Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Screening and Diagnostic Imaging. Authors: Emily F. Conant, MD, FSBI; Liane Philpotts, MD, FSBI
|
|
|
- Jared Holmes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Screening and Diagnostic Imaging Authors: Emily F. Conant, MD, FSBI; Liane Philpotts, MD, FSBI Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), which was FDA approved in 2011, is rapidly emerging as the new standard of care for x-ray imaging of the breast. Multiple studies have shown that when DBT is coupled with conventional 2D mammography, improvements in both sensitivity and specificity are achieved for screening and diagnostic breast imaging. A derivative of digital mammography, DBT is a form of limited angle tomography; it consists of multiple low-dose x-ray exposures which are acquired along a limited arc creating data which are reconstructed into a series of thin images or slices or planes of the breast. 1,2 The ability to scroll thru the stack of reconstructed layers of the breast minimizes the impact of overlapping tissue that can mask lesions making them difficult to detect in conventional 2D mammography. 3 The quasi three-dimensional format of the reconstructed DBT images also allows better localization of lesions and improves the conspicuity of both benign and malignant lesion margins. Details of acquisition of tomosynthesis imaging data and reconstruction vary by vendor and thus far, there has been no direct comparison of vendor-specific imaging in a clinical trial. In breast cancer screening, DBT outcome data have repeatedly demonstrated a reduction in false positive recalls as well as an increase in breast cancer detection when DBT is combined with conventional 2D mammography (Table 1). In most series, the incorporation of DBT imaging in screening is associated with an increase in the detection of invasive breast cancers often without a significant change in the detection of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). 4,7,8 This combination of improvements in specificity and sensitivity directly addresses the criticism of 2D mammographic screening too many false positives and too few cancers detected. In addition, the preferential increase in detection of invasive cancers (rather than DCIS) may address the concern that screening mammography may detect some indolent breast cancers (e.g. low grade DCIS) that may not otherwise become clinically evident over a woman s lifetime. When DBT screening outcomes are analyzed by breast density, studies show that the majority of women benefit from the incorporation of DBT. 8,14 Even women with less dense breasts (i.e., fatty or scattered densities) have been shown to benefit from the incorporation of DBT, perhaps due to breast parenchymal complexity on the 2D mammogram rather than just the degree of optical density or areas of masking dense breast tissue. In women with dense breasts, the improvement in outcomes with DBT appears to be achieved mostly in women with heterogeneously dense breasts. 14 While numbers are small for the sub-analysis of women with extremely dense breasts, there is a suggestion that tomosynthesis improves outcomes but not to the same extent as in the other 3 categories of lower breast density. 14 Interim results from the first year of a prospective, multicenter Italian study comparing handheld physician-performed screening ultrasound with combination digital mammography (DM) and DBT in women with dense breasts and negative conventional DM screening demonstrated that screening ultrasound found significantly more additional cancers than did DBT,
2 suggesting that supplemental screening (in addition to DBT) will continue to have a role in some women with dense breasts. 15 Further study of this important issue is ongoing. Much of the early data published on DBT screening have been in women at the first, prevalence round of DBT screening (with or without prior DM screening) and often without follow-up data to assess false negative and/or interval cancer rates. A recent, single site study of the first 3 consecutive years after complete conversion to DBT screening has shown a small prevalence effect in improved cancer detection at the first round of DBT compared to that at a second round of screening. 12 At the second round of screening (the first incident round), the cancer detection rate was very similar to the site s historic DM levels. At the third round of DBT screening (second incident screening round), the cancer detection rate was higher than seen at the first DBT screening round, perhaps due to continued learning of the DBT readers. (Although incident cancer detection rates are expected to be lower, cancers may be smaller in size due to earlier detection. However, there are no data to support this hypothesis at this time.) Importantly, the recall rate dropped with each consecutive DBT screening round. 12 Early data on false negative rates have also been promising with a trend to a reduction in interval 4, 12, 13 cancers with DBT screening compared to DM alone screening. Combination DM/DBT screening incurs a higher radiation dose (however, still within MQSA guidelines) than screening with DM alone. Recently, the FDA has approved the use of a reconstructed synthetic, 2D-like image (s2d) to replace the 2D dose portion of a DBT study thereby reducing the overall x-ray dose by up to 45%, or 1.2 fold that of standard DM. 4 However, there are few reported clinical studies comparing DBT using only synthetic images versus 2D mammography These studies will be important to assess if the improvement noted when DBT is combined with 2D can be maintained with s2d/dbt. Early data on the clinical implementation of s2d/dbt screening have shown that the combination is non-inferior to DM/DBT with similar or even lower recall rates and similar cancer detection rates. 19 While most literature to date on digital breast tomosynthesis focuses on screening, DBT is also being recognized as beneficial in the diagnostic setting. The impact of DBT on diagnostic imaging has been assessed in several ways. First, some facilities implementing DBT with a limited number of units, may choose to utilize DBT only for diagnostic patients. Such diagnostic exams will then include patients recalled after 2D mammography along with those seen for other diagnostic reasons. Early reader studies evaluating one or twoview DBT compared with conventional 2D diagnostic images found DBT was equivalent or superior Studies comparing conventional (2D) spot compression views found DBT comparable or superior in characterizing noncalcified lesions for diagnostic purposes Non-calcified lesions can often be assessed without obtaining multiple additional 2D views making diagnostic evaluations more efficient when DBT is used. Ultrasound should still be performed to fully characterize palpable abnormalities and to further evaluate masses seen on tomosynthesis. Magnification views are usually still needed to fully characterize the morphology and extent of any suspicious calcification. For patients who have already undergone DBT screening and are recalled for further evaluation of a finding, an abbreviated diagnostic workup may be possible. Due to the ability of DBT to both better localize and
3 characterize lesions, many patients recalled from DBT screening may go directly to targeted diagnostic ultrasound for further evaluation rather than having multiple additional mammographic views previously needed for 3D localization (i.e., mediolateral or rolled views) or margin characterization (i.e., spot compression views). 26 In addition, many asymptomatic patients in the diagnostic pool, e.g. women undergoing surveillance years after a diagnosis of breast cancer, are adequately served by standard DBT imaging alone. Indeed, in many centers, such women can be returned to screening using DBT. The reduction in additional diagnostic imaging in this population also increases the throughput of patients and can improve the efficiency of a breast center. 27 Beyond the reduction in screening recalls and improved efficiency of diagnostic workup of imaging findings, the use of DBT has been found to reduce the proportion of BI-RADS 3 cases by up to 50% when compared with 2D mammography. 9 DBT allows for more definitively benign or suspicious characterizations and fewer Probably Benign assessments, with a concomitant shift to a greater proportion of patients receiving BI-RADS 1 and 2 assessments, and thus returned to screening. Over time, this decrease in category 3 patients results in progressive shrinking of the number of patients undergoing diagnostic follow-up. With this decrease, changes in departmental workflow and resources can be anticipated. 28 Additionally, due to DBT s superior lesion assessment, the positive predictive value (PPV3) of diagnostic biopsy performed has also been observed to increase. A more than 50% increase in PPV over 2D mammography has been observed. 28 This results in fewer biopsies, improved efficiency, and thus saves costs, resources, and patient inconvenience and anxiety. For malignancy, the improved definition of shape and margins can result in improved assessment of lesion size along with the improved detection of multifocal and multicentric disease. While concern has been raised over the fact that the interpretation of combination DM/DBT studies takes approximately two times that of DM-only cases, the dramatic improvement in screening outcomes and diagnostic mammography workflow can partially counter this effect. Implementation of DBT imaging has resulted in changes in the workflow in breast imaging departments due to expedited work-ups, increased throughput of patients which allow the potential for additional patient centered service with online reading and the immediate delivery of both screening and diagnostic imaging results. It is important to note, however, that when implementing large volume DBT imaging, a radiology department should anticipate significantly increased storage requirement for the large DBT data files. Recent advances have been made to not only standardize the storage format across vendors but to also improve the data compression techniques for the DBT data to reduce storage demands. In summary, DBT imaging has had a dramatic impact on the delivery of screening and diagnostic breast imaging in just the 5 years since FDA approval. The innovative technology should no longer be considered as investigational but rather viewed as the new, better mammogram. In addition, the tomosynthesis platform continues to evolve with continued improvements in image quality, x-ray dose reduction and the development of navigational tools to help improve reading efficiency. As with any newly implemented technology, longer
4 term DBT outcomes and evolving data from ongoing trials will help to further clarify the role of DBT imaging in optimizing patient outcomes in both screening and diagnostic breast imaging.
5 Table 1. Comparison of outcomes in screening with digital mammography combined with tomosynthesis (DBT) compared to digital mammography alone (DM). Reference Study Type, Age of Patients and additional Comments Number of Screening Examinations Recall Rate Change in Cancer detection rate/1000 women screened from DM to DBT screening (absolute change as well as percent change) Skaane (Radiology 2013) Prospective single site, multiple arms with multiple independent reads of same patients. Age: years old Comments: Patients underwent both DM and DBT.Each arm interpreted by different radiologist with arbitration for positive studies, some patients included were symptomatic (i.e., lumps, discharge) 12,631 women DM: 6.1% DBT: 5.3% (15% DM: 6.1 DBT: 8.0 (increase of 1.9 cancers per 1000 screened; 31% Ciatto Prospective study at 2 sites women DM: 5.0% DM: 5.3 (Lancet 2013) Age: 48 years and over DBT: 4.3% DBT: 8.1
6 Comments: Patients underwent both DM and DBT. Consecutive reads of DM then DM plus DBT also double reading and so difficult to assess for false negative DM rate (17.2% decrease in conditional recall) (increase of 2.8 cancers per 1000 screened; 53% Haas Observational study at network sites. DM: 7058 DM: 12.0% DM: 5.2 (Radiology 2013) Comments: Potential for bias since concurrent DM screening. No follow-up data for false negatives DBT: 6100 DBT: 8.4% (30% DBT: 5.7 (increase of 0.5 cancers per 1000 screened; 9.6% Rose* Observational study at single site. DM: 13,856 DM: 8.7% DM: 4.0 (AJR 2013) DBT: 9,499 DBT: 5.5% DBT: 5.4 Comments: Potential for bias since concurrent DM screening. No follow-up data for false negatives (37% (increase of 1.4 cancers per 1000 screened; 35% Greenberg* Observational study at network sites. DM: 38,674 DM: DM: 4.9 (AJR 2014) DBT: 20,943 DBT: DBT: 6.3 Comments: Potential for bias since concurrent DM screening. No follow-up (16.1% (increase of 1.4 cancers per 1000 screened; 28.6%
7 data for false negatives Friedewald* (JAMA 2014) Observational, 13 U.S. sites combine MQSA outcome data. Comments: Potential for bias since concurrent DM screening. Also used historic DM for comparison. No patient level data or follow-up data for false negatives DM: 281,187 DBT: 173,663 DM: 10.7% DBT: 9.1% (15% DM: 4.2 DBT: 5.4 (increase of 1.2 cancers per 1000 screening; 29% McCarthy* Observational study at single site. DM: 10,729 DM: 10.4% DM: 4.6 (JNCI 2014) DBT: 15,571 DBT: 8.8% DBT: 5.8 Comments: Complete conversion to DBT with historic DM comparison. No follow-up data for false negatives. (15% (increase of 1.2 cancers per 1000 screened; 26% Lorenco Observational study at single site. DM: 12,577 DM: 9.3% DM: 5.4 (Radiology DBT: 12,921 DBT: 6.4% DBT: 4.6
8 2015) Comments: Complete conversion to DBT with historic DM comparison. No follow-up data for false negatives (31% (*cancer detection decreased by 0.8 cancers per 1000 screened; 17% Durand* Observational study at network sites. DM: 9,364 DM: 12.3% DM: 5.7 (Radiology 2015) Comments: Potential for bias since concurrent DM screening. No follow-up data for false negatives DBT: 8,591 DBT: 7.8% (36.6% DBT: 5.9 (increase of 0.2 cancers per 1000 screened; 3.5% Conant* (BCR&T 2016) Observational, multi-site. Patient level data with follow-up for false negative assessment. DM: 142,882 DBT: 55,998 DM: 10.4% DBT: 8.7% DM: 4.4 DBT: 5.9 Comments: Potential for bias since concurrent DM screening. (16% decrease; however, when adjusted for patient level factors, recall reduction was (increase of 1.5 cancers per 1000 screened; 34%. Also trend in decreased false negatives; 0.06 to 0.46/1000 for DM vs. DBT,
9 21%) n.s.) Range Range of 9-37% decrease in recall Range from a reduction of 0.2 to an increase of 2.8 cancers per 1000 screened Or, a 17% decrease to 53% increase in overall cancer detection rate *Trials which contain a degree of overlap of patient populations also reported in Friedewald et al 7
10 References: 1. Niklason LT, Christian BT, Niklason LE, et al., Digital tomosynthesis in breast imaging.radiology 1997;205(2): Sechopoulos I. A review of breast tomosynthesis. Part I. The image acquisition process. Med Phys 2013;40(1): Conant EF. Clinical implementation of digital breast tomosynthesis. Radiol Clin North Am 52(3), May Skaane, P., Bandos A.I., Gullien R., et al. Comparison of digital mammography alone and digital mammography plus tomosynthesis in a population-based screening program. Radiology, (1): p Ciatto S., Houssami N, Bernardi D, et al., Integration of 3D digital mammography with tomosynthesis for population breast-cancer screening (STORM): a prospective comparison study. Lancet Oncol, (7): p Rose S.L., Tidwell A.L., Bujnoch L.J., et al. Implementation of breast tomosynthesis in a routine screening practice: an observational study. AJR Am J Roentgenol, (6): p Friedewald S.M., Rafferty EA., Rose SL., et al., Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis in combination with digital mammography. JAMA, (24): p McCarthy A.M., Kontos D., Synnestvedt M., et al., Screening outcomes following implementation of digital breast tomosynthesis in a general-population screening program. J Natl Cancer Inst, (11). 9. Durand M.A., Haas BM, Xiapan Y., et al. Early Clinical Experience with Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Screening Mammography. Radiology, 2014: p Lourenco, A.P. Barry-Brooks M., Baird G.L., Tuttle A., Mainiero M.B. Changes in Recall Type and Patient Treatment Following Implementation of Screening Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. Radiology, 2014: p
11 11. Haas B.M., Kalr V., Geisel J., et al. Comparison of tomosynthesis plus digital mammography and digital mammography alone for breast cancer screening. Radiology, (3): p McDonald ES, Oustimov A, Weinstein SP, Synnestvedt M, Schnall M, Conant EF. Effectiveness of digital breast tomosynthesis compared with digital mammography: Outcomes analysis from 3 years of breast cancer screening. JAMA Onc. 2(6): 1-7, Conant EF, Beaber EF, Sprague BL, Herschorn SD, Weaver DL, Onega T, Tosteson ANA, McCarthy AM, Poplack SP, Haas JS, Armstrong K, Schnall MD, Barlow WE. Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis in combination with digital mammography compared to digital mammography alone: a cohort study within the PROSPR consortium. Breast Cancer Res Treat Feb;156(1): Rafferty EA, Durand MA, Conant EF, Copit DS, Friedewald SM, Plecha DM, Miller MS. Breast Cancer Screening Using Tomosynthesis and Digital Mammography in Dense and Non-Dense Breasts. JAMA epub 4/ Tagliafico AS, Calabrese M, Mariscotti, G, Durando M, Tosta S, Monetti F, Airaldi S, Bignotti B, Nori J, Bagni A, Signori A, Sormani MP, Houssami N. Adjunct Screening with Tomosynthesis or Ultrasound in Women with Mammography-Negative Dense Breasts: Interim Report of a Prospective Comparative Trial. Epub March 9, Skaane P, Bandos AI, Eben EB, Jebsen IN, Krager M, Haakenaasen U, Ekseth U, Izadi M, Hofvind S, Gullien R. Two-view digital breast tomosynthesis screening with synthetically reconstructed projection images: comparison with digital breast tomosynthesis with full-field digital mammographic images. Radiology. 2014;271(3): Gilbert FJ, Tucker LT, Gillan, MGC, Wilsher P, Cooke J, Duncan KA, Michell MJ, Dobson HM, Lim YY, Suaris T, Astley SM, Morrish O, Yond KC, Duffy SW. Accuracy of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Depicting Breast Cancer Subgroups in a UK Retrospective Reading Study (TOMMY Trial). Radiol 2015;277(3): Choi JS, Han B, Ko EY, Ko ES, Hahn SY, Shin JH, Kim MJ. Comparison between two-dimensional synthetic mammography reconstructed from digital breast tomosynthesis and full-field digital mammography for the detection of T1 breast cancer. Eur Radiol 2015.online Dec 2015.
12 19. Zuckerman SP, Conant EF, Keller BM, Maidment ADA, Barufaldi B, Weinstein SP, Synnestvedt M, McDonald ES. Implementation of Synthesized 2D Mammography in a Population-based Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Screening Program. Radiol 2017 in press (epub Aug 2016). 20. Poplack S, Tosteson T, Kogel C, Nagy H. Digital breast tomosynthesis: initial experience in 98 women with abnormal digital screening mammography. AJR, Am J Roentgenol 2007;189(3): Brandt KR, Craig DA, Hoskins TL, Henrichsen TL, Bendel EC, Brandt SR, Mandrekar J. Can digital breast tomosynthesis replace conventional diagnostic mammography views for screening recalls without calcifications? A comparison study in a simulated clinical setting. AJR, Am J Roentgenol 2013;200(2): Waldherr C, Cerny P, Altermatt HJ, et al. Value of one-view breast tomosynthesis versus two-view mammography in diagnostic workup of women with clinical signs and symptoms and in women recalled from screening. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013; 200(1): Noroozian M, Hadjiiski L, Rahnama-Moghadam S, Klein KA, Jeffries DO, Pinsky RW, Chan HP, Carson P, Helvie M, Roubidoux, M. Digital breast tomosynthesis is comparable to mammographic spot views for mass characterization. Radiology 2012;262(1): Tagliafico A, Astengo D, Cavagnetto F, et al. One-to-one comparison between digital spot compression view and digital breast tomosynthesis. Eur Radiol 2012;22(3): Zuley M, Bandos AI, Ganott MA, Sumkin JH, Kelly AE, Catullo VJ, Rathfon GY, Lu AH, Gur D. Digital breast tomosynthesis versus supplemental diagnostic mammographic views for evaluation of noncalcified breast lesions. Radiology 2013;266(1): Butler RS, Hui A, Staib LH, Hooley RJ, Philpotts LE. Downstream Effect of Tomosynthesis Screening A More Efficient Diagnostic Work-Up of Screening Recalls. RSNA annual meeting 2012(Chicago, IL) 27. Butler RS, Kalra V, Crenshaw J, Geisel J, Philpotts LE. Tomosynthesis in Diagnostic Mammography: Continued change after 4 years. RSNA annual meeting 2015
13 28. Raghu M, Durand MA, Andrejeva L, Goehler A, Michalski M, Geisel JL, Hooley RJ, Horvath LJ, Butler R, Forman HP, Philpotts LE. Tomosynthesis in the Diagnostic Setting: Changing Rates of BI-RADS Final Assessment Over Time. Radiology, epub May 3, 2016
Outline. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation. Tomosynthesis Dataset: 2D/3D (Hologic Combo Acquisition)
 Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
Subject: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) for Breast Cancer 3/10/16
 Subject: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) for Breast Cancer Policy Number: MCP-270 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: 3/10/16 Review Date: 6/22/17, 3/8/18 MCPC Approval Date: 3/8/18 DISCLAIMER
Subject: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) for Breast Cancer Policy Number: MCP-270 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: 3/10/16 Review Date: 6/22/17, 3/8/18 MCPC Approval Date: 3/8/18 DISCLAIMER
Corporate Medical Policy. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT)
 Corporate Medical Policy Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) Description of Procedure or Service DBT is a three-dimensional (3D) breast imaging technology that uses a rotating X-ray source to acquire multiple
Corporate Medical Policy Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) Description of Procedure or Service DBT is a three-dimensional (3D) breast imaging technology that uses a rotating X-ray source to acquire multiple
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography
 BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. Susan Orel Roth, MD
 Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become
 Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Financial Disclosures
 Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE?
 X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? TERMS (AKA) WHAT IS TOMOSYNTHESIS? 3/3/2014. Digital breast tomosynthesis =
 #46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
Breast cancer screening: Does tomosynthesis augment mammography?
 REVIEW TRACI A. TAKAHASHI, MD, MPH Director, Seattle VA Women Veterans Clinic at VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle CHRISTOPH
REVIEW TRACI A. TAKAHASHI, MD, MPH Director, Seattle VA Women Veterans Clinic at VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle CHRISTOPH
Dense Breasts, Get Educated
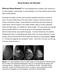 Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
TOMOSYNTHESIS. Daniela Bernardi. U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy
 TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
the one name in cancer care.
 the one name in cancer care. Landmark study evaluating close to half a million mammography exams published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) 1 Hologic 3D Mammography Significantly
the one name in cancer care. Landmark study evaluating close to half a million mammography exams published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) 1 Hologic 3D Mammography Significantly
MRI of the Breast Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scintimammography/Breast-Specific Gamma Imaging/Molecular Breast Imaging
 6.01.53 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Section Radiology Subsection Effective Date September 30, 2014 Original Policy Date June 28, 2013 Next Review Date September 2015 Description Digital breast tomosynthesis
6.01.53 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Section Radiology Subsection Effective Date September 30, 2014 Original Policy Date June 28, 2013 Next Review Date September 2015 Description Digital breast tomosynthesis
Comparison of one-view digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and two-view full-field digital mammography (FFDM)
 Comparison of one-view digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and two-view full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-2258 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Saguatti, P. Mainoldi,
Comparison of one-view digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and two-view full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-2258 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Saguatti, P. Mainoldi,
3D Mammography. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 What to Expect 3D Mammography The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense against breast
What to Expect 3D Mammography The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense against breast
Breast Tomosynthesis
 Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Strategies to Increase Cancer Detection: Review of True-Positive and False-Negative Results at Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Screening 1
 Breast Imaging 1954 This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Strategies to Increase Cancer Detection: Review of True-Positive and False-Negative Results at
Breast Imaging 1954 This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Strategies to Increase Cancer Detection: Review of True-Positive and False-Negative Results at
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D Mammography Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D Mammography Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D Mammography Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense
What s New in Breast Imaging. Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia
 What s New in Breast Imaging Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia Disclosure Hologic, Inc. Shareholder and research agreement. Volpara Solutions, Ltd. Shareholder
What s New in Breast Imaging Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia Disclosure Hologic, Inc. Shareholder and research agreement. Volpara Solutions, Ltd. Shareholder
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update. Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
 Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
Comparison of Tomosynthesis Plus Digital Mammography and Digital Mammography Alone for Breast Cancer Screening 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
Breast Tomosynthesis
 Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here. Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000
 WOMEN S HEALTH BREAST SOLUTIONS HEALTH The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast
WOMEN S HEALTH BREAST SOLUTIONS HEALTH The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast
ACR Appropriateness Criteria Breast Cancer Screening EVIDENCE TABLE. See Last Page for Key Revised 2017 Mainiero Page 1.
 1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7-0. Type Review/Other- N/A To estimate the numbers of new cancer cases and deaths that will occur in the United
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7-0. Type Review/Other- N/A To estimate the numbers of new cancer cases and deaths that will occur in the United
Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography
 Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography Overview of Current Challenges Barbara Monsees, Washington University Geographic Access, Equity and Impact on Quality Tracy Onega, Dartmouth Medical School
Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography Overview of Current Challenges Barbara Monsees, Washington University Geographic Access, Equity and Impact on Quality Tracy Onega, Dartmouth Medical School
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in the Diagnostic Environment: A Subjective Side-by-Side Review
 Women s Imaging Original Research Hakim et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Women s Imaging Original Research Christiane M. Hakim 1 Denise M. Chough 1 Marie A. Ganott 1 Jules H. Sumkin 1 Margarita L. Zuley
Women s Imaging Original Research Hakim et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Women s Imaging Original Research Christiane M. Hakim 1 Denise M. Chough 1 Marie A. Ganott 1 Jules H. Sumkin 1 Margarita L. Zuley
Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts. Reagan Leverett, MD, MS
 Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts Reagan Leverett, MD, MS Outline Anatomy and Density Risk of dense breasts Theory of Supplemental Screening Options for supplemental screening Tomosynthesis Ultrasound
Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts Reagan Leverett, MD, MS Outline Anatomy and Density Risk of dense breasts Theory of Supplemental Screening Options for supplemental screening Tomosynthesis Ultrasound
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
Implementation of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Routine Screening Practice: An Observational Study
 Women s Imaging Original Research Rose et al. Tomosynthesis in Routine Screening Women s Imaging Original Research Stephen L. Rose 1 Andra L. Tidwell Louis J. Bujnoch Anne C. Kushwaha Amy S. Nordmann Russell
Women s Imaging Original Research Rose et al. Tomosynthesis in Routine Screening Women s Imaging Original Research Stephen L. Rose 1 Andra L. Tidwell Louis J. Bujnoch Anne C. Kushwaha Amy S. Nordmann Russell
Jing Zhang, PhD, Lars J. Grimm, MD, MHS, Joseph Y. Lo, PhD, Karen S. Johnson, MD,
 This manuscript has been accepted for publication in Journal of the American College of Radiology. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published
This manuscript has been accepted for publication in Journal of the American College of Radiology. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Greenberg et al. Breast Cancer Screening Using 3D DBT Versus 2D DM Women s Imaging Original Research Julianne S. Greenberg 1 Marcia C. Javitt 2 Jason Katzen 1 Sara Michael
Women s Imaging Original Research Greenberg et al. Breast Cancer Screening Using 3D DBT Versus 2D DM Women s Imaging Original Research Julianne S. Greenberg 1 Marcia C. Javitt 2 Jason Katzen 1 Sara Michael
Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk, and the Breast Density Notification Law in California: A Consensus Document
 RSNA, 2013 Appendix E1 Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk, and the Breast Density Notification Law in California: A Consensus Document 1. I have been getting more questions
RSNA, 2013 Appendix E1 Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk, and the Breast Density Notification Law in California: A Consensus Document 1. I have been getting more questions
8/3/2016. DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis. Tomosynthesis Pedigree
 DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. University of Pennsylvania Department of Radiology Acknowledgements of Support Research support from the Komen Foundation,
DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. University of Pennsylvania Department of Radiology Acknowledgements of Support Research support from the Komen Foundation,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7): /ISSN: /IJCEM Ganime Dilek Emlik 1, Necdet Poyraz 1, Ayşegül Altunkeser 2
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):10668-10675 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0054405 Original Article Digital breast tomosynthesis and ultrasonography: diagnostic performance and effect on recall rates
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):10668-10675 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0054405 Original Article Digital breast tomosynthesis and ultrasonography: diagnostic performance and effect on recall rates
Effect of Mammographic Screening Modality on Breast Density Assessment: Digital Mammography versus Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BREAST IMAGING Effect of Mammographic Screening Modality on Breast Density Assessment: Digital Mammography versus Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Aimilia Gastounioti, PhD Anne Marie McCarthy,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BREAST IMAGING Effect of Mammographic Screening Modality on Breast Density Assessment: Digital Mammography versus Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Aimilia Gastounioti, PhD Anne Marie McCarthy,
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features.
 Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
Breast Tomosynthesis
 Breast Tomosynthesis Considerations for Routine Clinical Use Breast Tomosynthesis Considerations for routine clinical use Andrew Smith, Ph.D., Vice President - Imaging Sciences, Hologic This white paper
Breast Tomosynthesis Considerations for Routine Clinical Use Breast Tomosynthesis Considerations for routine clinical use Andrew Smith, Ph.D., Vice President - Imaging Sciences, Hologic This white paper
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS. The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here. Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000
 WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast cancer detection
WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast cancer detection
2018 PUBLIC REPORTING OF OUTCOMES
 2018 PUBLIC REPORTING OF OUTCOMES The Cancer Committee at Western Maryland Health System s Schwab Family Cancer Center reports annually on program and patient outcomes in compliance with the accreditation
2018 PUBLIC REPORTING OF OUTCOMES The Cancer Committee at Western Maryland Health System s Schwab Family Cancer Center reports annually on program and patient outcomes in compliance with the accreditation
Exa Mammo A Solution that Overcomes the Challenges of Implementing Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 Konica Minolta Healthcare Americas, Inc. Exa Mammo A Solution that Overcomes the Challenges of Implementing Digital Breast Tomosynthesis A WHITEPAPER INTRODUCTION Numerous published studies have shown
Konica Minolta Healthcare Americas, Inc. Exa Mammo A Solution that Overcomes the Challenges of Implementing Digital Breast Tomosynthesis A WHITEPAPER INTRODUCTION Numerous published studies have shown
TITLE: Digital Tomosynthesis for the Screening and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer: A Review of the Diagnostic Accuracy
 TITLE: Digital Tomosynthesis for the Screening and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer: A Review of the Diagnostic Accuracy DATE: 26 September 2013 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Breast cancer is the second leading
TITLE: Digital Tomosynthesis for the Screening and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer: A Review of the Diagnostic Accuracy DATE: 26 September 2013 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Breast cancer is the second leading
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Waldherr et al. One-View Breast Tomosynthesis Versus Two-View Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research Christian Waldherr 1 Peter Cerny 1 Hans J. Altermatt 2 Gilles
Women s Imaging Original Research Waldherr et al. One-View Breast Tomosynthesis Versus Two-View Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research Christian Waldherr 1 Peter Cerny 1 Hans J. Altermatt 2 Gilles
Selected Scientific Publications on Breast Tomosynthesis
 Selected Scientific Publications on Breast Tomosynthesis 2014 (P) Bernardi D, Caumo F, Macaskill P, Ciatto S, Pellegrini M, Brunelli S, Tuttobene P, Bricolo P, Fantò C, Valentini M, Montemezzi S, Houssami
Selected Scientific Publications on Breast Tomosynthesis 2014 (P) Bernardi D, Caumo F, Macaskill P, Ciatto S, Pellegrini M, Brunelli S, Tuttobene P, Bricolo P, Fantò C, Valentini M, Montemezzi S, Houssami
A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography, full-field digital mammography, and digital breast tomosynthesis
 Clinical Radiology xxx (2012) 1e6 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Clinical Radiology journal homepage: www.clinicalradiologyonline.net A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography,
Clinical Radiology xxx (2012) 1e6 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Clinical Radiology journal homepage: www.clinicalradiologyonline.net A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography,
Nehmat Houssami 1, Kristina Lång 2, Solveig Hofvind 3, Sophia Zackrisson 2, Daniela Bernardi 4, Kylie Hunter 5, Lisa Askie 5, Per Skaane 6
 Study Protocol Effectiveness of digital breast tomosynthesis (3D-mammography) in population breast cancer screening: a protocol for a collaborative individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis Nehmat
Study Protocol Effectiveness of digital breast tomosynthesis (3D-mammography) in population breast cancer screening: a protocol for a collaborative individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis Nehmat
Breast Cancer Screening Using Tomosynthesis in Combination With Digital Mammography
 Research Original Investigation Breast Cancer Screening Using in Combination With Sarah M. Friedewald, MD; Elizabeth A. Rafferty, MD; Stephen L. Rose, MD; Melissa A. Durand, MD; Donna M. Plecha, MD; Julianne
Research Original Investigation Breast Cancer Screening Using in Combination With Sarah M. Friedewald, MD; Elizabeth A. Rafferty, MD; Stephen L. Rose, MD; Melissa A. Durand, MD; Donna M. Plecha, MD; Julianne
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER BREAST IMAGING
 SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER BREAST IMAGING Liane Philpotts, MD, FSBI, FACR Professor, Radiology and Biomedical Imaging Division Chief, Breast Imaging Dec. 5, 2017 Warner, E. NEJM 2011 Screening for
SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER BREAST IMAGING Liane Philpotts, MD, FSBI, FACR Professor, Radiology and Biomedical Imaging Division Chief, Breast Imaging Dec. 5, 2017 Warner, E. NEJM 2011 Screening for
Screening Options in Dense Breasts. Donna Plecha, M.D. Co-Director UHCMC Breast Centers Associate Professor of Radiology Director of Breast Imaging
 Screening Options in Dense Breasts Donna Plecha, M.D. Co-Director UHCMC Breast Centers Associate Professor of Radiology Director of Breast Imaging Dense Breasted Women Decreased sensitivity of mammography
Screening Options in Dense Breasts Donna Plecha, M.D. Co-Director UHCMC Breast Centers Associate Professor of Radiology Director of Breast Imaging Dense Breasted Women Decreased sensitivity of mammography
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients
 Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
Scenarios for Clinicians
 Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk and Wisconsin Breast Density Notification Law (2017 Wisconsin Act 201) Scenarios for Clinicians Content adapted from the California Breast Density Information Group,
Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk and Wisconsin Breast Density Notification Law (2017 Wisconsin Act 201) Scenarios for Clinicians Content adapted from the California Breast Density Information Group,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: digital_breast_tomosynthesis 3/2011 6/2016 6/2017 11/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Conventional
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: digital_breast_tomosynthesis 3/2011 6/2016 6/2017 11/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Conventional
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM)
 Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- AIDED DETECTION (CAD) POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.012 06/28/2013 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 06/28/2013 Section: Radiology Place(s) of Service:
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.012 06/28/2013 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 06/28/2013 Section: Radiology Place(s) of Service:
Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese
 Dansk Radiologisk Selskab 9.årsmøde Odense 3.januar, 214 Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese Professor dr. med. Per Skaane Oslo University Hospital Ullevaal Breast Imaging Center Oslo / Norway PERSKA@ous-hf.no
Dansk Radiologisk Selskab 9.årsmøde Odense 3.januar, 214 Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese Professor dr. med. Per Skaane Oslo University Hospital Ullevaal Breast Imaging Center Oslo / Norway PERSKA@ous-hf.no
Additional US or DBT after digital mammography: which one is the best combination?
 Additional US or DBT after digital mammography: which one is the best combination? Poster No.: B-0926 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper A. Elizalde, P. Garcia Barquin, M.
Additional US or DBT after digital mammography: which one is the best combination? Poster No.: B-0926 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper A. Elizalde, P. Garcia Barquin, M.
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI
 Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Selected Scientific Publications on Breast Tomosynthesis
 Selected Scientific Publications on Breast Tomosynthesis 2013 (AB) Beck N, Butler R, Durand M, Andrejeva L, Hooley R, Horvath L, Raghu M, Philpotts L. One-View Versus Two-View Tomosynthesis: A Comparison
Selected Scientific Publications on Breast Tomosynthesis 2013 (AB) Beck N, Butler R, Durand M, Andrejeva L, Hooley R, Horvath L, Raghu M, Philpotts L. One-View Versus Two-View Tomosynthesis: A Comparison
Detection and Classification of Calcifications on Digital Breast Tomosynthesis and 2D Digital Mammography: A Comparison
 Women s Imaging Original Research Spangler et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Versus 2D Digital Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: M. Lee Spangler 1 Margarita L. Zuley 2 Jules H.
Women s Imaging Original Research Spangler et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Versus 2D Digital Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: M. Lee Spangler 1 Margarita L. Zuley 2 Jules H.
Breast Tomosynthesis. What is breast tomosynthesis?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
Electrical impedance scanning of the breast is considered investigational and is not covered.
 ARBenefits Approval: 09/28/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: Code(s): Medical Policy Title: Electrical Impedance Scanning of the Breast Document: ARB0127 Administered by: Public Statement:
ARBenefits Approval: 09/28/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: Code(s): Medical Policy Title: Electrical Impedance Scanning of the Breast Document: ARB0127 Administered by: Public Statement:
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound
 Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
01/2018 X 01/ /2017 X X 6/2017 X
 Digital breast Tomosynthesis vacuum assisted biopsy for Tomosynthesis-detected Sonographically occult lesions Ariaratnam NS, Little ST, Whitley MA, Ferguson K - Clinical Imaging Volume 47, January February
Digital breast Tomosynthesis vacuum assisted biopsy for Tomosynthesis-detected Sonographically occult lesions Ariaratnam NS, Little ST, Whitley MA, Ferguson K - Clinical Imaging Volume 47, January February
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research David Gur 1 Andriy I. Bandos 2 Howard E. Rockette 2 Margarita L. Zuley 3 Jules H. Sumkin 3 Denise M. Chough 3 Christiane M. Hakim 3 Gur
Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research David Gur 1 Andriy I. Bandos 2 Howard E. Rockette 2 Margarita L. Zuley 3 Jules H. Sumkin 3 Denise M. Chough 3 Christiane M. Hakim 3 Gur
Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis
 Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis Priya Thomas, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Cancer Prevention and Breast Medical Oncology University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosures Dr. Thomas has
Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis Priya Thomas, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Cancer Prevention and Breast Medical Oncology University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosures Dr. Thomas has
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening?
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
Disclosures. Breast Cancer. Breast Imaging Modalities. Breast Cancer Screening. Breast Cancer 6/4/2014
 : Information for the Primary Care Physician Disclosures No financial relationships with commercial entities producing health care products/services. Roxsann Roberts, MD Section Chief, MRI Erlanger/EmCare
: Information for the Primary Care Physician Disclosures No financial relationships with commercial entities producing health care products/services. Roxsann Roberts, MD Section Chief, MRI Erlanger/EmCare
Better detection. Clinically superior. Low dose The Selenia Dimensions 3D Mammography System
 Better detection. Clinically superior. Low dose. 1-13 The Selenia Dimensions 3D Mammography System Revolutionary Technology 1, 5-9 Simply a better mammogram. The Genius 3D Mammography exam from the Selenia
Better detection. Clinically superior. Low dose. 1-13 The Selenia Dimensions 3D Mammography System Revolutionary Technology 1, 5-9 Simply a better mammogram. The Genius 3D Mammography exam from the Selenia
The role of digital breast tomosynthesis in the breast assessment clinic: a review
 REVIEW ARTICLE The role of digital breast tomosynthesis in the breast assessment clinic: a review Suneeta Mall, BE, 1 Sarah Lewis, PhD, 1 Patrick Brennan, PhD, 1 Jennie Noakes, BMed(Newcastle), FRANZCR,
REVIEW ARTICLE The role of digital breast tomosynthesis in the breast assessment clinic: a review Suneeta Mall, BE, 1 Sarah Lewis, PhD, 1 Patrick Brennan, PhD, 1 Jennie Noakes, BMed(Newcastle), FRANZCR,
The Radiology Aspects
 REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities. Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine
 Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Issues in Emerging Health Technologies
 Issues in Emerging Health Technologies Tomosynthesis (3D Mammography) for Breast Cancer Screening Issue 135 May 2015 Summary Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) is a novel imaging technology that captures
Issues in Emerging Health Technologies Tomosynthesis (3D Mammography) for Breast Cancer Screening Issue 135 May 2015 Summary Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) is a novel imaging technology that captures
Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR)
 Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR) Christopher Comstock, MD, FACR, FSBI Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of our approach to screening
Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR) Christopher Comstock, MD, FACR, FSBI Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of our approach to screening
Breast Density and Breast Tomosynthesis. How have they changed our lives?
 Breast Density and Breast Tomosynthesis How have they changed our lives? Renee W. Pinsky, MD Associate Professor of Radiology University of Michigan The only thing that is constant is change Heraclitus
Breast Density and Breast Tomosynthesis How have they changed our lives? Renee W. Pinsky, MD Associate Professor of Radiology University of Michigan The only thing that is constant is change Heraclitus
BREAST HEALTH SOLUTIONS. See what others miss.
 HMH 3D Mammography BREAST HEALTH SOLUTIONS See what others miss. 2 BREAST HEALTH SOLUTIONS Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY exams are clinically proven to detect 41% More invasive breast cancer, while simultaneously
HMH 3D Mammography BREAST HEALTH SOLUTIONS See what others miss. 2 BREAST HEALTH SOLUTIONS Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY exams are clinically proven to detect 41% More invasive breast cancer, while simultaneously
Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer
 What to Expect Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer Every woman over 40 should be examined for breast cancer once a year. American Cancer Society What to
What to Expect Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer Every woman over 40 should be examined for breast cancer once a year. American Cancer Society What to
Factors Affecting Breast Cancer Detectability on Digital Breast Tomosynthesis and Two-Dimensional Digital Mammography in Patients with Dense Breasts
 Original Article Breast Imaging eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2019;20(1):58-68 Factors Affecting Breast Cancer Detectability on Digital Breast Tomosynthesis and Two-Dimensional Digital Mammography in
Original Article Breast Imaging eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2019;20(1):58-68 Factors Affecting Breast Cancer Detectability on Digital Breast Tomosynthesis and Two-Dimensional Digital Mammography in
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine
 International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
WHAT TO EXPECT. Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC. The Women's Health Company
 WHAT TO EXPECT Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC The Women's Health Company ...,. Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that
WHAT TO EXPECT Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC The Women's Health Company ...,. Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that
Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis
 Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis Poster No.: C-1604 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Van Ongeval, L. Cockmartin, A. Van Steen,
Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis Poster No.: C-1604 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Van Ongeval, L. Cockmartin, A. Van Steen,
Dense Breasts. A Breast Cancer Risk Factor and Imaging Challenge
 Dense Breasts A Breast Cancer Risk Factor and Imaging Challenge Renee Pinsky, MD University of Michigan Department of Radiology Division of Breast Imaging No Disclosures QUIZ: ARE YOU DENSE? a. Breast
Dense Breasts A Breast Cancer Risk Factor and Imaging Challenge Renee Pinsky, MD University of Michigan Department of Radiology Division of Breast Imaging No Disclosures QUIZ: ARE YOU DENSE? a. Breast
Superior Performance. Lower Dose.* 1,2. World s first and only. 3D breast biopsy. Breast Biopsy Guidance System. Affirm
 World s first and only 3D breast biopsy Superior Performance. Lower Dose.* 1,2 TM Affirm Breast Biopsy Guidance System For Stereotactic and Tomosynthesis Interventional Procedures Breast and Skeletal Health
World s first and only 3D breast biopsy Superior Performance. Lower Dose.* 1,2 TM Affirm Breast Biopsy Guidance System For Stereotactic and Tomosynthesis Interventional Procedures Breast and Skeletal Health
Features of Prospectively Overlooked Computer-Aided Detection Marks on Prior Screening Digital Mammograms in Women With Breast Cancer
 Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING Nariya Cho 1 Seung Ja Kim Hye Young Choi Chae Yeon Lyou Woo Kyung Moon Cho N, Kim SJ, Choi HY, Lyou CY, Moon WK Keywords:
Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING Nariya Cho 1 Seung Ja Kim Hye Young Choi Chae Yeon Lyou Woo Kyung Moon Cho N, Kim SJ, Choi HY, Lyou CY, Moon WK Keywords:
Improving Reading Time of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis with Concurrent Computer Aided Detection
 White Paper Improving Reading Time of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis with Concurrent Computer Aided Detection WHITE PAPER 2 3 Abstract PowerLook Tomo Detection, a concurrent computer-aided detection (CAD)
White Paper Improving Reading Time of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis with Concurrent Computer Aided Detection WHITE PAPER 2 3 Abstract PowerLook Tomo Detection, a concurrent computer-aided detection (CAD)
Foreword: Radiology Select Volume 8 Breast Imaging: Beyond Mammographic Screening
 Foreword: Radiology Select Volume 8 Breast Imaging: Beyond Mammographic Screening Dear Radiology Select Reader: In 2013, our fourth volume of Radiology Select was introduced, Breast Cancer Screening. This
Foreword: Radiology Select Volume 8 Breast Imaging: Beyond Mammographic Screening Dear Radiology Select Reader: In 2013, our fourth volume of Radiology Select was introduced, Breast Cancer Screening. This
Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations
 Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations Maureen Baxter, MD Radiologist Director of Ruth J. Spear Breast Center Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Alison Conlin, MD/MPH Medical Oncologist
Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations Maureen Baxter, MD Radiologist Director of Ruth J. Spear Breast Center Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Alison Conlin, MD/MPH Medical Oncologist
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Breast Cancer Screening
 Revised 2017 American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Breast Cancer Screening Variant 1: Breast cancer screening. Average-risk women: women with
Revised 2017 American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Breast Cancer Screening Variant 1: Breast cancer screening. Average-risk women: women with
now a part of Electronic Mammography Exchange: Improving Patient Callback Rates
 now a part of Electronic Mammography Exchange: Improving Patient Callback Rates Overview This case study explores the impact of a mammography-specific electronic exchange network on patient callback rates
now a part of Electronic Mammography Exchange: Improving Patient Callback Rates Overview This case study explores the impact of a mammography-specific electronic exchange network on patient callback rates
6 OBG Management August 2015 Vol. 27 No. 8 obgmanagement.com
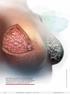 Dense breasts are composed of a lot of fibrous and glandular tissue, with less adipose tissue. Heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breast tissue (as illustrated here) make it difficult to detect
Dense breasts are composed of a lot of fibrous and glandular tissue, with less adipose tissue. Heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breast tissue (as illustrated here) make it difficult to detect
Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue. Public Meeting December 13, 2013
 Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue Public Meeting December 13, 2013 Agenda Meeting Convened 10am-10:15am Presentation of the Evidence and Voting Questions, Q&A 10:15am 11:15am Discussion
Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue Public Meeting December 13, 2013 Agenda Meeting Convened 10am-10:15am Presentation of the Evidence and Voting Questions, Q&A 10:15am 11:15am Discussion
Recall and Cancer Detection Rates for Screening Mammography: Finding the Sweet Spot
 Women s Imaging Original Research Grabler et al. Optimal Recall and Cancer Detection Rates for Screening Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research Paula Grabler 1 Dominique Sighoko 2 Lilian Wang 3
Women s Imaging Original Research Grabler et al. Optimal Recall and Cancer Detection Rates for Screening Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research Paula Grabler 1 Dominique Sighoko 2 Lilian Wang 3
