Citation for published version (APA): Xu, C. (2010). Tumor cell survival strategies in Hodgkin lymphoma Groningen: s.n.
|
|
|
- Pierce Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Groningen Tumor cell survival strategies in Hodgkin lymphoma Xu, Chuanhui IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version below. Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Publication date: 2010 Link to publication in University of Groningen/UMCG research database Citation for published version (APA): Xu, C. (2010). Tumor cell survival strategies in Hodgkin lymphoma Groningen: s.n. Copyright Other than for strictly personal use, it is not permitted to download or to forward/distribute the text or part of it without the consent of the author(s) and/or copyright holder(s), unless the work is under an open content license (like Creative Commons). Take-down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Downloaded from the University of Groningen/UMCG research database (Pure): For technical reasons the number of authors shown on this cover page is limited to 10 maximum. Download date:
2 CHAPTER 5 Expression of CD1d and Presence of Invariant NKT Cells in classical Hodgkin Lymphoma Chuanhui Xu (1), Riemer de Vries (1), Lydia Visser (1) Arjan Diepstra (1), Stephan D. Gadola (2), Sibrand Poppema (1) Anke van den Berg (1). (1) Department of Pathology and Medical Biology, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, Groningen, the Netherlands. (2) Division of Infection, Inflammation and Repair, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, Southampton, United Kingdom. In Press. American Journal of Hematology.
3 86 Expression of CD1d and Presence of Invariant NKT Cells Abstract We studied CD1d-restricted invariant natural killer T (inkt) cells in classical Hodgkin lymphoma (chl). Tumor cells stained positive for CD1d in 21/44 chl cases, whereas in non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) only 9/31 stained positive. In contrast, CD1c expression was more common in NHL. e percentage of inkt cells in chl cell suspensions was similar to the percentage in reactive lymph nodes and was not related to the CD1d expression status of the tumor cells. In conclusion, we found expression of CD1d in HRS cells in half of the chl cases, and also observed a substantial population of inkt cells in chl cell suspensions.
4 Tumor Cell Survival Strategies in Hodgkin Lymphoma 87 Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (chl) is a B-cell neoplasm characterized by a minority of neoplastic cells, the Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells, which are located within an extensive infiltrate of reactive cells, such as T cells, B cells, plasma cells, stromal cells, eosinophils and macrophages. HRS cells shape their microenvironment by attracting specific favorable T cell subsets, like regulatory T (Treg) and T helper (T H )-2 cells and producing factors such as CC-chemokine ligand 17 (CCL17 or TARC), transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and interleukin (IL)-10 [1]. Additionally, HLA class I is downregulated in HRS cells in 65% of the chl cases and HLA class II in 40%, possibly as a strategy to escape from an effective immune surveillance [2]. All together, these factors may suppress the development of an effective anti-tumor response and provide a microenvironment that is favorable for HRS cells. Recent studies have suggested that T cells restricted to non-classical MHC class I-like CD1 molecules may be involved in immune surveillance of hematological malignancies [3-6]. CD1 molecules are non-classical MHC class I-like molecules that present lipid antigens to T cells, triggering a specific immune response. Of the five CD1 isoforms (CD1a, CD1b, CD1c, CD1d and CD1e) expressed in human tissue, only CD1c and CD1d are expressed in B cells [7]. e T cell receptors (TCRs) of T cells that recognize CD1c are indistinguishable from those that recognize MHC class I or II complexes. Most CD1c-restricted T cells appear to be T H -1-like cells that provide adaptive immunity to microbial-lipid antigens [8]. In contrast, CD1d presents lipid antigens to natural killer T (NKT) cells. e best characterized CD1d-restricted NKT cells in humans are the invariant NKT (inkt) cells, also known as type I NKT cells. ese cells are characterized by the expression of an invariant Vα24Jα18 chain paired to a semi-invariant Vβ11 chain [9]. Two distinct functional subsets of human inkt cells are recognized in terms of cytokines production and cytotoxic activation. CD4- inkt cells are more likely to be cytotoxic and produce T H -1 type cytokines, whereas CD4+ inkt cells are more likely to produce both T H -1 and T H -2 type cytokines a er stimulation [10]. Several studies have shown the importance of inkt cells in B cell malignancies [4-6]. In chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) CD1d+ tumor cells loaded with αgalcer can activate
5 88 Expression of CD1d and Presence of Invariant NKT Cells inkt cells and in turn induce cell death of tumor cells [4]. Malignant multiple myeloma (MM) is characterized by a reversible functional defect in inkt cells in comparison with nonprogressive myeloma and premalignant myeloma [5]. Furthermore, inkt cells were shown to induce effective anti-lymphoma responses and were essential for the survival of mice in murine lymphoma models [6]. e role of inkt cells in the immune surveillance in chl is unknown. Here, we examined the expression of CD1c and CD1d in HRS cells and tumor infiltrating cells in 44 chl cases, as well as in four chl cell lines. Furthermore, we studied the presence of inkt cells in cell suspensions of ten chl cases. Table 5.1: Comparison of expression of CD1c and CD1d in chl and NHL. lymphoma CD1c positive CD1d positive chl (n=44) 0% 48% EBV+ 42% EBV- 57% NHL (n=39) 36% 23% CLL (n=13) 8% 31% MCL (n=7) 57% 14% FL (n=9) 67% 22% DLBCL (n=10) 30% 10% chl: classical Hodgkin lymphoma; NHL: non-hodgkin lymphoma; CLL: chronic lymphocytic leukemia; MCL: mantle cell lymphoma; FL: follicular lymphoma; DLBCL: diffuse large B cell lymphoma CD1c was undetectable in chl cell lines L428, KMH2, L1236 and U- HO1 (data not shown). In tonsil tissue, CD1c stained positive in the mantle zone (MZ) and predominantly negative in the germinal centers (GC) of secondary lymphoid follicles (Figure 5.1A) consistent with the previously reported expression pattern [11]. HRS cells in chl were consistently CD1c negative in all cases (Figure 5.1B), while 14 out of 39 non Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) were positive (Table 5.1). e absence of CD1c expression in both GC B cells and HRS cells is consistent with
6 Tumor Cell Survival Strategies in Hodgkin Lymphoma 89 Figure 5.1: CD1c and CD1d expression in chl. Both CD1c and CD1d are positive in the mantle zone area and predominantly negative in the germinal center area in tonsil (A and G). Original image magnification: 200x. CD1c is negative in HRS cells (arrows), but positive in reactive cells (B). CD1d is positive both in HRS cells (arrows) and reactive cells (H). Original magnification 400x. CD1d is weakly positive in U-HO1, and strongly positive in the other three chl cell lines (C-F). Original image magnification: 400x. the current assumption that HRS cells are derived from GC B cells [12]. CD1c expression has been reported in some other B-cell NHL subtypes, including GC B cell derived follicular lymphoma [11]. In B-cell NHL an inverse correlation was noticed between CD1c and the proliferative activity assessed by expression of Ki-67 [11]. is is in line with the lack of CD1c staining in GC B cells that show a high proliferation index and high CD1c expression in the MZ B cells that are in a resting state. Ki-67 was shown to be highly expressed in HRS cells [13] correlating with the lack of CD1c expression. CD1c expression was found in reactive cells in
7 90 Expression of CD1d and Presence of Invariant NKT Cells chl RLN Table 5.2: inkt cells in chl and RLN. cases Subtype CD1d in HRS % inkt % CD4+ inkt 1 NS NS NS NS NS MC NS MC NS NS all cases with a percentage varying from a few to the vast majority, similar to the CD1c expression pattern observed in interfollicular regions of tonsil tissue. In contrast, CD1d was detected in all four chl cell lines, varying from weakly positive in U-HO1 to strongly positive in the other three chl cell lines (Figure 5.1C-F). By flowcytometry we validated that CD1d was present on the membrane in chl cell lines (data not shown). In normal tonsil tissue CD1d staining was observed mainly in the MZ and showed no positive staining in the GC (Figure 5.1G) consistent with the reported results [14]. CD1d was detected in HRS cells in 21 out of 44 chl cases (48%) (Figure 5.1H, Table 5.1, Supplementary Table 5.1), showing both cytoplasmic and membranous staining. No correlation was found with EBV status and CD1d expression (Table 5.1). CD1d was also positive in the reactive background, usually in more than half of the reactive cells.
8 Tumor Cell Survival Strategies in Hodgkin Lymphoma 91 Nine of the 39 NHL cases were positive for CD1d (23%, Table 5.1), i.e. in 3 out of 19 GC B cell derived NHL and in 6 out of 20 non-gc B cell NHL (Table 5.1, Supplementary Table 5.1). e CD1d expression in HL is remarkable since GC B cells and the majority of the GC B cell derived NHL are negative. Positivity of HRS cells indicates that these cells might have acquired CD1d expression during malignant transformation. CD1d expression has been detected in some B cell malignancies, such as CLL [4] and MM [5]. In these B cell malignancies, inkt cells activated by α-galcer loaded CD1d+ tumor cells resulted in the induction of apoptosis of the tumor cells in vitro [4,5]. Since half of the chl cases were positive for CD1d in HRS cells, we further investigated the inkt cell population in cell suspensions of chl and reactive lymph node (RLN). e mean percentage of inkt cells was 4% (range 0.8-8%) in chl and 4% (range 0.4-7%) in RLN (Table 5.2). inkt cells were present at similar percentage in either CD1d positive or CD1d negative chl cases. Two distinct inkt subsets have been distinguished as T H -1 type (CD4- inkt) and T H -2 type (CD4+ inkt) in terms of cytokine production and cytotoxic activation [10]. We observed a similar percentage of CD4+ inkt cells, i.e. around 50%, in chl and RLN (Table 5.2). Given the high expression of CCL17 in HRS cells of chl [15] and the high expression of the CCL17 receptor, CCR4, on CD4+ inkt cells [16], it might be speculated that especially the CD4+ inkt cells are present in the close vicinity of HRS cells and might favor the survival and growth of HRS cells. Since it is known that the rosetting CD4+CD26- T cells in HL have several features of anergy [17], the CD1d-restricted inkt cells might also be dysfunctional or anergic favoring HRS cells survival by escaping from an effective immunosurveillance in chl. Taken together, we showed expression of CD1d in HRS cells of chl cell lines and a significant proportion of chl cases as well as the presence of a marked population of inkt cells in the reactive background of chl. e CD1d inkt cell axis might play a role in the disturbed immunoregulation in chl.
9 92 Expression of CD1d and Presence of Invariant NKT Cells 5.1 Methods Patient samples and cell lines. Frozen chl samples consisted of 39 cases of nodular sclerosis (NS), four cases of mixed cellularity (MC) and one case of not otherwise specified chl (NOS). Frozen samples of 39 NHL cases were used and consisted of 13 chronic lymphocytic leukemia, 7 mantle cell lymphoma, 9 follicular lymphoma and 10 diffuse large B cell lymphoma cases. Cell suspensions were available of eight NS and two MC chl cases. e chl cell lines L428, KMH2, L1236 and U- HO1 [18] were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (Lonza Walkersville, Walkersville, MD USA) supplemented with ultraglutamine-1, 100 U/ ml penicillin/streptomycin, 10% fetal calf serum (5% for L428) (Lonza Walkersville). Immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemistry was performed with monoclonal antibodies against CD1c (L161, Abd Serotec, Oxford, UK) and CD1d (NOR3.2, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) (both 1:100) on frozen chl tissue sections and cytospins using standard laboratory protocols and appropriate positive and negative controls. Cases were defined positive when more than 50% of HRS cells showed a clear staining. Flow Cytometry cells were stained simultaneously with PE labeled Mouse Anti-Human inkt Cell (clone 6B11, BD Bioscience, San Jose, CA ), FITC labeled anti-tcr Vβ11 (clone C21, Beckman Coulter, Fullerton, CA) and CyQ labeled anti-cd4 (clone Edu-2, IQ Products, Groningen, Netherlands). A total of 100,000 lymphocytes was collected. e percentage of inkt cells was determined by positive staining for both 6B11 and Vβ11, and the percentage of CD4+ inkt cells was determined by the percentage of CD4+ cells among the gated inkt cells by flow cytometer (Calibur, Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA). We used an inkt cell clone as a positive control, and samples without primary antibody were included as a negative control. chl cell lines were stained with PE labeled CD1d (clone 51.1, ebioscience, Hatfield, UK), and a IgG2b isotype control antibody, to show the presence of membrane CD1d.
10 Tumor Cell Survival Strategies in Hodgkin Lymphoma 93 References 1. Poppema S. Immunobiology and pathophysiology of Hodgkin lymphomas. Hematology 2005; 2005: Diepstra A, van Imhoff G, Karim-Kos H, et al. HLA Class II expression by Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells is an independent prognostic factor in classical Hodgkin s Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: Zheng Z, Venkatapathy S, Rao G, et al. Expression profiling of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia suggests deficient CD1-mediated immunity, polarized cytokine response, altered adhesion and increased intracellular protein transport and processing leukemic cells. Leukemia 2002; 16: Fais F, Morabito F, Stelitano C, et al. CD1d is expressed on B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and mediates alpha-galactosylceramide presentation to natural killer T lymphocytes. Int J Cancer 2004; 109: Dhodapkar M, Geller M, Chang D, et al. A reversible defect in natural killer T cell function characterizes the progression of premalignant to malignant multiple myeloma. J Exp Med 2003; 197: Renukaradhya G, Khan M, Vieira M, et al. Type I NKT cells protect (and type II NKT cells suppress) the host s innate antitumor immune response to a B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2008; 111: Brigl M, Brenner MB. CD1: antigen presentation and T cell function. Annu Rev Immunol 2004; 22: Sieling PA, Ochoa MT, Jullien D, et al. Evidence for human CD4+ T cells in the CD1 restricted repertoire: derivation of mycobacteria-reactive T cells from leprosy lesions. J Immunol 2000; 164: Dellabonna P, Padovan E, Casorati G, et al. An invariant V alpha 24- J alpha Q/ V beta 11 Tcell receptor is expressed in all individuals by clonally expanded CD4-CD8- T cells. J Exp Med 1994; 180: Gumperz J, Miyake S, Yamamura T, Brenner M. Functionally distinct subsets of CD1d-restricted natural killer T cells revealed by CD1d tetramer staining. J Exp Med 2002; 195:
11 94 Expression of CD1d and Presence of Invariant NKT Cells 11. Smith ME, omas JA, Bodmer WF. CD1c antigens are present in normal and neoplastic B-cells. J Pathol 1988; 156: Kanzler H, Kuppers R, Hansmann ML, Rajewsky K. Hodgkin and Reed- Sternberg cells in Hodgkin s disease represent the outgrowth of a dominant tumor clone derived from (crippled) germinal center B cells. J Exp Med 1996; 184: Kim LH, Eow GI, Peh SC, Poppema S. e role of CD30, CD40 and CD95 in the regulation of proliferation and apoptosis in classical Hodgkin s lymphoma. Pathology 2003; 35: Exley M, Garcia J, Wilson SB, et al. CD1d structure and regulation on human thymocytes, peripheral blood T cells, B cells and monocytes. Immunology 2000; 100: Niens M, Visser L, Nolte IM, et al. Serum chemokine levels in Hodgkin lymphoma patients: highly increased levels of CCL17 and CCL22. Br J Haematol 2008; 140: Kim C, Johnston B, Butcher E. Trafficking machinery of NKT cells: shared and differential chemokine receptor expression among Valpha 24+Vbeta 11+ NKT cell subsets with distinct cytokine-producing capacity. Blood 2002; 100: Ma Y, Visser L, Blokzijl T, et al. e CD4+CD26- T-cell population in classical Hodgkin s lymphoma displays a distinctive regulatory T-cell profile. Lab Invest 2008; 88: Mader A, Bruderlein S, Wegener S, et al. U-HO1, a new cell line derived from a primary refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Cytogenet Genome Res 2007; 119:
12 Tumor Cell Survival Strategies in Hodgkin Lymphoma 95 Supplementary Table 5.1: Expression of CD1c and CD1d in HL and NHL. Case diagnosis EBV status CD1c CD1d 1 HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS to be continuoued
13 96 Expression of CD1d and Presence of Invariant NKT Cells Expression of CD1c and CD1d in HL and NHL (Continoued). Case diagnosis EBV status CD1c CD1d 37 HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NS HL-NOS HL-MC HL-MC HL-MC CLL CLL CLL CLL CLL CLL CLL CLL CLL CLL CLL CLL CLL MCL MCL MCL MCL MCL MCL MCL FL FL FL FL FL FL FL FL FL - - to be continuoued
14 Tumor Cell Survival Strategies in Hodgkin Lymphoma 97 Expression of CD1c and CD1d in HL and NHL (Continoued). Case diagnosis EBV status CD1c CD1d 74 DLBCL DLBCL DLBCL DLBCL DLBCL DLBCL DLBCL DLBCL DLBCL DLBCL - + HL: Hodgkin lymphoma; NS: Nodular sclerosis; MC: mixed cellularity; NOS: not otherwise specified; CLL: chronic lymphocytic leukemia; MCL: mantle cell lymphoma; FL: follicular lymphoma; DLBCL: diffuse large B cell lymphoma
University of Groningen. The microenvironment of Hodgkin lymphoma Sattarzadeh, Ahmad
 University of Groningen The microenvironment of Hodgkin lymphoma Sattarzadeh, Ahmad IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen The microenvironment of Hodgkin lymphoma Sattarzadeh, Ahmad IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Dysregulation of transcription and cytokine networks in Hodgkin lymphomas with a focus on nodular lymphocyte predominance type of Hodgkin lymphoma Atayar, Cigdem IMPORTANT NOTE:
University of Groningen Dysregulation of transcription and cytokine networks in Hodgkin lymphomas with a focus on nodular lymphocyte predominance type of Hodgkin lymphoma Atayar, Cigdem IMPORTANT NOTE:
Immunopathology of Lymphoma
 Immunopathology of Lymphoma Noraidah Masir MBBCh, M.Med (Pathology), D.Phil. Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Lymphoma classification has been challenging to pathologists.
Immunopathology of Lymphoma Noraidah Masir MBBCh, M.Med (Pathology), D.Phil. Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Lymphoma classification has been challenging to pathologists.
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology
 Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know. Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC
 Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Overview B cell development T cell development
 Topics Overview B cell development T cell development Lymphocyte development overview (Cont) Receptor diversity is produced by gene rearrangement and is random Includes specificities that will bind to
Topics Overview B cell development T cell development Lymphocyte development overview (Cont) Receptor diversity is produced by gene rearrangement and is random Includes specificities that will bind to
New treatment strategies in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia van der Helm, Lidia Henrieke
 University of Groningen New treatment strategies in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia van der Helm, Lidia Henrieke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
University of Groningen New treatment strategies in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia van der Helm, Lidia Henrieke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
The development of T cells in the thymus
 T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo
 Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Small B-cell lymphomas Antigen selection NAIVE -B LYMPHOCYTE MEMORY B-CELL MCL FL LPL MZL CLL Small cell
Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Small B-cell lymphomas Antigen selection NAIVE -B LYMPHOCYTE MEMORY B-CELL MCL FL LPL MZL CLL Small cell
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies. I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this talk.
 Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this
HODGKIN LYMPHOMA DR. ALEJANDRA ZARATE OSORNO HOSPITAL ESPAÑOL DE MEXICO
 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA DR. ALEJANDRA ZARATE OSORNO HOSPITAL ESPAÑOL DE MEXICO HODGKIN LYMPHOMA CLASSIFICATION Lukes & Butler Rye WHO-2016 Linphocytic and/or histiocytic Nodular & diffuse Nodular Sclerosis Lymphocyte
HODGKIN LYMPHOMA DR. ALEJANDRA ZARATE OSORNO HOSPITAL ESPAÑOL DE MEXICO HODGKIN LYMPHOMA CLASSIFICATION Lukes & Butler Rye WHO-2016 Linphocytic and/or histiocytic Nodular & diffuse Nodular Sclerosis Lymphocyte
Contents. vii. Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii
 Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Fluorochrome Panel 1 Panel 2 Panel 3 Panel 4 Panel 5 CTLA-4 CTLA-4 CD15 CD3 FITC. Bio) PD-1 (MIH4, BD) ICOS (C398.4A, Biolegend) PD-L1 (MIH1, BD)
 Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
University of Groningen. Mutational landscape of Hodgkin lymphoma Abdul Razak, Fazlyn Reeny Binti
 University of Groningen Mutational landscape of Hodgkin lymphoma Abdul Razak, Fazlyn Reeny Binti IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Mutational landscape of Hodgkin lymphoma Abdul Razak, Fazlyn Reeny Binti IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
Improving quality of care for patients with ovarian and endometrial cancer Eggink, Florine
 University of Groningen Improving quality of care for patients with ovarian and endometrial cancer Eggink, Florine IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if
University of Groningen Improving quality of care for patients with ovarian and endometrial cancer Eggink, Florine IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if
Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU
 Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU Lecture outline Time 10:00 11:00 11:15 12:10 12:20 13:15 Content Introduction to lymphoma Review of lymphocyte biology
Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU Lecture outline Time 10:00 11:00 11:15 12:10 12:20 13:15 Content Introduction to lymphoma Review of lymphocyte biology
Burkitt lymphoma. Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8
 Heme 8 Burkitt lymphoma Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8 Most common is t(8;14) Believed to be the fastest growing tumor in humans!!!! Morphology
Heme 8 Burkitt lymphoma Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8 Most common is t(8;14) Believed to be the fastest growing tumor in humans!!!! Morphology
Immunology Lecture 4. Clinical Relevance of the Immune System
 Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies
 Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies Megan S. Lim MD PhD University of Pennsylvania October 8, 2018 Objectives To understand how the trend toward less invasive lymph
Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies Megan S. Lim MD PhD University of Pennsylvania October 8, 2018 Objectives To understand how the trend toward less invasive lymph
5/1/13. The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age. The cellular organization of the thymus
 T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. Lymphoma Tumor Board. January 5, 2018
 Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma Lymphoma Tumor Board January 5, 2018 Etiology Subtypes of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (chl)* Nodular sclerosing HL Most common subtype Composed of large tumor
Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma Lymphoma Tumor Board January 5, 2018 Etiology Subtypes of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (chl)* Nodular sclerosing HL Most common subtype Composed of large tumor
Citation for published version (APA): Bleeker, W. A. (2001). Therapeutic considerations in Dukes C colon cancer s.n.
 University of Groningen Therapeutic considerations in Dukes C colon cancer Bleeker, Willem Aldert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Therapeutic considerations in Dukes C colon cancer Bleeker, Willem Aldert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Daratumumab, a novel human CD38 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of B cell Non Hodgkin Lymphoma
 Daratumumab, a novel human CD38 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of B cell Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Anna Vidal Department of Hemato Oncology IDIBAPS, Barcelona, Spain B cell lymphoid malignancies seen
Daratumumab, a novel human CD38 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of B cell Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Anna Vidal Department of Hemato Oncology IDIBAPS, Barcelona, Spain B cell lymphoid malignancies seen
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy
 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow
 The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow Anna Porwit Lund University Faculty of Medicine Dept. of Clinical Sciences Div. Oncology and Pathology anna.porwit@med.lu.se Disclosure of speaker s interests
The spectrum of flow cytometry of the bone marrow Anna Porwit Lund University Faculty of Medicine Dept. of Clinical Sciences Div. Oncology and Pathology anna.porwit@med.lu.se Disclosure of speaker s interests
T cell lymphoma diagnostics and differential diagnosis to Hodgkin lymphoma
 T cell lymphoma diagnostics and differential diagnosis to Hodgkin lymphoma Sylvia Hartmann Dr. Senckenberg Institute of Pathology Goethe University Frankfurt Overview Borderline ALCL classical HL Borderline
T cell lymphoma diagnostics and differential diagnosis to Hodgkin lymphoma Sylvia Hartmann Dr. Senckenberg Institute of Pathology Goethe University Frankfurt Overview Borderline ALCL classical HL Borderline
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
The Development of Lymphocytes: B Cell Development in the Bone Marrow & Peripheral Lymphoid Tissue Deborah A. Lebman, Ph.D.
 The Development of Lymphocytes: B Cell Development in the Bone Marrow & Peripheral Lymphoid Tissue Deborah A. Lebman, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how ordered Ig gene rearrangements lead to the development
The Development of Lymphocytes: B Cell Development in the Bone Marrow & Peripheral Lymphoid Tissue Deborah A. Lebman, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how ordered Ig gene rearrangements lead to the development
Alessandra Franco, M.D., Ph.D. UCSD School of Medicine Department of Pediatrics Division of Allergy, Immunology and Rheumatology
 Natural regulatory T cells recognize the heavy constant region (Fc) of immunoglobulins: a novel mechanism for IVIG immunotherapy in Pediatric Immune-mediated diseases Alessandra Franco, M.D., Ph.D. UCSD
Natural regulatory T cells recognize the heavy constant region (Fc) of immunoglobulins: a novel mechanism for IVIG immunotherapy in Pediatric Immune-mediated diseases Alessandra Franco, M.D., Ph.D. UCSD
Case Report PAX5-Negative Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Case Report of a Rare Entity and Review of the Literature
 Hindawi Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2017, Article ID 7531729, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7531729 Case Report PAX5-Negative Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Case Report of a Rare Entity and
Hindawi Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2017, Article ID 7531729, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7531729 Case Report PAX5-Negative Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Case Report of a Rare Entity and
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies. Mixed follicular and paracortical hyperplasia. Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia
 Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia Follicular hyperplasia (B-cells) Paracortical
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia Follicular hyperplasia (B-cells) Paracortical
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells. Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital
 Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy. Faizi Ali, MD
 88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy Faizi Ali, MD Clinical History A 88-year-old caucasian female presented to our hospital with the complaints of nausea, vomiting,diarrhea, shortness of breath and
88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy Faizi Ali, MD Clinical History A 88-year-old caucasian female presented to our hospital with the complaints of nausea, vomiting,diarrhea, shortness of breath and
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Incidence. Bimodal age incidence 15-40, >55 years Childhood form (0-14) more common in developing countries M:F=1.5:1; in all subtypes except NS
 Hodgkin Lymphoma Hodgkin Lymphoma 30% of all lymphomas Absolute incidence unchanged Arise in lymph node, cervical region Neoplastic tissues usually contain a small number of tumor cells Incidence Bimodal
Hodgkin Lymphoma Hodgkin Lymphoma 30% of all lymphomas Absolute incidence unchanged Arise in lymph node, cervical region Neoplastic tissues usually contain a small number of tumor cells Incidence Bimodal
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
7 Omar Abu Reesh. Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour
 7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
 The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
, , 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA
 European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis
 Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
University of Groningen. Cardiotoxicity after anticancer treatment Perik, Patrick Jozef
 University of Groningen Cardiotoxicity after anticancer treatment Perik, Patrick Jozef IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Cardiotoxicity after anticancer treatment Perik, Patrick Jozef IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Small B-cell (Histologically Low Grade) Lymphoma
 Frequency of Lymphoid Neoplasms Small B-cell (Histologically Low Grade) Lymphoma Stephen Hamilton-Dutoit Institute of Pathology Aarhus University Hospital B-cell neoplasms 88% Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Frequency of Lymphoid Neoplasms Small B-cell (Histologically Low Grade) Lymphoma Stephen Hamilton-Dutoit Institute of Pathology Aarhus University Hospital B-cell neoplasms 88% Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
CD40L TCR IL-12 TLR-L
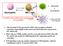 CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
Primer on Tumor Immunology. International Society for Biological Therapy of Cancer. C. H. June, M.D. November 10, 2005
 Primer on Tumor Immunology International Society for Biological Therapy of Cancer C. H. June, M.D. November 10, 2005 Outline: Primer on Tumor Immunology T Cell Receptors T Cell Biology Tumor immunology
Primer on Tumor Immunology International Society for Biological Therapy of Cancer C. H. June, M.D. November 10, 2005 Outline: Primer on Tumor Immunology T Cell Receptors T Cell Biology Tumor immunology
CD30 expression utilization for the accuracy of classical Hodgkin s lymphoma staging
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(2):113 117 ORIGINAL PAPER CD30 expression utilization for the accuracy of classical Hodgkin s lymphoma staging CORINA FLANGEA 1), ELENA POTENCZ 2),
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(2):113 117 ORIGINAL PAPER CD30 expression utilization for the accuracy of classical Hodgkin s lymphoma staging CORINA FLANGEA 1), ELENA POTENCZ 2),
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE
 CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
The Immune System. Innate. Adaptive. - skin, mucosal barriers - complement - neutrophils, NK cells, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils
 Objectives - explain the rationale behind cellular adoptive immunotherapy - describe methods of improving cellular adoptive immunotherapy - identify mechanisms of tumor escape from cellular adoptive immunotherapy
Objectives - explain the rationale behind cellular adoptive immunotherapy - describe methods of improving cellular adoptive immunotherapy - identify mechanisms of tumor escape from cellular adoptive immunotherapy
University of Groningen. BNP and NT-proBNP in heart failure Hogenhuis, Jochem
 University of Groningen BNP and NT-proBNP in heart failure Hogenhuis, Jochem IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen BNP and NT-proBNP in heart failure Hogenhuis, Jochem IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Pathology #07. Hussein Al-Sa di. Dr. Sohaib Al-Khatib. Mature B-Cell Neoplasm. 0 P a g e
 Pathology #07 Mature B-Cell Neoplasm Hussein Al-Sa di Dr. Sohaib Al-Khatib 0 P a g e Thursday 18/2/2016 Our lecture today (with the next 2 lectures) will be about lymphoid tumors This is a little bit long
Pathology #07 Mature B-Cell Neoplasm Hussein Al-Sa di Dr. Sohaib Al-Khatib 0 P a g e Thursday 18/2/2016 Our lecture today (with the next 2 lectures) will be about lymphoid tumors This is a little bit long
University of Groningen. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba
 University of Groningen Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
University of Groningen. Hidradenitis suppurativa Dickinson-Blok, Janine Louise
 University of Groningen Hidradenitis suppurativa Dickinson-Blok, Janine Louise IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Hidradenitis suppurativa Dickinson-Blok, Janine Louise IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation. Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
 New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas
 Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response
 chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
Sorting and trafficking of proteins in oligodendrocytes during myelin membrane biogenesis Klunder, Lammert
 University of Groningen Sorting and trafficking of proteins in oligodendrocytes during myelin membrane biogenesis Klunder, Lammert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen Sorting and trafficking of proteins in oligodendrocytes during myelin membrane biogenesis Klunder, Lammert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
Immunology for the Rheumatologist
 Immunology for the Rheumatologist Rheumatologists frequently deal with the immune system gone awry, rarely studying normal immunology. This program is an overview and discussion of the function of the
Immunology for the Rheumatologist Rheumatologists frequently deal with the immune system gone awry, rarely studying normal immunology. This program is an overview and discussion of the function of the
Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype. Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital
 Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital Function of the Lymph System Lymph Node Lymphocytes B-cells develop in the bone marrow and influence the immune
Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital Function of the Lymph System Lymph Node Lymphocytes B-cells develop in the bone marrow and influence the immune
Tumor Immunology. Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant
 Tumor Immunology Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant 1) Immune responses that develop to cancer cells 2) Escape of cancer cells 3) Therapies: clinical and experimental Cancer cells can be
Tumor Immunology Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant 1) Immune responses that develop to cancer cells 2) Escape of cancer cells 3) Therapies: clinical and experimental Cancer cells can be
DETERMINATION OF A LYMPHOID PROCESS
 Chapter 2 Applications of Touch Preparation Cytology to Intraoperative Consultations: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Tissues for Evaluation of Hematolymphoid Disorders INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chap. 1,
Chapter 2 Applications of Touch Preparation Cytology to Intraoperative Consultations: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Tissues for Evaluation of Hematolymphoid Disorders INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chap. 1,
Defensive mechanisms include :
 Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
7/6/2009. The study of the immune system and of diseases that occur as a result of inappropriate or inadequate actions of the immune system.
 Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Immunology. T-Lymphocytes. 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters,
 Immunology T-Lymphocytes 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters, karin.peters@rub.de The role of T-effector cells in the immune response against microbes cellular immunity humoral immunity
Immunology T-Lymphocytes 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters, karin.peters@rub.de The role of T-effector cells in the immune response against microbes cellular immunity humoral immunity
University of Groningen. Real-world influenza vaccine effectiveness Darvishian, Maryam
 University of Groningen Real-world influenza vaccine effectiveness Darvishian, Maryam IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Real-world influenza vaccine effectiveness Darvishian, Maryam IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
Gene expression in Hodgkin lymphoma. The role of mir-155 in normal and malignant B cells Kluiver, Joost
 University of Groningen Gene expression in Hodgkin lymphoma. The role of mir-155 in normal and malignant B cells Kluiver, Joost IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen Gene expression in Hodgkin lymphoma. The role of mir-155 in normal and malignant B cells Kluiver, Joost IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F Lyon
 Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F-69008 Lyon www.dendritics.net Human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells (PDCs) are considered the main sentinels
Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F-69008 Lyon www.dendritics.net Human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells (PDCs) are considered the main sentinels
Monocyte subsets in health and disease. Marion Frankenberger
 Monocyte subsets in health and disease Marion Frankenberger main cellular components: Leukocytes Erythrocytes Composition of whole blood Monocytes belong to the cellular components of peripheral blood
Monocyte subsets in health and disease Marion Frankenberger main cellular components: Leukocytes Erythrocytes Composition of whole blood Monocytes belong to the cellular components of peripheral blood
Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma)
 Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma) Common lymphoid neoplasm, present at old age (70 years average) Remember: plasma cells are terminally differentiated B-lymphocytes that produces antibodies. B-cells
Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma) Common lymphoid neoplasm, present at old age (70 years average) Remember: plasma cells are terminally differentiated B-lymphocytes that produces antibodies. B-cells
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
The immune response against cancer
 The immune response against cancer Maries van den Broek Institute of Experimental Immunology vandenbroek@immunology.uzh.ch The immune system Main cells of the immune system Dendritic cell Monocyte Macrophage
The immune response against cancer Maries van den Broek Institute of Experimental Immunology vandenbroek@immunology.uzh.ch The immune system Main cells of the immune system Dendritic cell Monocyte Macrophage
Follicular Lymphoma. ced3 APOPTOSIS. *In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans 131 of the organism's 1031 cells die during development.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology. Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport
 From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport I have no Conflict of Interest. FNA on Lymphoproliferative
From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport I have no Conflict of Interest. FNA on Lymphoproliferative
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
In vitro studies on the cytoprotective properties of Carbon monoxide releasing molecules and N-acyl dopamine derivatives Stamellou, Eleni
 University of Groningen In vitro studies on the cytoprotective properties of Carbon monoxide releasing molecules and N-acyl dopamine derivatives Stamellou, Eleni IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult
University of Groningen In vitro studies on the cytoprotective properties of Carbon monoxide releasing molecules and N-acyl dopamine derivatives Stamellou, Eleni IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Text Results In vitro activation experiments established that treatment with anti-cd3 plus anti- CD28 was sufficient to promote EBI2 transcript on CD4 T cells (Extended Data Fig. 1d, e).
Supplementary Text Results In vitro activation experiments established that treatment with anti-cd3 plus anti- CD28 was sufficient to promote EBI2 transcript on CD4 T cells (Extended Data Fig. 1d, e).
IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
 LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
Hodgkin Lymphomas: An Update
 Hodgkin Lymphomas: An Update Roberto N. Miranda, M.D. Professor UT MD Anderson Cancer Center November 10 th, 2018 Disclosures Scientific Advisory Board, Allergan Inc, 2018 Hodgkin Lymphomas Classical Hodgkin
Hodgkin Lymphomas: An Update Roberto N. Miranda, M.D. Professor UT MD Anderson Cancer Center November 10 th, 2018 Disclosures Scientific Advisory Board, Allergan Inc, 2018 Hodgkin Lymphomas Classical Hodgkin
University of Groningen. Mutational landscape of Hodgkin lymphoma Abdul Razak, Fazlyn Reeny Binti
 University of Groningen Mutational landscape of Hodgkin lymphoma Abdul Razak, Fazlyn Reeny Binti IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Mutational landscape of Hodgkin lymphoma Abdul Razak, Fazlyn Reeny Binti IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
The Adaptive Immune Response. T-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response T-cells T Lymphocytes T lymphocytes develop from precursors in the thymus. Mature T cells are found in the blood, where they constitute 60% to 70% of lymphocytes, and in T-cell
The Adaptive Immune Response T-cells T Lymphocytes T lymphocytes develop from precursors in the thymus. Mature T cells are found in the blood, where they constitute 60% to 70% of lymphocytes, and in T-cell
Citation for published version (APA): Minich, D. M. (1999). Essential fatty acid absorption and metabolism Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Essential fatty acid absorption and metabolism Minich, Deanna Marie IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Essential fatty acid absorption and metabolism Minich, Deanna Marie IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma plasma B cell.
 Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology
 Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
Prepared by: Dr.Mansour Al-Yazji
 C L L CLL Prepared by: Abd El-Hakeem Abd El-Rahman Abu Naser Ahmed Khamis Abu Warda Ahmed Mohammed Abu Ghaben Bassel Ziad Abu Warda Nedal Mostafa El-Nahhal Dr.Mansour Al-Yazji LEUKEMIA Leukemia is a form
C L L CLL Prepared by: Abd El-Hakeem Abd El-Rahman Abu Naser Ahmed Khamis Abu Warda Ahmed Mohammed Abu Ghaben Bassel Ziad Abu Warda Nedal Mostafa El-Nahhal Dr.Mansour Al-Yazji LEUKEMIA Leukemia is a form
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 16 THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? The adaptive immune system protects us from many infections The adaptive immune system has memory so we are not infected by the same pathogen
CHAPTER 16 THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? The adaptive immune system protects us from many infections The adaptive immune system has memory so we are not infected by the same pathogen
Immune Regulation and Tolerance
 Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
