Normal Cell Growth and Development
|
|
|
- Percival Copeland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Normal Cell Growth and Development Noncancerous Versus Cancerous Tumors Cancerous Cell Growth and Development Cancer Genetics Causes of Cancer Epidemiology of Cancer Types of Cancer Resources Normal Cell Growth and Development by Elizabeth Peterson, MFA En Español (Spanish Version) In normal tissues, the rates of new cell growth and old cell death are kept in balance. Every day thousands of our body s cells die off. Every day exactly the right number of exactly the right types of cells take the place of those that die off. And if everything is in proper working order, we never even notice. Normal Cell Growth To illustrate this process, let s look at the cells of the epidermis (the outermost layer of the skin). The outer layer of the skin is approximately a dozen cells thick. Under normal circumstances, cells at the bottom of this layer, called the basal layer, divide at exactly the same rate as dead cells are shed from the surface. Each time one of these basal cells divides, it produces two cells. One remains in the basal layer and goes on to divide again. The other migrates out of the basal layer and can no longer divide. This way, the number of dividing cells in the basal layer, and the number of non-dividing cells in the outer layer stays the same. Image 1 illustrates normal cell growth. Image 1: Normal Cell Growth In order for this process to unfold with such precision, two important cellular processes must balance each other perfectly: Proliferation Apoptosis Proliferation refers to the growth and reproduction of cells. Apoptosis or "cell suicide," is the mechanism by which old or damaged cells normally self-destruct. If these carefully balanced processes are disrupted and cells proliferate uncontrollably, fail to die off at the appropriate time, or both, the end result may be cancer. Image 2 illustrates the difference between normal cell division and cancerous cell division. Page 1 of 6
2 Image 2: Normal Cell Division The Cell Cycle In order to proliferate both normal and cancerous cells must undergo the process of cell division. This process is the end result of the cell cycle. The cell cycle has two major phases: Mitosis Interphase Mitosis is the process by which a parent cell produces a pair of genetically identical daughter cells. It is part of the normal cell cycle. The cell cycle is divided into two distinct periods: Interphase (cell growth) Mitotic phase (cell division) Interphase is the period of a cell s life when it carries out its normal growth and metabolic activities. It is also the time during which a cell undergoes a closely ordered sequence of activities in preparation for cell division. Interphase is made up of three sub-phases. During the G1 phase, the cell produces the proteins needed to copy the cellular DNA, which occurs during the second S phase of the cell cycle. There must be two identical copies of the DNA so that one copy is passed to each of the daughter cells. During the final G2 phase, which lies between the replication of the DNA and the beginning of mitosis (when the cell actually divides), the cell produces proteins needed for cell division. Image 3 illustrates the phases of the cell cycle. See the Focus Box below to learn more about how chemotherapy drugs are designed to disrupt this cycle. Page 2 of 6
3 Image 3: Cell Cycle Focus Box: Chemotherapy Drugs Many chemotherapy drugs are designed to attack cancer cells during a specific phase of the cell cycle where they interrupt the process of cell division. For example, antimetabolites destroy cells that are in the S phase of the cell cycle, while alkylating agents destroy cells in multiple phases of the cell cycle. This is part of the rationale for using combination chemotherapy. Since most tumors are heterogeneous, meaning they are made up of cells in different phases of the cell cycle, they are sensitive to different types of drugs. Combining different chemotherapeutic agents, therefore, increases the likelihood that more cancer cells will be destroyed, which in turn increases the overall effectiveness of the therapy. This approach also allows physicians to gain maximum effect from the treatment without increasing the risk of unpleasant side effects because the dosage of each individual drug is lower. To learn more about the different classes of chemotherapeutic drugs, refer to chemotherapy treatment. During normal mitosis, the parent cell splits into two perfectly identical daughter cells, each containing one copy of DNA. After mitosis, the new daughter cells will either enter another G1 phase and divide again (like the cells of the basal layer of the epidermis), or they may enter a G0 phase, during which no mitosis-related activity occurs. G0 may last for days (like the cells in the outer layer of the epidermis), weeks, years, or a lifetime. Image 4 illustrates the processes of cell mitosis and division. Image 4: Cell mitosis and division. Normal Differentiation Cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell changes its structure so that it can perform a specific function. Cells can range from poorly differentiated to well-differentiated. The most poorly differentiated cells (generally called stem cells) are capable of acquiring a range of new functions. Stem cells are important to your overall health. For example, after severe trauma, they provide a pool of cells that can differentiate into specific cell types and repair tissue. Well-differentiated cells are mature, fully developed cells that are ready to carry out their particular function. A good example of cell differentiation is blood cells. There are three major types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Each has specific characteristics, functions, and life spans, yet all have differentiated from stem cells. Image 5 illustrates the process of cellular differentiation. See the Focus Box below to learn more about the relationship between cell differentiation and cancer. Page 3 of 6
4 Image 5: Cell differentiation Focus Box: Cell Differentiation and Cancer Cell differentiation is important to the study of cancer because a cell s degree of differentiation is associated with its ability to proliferate. Poorly differentiated cells are highly proliferative, moderately differentiated cells are moderately proliferative, and well-differentiated cells are either unable to proliferate or proliferate at a very slow rate. Aggressive cancers are often characterized by poorly differentiated cells, while less aggressive cancers tend to contain moderately or well-differentiated cells. To learn more about how a cancer cell s degree of differentiation affects a patient s prognosis and a physician s treatment strategy, see the Cancer Staging and Grading section in Cancer 201. In healthy tissues, the processes of mitosis and differentiation are tightly regulated. This is how the body ensures that only the correct number of cells is produced. The body has two methods for controlling the rate of cell proliferation: Growth factors Contact inhibition Growth factors stimulate mitosis and/or cellular differentiation. If a cell needs to be replaced (due to damage, natural apoptosis, or some other reason), it will secrete growth factors that stimulate the cell to either undergo mitosis or differentiate. Contact inhibition stops cells from proliferating. Normally, individual cells maintain a small amount of personal space. Under normal conditions, cells that become crowded and begin to touch each other will simply stop growing. Exactly how contact inhibition works is still unknown, however scientists believe that contact between cells triggers the release of growth inhibitory factors. Unlike growth factors, growth inhibitory factors tell cells to stop dividing. Abnormal Cell Growth In order for the tissues of the body to maintain such precise control over the growth of its cells, it has developed a system of feedback loops that detect and compensate for deviations from the norm. For every situation controlled by a feedback loop, the body has a set point it recognizes as normal. One example of this is your own body temperature. If your body temperature becomes too warm, a series of physiologic reactions are triggered in an Page 4 of 6
5 effort to return it towards 98.6 F. If your body s temperature becomes too cold, a different series of reactions are triggered to warm you up. This is an example of a negative feedback loop. In a positive feedback loop, on the other hand, changes in one direction tend to produce even more change in that same direction. In the case of normal cell proliferation,when the appropriate number of cells has been produced (and cells begin to crowd each other) growth inhibitory factors trigger a negative feedback mechanism to reduce the rate of cell growth. While positive feedback can occur normally, the production of excess growth factors by cells drives an abnormal positive feedback loop. Not all abnormally growing cells are cancerous. For example, the term hyperplasia refers to a type of noncancerous growth consisting of rapidly dividing cells, which leads to a larger than usual number of structurally normal cells. Hyperplasia may be a normal tissue response to an irritating stimulus. For example, the callus that forms on your hand when you first learn to swing a tennis racket or a golf club is an example of hyperplastic skin cells. Although hyperplasia is considered reversible, it some cases it indicates an increased risk of cancer. An example is hyperplasia of the lining of the uterus (endometrium). Dysplasia is another noncancerous type of abnormal cell growth characterized by the loss of normal tissue arrangement and cell structure. Dysplastic cells lose the normal architecture that characterizes normal tissues, and may show physical and chemical changes that distinguish them from their normal counterparts. They may have changes in their DNA, or they may have visible changes in their cell structures (*especially the cell nucleus) that can be seen under the microscope. These visible changes are often useful in detecting dysplasia early, before it progresses, as it sometimes (but not always) does lead to cancer. An example is cervical dysplasia, which may become cervical cancer if left untreated over a long period of time. The most severe form of dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, can actually be considered a form of cancer. In Latin, the term "in situ" means "in place," so carcinoma in situ refers to an uncontrolled growth of cells that remains in the original location (in place) and does not invade surrounding tissue as cancer cells eventually do. Carcinoma in situ, however, is considered more serious than moderate dysplasia because the risk of local invasion is much higher. This is why, when discovered, carcinoma in situ is usually removed surgically. Image 6 illustrates the different types of abnormal cell growth. Image 6: Types of abnormal cell growth What is the difference between a noncancerous and a cancerous tumor? How do cancerous cells grow and develop? What is a cancer gene? How do they occur? What causes cancer? What is the epidemiology of cancer? What are the different types of cancer? REFERENCES: Page 5 of 6
6 American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society, Inc;2003. Bast RC, Kufe DW, Pollock RE, et al. Eds. Cancer Medicine. 5th ed. Hamilton, ON: Decker Inc; Cancer. Merck Manual of Medical Information website. Available at: Accessed March 25, Defining cancer. National Cancer Institute website. Available at: Accessed August 1, Detailed guide. American Cancer Society website. Available at: Accessed August 1, Finley RS, Balmer C. Concepts in Oncology Therapeutics. 2nd ed. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists;1998. Fox SI. Human Physiology. 4th ed. Dubuque, IA: William C. Brown Publishers;1993. Last reviewed May 2010 by Igor Puzanov, MD Last Updated: 5/25/10 Page 6 of 6
Cell Growth and Division
 Name Class Date 10 Cell Growth and Division Big idea Growth, Development, and Reproduction Q: How does a cell produce a new cell? WHAT I KNOW WHAT I LEARNED 10.1 Why do cells divide? 10.2 How do cells
Name Class Date 10 Cell Growth and Division Big idea Growth, Development, and Reproduction Q: How does a cell produce a new cell? WHAT I KNOW WHAT I LEARNED 10.1 Why do cells divide? 10.2 How do cells
Introduction to Basic Oncology
 Introduction to Basic Oncology Cancer Cell AHS 102 Med Term Dr. Susie Turner 1/3/13 General Oncology Study of Tumors Neoplasms/Tumors Abnormal growth of new tissue Are either; Benign or Malignant Onc/o
Introduction to Basic Oncology Cancer Cell AHS 102 Med Term Dr. Susie Turner 1/3/13 General Oncology Study of Tumors Neoplasms/Tumors Abnormal growth of new tissue Are either; Benign or Malignant Onc/o
Almost every cell in the human body has an identical set of 46 chromosomes, produced through the process of mitosis.
 M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
Question #1 Controls on cell growth and division turned on and off
 Lesson Overview 10.3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Question #1 Controls on cell growth and division turned on and off When cells are grown in the laboratory, most cells will divide until they come into contact
Lesson Overview 10.3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Question #1 Controls on cell growth and division turned on and off When cells are grown in the laboratory, most cells will divide until they come into contact
Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle
 Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Vocabulary: Cyclin Cancer Key Concepts: How is the cell cycle regulated? How are cancer cells different from other cells? I. Introduction A. An Interesting Fact About
Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Vocabulary: Cyclin Cancer Key Concepts: How is the cell cycle regulated? How are cancer cells different from other cells? I. Introduction A. An Interesting Fact About
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013
 CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at related terminology Discuss the cell cycle Look at the purpose of cell division Consider what is Mitosis Look at the
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at related terminology Discuss the cell cycle Look at the purpose of cell division Consider what is Mitosis Look at the
Regulating the Cell Cycle. Lesson Overview THINK ABOUT IT. How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide?
 THINK ABOUT IT How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide? Controls on Cell Division How is the cell cycle regulated? The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins both inside
THINK ABOUT IT How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide? Controls on Cell Division How is the cell cycle regulated? The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins both inside
Aberrant cell Growth. Younas Masih New Life College of Nursing Karachi. 3/4/2016 Younas Masih ( NLCON)
 Aberrant cell Growth Younas Masih New Life College of Nursing Karachi 1 Objectives By the end of this session the learners will be able to, Define the characteristics of the normal cell Describe the characteristics
Aberrant cell Growth Younas Masih New Life College of Nursing Karachi 1 Objectives By the end of this session the learners will be able to, Define the characteristics of the normal cell Describe the characteristics
The Cell Cycle 1 What controls the life and development of a cell?
 The Cell Cycle 1 What controls the life and development of a cell? Why? An old piece of poetry says to everything there is a season... a time to be born, a time to die. For cells, the line might say a
The Cell Cycle 1 What controls the life and development of a cell? Why? An old piece of poetry says to everything there is a season... a time to be born, a time to die. For cells, the line might say a
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle
 Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5-6 DNA Replication Notes 7-8 DNA replication
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5-6 DNA Replication Notes 7-8 DNA replication
Genes and Proteins. Key points: The DNA must be copied and then divided exactly so that each cell gets an identical copy.
 Mitosis Genes and Proteins Proteins do the work of the cell: growth, maintenance, response to the environment, reproduction, etc. Proteins are chains of amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in each
Mitosis Genes and Proteins Proteins do the work of the cell: growth, maintenance, response to the environment, reproduction, etc. Proteins are chains of amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in each
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
You might be interested in reading an excerpt from Dimensions
 Take notes (minimum 1 page) on the following reading. Then review using the animation (link at bottom) and answer the quiz questions at the bottom of the webpage. To get credit for this assignment you
Take notes (minimum 1 page) on the following reading. Then review using the animation (link at bottom) and answer the quiz questions at the bottom of the webpage. To get credit for this assignment you
Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle
 Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Why are cells small? What are some of the difficulties a cell faces as it increases in size? Difficulties Larger Cells Have: More demands on its DNA Less efficient
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Why are cells small? What are some of the difficulties a cell faces as it increases in size? Difficulties Larger Cells Have: More demands on its DNA Less efficient
Cancer and Cell Differentiation
 Cancer and Cell Differentiation Recall The cell cycle consists of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. Recall During S phase of interphase, the DNA is replicated to prepare for mitosis. Each daughter
Cancer and Cell Differentiation Recall The cell cycle consists of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. Recall During S phase of interphase, the DNA is replicated to prepare for mitosis. Each daughter
Functional Limitations
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
NOTES. Cell Cycle & Mitosis
 NOTES for Cell Cycle & Mitosis Biology 2016 Johnson I. The Cell Cycle II. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q6uckwiifmg (2:15-4:25) III. http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm A. Limits to Cell Size 1. As
NOTES for Cell Cycle & Mitosis Biology 2016 Johnson I. The Cell Cycle II. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q6uckwiifmg (2:15-4:25) III. http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm A. Limits to Cell Size 1. As
Cancer Cells. It would take another 20 years and a revolution in the techniques of biological research to answer these questions.
 Cancer Cells Cancer, then, is a disease in which a single normal body cell undergoes a genetic transformation into a cancer cell. This cell and its descendants, proliferating across many years, produce
Cancer Cells Cancer, then, is a disease in which a single normal body cell undergoes a genetic transformation into a cancer cell. This cell and its descendants, proliferating across many years, produce
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Cancer arises from the mutation of a normal gene. A factor which brings about a mutation is called a mutagen.
 Cancer Single cells divide by mitosis to form many cells. This cells undergo physical and chemical changes in order to perform specific functions. (we say the cells have Differentiated) in this way we
Cancer Single cells divide by mitosis to form many cells. This cells undergo physical and chemical changes in order to perform specific functions. (we say the cells have Differentiated) in this way we
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle
 Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5 DNA Replication Video 6 Cancer Notes 15-16
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5 DNA Replication Video 6 Cancer Notes 15-16
Overview of Cancer. Mylene Freires Advanced Nurse Practitioner, Haematology
 Overview of Cancer Mylene Freires Advanced Nurse Practitioner, Haematology Aim of the Presentation Review basic concepts of cancer Gain some understanding of the socio-economic impact of cancer Order of
Overview of Cancer Mylene Freires Advanced Nurse Practitioner, Haematology Aim of the Presentation Review basic concepts of cancer Gain some understanding of the socio-economic impact of cancer Order of
Chapter 14 Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 14 Cellular Reproduction Biology 3201 Introduction One of the important life functions of living things is their ability to reproduce. Reproduction depends on the cell. Cells reproduce in order
Chapter 14 Cellular Reproduction Biology 3201 Introduction One of the important life functions of living things is their ability to reproduce. Reproduction depends on the cell. Cells reproduce in order
- is a common disease - 1 person in 3 can expect to contract cancer at some stage in their life -1 person in 5 can expect to die from it
 MBB157 Dr D Mangnall The Molecular Basis of Disease CANCER Lecture 1 One of the simpler (and better) definitions of cancer comes from the American Cancer Society, who define cancer as; 'Cancer is a group
MBB157 Dr D Mangnall The Molecular Basis of Disease CANCER Lecture 1 One of the simpler (and better) definitions of cancer comes from the American Cancer Society, who define cancer as; 'Cancer is a group
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
5.1. KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 68 Reinforcement Unit 2 Resource Book
 5.1 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Cells have a regular pattern of growth, DNA duplication, and division that is called the cell cycle.
5.1 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Cells have a regular pattern of growth, DNA duplication, and division that is called the cell cycle.
Cell Growth and Division *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46034 1 Cell Growth and Division * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46034 1 Cell Growth and Division * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes-
 Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cell Division. Introduction. Chromatin, Chromosomes, and Chromatids, Oh My! The Cell Cycle
 Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CANCER.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
Keywords: Daughter Cells Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Chromosomes Chromatin Homologous Chromosomes Diploid
 Name: CP Biology Unit 6: Cell Growth and Development Students will be able to: 6.1 Understand and explain the different aspects of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how cell size is related to cell division
Name: CP Biology Unit 6: Cell Growth and Development Students will be able to: 6.1 Understand and explain the different aspects of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how cell size is related to cell division
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Cellular Reproduction
 9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
Cell Death and Cancer. SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou
 Cell Death and Cancer SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou How do cells die? Necrosis Death due to unexpected and accidental cell damage. This is an unregulated cell death. Causes: toxins, radiation, trauma, lack of
Cell Death and Cancer SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou How do cells die? Necrosis Death due to unexpected and accidental cell damage. This is an unregulated cell death. Causes: toxins, radiation, trauma, lack of
A factor which brings about a mutation is called a mutagen. Any agent that causes cancer is called a carcinogen and is described as carcinogenic.
 Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
Cell Cycle - Introduction
 Cell Cycle - Introduction Key Concepts Cell division results in two identical cells During cell division the ability to organize DNA in time and space (location in the cell) is critical! The mitotic phase
Cell Cycle - Introduction Key Concepts Cell division results in two identical cells During cell division the ability to organize DNA in time and space (location in the cell) is critical! The mitotic phase
Warm Up- page 84. Name the 3 phases of the Cell Cycle and their purpose. List the phases of Mitosis! Explain the cartoon.
 Warm Up- page 84 Name the 3 phases of the Cell Cycle and their purpose. List the phases of Mitosis! Explain the cartoon. Agenda: Egg Lab Cell Regulation and Diff. Notes Concept Map Bell Work Can you fill
Warm Up- page 84 Name the 3 phases of the Cell Cycle and their purpose. List the phases of Mitosis! Explain the cartoon. Agenda: Egg Lab Cell Regulation and Diff. Notes Concept Map Bell Work Can you fill
BIT 120. Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture
 BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
Cell Death & Renewal (part 2)
 17 Cell Death & Renewal (part 2) Programmed Cell Death A major signaling pathway that promotes cell survival is initiated by the enzyme PI 3-kinase, which phosphorylates PIP2 to form PIP3, which activates
17 Cell Death & Renewal (part 2) Programmed Cell Death A major signaling pathway that promotes cell survival is initiated by the enzyme PI 3-kinase, which phosphorylates PIP2 to form PIP3, which activates
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
A Simulation of DNA Mutations and Cancer
 Lab 13 A Simulation of DNA Mutations and Cancer PROBLEM How can the changes in DNA that lead to cancer be modeled? BACKGROUND Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cells that produces tumors. Cancer is
Lab 13 A Simulation of DNA Mutations and Cancer PROBLEM How can the changes in DNA that lead to cancer be modeled? BACKGROUND Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cells that produces tumors. Cancer is
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century. Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013
 Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40
Cell Cycle Phase. Interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ) Mitotic Phase (M phase) Prophase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase
 Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1
 Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis (pp. 136-151) The Importance of Cell Division Cells, like all living things, eventually wear out and cannot sustain life anymore. They need to be
Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis (pp. 136-151) The Importance of Cell Division Cells, like all living things, eventually wear out and cannot sustain life anymore. They need to be
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Cell Growth and Division
 Cell Growth and Division Things to ponder When living things grow, what happens to its cells?? OR? Things to ponder When living things grow, what happens to its cells? For example: When a 7lb baby grows
Cell Growth and Division Things to ponder When living things grow, what happens to its cells?? OR? Things to ponder When living things grow, what happens to its cells? For example: When a 7lb baby grows
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
2.1 VIRUSES. 2.1 Learning Goals
 2.1 VIRUSES 2.1 Learning Goals To understand the structure, function, and how Viruses replicate To understand the difference between Viruses to Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes; namely that viruses are not classified
2.1 VIRUSES 2.1 Learning Goals To understand the structure, function, and how Viruses replicate To understand the difference between Viruses to Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes; namely that viruses are not classified
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Notes 7.5: Mitosis Gone Wrong
 Notes 7.5: Mitosis Gone Wrong Central Dogma Review Information to make a protein is stored in a gene Gene: Segment of DNA that codes for a protein Proteins are used for: growth of tissue and organs, energy,
Notes 7.5: Mitosis Gone Wrong Central Dogma Review Information to make a protein is stored in a gene Gene: Segment of DNA that codes for a protein Proteins are used for: growth of tissue and organs, energy,
Keywords: Daughter Cells Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Chromosomes Chromatin Homologous Chromosomes Diploid
 Name: CP Biology Unit 5: Cell Growth and Development Students will be able to: 5.1 Understand and explain the different aspects of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how cell size is related to cell division
Name: CP Biology Unit 5: Cell Growth and Development Students will be able to: 5.1 Understand and explain the different aspects of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how cell size is related to cell division
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction
 Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction Cell Size Are whale cells the same size as sea stars cells? Yes! Cell Size Limitations Cells that are too big will have difficulty diffusing materials
Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction Cell Size Are whale cells the same size as sea stars cells? Yes! Cell Size Limitations Cells that are too big will have difficulty diffusing materials
SNC2D BIOLOGY 3/17/2013 STAGE 3. TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L The Cell Cycle (P.28-32) The Cell Cycle. The Cell Cycle
 SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L The Cell Cycle (P.28-32) The Cell Cycle Cell division affects how an organism grows, repairs injuries, and reproduces. Just as you will go through many stages
SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L The Cell Cycle (P.28-32) The Cell Cycle Cell division affects how an organism grows, repairs injuries, and reproduces. Just as you will go through many stages
Cell cycle The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replicatio
 Cell Division Cell cycle The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells.
Cell Division Cell cycle The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells.
Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division 1 Background Info Formation of New Cells ~2 trillion cells formed/day in human body ~25 million cells/second Cell division = cell reproduction DNA must be copied before
Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division 1 Background Info Formation of New Cells ~2 trillion cells formed/day in human body ~25 million cells/second Cell division = cell reproduction DNA must be copied before
Cell Growth and Division. Chapter 10
 Cell Growth and Division Chapter 10 Cell Division Before a cell becomes too large, it undergoes cell division, in which the cell divides and becomes 2 daughter cells. Before cell division occurs, the cell
Cell Growth and Division Chapter 10 Cell Division Before a cell becomes too large, it undergoes cell division, in which the cell divides and becomes 2 daughter cells. Before cell division occurs, the cell
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 Genetics and Information Transfer Big Idea 3 INVESTIGATION 7 CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS How do eukaryotic cells divide to produce genetically identical cells or to produce gametes with half the
Genetics and Information Transfer Big Idea 3 INVESTIGATION 7 CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS How do eukaryotic cells divide to produce genetically identical cells or to produce gametes with half the
Understanding Your Pap Test Results
 Understanding Your Pap Test Results Most laboratories in the United States use a standard set of terms called the Bethesda System to report pap test results. Normal: Pap samples that have no cell abnormalities
Understanding Your Pap Test Results Most laboratories in the United States use a standard set of terms called the Bethesda System to report pap test results. Normal: Pap samples that have no cell abnormalities
Mitosis & Meiosis. Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair
 Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Mitosis and Cellular Division. EQ: How do the cells in our body divide?
 Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Cell Cycle. Cell Cycle the cell s life cycle that extends from one division to the next G1 phase, the first gap phase. S phase, synthesis phase
 Cell Cycle the cell s life cycle that extends from one division to the next G1 phase, the first gap phase Cell Cycle interval between cell division and DNA replication accumulates materials needed to replicate
Cell Cycle the cell s life cycle that extends from one division to the next G1 phase, the first gap phase Cell Cycle interval between cell division and DNA replication accumulates materials needed to replicate
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis. Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval
 Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
1.2. The Cell Cycle and Mitosis. The Life and Death of Skin Cells
 1.2 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: The life cycle of a cell has four phases. Growth and repair of cells is accomplished by mitosis. Cancer cells have
1.2 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: The life cycle of a cell has four phases. Growth and repair of cells is accomplished by mitosis. Cancer cells have
Cell Growth and Reproduction
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Before You Read SC.F.1.4.8 The student knows that cell behavior can be affected by molecules from other parts of the organism or even from other organisms. SC.F.2.4.2 The student
Cell Growth and Reproduction Before You Read SC.F.1.4.8 The student knows that cell behavior can be affected by molecules from other parts of the organism or even from other organisms. SC.F.2.4.2 The student
Unit 5 Section 1. Evidence 1: Why aren t all organisms made of just one cell? Why do cells divide, instead of simply growing larger?
 Unit 5 Section 1 Evidence 1: Why aren t all organisms made of just one cell? Why do cells divide, instead of simply growing larger? Cell Theory states the following 1. All organisms are made of cells 2.
Unit 5 Section 1 Evidence 1: Why aren t all organisms made of just one cell? Why do cells divide, instead of simply growing larger? Cell Theory states the following 1. All organisms are made of cells 2.
Mitosis. Cell Cycle. interphase. Five Phases. prophase. metaphase
 Mitosis Have you ever wondered how living things grow? Living things are made of cells. To grow bigger, they need more cells. Where do the new cells come from? Each cell divides, turning into two cells.
Mitosis Have you ever wondered how living things grow? Living things are made of cells. To grow bigger, they need more cells. Where do the new cells come from? Each cell divides, turning into two cells.
Omnis cellula e cellula
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Regulation of Cell Division
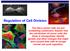 Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
THE CELL CYCLE. 1. What is meant by the cell cycle or cell division cycle?
 THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These events can be divided
THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These events can be divided
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century. Linda Lowe-Krentz
 Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
Mitosis and Meiosis. Chapters 8 & 10
 Mitosis and Meiosis Chapters 8 & 10 O Quiz #6: December 6th Learning Goals O Describe what happens during interphase O Identify steps of mitosis/meiosis by picture and function O Explain the diseases that
Mitosis and Meiosis Chapters 8 & 10 O Quiz #6: December 6th Learning Goals O Describe what happens during interphase O Identify steps of mitosis/meiosis by picture and function O Explain the diseases that
Mitosis vs. Meiosis. The Somatic Cell Cycle (Mitosis) The somatic cell cycle consists of 3 phases: interphase, m phase, and cytokinesis.
 Mitosis vs. Meiosis In order for organisms to continue growing and/or replace cells that are dead or beyond repair, cells must replicate, or make identical copies of themselves. In order to do this and
Mitosis vs. Meiosis In order for organisms to continue growing and/or replace cells that are dead or beyond repair, cells must replicate, or make identical copies of themselves. In order to do this and
Cellular Reproduction
 Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
Part I: The Cell Cycle
 Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Cancer. October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month
 Cancer October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month Objectives 1: Gene regulation Explain how cells in all the different parts of your body develop such different characteristics and functions. Contrast
Cancer October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month Objectives 1: Gene regulation Explain how cells in all the different parts of your body develop such different characteristics and functions. Contrast
Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages )
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages 241 243) Key Concept What problems does growth cause for cells? Limits to Cell Growth (pages 241 243) 1 What are two reasons why cells
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages 241 243) Key Concept What problems does growth cause for cells? Limits to Cell Growth (pages 241 243) 1 What are two reasons why cells
Cell Division. During interphase, a cell s DNA is in a loose form called. It condenses into tightly coiled structures called chromosomes during.
 Cell Division The is a cell s total DNA. Prokaryotes DNA is found mostly in a single called the and also in small circles called. Eukaryotes have several DNA double helices packaged into. During interphase,
Cell Division The is a cell s total DNA. Prokaryotes DNA is found mostly in a single called the and also in small circles called. Eukaryotes have several DNA double helices packaged into. During interphase,
Table of Contents. 1. Overview. 2. Interpretation Guide. 3. Staining Gallery Cases Negative for CINtec PLUS
 Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP
 Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
Name: Date: Block: 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet
 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
REGULATING the CELL CYCLE.
 REGULATING the CELL CYCLE http://www.travel-net.com/~andrews/images/animations/traffic.gif CELL DIVISION GENES Some cells divide frequently (some human skin cells divide once/hour) Some cells divide occasionally
REGULATING the CELL CYCLE http://www.travel-net.com/~andrews/images/animations/traffic.gif CELL DIVISION GENES Some cells divide frequently (some human skin cells divide once/hour) Some cells divide occasionally
Today you need: notebook, pen or pencil, textbook, colors to share, colored paper foldable. later
 CELL DIVISION Objectives Students will learn what causes a cell to divide and how it happens. They will explore all parts of the cell cycle and mitosis. They will discuss what happens when this process
CELL DIVISION Objectives Students will learn what causes a cell to divide and how it happens. They will explore all parts of the cell cycle and mitosis. They will discuss what happens when this process
Cell Size Limitations
 Cell Size Limitations Cells come in a wide variety of sizes and shapes. Considering this wide range of cells sizes, why then can t most organisms be just one giant cell? Diffusion limits cell size Although
Cell Size Limitations Cells come in a wide variety of sizes and shapes. Considering this wide range of cells sizes, why then can t most organisms be just one giant cell? Diffusion limits cell size Although
Title: Chapter 14 (1 of 54) Chapter 14 Cellular Reproduction
 Title: Chapter 14 (1 of 54) Chapter 14 Cellular Reproduction Title: 14.1 (2 of 54) Section 14.1 How Body Cells Reproduce The Cell Cycle One vital ability for all living things is the capacity for reproduction.
Title: Chapter 14 (1 of 54) Chapter 14 Cellular Reproduction Title: 14.1 (2 of 54) Section 14.1 How Body Cells Reproduce The Cell Cycle One vital ability for all living things is the capacity for reproduction.
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles Sexual reproduction mitosis
 meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12)
 Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
