 1482, September 2000 Case Report MR Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Adult Krabbe Disease Laura Farina, Alberto Bizzi, Gaetano Finocchiaro, Davide Pareyson, Angelo Sghirlanzoni,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1478 1482, September 2000 Case Report MR Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Adult Krabbe Disease Laura Farina, Alberto Bizzi, Gaetano Finocchiaro, Davide Pareyson, Angelo Sghirlanzoni,
Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions
 Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions Poster No.: C-3394 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro - Your latest results Authors: J. R. Docampo, M. Cabrini, C. Morales,
Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions Poster No.: C-3394 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro - Your latest results Authors: J. R. Docampo, M. Cabrini, C. Morales,
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
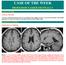 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE A 40 Years old female patient, known to be suffering from multiple sclerosis, was presented clinically with painful diminution of vision in the right aye and mild weakness
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE A 40 Years old female patient, known to be suffering from multiple sclerosis, was presented clinically with painful diminution of vision in the right aye and mild weakness
Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain John R. Hesselink, M.D. T1-Weighted Images Normal White Matter Contents Axons with envelope of myelin Neuroglia
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain John R. Hesselink, M.D. T1-Weighted Images Normal White Matter Contents Axons with envelope of myelin Neuroglia
SHORTLY AFTER ITS FIRST DEpiction
 OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions
 Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions Poster No: C-3394 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: J R Docampo, M Cabrini, C Morales, C Bruno; Buenos Aires/ AR
Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions Poster No: C-3394 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: J R Docampo, M Cabrini, C Morales, C Bruno; Buenos Aires/ AR
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
Periventricular white matter injury, that is, periventricular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Yoshida K. Hayakawa A. Yamamoto T. Kanda Y. Yamori Pontine Hypoplasia in Children with Periventricular Leukomalacia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The brain stem in patients with periventricular
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Yoshida K. Hayakawa A. Yamamoto T. Kanda Y. Yamori Pontine Hypoplasia in Children with Periventricular Leukomalacia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The brain stem in patients with periventricular
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation
 MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
Study of the CNS. Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David Norman Thomas H. Newton
 271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease
 Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease Giuseppe Fariello, Carlo Dionisi-Vici, Cinzia Orazi, Saverio Malena, Andrea Bartuli, Paolo Schingo, Enza Carnevale, Isora Saponara, and Gaetano Sabetta
Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease Giuseppe Fariello, Carlo Dionisi-Vici, Cinzia Orazi, Saverio Malena, Andrea Bartuli, Paolo Schingo, Enza Carnevale, Isora Saponara, and Gaetano Sabetta
Pediatric CNS Tumors. Disclosures. Acknowledgements. Introduction. Introduction. Posterior Fossa Tumors. Whitney Finke, MD
 Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
Fig.1: A, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a
 Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Actualização no diagnóstico e tratamento das doenças desmielinizantes na infância. Silvia Tenembaum
 Actualização no diagnóstico e tratamento das doenças desmielinizantes na infância Silvia Tenembaum Acquired CNS inflammatory/demyelinating disorders: Background information More frequent in children than
Actualização no diagnóstico e tratamento das doenças desmielinizantes na infância Silvia Tenembaum Acquired CNS inflammatory/demyelinating disorders: Background information More frequent in children than
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Pediatric acute demyelinating encephalomyelitis in Denmark: a nationwide population-based study
 Pediatric acute demyelinating encephalomyelitis in Denmark: a nationwide population-based study Magnus Spangsberg Boesen November, 2016 Supervisors: P. Born, P. Uldall, M. Blinkenberg, M. Magyari, F. Sellebjerg
Pediatric acute demyelinating encephalomyelitis in Denmark: a nationwide population-based study Magnus Spangsberg Boesen November, 2016 Supervisors: P. Born, P. Uldall, M. Blinkenberg, M. Magyari, F. Sellebjerg
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE
 RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a motor neuron disease
 ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
Isolated Demyelinating Syndromes: Comparison of Different MR Imaging Criteria to Predict Conversion to Clinically Definite Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:702 706, April 2000 Isolated Demyelinating Syndromes: Comparison of Different MR Imaging Criteria to Predict Conversion to Clinically Definite Multiple Sclerosis Mar Tintoré, Alex
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:702 706, April 2000 Isolated Demyelinating Syndromes: Comparison of Different MR Imaging Criteria to Predict Conversion to Clinically Definite Multiple Sclerosis Mar Tintoré, Alex
Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging
 Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging Meghan Elkins, OD, FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others can sit. Unauthorized recording of this session is
Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging Meghan Elkins, OD, FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others can sit. Unauthorized recording of this session is
Dean Shibata, M.D. Department of Radiology, University of Washington. White Matter, Metabolic, and Degenerative Disease.
 White Matter, Metabolic, and Degenerative Disease UW Radiology Review 2015 Dean Shibata, M.D Neuroradiology Department of Radiology, University of Washington MS (Multiple Sclerosis) ADEM (Acute Disseminated
White Matter, Metabolic, and Degenerative Disease UW Radiology Review 2015 Dean Shibata, M.D Neuroradiology Department of Radiology, University of Washington MS (Multiple Sclerosis) ADEM (Acute Disseminated
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Keywords: Multiple Sclerosis; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Diffuse. Introduction. Abstract Objective
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Diffuse Weighted Imaging and Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recovery Sequences of MRI in Brain Multiple Sclerosis Plaques Detection How to Cite This Article: Nafisi-Moghadam
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Diffuse Weighted Imaging and Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recovery Sequences of MRI in Brain Multiple Sclerosis Plaques Detection How to Cite This Article: Nafisi-Moghadam
Gliomatosis Cerebri: Imaging Findings on Traditional and Advanced Techniques
 Gliomatosis Cerebri: Imaging Findings on Traditional and Advanced Techniques Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Cruz Hernandez, I. Herrera, A. L. Reyes Ortiz,
Gliomatosis Cerebri: Imaging Findings on Traditional and Advanced Techniques Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Cruz Hernandez, I. Herrera, A. L. Reyes Ortiz,
Brain Space Occupying Lesions by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Prospective Study
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/523 Brain Space Occupying Lesions by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Prospective Study Bulabai Karpagam 1, V Vadanika 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology,
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/523 Brain Space Occupying Lesions by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Prospective Study Bulabai Karpagam 1, V Vadanika 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology,
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods
 Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature.
 Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature. Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Chaves, M. S. TORONCHIK, P. M.
Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature. Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Chaves, M. S. TORONCHIK, P. M.
Primary central nervous system lymphomas: CT, MRI and MR spectroscopy findings at presentation
 Primary central nervous system lymphomas: CT, MRI and MR spectroscopy findings at presentation Poster No.: C-2577 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Brakus, K. Petrovic, N. Vuckovic,
Primary central nervous system lymphomas: CT, MRI and MR spectroscopy findings at presentation Poster No.: C-2577 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Brakus, K. Petrovic, N. Vuckovic,
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
